北师大版(2019)必修第二册 Unit6 The admirable Lesson 1 A Medical Pioneer名师教学设计
文档属性
| 名称 | 北师大版(2019)必修第二册 Unit6 The admirable Lesson 1 A Medical Pioneer名师教学设计 |

|
|
| 格式 | docx | ||
| 文件大小 | 553.2KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 北师大版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-03-07 18:06:04 | ||
图片预览




文档简介
Unit6 Lesson 1 名师教学设计
课时内容:
A Medical Pioneer
主题语境:人与社会
主题群:历史、社会与文化
子主题:对社会有突出贡献的人物语篇类型:人物通讯
文本分析:
[What]本文是一篇新闻报道,主要报道了中国抗疟有效单体青蒿素的发现者屠呦呦于2015年10月获得诺贝尔生理学或医学奖以及她的主要贡献。接着简单介绍了屠呦呦的出生、学习和工作情况,详细地描述了青蒿素发现的历史背景、发现的主要过程、青蒿素药物临床试验以及成为治疗疟疾的重要药物。文章最后引用了屠呦呦的获奖感言。
[Why]本文报道了中国第一个诺贝尔生理学或医学奖获得者屠呦呦的生平、主要贡献、发现与研究青蒿素的艰辛漫长的过程和屠呦呦的获奖感言。教师应鼓励学生学习她坚韧不拔的精神和独特的人格魅力。
[How]该语篇以时间顺序记叙了屠呦呦的成长及与团队发现青蒿素的艰辛过程,尤其是直接引用了诺贝尔奖评委对屠呦呦的高度评价和她的获奖感言,突显了屠呦呦作为一名科学家的可贵品质和求实的精神。
课时目标:
1. 获取与梳理出屠呦呦及其团队发现青蒿素的艰辛过程。
2. 赏析语篇的文体特征与修辞手法,探讨其与主题意义的关联。
3. 用恰当的语言说明伟大科学家屠呦呦的高尚的品格、对科学执着的信念、坚韧的意志和独特的人格魅力
4. 能够熟练掌握定语从句的用法。
重点难点:
重点:
1. 获取与梳理出屠呦呦及其团队发现青蒿素的艰辛过程和她的主要成就。
2. 赏析语篇的文体特征与修辞手法,探讨其与主题意义的关联。
难点:
用恰当的语言说明伟大科学家屠呦呦的高贵的品格学习她对科学执着的信念、坚韧的意志和独特的人格魅力,帮助学生形成正确的价值观。
教学准备:
教师准备:
提前准备一些有关屠呦呦主要事迹、主要贡献和发现青蒿素的过程等信息。
学生准备:
1. 预习本课的词汇和课文内容。
2. 利用网络资源了解屠呦呦团队发现青蒿素的过程、主要成就等信息。
教学过程:
Step I学习理解
活动一:感知与注意
1. Talk about pioneers.
(1) Write the heading “pioneer” on the blackboard. Ask students their understanding about the word. Use a dictionary if necessary. Explain that a pioneer is similar to a hero but is different because they achieve or discover something new.
(2) Encourage students to think of other pioneers, e. g., Christopher Columbus, Neil Armstrong, Alexander Fleming..
(3) Encourage students to find out what these pioneers are remembered for.
Christopher Columbus discovered a new continent;
Neil Armstrong was the first man to set foot on the Moon;
Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin, which is used in antibiotics.
2. Facts about malaria. (Part 1, P52)
Ask students to read through the facts silently and tick the information that they find most striking or interesting.
3. Information about Tu youyou.
Ask students to share with their partners what they know about Tu Youyou.
