2023届高考英语语法复习课攻略长难句(二)非简单句:并列句和主从复合句课件 (共47张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2023届高考英语语法复习课攻略长难句(二)非简单句:并列句和主从复合句课件 (共47张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 725.1KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-03-27 14:41:56 | ||
图片预览






文档简介
(共47张PPT)
攻略长难句
(二)
老师:XXX
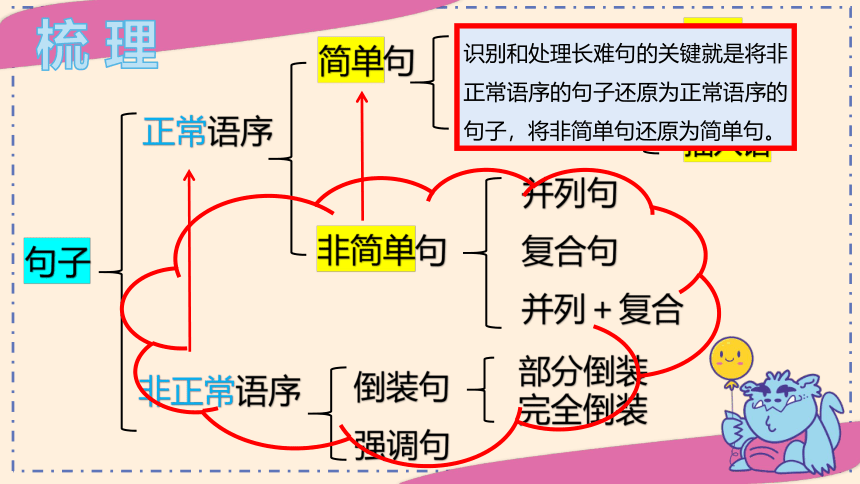
句子
正常语序
非正常语序
简单句
五大基本句型
四大成分
定语
状语
同位语
插入语
并列句
复合句
并列+复合
倒装句
强调句
部分倒装
完全倒装
非简单句
识别和处理长难句的关键就是将非正常语序的句子还原为正常语序的句子,将非简单句还原为简单句。
梳 理
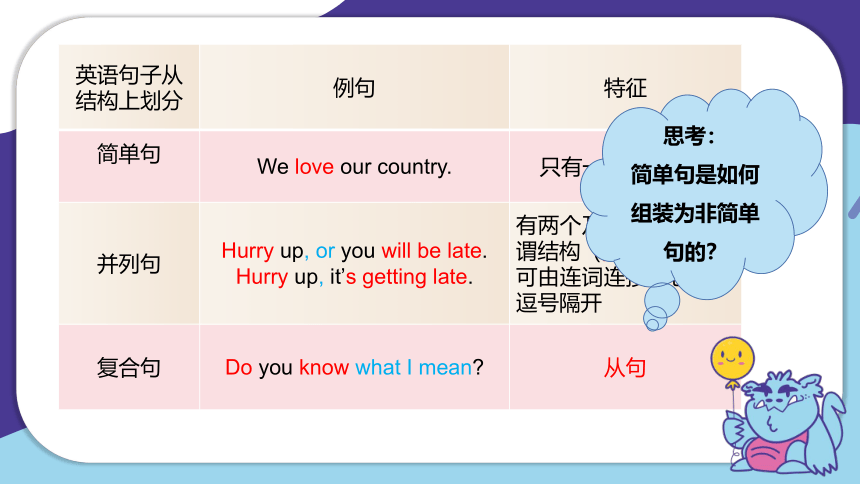
英语句子从结构上划分 例句 特征
简单句 We love our country. 只有一个主谓结构
并列句 Hurry up, or you will be late. Hurry up, it’s getting late. 有两个及以上独立的主谓结构(分句)
可由连词连接,也可用逗号隔开
复合句 Do you know what I mean 从句
思考:
简单句是如何组装为非简单句的?
简单句组装成非简单句遵循2个规则:
主从复合句——遵循主句专一原则
① 一个句子只能有一个主句,主句中不能有连接词。
② 有n个分句,就只能有n-1个连接词。
并列句——遵循并列对等原则(并列成分、并列连词),其前后部分必须对等。
主句:句子的主语(句子开头的第一个独立名词)。
独立名词指之前没有介词、连接词(从属连接词)
连接词:关系代词:that, who, whom, which, what, whose.
关系连词:when, where, why, although.
标点 冒号(:)分号(;)破折号(——)
并列连词
主从复合句(三大从句)
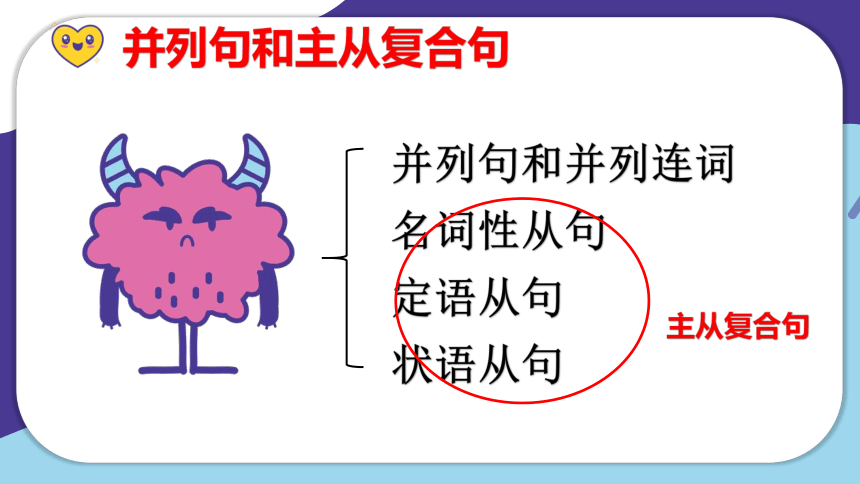
并列句
并列句和并列连词
名词性从句
定语从句
状语从句
并列句和主从复合句
主从复合句
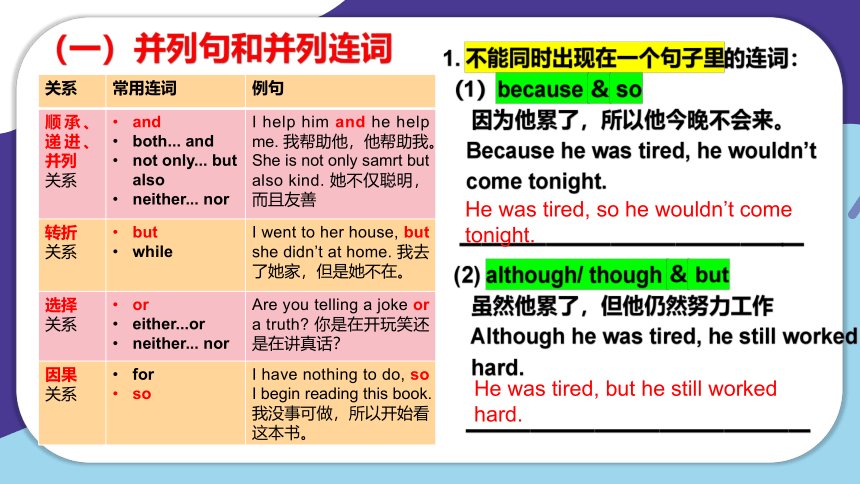
(一)并列句和并列连词
关系 常用连词 例句
顺承、递进、并列 关系 and both... and not only... but also neither... nor I help him and he help me. 我帮助他,他帮助我。
She is not only samrt but also kind. 她不仅聪明,而且友善
转折 关系 but while I went to her house, but she didn’t at home. 我去了她家,但是她不在。
选择 关系 or either...or neither... nor Are you telling a joke or a truth 你是在开玩笑还是在讲真话?
