2023年安徽省中考英语总复习二轮专题: 语法专题精讲(64页)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2023年安徽省中考英语总复习二轮专题: 语法专题精讲(64页) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 800.3KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-05-01 12:23:51 | ||
图片预览



文档简介
2023年安徽省中考英语总复习二轮专题
第二部分 语法专题精讲
编者按:此部分11个专题的练习题见《教材词句&语法精练》第三部分常考语法点精练。
句子成分及五大基本句型
句子成分
1. 主语
【作用】句子说明的人或事物。
【位置】陈述句:通常位于句首;
疑问句:位于系动词、助动词或情态动词之后。
【组成部分】名词、代词、数词、动名词、动词不定式、从句等。
【例句】The apple is red.
Three is enough.
Smoking is bad for you.
2. 谓语
【作用】对主语加以说明,表示主语的行为或状态。
【位置】通常位于主语之后。
【组成部分】动词或动词短语。
【例句】The man borrowed two books.
The plane took off at ten o’clock.
3. 宾语
【作用】动作的对象或承受者。
【位置】动词或介词后。
【组成部分】名词、代词、数词、动名词、动词不定式、名词性从句等,宾语分为直接宾语(指物)和间接宾语(指人)。
【例句】I like China. I want to watch the new movie.
He told me that he would go to college the next year.
He gave me some bananas.
4. 宾语补足语
【作用】对宾语的补充。
【位置】宾语后。
【组成部分】名词、形容词、副词、动词不定式、分词等。
【例句】We elected him monitor.
She found the window broken when she came back home.
5. 表语
【作用】表示主语的性质、状态或特征。
【位置】系动词之后。
【组成部分】名词、数词、代词、形容词、副词、动词不定式、介词短语、形容词化的分词和表语从句等。
【例句】He is a teacher.
All I could do was to wait.
6. 定语
【作用】修饰或限制名词或代词的词、词组或句子。
【位置】单词作定语通常放在所修饰的词之前;短语或从句放在所修饰的成分之后。
【组成部分】名词、名词所有格、代词、数词、形容词、介词短语、现在分词、过去分词、动词不定式短语、定语从句等。
【例句】The woman with a baby in her arms is my sister.
The car parked outside is mine.
7. 状语
【作用】说明时间、地点、方式、原因、目的、结果、条件、程度等,用于修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子。
【位置】位置灵活:一般放在句末,但也可放在句首或句中。
【组成部分】副词、介词短语、动词不定式、分词和分词短语、相当于副词的词或短语、从句等。
【例句】You are quite right.
If you study hard, you will pass the exam.
五大基本句型
句型一:主语+谓语(不及物动词)。
例: It rains.
↓ ↓
主语 谓语
句型二:主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语。
例:①Children often sing this song.
↓ ↓ ↓
主语 谓语 宾语
②He has accepted our invitation.
↓ ↓ ↓
主语 谓语 宾语
句型三:主语+系动词+表语。
例:①The bike is new.
↓ ↓ ↓
主语 系动词 表语
②The milk went sour.
↓ ↓ ↓
主语 系动词 表语
句型四:主语+谓语(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语。
例:She showed her friends all her pictures.
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
主语 谓语 间接宾语 直接宾语
句型五:主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语+宾语补足语。
例:① We keep our classroom clean and tidy.
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
主语 谓语 宾语 宾语补足语
② We have invited all our friends to come.
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
主语 谓语 宾语 宾语补足语
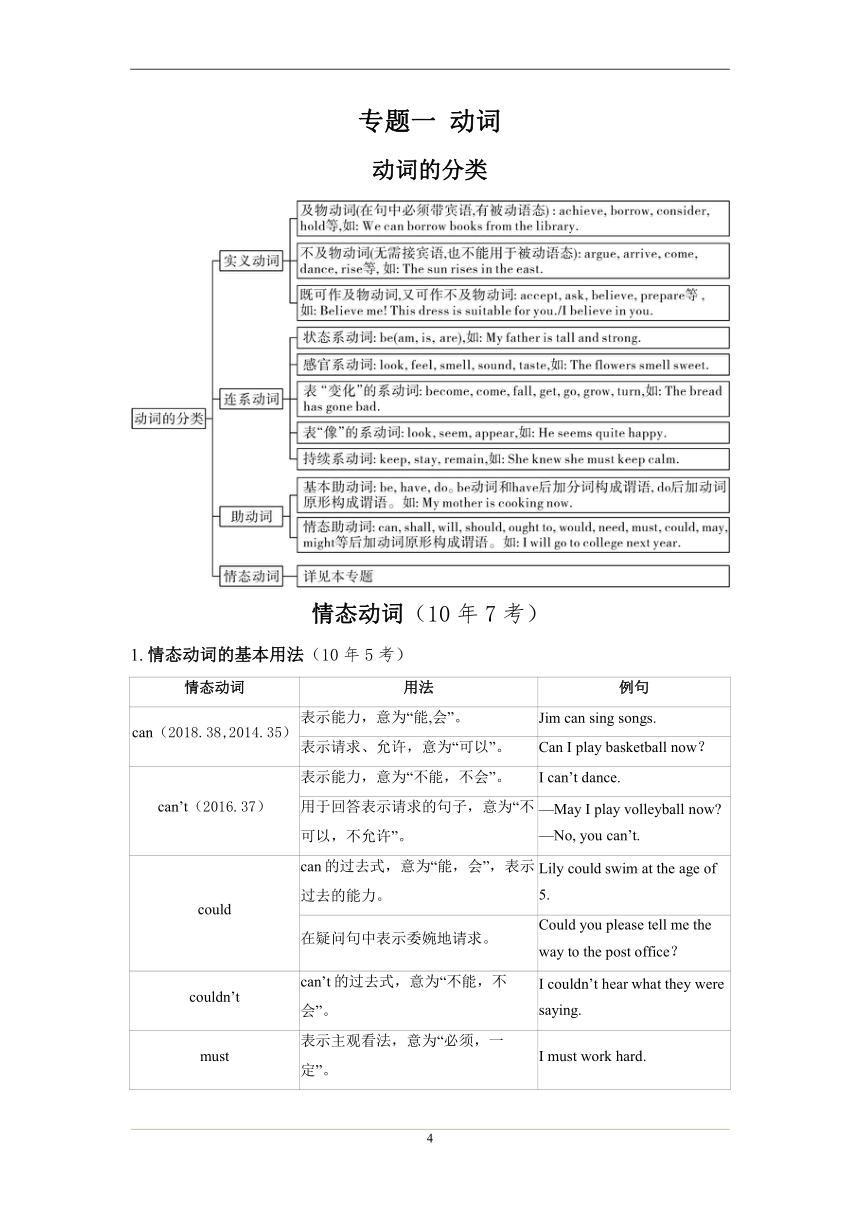
专题一 动词
动词的分类
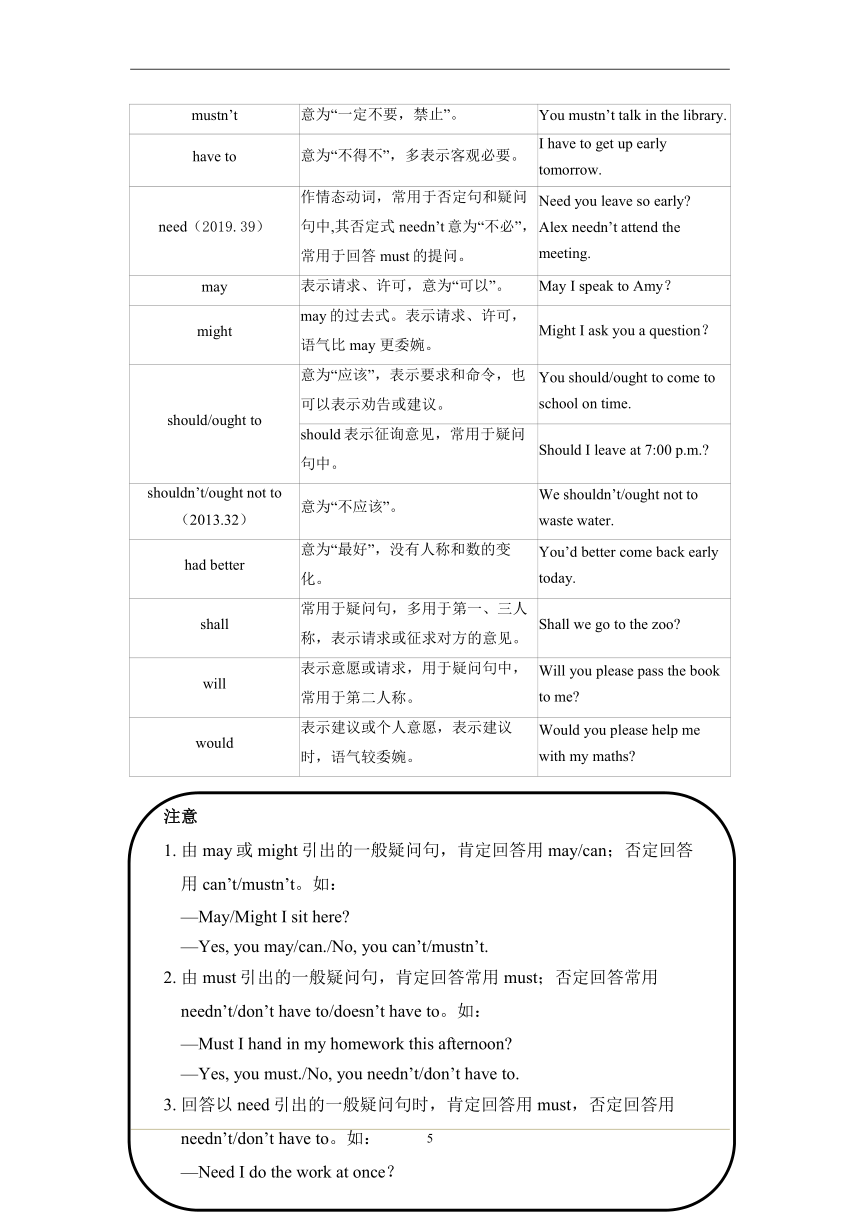
情态动词(10年7考)
1. 情态动词的基本用法(10年5考)
情态动词 用法 例句
can(2018.38,2014.35) 表示能力,意为“能,会”。 Jim can sing songs.