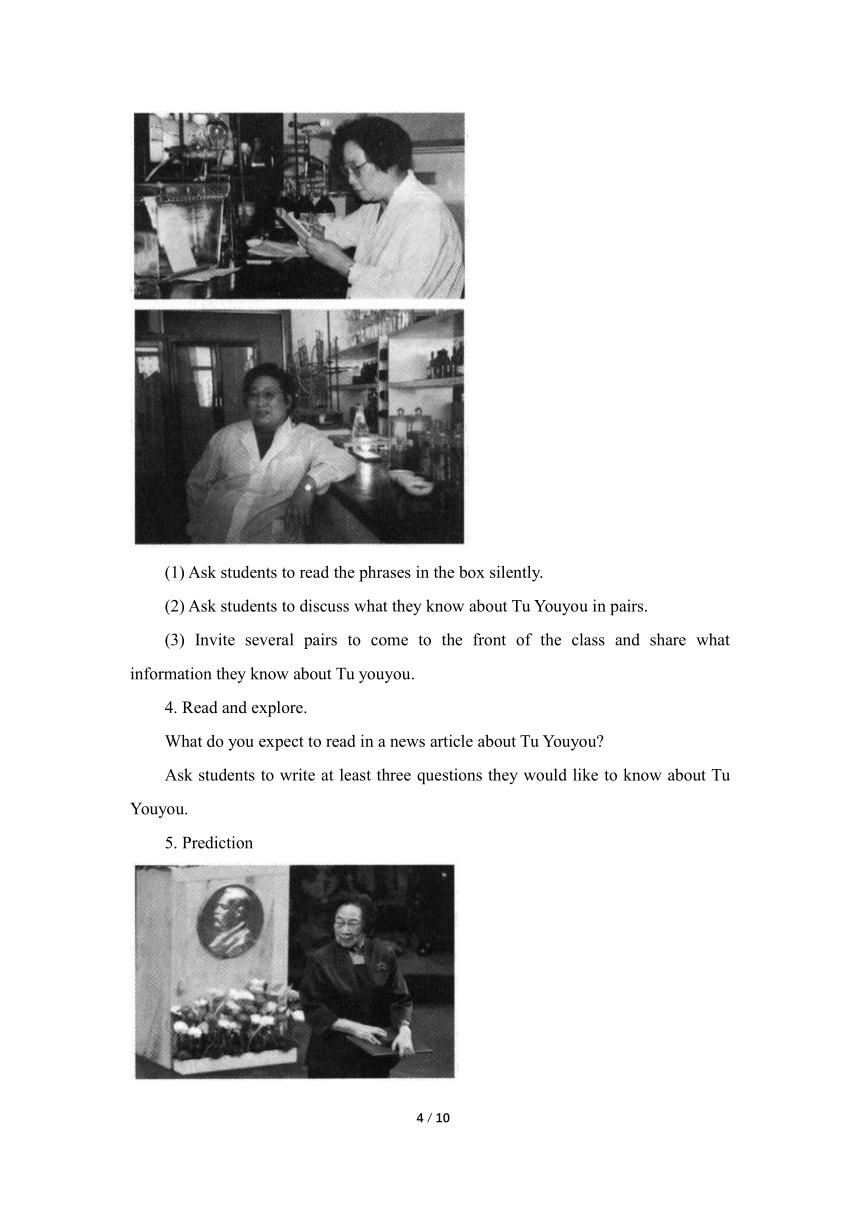
(1) Ask students to read the phrases in the box silently.
(2) Ask students to discuss what they know about Tu Youyou in pairs.
(3) Invite several pairs to come to the front of the class and share what information they know about Tu youyou.
4. Read and explore.
What do you expect to read in a news article about Tu Youyou
Ask students to write at least three questions they would like to know about Tu Youyou.
5. Prediction
Ask students to look at the picture on Page 52 and predict what the text is probably about.
Suggested answers: The text is probably about Tu Youyou and her basic information and achievement.
【设计意图】在阅读前,通过了解著名先驱、疟疾、屠呦呦的相关信息,预测文本大意等活动,激活学生已有的背景知识,形成阅读期待,为提高阅读效率奠定基础。
活动二:获取与梳理
1. Read and match.
Ask students to read the article and match the main idea of each paragraph.
