牛津译林版(2020) 必修第二册Unit 4 Exploring literature Grammar and usage 语法点课件(共33张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 牛津译林版(2020) 必修第二册Unit 4 Exploring literature Grammar and usage 语法点课件(共33张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 2.7MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津译林版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-03-22 12:14:40 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共33张PPT)
Unit4 Reading
The wonder of literature
Grammar and usage
Modal verbs
There are things that (1)_____ be done
That are not yet begun
Things that I (2)_____ do
When I want to be with you
Although we`re far apart
You`re with me in my heart
No one else (3)_____ do
I just want to be with you
I want to be with you
(4)______ you hear me
I (5)_______ you near me
I want to be with you
I (6)_____ you near me, my love
There are things that (1)_____ be done
That are not yet begun
Things that I (2)_____ do
When I want to be with you
Although we`re far apart
You`re with me in my heart
No one else (3)_____ do
I just want to be with you
must
must
will
I want to be with you
(4)_____ you hear me
I (5)______you near me
I want to be with you
I (6)_____you near me, my love
Can’t
need
need
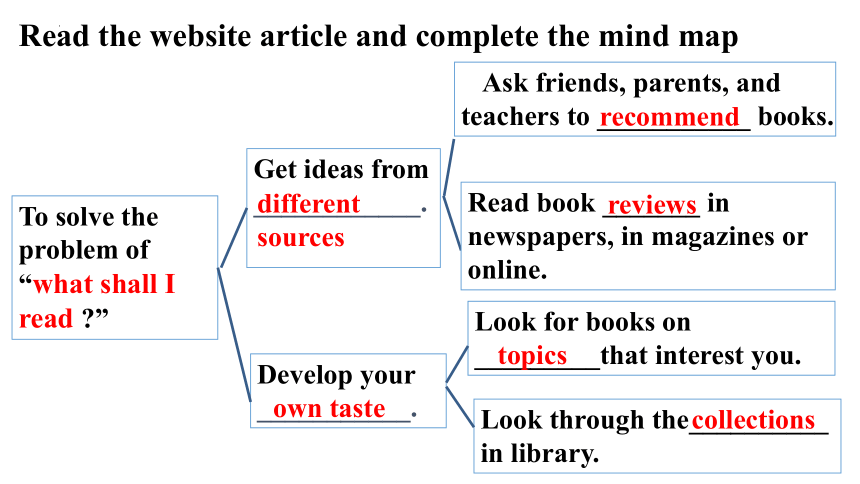
Read the website article and complete the mind map
To solve the problem of “what shall I read ”
Get ideas from ____________.
Develop your
___________.
Ask friends, parents, and teachers to ___________ books.
Read book _______ in newspapers, in magazines or online.
Look for books on
_________that interest you.
Look through the__________
in library.
different sources
own taste
recommend
reviews
topics
collections
Find these Modal verbs words in the article of Part A
Suggestion
Ability
Necessity
Possibility
What shall I read
2.…you can get ideas from different sources…
5.You can also read book reviews in newspapers in magazines or online.
4.Teachers in particular can provide suggestions for interesting reading materials that can be found in the library or bookshop easily.
6.A book review can also tell you whether a book is worth reading or not.
3.…what books you ought to read.
8. However, you must also decide for yourself what kind of books to read.
9.You do not have to read a book just because everyone recommends it.
1.You might have asked yourself this question more than once.
7.These ideas should point you in the right direction.
10.…you may find yourself better able to seek out books to your taste…
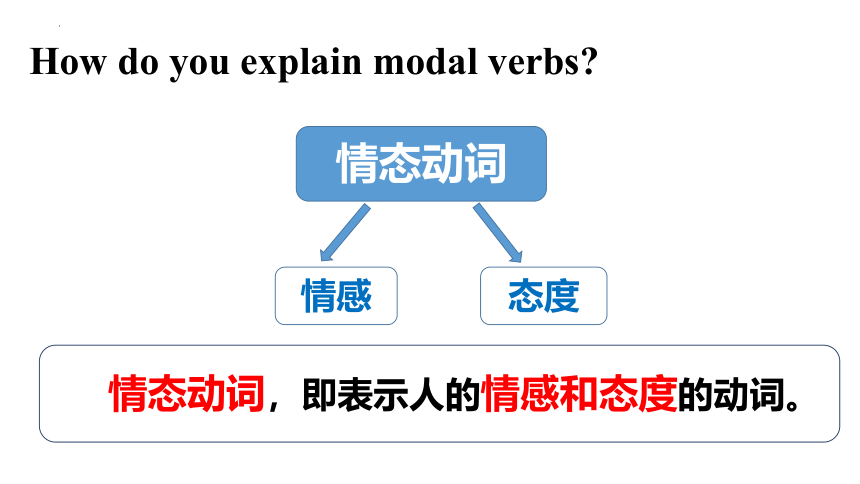
How do you explain modal verbs
情态动词
情感
态度
情态动词,即表示人的情感和态度的动词。
情态动词的特点:
1.情态动词有词义,可表示能力,许可,责任,义务,劝告等。
2.情态动词不能单独使用,它必须和另一个动词原形一起构成谓语.