表示请求、允许,意为“可以”。 Can I play basketball now?
can’t(2016.37) 表示能力,意为“不能,不会”。 I can’t dance.
用于回答表示请求的句子,意为“不可以,不允许”。 —May I play volleyball now —No, you can’t.
could can的过去式,意为“能,会”,表示过去的能力。 Lily could swim at the age of 5.
在疑问句中表示委婉地请求。 Could you please tell me the way to the post office?
couldn’t can’t的过去式,意为“不能,不会”。 I couldn’t hear what they were saying.
must 表示主观看法,意为“必须,一定”。 I must work hard.
mustn’t 意为“一定不要,禁止”。 You mustn’t talk in the library.
have to 意为“不得不”,多表示客观必要。 I have to get up early tomorrow.
need(2019.39) 作情态动词,常用于否定句和疑问句中,其否定式needn’t意为“不必”,常用于回答must的提问。 Need you leave so early Alex needn’t attend the meeting.
may 表示请求、许可,意为“可以”。 May I speak to Amy?
might may的过去式。表示请求、许可,语气比 may 更委婉。 Might I ask you a question?
should/ought to 意为“应该”,表示要求和命令,也可以表示劝告或建议。 You should/ought to come to school on time.
should表示征询意见,常用于疑问句中。 Should I leave at 7:00 p.m.
shouldn’t/ought not to(2013.32) 意为“不应该”。 We shouldn’t/ought not to waste water.
had better 意为“最好”,没有人称和数的变化。 You’d better come back early today.
shall 常用于疑问句,多用于第一、三人称,表示请求或征求对方的意见。 Shall we go to the zoo
will 表示意愿或请求,用于疑问句中,常用于第二人称。 Will you please pass the book to me
would 表示建议或个人意愿,表示建议时,语气较委婉。 Would you please help me with my maths
2. 情态动词表推测的用法(10年2考)
情态动词 用法 例句
must 表示非常有把握的肯定推测,意为“一定,肯定”。 It must be raining outside. My father’s clothes are so wet.
can’t 表示十分有把握的否定推测,意为“一定不,不可能”。 He can’t be having a meeting. I saw him just now.
may(2017.39,2015.44) 表示把握不大的肯定推测,意为“有可能,也许”。 John may come back at 5: 00 p.m.
和not连用,表示把握不大的否定推测,意为“可能不”。 Mandy may not come tonight.
might/could 表示没有把握的肯定推测,意为“有可能,也许”,可能性低于may。 The pencil might/could be Bob’s.
动词的时态(必考:每年1~2道)
常见六种时态的构成及用法:
时态 基本结构及标志词 常见用法及例句
一般现在时(2018.35) 结构 1. 主语+am/is/are(+表语) 2. 主语+动词原形/动词单三形式(+宾语) 1. 表示现阶段经常性、习惯性的动作,常与频度副词连用。 2. 表示客观真理、客观存在或自然现象。如: The earth moves around the sun. (注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是一般过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。) 3. 主将从现:若一个复合句中含有由when, after, before, until, as soon as等引导的时间状语从句或由if, unless, as long as, once等引导的条件状语从句, 主句若用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时表将来。如: I will tell Kate the good news as soon as she comes back. 4. 表示按计划或安排好的将要发生的动作,用一般现在时表将来,但仅限于start, begin, leave, go, come, arrive等动词。如: The train leaves at six tomorrow morning.
标志词 1. 频度副词:always, usually, often, sometimes, seldom, never, hardly 2. 频率词组:once a year, twice a month, three times a day等 3. 其他词组:in the morning, on Sundays, at weekends, every day/year…(every系列)
一般过去时(2014.48) 结构 1. 主语+was/were(+表语) 2. 主语+动词过去式(+宾语) 1. 表示过去某个时间里发生的动作或存在的状态。如: We went to the City Library last week. 2. 表示过去常常或反复发生的动作,常与频度副词连用。如: When I was a child, I often played basketball on the playground. 3. 在since引导的时间状语从句中,主句用现在完成时,从句用一般过去时。
标志词 1. ago及ago词组 2. yesterday及yesterday词组 3. last及last词组 4. just now, in the past, in 1920等 5. at the age of…, used to… 6. one day, long long ago, once upon a time
一般将来时(2022.27,2014.41) 结构 1. 主语+will/shall+动词原形(+表语/宾语) 2. 主语+am/is/are going to+动词原形(+表语/宾语) 1. 表示将来某个时间会发生的动作或存在的状态。如: They are leaving for Shanghai next week. 2. 表示某种必然的趋势。如: Fish will die without water. 3. be going to+动词原形,表示计划、打算做某事,表示已决定的,很可能发生的事,或有某种迹象表明要发生的事情。如: What are you going to do next Sunday?(计划) Look at the dark clouds. There is going to be a storm. (客观迹象) 4. “be about to +动词原形”和“be to +动词原形”结构也可表示即将发生的动作。如: The train is about to leave. 5. 在“祈使句+and/or+陈述句”句型中,陈述 句常用一般将来时。 6. 主将从现。(具体讲解见本表格一般现在时)
标志词 1. tomorrow, soon 2. next week/month(next系列) 3. in a week, in 2024, in+一段时间 4. one day, in the (near) future
现在进行时(2015.37,2013.36) 结构 主语+am/is/are +动词现在分词(+宾语) 1. 表示此时此刻正在进行的动作。如: —What are you doing? —I am reading English. 2. 表示现阶段一直在进行的动作,此刻不一定在进行,常用时间状语有:this/these+表示一段时间的名词。如: They are studying hard this term. 3. be doing表示将来,常用于这种结构的动词有go, come, leave, stay, start, begin, 表示即将发生或安排好要做的事情。如: She is going there tomorrow.
标志词 1. now, right now 2. at present, at this time, at the/this moment 3. these days 4. when, while 5. Look!/Listen!
过去进行时(2016.41) 结构 主语+was/were+动词现在分词(+宾语) 1. 表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作。如: —What were you doing at nine last night? —I was watching TV at that time.
过去进行时 标志词 1. then 2. at that time, at ten yesterday, at this time yesterday 3. when/while引导的表示过去时间的状语从句 2. 表示过去某段时间内持续进行的动作。如: What were you doing from seven to nine yesterday 3. 常和always等时间副词连用,表示过去频繁发生的习惯性动作,此时带有一定的感彩。如: Alice was always changing her mind. (表示厌烦)
现在完成时(10年4考) 结构 主语+have/has+动词过去分词(+表语/宾语) 1. 表示过去发生的动作或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响。如: —Have you had your lunch yet? —Yes. I’ve just had it. 2. 表示从过去开始持续到现在的动作或状态,也许还要持续下去,常和for, since连用,动词应用延续性动词。如: We have lived here since 2000. 3. 在“It/This is the+序数词+time that…”句型中,that引导的从句用现在完成时。 4. 特殊用法: (1)have gone to已去某地(未回) have been to曾去过某地(已回) have been in待在某地 (2)It has been+时间段+since+一般过去时的句子
标志词 1. already, ever, never, just, yet, still 2. recently, lately, so far, up till now 3. in the past/last three years/… 4. since 1998, since+一段时间 5. for three years, for+一段时间
动词的语态(10年5考)
1. 被动语态的构成
时态 结构 例句
一般现在时 am/is/are+done(2018.44) My homework is always finished on time. 我的作业总是按时完成。
一般过去时 was/were+done(2017.42, 2016.34) The breakfast was cooked by Linda.早餐是琳达做的。
一般将来时 will/shall/be going to be+done(2019.42) Jim’s room will be cleaned tonight. 今晚,吉姆的房间将被打扫。
情态动词 情态动词+be+done(2013.46) The flower should (not) be watered every day. 这种花(不)应该每天被浇水。
2. 主动语态变被动语态的方法
口诀:宾变主,主变宾,谓语动词用被动。
拓展
主动语态变被动语态的特殊情况
主动语态中有些感官动词(如:hear,see, watch, notice等)和使役动词(如:make, let等)后用不带to的不定式作宾语补足语,变为被动语态时,要把不定式符号to还原,如:
hear/see sb. do sth.→sb. be heard/seen to do sth.
make sb. do sth.→sb. be made to do sth.
3. 主动结构表被动意义的情况
(1)open, lock, write, read, sell, wash, clean, watch, cut, burn, drive 等作不及物动词时,其主语为物,可用主动结构表被动意义。如:
This kind of pen writes very smoothly.
(2)look, sound, taste, smell 等系动词用主动结构表被动意义。如:
Mooncakes taste delicious.
(3)be worth doing 意为“值得做”,用主动结构表被动意义。如:
This book is worth reading.
(4)“need/require+doing”相当于“need/require+to be done”,to be done是不定式的被动结构。如:
Your car needs washing.=Your car needs to be washed.
非谓语动词(近10年未考)
1. 动词不定式
(1)动词不定式的用法
基本形式:①to +动词原形;②(省略不定式符号to的不定式)
否定形式:not to +动词原形
作宾语
接动词不定式作宾语的动词(词组)(v.+to do sth.):
afford负担得起 agree同意 choose选择
dare敢 decide决定 expect期待
fail未能 happen发生 hope/wish希望
learn学习 manage设法完成 offer主动提出
plan计划 prefer更喜欢 prepare准备
pretend假装 promise承诺 refuse拒绝
rush急促 seem似乎 wait等待
can’t wait迫不及待 used to过去常常 want/would like想要
作宾语补足语
①接动词不定式作宾补的动词(词组)(v.+sb.+to do sth.):
advise建议 allow允许 ask要求
encourage鼓励 expect期望 force强迫
invite邀请 order命令 teach教
tell告诉 warn警告 wish希望
want/would like想要 request要求,请求 remind提醒
②接省略to的动词不定式作宾补的动词(词组)(v.+sb.+do sth.):
一感 feel感觉到
一听 hear听到
三看 see看到 watch观看 notice注意到
三使 let让 make使 have让,使
注意:一些使役动词和感官动词后接动词不定式作宾补变被动语态时,要还原to。
作状语
①作目的状语
Jim got up early to cook breakfast for his mother.
②作结果状语
Paul is too excited to say anything.
③作原因状语
I am very happy to talk with you.
