第十章动词的时态(思维导图+知识梳理+好题精炼)2022-2023初中英语中考语法归纳
文档属性
| 名称 | 第十章动词的时态(思维导图+知识梳理+好题精炼)2022-2023初中英语中考语法归纳 |  | |
| 格式 | docx | ||
| 文件大小 | 152.9KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-04-04 07:07:11 | ||
图片预览



文档简介
第十章 动词的时态
思维导图
知识梳理
在英语中,不同时间里以不同方式发生的动作或存在的状态,要用不同的动词形式来表示,动词的这种不同形式称为动词的时态.
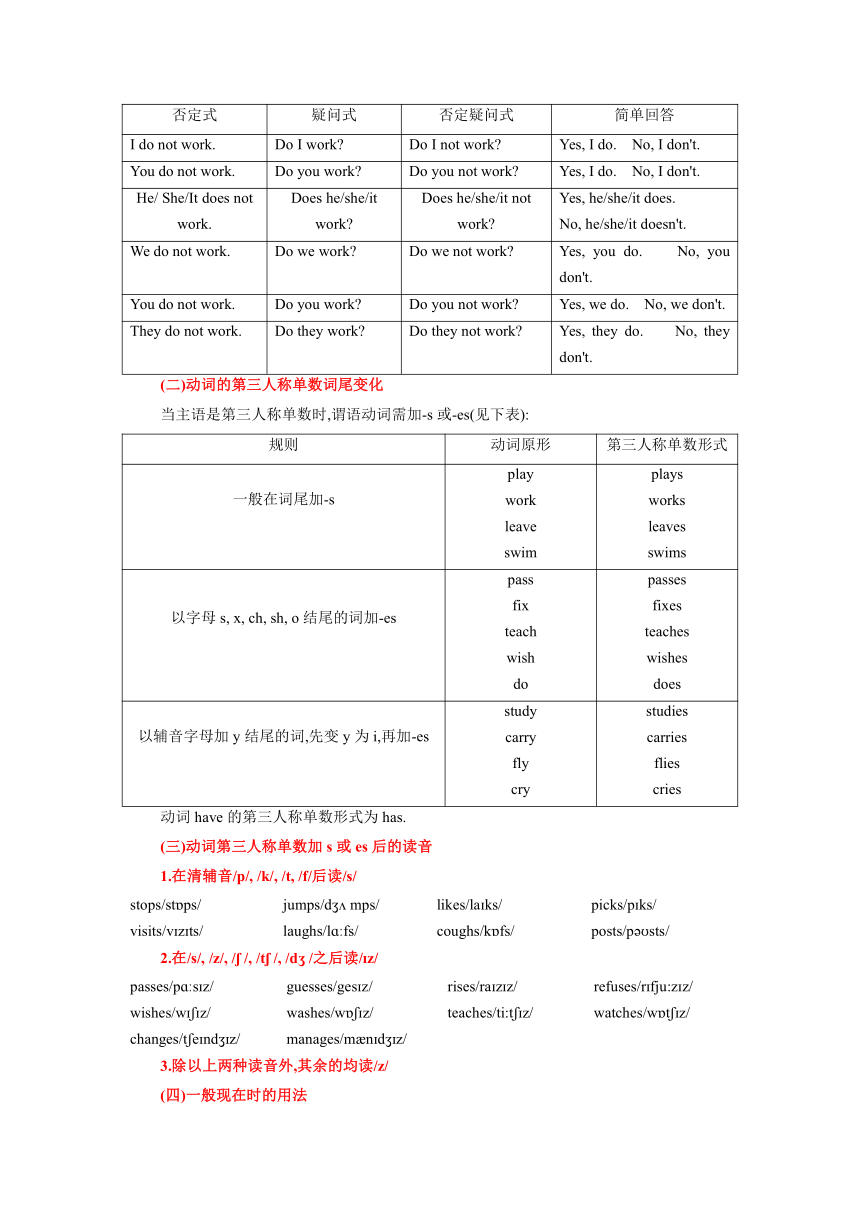
英语的时态从时间上划分,可以分为现在时、过去时、将来时和过去将来时;从行为方式上划分,每一类又可以分为一般式、进行式、完成式和完成进行式.这样,英语动词合起来共有16种时态.现以动词work为例,将16种时态形式列表如下:
现在时 过去时 将来时 过去将来时
一般式 work works worked shall work will Should work should
进行式 am are working is was working were shall be working will should be working would
完成式 has worked have had worked shall have worked will should have worked would
完成进 行式 have been working has had been working shall have been working will should have been working would
这些时态中常用的有:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时以及过去将来时8种.
一、一般现在时
(一)一般现在时的构成
一般现在时的否定式、疑问式、否定疑问式和简单回答形式,以work为例,列表如下:
否定式 疑问式 否定疑问式 简单回答
I do not work. Do I work Do I not work Yes, I do. No, I don't.
You do not work. Do you work Do you not work Yes, I do. No, I don't.
He/ She/It does not work. Does he/she/it work Does he/she/it not work Yes, he/she/it does. No, he/she/it doesn't.
We do not work. Do we work Do we not work Yes, you do. No, you don't.
You do not work. Do you work Do you not work Yes, we do. No, we don't.
They do not work. Do they work Do they not work Yes, they do. No, they don't.
(二)动词的第三人称单数词尾变化
当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词需加-s或-es(见下表):
规则 动词原形 第三人称单数形式
一般在词尾加-s play work leave swim plays works leaves swims
以字母s, x, ch, sh, o结尾的词加-es pass fix teach wish do passes fixes teaches wishes does
以辅音字母加y结尾的词,先变y为i,再加-es study carry fly cry studies carries flies cries
动词have的第三人称单数形式为has.
(三)动词第三人称单数加s或es后的读音
1.在清辅音/p/, /k/, /t, /f/后读/s/
stops/st ps/ jumps/d mps/ likes/la ks/ picks/p ks/
visits/v z ts/ laughs/lɑ fs/ coughs/k fs/ posts/p sts/
2.在/s/, /z/, / /, /t /, /d /之后读/ z/
passes/pɑ s z/ guesses/ges z/ rises/ra z z/ refuses/r fju:z z/
wishes/w z/ washes/w z/ teaches/ti:t z/ watches/w t z/
changes/t e nd z/ manages/m n d z/
3.除以上两种读音外,其余的均读/z/
(四)一般现在时的用法
1.表示经常的或习惯性的动作
常与often, always, sometimes, every day, on Sundays/Mondays等表示频度的时间状语连用.
My father often gets up early in the morning.我父亲早晨经常早起.
He has breakfast at 7:00 every morning.他每天早晨七点吃早饭.
2.表示现在的状态
My father is at work. He is very busy.我父亲在工作,他很忙.
The boy is twelve.这个男孩儿12岁.
3.表示主语具备的性格、能力和特征
I like to listen to music.我喜欢听音乐.
They speak English very well.他们英语说得非常好.
This taxi driver knows the city of Beijing like the back of his hand.这位出租车司机对北京城了如指掌.
4.表示客观事实和普遍真理
Two plus two is four.2加2等于4.
The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.太阳从东方升起,从西方落下.
5.表示计划安排好的将来动作,也可用一般现在时,只限于: go, come, leave, start, begin, arrive, be等动
The plane takes off at 11 a.m.飞机上午11点起飞.
We leave Beijing next month.下月我们离开北京.
He comes back tonight.他今晚回来.
6.在时间、条件状语从句中,用一般现在时代替一般将来时
I'll write to you as soon as I get to Shanghai.我一到上海就给你写信.
Turn off the lights before you leave.走前关灯.
If it doesn't rain tomorrow, we'll go to the park.如果明天不下雨,我们就去公园.
If it rains tomorrow, we won't go to the park.如果明天下雨,我们就不去公园.
7.表示(书、信、报纸、通知、牌示、广播等)“说”“报导”,用一般现在时,主要是动词say
The notice says,“ No Parking.”通知说:“不准停放车辆.”
The radio says heavy rain in the afternoon.广播预报下午有大雨.
8.叙述历史,常用一般现在时,以使其生动
Jeanne is sitting in the park. Mathilde walks towards her, and she stops and speaks to Jeanne.
珍妮在公园里坐着.玛蒂尔德向她走来,停下来和珍妮谈话.
二、一般过去时
(一)一般过去时的构成(以动词work为例)
否定式 疑问式 否定疑问式 简单回答
I did not work. Did I work Did I not work Yes, I did. No, I didn't.
You did not work. Did you work Did you not work Yes, I did. No, I didn't.
He/ She/ It did not work. Did he/she/it work Did he/she/it not work Yes, he/she/it did. No, he/she/it didn't.
We did not work. Did we work Did we not work Yes, you did. No, you didn't.
You did not work. Did you work Did you not work Yes, we did. No, we didn't.
They did not work. Did they work Did they not work Yes, they did. No, they didn't.
(二)动词过去式的词尾变化(规则变化)
构成规则 原形 过去式
-般在动词末尾加-ed work plant play worked planted played
结尾是e的动词在末尾加-d like live change liked lived changed
末尾只有一个辅音字母的重读闭音节词,先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ed plan stop drop planned stopped dropped
以辅音字母加y结尾的,先变y为i再加-ed carry study cry carried studied cried
点拨
(1)prefer的过去式要先双写末尾辅音字母r再加-ed: preferred.
(2)travel的过去式可双写1再加-ed; travelled(英式英语);也可以直接加-ed; traveled(美式英语).