3.情态动词无人称和数的变化,但是有时态的变化。
情态动词
What Modal Verbs do you know
1.常见的情态动词
can, could, may, might, must, ought to, shall, should, will 和 would。共10个。
2.具有情态动词特征的词还有
dare, need, have to 和 used to
(共4个)兼具情态动词和实义动词
(直接做谓语)两种身份。
1. can & could
1. 表能够做某事(具备某种能力);could主要指过去能够;
1>Two eyes can see more than one.
2> Could the girl read before she went to school
2. 表示请求和许可/建议(could表示更委婉的语气,回答时只能用can);用于否定句中表不允许。
1>-----Can/could I use your bike
----Yes, you can.
2>You can’t wear jeans at work.
3. 疑问句和否定句,表示猜测,意为“可能”;
What can they be doing now
4. 习惯用法“cannot...too...”表示“无论怎样……都不过分,越……越好”。有时cannot可用can never替代。
We cannot thank you too much for what you’ve done for us.
2. may/ might
1. 表允许,以may/might开头的问句中,否定回答中要用may not/can’t。
1)You may take this seat iy you like.
2)--May (Might) I ask for a photo of your baby
--No, you may not/ can’t.
2. 表可能。might可能性小。
She may/might not know about it.
3.may还可用于祈使句表示祝愿。 May you succeed!
have to “必须、不得不“,强调 客观需求,
有时态的变化(has to/ had to / will have to...)
否定形式为 don't / doesn't / didn't have to...
We will have to think of a new plan.
You don't have to run.
3. have to
4. must
1. 用于肯定句中表说话人的意志或义务;坚决要求做某事;
否定mustn’t 表禁止。
1)You must keep your word.
2) Cars mustn’t park in front of the entrance.
2. 在以must 开头的疑问句中,肯定回答用must;
否定回答用needn’t 或don’t have to。
—Must he hand in his exercise books now
—Yes, he must. / No, he needn’t. / No, he don’t have to.
3. 表示可能性或肯定的推断。意为“想必、准是、一定”等,
只用于肯定句。
1) He must be ill. His cheeks are so pale.
2) There must be other ways to solve the problem.
must have to
强调主观看法 不得不(客观)
肯定:must do 肯定:have/has/had to do,will have to do
否定:needn‘t do don’t/doesn’t/didn’t/won’t have to do
(1)shall:表征询意见或请求允许,多与I或we连用。
1) What shall we do this weekend
2) When shall my brother be able to leave hospital
(2) 常用于主语是第三人称的条约、法律法规、规章制度等文件中表“义务”或“规定”。
Every student shall wear school uniform at school.
5. shall should/ought to
6. will & would
1. 表意愿,用于各种人称的陈述句;
I will do anything for you.
They said that they would fight against the haze.
2. 表请求允许,用于疑问句;
Will/Would you please take a message for me
3. 表习惯;
He would spend hours on the telephone.
7. will & would
She will listen to music, alone in her room, for hours.
They won’t lend us any more money.
Would you mind leaving me alone for a few minutes
Fish will die without water.
习惯
意愿
请求允许
习惯
8.双性动词need, dare
1. need 可以作实义动词或情态动词。
We need to finish the job before dark.
You needn’t hurry as there’s plenty time left.
2. dare可以作实义动词(+to do sth )或情态动词。
He dared to travel abroad when he was young.
How dare you let your little child go out alone
4 need (表示必要性)----needn’t “不必”
(1)need表示需要,主要用于否定句和疑问句中,
(2)用need提问时,
肯定回答用must;否定回答用needn't或don't have to
Need I stay here any longer
肯定:Yes, you must.