作主语
①动词不定式作主语时,常用it作形式主语,真正的主语——动词不定式则被后置。如:
It’s good for you to take exercise.
②若动词不定式位于句首作主语,谓语动词应用第三人称单数形式。如:
To help others makes James happy.
作定语
动词不定式作定语时,要置于被修饰的名词之后,作后置定语。如:
I am not free now. I have lots of things to do.
作表语
动词不定式常位于系动词之后。如:
To see is to believe. 眼见为实/百闻不如一见。
(2)动词不定式的常用句型
①too+adj.+to do sth.太……而不能做某事
②adj.+enough to do sth.足够……做某事
③prefer to do sth. rather than do sth.宁愿做某事而不愿做某事
④It’s+adj.(+for sb.)+to do sth.(对于某人而言,)做某事是……的
⑤It’s+adj.+of sb.+to do sth.某人做某事是……的
⑥It’s time to do sth.该是做某事的时候了
⑦It’s one’s turn to do sth.轮到某人做某事了
⑧It takes/took sb. some time to do sth.某人花费多长时间做某事
⑨find/think/feel it+adj.+to do sth.发现/认为/感到做某事是……的
(3)“疑问词+动词不定式”的用法
①动词不定式与疑问词连用可作主语、宾语或表语。如:
When to go to Beijing hasn’t been decided yet.(作主语)
I haven’t decided when to leave Beijing.(作宾语)
My question is how to go to Beijing. (作表语)
②“疑问词+动词不定式”作宾语时可以转化为宾语从句。如:
Can you tell me where to buy a cup =Can you tell me where I can buy a cup
2. 动名词
(1)动名词(v.-ing)的用法
用法 例句 注意
作宾语 动词宾语 I like playing football very much. 表示一般的习惯、抽象行为或经常性动作
介词宾语 I have no experience in teaching English.
作主语 Getting up early is a good habit. 谓语动词用单数
作表语 His job is teaching Chinese in a school.=Teaching Chinese in a school is his job. 多数情况下,动名词作表语可转换成作主语
作定语 We need a washing machine. 表示它所修饰的词的用途、所属等,置于被修饰词之前
(2)接动名词作宾语的动词(词组)、句型
admit承认 advise建议 avoid避免
complete完成 consider考虑 enjoy喜欢
finish完成 imagine想象 keep坚持
mind介意 miss错过 practic(s)e练习
risk冒险 stop停止 suggest建议
be busy (in) doing sth.忙于做某事
be good at/do well in doing sth.擅长做某事
be interested (in) doing sth.对做某事感兴趣
be worth doing sth.值得做某事
be/get/become used to doing sth.习惯于做某事
can’t/couldn’t help doing sth.情不自禁做某事
feel like doing sth.想要做某事
give up doing sth.放弃做某事
have fun (in) doing sth.做某事很开心
hold on to/stick to doing sth.坚持做某事
look forward to doing sth.期待做某事
pay attention to doing sth.注意做某事
succeed (in) doing sth.成功做某事
【注意】有些动词后面既可接动词不定式,也可接动名词,但意思有区别,常见的有:
begin/start begin/start to do sth.= begin/start doing sth.开始做某事
like like to do sth.= like doing sth.喜欢做某事
love love to do sth.= love doing sth.热爱做某事
prefer prefer to do sth.=prefer doing sth.更喜欢做某事
hate hate to do sth.= hate doing sth.讨厌做某事
continue continue to do sth.继续做另一件事
continue doing sth.继续做同一件事
forget forget to do sth.忘记要做某事(未做)
forget doing sth.忘记做过某事(已做)
remember remember to do sth.记得要做某事(未做)
remember doing sth.记得做过某事(已做)
regret regret to do sth.遗憾要做某事(未做)
regret doing sth.懊悔做过某事(已做)
stop stop to do sth.停下来去做另一件事
stop doing sth.停止正在做的某件事
mean mean to do sth.打算做某事
mean doing sth.意味着做某事
try try to do sth.努力做某事
try doing sth.尝试做某事
need need to do sth.(某人)需要做某事
need doing sth.(某物)需要被……
3. 分词
(1)分词的用法
分词包括现在分词(v.-ing)和过去分词(v.-ed),其常见用法有:
用法 例句
作补足语 现在分词作补足语,被修饰的宾语或主语是它的逻辑主语(即主动关系)。 I hear my sister singing.
过去分词作补足语,被修饰的宾语或主语是它的逻辑宾语(即动宾关系)。 I had my hair cut last night.
作定语 现在分词作定语,所修饰的词是其逻辑主语。 Do you know the boy playing football
过去分词作定语,所修饰的词是其逻辑宾语。 Please hand in your written exercises.
(2)现在分词与过去分词的区别
角度 意义 示例
语态 现在分词表示主动意义 a sleeping girl一个睡着的女孩
过去分词表示被动意义 the moved people被感动的人们
时间 现在分词表示正在进行的动作 the developing country发展中国家
过去分词表示已完成的动作 the developed country发达国家
主谓一致与 There be句型(2015.43)
1. 主谓一致(近10年未考)
(1)语法一致原则
语法一致表示谓语动词与主语在单、复数形式上保持一致。
主语 谓语 例句
不可数名词 单数 Water is important to everyone.
可数名词单数,第三人称单数及it 单数 The young man is from Paris.
名词复数、人称代词复数、第一人称单数I及第二人称单数you 复数 The children were in the classroom two hours ago.
one of+可数名词复数/代词复数 单数 One of the books is boring.
and或both… and…连接的名词 复数 Both Jenny and Kate are my friends.
either, neither, each, every或no +单数名词 单数 Each person has a new book.
复合不定代词 单数 Everybody has a chance to win.
主语后面跟有with, together with, except, but, like, as well as, rather than, including等 取决于主语的数 The mother together with her three sons was happy.
分数/百分数+of+名词 取决于名词的数 60%of the students in our class are girls.
a lot of/lots of/plenty of/the rest of+名词
A lot of people are in the classroom.
动词不定式短语、动名词短语或从句 单数 What he said is very meaningful.
a number of+可数名词复数 复数 A number of books were given to the poor students.
the number of+可数名词复数 单数 The number of the apples is 12.
(2)意义一致原则
意义一致就是概念一致,即谓语动词的形式要和主语所表达的概念一致。
主语 谓语 例句
表示重量、度量、时间、长度、价格等的词或短语 单数 Two meters is not as high as you think.
the+姓氏名词复数,表示“……一家人;……夫妇” 复数 The Smiths have decided to go to Kunming for holiday.
the+形容词,表示一类人 复数 The young are energetic.
集体名词(如:family /class /team/group等) 整体看待→单数 强调成员→复数 His family is going to move to Beijing. The whole family are looking forward to the holiday.
由(both…)and连接的两个名词指代同一个人 单数 The writer and actor has come.
(3)就近原则
就近原则指谓语动词的形式不与主语一致,而是和靠近它的名词或代词保持一致。
主语 谓语 例句
由either… or…, neither… nor…, not only… but(also)…, not… but… 或 or连接的两个并列主语 和距其较近的主语在数上保持一致 Either Jimmy or I am going to give a speech.
There/Here be…句型中 be动词与距其最近的主语在数上保持一致 Here is a book and two notebooks for you.
2. There be句型(2015.43)
“There be+ sb./sth.+地点状语”表示“某地有某人/某物”。
(1)基本结构
句式 结构 例句
肯定 There be+ sb./sth.+其他 There is a dog in the room.
否定 There be+ not/not any/no+ sb./sth.+其他 There is no water in the bottle.
疑问 Be there+sb./sth.+其他 Is there water in the bottle
(2)时态
时态 There be句型结构
一般现在时 There is/are…
一般过去时 There was/were…
一般将来时 There will be…/There is/are going to be…
现在完成时 There has/have been…
“There be句型”还可以和助动词或情态动词连用。如:
There will be/There is going to be a new film on Monday.
There must be a mistake somewhere.
(3)be动词的单复数:be动词的单复数必须和其后所接的名词的数保持一致。若be动词后接两个或两个以上的并列名词时,be动词和距其最近的名词的数保持一致,即遵循“就近原则”。如:
There is a girl and two boys in the classroom.
(4)答语
回答“Be there+其他”时,常用“Yes/No, there+be动词(not)”。其中, be动词的数和时态与问句保持一致。如:
—Was there a park in your city 20 years ago?
—Yes, there was.