因果 关系 for so I have nothing to do, so I begin reading this book.
我没事可做,所以开始看这本书。
1. 不能同时出现在一个句子里的连词:
(1)because & so
因为他累了,所以他今晚不会来。
Because he was tired, he wouldn’t
come tonight.
————————————————
(2) although/ though & but
虽然他累了,但他仍然努力工作
Although he was tired, he still worked
hard.
————————————————
He was tired, so he wouldn’t come tonight.
He was tired, but he still worked hard.
并列句和并列连词
观察例句思考:and和or用于否定句中的区别 I can’t sing or dance. Lucy and Lily can't speak Chinese. 当列举成分是主语,又在否定词之前时,用 and连接;当列举成分在否定词之后,用 or 构成完全否定。
There is no water and no air on the moon. 在否定句中,如果连接的两部分都有否定词,只能用and。
Man can't live without air and water. Man will die without air or water 在否定句中,without之后若有列举成分,则用and连接,构成完全否定;
在肯定句中,without 之后的列举成分要用 or 连接才能构成完全否定。
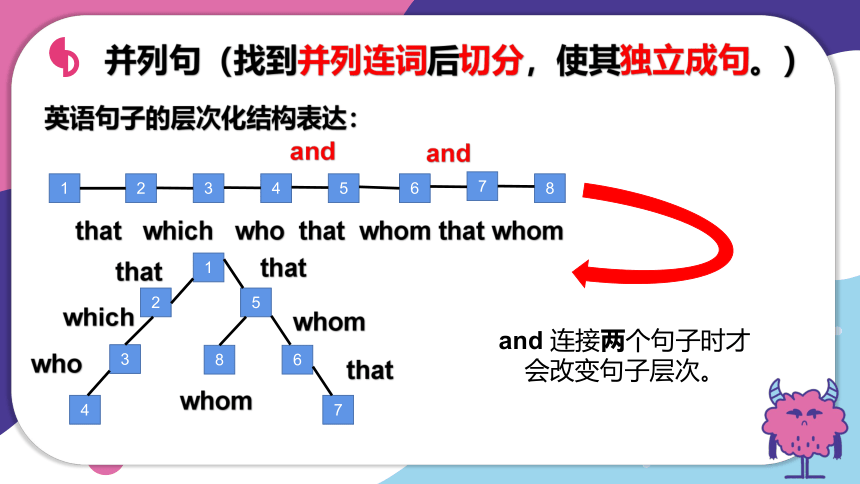
并列句(找到并列连词后切分,使其独立成句。)
英语句子的层次化结构表达:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
5
3
4
8
6
7
that which who that whom that whom
that
which
who
that
whom
whom
that
and
and
and 连接两个句子时才会改变句子层次。
(二)名词性从句
在句子中起名词作用的句子。而名词在句子中可以作的成分有
————、————、————、————。
因此,名词性从句在句子中可以作__________、__________、
__________、____________。
主语
宾语
表语
同位语
主语从句
同位语从句
表语从句
宾语从句
思考从句和分句的区别:
分句:由1个or1个以上的短语构成
包含1个主谓结构
分为独立分句&非独立分句
独立分句:可以单独存在,本身能构成一个完整的简单句。
并列句中的分句
复合句中的主句
非独立分句:不能单独存在,属于另一独立分句,存在于复合句之中。
从句:从属分句
判断红色部分是独立分句,还是非独立分句(从句)
a. Zoe always goes to school by bus.
b. Zoe always goes to school by bus but Jack always goes to school by bike.
c. Zoe goes to school on foot now because she lives close to the school.
d. Zoe used to go to school by bus when she was little.
e. Why Zoe always goes to school by bus is a mystery.
f. We have no idea why Zoe goes to school by bus.
独立分句
独立分句
独立分句
非独立分句
非独立分句
独立分句
并列句中的分句
复合句中的主句
主语从句
同位语从句
简单句
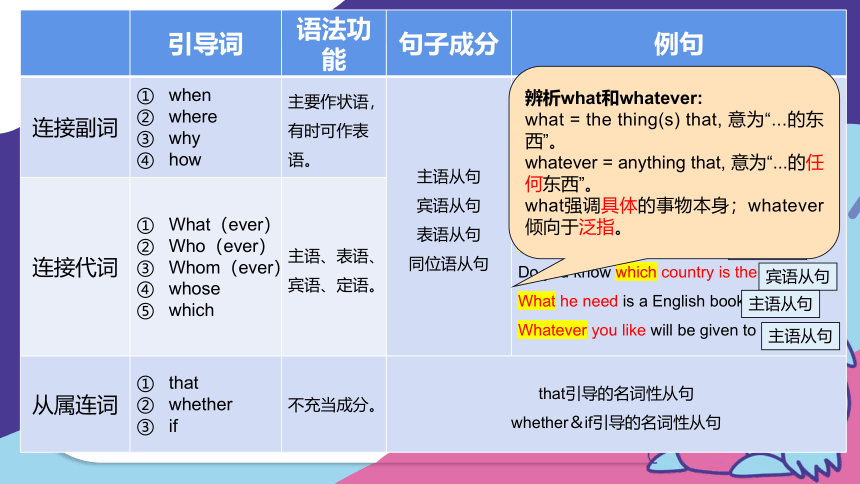
引导词 语法功能 句子成分 例句
连接副词 when where why how 主要作状语,有时可作表语。 主语从句 宾语从句 表语从句 同位语从句 It makes no difference where we shall have the meeting.
The problem is what we should say.
I can’t imagine how she did it.
Whose the money is doesn’t concern me.
Whom she saw didn't matter.
Do you know which country is the largest
What he need is a English book.
Whatever you like will be given to you.
连接代词 What(ever) Who(ever) Whom(ever) whose which 主语、表语、宾语、定语。 从属连词 that whether if 不充当成分。 that引导的名词性从句 whether&if引导的名词性从句 主语从句
表语从句
宾语从句
主语从句
主语从句
宾语从句
主语从句
主语从句
辨析what和whatever:
what = the thing(s) that, 意为“...的东西”。
whatever = anything that, 意为“...的任何东西”。
what强调具体的事物本身;whatever倾向于泛指。
That引导的名词性从句
That price will go up is certain.
