外研版(2019)高中英语必修第二册 Unit2 Let's celebrate! Using language 公开课课件(共34张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版(2019)高中英语必修第二册 Unit2 Let's celebrate! Using language 公开课课件(共34张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.7MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-02-26 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览





文档简介
(共34张PPT)
Unit 2 Let’s celebrate
Using Language
目录页
Grammar
I
Homework
Ⅳ
Vocabulary building
II
Listening & speaking
III
contents
Ⅰ
Grammar
Grammar: Modals (2)
Please translate the following sentences and find the differences among them.
Grammar: Modals (2)
That is why Letters from Father Christmas could be the perfect book...
That is why Letters from Father Christmas must be the perfect book...
That is why Letters from Father Christmas might be the perfect book...
这就是为什么《圣诞老人的来信》一定是一本完美的书。
这就是为什么《圣诞老人的来信》可能是一本完美的书。
这就是为什么《圣诞老人的来信》可能一本完美的书。
indicate possibility
The speaker is quite sure about the statement
has the similar meaning to “could”
Grammar: Modals (2)
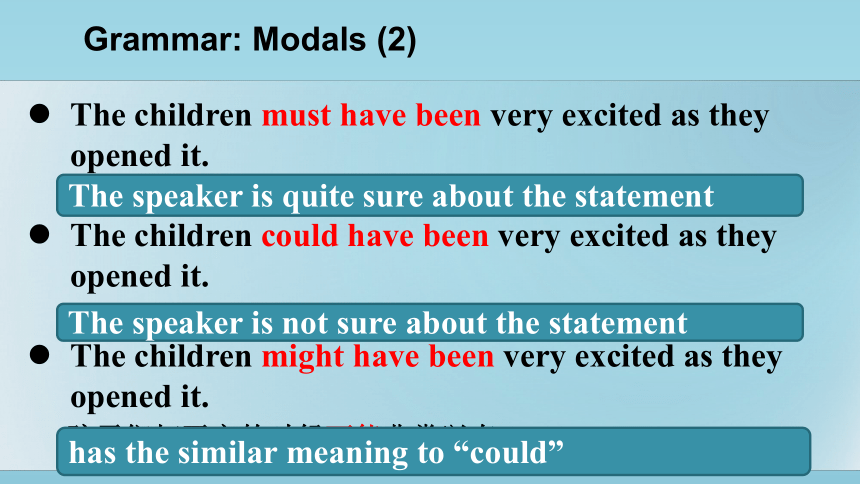
The children must have been very excited as they opened it.
The children could have been very excited as they opened it.
The children might have been very excited as they opened it.
孩子们打开它的时候一定很兴奋。
孩子们打开它的时候可能非常兴奋。
孩子们打开它的时候可能非常兴奋。
The speaker is quite sure about the statement
The speaker is not sure about the statement
has the similar meaning to “could”
Grammar: Modals (2)
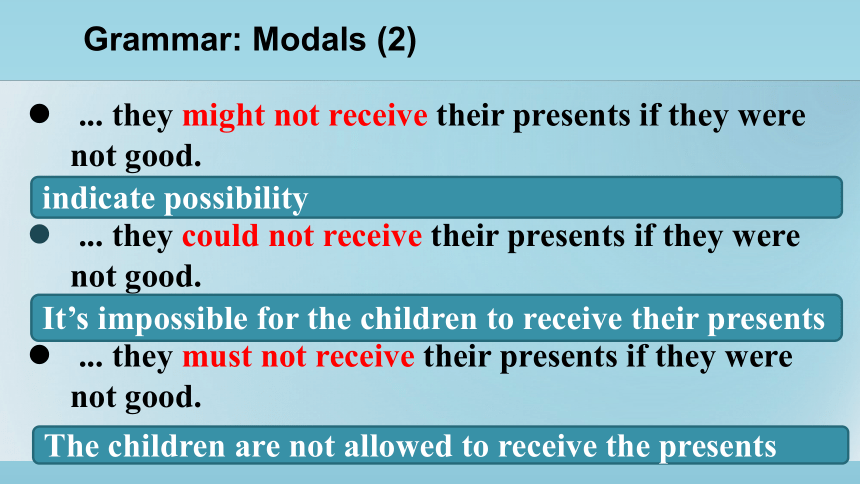
... they might not receive their presents if they were not good.