注意
“There be句型”强调某地有某物,不表示所属关系,故其不能和“have(有)”同时使用。如:
There is going to have a basketball game this afternoon.(×)
There is going to be a basketball game this afternoon.(√)
动词填空(必考:每年1~2道)
1. 考查方式
2. 解题技巧
先判定空格处是否填动词
(1)根据括号内的汉语提示词和首字母直接判断;
(2)若括号内的汉语提示表明所填词既可作名词,又可作动词,则需根据题干的句子成分判断所填词在句中作什么成分;如果句中缺谓语,则可判定此处应填动词。
再确定动词是否需要变形
(1)填动词原形(10年7考)
①位于情态动词或其否定形式之后;
②位于动词不定式符号to之后;
③祈使句中以动词原形开头;
④当时态为一般现在时且主语为可数名词复数、复数人称代词或I;
⑤位于助动词(do/does/did/will)或其否定形式之后。
(2)填单三形式(10年6考)
若句子用一般现在时,在以下情况中,谓语动词用单三形式:
①不可数名词作主语;
②“a/an/the+可数名词单数”作主语;
③人称代词第三人称he, she, it 作主语;
④单个人名、地名作主语;
⑤不定代词(every系列/some系列/any系列/no系列)作主语;
⑥指示代词(this/that/it)作主语;
⑦非谓语动词(动词不定式/动名词) 作主语;
⑧主谓一致【见P51的讲解】。
(3)填现在分词(2017.93)
用于现在/过去进行时(am/is/are/was/were+doing)结构中。
(4)填过去式(2021.77)
①有明显的表示过去的时间标志词。如: yesterday, just now, two days ago, last night/week/month/year等;
②过去式+ and/or +过去式;
③主从复合句中,若从句用一般过去时,主句通常也用过去的某种时态;
④根据上下文语境和时态判断。
【拓展】
1. 动词的基本形式变化表
类别 构成方法 例词
原形 没有任何形式变化的动词 do, dance,leave
第三人称单数 一般在动词原形后直接加-s work→works read→reads
以s, o, x, sh, ch结尾的动词,后加-es go→goes wash→washes
辅音字母加y结尾的动词,应将y改为i再加-es fly→flies study→studies
过去式与过去分词 一般在动词原形后直接加-ed work→worked stay→stayed
以e结尾的动词后只加-d close→closed like→liked
以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,应将y改为i再加-ed study→studied carry→carried
以重读闭音节结尾且末尾只有一个辅音字母的动词,双写此辅音字母再加-ed stop→stopped plan→planned
现在分词 一般在动词原形后直接加-ing sleep→sleeping wait→waiting
以不发音的e结尾的动词,去e再加-ing smile→smiling move→moving
以重读闭音节结尾且末尾只有一个辅音字母的动词,双写此辅音字母再加-ing sit→sitting dig→digging plan→planning
少数以ie结尾的动词,变ie为y,再加-ing die→dying lie→lying tie→tying
2. 动词过去式和过去分词的不规则变化
①AAA型
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
cost cost cost 花费
cut cut cut 切;割
hit hit hit 撞;击
hurt hurt hurt 受伤
let let let 让
put put put 放
read read read 读
set set set 设置
shut shut shut 关闭
spread spread spread 传播
②ABA型
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
become became become 成为
come came come 来
run ran run 跑
③ABB型
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
bring brought brought 带来
build built built 建造
buy bought bought 买
catch caught caught 捉;抓
deal dealt dealt 处理
dig dug dug 挖(洞);凿(孔)
feed fed fed 喂
feel felt felt 感到
fight fought fought 打架
find found found 发现
get got got/gotten 得到
hang hung hung 悬挂
have had had 有
hear heard heard 听见
hold held held 握住
keep kept kept 保持
lay laid laid 放置
lead led led 导致
leave left left 离开
lend lent lent 借给
lose lost lost 丢失
make made made 制造
mean meant meant 意思是
meet met met 遇到
pay paid paid 付钱
say said said 说
sell sold sold 卖
send sent sent 送;寄
shine shone shone 发光;照耀
sit sat sat 坐
sleep slept slept 睡
speed sped sped 加速
spend spent spent 花费
stand stood stood 站
stick stuck stuck 粘贴;将……刺入
teach taught taught 教
tell told told 告诉
think thought thought 想;认为
understand understood understood 理解
win won won 赢
④ABC型
原形→ew→own
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
blow blew blown 吹
fly flew flown 飞
grow grew grown 生长
know knew known 知道
i→a→u
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
begin began begun 开始
drink drank drunk 喝
ring rang rung 打电话
sing sang sung 唱
swim swam swum 游泳
原形→过去式→过去式+(e)n/过去式去掉字母e+n/过去式双写末尾字母+en
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
bear bore born 负担;忍受
break broke broken 破;裂;碎
choose chose chosen 选择
forget forgot forgotten 忘记
hide hid hidden 藏
speak spoke spoken 说
steal stole stolen 偷
wake woke woken 醒来
wear wore worn 穿
原形→过去式→原形+(e)n
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
draw drew drawn 画
drive drove driven 开车
eat ate eaten 吃
fall fell fallen 落下
give gave given 给
mistake mistook mistaken 误会
rise rose risen 升起;增加;提高
see saw seen 看见
shake shook shaken 摇动;抖动
show showed shown/showed 展示;给……看
take took taken 买下;拿;取
throw threw thrown 扔掉
⑤有两种形式
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
burn burned burned 燃烧
burnt burnt
dream dreamed dreamed 做梦;梦想
dreamt dreamt
learn learned learned 学
learnt learnt
lie lied lied 说谎
lay lain 躺;位于
light lighted lighted 照亮
lit lit
smell smelled smelled 闻
smelt smelt
spell spelled spelled 拼写
spelt spelt
⑥其他形式
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
be(am, is, are) was, were been 是
beat beat beaten 敲打;打败
do did done 做
go went gone 去;走
ride rode ridden 骑
write wrote written 写
can could / 能;会
may might / 也许;可能;可以
must must / 必须
shall should / 将要;将会
will would / 将要;会
专题二 名词填空(必考:每年1~3道)
1. 考查方式
2. 解题技巧
先判断空格处是否填名词
(1)根据题干所给汉语提示词和首字母判断。如:2021年78题,汉语提示词为“英雄”,考生可直接确定空处填名词;
(2)根据语境和句子结构判断。具体方法如下:
①位于系动词后作表语;
②位于冠词、数词、形容词性物主代词、名词所有格后;
③位于动词或介词后作宾语;
④位于形容词后;
⑤位于句首,在句中作主语;
⑥位于限定词this, these, that, those, many, some, any, a lot of等后。
判断所填名词是可数名词还是不可数名词
类型 特点
可数名词 ①有单数和复数两种形式,表示一个或者多个,如:a desk→two desks;
可数名词 ②前面可以被不定冠词(a/an)、基数词、序数词、指示代词、 many、 a few 等词直接修饰,如:an egg, three girls, many singers。
不可数名词 ①没有复数形式,如:beef, ice,作主语时,谓语动词用单数; ②前面可用much, little等词修饰,不可以被不定冠词(a/an)、基数词、序数词、指示代词, many, a few 等词直接修饰。 ③若表示具体的量,可用量词来修饰,如:a piece of cake, two cups of coffee。
(1)若判断所给名词为不可数名词,无需变形(不可数名词没有复数形式)。常见的不可数名词主要有三类:专有名词、物质名词和抽象名词。
(2)若判断所给名词是可数名词,要考虑是否需要变形。
注意:英语中有一些名词既可以作可数名词,也可以作不可数名词,但含义不同,常见的有:
名词 可数 不可数 名词 可数 不可数
chicken 小鸡 鸡肉 orange 橙子 橙汁
experience 经历 经验 paper 试卷;论文 纸
exercise 练习 锻炼 radio 收音机 无线电
glass 玻璃杯 玻璃 room 房间 空间
iron 熨斗 铁 time 次数;倍数 时间
life 生命 生活 wood 树林 木头;木材
light 电灯 光;光线 work 作品 工作
拓展
可数名词和不可数名词的常见修饰语
1. 只修饰可数名词的修饰语:
few很少;几乎没有 a few一些;几个
several几个 different不同的
a couple of两个 many (a) 很多
a number of若干;许多
a great/large number of许多
2. 只修饰不可数名词的修饰语:
little很少;几乎没有
a little一点儿;少量
much很多
a good/great deal of很多
a bit of有一点儿
a large amount of大量的
3. 既可修饰可数名词又可修饰不可数名词的修饰语:
some一些 a lot of很多
lots of很多 plenty of充足的
most大多数的 all全部的
the rest of剩下的
判断可数名词是否需要变形
(1)填单数名词的判定方法
①a/an/this/that/every/each/another/either/one/序数词/any other+可数名词单数。如:
a clear idea(2019.91)
has a role to play(2018.92)
②可数名词单数(主语)+be动词单数形式/谓语动词的单三形式。如:
My main task was to prepare for the meeting.
③结合上下文语境或者句中对应的提示词,如:it, its。
My father’s T-shirt has completely lost its shape.(2017.92)
④专有名词,如:the Great Wall。
(2)填复数名词的判定方法
①these/those/普通不定代词(many/some/several/few/a few/both/all/other 等)/大于1的基数词/one of(+形容词最高级)/quite a few/a pair of/a couple of/a (great/large) number of/different kinds of/all kinds of+可数名词复数;
②both/either/neither/all/none of+可数名词复数;
③可数名词复数(主语)+be 动词复数形式/动词原形;
④结合上下文语境或句中对应的提示词,如:them, their;
⑤通常用复数或只有复数形式的名词:chopsticks 筷子,clothes 衣服,glasses 眼镜, scissors 剪刀, socks 袜子, trousers 裤子。
【拓展】
1. 可数名词单数变复数的规则变化表
构成方法 示例
一般情况加 -s star→stars gift→gifts invention→inventions
以字母s, x, sh, ch结尾的词加 -es class→classes box→boxes brush→brushes watch→watches 特例:stomach→stomachs
以f或fe结尾的词变f或fe为v再加 -es leaf→leaves knife→knives shelf→shelves wife→wives 特例:roof→roofs proof→proofs belief→beliefs
以辅音字母加y结尾的词先变y为i,再加 -es party →parties baby→babies story→stories family →families
以元音字母加y结尾的词加 -s key→keys holiday→holidays monkey→monkeys
以ce, se, ze, ge等结尾的词加 -s face→faces license→licenses prize→prizes orange→oranges
以o结尾有生命的加 -es, 无生命的加 -s tomato→tomatoes hero→heroes potato→potatoes photo→photos piano→pianos
2. 可数名词单数变复数的不规则变化表
构成方法 示例
a→e型 man→men woman→women fireman→firemen postman→postmen gentleman→gentlemen policeman→policemen policewoman→policewomen 特例:human→humans
oo→ee型 foot→feet tooth→teeth 特例:boot→boots
“某国人”变化口诀 ①中日永不变 Chinese→Chinese Japanese→Japanese ②英法a变e Englishman→Englishmen Frenchman→Frenchmen ③其余s加后面 American→Americans Canadian→Canadians German→Germans Indian→Indians Russian→Russians
单复数同形 deer→deer sheep→sheep
合成词:将主体词变为复数 passer-by→passers-by toothbrush→toothbrushes
其他 mouse→mice child→children
专题三 形容词和副词
形容词和副词的比较等级(10年2考)
1. 标志词
原级:(not)as… as…
比较级:than;the+比较级,the+比较级;比较级+and+比较级
最高级:one of…;含有among, in或of等短语表示的范围
2. 原级的用法
用法 例句
描述人物或事物性质,如:“so/very/too/quite+原级”表示“如此/非常/太/相当……”。 The story is quite interesting.
“A+be动词/实义动词+as+原级+as+B”表示“A和B一样……”。 Is Fuyang as big as Hefei
“A+be动词/实义动词(否定)+so/as+原级+as+B”表示“A不如B……”。 Jack is not as tall as Jim.
“A+实义动词+as+much/many+名词+as+B”表示“A和B的……数量相同”。 Linda has as many books as Lily.