That she is the winner is the situation.
It is natural that we have different ideas.
It is a pity that you can’t go with us.
It happened that she wasn’t in that day.
It is said that he has arrived in Shanghai.
观察例句,
总结规律!
That price will go up is certain.
That she is the winner is the situation.
It is natural that we have different ideas.
It is a pity that you can’t go with us.
It happened that she wasn’t in that day.
It is said that he has arrived in Shanghai.
无先行词
有先行词
把that引导的主语从句放句首的情况很少,只有为了强调or谓语比较长时才这用这样的表达。
It + be + adj +that从句
It + be + 名词(名词词组)+that从句
It + be + 过去分词 【动词的被动语态】+that从句
It +动词+that从句
It 作形式主语,真正的主语是that后面的句子。
I know (that) she was against us.
Who can guarantee that he’ll keep his word
I feel that you have a strong will.
You can depend on it, I shall be there.
I feel it a terrible thing that you lied to me.
You can depend on it that I shall always help you.
与刚刚的例句相比有什么不同?
放在动词之后,that从句作宾语。有时that可以省略。
it作先行宾语,真正的宾语是that后面的句子。
哪些动词后面的that连词可以省略:
believe
suppose
presume
think
在say, see, know, hear, propose, understand
和be told之后,that可省略可不省略。
尝试造句!
That引导的名词性从句在句子中可以作:
主语:常用 it 作形式主语。
宾语:及物动词+it+宾补+that从句
动词(动词短语)+it +that从句
表语
My decision is that the meeting will be held at 10
o’clock this morning. (that 一般不省略)
Whether&if引导的名词性从句
whether / if 都可以
只能用 whether的情况
只能用 if 的情况
whether / if 都可以:
Let me know whether you can finish the paper tonight.
He asked me if I could help him.
It’s uncertain whether he will come this evening.
It’s doubtful whether Mary will come.
二者都能引导宾语从句,常放在see,ask,learn,tell,wonder,doubt,find out 等动词(动词短语)后。
二者都可以用在 it 作形式主语的从句中。
if
whether
if
if
只能用 whether的情况:
Whether the meeting will be held is still a problem.
The question is whether it is worth doing
The idea whether it is right depends on the result.
Success depends on whether we make efforts.
Please tell me whether to go or stay here.
We discussed whether he should leave this city.
以下是只能用whether的例句,小组讨论,总结出6种规则吧!
置于句首,引导主语从句时
引导表语从句时
放在名词后,引导同位语从句时
放在介词后,引导宾语从句时
后接不定式时
放在动词discuss之后时
只能用 if 的情况:
在引导否定概念的宾语从句时,只能用if:
He asked me if I hadn’t finished the project.
Mary wonders if you can’t go to the party tonight.
whether和if 都可以引导宾语从句。
介宾搭配只能用whether
含有否定词的宾语从句只能用if引导
分清楚了吗?
(1)注意“引导词”的句法功能:
一般说来,用作主语或宾语时,要用连接代词,用作状语,用连接副词。另外注意,连接词that, whether不充当句子成分。
(2)注意句子意思:
根据题干的语境再结合连接代词或连接副词的意思,选择出最佳答案。
(3)注意关系代词型what所引导的名词性从句:
将它理解为“先行词+关系代词”,如What he said astonished us.=The thing that he said astonished us.)。
名词性从句的解题技巧:5个注意
(4)注意由-ever词引导的名词性从句:
尤其要注意它(whoever, whichever, whatever)与引导让步状语从句时的区别。
whoever相当于 anybody who
whichever相当于 the person or the thing that
whatever相当于 anything that
(5)注意同位语从句与定语从句的区别:
引导词的区别,先行词的区别等。
同位语从句与定语从句的区别:
(1)被修饰的词不同:
同位语从句的前面一般是数量有限的、表示抽象意义的名词;而定语从句的先行词是指人或物的名词。
(2)从句的作用不同:
同位语从句表示同位名词的具体内容;而定语从句是对先行词的限制、描绘或说明。
(3)引导词的作用不同:
引导同位语从句的that是连词,在从句中不担任任何成分,但不能省略;而引导定语从句的that为关系代词,在从句中担任句子的某种成分,当担任定语从句中的宾语时,that可以省略。
(4)引导词不同:
定语从句不能用what, how, whether引导;而同位从句可以用what, how, whether引导。
(5)判定定语从句和同位语从句的方法:
同位语从句可充当同位名词的表语;而定语从句不能充当先行词的表语。
1. She just wants to be noticed, which is ______ she dresses so strangely.
A. how B. why C. where D. what
2. Why do they never go on holiday I mean it’s not ______ they’re poor, is it
A. that B. when C. as if D. how
3. Sales of the dictionary are twice ______ they were in the same quarter last year.
A. those B. as if C. that D. what
4. The mill produces ______ is widely acknowledged to be the finest wool in the world.
A. which B. it C. what D. that
5. Why not try your lick downtown, Bob That’s _______ the best jobs are. (浙江卷)
A. where B. what C.when D. why
及时训练
as if 可以引导表语从句、状语从句,or虚拟语气
这部词典的销售量是去年同季度的两倍。
句子不完整,可以排除A,B,C
同位语从句
1. _______ matters most in learning English is enough practice. (全国II)
A. What B. Why C.Where D. Which
2. _______ parents say and do has a life-long effect on their children. (陕西卷)
A. That B. Which C.What D. As
3. Patience is a kind of quality ― and that is ______ it takes to do anything well.
A. what B. which C. which D. how
4. Country life gives him peace and quiet, which is ______ he can’t enjoy while living in
big cities.
A. that B. why C. where D. what
及时训练
1. Don’t you know, my dear friend, ______ it is your money not you that she loves
A. who B. which C. that D. what
2. Can you imagine ______ it would be like to live without electricity
A. that B. why C. where D. what
3. Everyone knows, perhaps except you, ______ your girl-friend is a cheat.
A. who B. which C. that D. what
4. Choosing the right dictionary depends on _______ you want to use it for. (江苏卷)
A. what B. why C.how D. whether
5. Could I speak to _______ is in charge of International Sales, please (山东卷)
A. anyone B. someone C.whoever D. no matter who
及时训练
句中的whoever引导宾语从句,用作介词to的宾语,故选C不选D。
1. Having checked the doors were closed, and _______ all the lights were off, the
boy opened the door to his bedroom. (湖南卷)
A. why B. that C.when D. ours
2. A warm thought suddenly came to me _______ I might use the pocket money to buy
some flowers for my mother’s birthday. (安徽卷)
A. if B. when C.that D. which
3. Since none of us know this place well, we’ll have to eat at ______ restaurant has
a free table.