(三)动词过去式与过去分词的读音
1.清辅音后面的-ed读/t/音
stopped/st pt/停止 laughed/lɑ ft/笑 asked/ɑ skt/提问
hoped/h pt/希望 dressed/drest/穿衣 marched/mɑ t t/行军
watched/w t t/看 pushed/p t/推
2.浊辅音及元音后面的-ed读/d/音
rubbed/r bd/擦 tried/tra d/试图,努力 lived/l vd/生活
begged/begd/请求 named/ne md/取名 agreed/ gri:d/同意
rained/re nd/下雨 moved/mu:vd/移动
3.t,d后面加-ed读/d/音
united/ju: na t d/联合 heated/hi:t d/加热 ended/end d/结束
needed/ni:d d/需要 wanted/w nt d/想要 guided/'ga d d/指引
4.以-ed结尾的过去分词作形容词用时读/ d /音
aged/e d d/年老的 learned/1 n d/有学问的
wicked/w k d/罪恶的 interested/ ntr st d/感兴趣的
(四)不规则动词的过去式和过去分词
原形 过去式 过去分词 词义
Cost Cut Hit Hurt Let Put Read cost cut hit hurt let put read cost cut hit hurt let put read 花费 削、砍 打击 伤害、使受伤 让 放 读
Become Come Run became came ran become come run 成为 来 跑
Bring Buy Fight Think Catch Teach brought bought fought thought caught taught brought bought fought thought caught taught 带来 买 打架 想 抓住 教
Build Lend Send Spend Lose Smell built lent sent spent lost smelt/smelled built lent sent spent lost smelt/smelled 建筑 借给 送,寄 花(钱、时间) 丢失 闻
Feel Keep Sleep Sweep Leave Meet felt kept slept swept left met felt kept slept swept left met 感觉 保持 睡觉 扫 离开 遇见
Burn Learn Mean burnt/burned learnt/learned meant burnt/burned learnt/learned meant 燃烧 学会 意思是
Sell Tell sold told sold told 卖 告诉
Hold held held 抓住、握住
Shine Win Get Stand Understand Dig Hang have(has) hear make pay shone/shined won got stood understood dug hung/hanged had heard made paid shone/shined won got stood understood dug hung/hanged had heard made paid 照耀,使光亮 赢 得到 站 理解、懂得 挖 挂/绞死 有 听见 制造 付(钱)
say sit find said sat found said sat found 说 坐 发现
am, is are do go wear lie see was were did went wore lay saw been been done gone worn lain seen 是 是 做 去 穿着 躺 看见
begin drink ring sing swim began drank rang sang swam begun drunk rung sung swum 开始 喝 打电话,(铃)响 唱 游泳
drive rise ride write drove rose rode wrote driven risen ridden written 驾驶 升起 骑(马、自行车) 写
blow grow know throw fly blew grew knew threw flew blown grown known thrown flown 吹 生长 知道 投掷 飞
draw show drew showed drawn shown 画、拉 出示
break speak choose take mistake wake broke spoke chose took mistook waked/woke broken spoken chosen taken mistaken waked/woken 打断,打破 讲 选择 拿走 弄错 唤醒
beat eat fall give forget beat ate fell gave forgot beaten eaten fallen given forgotten 打 吃 落下 给 忘记
(五)一般过去时的用法
1.表示过去某个特定时间发生的动作或存在的状态
这时常与yesterday, last week, a moment ago, in 1949等表示过去时间的状语连用.
What did you have for breakfast this morning 今天早饭吃的什么
I had two eggs and a glass of milk.早饭吃了两个鸡蛋和一杯牛奶.
The police stopped him on his way home last night.昨晚在回家的路上警察拦住了他.
My sister passed her examination because she studied very hard.我妹妹通过了考试,因为她学习非常努力.
2.表示过去某一段时间内经常或反复发生的动作,这时常和表示频度的状语连用
Last term we often did experiments.上学期我们经常做试验.
He always went to work by bus.他过去总是乘车去上班.
She gave her teacher presents every Christmas.她每年都给她的老师送圣诞礼物.
点拨
used to do的否定式和疑问式有两种构成法.
(1)借助did,即:didn't use to do
He didn't use to do it, did he 他过去不经常这么做,是吗
Did you use to play football 你过去经常踢足球吗
(2)不用did,即:usedn't to do
She usedn't to make those mistakes.她以前并不经常出那些错的.
Used you to play football 你过去经常踢足球吗
3.在时间、条件状语从句中,常用一般过去时代替过去将来时
He said he would not go if it rained.他说如果天下雨就不去了.
They told us that they would not leave until she came back.他们告诉我们直到她回来他们才会离开.
4.常用“would+ do”表示过去经常反复发生的动作
I would ask you to think carefully before you spoke.我劝你在讲话之前要认真考虑一下.
We would turn to him for help when we were in trouble.我们一遇麻烦,就向他请求帮助.
三、一般将来时
(一)一般将来时的构成
一般将来时的否定式、疑问式、否定疑问句式和简单回答形式,以study为例:
否定式 疑问式 否定疑问句式 简单回答
I shall/will not study. Shall I study Shall I not study (Shan't I study ) Yes, you will. No, you won't.
You will not study. Will you not study Will you study (Won't you study ) Yes, I shall/will. No, I shan't/won't.
He/ She/It will not study. Will he/she/it not study Will he/she/it study (Won't he/she/it study ) Yes, he/she/it will. No, he/she/it won't.
We shall/will not study. Shall we study Shall we not study (Shan't we study ) Yes, you will. No, you won't.
You will not study Will you study Will you not study (Won't you study ) Yes, we shall/will. No, we shan't/won't.
They will not study. Will they study Will they not study (Won't they study ) Yes, they will. No, they won't.
shall用于第一人称I(we)shall; will可用于各人称.美式英语中,不论什么人称和数,一律用will+动词原形.在口语中,will常缩写为’ll与主语连写在一起.
如:I'll, you'll, he'11和she'll we’ll, they'll, shall not 常缩写为shan't, will not常缩写为won't.
在疑问中,主语为第一人称(I和We)时,常用助动词shall.
(二)一般将来时的用法
1.一般将来时表示在将来某个时间将要发生的动作或存在的状态.常与表示将来的时间状语如tomorrow, next week/month/year等连用
I'll come to pick you up at 6:00 on Wednesday evening.我星期三晚上6点来接您.
I'll have a party next Saturday. I hope you can come.下周六我要举行聚会,希望你能来.
If it doesn't rain tomorrow, we are going to the Summer Palace.如果明天不下雨,我们就去颐和园.
My daughter will be twenty years old next year.我女儿明年就20岁了.
He will be here in ten minutes.他10分钟后在这儿.
2.表示将来经常或反复发生的动作
I'll come and see you every Sunday next year.明年我将每个星期天来看你.
We shall come and work in this factory every year.我们将每年到这个工厂来劳动.
3.表示揣测
This will be the dictionary you're looking for.这大概是你要找的那本词典吧.
The game will be finished by now.球赛大概已经结束了.
4.“be going to+动词原形”结构
表示现在打算在最近或将来要做的事,或表示说话人根据已有的迹象认为很可能要发生的事情.如:
We are going to have a new subject this year.今年我们将学一门新学科.
It's going to rain this afternoon.今天下午天要下雨.
I'm not going to write letters.我不打算写信.
5.“be+动词不定式”结构表示按计划要发生的事,或用来征求对方意见
Where are we to stay tonight 今晚我们在哪儿过夜
What is to do 怎么办
6.“be about+动词不定式”结构表示即将做某事
I haven't gone yet, I'm about to.我还没走,正要走呢.
The Sports Meeting is about to start now.运动会即将开始.
点拨
有些表示位置转移的动词,如come, go, leave, start, arrive, fly等的现在进行时可表示按计划或安排将要发生的动作,常与表示将来的时间状语连用.
He is leaving for Shanghai tomorrow.他明天动身去上海.
They are arriving tomorrow afternoon.他们明天下午到达.
(三)需注意的几点
1.在回答Shall I...问句时,应该说:Yes, please./Please do.或No, please don't./Please don't.不可说:Yes, you shall.或No, you shall not.
2.在回答 Shall we...问句时,应该说:Yes, let's... 或 No, I don't think we shall./No, let's not.
(四)will和be going to的比较
1.will和be going to 都可表示某种意愿
但其含义和用法有所不同.
be going to往往表示经过考虑的打算,而will多表示意愿、决心.
We are going to watch the football game.我们打算观看这场足球赛.
I will tell you all about it.我将把全部情况告诉你.
2.will可用于条件从句表示将来的意愿,而be going to用于条件从句,只是表示单纯的将来,试比较
Miss Gao will tell you the answer if you ask her.如果你去问高老师,她会告诉你答案的.
If you are going to attend the meeting, you'd better leave now.如果你要参加会议,最好现在就走.
四、现在进行时
(一)现在进行时的构成
现在进行时由“am/is/are+动词现在分词”构成.
现在进行时的肯定式、否定式和疑问式及简单回答形式:(以动词work为例)
肯定式 I am/'m working. He (She, It)is/isn't working. We(You, They) are/'re working.
否定式 I am not/'m not working. He(She, It)is not/isn't working. We(You, They) are not/aren't working.
疑问式 Am I working... Is he(she, it)working... Are you(we, they)working...
简单回答 Yes, you are. No, you aren't. Yes, I am. No, I'm not. Yes, he(she it) is. No, he(she ,it)isn't. Yes, we(you, they) are. No, we(you, they) aren't.