“A+be动词/实义动词+倍数+as+原级+as+B”表示“A是B的……倍”。 My room is twice as big as his.
3. 比较级的用法(2020.46,2017.35)
用法 例句
“the+比较级,the +比较级”表示“越……,就越……”。 The harder we study, the better grades we’ll get.
“比较级+and+比较级/more and more+多音节形容词/副词”表示“越来越……”。 This song is becoming more and more popular.
“A+be动词/实义动词+比较级+than+B”表示“A比B……”。 The blue cup is bigger than the green one.
“A+be动词/实义动词+less+多音节形容词/副词原级+than+B”表示“A不及B……”。 I am less careful than you.
“Which/Who+be动词/实义动词+比较级,A or B ”表示“A、B两者中哪一个/谁更……” Who is taller, you or Tom?
“A+be动词/实义动词+比较级+than+any other+可数名词单数”/“A+be动词/实义动词+比较级+than+the other+可数名词复数”表示“A比其他任何一个都……”(比较级结构表示最高级含义)。 He is taller than any other boy in his class.=He is taller than the other boys in his class.
“A+be动词/实义动词+倍数+比较级+than+B”表示“A是B的……倍……”。 This box is three times bigger than that box.
注意
1. 当形容词或副词由表示程度的副词(词组)a little, a bit, a lot, much, even, far等修饰时, 常用该形容词或副词的比较级形式。如:
It is even colder today. 今天甚至更冷了。
2. 表示“(两者之中)较……的一个”时, 常用“the+比较级”结构。如:
My brother is the taller one of the two. 我哥哥/弟弟是这两个人中较高的那一个。
4. 最高级的用法
用法 例句
“A+be动词/实义动词(+the)+最高级+范围”表示“A是……中最……”。 I am the tallest student in our class.
“A+be动词/实义动词+one of the+最高级+可数名词复数”表示“A是最……的……之一”。 Lang Ping is one of the most famous volleyball coaches in the world.
“Which/Who+be动词/实义动词(+the)+最高级, A, B or C ”表示“A、B、C三者中,哪个/谁最……”。 Which is the biggest, the sun, the moon or the earth
“A+be动词/实义动词+the+序数词+最高级+名词+范围”表示“A是……中第几……”。 The Yellow River is the second longest river in China.
注意
1. 形容词最高级前必须加定冠词the, 副词最高级前可以不加the。如:
This picture is the best of all.
He draws (the) most wonderfully.
2. 形容词最高级前面有物主代词、指示代词、名词所有格等修饰时, 不再加定冠词the。如:
She is my best friend.
形容词和副词填空(必考:每年1~3道)
1. 读汉语,定词性
在单词拼写中,所填形容词和副词均为原形,没有任何变形,因此考生根据题干所给汉语提示和首字母即可联想到所填词。
2. 读语境,定单词
对于根据汉语提示不能确定词性的单词,考生可分析语境和句子结构,再次判断词性,并进一步确定单词。
(1)填形容词的判定方法
①所填词位于名词前作定语;
②所填词位于be动词后作表语;
③所填词位于形容词短语中,其结构为:be动词+形容词+介词;
④所填词位于感官动词和连系动词look, sound, smell, taste, feel, seem, become, grow, get, turn, keep, remain之后;
⑤所填词位于复合不定代词后作后置定语;
⑥所填词位于定冠词the后表示一类人;
⑦所填词位于固定句型It is+adj.(+for/of sb.)+to do sth.中;
⑧所填词位于“形容词+ and/or+形容词”结构中;
⑨所填词位于宾语之后作宾补,常与make, leave, keep等动词连用;
⑩在as… as… 结构中,且空前有系动词。
(2)填副词的判定方法
①所填词修饰动词或动词短语;
②所填词修饰形容词或其他副词;
③所填词修饰介词短语;
④所填词位于句首,作状语,修饰整个句子;
⑤在as…as结构中,且谓语动词为实义动词。
专题四 代词
人称代词、物主代词与反身代词(10年2考)
1. 人称代词、物主代词与反身代词一览表
类别 人称 人称代词 物主代词 反身代词
主格 宾格 形容词性 名词性
第一人称 单数 I me my mine myself
复数 we us our ours ourselves
第二人称 单数 you you your yours yourself
复数 you you your yours yourselves
第三人称 单数 he him his his himself
she her her hers herself
it it its its itself
复数 they them their theirs themselves
2. 人称代词的用法以及所作的成分(2015.51)
类别 用法 成分 例句
主格 用在动词/系动词/情态动词之前。 作主语 They all like sports.
宾格 用在动词/介词之后。 作宾语 My mother will take me to the park. Let’s go and look for him.
用在系动词之后。 作表语 The boy in the picture is me.
3. 物主代词的用法以及所作的成分
类别 用法 成分 示例
形容词性物主代词 相当于形容词,用在名词之前。 作定语 This is my pet cat.
固定搭配中(特例) try one’s best
名词性物主代词 等同于形容词性物主代词+名词,其后不能接 名 词。 用在动词/系动词之前。 作主语 That’s her eraser. Mine is on the desk.
用在动词/介词之后。 作宾语 I left my dictionary at home. Can you lend yours to me
用在系动词之后。 作表语 This pencil is his.
4. 反身代词的用法以及所作的成分(2013.64)
用法 成分 例句
用在动词/介词之后。 作宾语 The little girl can’t dress herself. Charles said to himself, “I must work hard.”
用在系动词之后。 作表语 The man in the story was myself.
用在名词/代词之后或句末。 作同位语 The boy/He himself finished the task.=The boy/He finished the task himself.
普通不定代词
1. both, either, neither, all与none(10年3考)
普通不定代词 含义 谓语形式 短语
both 两者都 复数 both… and………和……都both of… ……都
either(2014.45) 两者中的任意一个 单数 either… or…或者……或者…… either of…两者中的任意一个……
neither(2016.33) 两者都不 单数 neither…nor… ……和……都不neither of………都不
all 三者或三者以上都 根据它所指代或修饰的名词的数来决定 all of………都
none 三者或三者以上都不 根据它所指代或修饰的名词的数来决定 none of… ……都不
2. a little, little, a few与few
肯定含义 否定含义 所跟名词
a little一点儿 little几乎没有 不可数名词
a few一些;几个 few几乎没有 可数名词复数
3. many与much
普通不定代词 相同点 不同点
many 都意为“很多”,可单独使用,也可跟of短语,也可与表示程度的副词so或too连用。 指代或修饰可数名词复数。
much 指代或修饰不可数名词。
4. some与any
普通不定代词 相同点 不同点
some 意为“一些”,均可指代或修饰可数名词复数或不可数名词。 一般用于肯定句中,也可用于表建议或请求的疑问句中,表示说话人希望得到肯定的回答。
any 意为“一些”,均可指代或修饰可数名词复数或不可数名词。 一般用于肯定句中,也可用于表建议或请求的疑问句中,表示说话人希望得到肯定的回答。
5. every与each
普通不定代词 every each
不同点 修饰名词单数,不可单独使用。 既可修饰名词单数也可单独使用。
指三者或三者以上的人或事物中的“每一个”。 指两者或两者以上的人或事物中的“每一个”。
后不可跟of短语。 后可跟of短语。
相同点 “every/each+名词单数”作主语时,谓语动词要用单数形式。
6. other, others, the other, the others与another
普通不定代词 含义 用法
other 其他的;另外的 常接名词复数,表示除去一部分以外的另外的部分,但不是剩下的全部。
others 泛指别的人或物 =other+可数名词复数,表示除去一部分以外另外的部分,但不是剩下的全部。
the other 两者中的另一个。 后接可数名词单数,常用短语:one… the other…
两部分中的另外一部分。 后接可数名词复数,表示其余的全部,常用短语:some… the other…
the others 特指其余的人或物。 =the other+可数名词复数,表示其余的全部。
another(2015.32) 任何一个;另一个。 后接可数名词单数,表示“另一个……”
不接名词,指代三者或三者以上中的另一个。
another +数词 +可数名词复数 = 数词+ more +可数名词复数
复合不定代词(10年6考)
1. 初中常见的复合不定代词如下表:
词缀 词根 -one/-body(指人) -thing(指物)
some-(肯定) someone/somebody某人 something某事,某物
any-(否定/肯定) anyone/anybody任何人 anything任何事
every-(肯定) everyone/everybody每个人 everything每件事,一切
no-(否定) no one/nobody没有人 nothing什么都没有
2. 复合不定代词的用法
(1)由some- 和any- 构成的复合不定代词,其区别同some和any。
(2)当形容词或else修饰复合不定代词时, 形容词或else必须放在复合不定代词之后。如:
Is there anything interesting in this book
(3)复合不定代词可作主语、宾语和表语,不能作定语。作主语时, 谓语动词通常用单数。如:
Everyone is happy to hear the news.
(4)somebody还可意为 “大人物,重要人物”;nobody还可意为 “小人物,无名小卒”。如:
I’d like to be somebody.
3. 含复合不定代词的常用句型
(1)There is something/nothing wrong with… ……出问题了/没有问题。
(2)have something/nothing to do with…和……有关/无关。
(3)sb. can do nothing but… 某人什么都不能做,只能……
指示代词(10年3考)
1. 初中常见的指示代词的用法如下表:
单词 用法
this(复数式:these) ①近指,指时间或空间上离说话人较近的人或物 ②指代下文要提到的人或物 ③在电话用语中,常用this介绍自己是谁
that(复数式:those) ①指时间或空间上离说话人较远的人或物 ②指前面刚提到过的事情或已经完成的事情 ③在电话用语中, 常用that询问对方是谁 ④常用于比较结构中,代替前面提到的名词,以避免重复。当前面的名词为可数名词单数或不可数名词时用that,为可数名词复数时用those。
2. 辨析it与one(10年3考)
代词 用法
it(复数是them)(2017.32) 特指上文提到的同一事物(同类同物)。
one(复数是ones)(2018.33,2013.38) 泛指上文提到的同类人或事物中的一个(同类而不同物)。
拓展
it的特殊用法
1. it作形式主语时, 常用于下列句型中:
(1)It’s+adj.(+for/of sb.)+to do sth.做某事(对某人来说)是……/(某人)做某事真是……。
(2)It’s time to do sth./for sth./that… 是(做)……的时候了。
(3)It’s one’s turn to do sth.轮到某人做某事。
(4)It seems that… 好像/似乎……
(5)It’s+adj.+that从句 ……是……
(6)It takes (sb.)+一段时间+to do sth.做某事花费(某人)多长时间。
2. it作形式宾语时, 代替由动词不定式或从句等表示的真正宾语, 常用在find, think, make, consider, feel等动词之后。如:
Do you think it important to protect our environment
I find it necessary that we do some exercise every day.