... they could not receive their presents if they were not good.
... they must not receive their presents if they were not good.
如果他们表现不好,他们可能收不到礼物。
如果他们表现不好,他们就收不到礼物。
如果他们表现不好,他们决不能收到礼物。
indicate possibility
It’s impossible for the children to receive their presents
The children are not allowed to receive the presents
Grammar: Modals (2)
That is why Letters from Father Christmas could be the perfect book...
The children must have been very excited as they opened it.
这就是为什么《圣诞老人的来信》可能是一本完美的书。
孩子们打开它的时候一定很兴奋。
情态动词 + 动词原形,表示对现在的推测
情态动词 + 完成式,表示对已发生情况的推测
Grammar: Modals (2)
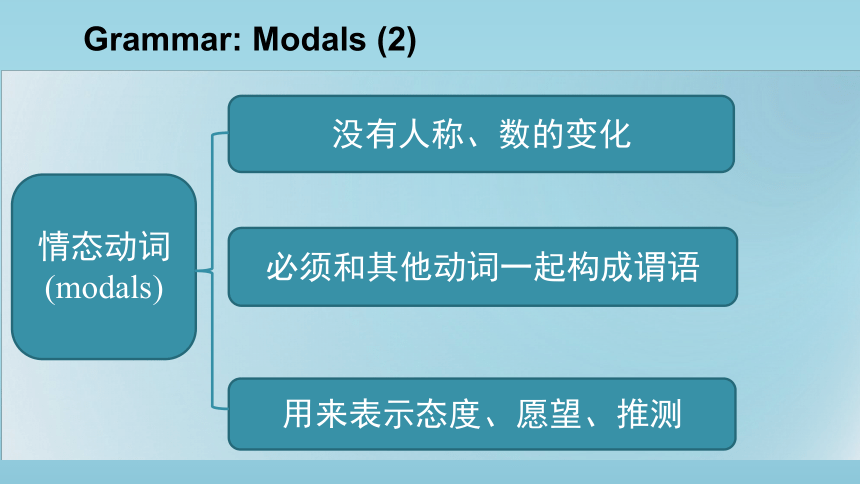
情态动词
(modals)
没有人称、数的变化
必须和其他动词一起构成谓语
用来表示态度、愿望、推测
Grammar: Modals (2)
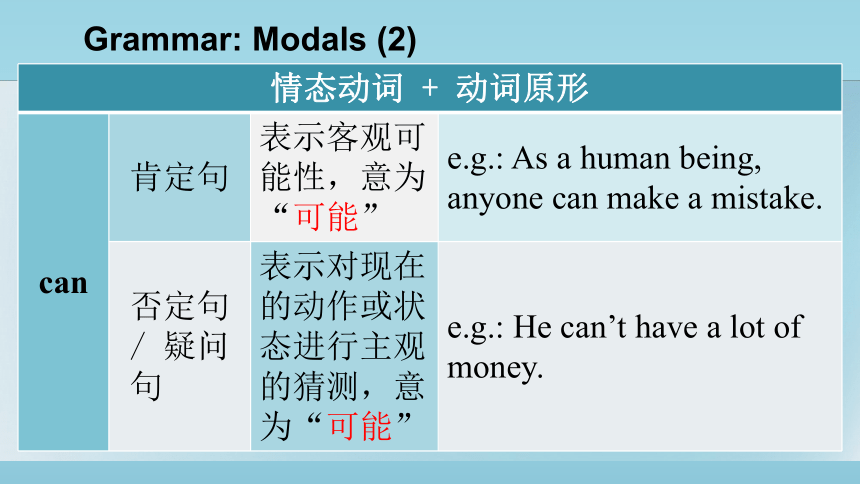
情态动词 + 动词原形 can 肯定句 表示客观可能性,意为“可能” e.g.: As a human being, anyone can make a mistake.
否定句 / 疑问句 表示对现在的动作或状态进行主观的猜测,意为“可能” e.g.: He can’t have a lot of money.