(二)动词-ing形式的构成及其读音
1.一般在动词原形末尾加-ing
stay-staying/'ste / do-doing/'du: /
listen-listening/'l sn / suffer-suffering/'s f r /
work-working/'w k / spend-spending/'spend /
look-looking/'l k /
2.以不发音的字母e结尾的动词,先去掉e,再加-ing
make-making/'me k / take-taking/'te k /
give-giving/'g v / ride-riding/'ra d /
please-pleasing/'pli:z / refuse-refusing/'r 'fju:z /
close-closing/'kl z / operate-operating/' p re t /
3.以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节词,先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ing
put-putting/'p t / sit-sitting/'s t /
run-running/'r n / win-winning/'w n /
begin-beginning/b 'g n /
4.以ie结尾的动词,先去掉e,把i变为y,再加-ing
lie-lying/'la / tie-tying/'ta / die-dying/'da /
5.以re结尾的动词,先去掉e,再加-ing
prepare-preparing/pr 'pe r / interfere-interfering/ nt 'f r g/
tire-tiring/'ta r / bore-boring/'b :r /
cure-curing/kj r /
6.以er结尾的动词,如果是重读音节结尾,先双写r,再加-ing;如果不是重读音节结尾,就直接加-ing
prefer-preferring water(浇水)-watering
(三)现在进行时的用法
1.表示说话时正在进行或发生的动作
这时可以不用时间状语,也可以和now, at present, at the moment等时间状语连用.有时用一个动词.如look(看),listen(听).
What are you reading now 你在读什么
His mother is watching TV at the present.此刻,他的妈妈正在看电视.
I'm writing a novel at present.眼下我正在写一部小说.
Look! The bus is crossing the bridge.看!这辆公共汽车在过桥.
Listen! Someone is singing in the classroom.听!有人在教室里唱歌.
2.表示当前一段时期内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作(说话时动作不一定正在进行),常与表示一段时间的状语these days, this week等连用
They are working in a factory these days.他们这几天正在工厂劳动.
More and more people are giving up smoking.越来越多的人在戒烟.
They are working in a factory these days.他们这几天在工厂劳动.
They're visiting Beijing this week.这周他们在北京观光.
3.现在进行时常与always, continually, constantly, forever等表示频度的副词连用,表示经常、反复发生的动作,常表示厌烦、不满、赞扬等情感
He is always thinking of his work.他总是想着他的工作.
They're forever quarrelling about something.他们老是为某件事争吵不休.(不满)
4.现在进行时有时也用来代替一般现在时,表示一个经常性的动作或状态,或是为了表示一种感情(如赞叹、厌烦等)或是为了强调情况的暂时性
How are you feeling today 你今天觉得怎么样 (亲切)
Linda is doing fine work at school.琳达在学校学习挺不错.(赞美之意)
5.有些动词:如come, go, leave, arrive, begin, start, stay等的现在进行时可表示将要发生的动作,一般跟时间状语,表明动作发生的时间
The train is arriving soon.火车要到了.
We are leaving on Saturday.我们星期六动身.
Are you going anywhere tomorrow 明天你到哪儿去吗
(四)有的动词不能用于现在进行时
这些词通常是表示感觉、感情、存在、从属、思维等的动词.
表示感觉的动词:see, hear, smell, taste, feel, notice, look, seem, appear
表示感情的动词:hate, love, fear, like, want, wish, prefer, refuse, forgive(原谅)
表示存在状况:be, exist(存在), remain(保持), stay, obtain(获得)
表示从属或占用:have, possess(拥有), own(拥有), contain(包含), belong(属于),consist of(由······组成), form(形成)
表示思考、理解:understand ,know, believe, think, doubt, forget, remember
五、过去进行时
(一)过去进行时的构成
过去进行时由“was/were+现在分词”构成.
过去进行时的肯定式,否定式和疑问式及简单回答.(以动词work为例)
肯定式 I(He, She, It)was working. We(You, They)were working.
否定式 I(He, She, It)was not working We(You, They)were not working.
疑问式 Was I(he, she, it)working.. Were we(you, they)working...
简单回答 Yes, you were. No, you were not. Yes, I was No, I was not Yes, he(she, it) was. No, he(she, it) was not. Yes, you(we, they)were. No, you(we, they) were not.
(二)过去进行时的用法
1.过去进行时表示过去某一个时刻或某一段时间内正在进行或发生的动作.通常与表示过去的时间状语连用.then, at this/that time, yesterday, at nine, last night等
At 8:00 o'clock yesterday evening I was having dinner with some friends.
昨天晚上八点,我在和几位朋友一起吃饭.
The doorbell rang while my mother was cooking the dinner.在妈妈做饭时,门铃响了.
Mary fell asleep while she was watching TV.玛丽看着电视睡着了.
My son was learning English in Australia last autumn.去年秋天我儿子在澳大利亚学习英语.
I was reading an interesting book last month.上个月我在看一本有趣的书.
2.表示移动的动词.如:come, start, stay, leave, fly等词的过去进行时,可以表示过去将要发生的动作
He was leaving the following day.他第二天将要离开.
She asked when I was starting.她问我何时动身.
3.过去进行时动词常与always, forever, continually, constantly, frequently等副词连用,代替一般过去时,强调过去经常性或习惯性动作,表现出说话人的赞美、厌烦等情绪
He was forever complaining about something.他老是怨这怨那.
He was constantly asking questions.他老是没完没了地提问题.
4.在含有时间状语从句的复合句中,延续时间较长的动作用过去进行时,另一个动作用一般过去时.若表示两个延续动作在过去某一时刻同时发生,则主句和从句的谓语动词都用过去进行时
What was Jim doing when the teacher came in 老师进来的时候吉姆在做什么
He read a piece of newspaper while he was waiting for the bus.他一边等车,一边看报.
The students were reading while the teacher was grading their homework.
学生们在看书,而老师在批改他们的家庭作业.
点拨
(1)静态动词如be, have, seem, depend on(依靠)等一般不能用于进行时态.
(2)表示知觉、认识或情感的动词如see, hear, believe, know, like, love, want, wish等一般也没有进行时态.
(三)一般过去时与过去进行时的用法比较
一般过去时表示在过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态;而过去进行时则表示在过去某个特定时间正在进行的动作.
Mary wrote a letter to her friend last night.玛丽昨晚给她朋友写了封信.(信已写完)
Mary was writing a letter to her friend at 8:00 o'clock last night.
昨晚八点钟玛丽在给她的朋友写信.(信不一定写完,只说明了动作的延续)
It was raining this time yesterday.昨天这个时间在下雨.(动作延续)
It rained yesterday.昨天下过雨.(动作完成)
六、现在完成时
(一)现在完成时的构成
现在完成时由“have/has+过去分词”构成.
现在完成时的肯定式、否定式和疑问式及简单回答.(以动词work为例)
肯定式 I(You) have worked. He(She, It) has worked. We(You, They) have worked.
否定式 I(You) have not/haven't worked. He(She, It) has not/hasn't worked. We(You, They) have not/haven't worked.
疑问式 Have I(you) worked... Has he(she, it) worked... Have we(you, they) worked...
简单回答 Yes, you(I) have. No, you(I) have not/haven't. Yes, he(she, it) has. No, he(she, it) has not/hasn't. Yes, you(we, they) have. No, you(we, they) have not/haven't.
说明:①助动词have和has可以与前面的主语缩略为’ve和’s.如:we've, they've, he's, it's等.
②have not常缩略为haven't, has not常缩略为hasn't.
(二)现在完成时的词尾变化
现在完成时由“助动词have/has+过去分词”构成.规则变化的过去分词与动词过去式的变化一样,在动词词尾加-ed;不规则变化的过去分词见“一般过去时”一节的不规则动词表.
(三)现在完成时的用法
1.表示过去已经开始,持续到现在(也许还会继续进行下去)的动作或状态;常和表示一段时间的状语,如:today, these days, since, for, this month, now等连用
I'm hungry. I haven't eaten anything since breakfast.我饿了,早饭以来我还什么东西都没吃.
I have worked at this school for 20 years.我在这所学校工作20年了.
They have lived in Beijing since 1972.他们从1972年以来就住在北京.
He has drunk four cups of coffee today.他今天喝了4杯咖啡了.
It's nice to see you again. We haven't seen each other for a long time.
再次见到你很高兴,我们有很长时间没见面了.
2.表示过去发生或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果
I have just posted a letter.我刚把信邮寄了.
She has lost her watch.她把表丢了.
Someone has broken the window.有人把窗户打碎了.
We have lived in Beijing.我们一直住在北京.
I understand what she has said to me.我理解她对我说的话.
We know that he has passed the English exam.我们知道他英语考试及格了.
(四)现在完成时需注意的问题
1.表示短暂性的动词不能与表示一段时间的状语连用这类动词常见的有:appear, begin, borrow, buy, close, come, die, fall, find, finish, join, kill, leave, lend, sell, start, stop等.
2.现在完成时不能和明确指出过去时间的状语连用,但可以和不明确指出时间的状语连用,也可以和包括现在在内的时间状语连用明确指出过去的时间状语:如yesterday, last week, in 1999,two days ago, just now, when I came in不明确指出时间的状语:如already, yet, sometimes, always, often, just, before, never, ever, lately, once包括现在在内的时间状语:如this morning, today, this week, this year
(五)have(has) been和 have(has)gone的区别
表示“曾到过某地”要用“have(has)been”;表示“已经去某地”要用“have(has) gone”.试比较:
Where has he been 他刚才到哪儿去了 (他已回来)
Where has he gone 他上哪儿去了 (他现在不在这里)
They have been to Beijing.他们到过北京.(现在已不在北京了)
They have gone to Beijing.他们到北京去了.(他们可能在去北京的路上,或者已到北京)
(六)现在完成时与一般过去时在意义上的区别
现在完成时表示过去发生的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果,强调的是现在的情况.因此,它不能和表示过去的时间状语连用,如:yesterday, last night, three weeks ago, in 2000等.而一般过去时只表示过去的动作或状态,和现在不发生关系,它可以和表示过去的时间状语连用.试比较:
I have seen him.我已见过他了.(我了解他的情况)
I saw him yesterday.我昨天看到他的.(只说明昨天我看到他,并不涉及现在的情况)
I have been ill for a week.我已病了一周了.(现在还在生病)
I was ill for a week.我病了一周.(过去病了一周)
(七)延续性动词与非延续性动词的用法
1.现在完成时表示动作从过去某个时候开始一直持续到现在,与一段时间连用时应注意句中的谓语动词应是延续性动词,非延续性动词在肯定句中不可和一段时间连用
我离开这所学校已经八年了.