否定:No, you needn't./don't have to.
(2)need 作实义动词 (行为动词),此时有人称、数和时态的变化,
如果是人作主语,need to do sth
I need to do it right now.
如果是物作主语,need +doing =need to be done
The door needs painting.
=The door needs to be painted. 门需要被油漆。
二. 情态动词的几种形式
情态动词有进行式、完成式和被动式几种形式。其构成见下表。
形式 用法 例句
进行式(情态动词+be doing) 情态动词与主动词的进行式合用,表示某动作正在进行 Jack may be reading in the library.
杰克也许正在图书馆看书。
完成式(情态动词+have done) 情态动词与主动词的完成式合用,表示过去发生的动作
Tom must have arrived home by now.
现在汤姆肯定已经到家了。
被动式(情态动词+be done) 情态动词可以与主动词的被动式合用,表示被动
The road may be blocked.
公路也许被堵了。
情态动词+ have+ done的用法
must have done: 过去一定做过某事
can/could have done: 过去可能做过某事
can’t have done/ couldn’t have done: 过去不可能做某事
may/might(not) have done: 过去可能(没)做过某事
1. 对过去情况的推测
1)From what you said,she must have told you all about it.
2)Tom could have finished the paper on his own.
4)You might have read about the news in the papers.
3)He couldn’t have done the research without your support.
should/ought to have done
表过去本该做却没有做
shouldn’t/ ought not to have done
表过去本不该做却做了
could have done
表本可以/本可能做某事却没做
might have done
表本可能但实际没有发生的事
needn’t have done
表本来不需要做却做了
You should have prepared for the exam, but you spent your time playing.
You shouldn’t have watched that movie — it’ll give you horrible dreams.
You could have done better,but you were too careless.
He may/might have missed the bus. But I’m still not sure about it.
I needn’t have worried before I came to the new school.
2:情态动词+ have done 的其他用法
练习: 选用括号内合适的内容补全下面句子。
1. I'm sorry I couldn't get in touch with him before he left. I __________________ (should have phoned, have phoned) him earlier.
2. Since they aren't answering their telephone, they ______________ (can have left, must have left).
3. You ________ (will, may) lead a horse to the water but you ________ (dare, can) not make it drink.
4. Mary _____________________ (couldn't have received, needn't have received) my email; otherwise she would have replied before now.
5. You _________ (mustn't, needn't) do that if you don't want to.
should have phoned
must have left
may
can
couldn't have received
needn't
6. I don't believe him. He ________ (may not, can't) be serious.
7. If you don't like to swim, you _______________ (may as well, may well) stay at home.
8. They hurried there only to find the meeting canceled. In fact, they __________________ (needn't have gone, wouldn't have gone) at all.
9. She was ill. She ______________________ (couldn't have attended, mustn't attend) the meeting here.
10. Carey didn't go to the party last night because she ________________ (should look after, had to look after) the baby for her sister until 9:30.
needn't have gone
couldn't have attended
had to look after
can't
may as well
(4组) can/could,
may/might,
shall/should,
will/would
(4对) have to, had better,
ought to, used to
(3个) must, need, dare
Review
常见的情态动词归纳
Applying the rules P49
B1 For the following groups of three sentences, tick the sentence which uses the modal verb differently from the other two.
a Can I keep the book for more than two weeks
b Nick can read more in an afternoon than I can in a week!
c Can Mary finish War and Peace in a month
a I am afraid I may be unable to finish this novel today.
b It may be difficult for people to agree on what good literature is.
c You may go to the library tomorrow afternoon, if you have time.
√
√
request
ability
ability
possibility
possibility
suggestion
Applying the rules
B1 For the following groups of three sentences, tick the sentence which uses the modal verb differently from the other two.
a I must finish writing the book review and hand it in before Wednesday.
b You must be tired after three hours’ reading.
c Students must develop the habit of reading classic literature.
a Henry should be reading books in the library.
b I have fifty dollars—that should be enough for three books.
c Reading English novels has greatly increased my vocabulary — you should try it too.
√
√
necessity
possibility
necessity
possibility
possibility
suggestion
B2 Below is an entry in a student’s reading plete the entry with the correct model verbs in brackets.
When my English teacher suggested that I read Charles Dickens’s A Christmas Carol, I thought, “I (1) (can’t/shouldn’t) read this! It (2) (has to/must) be very boring.” Surprisingly, it turned out the exact opposite. I (3) (could/might) not stop turning the pages!