A. what B. which C. whenever D. whichever
及时训练
that引导的宾语从句,为having checked的宾语。
that引导的同位语从句,修饰名词thought。
从语境下手:无论哪一个
1. The simple county life is quite different _____ the city people are used to.
A. in which B. in what C. from which D. from what
2. Hearing what he said to me, I realized ______ silly a mistake I had made.
A. which B. that C. how D. what
3. The plan’s success depends on ______ skillfully you deal with the people around you.
A. which B. what C. when D. how
4. ______ of us gets home first starts cooking.
A. Which B. What C. Whichever D. Whatever
5. Bring these with you and give it to ______ you see in the meeting-room.
A. whichever B. whatever C. whoever D. however
及时训练
whoever相当于 anybody who
whichever相当于 the person or the thing that
whatever相当于 anything that
(三)形容词性从句:定语从句
含义:在主从复合句中,放在名词or代词后面充当
定语的从句。被定语从句修饰的词叫先行词,通常
位于定语从句之前。
结构:关系词位于先行词和从句之间,它既起连接
作用,又充当从句中的一个成分。
先行词+关系词+从句
定语从句
先行词 关系代词在定语从句中的成分 关系词
指人 主语 who, that
宾语 who, whom, that
定语 whose
指物 主语 which, that
宾语 which, that
定语 whose
指时间 状语 when
指地点 状语 where
指原因 状语 why
关系代词
关系副词
介词+关系代词
① I still remembe the day _____ I first came to your home on.
② I still remember the day _____ I first came to your home.
A. which
B. that
C. on which
D.when
AB
CD
When = on which
Where = in which
Why = for which
限制性定语从句 非限制性定语从句
与关系词联系紧密,删除后影响整个句子的表达。 与关系词联系不紧密,是一种补充说明,删除后不影响整个句子的表达。
前面通常不用逗号隔开 前面通常用逗号隔开
that, which, who, whom, whose, when, where, why, as. which, who, whom, whose, when, where, as.
People who take physical exercise live longer.
I need the book which you took away last night.
The only thing that you can do is to study hard.
I remember the day when you came back to me.
His daughter, who is in Beijing now, is coming home next week.
This is the reason why he was late.
These apple trees,which I planted three years ago,have not borne any fruit.
She was very patient towards the children,which her husband seldom was.
In the presence of so many people he was little tense, which was understandable.
限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句
补充说明:非限制性定语从句
补充说明:非限制性定语从句
补充说明:非限制性定语从句
补充说明:非限制性定语从句
不影响主干句子想表达的意思。
逗号后面一定就要用which吗?
If a book is in English, _____ means slow progress for you.
A. as B. which C. what D. that
解析:逗号前是一个条件状语从句,逗号后是该状语从句的主句,that 在此代表前文所述的情况,用作主句的主语。
及时训练
1. If you want to go, _______is quite all right with me.
A. that B. which C. and it D. so
2. When I say two hours, _____ includes time for eating.
A. as B. which C. what D. that
3. If you want a double room , _____ will cost another £15.
A. as B. which C. what D. that
4. If you have the money, _____ will be OK.
A. as B. which C. and it D. that
5. Unless I’m very much mistaken, ______ is my watch you’re wearing!
A. as B. which C. what D. that
及时训练
that
限制性定语从句中只用that的情况 当先行词指事 / 物时,只用which的情况
当先行词是all, everything, anything, nothing, none, little, few等时。 引导非限制性定语从句,通常要用which:
The current, which is very rapid, makes the river dangerous.
直接放在介词之后作宾语时,通常要用which:
She may be late, in which case we ought to wait for her.
有时“介词+which”引导的定语从句可以转换成“介词+which+不定式”的结构:
She had a gun with which he could defend herself.
She had a gun with which to defend herself.
当先行词被the only, the very, any, every, all, much, few, little, no, the last等词修饰时。 当先行词是形容词最高级or被形容词最高级修饰时。 当先行词是序数词or被序数词修饰时。 当先行词是既有人又有物的并列词组时。 主句是以which开头的特殊疑问句时。
1. By serving others, a person focuses on someone other than himself or herself, _______ can be very eye-opening and rewarding.
A. who B. which C.what D. that
2. Chan’s restaurant on Baker Street, _______ used to be poorly run, is now a successful business.
A. that B. which C.who D. where
3. He was educated at the local high school, _______ he went on to Beijing
University.
A. after which B. after that C. in which D. in that
及时训练
及时训练
1. _____ comes to see me, tell him I’m out.
A. Anyone B. Who C. Whoever D. Everyone
2. It was the boy _____ had been in prison _____ stole the money.
A. who, where B. that, how C. who, that D. that, which
3. Is this the reason ______ at the meeting for his carelessness in his work
A. he explained B. what he explained
C. how he explained D. why he explained
4. When he was working there he caught a serious illness from ______ efforts he still suffers.
A. which B. that C. whose D. what
5. The old building, behind ______ was a famous church, was ______ we used to work.
A. that, the place B. it, the place C. which, where D. what, where
whoever 引导的是让步状语从句,相当于 no matter who。
全句为强调句,被强调成分是 the boy (以及修饰它的定语从句who had been in prison)。
动词explained缺宾语。
whose 在定语从句中用作定语,修饰 efforts,表示所属关系。
4. When he was working there he caught a serious illness from ______ efforts he still suffers.
A. which B. that C. whose D. what
(1) whose 引导的定语从句,其后应紧跟名词,构成“whose+名词”,表示所属关系。
(2) whose 引导的定语从句,其先行词不仅可以指人,还可以指物。
(3) whose 引导的定语从句指物时,可用 of which 代替whose,但词序不同,即whose+名词=the +名词+of which。
When he was working there he caught a serious illness the efforts of which he still suffers.
1. The train, ______ takes only two hours to get there, is quicker than the bus, ______
takes three.
A. which, it B. it, which C. which, which D. it, it
2. The crisis has reached a point ______ the receiver will have to be called in.
A. when B. where C. that D. who
3. I’m looking for a new job, one ______ I get a bit more job satisfaction.
A. when B. where C. that D. which
4. We need someone with a fresh point of view, ______ can suggest changes.
A. that B. which C. who D. what
5. There is no one else ______, so we have to come for help again.
A. who to turn to B. we can turn to C. for whom to turn D. for her to turn
及时训练
that在定语从句中做主语,宾语或表语.而point表示的是in the point case,所以此处因为where引导的定语从句,修饰a point.
首先从句 I get a bit more job satisfaction这个句子是完整的,不缺成分,所以不选B,D,而根据语意,找份“从中”能获得更多满意的新工作,这里的where相当于from which。
阅读中定语从句的语序障碍和解决办法
识别 作用 ① 修饰限定名词or句子
② 连接两个具有共同名词的句子
③ 表示因果关系
连接两个具有共同名词的句子:
I have three books, the red of those books is my favorite.