3. 指代婴儿或身份不明的人。如:
There is a knock on the door. It must be the postman. 有人在敲门,一定是邮递员。
专题五 介词(10年13考)
1. 介词in, on与at的用法
介词 类别 用法 示例/例句
in(2015.33) 时间介词 后接较长的一段时间(如世纪、年份、季节、月份等)。 in the 21st century in 2009 in summer in July
用在泛指的上午、下午、晚上前。 in the morning/afternoon/evening
表示多长时间或多久以后,常用于一般将来时。 in an hour in two days
方位介词 某人或某物在某地点。 Xiaoming is in the room now.
某一小地点在另一大地点之内。 Japan lies in the east of Asia.
用于较大的地方前(如:国家、城市、乡镇、水域等)。 in China in Lijiang River
方式介词 使用,后接某种语言或声音等。 in Chinese in a high/low voice
其他介词 穿着;戴着。 Lily was in a beautiful dress.
on 时间介词 用在具体的某天或某天的上午、下午、晚上或节日前。 on Tuesday on September 1st on a cold morning on National Day
方位介词 在……表面上(意指接触物体表面)。 There is a book on the desk.
在广阔的平面上。 on the lake
两地不在同一范围内,但接壤。 India is on the southwest of China.
方式介词 “on+通讯工具/电子产品”意为“通过……”。 on TV/the radio talk on the phone
其他介词 关于。 a movie on South Africa
at 时间介词 用在某个时刻或黎明、正午、黄昏、午夜前。 at 7:00 at noon at midnight
方位介词 用于某个较小的地方(如:建筑物、公共机关、机场、街道等)。 She works at the post office.
向;朝。 look at
其他介词 在……岁时。 She got married at 25.
2. 时间介词
介词 用法 示例/例句
from 从……开始,常和表示时间的介词to(到……,至……)连用。 from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. from Monday to Sunday from 1987 to 2018
before 在……之前。 Annie was born a few weeks before Christmas.
after(2014.32) ……之后,与一般将来时连用时,后接时间点。 He’ll come back after two o’clock.
……之后,与一般过去时连用时,后接时间段。 He came back from Canada after three weeks.
since “since+时间点/since+一段时间+ago”意为“自……以来”,表示从过去某时直至现在,主句用现在完成时或过去完成时。 I have been here since 1989. She has lived in this city since five years ago.
for “for+时间段”表示动作的延续,主句常用现在完成时或过去完成时。 I have studied in the school for 2 years.
by 不迟于某时,包括某时在内。 I will finish the work by Friday.
until 直到……,到……为止,后常接时间点。 My mother didn’t get home until 9:00 p.m.
3. 方位介词
介词 用法 示例/例句
to 到;去;向;朝。有一定的方向性。 I went to the park this morning.
表示在某一地域之外且不接壤。 Japan lies to the east of China.
below 在……下方(两者不接触,也不一定垂直)。 There is a chair below the window.
under 在……正下方(两者不接触)。 A dog is sitting under the tree.
above 在……上方(两者不接触,也不一定垂直)。 He lifted his hands above his head.
over(2013.37) 在……正上方(两者不接触)。 They will build a bridge over the river.
在……上面,表示部分覆盖或全部覆盖。 She put a blanket over the sleeping child.
behind(2017.38,2016.53) 在……后面。 There is a cat behind the door.
beside 在……旁边。 Mary sat beside me.
outside 在……外面。 You can park your car outside our house.
against 紧靠;倚。 Place the ladder against the wall.
along 顺着;沿着。 Walk along the road, and you will see a bank on the left.
around 四周;在……周围。 Would you like to walk around the factory this afternoon
by(2019.38) 在……旁边;靠近。 There is a piano by the window.
near 在……附近。 Do you live near here
next to 紧挨着……。 My home is next to the bank.
4. 方式介词
介词 用法 示例/例句
by 通过某种方式或手段,后常跟动名词、名词。 I learn English by using the iPad.
“by+交通工具”意为“乘……”。 by bike/bus
with 使用,后接具体有形的工具。 He broke the window with a stone.
through 以;凭借;通过。 He won what he wanted through hard work.
5. 其他常见介词
介词 用法 示例/例句
for 为了(表目的)。 What can I do for you?
支持。 We are for the idea.
给;对。 It’s a book for children.
without 没有;缺乏。 We got there without any trouble.
不和……在一起;无……相伴。 Don’t go without me.
不(做某事)。 He left without saying anything.
with 和……在一起。 I like staying with my parents.
带有;具有。 I have no money with me.
about 关于。 Could you tell me about your life
against(2018.36) 碰;撞。 The rain is beating against the window.
反对,其反义词是for。 He is against your ideas.
对抗;和……竞争。 Our team will play against yours this afternoon.
as 作为;以……身份。 He came to China as a tourist five years ago.
像;如同;跟……一样。 She describes herself as a reporter.
from 来自(表示来源)。 Where are you from
like 像;与……相似。 Tom looks like his mother.
……怎么样。 What is she like
例如。 I like reading English novels like Little Women and Three Days to See.
of 属于(某人或某物);关于(某人或某物)。 the window of the room a photo of my dog
except 除……之外(其他的都) Everyone is happy except John.
besides 除……之外(其他的也) I learn English and math besides Chinese.
6. 常见介词短语(10年4考)——见背面《晨读核心词句篇》P57;
常见介词与形容词的固定搭配(2015.50)——见背面《晨读核心词句篇》P55;
常见介词与动词的固定搭配(2021.24)——见背面《晨读核心词句篇》P50。
专题六 数词(近10年未考)
基数词与序数词
1. 基数词和序数词的构成
1~9 11~19 10~90(整十数) ≥100
基数词 序数词 基数词 序数词 基数词 序数词 基数词 序数词
one first eleven eleventh ten tenth hundred hundredth
two second twelve twelfth twenty twentieth thousand thousandth
three third thirteen thirteenth thirty thirtieth million millionth
four fourth fourteen fourteenth forty fortieth billion billionth
five fifth fifteen fifteenth fifty fiftieth
six sixth sixteen sixteenth sixty sixtieth
seven seventh seventeen seventeenth seventy seventieth
eight eighth eighteen eighteenth eighty eightieth
nine ninth nineteen nineteenth ninety ninetieth
2. 基数词的用法
(1)表示数量。表示事物或人物的确切数量,用“基数词+可数名词单数/复数”。如:
one apple一个苹果;two pears两个梨。
(2)表示时刻。
①表示“……点”用“基数词+o’clock”。如:nine o’clock 九点钟;
②表示“……点过……分”时,若分钟数小于或等于30分钟,用“基数词+past+基数词”。如:
twenty past three三点二十分;
③表示“差……分到……点”时,若分钟数小于30分钟,用“基数词+to+基数词”。如:twenty to three 两点四十分。
(3)表示年份。如:in 2019在2019年;
(4)表示年代。“in the+年份后加-s”表示“在……世纪……年代”。如:
in the 1860s 在十九世纪六十年代。
(5)表达年龄。
①用基数词(+year/years old)表达。如:twenty (years old) 二十岁;
②at the age of+基数词。如:
at the age of twenty在二十岁的时候;
③表示不确切的岁数时,常用几十的复数形式。如:
in his thirties在他三十多岁时。
(6)表示电话号码。数字可单个读,重复的数字也可以读“double+数字”。如:53882069 读作:five three double eight two zero six nine。
(7)表示长、宽、高等。用基数词+单位词(meter, kilogram等)+形容词(long, wide, high等)表示。如:three meters long 三米长;four meters high四米高。
(8)表示时间、距离。使用含基数词的名词所有格形式作定语。如:twenty years’ time二十年的时间;five minutes’ walk 步行五分钟的路程。
(9)“基数词+名词(+形容词)”复合结构作定语:名词用单数形式,各部分间要用连字符“-”来连接。如:a fifteen-minute drive十五分钟的车程;a sixteen-year-old girl一个十六岁的女孩。
3. 序数词的用法
(1)序数词前通常加the,其后接名词单数,但当序数词前有形容词性物主代词、名词所有格等限定词时,不能加the。如:
I like the third photo.我喜欢第三张照片。
It is my second time to visit Hefei. 这是我第二次游览合肥。
(2)序数词前面有不定冠词a或an,表示“又一,再一”。如:
I have read this novel three times, but I
want to read it a fourth time. 这本小说我已经读了三遍了,但是我还想再读一遍。
(3)“the+序数词+形容词最高级+名词单数”表示“第几……”。如:
The Yellow River is the second longest river in China. 黄河是中国第二长河。
(4)表示日期、年和月用基数词,日用序数词。如:
on Sept.12th, 2021 2021年9月12日。
注意
1. 在表示顺序和编号时,既可以用序数词,也可以用基数词。如:
the eighth lesson=Lesson Eight第八课;
the twelfth page=Page Twelve第十二页。
2. one的副词是once (一次),two的副词是twice (两次),都常用来表示频率。如:
once a day一天一次;
twice a week一周两次。
确数词与概数词
确数词与概数词的具体用法如下:
类别 含义 用法 示例
确数词 表示确切的数字 基数词+hundred/thousand/million/billion (+可数名词复数) three hundred 三百 five thousand years 五千年
概数词 表示不确切的数字 hundreds/thousands/millions/billions+of+可数名词复数 hundreds of animals 成百上千只动物
专题七 冠词(近10年未考)
不定冠词a/an
1. 基本用法
用法 例句
用于第一次提到的某人或某物前。 A little girl is smiling at me.
指一类人、一类事物或某一类中的某一个。 An ant is much smaller than an elephant. I want to be a nurse when I grow up.
用于序数词前,表示“又一; 再一”。 The cake is delicious, and I’d like a second one.
用于表示时间、速度、价格等意义的名词前, 表示“每一”。 I go skiing once a week.