The book’s main character is Scrooge, a rich but mean old man. He hates all kinds of celebrations. On Christmas eve, he is transported to different points in his life by three spirits. In the end, he reflects on these moments and realizes his mistakes. Then he decides that he (4) (might/must) change himself.
can’t
must
could
must
On Christmas morning, he sends a large turkey to a poor man for Christmas dinner. He also tries to make his family and friends happy by spending time with them.
There is something that (5) (can/must) be learnt from A Christmas Carol: we (6) (should/may) treat others with kindness, generosity and love. I think everyone (7) (would/ought to) read this book.
can
should
ought to
C Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the verbs in the brackets, using the proper modal verbs. P76 (选作)
1.— What’s the weather like in your hometown Is it cold in winter
— Yes, it (be) as cold as -30℃ in winter.
2. — I want to invite Tom to see a film tonight. Has he arrived yet
— Yes, he just arrived. But after four hours’ ride, he ______________ (be) tired now and he (prefer) to stay in tonight.
3. — Is Betty still playing the piano
— Yes. I asked her to stop and take a rest, but she______________ (not listen).
can be
must/may/might be
wouldn’t listen
may/might prefer
C Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the verbs in the brackets, using the proper modal verbs. P76
4.—What does the rule say about using the reading room
— No one (talk) loudly.
5.— Your car looks great. It (cost) you a lot of money.
— Yes, it’s quite expensive.
6.— How long can I keep the book
— The books that students borrow (return) to the library within two weeks.
shall/should talk
must have cost
must/shall be returned
Unit4 Reading
The wonder of literature
Grammar and usage
Modal verbs
There are things that (1)_____ be done
That are not yet begun
Things that I (2)_____ do
When I want to be with you
Although we`re far apart
You`re with me in my heart
No one else (3)_____ do
I just want to be with you
I want to be with you
(4)______ you hear me
I (5)_______ you near me
I want to be with you
I (6)_____ you near me, my love
There are things that (1)_____ be done
That are not yet begun
Things that I (2)_____ do
When I want to be with you
Although we`re far apart
You`re with me in my heart
No one else (3)_____ do
I just want to be with you
must
must
will
I want to be with you
(4)_____ you hear me
I (5)______you near me
I want to be with you
I (6)_____you near me, my love
Can’t
need
need
Read the website article and complete the mind map
To solve the problem of “what shall I read ”
Get ideas from ____________.
Develop your
___________.
Ask friends, parents, and teachers to ___________ books.
Read book _______ in newspapers, in magazines or online.
Look for books on
_________that interest you.
Look through the__________
in library.
different sources
own taste
recommend
reviews
topics
collections
Find these Modal verbs words in the article of Part A
Suggestion
Ability
Necessity
Possibility
What shall I read
2.…you can get ideas from different sources…
5.You can also read book reviews in newspapers in magazines or online.
4.Teachers in particular can provide suggestions for interesting reading materials that can be found in the library or bookshop easily.
6.A book review can also tell you whether a book is worth reading or not.
3.…what books you ought to read.
8. However, you must also decide for yourself what kind of books to read.
9.You do not have to read a book just because everyone recommends it.
1.You might have asked yourself this question more than once.
7.These ideas should point you in the right direction.
10.…you may find yourself better able to seek out books to your taste…
How do you explain modal verbs
情态动词
情感
态度
情态动词,即表示人的情感和态度的动词。
情态动词的特点:
1.情态动词有词义,可表示能力,许可,责任,义务,劝告等。
2.情态动词不能单独使用,它必须和另一个动词原形一起构成谓语.
3.情态动词无人称和数的变化,但是有时态的变化。
情态动词
What Modal Verbs do you know
1.常见的情态动词
can, could, may, might, must, ought to, shall, should, will 和 would。共10个。
2.具有情态动词特征的词还有
dare, need, have to 和 used to
(共4个)兼具情态动词和实义动词
(直接做谓语)两种身份。
1. can & could
1. 表能够做某事(具备某种能力);could主要指过去能够;
1>Two eyes can see more than one.
2> Could the girl read before she went to school
2. 表示请求和许可/建议(could表示更委婉的语气,回答时只能用can);用于否定句中表不允许。
1>-----Can/could I use your bike
----Yes, you can.
2>You can’t wear jeans at work.