误:I've left this school for eight years.
正:I've been away from this school for eight years.
他借用我的词典已两天了.
误:He has borrowed my dictionary for two days.
正:He has kept my dictionary for two days.
不过,在否定句中非延续性动词可与一段时间连用.
I haven't gone to see him for several months.我已经好几个月没去看他了.
2.非延续性动词与一段时间连用时可采用下列两种方法
(1)将非延续性动词转化为延续性动词.
buy→ have borrow→ keep
open→ be open close→ be closed
begin/start→ be on come→ be here
go→ be there finish→ be over
die→ be dead catch a cold→ have a cold
put on→ wear get up→ be up
wake up→ be awake fall asleep→ be asleep
lose→ not have join→ be in/be a member of
leave→ be away arrive/reach→ be
marry/get married→ be married
(2)用句型“Iris+一段时间+since从句(从句中的谓语动词用非延续性动词的过去式)”表示.
It is two years since the old man died.这个老人去世两年了.
七、过完成时
(一)过去完成时的构成
过去完成时由“助动词had+过去分词”构成.
所有人称和数都用“had+过去分词”,其否定式had not 常缩写为hadn't.过去完成时的肯定式和疑问式及简单回答形式:(以动词work为例)I(You)
肯定式 I(You) He(She, It) had worked. We(You, They)
否定式 I(you) He(She, It) had not/hadn't worked. We(You, They)
疑问式 I(you) Had he(she, it) worked... we(you, they)
简单回答 I(you) I(you) Yes, he(she, it) had No, he(she, it) had not/hadn’d we(you, they) we(you, they)
(二)过去完成时的用法
1.表示在过去某一时间之前(也称为“过去的过去”)已经发生或完成的动作.常与“by/before+过去的时间”构成的短语连用
How many English songs had you learned by the end of last term 到上学期末,你们学了几首英文歌
By the end of last year, we had planted 10,000 trees.到去年年底,我们一共栽种了1万棵树了.
I had never seen such a wonderful match before that day.那天之前我从未看到过那么精彩的比赛.
The boys had got to school before 7:00 in the morning.这些男孩儿7点以前就到校了.
2.用于以连词when, as soon as, as... as, before, until, now that引导的状语从句中或一些宾语从句中以表示动作发生的时间早于主句所表示的动作,可表示原因、动作先后等关系
I saw Li Ping yesterday. We had not seen each other since I left Beijing.
我昨天见到了李平.自我离开北京以来,我们就没见过面.
He went out after he had put on his coat and hat.他穿上大衣、戴上帽子后,便出去了.
The train had just left when they got to the station.当他们到达火车站时,火车刚刚开走.
How long had Mr. Li taught in the south before he came here 李先生在来这儿之前,在南方教了几年书
Mr. and Mrs. Brown had lived in Boston before they moved to Washington.
布朗夫妇在搬到华盛顿之前,在波士顿居住.
3.某些表示意愿、意图等的动词,如:think, hope, want, intend, plan, mean等,其过去完成时常表示本来打算做而没有做的事
I had meant to buy, but I brought no money.我本想买,但身上没带钱.
He had intended to speak, but time did not permit.他本想发言,可是时间不允许.
I had thought that they all knew about it.我还以为他们都知道这件事呢.(实际上他们并不知道)
I had hoped that you would come, but you didn't.我本希望你能来,可你没有来.
4.在No sooner...than...;Hardly(scarcely)...when...的结构中,前面的动词多用过去完成时
No sooner had he arrived home than he was asked to start on another journey.
他刚到家就被要求做另一次旅行.
Hardly had we got into the country when it began to rain.我们刚到乡间就下雨了.
5.用于表示与过去事实相反的虚拟条件从句
If he had seen you yesterday, he would have asked you about it.假如他昨天看到你,他就会问你这件事了.
I should have called you if I had known your telephone number.
要是我知道你的电话号码,我就给你打电话了.
(三)用一般过去时代替过去完成时的情况
1.含有动作已经完成意义的动词,如arrive, enter, open等,当主句和从句的两个动作紧紧相连时,两个动作都可以用一般过去时
When I arrived at the station, I learnt the train had already left.我一到车站,就听说火车已经离开了.
When he entered the office, he heard the telephone ringing.他一进入办公室,就听到电话铃响了.
2.由连词before, after, as soon as等引导的从句,由于连词本身意义已经说明主句和从句两个动作先后发生的关系,因此,两个动作都可以用一般过去时
After he dosed(=had closed) the door, he left the house.他关好门后离开房子.
I telephoned you as soon as I got home.我一到家,就给你打了电话.
八、过去将来时
(一)过去将来时的构成
1.过去将来时由“助动词would+动词原形”构成.助动词would常简写为“’d”.例如:“I'd" “you'd” “he'd”等;would not 常简写为”wouldn't"
2.过去将来时还可以用“was(were)+going to+动词原形”来表示
(二)过去将来时的用法
1.表示从过去某一时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态
过去将来时在宾语从句里最常见.
I wondered why he wouldn't go with us.我想知道,他为什么不和我们一起去.
They asked how they would go to Paris.他们问他们将怎么去巴黎.
He asked when the meeting would end.他问会议将在什么时候结束.
I wondered if our team would win.我想知道,我们队是否会赢.
He said there would be a concert this evening.他说今晚有一场音乐会.
2.过去将来时也可用“was/were going to+动词原形”构成,表示曾经打算或准备要做的动作
I thought it was going to rain soon.我认为很快就会下雨.
He told me he was going to wait for me there.他告诉我他打算在那儿等我.
He said he was not going to be there.他说他不准备在那儿.
She said she wasn't going to be free this Saturday.她说她这个周六没有空.
I was sure(that)they were going to do that.我确信他们要做那件事.
3.过去将来时还可用“was/were+动词不定式”或“was/were about+动词不定式”结构,表示某种过去将来的意义
She said that they were to see their English teacher next week.她说下个星期她们要去看她们的英语老师.
We were to finish the work in three days.我们打算三天内完成任务.
4.过去将来时常用来表示过去的习惯性动作,这时往往有一个时间状语陪衬
Every evening she would teach us to read and write.每天晚上她都来教我们读写.
好题精练
一、选择填空
1.Never trouble me while I_________ in my room.
A. will sleep B. asleep C. am sleeping D. slept
2.Lin Tao often_________ his homework at home in the evening, then he_________ over his lessons.
A. do; go B. does; goes C. did; goes D. does; went
3.your father usually go to work early every day
A. Was B.Is C. Did D. Does
4.Miss Gao isn't here. She_________ to the station to meet Mr. Brown.
A. went B. has gone C. has been D. would go
5.Mr.Li is out. But he_________ here ten minutes ago.
A. was B. is C. will D. would be
6.There_________ a talk about science in our school next Monday.
A. will have B. will be C. have D. has
7.His uncle_________ English in this school two years ago.
A. has taught B. had taught C. taught D .teaches
8.My father is very busy, he_________ TV after supper.
A. don't watch B. isn't watch C. didn't watch D. doesn't watch
9.Mr.King_________ China last year.
A. visit B. visited C. visits D. visiting
10.Tom has gone out. He'll_________ back in an hour.
A. am B. is C. are D. be
11.Mr.Brown_________ many friends since he came to China.
A. has made B. had made C. makes D. made
12.-How long has Jim_________
-For about eight weeks.
A. gone away B. left home C. been away D. left
13.- _________ you_________ a new dictionary
-Not yet.
A. Has; buy B. Has; bought C. Did; buy D. Have; bought
14.Mr.Smith_________ to visit Beijing in two days.
A. come B. came C. comes D. will come
15.Han Mei_________ worried because her mother_________ ill.
A. looks; is B. look; is C. look; was D. looked; is
16.Mrs.Smith_________ never_________ to China.
A. did; go B. does; come C. has; come D. has; been
17.Li Ming and Wang Lin_________ League members.
A .is B. both are C. are both D. are all
18.-What did you do last night
-I did my homework and_________ TV.
A. watch B. watched C. will watch D. am watching
19.Ir's cold outside. Alice, here's your coat. _________, please.
A. Put it on B. Put it up C. Take it off D. Take it away
20.How long may I_________ this book
A. borrow B. lend C. return D. keep
21.-How long_________ you_________ the bicycle
-About two weeks.
A. have; had B. have; bought C. did; buy D. have; get
22.Tom_________ more than 200 Chinese stamps since he came to China.
A. collects B. collected C. will collect D. has collected
23.There_________ many flowers in the street.
A. is B. are C. be D. am
24.I_________ to bed until my granny came back home.
A. didn't go B. went C. had gone D. have gone
25.Li Ming will buy a watch if his father_________ him money.
A. give B. gives C. gave D. will give
26.Aunt Li_________ her home town for a long time.
A. has left B. left C. has gone to D. has been away from
27.Mary isn't in. She_________ to the market.
A. went B. is going C. has been D. has gone
28.The Whites_________ many places of interest since they came to China.
A. have visited B. will visit C. visited D. visit
29. _________ he_________ the doctor the day before yesterday
A. Have ;seen B. Has; seen C. Did; see D. Does; see
30.-Where is Mr. Zhang
-He has_________ America.
A. been to B. gone to C. been D. gone
31.-How many students_________ in your class
-Forty.
A. is there B. are there C. there is D. there are
32.-I have finished my homework.
-When_________ you_________ it
A. do; finish B. will; finish C. have; finished D. did; finish
33.If Zhang Hua_________ hard, he'll do better in math.
A. will study B. study C. studies D. is studying
34.Thereis something on the floor. Please_________.
A. pick up it B. pick up them C. pick it up D. pick them up
35.Please go out to climb the hill if it_________ tomorrow.