I have three books
The red one of those books is my favorite.
I have three books of which the red is my favorite.
更加紧凑
定语从句的语序障碍和解决办法
识别 作用 ① 修饰限定名词or句子
② 连接两个具有共同名词的句子
③ 表示因果关系
连接两个具有共同名词的句子:
I have three books, the red of those books is my favorite.
I have three books
The red one of those books is my favorite.
I have three books of which the red is my favorite.
更加紧凑
具体操作方法:
Step1: 找准切分点(关系代词前,介词前,关系连词前后都行) 关系连词后面切 End
关系连词前面切
Step2:确定指代对象 做主语 End
做宾语/表语
Step3:调整代词or代词+介词的位置
This is the expert to whom we are turning.
This is the expert to whom we are turning.
动手试一试
(四) 副词性从句:状语从句
状语从句即指在主从复合句用作状语的从句。
状语从句是高中英语学习中的一个语法重点,也是历年高考重点考查的内容之一。学习状语从句主要应注意引导状语从句的从属连词的用法与区别,以及从属连词在一定的语言环境中的意义与用法。
状语从根据其用途可分为:
时间状语从句
条件状语从句
原因状语从句
目的状语从句
结果状语从句
让步状语从句
比较状语从句
地点状语从句等
1. 引导时间状语从句的从属连词很多,常见的有before, after, when, while, as, since, till, until, as soon as 等。
2. 表示“当…时候”的 while, when, as 的用法区别是:
while从句中的谓语动词必须是延续性动词;表示带有规律性的“每当”或当主、从句谓语动词的动作发生有先后时,只能用 when;当表示“一边…一边…”或“随着”时,只能用 as。另外,用于此义的 as 所引导的时间状语从句谓语只能是动作动词,不能是状态动词:
“I’m going to the post office.”
“_____ you’re there, can you get me some stamps ”
A. As B. While C. Because D. If
时间状语从句
3. until 在肯定句中通常只连用延续性动词,表示相应动作结束的时间;在否定句中通常连用非延续性动词,表示相应动作开始的时间,意为“直到…才”。如:
He waited until she was about to leave. 他等着一直到她准备离开。
I did not begin to work untill he had gone. 他走了后我才开始工作。
4. 表示“一…就”除用 as soon as 外,还可用 the minute, the second, the instant, immediately, directly, instantly, no sooner…than, hardly…when 等。如:
I came immediately you called. 你一来电话我就来了。
Hardly had she arrived when it began to snow. 她刚到就下起雪来了。
The moment I have finished I'll give you a call. 我一干完就给你打电话。
1. 引导条件状语从句的从属连词主要有 if, unless, as (so) long as等。如:
Don’t come unless I telephone. 除非我打电话,否则你别来。
If you watch carefully you will see how to do it. 如果你仔细瞧你会看出该怎样做。
As long as you do your best, we’ll be happy. 只要你尽力,我们就满意了。
2. in case 也可引导条件状语从句,其意为“如果”、“万一”。如:
In case I forget, please remind me about it. 如果我忘了,请提醒我。
条件状语从句
1. 引导让步状语从句的从属连词主要有 although, though, however (=no matter how), even if(即使), whether…or(不论…还是)等连词。如:
The speech is good, though it could be better. 这次演讲不错,虽然还可以再好一点。
He went out even though it was raining. 尽管下雨,他还是出去了。
2. as 也可引导让步状语从句,但要将名词、形容词或副词等提到 as 前,若提前的是单数可数名词,要省略 a / an。如:
Teacher as he is, he can’t know everything. 虽然是老师,他也不可能什么都懂。
注:表示“虽然”的 though, although 不可与 but 连用,但可与 yet, still 连用。
让步状语从句
3. 连词 while 有时也可表示“尽管”、“虽然”,引导让步状语从句。如:
While we don’t agree we continue to be friends. 尽管我们意见不同,我们还是朋友。
4. whatever, whoever, however, whenever, wherever 等引导让步状语从句。如:
Don’t lose heart whatever you do. 不管你做什么,都不要灰心。
Whoever you are, you can’t pass this way. 不管你是谁,你都不能从这里通过。
它们引导让步状语从句时,通常可换成no matter…,如说:
No matter what you say, I believe you. 无论你说什么,我都相信你。
No matter when you come, you are welcome. 你什么时候来,我们都欢迎。
No matter how much he eats, he never gets fat. 无论他吃多少, 他都不发胖。
攻略长难句
(二)
老师:XXX
句子
正常语序
非正常语序
简单句
五大基本句型
四大成分
定语
状语
同位语
插入语
并列句
复合句
并列+复合
倒装句
强调句
部分倒装
完全倒装
非简单句
识别和处理长难句的关键就是将非正常语序的句子还原为正常语序的句子,将非简单句还原为简单句。
梳 理
英语句子从结构上划分 例句 特征
简单句 We love our country. 只有一个主谓结构
并列句 Hurry up, or you will be late. Hurry up, it’s getting late. 有两个及以上独立的主谓结构(分句)
可由连词连接,也可用逗号隔开
复合句 Do you know what I mean 从句
思考:
简单句是如何组装为非简单句的?
简单句组装成非简单句遵循2个规则:
主从复合句——遵循主句专一原则
① 一个句子只能有一个主句,主句中不能有连接词。
② 有n个分句,就只能有n-1个连接词。
并列句——遵循并列对等原则(并列成分、并列连词),其前后部分必须对等。
主句:句子的主语(句子开头的第一个独立名词)。
独立名词指之前没有介词、连接词(从属连接词)
连接词:关系代词:that, who, whom, which, what, whose.
关系连词:when, where, why, although.
标点 冒号(:)分号(;)破折号(——)
并列连词
主从复合句(三大从句)
并列句
并列句和并列连词
名词性从句
定语从句
状语从句
并列句和主从复合句
主从复合句
(一)并列句和并列连词
关系 常用连词 例句
顺承、递进、并列 关系 and both... and not only... but also neither... nor I help him and he help me. 我帮助他,他帮助我。
She is not only samrt but also kind. 她不仅聪明,而且友善
转折 关系 but while I went to her house, but she didn’t at home. 我去了她家,但是她不在。
选择 关系 or either...or neither... nor Are you telling a joke or a truth 你是在开玩笑还是在讲真话?
因果 关系 for so I have nothing to do, so I begin reading this book.
我没事可做,所以开始看这本书。
1. 不能同时出现在一个句子里的连词:
(1)because & so
因为他累了,所以他今晚不会来。
Because he was tired, he wouldn’t
come tonight.
————————————————
(2) although/ though & but
虽然他累了,但他仍然努力工作
Although he was tired, he still worked
hard.
————————————————
He was tired, so he wouldn’t come tonight.
He was tired, but he still worked hard.