3. 疑问句和否定句,表示猜测,意为“可能”;
What can they be doing now
4. 习惯用法“cannot...too...”表示“无论怎样……都不过分,越……越好”。有时cannot可用can never替代。
We cannot thank you too much for what you’ve done for us.
2. may/ might
1. 表允许,以may/might开头的问句中,否定回答中要用may not/can’t。
1)You may take this seat iy you like.
2)--May (Might) I ask for a photo of your baby
--No, you may not/ can’t.
2. 表可能。might可能性小。
She may/might not know about it.
3.may还可用于祈使句表示祝愿。 May you succeed!
have to “必须、不得不“,强调 客观需求,
有时态的变化(has to/ had to / will have to...)
否定形式为 don't / doesn't / didn't have to...
We will have to think of a new plan.
You don't have to run.
3. have to
4. must
1. 用于肯定句中表说话人的意志或义务;坚决要求做某事;
否定mustn’t 表禁止。
1)You must keep your word.
2) Cars mustn’t park in front of the entrance.
2. 在以must 开头的疑问句中,肯定回答用must;
否定回答用needn’t 或don’t have to。
—Must he hand in his exercise books now
—Yes, he must. / No, he needn’t. / No, he don’t have to.
3. 表示可能性或肯定的推断。意为“想必、准是、一定”等,
只用于肯定句。
1) He must be ill. His cheeks are so pale.
2) There must be other ways to solve the problem.
must have to
强调主观看法 不得不(客观)
肯定:must do 肯定:have/has/had to do,will have to do
否定:needn‘t do don’t/doesn’t/didn’t/won’t have to do
(1)shall:表征询意见或请求允许,多与I或we连用。
1) What shall we do this weekend
2) When shall my brother be able to leave hospital
(2) 常用于主语是第三人称的条约、法律法规、规章制度等文件中表“义务”或“规定”。
Every student shall wear school uniform at school.
5. shall should/ought to
6. will & would
1. 表意愿,用于各种人称的陈述句;
I will do anything for you.
They said that they would fight against the haze.
2. 表请求允许,用于疑问句;
Will/Would you please take a message for me
3. 表习惯;
He would spend hours on the telephone.
7. will & would
She will listen to music, alone in her room, for hours.
They won’t lend us any more money.
Would you mind leaving me alone for a few minutes
Fish will die without water.
习惯
意愿
请求允许
习惯
8.双性动词need, dare
1. need 可以作实义动词或情态动词。
We need to finish the job before dark.
You needn’t hurry as there’s plenty time left.
2. dare可以作实义动词(+to do sth )或情态动词。
He dared to travel abroad when he was young.
How dare you let your little child go out alone
4 need (表示必要性)----needn’t “不必”
(1)need表示需要,主要用于否定句和疑问句中,
(2)用need提问时,
肯定回答用must;否定回答用needn't或don't have to
Need I stay here any longer
肯定:Yes, you must.
否定:No, you needn't./don't have to.
(2)need 作实义动词 (行为动词),此时有人称、数和时态的变化,
如果是人作主语,need to do sth
I need to do it right now.
如果是物作主语,need +doing =need to be done
The door needs painting.
=The door needs to be painted. 门需要被油漆。
二. 情态动词的几种形式
情态动词有进行式、完成式和被动式几种形式。其构成见下表。
形式 用法 例句
进行式(情态动词+be doing) 情态动词与主动词的进行式合用,表示某动作正在进行 Jack may be reading in the library.
杰克也许正在图书馆看书。
完成式(情态动词+have done) 情态动词与主动词的完成式合用,表示过去发生的动作
Tom must have arrived home by now.
现在汤姆肯定已经到家了。
被动式(情态动词+be done) 情态动词可以与主动词的被动式合用,表示被动
The road may be blocked.
公路也许被堵了。
情态动词+ have+ done的用法
must have done: 过去一定做过某事
can/could have done: 过去可能做过某事
can’t have done/ couldn’t have done: 过去不可能做某事
may/might(not) have done: 过去可能(没)做过某事
1. 对过去情况的推测
1)From what you said,she must have told you all about it.
2)Tom could have finished the paper on his own.
4)You might have read about the news in the papers.
3)He couldn’t have done the research without your support.
should/ought to have done
表过去本该做却没有做
shouldn’t/ ought not to have done
表过去本不该做却做了
could have done
表本可以/本可能做某事却没做
might have done
表本可能但实际没有发生的事
needn’t have done
表本来不需要做却做了
You should have prepared for the exam, but you spent your time playing.