A. rains B. raining C. won't rain D. doesn't rain
答案:
1-5CBDBA 6-10 BCDBD
11-15ACDDA 16-20DCBAD
21-25 ADBAB 26-30DDACB
31-35BDCCD
二、用括号中动词的适当形式填空
Ted Robinson has been worried all the week. Last Tuesday, he 1 (receive)a letter from the police station. In the letter he 2 (ask) to call at(到)the station. Ted didn't know why he 3 (want) by the police, but he 4 (go) to the station yesterday and now he 5 (not, worry) any more. At the station he 6 (tell) by a smiling policeman that his bicycle 7 (find) . Five days ago, the policeman 8 (tell) him the bicycle 9 (pick) up in a small village four hundred miles away. Now it 10 (send) to his home on the way by train. Ted 11 (surprise)when he 12 (hear) the news. He was amused(逗乐)too, because he never thought that the bicycle 13 (can, find)again. It 14 (take)away by someone twenty years ago when he 15 (be)a boy of fifteen!
答案:
1.received 2.was asked
3.was wanted 4.went
5.is not worried 6.was told
7.had been found 8.told
9.was picked 10.is being sent
11.was surprised 12.heard
13.could be found 14.was taken
15.was
三、改正下列句子中的错误.
1.I'll tell him about it as soon as he will come here tomorrow.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
2.Do you know whom the book is belonging to
____________________________________________________________________________________________
3.The teacher told his pupils that the sun will rise in the east.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
4.When has Mary started to learn Chinese
____________________________________________________________________________________________
5.It gets dark. We have to go home at once.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
6.He is having a new dictionary.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
7.Here she is coming.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
8.They went to bed until they had done all the work.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
9.He said that England lay in Europe.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
答案:
1.will come→ comes
2.is belonging to→ belongs to
3.will rise→ rises
4.has...started→ did...start
5.gets→is getting
6.is having→ has
7.is coming→ comes
8.went→didn't go
9.lay→lies
思维导图
知识梳理
在英语中,不同时间里以不同方式发生的动作或存在的状态,要用不同的动词形式来表示,动词的这种不同形式称为动词的时态.
英语的时态从时间上划分,可以分为现在时、过去时、将来时和过去将来时;从行为方式上划分,每一类又可以分为一般式、进行式、完成式和完成进行式.这样,英语动词合起来共有16种时态.现以动词work为例,将16种时态形式列表如下:
现在时 过去时 将来时 过去将来时
一般式 work works worked shall work will Should work should
进行式 am are working is was working were shall be working will should be working would
完成式 has worked have had worked shall have worked will should have worked would
完成进 行式 have been working has had been working shall have been working will should have been working would
这些时态中常用的有:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时以及过去将来时8种.
一、一般现在时
(一)一般现在时的构成
一般现在时的否定式、疑问式、否定疑问式和简单回答形式,以work为例,列表如下:
否定式 疑问式 否定疑问式 简单回答
I do not work. Do I work Do I not work Yes, I do. No, I don't.
You do not work. Do you work Do you not work Yes, I do. No, I don't.
He/ She/It does not work. Does he/she/it work Does he/she/it not work Yes, he/she/it does. No, he/she/it doesn't.
We do not work. Do we work Do we not work Yes, you do. No, you don't.
You do not work. Do you work Do you not work Yes, we do. No, we don't.
They do not work. Do they work Do they not work Yes, they do. No, they don't.
(二)动词的第三人称单数词尾变化
当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词需加-s或-es(见下表):
规则 动词原形 第三人称单数形式
一般在词尾加-s play work leave swim plays works leaves swims
以字母s, x, ch, sh, o结尾的词加-es pass fix teach wish do passes fixes teaches wishes does
以辅音字母加y结尾的词,先变y为i,再加-es study carry fly cry studies carries flies cries
动词have的第三人称单数形式为has.
(三)动词第三人称单数加s或es后的读音
1.在清辅音/p/, /k/, /t, /f/后读/s/
stops/st ps/ jumps/d mps/ likes/la ks/ picks/p ks/
visits/v z ts/ laughs/lɑ fs/ coughs/k fs/ posts/p sts/
2.在/s/, /z/, / /, /t /, /d /之后读/ z/
passes/pɑ s z/ guesses/ges z/ rises/ra z z/ refuses/r fju:z z/
wishes/w z/ washes/w z/ teaches/ti:t z/ watches/w t z/
changes/t e nd z/ manages/m n d z/
3.除以上两种读音外,其余的均读/z/
(四)一般现在时的用法
1.表示经常的或习惯性的动作
常与often, always, sometimes, every day, on Sundays/Mondays等表示频度的时间状语连用.
My father often gets up early in the morning.我父亲早晨经常早起.
He has breakfast at 7:00 every morning.他每天早晨七点吃早饭.
2.表示现在的状态
My father is at work. He is very busy.我父亲在工作,他很忙.
The boy is twelve.这个男孩儿12岁.
3.表示主语具备的性格、能力和特征
I like to listen to music.我喜欢听音乐.
They speak English very well.他们英语说得非常好.
This taxi driver knows the city of Beijing like the back of his hand.这位出租车司机对北京城了如指掌.
4.表示客观事实和普遍真理
Two plus two is four.2加2等于4.
The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.太阳从东方升起,从西方落下.
5.表示计划安排好的将来动作,也可用一般现在时,只限于: go, come, leave, start, begin, arrive, be等动
The plane takes off at 11 a.m.飞机上午11点起飞.
We leave Beijing next month.下月我们离开北京.
He comes back tonight.他今晚回来.
6.在时间、条件状语从句中,用一般现在时代替一般将来时
I'll write to you as soon as I get to Shanghai.我一到上海就给你写信.
Turn off the lights before you leave.走前关灯.
If it doesn't rain tomorrow, we'll go to the park.如果明天不下雨,我们就去公园.
If it rains tomorrow, we won't go to the park.如果明天下雨,我们就不去公园.
7.表示(书、信、报纸、通知、牌示、广播等)“说”“报导”,用一般现在时,主要是动词say
The notice says,“ No Parking.”通知说:“不准停放车辆.”
The radio says heavy rain in the afternoon.广播预报下午有大雨.
8.叙述历史,常用一般现在时,以使其生动
Jeanne is sitting in the park. Mathilde walks towards her, and she stops and speaks to Jeanne.
珍妮在公园里坐着.玛蒂尔德向她走来,停下来和珍妮谈话.
二、一般过去时
(一)一般过去时的构成(以动词work为例)
否定式 疑问式 否定疑问式 简单回答
I did not work. Did I work Did I not work Yes, I did. No, I didn't.
You did not work. Did you work Did you not work Yes, I did. No, I didn't.
He/ She/ It did not work. Did he/she/it work Did he/she/it not work Yes, he/she/it did. No, he/she/it didn't.
We did not work. Did we work Did we not work Yes, you did. No, you didn't.
You did not work. Did you work Did you not work Yes, we did. No, we didn't.
They did not work. Did they work Did they not work Yes, they did. No, they didn't.
(二)动词过去式的词尾变化(规则变化)
构成规则 原形 过去式
-般在动词末尾加-ed work plant play worked planted played
结尾是e的动词在末尾加-d like live change liked lived changed
末尾只有一个辅音字母的重读闭音节词,先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ed plan stop drop planned stopped dropped
以辅音字母加y结尾的,先变y为i再加-ed carry study cry carried studied cried
点拨
(1)prefer的过去式要先双写末尾辅音字母r再加-ed: preferred.
(2)travel的过去式可双写1再加-ed; travelled(英式英语);也可以直接加-ed; traveled(美式英语).
(三)动词过去式与过去分词的读音
1.清辅音后面的-ed读/t/音
stopped/st pt/停止 laughed/lɑ ft/笑 asked/ɑ skt/提问
hoped/h pt/希望 dressed/drest/穿衣 marched/mɑ t t/行军
watched/w t t/看 pushed/p t/推
2.浊辅音及元音后面的-ed读/d/音
rubbed/r bd/擦 tried/tra d/试图,努力 lived/l vd/生活
begged/begd/请求 named/ne md/取名 agreed/ gri:d/同意
rained/re nd/下雨 moved/mu:vd/移动
3.t,d后面加-ed读/d/音
united/ju: na t d/联合 heated/hi:t d/加热 ended/end d/结束
needed/ni:d d/需要 wanted/w nt d/想要 guided/'ga d d/指引
4.以-ed结尾的过去分词作形容词用时读/ d /音
aged/e d d/年老的 learned/1 n d/有学问的
wicked/w k d/罪恶的 interested/ ntr st d/感兴趣的
(四)不规则动词的过去式和过去分词
原形 过去式 过去分词 词义
Cost Cut Hit Hurt Let Put Read cost cut hit hurt let put read cost cut hit hurt let put read 花费 削、砍 打击 伤害、使受伤 让 放 读
Become Come Run became came ran become come run 成为 来 跑
Bring Buy Fight Think Catch Teach brought bought fought thought caught taught brought bought fought thought caught taught 带来 买 打架 想 抓住 教
Build Lend Send Spend Lose Smell built lent sent spent lost smelt/smelled built lent sent spent lost smelt/smelled 建筑 借给 送,寄 花(钱、时间) 丢失 闻
Feel Keep Sleep Sweep Leave Meet felt kept slept swept left met felt kept slept swept left met 感觉 保持 睡觉 扫 离开 遇见
Burn Learn Mean burnt/burned learnt/learned meant burnt/burned learnt/learned meant 燃烧 学会 意思是
Sell Tell sold told sold told 卖 告诉
Hold held held 抓住、握住
Shine Win Get Stand Understand Dig Hang have(has) hear make pay shone/shined won got stood understood dug hung/hanged had heard made paid shone/shined won got stood understood dug hung/hanged had heard made paid 照耀,使光亮 赢 得到 站 理解、懂得 挖 挂/绞死 有 听见 制造 付(钱)
say sit find said sat found said sat found 说 坐 发现
am, is are do go wear lie see was were did went wore lay saw been been done gone worn lain seen 是 是 做 去 穿着 躺 看见
begin drink ring sing swim began drank rang sang swam begun drunk rung sung swum 开始 喝 打电话,(铃)响 唱 游泳
drive rise ride write drove rose rode wrote driven risen ridden written 驾驶 升起 骑(马、自行车) 写
blow grow know throw fly blew grew knew threw flew blown grown known thrown flown 吹 生长 知道 投掷 飞
draw show drew showed drawn shown 画、拉 出示
break speak choose take mistake wake broke spoke chose took mistook waked/woke broken spoken chosen taken mistaken waked/woken 打断,打破 讲 选择 拿走 弄错 唤醒
beat eat fall give forget beat ate fell gave forgot beaten eaten fallen given forgotten 打 吃 落下 给 忘记
(五)一般过去时的用法
1.表示过去某个特定时间发生的动作或存在的状态
这时常与yesterday, last week, a moment ago, in 1949等表示过去时间的状语连用.
