人教版(2019)必修第二册Unit 4 History and traditions Reading and Thinking 课件-(28张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版(2019)必修第二册Unit 4 History and traditions Reading and Thinking 课件-(28张ppt) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 6.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-02-28 14:22:56 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共28张PPT)
Unit 4 History and Traditions
Reading and Thinking
1. What are the provinces called in England
A. departments
B. states
C. counties
Let’s have a competition.
√
Lead-in
Let’s have a competition.
Lead-in
A. B. C.
The Union Jack
2. Which is the national flag of the UK
√
Let’s have a competition.
Lead-in
3. Who rules the country
A. The Queen/the King
B. The Prime Minister
C. both
Rishi Sunak
里希·苏纳克
The king—the head of state, but in name only. The most powerful one is the Prime Minister, who controls everything in the UK.
Charles III
√
Let’s have a competition.
Lead-in
4. Which is the bank note of the UK
A. U.S. Dollar $ B. Euros ? C. Pounds
√
Lead-in
What do these different names mean
Great Britain
the United Kingdom
England
Britain
the UK
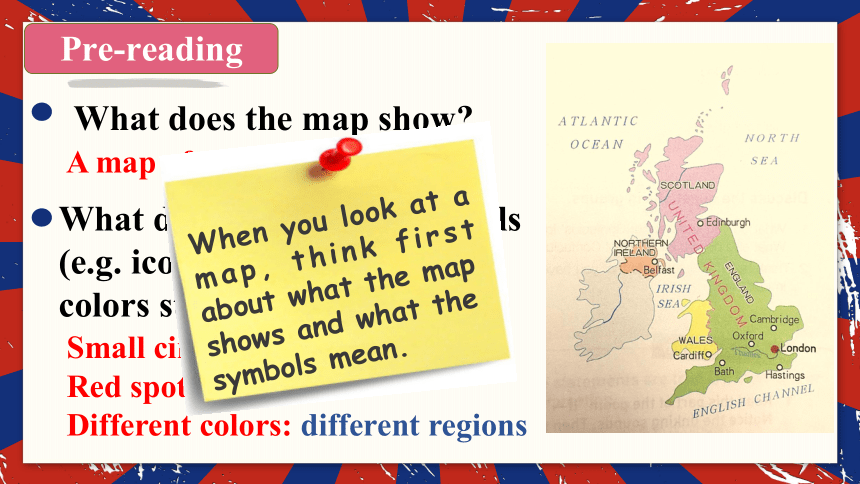
What does the map show
A map of the United Kingdom
What do the different symbols (e.g. icons, circles, spots) and colors stand for
Small circles: big cities
Red spot: the capital
Different colors: different regions
When you look at a map, think first about what the map shows and what the symbols mean.
Pre-reading
What’s in a name
PUZZLE !
Pre-reading
Paragraphs Main Ideas
Para 1 Getting to know British helps you solve the puzzle of different of the country.
Para 2 How the United Kingdom .
Para 3 The and of the four countries.
Para 4 The history of the UK helps us to learn more about the and .
Para 5 Learning the country’s history makes your journey more .
history
names
formed
similarities
differences
country
traditions
enjoyable
While-reading
Paragraph 1
How does the author introduce the passage
Solution
Question
16th Century
18th Century
19th Century
20th Century
+
+
=
=
Wales
England
England
Scotland
England
the Kingdom of Great Britain
be joined to
be joined to
Paragraph 2
16th Century
18th Century
19th Century
20th Century
+
-
=
=
Ireland
Great Britain
the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
Southern part of Ireland
the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
be added to
break away from
Paragraph 2
Wales
Scotland
England
Northern Ireland
Do the four countries work together in all areas
Paragraph 2
What are the similarities and differences of the four countries
Similarities: They use the same_______, share the same _________and ________________.
flag
currency
military defence
Differences: They have different __________ and _______ systems. They also have their own _________ and even own _________for competitions.