用于可视为一个整体的两个名词前。 Please give me a knife and fork.
2. a和an的区别
(1)a用在以辅音音素开头的单词前;an用在以元音音素开头的单词前。如:a big house一所大房子;an old man一位老人。
(2)初中常见的前面用an的单词如下表所示:
类别 示例
前面用an的名词 actor; actress; airport; apple; artist; aunt; earthquake; egg; hour; idea; invention; orange; opinion; umbrella
前面用an的形容词 American;Asian;English;exciting;expensive;excellent;honest;important; interesting; old; outgoing; unusual; unhappy; ugly
前面用an的数词 eight(h); eleven(th); eighteen(th); eighty; eightieth
注意
以元音字母开头,但以辅音音素开头的单词前面要用a,初中常见的这类单词有:university; useful; usual; European; UFO。
3. 固定搭配
a couple of两个;一对;几个 a few一些;少数
a little一点儿;少量
a little bit有点儿;稍微
a lot of/a number of许多
a piece of一片/块/条
all of a sudden突然;猛地
as a result结果;因此
come to an end结束
go to a doctor去看医生
give sb. a hand帮助某人
have a good time玩得愉快
have/take a look看一看 have a point有道理
have a rest休息 take a break 休息
have a try试一试 in a word总而言之
in a hurry匆忙地
make a decision做决定
make a difference有影响
make an effort付出努力
make a living谋生
make a mess弄得一团糟
make a mistake犯错误 make a wish许愿
once in a while偶尔;间或
once upon a time从前
pay a visit to sb.拜访某人
quite a few相当多
ride a bike骑自行车
take a message捎个口信
take a risk冒险
take a shower洗淋浴
take a trip去旅游 take a walk散步
play a role/part in… 在……中发挥作用
catch/have a cold/fever/headache/stomachache感冒/发烧/头疼/胃疼
take a bus/car/plane/ship乘公交车/汽车/飞机/轮船
定冠词the
1. 基本用法
用法 示例
用在上文已提及的人或事物前。 I saw a film yesterday. The film was very interesting.
用在由限制性定语所修饰的人或事物前。 The notebook on the desk isn’t mine.
用在谈话双方都知道的人或事物前。 Can you give me the pencil
用在序数词、形容词或副词的最高级之前(副词最高级前的the也可以省略)。 the second floor the tallest boy
用在表示西洋乐器的名词之前。 play the piano/violin/ drums
用在某些形容词前,表示某一类人或事物。 the poor the rich
用在可数名词单数前,表示某一类人或事物。 The elephant is my favorite animal.
用在专有名词前。 the Terracotta Army the Great Wall
用在表示具体的方位、时间前。 on the left in the evening
用在世界上独一无二的事物前。 the sun the moon
2. 固定搭配
all the time一直
all (the) year round一年到头
around the world全世界
at the age of在……岁时
at the beginning of在……开始
at the end of在……的末尾
at the same time同时
at the top of在……顶部
by the way顺便说/提一下
do the dishes清洗餐具
go to the doctor去看医生
go to the movies去看电影
in the countryside在农村
in the end最后
in the future在未来
in the middle of在……的中间
in the morning/in the afternoon/in the evening在早上/在下午/在晚上
in the past在过去
on the Internet在网上
the day after tomorrow后天
the day before yesterday前天
the Olympic Games奥林匹克运动会
the same as和……相同
by the end of在……(某时间点)以前
get in the way of挡……的路;妨碍
in the face of面对(问题、困难等)
make the soccer team加入足球队
on (the) one hand… on the other hand… 一方面……另一方面……
the more… the more… 越……,就越……
with the help of在……的帮助下
零冠词
用法 示例
三餐、球类、棋类、学科和语言前不用冠词。 have breakfast play basketball play chess learn English
by与交通工具连用时不用冠词。 by bike/bus/car/plane/ship/taxi/train
节日、季节、月份、星期前不用冠词。 on Mother’s Day in summer in February on Monday
名词前有物主代词、指示代词、不定代词、疑问代词或名词所有格修饰时不用冠词。 her daughter that book both sweaters which school Jason’s computer
不可数名词或名词复数表示泛指时,其前不用冠词。 Students should study hard.
某些专有名词(如:人名、地名、国名)前不用冠词。 in London go to Canada 特例:the US the UK the UN
街名、路名、山名等词前不用冠词。 Hainan Island Nanjing Road
专题八 简单句
疑问句(10年3考)
1. 一般疑问句:能用yes或no来回答的疑问句。
形式 答语
Be+主语+其他? Yes(,主语+be)./No(,主语+be+not).
情态动词+主语+动词原形+其他? Yes(,主语+情态动词)./No(,主语+情态动词+not).
助动词(Do/Does/Did/Have/Has/Had)+主语+动词原形/过去分词+其他? Yes(,主语+助动词)./No(,主语+助动词+not).
2. 特殊疑问句:用特殊疑问词引导的疑问句。其不能用yes或no来回答。
疑问词(组) 含义及用法 答语
what(2015.31) 什么,询问物品、职业或身份。 根据实际情况作答。
who/whom 谁,询问人物。
which 哪一个,询问特定范围内的人或物。
whose 谁的,询问所属。
when 什么时候,询问时间。
why(2013.40) 为什么,询问原因。
where 哪里,询问地点或位置。
how 如何,询问方式。
how much 多少,询问不可数名词的量。 冠词/数词+单位名词+of+不可数名词。
多少钱,询问价格。 根据实际情况作答。
how many 多少,询问可数名词的数量。 数词(+单位名词+of+可数名词复数).
how often 多久一次,询问频率。 次数+a(n)/one+表示时间的名词.
how long 多长,询问物体长度。 数词+单位名词+long.
多长时间,询问时间长短。 For+时间段.
how soon(2013.34) 多久以后。 In+时间段.
how far 多远,询问距离。 根据实际情况作答。
3. 反意疑问句
形式 例句
肯定陈述句+否定疑问句 Jack is waiting for you, isn’t he
否定陈述句+肯定疑问句? Max didn’t play basketball yesterday, did he
Let’s+do sth., shall we Let’s make our weekend plan, shall we
Let us +do sth., will you Let us check the answer again, will you
肯定祈使句,will/won’t you Stand up, will/won’t you?
否定祈使句, will you? Don’t be late again, will you
注意
回答反意疑问句时,不论陈述部分是肯定句还是否定句, 若事实是肯定的, 答语就要用yes;若事实是否定的, 答语就要用no。注意在“前否后肯”的反意疑问句的答语中, yes意为“不”, no意为“是的”。如:
—Mike didn’t come to your party last night, did he 迈克昨晚没有来你的聚会,是吗?
—Yes, he did./No, he didn’t.不,他来了。/是的,他没来。
感叹句(近10年未考)
引导词 结构 例句
what What+ a/an+形容词+可数名词单数(+主语+谓语)! What a kind girl(she is)!
What+形容词+可数名词复数(+主语+谓语)! What beautiful dresses (they are)!
What+形容词+不可数名词(+主语+谓语)! What good news (it is)!
how How+形容词/副词(+主语+谓语)! How fine the weather is!
How+形容词+a/an+可数名词单数(+主语+谓语)! How beautiful a present (it is)!
How+主语+谓语! How time flies!
祈使句(近10年未考)
形式 结构 例句
肯定形式 动词原形/Be+其他. Open the door, please. Be happy.
Let’s+动词原形+其他. Let’s go swimming.
否定形式 Don’t+动词原形+其他. Don’t play with fire.
否定形式 Let’s+not+动词原形+其他. Let’s not play games here.
No+名词/动名词. No photos! No parking!
Never+动词原形. Never give up!
专题九 并列复合句(10年7考)
1. 并列连词
并列连词 含义及用法 例句
and(2019.36,2013.35) 和,又,表并列或顺承关系。 My aunt bought me a dictionary, and I like it very much.
用于“祈使句, and+陈述句”结构。 Work hard, and you will make much progress.
but(2018.41,2016.48,2015.40) 但是,表转折关系,不能与though和although连用。 I failed again, but I won’t give up.
or(2017.36,2014.47) 或者,表选择关系。 Does he work at school or in the hospital
否则,表条件。 Study hard, or your math will be worse.
so 所以,因此,表因果关系。 I have a cold, so I have to see a doctor.
2. 并列连词短语
连词短语 含义及用法 例句
not only…but also… 不但……而且……,连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词遵循“就近原则”。 Not only you but also he does well in French.
both… and… ……和……都,连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词用复数。 Both he and I want to go skating.
neither…nor… ……和……都不,连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词遵循“就近原则”。 Neither she nor her children like beef.
either… or… 或者……或者……,连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词遵循“就近原则”。 Either you or I am going to the party.
专题十 主从复合句
宾语从句(10年8考)
三要素 构成及用法 例句
引导词 that 在从句中无意义,不充当句子成分,在口语中常可省略。 I believe (that) you will succeed.
连接代词(what/which/who/whom/whose) 在从句中作一定的成分,如主语、宾语、定语等。 Lisa wonders what she should do next. Do you know whose coat it is?
连接副词(where/when/why/how/how词组)(10年7考) 在从句中作状语。 Jessie hasn’t decided when she will leave for Paris.
if/whether(2021.28) 意为“是否”,不作句子成分,但不能省略。 I don’t know if/whether my sister will come to the party.
语序 陈述句语序:主语+谓语+其他。 I wonder how Jim came to school this morning.
时态 主句:现在的某种时态; 从句:根据实际情况使用相应时态。 I remember Linda came here two days ago.
主句:过去的某种时态; 从句:过去的某种时态。 John told me he had finished his homework.
从句若为客观事实、真理、自然现象等,不管主句使用什么时态,从句都用一般现在时。 Our geography teacher told us that the earth travels around the sun.
拓展
1. 在介词之后、动词不定式之前或与or not连用时,只能用whether,不用if。除此之外,whether引导的从句可以放在句首,if不可以。如:
I can’t decide whether to buy this bike or not.
2. 宾语从句的否定前移
在宾语从句中,当主语为第一人称,主句的谓语动词为think, believe, expect, imagine, suppose等且无其他修饰语时, 从句中表示否定意义的not应移到这些词之前。如:
I don’t think you are right.我认为你是不对的。
3. 如果复合句中的宾语从句很长, 那么可以用it作形式宾语, 以免句子头重脚轻。如:
He made it quite clear that he preferred to study English.