What did you have for breakfast this morning 今天早饭吃的什么
I had two eggs and a glass of milk.早饭吃了两个鸡蛋和一杯牛奶.
The police stopped him on his way home last night.昨晚在回家的路上警察拦住了他.
My sister passed her examination because she studied very hard.我妹妹通过了考试,因为她学习非常努力.
2.表示过去某一段时间内经常或反复发生的动作,这时常和表示频度的状语连用
Last term we often did experiments.上学期我们经常做试验.
He always went to work by bus.他过去总是乘车去上班.
She gave her teacher presents every Christmas.她每年都给她的老师送圣诞礼物.
点拨
used to do的否定式和疑问式有两种构成法.
(1)借助did,即:didn't use to do
He didn't use to do it, did he 他过去不经常这么做,是吗
Did you use to play football 你过去经常踢足球吗
(2)不用did,即:usedn't to do
She usedn't to make those mistakes.她以前并不经常出那些错的.
Used you to play football 你过去经常踢足球吗
3.在时间、条件状语从句中,常用一般过去时代替过去将来时
He said he would not go if it rained.他说如果天下雨就不去了.
They told us that they would not leave until she came back.他们告诉我们直到她回来他们才会离开.
4.常用“would+ do”表示过去经常反复发生的动作
I would ask you to think carefully before you spoke.我劝你在讲话之前要认真考虑一下.
We would turn to him for help when we were in trouble.我们一遇麻烦,就向他请求帮助.
三、一般将来时
(一)一般将来时的构成
一般将来时的否定式、疑问式、否定疑问句式和简单回答形式,以study为例:
否定式 疑问式 否定疑问句式 简单回答
I shall/will not study. Shall I study Shall I not study (Shan't I study ) Yes, you will. No, you won't.
You will not study. Will you not study Will you study (Won't you study ) Yes, I shall/will. No, I shan't/won't.
He/ She/It will not study. Will he/she/it not study Will he/she/it study (Won't he/she/it study ) Yes, he/she/it will. No, he/she/it won't.
We shall/will not study. Shall we study Shall we not study (Shan't we study ) Yes, you will. No, you won't.
You will not study Will you study Will you not study (Won't you study ) Yes, we shall/will. No, we shan't/won't.
They will not study. Will they study Will they not study (Won't they study ) Yes, they will. No, they won't.
shall用于第一人称I(we)shall; will可用于各人称.美式英语中,不论什么人称和数,一律用will+动词原形.在口语中,will常缩写为’ll与主语连写在一起.
如:I'll, you'll, he'11和she'll we’ll, they'll, shall not 常缩写为shan't, will not常缩写为won't.
在疑问中,主语为第一人称(I和We)时,常用助动词shall.
(二)一般将来时的用法
1.一般将来时表示在将来某个时间将要发生的动作或存在的状态.常与表示将来的时间状语如tomorrow, next week/month/year等连用
I'll come to pick you up at 6:00 on Wednesday evening.我星期三晚上6点来接您.
I'll have a party next Saturday. I hope you can come.下周六我要举行聚会,希望你能来.
If it doesn't rain tomorrow, we are going to the Summer Palace.如果明天不下雨,我们就去颐和园.
My daughter will be twenty years old next year.我女儿明年就20岁了.
He will be here in ten minutes.他10分钟后在这儿.
2.表示将来经常或反复发生的动作
I'll come and see you every Sunday next year.明年我将每个星期天来看你.
We shall come and work in this factory every year.我们将每年到这个工厂来劳动.
3.表示揣测
This will be the dictionary you're looking for.这大概是你要找的那本词典吧.
The game will be finished by now.球赛大概已经结束了.
4.“be going to+动词原形”结构
表示现在打算在最近或将来要做的事,或表示说话人根据已有的迹象认为很可能要发生的事情.如:
We are going to have a new subject this year.今年我们将学一门新学科.
It's going to rain this afternoon.今天下午天要下雨.
I'm not going to write letters.我不打算写信.
5.“be+动词不定式”结构表示按计划要发生的事,或用来征求对方意见
Where are we to stay tonight 今晚我们在哪儿过夜
What is to do 怎么办
6.“be about+动词不定式”结构表示即将做某事
I haven't gone yet, I'm about to.我还没走,正要走呢.
The Sports Meeting is about to start now.运动会即将开始.
点拨
有些表示位置转移的动词,如come, go, leave, start, arrive, fly等的现在进行时可表示按计划或安排将要发生的动作,常与表示将来的时间状语连用.
He is leaving for Shanghai tomorrow.他明天动身去上海.
They are arriving tomorrow afternoon.他们明天下午到达.
(三)需注意的几点
1.在回答Shall I...问句时,应该说:Yes, please./Please do.或No, please don't./Please don't.不可说:Yes, you shall.或No, you shall not.
2.在回答 Shall we...问句时,应该说:Yes, let's... 或 No, I don't think we shall./No, let's not.
(四)will和be going to的比较
1.will和be going to 都可表示某种意愿
但其含义和用法有所不同.
be going to往往表示经过考虑的打算,而will多表示意愿、决心.
We are going to watch the football game.我们打算观看这场足球赛.
I will tell you all about it.我将把全部情况告诉你.
2.will可用于条件从句表示将来的意愿,而be going to用于条件从句,只是表示单纯的将来,试比较
Miss Gao will tell you the answer if you ask her.如果你去问高老师,她会告诉你答案的.
If you are going to attend the meeting, you'd better leave now.如果你要参加会议,最好现在就走.
四、现在进行时
(一)现在进行时的构成
现在进行时由“am/is/are+动词现在分词”构成.
现在进行时的肯定式、否定式和疑问式及简单回答形式:(以动词work为例)
肯定式 I am/'m working. He (She, It)is/isn't working. We(You, They) are/'re working.
否定式 I am not/'m not working. He(She, It)is not/isn't working. We(You, They) are not/aren't working.
疑问式 Am I working... Is he(she, it)working... Are you(we, they)working...
简单回答 Yes, you are. No, you aren't. Yes, I am. No, I'm not. Yes, he(she it) is. No, he(she ,it)isn't. Yes, we(you, they) are. No, we(you, they) aren't.
(二)动词-ing形式的构成及其读音
1.一般在动词原形末尾加-ing
stay-staying/'ste / do-doing/'du: /
listen-listening/'l sn / suffer-suffering/'s f r /
work-working/'w k / spend-spending/'spend /
look-looking/'l k /
2.以不发音的字母e结尾的动词,先去掉e,再加-ing
make-making/'me k / take-taking/'te k /
give-giving/'g v / ride-riding/'ra d /
please-pleasing/'pli:z / refuse-refusing/'r 'fju:z /
close-closing/'kl z / operate-operating/' p re t /
3.以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节词,先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ing
put-putting/'p t / sit-sitting/'s t /
run-running/'r n / win-winning/'w n /
begin-beginning/b 'g n /
4.以ie结尾的动词,先去掉e,把i变为y,再加-ing
lie-lying/'la / tie-tying/'ta / die-dying/'da /
5.以re结尾的动词,先去掉e,再加-ing
prepare-preparing/pr 'pe r / interfere-interfering/ nt 'f r g/
tire-tiring/'ta r / bore-boring/'b :r /
cure-curing/kj r /
6.以er结尾的动词,如果是重读音节结尾,先双写r,再加-ing;如果不是重读音节结尾,就直接加-ing
prefer-preferring water(浇水)-watering
(三)现在进行时的用法
1.表示说话时正在进行或发生的动作
这时可以不用时间状语,也可以和now, at present, at the moment等时间状语连用.有时用一个动词.如look(看),listen(听).
What are you reading now 你在读什么
His mother is watching TV at the present.此刻,他的妈妈正在看电视.
I'm writing a novel at present.眼下我正在写一部小说.
Look! The bus is crossing the bridge.看!这辆公共汽车在过桥.
Listen! Someone is singing in the classroom.听!有人在教室里唱歌.
2.表示当前一段时期内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作(说话时动作不一定正在进行),常与表示一段时间的状语these days, this week等连用
They are working in a factory these days.他们这几天正在工厂劳动.
More and more people are giving up smoking.越来越多的人在戒烟.
They are working in a factory these days.他们这几天在工厂劳动.
They're visiting Beijing this week.这周他们在北京观光.
3.现在进行时常与always, continually, constantly, forever等表示频度的副词连用,表示经常、反复发生的动作,常表示厌烦、不满、赞扬等情感
He is always thinking of his work.他总是想着他的工作.