education
legal
football teams
traditions
Giving Examples
Paragraph 3
5th Century
8th Century
1th Century
“The United Kingdom has a long and interesting history to explore”
11th Century
groups of people
changes
the Romans
towns and roads
the Anglo-Saxons
language and the way
houses were built
the Viking
vocabulary and the names of locations
the Normans
castles, legal system, and new words from French
Paragraph 4
What’s the author’s attitude towards studying the history
Supportive
Why is London said to be a great place to start
Supporting details
Who are the target readers of the passage
Visitors
Paragraph 5
Advantages
Para 1-3
Para 4
Para 5
Help us understand why the UK has many different names
Help us understand more about the country and its traditions
Make our visit more enjoyable
Main idea: advantages of studying
British history
Are there any other advantages of studying the history of a country
Summary
What’s in a name
In a name, there is a _________.
history
English language
British culture
Further Thinking
Is it important for a people (民族) to know their history and traditions Why
a person
a people
National Responsibility
National Cohesion
National Confidence
Discussion
一个不了解自己历史、起源和文化的民族,就如同一颗无根之树。
Appreciation
Language points
1.So what is the difference between them, if any
所以如果有区别的话,区别是什么呢?
if necessary 如果有必要的话
if possible 如果可能的话
if not 如果不是的话 if so 如果是这样的话
if ever 如果有过/发生过的话
重点结构:“if+any”的省略结构,是if there is/are any at all的省略形式,起加强语气的作用。
Will you get a free evening next week , let’s have a dinner.
Is everybody feeling cold , let’s open the window.
, you can turn to me for help.
Please try to find out the differences between the two words. , speak it out.
If so
If not
If necessary
If any
2.They had castles built all around England, and made changes to the legal system.
(1)“have+sth. (宾语)+过去分词 说明宾语与过去分词表示的动作之间是被动关系。
(2)have sb. do sth. 让某人做某事(一次性动作)
(3)have sb./sth. doing 让某人一直在做某事/让某事一直发生
(4)have sth. to do 有某事要做(动作未完成)
I will have my room ___________ (decorate)this summer because it is a bit old.
decorated
单句语法填空
①I fell down and broke three of my teeth. I wonder how many times I have to come here and have my false teeth _____ (fix).
②I won't have you ________ (make)the same mistake again and again.
③When his mother had him do his homework, he decided to have his light __________ (burn) all night to pretend he was working hard.
④I have a lot of readings _____________(complete) before the end of this term.
fixed
making
to complete
burning
e.g.Hainan Island is joined to the mainland by a bridge.
海南岛通过一座桥与大陆 。
相连
join to 连接到;联结
join...to... 把......和......连接或联络起来
join in 参加;加入
join the club/army/party 加入俱乐部/参军/入党
join up(with sb) (与某人)集合;会合
3. In the 16th century, the nearby country of Wales was joined to the Kingdom of England.
16世纪时,邻国威尔士并入英格兰王国。
单据语法填空
(1)We joined point A point B in a straight line.
我们把A点和B点连起来成一根直线。
(2) We plan to join with the other climbers on the other side of the mountain.
我们打算和在山另一边的登山者会合。
(3) Everybody has to join the training.
每个人都必须参与训练。
to
up
in
Thank You !
Unit 4 History and Traditions
Reading and Thinking
1. What are the provinces called in England
A. departments
B. states
C. counties
Let’s have a competition.
√
Lead-in
Let’s have a competition.
Lead-in
A. B. C.
The Union Jack
2. Which is the national flag of the UK
√
Let’s have a competition.
Lead-in
3. Who rules the country
A. The Queen/the King
B. The Prime Minister
C. both
Rishi Sunak
里希·苏纳克
The king—the head of state, but in name only. The most powerful one is the Prime Minister, who controls everything in the UK.
Charles III
√
Let’s have a competition.
Lead-in
4. Which is the bank note of the UK
A. U.S. Dollar $ B. Euros ? C. Pounds
√
Lead-in
What do these different names mean
Great Britain
the United Kingdom
England
Britain
the UK
What does the map show
A map of the United Kingdom
What do the different symbols (e.g. icons, circles, spots) and colors stand for
Small circles: big cities
Red spot: the capital
Different colors: different regions
When you look at a map, think first about what the map shows and what the symbols mean.
Pre-reading
What’s in a name
PUZZLE !
Pre-reading
Paragraphs Main Ideas
Para 1 Getting to know British helps you solve the puzzle of different of the country.
Para 2 How the United Kingdom .