Grammar: Modals (2)
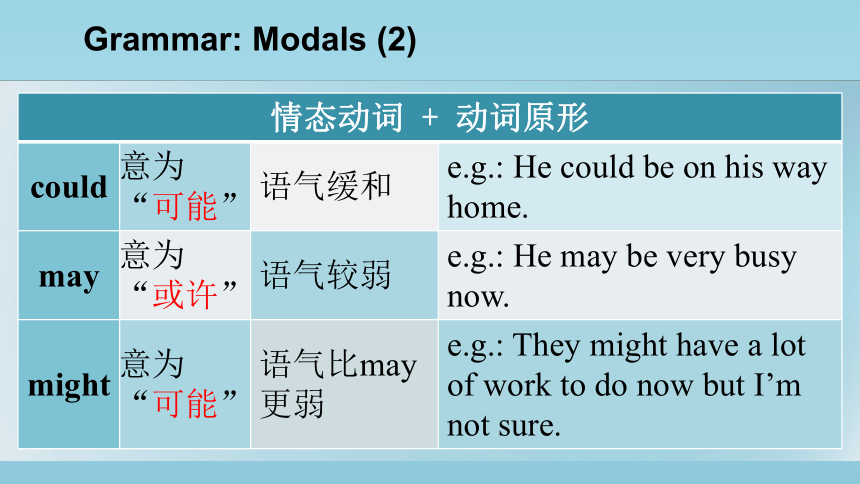
情态动词 + 动词原形 could 意为“可能” 语气缓和 e.g.: He could be on his way home.
may 意为“或许” 语气较弱 e.g.: He may be very busy now.
might 意为“可能” 语气比may更弱 e.g.: They might have a lot of work to do now but I’m
not sure.
Grammar: Modals (2)
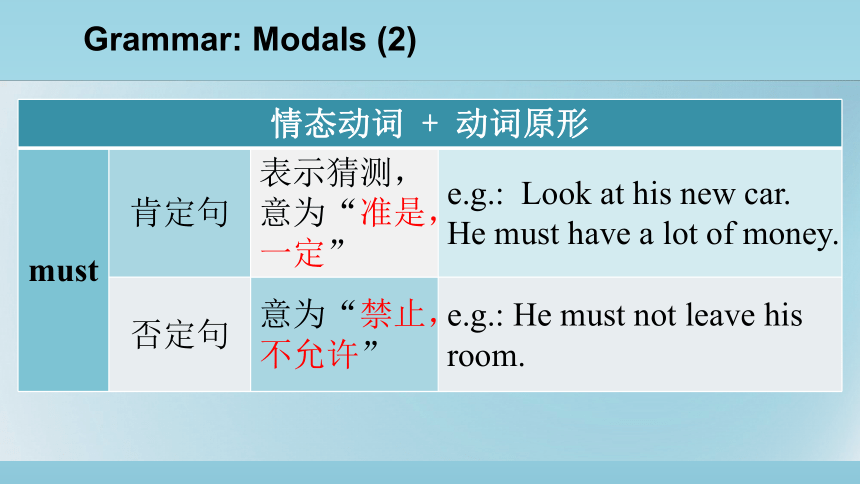
情态动词 + 动词原形 must 肯定句 表示猜测,意为“准是,一定” e.g.: Look at his new car. He must have a lot of money.
否定句 意为“禁止,不允许” e.g.: He must not leave his room.
Grammar: Modals (2)
情态动词 + 完成式 can 否定句 过去不可能做 e.g.: He can’t have forgotten it.
could 肯定句 过去有可能做 e.g.: She could have gone out with some friends.
may / might 肯定句 过去也许做了 e.g.: It’s too late. I think he may have gone to bed.
must 肯定句 过去一定做了 e.g.: It must have rained last night, for the road is wet.
Grammar: Modals (2)
Please rewrite the underlined sentences in the conversation using can / could , may / might and must.
Grammar: Modals (2)
You must be tired now!
It may / might / could be him.
That must be Lucy.
That can’t be Lucy.
They may / might / could be from our school.
Grammar: Modals (2)
Look at the picture and make as many sentences as possible using can / could, may / might and must.