They're forever quarrelling about something.他们老是为某件事争吵不休.(不满)
4.现在进行时有时也用来代替一般现在时,表示一个经常性的动作或状态,或是为了表示一种感情(如赞叹、厌烦等)或是为了强调情况的暂时性
How are you feeling today 你今天觉得怎么样 (亲切)
Linda is doing fine work at school.琳达在学校学习挺不错.(赞美之意)
5.有些动词:如come, go, leave, arrive, begin, start, stay等的现在进行时可表示将要发生的动作,一般跟时间状语,表明动作发生的时间
The train is arriving soon.火车要到了.
We are leaving on Saturday.我们星期六动身.
Are you going anywhere tomorrow 明天你到哪儿去吗
(四)有的动词不能用于现在进行时
这些词通常是表示感觉、感情、存在、从属、思维等的动词.
表示感觉的动词:see, hear, smell, taste, feel, notice, look, seem, appear
表示感情的动词:hate, love, fear, like, want, wish, prefer, refuse, forgive(原谅)
表示存在状况:be, exist(存在), remain(保持), stay, obtain(获得)
表示从属或占用:have, possess(拥有), own(拥有), contain(包含), belong(属于),consist of(由······组成), form(形成)
表示思考、理解:understand ,know, believe, think, doubt, forget, remember
五、过去进行时
(一)过去进行时的构成
过去进行时由“was/were+现在分词”构成.
过去进行时的肯定式,否定式和疑问式及简单回答.(以动词work为例)
肯定式 I(He, She, It)was working. We(You, They)were working.
否定式 I(He, She, It)was not working We(You, They)were not working.
疑问式 Was I(he, she, it)working.. Were we(you, they)working...
简单回答 Yes, you were. No, you were not. Yes, I was No, I was not Yes, he(she, it) was. No, he(she, it) was not. Yes, you(we, they)were. No, you(we, they) were not.
(二)过去进行时的用法
1.过去进行时表示过去某一个时刻或某一段时间内正在进行或发生的动作.通常与表示过去的时间状语连用.then, at this/that time, yesterday, at nine, last night等
At 8:00 o'clock yesterday evening I was having dinner with some friends.
昨天晚上八点,我在和几位朋友一起吃饭.
The doorbell rang while my mother was cooking the dinner.在妈妈做饭时,门铃响了.
Mary fell asleep while she was watching TV.玛丽看着电视睡着了.
My son was learning English in Australia last autumn.去年秋天我儿子在澳大利亚学习英语.
I was reading an interesting book last month.上个月我在看一本有趣的书.
2.表示移动的动词.如:come, start, stay, leave, fly等词的过去进行时,可以表示过去将要发生的动作
He was leaving the following day.他第二天将要离开.
She asked when I was starting.她问我何时动身.
3.过去进行时动词常与always, forever, continually, constantly, frequently等副词连用,代替一般过去时,强调过去经常性或习惯性动作,表现出说话人的赞美、厌烦等情绪
He was forever complaining about something.他老是怨这怨那.
He was constantly asking questions.他老是没完没了地提问题.
4.在含有时间状语从句的复合句中,延续时间较长的动作用过去进行时,另一个动作用一般过去时.若表示两个延续动作在过去某一时刻同时发生,则主句和从句的谓语动词都用过去进行时
What was Jim doing when the teacher came in 老师进来的时候吉姆在做什么
He read a piece of newspaper while he was waiting for the bus.他一边等车,一边看报.
The students were reading while the teacher was grading their homework.
学生们在看书,而老师在批改他们的家庭作业.
点拨
(1)静态动词如be, have, seem, depend on(依靠)等一般不能用于进行时态.
(2)表示知觉、认识或情感的动词如see, hear, believe, know, like, love, want, wish等一般也没有进行时态.
(三)一般过去时与过去进行时的用法比较
一般过去时表示在过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态;而过去进行时则表示在过去某个特定时间正在进行的动作.
Mary wrote a letter to her friend last night.玛丽昨晚给她朋友写了封信.(信已写完)
Mary was writing a letter to her friend at 8:00 o'clock last night.
昨晚八点钟玛丽在给她的朋友写信.(信不一定写完,只说明了动作的延续)
It was raining this time yesterday.昨天这个时间在下雨.(动作延续)
It rained yesterday.昨天下过雨.(动作完成)
六、现在完成时
(一)现在完成时的构成
现在完成时由“have/has+过去分词”构成.
现在完成时的肯定式、否定式和疑问式及简单回答.(以动词work为例)
肯定式 I(You) have worked. He(She, It) has worked. We(You, They) have worked.
否定式 I(You) have not/haven't worked. He(She, It) has not/hasn't worked. We(You, They) have not/haven't worked.
疑问式 Have I(you) worked... Has he(she, it) worked... Have we(you, they) worked...
简单回答 Yes, you(I) have. No, you(I) have not/haven't. Yes, he(she, it) has. No, he(she, it) has not/hasn't. Yes, you(we, they) have. No, you(we, they) have not/haven't.
说明:①助动词have和has可以与前面的主语缩略为’ve和’s.如:we've, they've, he's, it's等.
②have not常缩略为haven't, has not常缩略为hasn't.
(二)现在完成时的词尾变化
现在完成时由“助动词have/has+过去分词”构成.规则变化的过去分词与动词过去式的变化一样,在动词词尾加-ed;不规则变化的过去分词见“一般过去时”一节的不规则动词表.
(三)现在完成时的用法
1.表示过去已经开始,持续到现在(也许还会继续进行下去)的动作或状态;常和表示一段时间的状语,如:today, these days, since, for, this month, now等连用
I'm hungry. I haven't eaten anything since breakfast.我饿了,早饭以来我还什么东西都没吃.
I have worked at this school for 20 years.我在这所学校工作20年了.
They have lived in Beijing since 1972.他们从1972年以来就住在北京.
He has drunk four cups of coffee today.他今天喝了4杯咖啡了.
It's nice to see you again. We haven't seen each other for a long time.
再次见到你很高兴,我们有很长时间没见面了.
2.表示过去发生或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果
I have just posted a letter.我刚把信邮寄了.
She has lost her watch.她把表丢了.
Someone has broken the window.有人把窗户打碎了.
We have lived in Beijing.我们一直住在北京.
I understand what she has said to me.我理解她对我说的话.
We know that he has passed the English exam.我们知道他英语考试及格了.
(四)现在完成时需注意的问题
1.表示短暂性的动词不能与表示一段时间的状语连用这类动词常见的有:appear, begin, borrow, buy, close, come, die, fall, find, finish, join, kill, leave, lend, sell, start, stop等.
2.现在完成时不能和明确指出过去时间的状语连用,但可以和不明确指出时间的状语连用,也可以和包括现在在内的时间状语连用明确指出过去的时间状语:如yesterday, last week, in 1999,two days ago, just now, when I came in不明确指出时间的状语:如already, yet, sometimes, always, often, just, before, never, ever, lately, once包括现在在内的时间状语:如this morning, today, this week, this year
(五)have(has) been和 have(has)gone的区别
表示“曾到过某地”要用“have(has)been”;表示“已经去某地”要用“have(has) gone”.试比较:
Where has he been 他刚才到哪儿去了 (他已回来)
Where has he gone 他上哪儿去了 (他现在不在这里)
They have been to Beijing.他们到过北京.(现在已不在北京了)
They have gone to Beijing.他们到北京去了.(他们可能在去北京的路上,或者已到北京)
(六)现在完成时与一般过去时在意义上的区别
现在完成时表示过去发生的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果,强调的是现在的情况.因此,它不能和表示过去的时间状语连用,如:yesterday, last night, three weeks ago, in 2000等.而一般过去时只表示过去的动作或状态,和现在不发生关系,它可以和表示过去的时间状语连用.试比较:
I have seen him.我已见过他了.(我了解他的情况)
I saw him yesterday.我昨天看到他的.(只说明昨天我看到他,并不涉及现在的情况)
I have been ill for a week.我已病了一周了.(现在还在生病)
I was ill for a week.我病了一周.(过去病了一周)
(七)延续性动词与非延续性动词的用法
1.现在完成时表示动作从过去某个时候开始一直持续到现在,与一段时间连用时应注意句中的谓语动词应是延续性动词,非延续性动词在肯定句中不可和一段时间连用
我离开这所学校已经八年了.
误:I've left this school for eight years.
正:I've been away from this school for eight years.
他借用我的词典已两天了.
误:He has borrowed my dictionary for two days.
正:He has kept my dictionary for two days.
不过,在否定句中非延续性动词可与一段时间连用.
I haven't gone to see him for several months.我已经好几个月没去看他了.
2.非延续性动词与一段时间连用时可采用下列两种方法
(1)将非延续性动词转化为延续性动词.
buy→ have borrow→ keep
open→ be open close→ be closed
begin/start→ be on come→ be here
go→ be there finish→ be over
die→ be dead catch a cold→ have a cold
put on→ wear get up→ be up
wake up→ be awake fall asleep→ be asleep
lose→ not have join→ be in/be a member of
leave→ be away arrive/reach→ be
marry/get married→ be married
(2)用句型“Iris+一段时间+since从句(从句中的谓语动词用非延续性动词的过去式)”表示.
It is two years since the old man died.这个老人去世两年了.
七、过完成时
(一)过去完成时的构成
过去完成时由“助动词had+过去分词”构成.
所有人称和数都用“had+过去分词”,其否定式had not 常缩写为hadn't.过去完成时的肯定式和疑问式及简单回答形式:(以动词work为例)I(You)
肯定式 I(You) He(She, It) had worked. We(You, They)
否定式 I(you) He(She, It) had not/hadn't worked. We(You, They)
疑问式 I(you) Had he(she, it) worked... we(you, they)
简单回答 I(you) I(you) Yes, he(she, it) had No, he(she, it) had not/hadn’d we(you, they) we(you, they)
(二)过去完成时的用法
1.表示在过去某一时间之前(也称为“过去的过去”)已经发生或完成的动作.常与“by/before+过去的时间”构成的短语连用
How many English songs had you learned by the end of last term 到上学期末,你们学了几首英文歌
By the end of last year, we had planted 10,000 trees.到去年年底,我们一共栽种了1万棵树了.