You shouldn’t have watched that movie — it’ll give you horrible dreams.
You could have done better,but you were too careless.
He may/might have missed the bus. But I’m still not sure about it.
I needn’t have worried before I came to the new school.
2:情态动词+ have done 的其他用法
练习: 选用括号内合适的内容补全下面句子。
1. I'm sorry I couldn't get in touch with him before he left. I __________________ (should have phoned, have phoned) him earlier.
2. Since they aren't answering their telephone, they ______________ (can have left, must have left).
3. You ________ (will, may) lead a horse to the water but you ________ (dare, can) not make it drink.
4. Mary _____________________ (couldn't have received, needn't have received) my email; otherwise she would have replied before now.
5. You _________ (mustn't, needn't) do that if you don't want to.
should have phoned
must have left
may
can
couldn't have received
needn't
6. I don't believe him. He ________ (may not, can't) be serious.
7. If you don't like to swim, you _______________ (may as well, may well) stay at home.
8. They hurried there only to find the meeting canceled. In fact, they __________________ (needn't have gone, wouldn't have gone) at all.
9. She was ill. She ______________________ (couldn't have attended, mustn't attend) the meeting here.
10. Carey didn't go to the party last night because she ________________ (should look after, had to look after) the baby for her sister until 9:30.
needn't have gone
couldn't have attended
had to look after
can't
may as well
(4组) can/could,
may/might,
shall/should,
will/would
(4对) have to, had better,
ought to, used to
(3个) must, need, dare
Review
常见的情态动词归纳
Applying the rules P49
B1 For the following groups of three sentences, tick the sentence which uses the modal verb differently from the other two.
a Can I keep the book for more than two weeks
b Nick can read more in an afternoon than I can in a week!
c Can Mary finish War and Peace in a month
a I am afraid I may be unable to finish this novel today.
b It may be difficult for people to agree on what good literature is.
c You may go to the library tomorrow afternoon, if you have time.
√
√
request
ability
ability
possibility
possibility
suggestion
Applying the rules
B1 For the following groups of three sentences, tick the sentence which uses the modal verb differently from the other two.
a I must finish writing the book review and hand it in before Wednesday.
b You must be tired after three hours’ reading.
c Students must develop the habit of reading classic literature.
a Henry should be reading books in the library.
b I have fifty dollars—that should be enough for three books.
c Reading English novels has greatly increased my vocabulary — you should try it too.
√
√
necessity
possibility
necessity
possibility
possibility
suggestion
B2 Below is an entry in a student’s reading plete the entry with the correct model verbs in brackets.
When my English teacher suggested that I read Charles Dickens’s A Christmas Carol, I thought, “I (1) (can’t/shouldn’t) read this! It (2) (has to/must) be very boring.” Surprisingly, it turned out the exact opposite. I (3) (could/might) not stop turning the pages!
The book’s main character is Scrooge, a rich but mean old man. He hates all kinds of celebrations. On Christmas eve, he is transported to different points in his life by three spirits. In the end, he reflects on these moments and realizes his mistakes. Then he decides that he (4) (might/must) change himself.
can’t
must
could
must
On Christmas morning, he sends a large turkey to a poor man for Christmas dinner. He also tries to make his family and friends happy by spending time with them.
There is something that (5) (can/must) be learnt from A Christmas Carol: we (6) (should/may) treat others with kindness, generosity and love. I think everyone (7) (would/ought to) read this book.
can
should
ought to
C Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the verbs in the brackets, using the proper modal verbs. P76 (选作)
1.— What’s the weather like in your hometown Is it cold in winter
— Yes, it (be) as cold as -30℃ in winter.
2. — I want to invite Tom to see a film tonight. Has he arrived yet
— Yes, he just arrived. But after four hours’ ride, he ______________ (be) tired now and he (prefer) to stay in tonight.
3. — Is Betty still playing the piano
— Yes. I asked her to stop and take a rest, but she______________ (not listen).
can be
must/may/might be
wouldn’t listen
may/might prefer
C Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the verbs in the brackets, using the proper modal verbs. P76
4.—What does the rule say about using the reading room
— No one (talk) loudly.
5.— Your car looks great. It (cost) you a lot of money.
— Yes, it’s quite expensive.
6.— How long can I keep the book
— The books that students borrow (return) to the library within two weeks.
shall/should talk
must have cost
must/shall be returned