Para.1 A. Her missions and research.
Para.2 B. Her attitude towards fame.
Para.3 C. Her achievements
Para.4 D. Her personal information.
Para.5 E. The challenges she and her team faced
Suggested answers: Para.1—C Para. 2—D Para. 3—A Para. 4—E Para. 5—B
2. Read for detailed information.
Ask students to read the article carefully and choose the best answer.
(1) How old was she when Tu Youyou got the Nobel Prize
A. 82. B. 83 C. 84 D. 85.
(2) Who helped Tu Youyou discover the life-saving drug
A. Her friends. B. Her family. C. No one. D. Her team.
(3) How long did Tu Youyou study Chinese medicine with experts in the field
A. Two and a half years.
B. One and a half years.
C. A half year.
D. Three and a half years.
(4) Why was it difficult for them to discover artemisinin
A. The team didn’t have enough time.
B. The team didn’t have enough resources.
C. The team didn’t have enough books.
D. The team wasn’t good at doing experiments.
(5) What can we learn from the text
A. Tu is not interested in fame.
B. She doesn’t continue to conduct research today because of her age.
C. Tu was forced to be the first human subject.
D. Tu used traditional research methods to study the Chinese herbs.
Suggested answers: (1)C (2)D (3)A (4)B (5)A
3. Read and complete. (Part 5, P54)
Ask students to read the article and complete the information.
Suggested answers: Basic information: (1) Born on 30 December, 1930 (2) Born in Zhejiang Province (3) Studied medicine at Peking University Health Science Centre. Scientific work: (1) Chosen to establish a team to find a cure for malaria; The team had limited resources. They didn’t have enough staff, and the laboratory where they worked had poor air quality. (2) Tested more than 240, 000 chemicals: Researched hundreds of traditional recipes connected to anti-malarial cures: Tested herself. (3) Artemisinin Attitudes: (1) Not interested in fame. (2) Feels it's a recognition and motivation for all scientists in China.
【设计意图】在阅读的过程中,通过完成匹配段落大意、回答问题、完成表格等不同形式的活动,让学生加深对课文意义的理解。通过解决这些间题,学生能够感知和理解语篇中语言所表达的意义。
4. Focus on language:relative clauses.
[备注]语法知识点讲解详见第二教案“重点语法精讲”。
活动三:概括与整合
Ask students to share the feelings of the article by answering the following question:Have you found anything you feel excited, inspired, attractive about Tu Youyou?
【设计意图】本活动通过分享阅读感受为主线串联文本信息。学生主动地与文本展开对话后分享自己的真实感受,在回答中透射出他们对问题的独立思考和个性化理解,使阅读过程真正成为学生个性化体验与意义构建的过程。
Sept Ⅱ 应用实践
活动四:描述与阐述
1. Talk about Tu Youyou’s work and achievement.
Ask students to draw a line to match the words and phrases in columns A and B. Then use the phrases to talk about Tu Youyou’s work and achievement.
A B study a cure establish hundreds of traditional recipes find Chinese medicine use a team have a promising chemical come across modern research methods discover a Nobel Prize be awarded artemisinin
2. Summary writing.
Ask students to write a summary of the article in less than 60 words.
活动五:分析与判断
Remind students about quality of admirable people.
(1) Ask students to discuss Tu Youyou’s personal quality in small groups. And encourage students to provide reasons for their answers.
(2) Ask students to use three words or phrases to summarise Tu Youyou’s personal quality. And give their reasons and find evidences from the text.
(3) Assign one representative to share his or her group's answers with the class.
【设计意图】在学习理解类活动的基础上,教师引导学生围绕主题和所形成的新的知识结构谈论屠呦呦的工作和成就,完成课文的概要写作,用三个单词或短语总结屠呦呦的个人品质,并给出原因,找出相关证据。以此逐步实现对语言知识和文化知识的内化,巩固新的知识结构,促进语言运用的自动化,助力学生将知识转化为能力。
Step Ⅲ 迁移创新
活动六:推理与论证
Ask students to work in groups and answer the following questions:
What is the purpose of the news article
How did the author make his purpose clear
Suggested answers:
To introduce Tu Youyou’s work and achievement.