I had never seen such a wonderful match before that day.那天之前我从未看到过那么精彩的比赛.
The boys had got to school before 7:00 in the morning.这些男孩儿7点以前就到校了.
2.用于以连词when, as soon as, as... as, before, until, now that引导的状语从句中或一些宾语从句中以表示动作发生的时间早于主句所表示的动作,可表示原因、动作先后等关系
I saw Li Ping yesterday. We had not seen each other since I left Beijing.
我昨天见到了李平.自我离开北京以来,我们就没见过面.
He went out after he had put on his coat and hat.他穿上大衣、戴上帽子后,便出去了.
The train had just left when they got to the station.当他们到达火车站时,火车刚刚开走.
How long had Mr. Li taught in the south before he came here 李先生在来这儿之前,在南方教了几年书
Mr. and Mrs. Brown had lived in Boston before they moved to Washington.
布朗夫妇在搬到华盛顿之前,在波士顿居住.
3.某些表示意愿、意图等的动词,如:think, hope, want, intend, plan, mean等,其过去完成时常表示本来打算做而没有做的事
I had meant to buy, but I brought no money.我本想买,但身上没带钱.
He had intended to speak, but time did not permit.他本想发言,可是时间不允许.
I had thought that they all knew about it.我还以为他们都知道这件事呢.(实际上他们并不知道)
I had hoped that you would come, but you didn't.我本希望你能来,可你没有来.
4.在No sooner...than...;Hardly(scarcely)...when...的结构中,前面的动词多用过去完成时
No sooner had he arrived home than he was asked to start on another journey.
他刚到家就被要求做另一次旅行.
Hardly had we got into the country when it began to rain.我们刚到乡间就下雨了.
5.用于表示与过去事实相反的虚拟条件从句
If he had seen you yesterday, he would have asked you about it.假如他昨天看到你,他就会问你这件事了.
I should have called you if I had known your telephone number.
要是我知道你的电话号码,我就给你打电话了.
(三)用一般过去时代替过去完成时的情况
1.含有动作已经完成意义的动词,如arrive, enter, open等,当主句和从句的两个动作紧紧相连时,两个动作都可以用一般过去时
When I arrived at the station, I learnt the train had already left.我一到车站,就听说火车已经离开了.
When he entered the office, he heard the telephone ringing.他一进入办公室,就听到电话铃响了.
2.由连词before, after, as soon as等引导的从句,由于连词本身意义已经说明主句和从句两个动作先后发生的关系,因此,两个动作都可以用一般过去时
After he dosed(=had closed) the door, he left the house.他关好门后离开房子.
I telephoned you as soon as I got home.我一到家,就给你打了电话.
八、过去将来时
(一)过去将来时的构成
1.过去将来时由“助动词would+动词原形”构成.助动词would常简写为“’d”.例如:“I'd" “you'd” “he'd”等;would not 常简写为”wouldn't"
2.过去将来时还可以用“was(were)+going to+动词原形”来表示
(二)过去将来时的用法
1.表示从过去某一时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态
过去将来时在宾语从句里最常见.
I wondered why he wouldn't go with us.我想知道,他为什么不和我们一起去.
They asked how they would go to Paris.他们问他们将怎么去巴黎.
He asked when the meeting would end.他问会议将在什么时候结束.
I wondered if our team would win.我想知道,我们队是否会赢.
He said there would be a concert this evening.他说今晚有一场音乐会.
2.过去将来时也可用“was/were going to+动词原形”构成,表示曾经打算或准备要做的动作
I thought it was going to rain soon.我认为很快就会下雨.
He told me he was going to wait for me there.他告诉我他打算在那儿等我.
He said he was not going to be there.他说他不准备在那儿.
She said she wasn't going to be free this Saturday.她说她这个周六没有空.
I was sure(that)they were going to do that.我确信他们要做那件事.
3.过去将来时还可用“was/were+动词不定式”或“was/were about+动词不定式”结构,表示某种过去将来的意义
She said that they were to see their English teacher next week.她说下个星期她们要去看她们的英语老师.
We were to finish the work in three days.我们打算三天内完成任务.
4.过去将来时常用来表示过去的习惯性动作,这时往往有一个时间状语陪衬
Every evening she would teach us to read and write.每天晚上她都来教我们读写.
好题精练
一、选择填空
1.Never trouble me while I_________ in my room.
A. will sleep B. asleep C. am sleeping D. slept
2.Lin Tao often_________ his homework at home in the evening, then he_________ over his lessons.
A. do; go B. does; goes C. did; goes D. does; went
3.your father usually go to work early every day
A. Was B.Is C. Did D. Does
4.Miss Gao isn't here. She_________ to the station to meet Mr. Brown.
A. went B. has gone C. has been D. would go
5.Mr.Li is out. But he_________ here ten minutes ago.
A. was B. is C. will D. would be
6.There_________ a talk about science in our school next Monday.
A. will have B. will be C. have D. has
7.His uncle_________ English in this school two years ago.
A. has taught B. had taught C. taught D .teaches
8.My father is very busy, he_________ TV after supper.
A. don't watch B. isn't watch C. didn't watch D. doesn't watch
9.Mr.King_________ China last year.
A. visit B. visited C. visits D. visiting
10.Tom has gone out. He'll_________ back in an hour.
A. am B. is C. are D. be
11.Mr.Brown_________ many friends since he came to China.
A. has made B. had made C. makes D. made
12.-How long has Jim_________
-For about eight weeks.
A. gone away B. left home C. been away D. left
13.- _________ you_________ a new dictionary
-Not yet.
A. Has; buy B. Has; bought C. Did; buy D. Have; bought
14.Mr.Smith_________ to visit Beijing in two days.
A. come B. came C. comes D. will come
15.Han Mei_________ worried because her mother_________ ill.
A. looks; is B. look; is C. look; was D. looked; is
16.Mrs.Smith_________ never_________ to China.
A. did; go B. does; come C. has; come D. has; been
17.Li Ming and Wang Lin_________ League members.
A .is B. both are C. are both D. are all
18.-What did you do last night
-I did my homework and_________ TV.
A. watch B. watched C. will watch D. am watching
19.Ir's cold outside. Alice, here's your coat. _________, please.
A. Put it on B. Put it up C. Take it off D. Take it away
20.How long may I_________ this book
A. borrow B. lend C. return D. keep
21.-How long_________ you_________ the bicycle
-About two weeks.
A. have; had B. have; bought C. did; buy D. have; get
22.Tom_________ more than 200 Chinese stamps since he came to China.
A. collects B. collected C. will collect D. has collected
23.There_________ many flowers in the street.
A. is B. are C. be D. am
24.I_________ to bed until my granny came back home.
A. didn't go B. went C. had gone D. have gone
25.Li Ming will buy a watch if his father_________ him money.
A. give B. gives C. gave D. will give
26.Aunt Li_________ her home town for a long time.
A. has left B. left C. has gone to D. has been away from
27.Mary isn't in. She_________ to the market.
A. went B. is going C. has been D. has gone
28.The Whites_________ many places of interest since they came to China.
A. have visited B. will visit C. visited D. visit
29. _________ he_________ the doctor the day before yesterday
A. Have ;seen B. Has; seen C. Did; see D. Does; see
30.-Where is Mr. Zhang
-He has_________ America.
A. been to B. gone to C. been D. gone
31.-How many students_________ in your class
-Forty.
A. is there B. are there C. there is D. there are
32.-I have finished my homework.
-When_________ you_________ it
A. do; finish B. will; finish C. have; finished D. did; finish
33.If Zhang Hua_________ hard, he'll do better in math.
A. will study B. study C. studies D. is studying
34.Thereis something on the floor. Please_________.
A. pick up it B. pick up them C. pick it up D. pick them up
35.Please go out to climb the hill if it_________ tomorrow.
A. rains B. raining C. won't rain D. doesn't rain
答案:
1-5CBDBA 6-10 BCDBD
11-15ACDDA 16-20DCBAD
21-25 ADBAB 26-30DDACB
31-35BDCCD
二、用括号中动词的适当形式填空
Ted Robinson has been worried all the week. Last Tuesday, he 1 (receive)a letter from the police station. In the letter he 2 (ask) to call at(到)the station. Ted didn't know why he 3 (want) by the police, but he 4 (go) to the station yesterday and now he 5 (not, worry) any more. At the station he 6 (tell) by a smiling policeman that his bicycle 7 (find) . Five days ago, the policeman 8 (tell) him the bicycle 9 (pick) up in a small village four hundred miles away. Now it 10 (send) to his home on the way by train. Ted 11 (surprise)when he 12 (hear) the news. He was amused(逗乐)too, because he never thought that the bicycle 13 (can, find)again. It 14 (take)away by someone twenty years ago when he 15 (be)a boy of fifteen!
答案:
1.received 2.was asked
3.was wanted 4.went
5.is not worried 6.was told
7.had been found 8.told
9.was picked 10.is being sent
11.was surprised 12.heard
13.could be found 14.was taken
15.was
三、改正下列句子中的错误.
1.I'll tell him about it as soon as he will come here tomorrow.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
2.Do you know whom the book is belonging to
____________________________________________________________________________________________
3.The teacher told his pupils that the sun will rise in the east.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
4.When has Mary started to learn Chinese
____________________________________________________________________________________________
5.It gets dark. We have to go home at once.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
6.He is having a new dictionary.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
7.Here she is coming.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
8.They went to bed until they had done all the work.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
9.He said that England lay in Europe.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
答案:
1.will come→ comes
2.is belonging to→ belongs to
3.will rise→ rises
4.has...started→ did...start
5.gets→is getting
6.is having→ has
7.is coming→ comes
8.went→didn't go
9.lay→lies
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