Para 3 The and of the four countries.
Para 4 The history of the UK helps us to learn more about the and .
Para 5 Learning the country’s history makes your journey more .
history
names
formed
similarities
differences
country
traditions
enjoyable
While-reading
Paragraph 1
How does the author introduce the passage
Solution
Question
16th Century
18th Century
19th Century
20th Century
+
+
=
=
Wales
England
England
Scotland
England
the Kingdom of Great Britain
be joined to
be joined to
Paragraph 2
16th Century
18th Century
19th Century
20th Century
+
-
=
=
Ireland
Great Britain
the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
Southern part of Ireland
the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
be added to
break away from
Paragraph 2
Wales
Scotland
England
Northern Ireland
Do the four countries work together in all areas
Paragraph 2
What are the similarities and differences of the four countries
Similarities: They use the same_______, share the same _________and ________________.
flag
currency
military defence
Differences: They have different __________ and _______ systems. They also have their own _________ and even own _________for competitions.
education
legal
football teams
traditions
Giving Examples
Paragraph 3
5th Century
8th Century
1th Century
“The United Kingdom has a long and interesting history to explore”
11th Century
groups of people
changes
the Romans
towns and roads
the Anglo-Saxons
language and the way
houses were built
the Viking
vocabulary and the names of locations
the Normans
castles, legal system, and new words from French
Paragraph 4
What’s the author’s attitude towards studying the history
Supportive
Why is London said to be a great place to start
Supporting details
Who are the target readers of the passage
Visitors
Paragraph 5
Advantages
Para 1-3
Para 4
Para 5
Help us understand why the UK has many different names
Help us understand more about the country and its traditions
Make our visit more enjoyable
Main idea: advantages of studying
British history
Are there any other advantages of studying the history of a country
Summary
What’s in a name
In a name, there is a _________.
history
English language
British culture
Further Thinking
Is it important for a people (民族) to know their history and traditions Why
a person
a people
National Responsibility
National Cohesion
National Confidence
Discussion
一个不了解自己历史、起源和文化的民族,就如同一颗无根之树。
Appreciation
Language points
1.So what is the difference between them, if any
所以如果有区别的话,区别是什么呢?
if necessary 如果有必要的话
if possible 如果可能的话
if not 如果不是的话 if so 如果是这样的话
if ever 如果有过/发生过的话
重点结构:“if+any”的省略结构,是if there is/are any at all的省略形式,起加强语气的作用。
Will you get a free evening next week , let’s have a dinner.
Is everybody feeling cold , let’s open the window.
, you can turn to me for help.
Please try to find out the differences between the two words. , speak it out.
If so
If not
If necessary
If any
2.They had castles built all around England, and made changes to the legal system.
(1)“have+sth. (宾语)+过去分词 说明宾语与过去分词表示的动作之间是被动关系。
(2)have sb. do sth. 让某人做某事(一次性动作)
(3)have sb./sth. doing 让某人一直在做某事/让某事一直发生
(4)have sth. to do 有某事要做(动作未完成)
I will have my room ___________ (decorate)this summer because it is a bit old.
decorated
单句语法填空
①I fell down and broke three of my teeth. I wonder how many times I have to come here and have my false teeth _____ (fix).
②I won't have you ________ (make)the same mistake again and again.
③When his mother had him do his homework, he decided to have his light __________ (burn) all night to pretend he was working hard.
④I have a lot of readings _____________(complete) before the end of this term.
fixed
making
to complete
burning
e.g.Hainan Island is joined to the mainland by a bridge.
海南岛通过一座桥与大陆 。
相连
join to 连接到;联结
join...to... 把......和......连接或联络起来
join in 参加;加入
join the club/army/party 加入俱乐部/参军/入党
join up(with sb) (与某人)集合;会合
3. In the 16th century, the nearby country of Wales was joined to the Kingdom of England.
16世纪时,邻国威尔士并入英格兰王国。
单据语法填空
(1)We joined point A point B in a straight line.
我们把A点和B点连起来成一根直线。
(2) We plan to join with the other climbers on the other side of the mountain.
我们打算和在山另一边的登山者会合。
(3) Everybody has to join the training.
每个人都必须参与训练。
to
up
in
Thank You !