Grammar: Modals (2)
The man with a wallet in his hand might be a bit unwilling to pay.
Grammar: Modals (2)
The woman in red must be very excited to buy so many things.
Grammar: Modals (2)
The woman with glasses may be very tired to get up so early and carry so many bags.
Grammar: Modals (2)
The cashier might be feeling uncomfortable as he is sweating a lot.
Ⅱ
Vocabulary building
Vocabulary building:
Underline the words and expressions about celebrations during the Lantern Festival in the speech bubbles and complete the mind map. Add any more you can think of.
Vocabulary building:
Vocabulary building:
flowers, a scarf
a red envelope
rice balls
balloons
hold a lantern fair
hold a lantern riddles competition; let off fireworks
posters
III
Listening & speaking
Listening & speaking: Before listening
Traditionally, people send written invitations for formal events such as weddings. Similarly, these invitations are answered in writing. For more informal events, however, spoken invitations are more common.
Listening & speaking: Before listening
Remember to arrive on time if you accept the invitation. Depending on regional customs, it may be acceptable to be 15 to 30 minutes late. It is not advisable to be early, as the host may not be ready.
Listening & speaking: While-listening
Listen to the conversation and complete the sentences with the correct ending.
Listening & speaking: While-listening
1. Tony would like to _____
2. Hugo wants to find out ______
3. On that day they will ______
go to Hugo’s apartment to give thanks
invite Hugo to his apartment to celebrate Thanksgiving
what he needs to bring to the party
what he should say at the party
go shopping together and watch the parade
watch an American football game on TV
b
c
f
Listen again and complete the notes.
Occasion: a 1. _____________ party
When: the fourth 2. _____________ in 3. _____________
Where: Tony’s 4. ______________
Thanksgiving
Thursday
November
apartment
Listening & speaking: While-listening
Listen again and complete the notes.
What to eat: a 5. _____________ with all the side dishes and homemade 6. ___________
What to bring: some flowers or 7. _____________
What to wear: 8. ______________
big turkey
apple pie
candies
anything you like
Listening & speaking: While-listening
Listening & speaking: Speaking
Work in pairs. Act out the conversation about extending and accepting an invitation.
Student A: Turn to Page 81.
Student B: Turn to Page 85.
Ⅳ
Homework
Homework:
Work in groups. Think about a similar situation and have a conversation .
Unit 2 Let’s celebrate
Using Language
目录页
Grammar
I
Homework
Ⅳ
Vocabulary building
II
Listening & speaking
III
contents
Ⅰ
Grammar
Grammar: Modals (2)
Please translate the following sentences and find the differences among them.
Grammar: Modals (2)
That is why Letters from Father Christmas could be the perfect book...
That is why Letters from Father Christmas must be the perfect book...
That is why Letters from Father Christmas might be the perfect book...
这就是为什么《圣诞老人的来信》一定是一本完美的书。
这就是为什么《圣诞老人的来信》可能是一本完美的书。
这就是为什么《圣诞老人的来信》可能一本完美的书。
indicate possibility
The speaker is quite sure about the statement
has the similar meaning to “could”
Grammar: Modals (2)
The children must have been very excited as they opened it.
The children could have been very excited as they opened it.
The children might have been very excited as they opened it.
孩子们打开它的时候一定很兴奋。
孩子们打开它的时候可能非常兴奋。
孩子们打开它的时候可能非常兴奋。
The speaker is quite sure about the statement
The speaker is not sure about the statement
has the similar meaning to “could”
Grammar: Modals (2)
... they might not receive their presents if they were not good.
... they could not receive their presents if they were not good.
... they must not receive their presents if they were not good.
如果他们表现不好,他们可能收不到礼物。
如果他们表现不好,他们就收不到礼物。
如果他们表现不好,他们决不能收到礼物。
indicate possibility
It’s impossible for the children to receive their presents
The children are not allowed to receive the presents
Grammar: Modals (2)
That is why Letters from Father Christmas could be the perfect book...
The children must have been very excited as they opened it.