并列句和并列连词
观察例句思考:and和or用于否定句中的区别 I can’t sing or dance. Lucy and Lily can't speak Chinese. 当列举成分是主语,又在否定词之前时,用 and连接;当列举成分在否定词之后,用 or 构成完全否定。
There is no water and no air on the moon. 在否定句中,如果连接的两部分都有否定词,只能用and。
Man can't live without air and water. Man will die without air or water 在否定句中,without之后若有列举成分,则用and连接,构成完全否定;
在肯定句中,without 之后的列举成分要用 or 连接才能构成完全否定。
并列句(找到并列连词后切分,使其独立成句。)
英语句子的层次化结构表达:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
5
3
4
8
6
7
that which who that whom that whom
that
which
who
that
whom
whom
that
and
and
and 连接两个句子时才会改变句子层次。
(二)名词性从句
在句子中起名词作用的句子。而名词在句子中可以作的成分有
————、————、————、————。
因此,名词性从句在句子中可以作__________、__________、
__________、____________。
主语
宾语
表语
同位语
主语从句
同位语从句
表语从句
宾语从句
思考从句和分句的区别:
分句:由1个or1个以上的短语构成
包含1个主谓结构
分为独立分句&非独立分句
独立分句:可以单独存在,本身能构成一个完整的简单句。
并列句中的分句
复合句中的主句
非独立分句:不能单独存在,属于另一独立分句,存在于复合句之中。
从句:从属分句
判断红色部分是独立分句,还是非独立分句(从句)
a. Zoe always goes to school by bus.
b. Zoe always goes to school by bus but Jack always goes to school by bike.
c. Zoe goes to school on foot now because she lives close to the school.
d. Zoe used to go to school by bus when she was little.
e. Why Zoe always goes to school by bus is a mystery.
f. We have no idea why Zoe goes to school by bus.
独立分句
独立分句
独立分句
非独立分句
非独立分句
独立分句
并列句中的分句
复合句中的主句
主语从句
同位语从句
简单句
引导词 语法功能 句子成分 例句
连接副词 when where why how 主要作状语,有时可作表语。 主语从句 宾语从句 表语从句 同位语从句 It makes no difference where we shall have the meeting.
The problem is what we should say.
I can’t imagine how she did it.
Whose the money is doesn’t concern me.
Whom she saw didn't matter.
Do you know which country is the largest
What he need is a English book.
Whatever you like will be given to you.
连接代词 What(ever) Who(ever) Whom(ever) whose which 主语、表语、宾语、定语。 从属连词 that whether if 不充当成分。 that引导的名词性从句 whether&if引导的名词性从句 主语从句
表语从句
宾语从句
主语从句
主语从句
宾语从句
主语从句
主语从句
辨析what和whatever:
what = the thing(s) that, 意为“...的东西”。
whatever = anything that, 意为“...的任何东西”。
what强调具体的事物本身;whatever倾向于泛指。
That引导的名词性从句
That price will go up is certain.
That she is the winner is the situation.
It is natural that we have different ideas.
It is a pity that you can’t go with us.
It happened that she wasn’t in that day.
It is said that he has arrived in Shanghai.
观察例句,
总结规律!
That price will go up is certain.
That she is the winner is the situation.
It is natural that we have different ideas.
It is a pity that you can’t go with us.
It happened that she wasn’t in that day.
It is said that he has arrived in Shanghai.
无先行词
有先行词
把that引导的主语从句放句首的情况很少,只有为了强调or谓语比较长时才这用这样的表达。
It + be + adj +that从句
It + be + 名词(名词词组)+that从句
It + be + 过去分词 【动词的被动语态】+that从句
It +动词+that从句
It 作形式主语,真正的主语是that后面的句子。
I know (that) she was against us.
Who can guarantee that he’ll keep his word
I feel that you have a strong will.
You can depend on it, I shall be there.
I feel it a terrible thing that you lied to me.
You can depend on it that I shall always help you.
与刚刚的例句相比有什么不同?
放在动词之后,that从句作宾语。有时that可以省略。
it作先行宾语,真正的宾语是that后面的句子。
哪些动词后面的that连词可以省略:
believe
suppose
presume
think
在say, see, know, hear, propose, understand
和be told之后,that可省略可不省略。
尝试造句!
That引导的名词性从句在句子中可以作:
主语:常用 it 作形式主语。
宾语:及物动词+it+宾补+that从句
动词(动词短语)+it +that从句
表语
My decision is that the meeting will be held at 10
o’clock this morning. (that 一般不省略)
Whether&if引导的名词性从句
whether / if 都可以
只能用 whether的情况
只能用 if 的情况
whether / if 都可以:
Let me know whether you can finish the paper tonight.
He asked me if I could help him.
It’s uncertain whether he will come this evening.
It’s doubtful whether Mary will come.
二者都能引导宾语从句,常放在see,ask,learn,tell,wonder,doubt,find out 等动词(动词短语)后。
二者都可以用在 it 作形式主语的从句中。
if
whether
if
if
只能用 whether的情况:
Whether the meeting will be held is still a problem.
The question is whether it is worth doing
The idea whether it is right depends on the result.
Success depends on whether we make efforts.
Please tell me whether to go or stay here.
We discussed whether he should leave this city.
以下是只能用whether的例句,小组讨论,总结出6种规则吧!
置于句首,引导主语从句时
引导表语从句时
放在名词后,引导同位语从句时
放在介词后,引导宾语从句时
后接不定式时
放在动词discuss之后时
只能用 if 的情况:
在引导否定概念的宾语从句时,只能用if:
He asked me if I hadn’t finished the project.
Mary wonders if you can’t go to the party tonight.
whether和if 都可以引导宾语从句。
介宾搭配只能用whether
含有否定词的宾语从句只能用if引导
分清楚了吗?
(1)注意“引导词”的句法功能:
一般说来,用作主语或宾语时,要用连接代词,用作状语,用连接副词。另外注意,连接词that, whether不充当句子成分。
(2)注意句子意思:
根据题干的语境再结合连接代词或连接副词的意思,选择出最佳答案。
(3)注意关系代词型what所引导的名词性从句:
将它理解为“先行词+关系代词”,如What he said astonished us.=The thing that he said astonished us.)。
名词性从句的解题技巧:5个注意
(4)注意由-ever词引导的名词性从句:
尤其要注意它(whoever, whichever, whatever)与引导让步状语从句时的区别。
whoever相当于 anybody who
whichever相当于 the person or the thing that
whatever相当于 anything that
(5)注意同位语从句与定语从句的区别:
引导词的区别,先行词的区别等。
同位语从句与定语从句的区别:
(1)被修饰的词不同:
同位语从句的前面一般是数量有限的、表示抽象意义的名词;而定语从句的先行词是指人或物的名词。
(2)从句的作用不同:
同位语从句表示同位名词的具体内容;而定语从句是对先行词的限制、描绘或说明。
(3)引导词的作用不同:
引导同位语从句的that是连词,在从句中不担任任何成分,但不能省略;而引导定语从句的that为关系代词,在从句中担任句子的某种成分,当担任定语从句中的宾语时,that可以省略。
(4)引导词不同:
定语从句不能用what, how, whether引导;而同位从句可以用what, how, whether引导。
(5)判定定语从句和同位语从句的方法:
同位语从句可充当同位名词的表语;而定语从句不能充当先行词的表语。
1. She just wants to be noticed, which is ______ she dresses so strangely.
A. how B. why C. where D. what
2. Why do they never go on holiday I mean it’s not ______ they’re poor, is it
A. that B. when C. as if D. how
3. Sales of the dictionary are twice ______ they were in the same quarter last year.
A. those B. as if C. that D. what
4. The mill produces ______ is widely acknowledged to be the finest wool in the world.
A. which B. it C. what D. that
5. Why not try your lick downtown, Bob That’s _______ the best jobs are. (浙江卷)
A. where B. what C.when D. why
及时训练
as if 可以引导表语从句、状语从句,or虚拟语气
这部词典的销售量是去年同季度的两倍。
句子不完整,可以排除A,B,C
同位语从句
1. _______ matters most in learning English is enough practice. (全国II)
A. What B. Why C.Where D. Which
2. _______ parents say and do has a life-long effect on their children. (陕西卷)
A. That B. Which C.What D. As
3. Patience is a kind of quality ― and that is ______ it takes to do anything well.
A. what B. which C. which D. how
4. Country life gives him peace and quiet, which is ______ he can’t enjoy while living in
big cities.
A. that B. why C. where D. what
及时训练
1. Don’t you know, my dear friend, ______ it is your money not you that she loves
A. who B. which C. that D. what
2. Can you imagine ______ it would be like to live without electricity
A. that B. why C. where D. what
3. Everyone knows, perhaps except you, ______ your girl-friend is a cheat.
A. who B. which C. that D. what
4. Choosing the right dictionary depends on _______ you want to use it for. (江苏卷)
A. what B. why C.how D. whether
5. Could I speak to _______ is in charge of International Sales, please (山东卷)
A. anyone B. someone C.whoever D. no matter who
及时训练
句中的whoever引导宾语从句,用作介词to的宾语,故选C不选D。
1. Having checked the doors were closed, and _______ all the lights were off, the
boy opened the door to his bedroom. (湖南卷)
A. why B. that C.when D. ours
2. A warm thought suddenly came to me _______ I might use the pocket money to buy
some flowers for my mother’s birthday. (安徽卷)
A. if B. when C.that D. which
3. Since none of us know this place well, we’ll have to eat at ______ restaurant has
a free table.
A. what B. which C. whenever D. whichever
及时训练
that引导的宾语从句,为having checked的宾语。
that引导的同位语从句,修饰名词thought。
从语境下手:无论哪一个
1. The simple county life is quite different _____ the city people are used to.
A. in which B. in what C. from which D. from what
2. Hearing what he said to me, I realized ______ silly a mistake I had made.
A. which B. that C. how D. what
3. The plan’s success depends on ______ skillfully you deal with the people around you.
A. which B. what C. when D. how
4. ______ of us gets home first starts cooking.
A. Which B. What C. Whichever D. Whatever
5. Bring these with you and give it to ______ you see in the meeting-room.
A. whichever B. whatever C. whoever D. however
及时训练
whoever相当于 anybody who
whichever相当于 the person or the thing that
whatever相当于 anything that
(三)形容词性从句:定语从句
含义:在主从复合句中,放在名词or代词后面充当
定语的从句。被定语从句修饰的词叫先行词,通常
位于定语从句之前。
结构:关系词位于先行词和从句之间,它既起连接
作用,又充当从句中的一个成分。
先行词+关系词+从句
定语从句
先行词 关系代词在定语从句中的成分 关系词
指人 主语 who, that
宾语 who, whom, that
定语 whose
指物 主语 which, that
宾语 which, that
定语 whose
指时间 状语 when
指地点 状语 where
指原因 状语 why
关系代词
关系副词
介词+关系代词
① I still remembe the day _____ I first came to your home on.
② I still remember the day _____ I first came to your home.
A. which
B. that
C. on which
D.when
AB
CD
When = on which
Where = in which
Why = for which
限制性定语从句 非限制性定语从句
与关系词联系紧密,删除后影响整个句子的表达。 与关系词联系不紧密,是一种补充说明,删除后不影响整个句子的表达。
前面通常不用逗号隔开 前面通常用逗号隔开
that, which, who, whom, whose, when, where, why, as. which, who, whom, whose, when, where, as.
People who take physical exercise live longer.
I need the book which you took away last night.
The only thing that you can do is to study hard.
I remember the day when you came back to me.
His daughter, who is in Beijing now, is coming home next week.
This is the reason why he was late.
These apple trees,which I planted three years ago,have not borne any fruit.
She was very patient towards the children,which her husband seldom was.
In the presence of so many people he was little tense, which was understandable.
限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句
补充说明:非限制性定语从句
补充说明:非限制性定语从句
补充说明:非限制性定语从句
补充说明:非限制性定语从句
不影响主干句子想表达的意思。
逗号后面一定就要用which吗?
If a book is in English, _____ means slow progress for you.
A. as B. which C. what D. that
解析:逗号前是一个条件状语从句,逗号后是该状语从句的主句,that 在此代表前文所述的情况,用作主句的主语。
及时训练
1. If you want to go, _______is quite all right with me.
A. that B. which C. and it D. so
2. When I say two hours, _____ includes time for eating.
A. as B. which C. what D. that
3. If you want a double room , _____ will cost another £15.
A. as B. which C. what D. that
4. If you have the money, _____ will be OK.
A. as B. which C. and it D. that
5. Unless I’m very much mistaken, ______ is my watch you’re wearing!
A. as B. which C. what D. that
及时训练
that
限制性定语从句中只用that的情况 当先行词指事 / 物时,只用which的情况
当先行词是all, everything, anything, nothing, none, little, few等时。 引导非限制性定语从句,通常要用which:
The current, which is very rapid, makes the river dangerous.
直接放在介词之后作宾语时,通常要用which:
She may be late, in which case we ought to wait for her.
有时“介词+which”引导的定语从句可以转换成“介词+which+不定式”的结构:
She had a gun with which he could defend herself.
She had a gun with which to defend herself.
当先行词被the only, the very, any, every, all, much, few, little, no, the last等词修饰时。 当先行词是形容词最高级or被形容词最高级修饰时。 当先行词是序数词or被序数词修饰时。 当先行词是既有人又有物的并列词组时。 主句是以which开头的特殊疑问句时。
1. By serving others, a person focuses on someone other than himself or herself, _______ can be very eye-opening and rewarding.
A. who B. which C.what D. that
2. Chan’s restaurant on Baker Street, _______ used to be poorly run, is now a successful business.
A. that B. which C.who D. where
3. He was educated at the local high school, _______ he went on to Beijing
University.