The author wrote the article in the time sequence.
【设计意图】教师引导学生推断作者的写作目的、引发学生对屠呦呦精神的思考,加深学生对文本的深层理解。借助对写作手法的论证,理解作者的写作意图,帮助学生提高能力。
活动七:想象与创造
1. Ask students to work in groups to discuss and share their ideas.
Q1: Why is Tu Youyou considered as a medical pioneer
Q2: What typical writing features can you identify in the news article about Tu Youyou?
2. Assign one representative to share the group’s answers with the class.
【设计意图】学生利用所学语篇、语盲和文化知识,讨论屠呦呦被称为医学先驱的原因和文章的写作特色,探究主题意义,达到学以致用,提高解决问题的能力,实现深度学习,促进能力向素养的转化。
板书设计:
Unit 6 The Admirable Period Ⅱ Lesson1 I. 学习理解 活动一:感知与注意 1. Talk about pioneers. 2. Facts about malaria. 3. Information about Tu Youyou. 4. Read and explore. 5. Prediction 活动二:获取与梳理 1. Read and match. 2. Read for detailed information. 3. Read and complete. 4. Focus on language:relative clauses. 活动三:概括与整合 Ⅱ. 应用实践 活动四:描述与阐述 1. Talk about Tu Youyou’s work and achievement. 2. Summary writing. 活动五:分析与判断 Ⅲ. 迁移创新 活动六:推理与论证 活动七:想象与创造
2 / 2
课时内容:
A Medical Pioneer
主题语境:人与社会
主题群:历史、社会与文化
子主题:对社会有突出贡献的人物语篇类型:人物通讯
文本分析:
[What]本文是一篇新闻报道,主要报道了中国抗疟有效单体青蒿素的发现者屠呦呦于2015年10月获得诺贝尔生理学或医学奖以及她的主要贡献。接着简单介绍了屠呦呦的出生、学习和工作情况,详细地描述了青蒿素发现的历史背景、发现的主要过程、青蒿素药物临床试验以及成为治疗疟疾的重要药物。文章最后引用了屠呦呦的获奖感言。
[Why]本文报道了中国第一个诺贝尔生理学或医学奖获得者屠呦呦的生平、主要贡献、发现与研究青蒿素的艰辛漫长的过程和屠呦呦的获奖感言。教师应鼓励学生学习她坚韧不拔的精神和独特的人格魅力。
[How]该语篇以时间顺序记叙了屠呦呦的成长及与团队发现青蒿素的艰辛过程,尤其是直接引用了诺贝尔奖评委对屠呦呦的高度评价和她的获奖感言,突显了屠呦呦作为一名科学家的可贵品质和求实的精神。
课时目标:
1. 获取与梳理出屠呦呦及其团队发现青蒿素的艰辛过程。
2. 赏析语篇的文体特征与修辞手法,探讨其与主题意义的关联。
3. 用恰当的语言说明伟大科学家屠呦呦的高尚的品格、对科学执着的信念、坚韧的意志和独特的人格魅力
4. 能够熟练掌握定语从句的用法。
重点难点:
重点:
1. 获取与梳理出屠呦呦及其团队发现青蒿素的艰辛过程和她的主要成就。
2. 赏析语篇的文体特征与修辞手法,探讨其与主题意义的关联。
难点:
用恰当的语言说明伟大科学家屠呦呦的高贵的品格学习她对科学执着的信念、坚韧的意志和独特的人格魅力,帮助学生形成正确的价值观。
教学准备:
教师准备:
提前准备一些有关屠呦呦主要事迹、主要贡献和发现青蒿素的过程等信息。
学生准备:
1. 预习本课的词汇和课文内容。
2. 利用网络资源了解屠呦呦团队发现青蒿素的过程、主要成就等信息。
教学过程:
Step I学习理解
活动一:感知与注意
1. Talk about pioneers.
(1) Write the heading “pioneer” on the blackboard. Ask students their understanding about the word. Use a dictionary if necessary. Explain that a pioneer is similar to a hero but is different because they achieve or discover something new.