这就是为什么《圣诞老人的来信》可能是一本完美的书。
孩子们打开它的时候一定很兴奋。
情态动词 + 动词原形,表示对现在的推测
情态动词 + 完成式,表示对已发生情况的推测
Grammar: Modals (2)
情态动词
(modals)
没有人称、数的变化
必须和其他动词一起构成谓语
用来表示态度、愿望、推测
Grammar: Modals (2)
情态动词 + 动词原形 can 肯定句 表示客观可能性,意为“可能” e.g.: As a human being, anyone can make a mistake.
否定句 / 疑问句 表示对现在的动作或状态进行主观的猜测,意为“可能” e.g.: He can’t have a lot of money.
Grammar: Modals (2)
情态动词 + 动词原形 could 意为“可能” 语气缓和 e.g.: He could be on his way home.
may 意为“或许” 语气较弱 e.g.: He may be very busy now.
might 意为“可能” 语气比may更弱 e.g.: They might have a lot of work to do now but I’m
not sure.
Grammar: Modals (2)
情态动词 + 动词原形 must 肯定句 表示猜测,意为“准是,一定” e.g.: Look at his new car. He must have a lot of money.
否定句 意为“禁止,不允许” e.g.: He must not leave his room.
Grammar: Modals (2)
情态动词 + 完成式 can 否定句 过去不可能做 e.g.: He can’t have forgotten it.
could 肯定句 过去有可能做 e.g.: She could have gone out with some friends.
may / might 肯定句 过去也许做了 e.g.: It’s too late. I think he may have gone to bed.
must 肯定句 过去一定做了 e.g.: It must have rained last night, for the road is wet.
Grammar: Modals (2)
Please rewrite the underlined sentences in the conversation using can / could , may / might and must.
Grammar: Modals (2)
You must be tired now!
It may / might / could be him.
That must be Lucy.
That can’t be Lucy.
They may / might / could be from our school.
Grammar: Modals (2)
Look at the picture and make as many sentences as possible using can / could, may / might and must.
Grammar: Modals (2)
The man with a wallet in his hand might be a bit unwilling to pay.
Grammar: Modals (2)
The woman in red must be very excited to buy so many things.
Grammar: Modals (2)
The woman with glasses may be very tired to get up so early and carry so many bags.
Grammar: Modals (2)
The cashier might be feeling uncomfortable as he is sweating a lot.
Ⅱ
Vocabulary building
Vocabulary building:
Underline the words and expressions about celebrations during the Lantern Festival in the speech bubbles and complete the mind map. Add any more you can think of.
Vocabulary building:
Vocabulary building:
flowers, a scarf
a red envelope
rice balls
balloons
hold a lantern fair
hold a lantern riddles competition; let off fireworks
posters
III
Listening & speaking
Listening & speaking: Before listening
Traditionally, people send written invitations for formal events such as weddings. Similarly, these invitations are answered in writing. For more informal events, however, spoken invitations are more common.
Listening & speaking: Before listening
Remember to arrive on time if you accept the invitation. Depending on regional customs, it may be acceptable to be 15 to 30 minutes late. It is not advisable to be early, as the host may not be ready.
Listening & speaking: While-listening
Listen to the conversation and complete the sentences with the correct ending.
Listening & speaking: While-listening
1. Tony would like to _____
2. Hugo wants to find out ______
3. On that day they will ______
go to Hugo’s apartment to give thanks
invite Hugo to his apartment to celebrate Thanksgiving
what he needs to bring to the party
what he should say at the party
go shopping together and watch the parade
watch an American football game on TV
b
c
f
Listen again and complete the notes.
Occasion: a 1. _____________ party
When: the fourth 2. _____________ in 3. _____________
Where: Tony’s 4. ______________
Thanksgiving
Thursday
November
apartment
Listening & speaking: While-listening
Listen again and complete the notes.
What to eat: a 5. _____________ with all the side dishes and homemade 6. ___________
What to bring: some flowers or 7. _____________
What to wear: 8. ______________
big turkey
apple pie
candies
anything you like
Listening & speaking: While-listening
Listening & speaking: Speaking
Work in pairs. Act out the conversation about extending and accepting an invitation.
Student A: Turn to Page 81.
Student B: Turn to Page 85.
Ⅳ
Homework
Homework:
Work in groups. Think about a similar situation and have a conversation .