A. after which B. after that C. in which D. in that
及时训练
及时训练
1. _____ comes to see me, tell him I’m out.
A. Anyone B. Who C. Whoever D. Everyone
2. It was the boy _____ had been in prison _____ stole the money.
A. who, where B. that, how C. who, that D. that, which
3. Is this the reason ______ at the meeting for his carelessness in his work
A. he explained B. what he explained
C. how he explained D. why he explained
4. When he was working there he caught a serious illness from ______ efforts he still suffers.
A. which B. that C. whose D. what
5. The old building, behind ______ was a famous church, was ______ we used to work.
A. that, the place B. it, the place C. which, where D. what, where
whoever 引导的是让步状语从句,相当于 no matter who。
全句为强调句,被强调成分是 the boy (以及修饰它的定语从句who had been in prison)。
动词explained缺宾语。
whose 在定语从句中用作定语,修饰 efforts,表示所属关系。
4. When he was working there he caught a serious illness from ______ efforts he still suffers.
A. which B. that C. whose D. what
(1) whose 引导的定语从句,其后应紧跟名词,构成“whose+名词”,表示所属关系。
(2) whose 引导的定语从句,其先行词不仅可以指人,还可以指物。
(3) whose 引导的定语从句指物时,可用 of which 代替whose,但词序不同,即whose+名词=the +名词+of which。
When he was working there he caught a serious illness the efforts of which he still suffers.
1. The train, ______ takes only two hours to get there, is quicker than the bus, ______
takes three.
A. which, it B. it, which C. which, which D. it, it
2. The crisis has reached a point ______ the receiver will have to be called in.
A. when B. where C. that D. who
3. I’m looking for a new job, one ______ I get a bit more job satisfaction.
A. when B. where C. that D. which
4. We need someone with a fresh point of view, ______ can suggest changes.
A. that B. which C. who D. what
5. There is no one else ______, so we have to come for help again.
A. who to turn to B. we can turn to C. for whom to turn D. for her to turn
及时训练
that在定语从句中做主语,宾语或表语.而point表示的是in the point case,所以此处因为where引导的定语从句,修饰a point.
首先从句 I get a bit more job satisfaction这个句子是完整的,不缺成分,所以不选B,D,而根据语意,找份“从中”能获得更多满意的新工作,这里的where相当于from which。
阅读中定语从句的语序障碍和解决办法
识别 作用 ① 修饰限定名词or句子
② 连接两个具有共同名词的句子
③ 表示因果关系
连接两个具有共同名词的句子:
I have three books, the red of those books is my favorite.
I have three books
The red one of those books is my favorite.
I have three books of which the red is my favorite.
更加紧凑
定语从句的语序障碍和解决办法
识别 作用 ① 修饰限定名词or句子
② 连接两个具有共同名词的句子
③ 表示因果关系
连接两个具有共同名词的句子:
I have three books, the red of those books is my favorite.
I have three books
The red one of those books is my favorite.
I have three books of which the red is my favorite.
更加紧凑
具体操作方法:
Step1: 找准切分点(关系代词前,介词前,关系连词前后都行) 关系连词后面切 End
关系连词前面切
Step2:确定指代对象 做主语 End
做宾语/表语
Step3:调整代词or代词+介词的位置
This is the expert to whom we are turning.
This is the expert to whom we are turning.
动手试一试
(四) 副词性从句:状语从句
状语从句即指在主从复合句用作状语的从句。
状语从句是高中英语学习中的一个语法重点,也是历年高考重点考查的内容之一。学习状语从句主要应注意引导状语从句的从属连词的用法与区别,以及从属连词在一定的语言环境中的意义与用法。
状语从根据其用途可分为:
时间状语从句
条件状语从句
原因状语从句
目的状语从句
结果状语从句
让步状语从句
比较状语从句
地点状语从句等
1. 引导时间状语从句的从属连词很多,常见的有before, after, when, while, as, since, till, until, as soon as 等。
2. 表示“当…时候”的 while, when, as 的用法区别是:
while从句中的谓语动词必须是延续性动词;表示带有规律性的“每当”或当主、从句谓语动词的动作发生有先后时,只能用 when;当表示“一边…一边…”或“随着”时,只能用 as。另外,用于此义的 as 所引导的时间状语从句谓语只能是动作动词,不能是状态动词:
“I’m going to the post office.”
“_____ you’re there, can you get me some stamps ”
A. As B. While C. Because D. If
时间状语从句
3. until 在肯定句中通常只连用延续性动词,表示相应动作结束的时间;在否定句中通常连用非延续性动词,表示相应动作开始的时间,意为“直到…才”。如:
He waited until she was about to leave. 他等着一直到她准备离开。
I did not begin to work untill he had gone. 他走了后我才开始工作。
4. 表示“一…就”除用 as soon as 外,还可用 the minute, the second, the instant, immediately, directly, instantly, no sooner…than, hardly…when 等。如:
I came immediately you called. 你一来电话我就来了。
Hardly had she arrived when it began to snow. 她刚到就下起雪来了。
The moment I have finished I'll give you a call. 我一干完就给你打电话。
1. 引导条件状语从句的从属连词主要有 if, unless, as (so) long as等。如:
Don’t come unless I telephone. 除非我打电话,否则你别来。
If you watch carefully you will see how to do it. 如果你仔细瞧你会看出该怎样做。
As long as you do your best, we’ll be happy. 只要你尽力,我们就满意了。
2. in case 也可引导条件状语从句,其意为“如果”、“万一”。如:
In case I forget, please remind me about it. 如果我忘了,请提醒我。
条件状语从句
1. 引导让步状语从句的从属连词主要有 although, though, however (=no matter how), even if(即使), whether…or(不论…还是)等连词。如:
The speech is good, though it could be better. 这次演讲不错,虽然还可以再好一点。
He went out even though it was raining. 尽管下雨,他还是出去了。
2. as 也可引导让步状语从句,但要将名词、形容词或副词等提到 as 前,若提前的是单数可数名词,要省略 a / an。如:
Teacher as he is, he can’t know everything. 虽然是老师,他也不可能什么都懂。
注:表示“虽然”的 though, although 不可与 but 连用,但可与 yet, still 连用。
让步状语从句
3. 连词 while 有时也可表示“尽管”、“虽然”,引导让步状语从句。如:
While we don’t agree we continue to be friends. 尽管我们意见不同,我们还是朋友。
4. whatever, whoever, however, whenever, wherever 等引导让步状语从句。如:
Don’t lose heart whatever you do. 不管你做什么,都不要灰心。
Whoever you are, you can’t pass this way. 不管你是谁,你都不能从这里通过。
它们引导让步状语从句时,通常可换成no matter…,如说:
No matter what you say, I believe you. 无论你说什么,我都相信你。
No matter when you come, you are welcome. 你什么时候来,我们都欢迎。
No matter how much he eats, he never gets fat. 无论他吃多少, 他都不发胖。