(2) Encourage students to think of other pioneers, e. g., Christopher Columbus, Neil Armstrong, Alexander Fleming..
(3) Encourage students to find out what these pioneers are remembered for.
Christopher Columbus discovered a new continent;
Neil Armstrong was the first man to set foot on the Moon;
Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin, which is used in antibiotics.
2. Facts about malaria. (Part 1, P52)
Ask students to read through the facts silently and tick the information that they find most striking or interesting.
3. Information about Tu youyou.
Ask students to share with their partners what they know about Tu Youyou.
(1) Ask students to read the phrases in the box silently.
(2) Ask students to discuss what they know about Tu Youyou in pairs.
(3) Invite several pairs to come to the front of the class and share what information they know about Tu youyou.
4. Read and explore.
What do you expect to read in a news article about Tu Youyou
Ask students to write at least three questions they would like to know about Tu Youyou.
5. Prediction
Ask students to look at the picture on Page 52 and predict what the text is probably about.
Suggested answers: The text is probably about Tu Youyou and her basic information and achievement.
【设计意图】在阅读前,通过了解著名先驱、疟疾、屠呦呦的相关信息,预测文本大意等活动,激活学生已有的背景知识,形成阅读期待,为提高阅读效率奠定基础。
活动二:获取与梳理
1. Read and match.
Ask students to read the article and match the main idea of each paragraph.
Para.1 A. Her missions and research.
Para.2 B. Her attitude towards fame.
Para.3 C. Her achievements
Para.4 D. Her personal information.
Para.5 E. The challenges she and her team faced
Suggested answers: Para.1—C Para. 2—D Para. 3—A Para. 4—E Para. 5—B
2. Read for detailed information.
Ask students to read the article carefully and choose the best answer.
(1) How old was she when Tu Youyou got the Nobel Prize
A. 82. B. 83 C. 84 D. 85.
(2) Who helped Tu Youyou discover the life-saving drug
A. Her friends. B. Her family. C. No one. D. Her team.
(3) How long did Tu Youyou study Chinese medicine with experts in the field
A. Two and a half years.
B. One and a half years.
C. A half year.
D. Three and a half years.
(4) Why was it difficult for them to discover artemisinin
A. The team didn’t have enough time.
B. The team didn’t have enough resources.
C. The team didn’t have enough books.
D. The team wasn’t good at doing experiments.
(5) What can we learn from the text
A. Tu is not interested in fame.
B. She doesn’t continue to conduct research today because of her age.
C. Tu was forced to be the first human subject.
D. Tu used traditional research methods to study the Chinese herbs.
Suggested answers: (1)C (2)D (3)A (4)B (5)A
3. Read and complete. (Part 5, P54)
Ask students to read the article and complete the information.
Suggested answers: Basic information: (1) Born on 30 December, 1930 (2) Born in Zhejiang Province (3) Studied medicine at Peking University Health Science Centre. Scientific work: (1) Chosen to establish a team to find a cure for malaria; The team had limited resources. They didn’t have enough staff, and the laboratory where they worked had poor air quality. (2) Tested more than 240, 000 chemicals: Researched hundreds of traditional recipes connected to anti-malarial cures: Tested herself. (3) Artemisinin Attitudes: (1) Not interested in fame. (2) Feels it's a recognition and motivation for all scientists in China.
【设计意图】在阅读的过程中,通过完成匹配段落大意、回答问题、完成表格等不同形式的活动,让学生加深对课文意义的理解。通过解决这些间题,学生能够感知和理解语篇中语言所表达的意义。
4. Focus on language:relative clauses.
[备注]语法知识点讲解详见第二教案“重点语法精讲”。
活动三:概括与整合
Ask students to share the feelings of the article by answering the following question:Have you found anything you feel excited, inspired, attractive about Tu Youyou?
【设计意图】本活动通过分享阅读感受为主线串联文本信息。学生主动地与文本展开对话后分享自己的真实感受,在回答中透射出他们对问题的独立思考和个性化理解,使阅读过程真正成为学生个性化体验与意义构建的过程。
Sept Ⅱ 应用实践
活动四:描述与阐述
1. Talk about Tu Youyou’s work and achievement.
Ask students to draw a line to match the words and phrases in columns A and B. Then use the phrases to talk about Tu Youyou’s work and achievement.
A B study a cure establish hundreds of traditional recipes find Chinese medicine use a team have a promising chemical come across modern research methods discover a Nobel Prize be awarded artemisinin
2. Summary writing.
Ask students to write a summary of the article in less than 60 words.
活动五:分析与判断
Remind students about quality of admirable people.
(1) Ask students to discuss Tu Youyou’s personal quality in small groups. And encourage students to provide reasons for their answers.
(2) Ask students to use three words or phrases to summarise Tu Youyou’s personal quality. And give their reasons and find evidences from the text.
(3) Assign one representative to share his or her group's answers with the class.
【设计意图】在学习理解类活动的基础上,教师引导学生围绕主题和所形成的新的知识结构谈论屠呦呦的工作和成就,完成课文的概要写作,用三个单词或短语总结屠呦呦的个人品质,并给出原因,找出相关证据。以此逐步实现对语言知识和文化知识的内化,巩固新的知识结构,促进语言运用的自动化,助力学生将知识转化为能力。
Step Ⅲ 迁移创新
活动六:推理与论证
Ask students to work in groups and answer the following questions:
What is the purpose of the news article
How did the author make his purpose clear
Suggested answers:
To introduce Tu Youyou’s work and achievement.
The author wrote the article in the time sequence.
【设计意图】教师引导学生推断作者的写作目的、引发学生对屠呦呦精神的思考,加深学生对文本的深层理解。借助对写作手法的论证,理解作者的写作意图,帮助学生提高能力。
活动七:想象与创造
1. Ask students to work in groups to discuss and share their ideas.
Q1: Why is Tu Youyou considered as a medical pioneer
Q2: What typical writing features can you identify in the news article about Tu Youyou?
2. Assign one representative to share the group’s answers with the class.
【设计意图】学生利用所学语篇、语盲和文化知识,讨论屠呦呦被称为医学先驱的原因和文章的写作特色,探究主题意义,达到学以致用,提高解决问题的能力,实现深度学习,促进能力向素养的转化。
板书设计:
Unit 6 The Admirable Period Ⅱ Lesson1 I. 学习理解 活动一:感知与注意 1. Talk about pioneers. 2. Facts about malaria. 3. Information about Tu Youyou. 4. Read and explore. 5. Prediction 活动二:获取与梳理 1. Read and match. 2. Read for detailed information. 3. Read and complete. 4. Focus on language:relative clauses. 活动三:概括与整合 Ⅱ. 应用实践 活动四:描述与阐述 1. Talk about Tu Youyou’s work and achievement. 2. Summary writing. 活动五:分析与判断 Ⅲ. 迁移创新 活动六:推理与论证 活动七:想象与创造
2 / 2
同课章节目录
- Unit 4 Information technology
- Lesson 1 Avatars
- Lesson 2 Apps
- Lesson 3 Internet and Friendships
- Unit 5 Humans and nature
- Lesson 1 A Sea Story
- Lesson 2 Professional Rescue Team
- Lesson 3 Race to the Pole
- Unit 6 The admirable
- Lesson 1 A Medical Pioneer
- Lesson 2 History Makers
- Lesson 3 The Superhero Behind Superman