定语从句(2013.49)
1. 关系代词
(1)结构图示
(2)用法
关系代词 成分 先行词 例句
that(2013.49) 主语、宾语(可省)、表语 人、物 A dictionary is a book that gives the meanings of words.(作主语)
which 主语、宾语(可省)、表语 物 I’ll never forget the days (which) we spent together.(作宾语)
who 主语、宾语(可省) 人 Do you know the girl who often comes here (作主语)
whom 宾语(可省) 人 He’s the boy(whom) I talked with just now.(作宾语)
whose 定语 人、物 He is the writer whose name is Jerry.(作定语)
(3)特殊情况
①只能用that的情况:
1)先行词为不定代词anything, nothing, all, much, few, any, little等或the one时。如:
Is there anything that I can do for you
2)先行词被序数词、形容词最高级修饰时。如:
This is the first book that I bought.
3)先行词被all, any, every, some, no, few, the only, the very, the last等修饰时。如:
The only thing that I want to do is to have a good rest.
4)先行词既有人又有物时。如:
The film star and her film that you just talked about are really well-known.
5)当主句是以which开头的特殊疑问句时。如:
Which is the hotel that you like best
②只能用which的情况:
1)关系代词放在介词之后。如:
This is the company in which I once worked.
2)非限制性定语从句。如:
He made a wonderful discovery, which is important to the development of science.
2. 关系副词
(1)结构图示
(2)用法
关系词 成分 先行词 例句
when 时间状语 时间 I remember the day when we met for the first time.
where 地点状语 地点 This is the town where President Xi Jinping was born.
why 原因状语 原因 I want to know the reason why you didn’t come to school this morning.
状语从句(必考:每年1~3道)
引导词
1. 引导时间状语从句的从属连词(10年5考)
从属连词 含义 用法
when 当……时 具体用法和例句见下面的“何时用when,何时用while的判定方法”。
while
as引导的从句的动作与主句动作同时发生,但不用进行时,多用一般过去时。
as(2018.57)
until/till(2017.53) 直到 until和till通常可以互换,但是till不用于句首;“not…until/till”意为“直到……才……”。
before(2018.54) 在……之前 主句的动作发生在从句动作之前。
after 在……之后 主句的动作发生在从句动作之后。
since(2015.53,2014.34) 自从 从句用一般过去时,主句常用现在完成时。
as soon as 一……就…… 从句动作一发生,主句的动作随即发生,若主句用一般将来时,从句常用一般现在时表将来。
拓展
何时用when,何时用while的判定方法
(1)若主句的动词是短暂性动词,从句的动词是延续性动词,则when和while都可用。如:
Our teacher came into the classroom when/while we were chatting.
(2)若主句和从句表示两个同时进行的持续性动作,则要用while。如:
My mother was cooking dinner while I was reading a book.
(3)若从句的动词是短暂性动词,则要用when。如:
It was raining when she arrived at the station.
(4)若主句和从句的动作不是同时发生,而是有先后顺序,则要用when。如:
I will study abroad when I have enough money.
(5)when可用作并列连词,意为“这时(突然)”,while也可用作并列连词,意为“而,却”。如:
He was ready to leave home when the phone rang.
I like watching action movies while she likes watching comedies.
2. 引导条件状语从句的从属连词(10年4考)
从属连词 含义 用法
if(2016.44) 如果 若主句用一般将来时,从句常用一般现在时表将来。
unless(if…not)(10年3考) 除非
as long as 只要
3. 引导让步状语从句的从属连词(10年5考)
从属连词 含义 用法
although 虽然;尽管 不能与but连用,但是可以与yet或still连用。
though(10年5考)
even though/even if 即使;虽然 不能与but连用,但是可以与yet或still连用。
whenever 无论什么时候 引导让步状语从句时相当于no matter when。
wherever 无论在哪里 引导让步状语从句时相当于no matter where。
whatever 无论什么 引导让步状语从句时相当于no matter what。
whoever 无论谁 引导让步状语从句时相当于no matter who。
4. 引导原因状语从句的从属连词(10年2考)
从属连词 含义 用法
because(2021.34) 因为 表示造成某种情况的直接原因, 用来回答why引导的问句,不能与so同时使用。
since 既然 语气比because弱, 表示众所周知的原因。
as(2022.38) 由于, 因为 语气比since弱, 表示众所周知的原因或者在说话人看来已经很明显的原因, 引导的从句位于主句前后均可。
5. 引导目的状语从句的从属连词
从属连词 含义 用法
so that/in order that 为了;以便 后接句子,可互换使用。
6. 引导结果状语从句的从属连词
从属连词 含义 用法
so…that… 如此……以至于…… so+adj./adv.+ that从句 so+adj.+a/an+n.+that从句
such…that… such+a/an+adj.+可数名词单数+that从句 such+adj.+可数名词复数/不可数名词+that从句
注意
当名词前有many, much, few, little 修饰时,应该用so,不能用such。如:
There were so many people that I couldn’t find a good place to take photos.
Mrs. Smith thought so much that she couldn’t fall asleep the whole night.
时态
1. 主将从现:在含有时间状语从句、条件状语从句的复合句中,若主句为一般将来时,从句用一般现在时表将来。
(1)引导时间状语从句:when, as, while, after, before, until, as soon as等。如:
I’ll call you as soon as I get to Beijing.
(2)引导条件状语从句:if, unless, as long as, in case, once等。如:
If my mother allows me to go to the party, I will be very happy.
2. 若复合句含有由since引导的时间状语从句,从句用一般过去时,主句用现在完成时。如:
Our English teacher has worked in this school since she graduated from Peking University.
3. 主情从现:主句有情态动词,从句使用一般现在时。如:
You can get good grades if you study hard.
4. 主祈从现:主句为祈使句,从句使用一般现在时。如:
Be careful when you cut the fruit.
专题十一 情景交际
话题1 请求(10年4考)
【问句】
Would you mind (not)… (2020.21)
Would/Do you mind if I…
【答句】
表示不介意的回答
(No,)Not at all.
No, go ahead.
Certainly not./Of course not./No, I don’t mind.
表示介意的回答
You’d better not./(Sorry,)I’m afraid you can’t./I’m sorry, but…
Sorry, we’ll go and play in the park.
【问句】
Can/Could/May I… (2018.31, 2017.45, 2014.33)
I wonder if I can/could…
【答句】
表示同意的回答
Sure./Of course./Certainly.(2017.45)
Feel free./Yes, please./Go ahead, please./Sure, no problem./Here you are(2018.31, 2014.33)
表示不同意的回答
You’d better not./I’m afraid you can’t./I’m sorry, but you can’t … /No, you can’t./No, you mustn’t./No, please don’t.
【问句】
Can/Could/Will/Would you (please)…
【答句】
表示同意的回答
Sure./Certainly./Of course.
Yes, I’ll do it right away./No problem./With pleasure./All right./OK.
表示不同意的回答
(Sorry,)I’m afraid not./(Sorry,)I’m afraid I can’t.
话题2 观点(10年4考)
【问句】
What do you think of… /How do you like…
How is/was…
【答句】
I don’t mind them.
I love/like…(very much).
I don’t love/like…
Great!/Wonderful!/Excellent!/Very good!
It is great/interesting/exciting/boring …/It’s worth …/I can’t stand them.
【问句】Do you think…
【答句】Yes, I think so./No, I don’t think so.
【表达观点】
Reading a good book makes me happy.
This is really a wonderful movie.
We should try our best to protect the environment.
I think…/In my opinion,…/As far as I’m concerned,…/From my point of view, …
【回应观点】
表示同意的回答
I think so.
I agree(with you)./I can’t/couldn’t agree more./That’s true.(2022.30, 2021.30, 2016.45)
表示不同意的回答
I disagree./I don’t agree(with you)./I don’t think so.
表示不完全同意的回答
That depends./You may be right./Yes, maybe.(2018.45)
【表达观点】
I want to play basketball after school.
I am going to join the table tennis club next week.
【回应观点】
So do I./So am I./Me, too.
【表达观点】
I don’t feel like going out this evening.
I’m not sure if the idea is right.
【回应观点】
Neither do I./Neither am I./Me, neither.
话题3 鼓励(10年3考)
【描述担心】
I feel/am nervous about…
I’m anxious/worried about…
【鼓励】
Take it easy.(2017.31, 2013.42)
Don’t worry./There is nothing to worry about.
【描述担心】
I’m afraid. it’s too hard.
I am afraid I have to give up my dream of being a doctor.It’s too difficult.
… is too difficult for me. I will certainly lose.
【鼓励】
Come on./Cheer up. You can do it.(2014.50)
Don’t lose heart. I believe your dream can come true.
【表达伤心】
We lost the soccer game. I feel so sad.
I am so sad.I’ve failed my math exam.
【鼓励】
Cheer up.
话题4 赞美(2019.31)
【表达赞美】
You look so cool with your sunglasses.
You have done such a good job in…
Your dress is beautiful!
You look so beautiful (in this dress/sweater…).
Very good!/Well done!/Wonderful!/Excellent!(2019.31)
Perfect!/Good job!
【回应赞美】
Thank you (very much).
Thanks a lot./Many thanks.
话题5 问候与介绍(2016.31)
【问候】
How is it going(with you) /How’s everything(going with you)
How are you /How are you doing
【答句】
Pretty good!
Very well, thank you./Fine, thanks. And you /Not bad./I’m OK./Everything is OK.
【问候】How do you do
【答句】How do you do
【问候】Good morning/Good afternoon/Good evening.
【答句】Good morning/Good afternoon/Good evening.
【问候】Nice to meet you./Glad to see you./Pleased to meet you all.(2016.31)
【答句】Nice to meet you, too./Glad to see you, too.
【介绍】
Kelly, this is Tom. He is my new friend.
Hello, I’m Steven. I am a new student here.
【答句】
Nice to meet you./It’s a pleasure to know you./I’m pleased to know you.
话题6 建议、提醒或劝告(2014.42)
【建议】
S
第二部分 语法专题精讲
编者按:此部分11个专题的练习题见《教材词句&语法精练》第三部分常考语法点精练。
句子成分及五大基本句型
句子成分
1. 主语
【作用】句子说明的人或事物。
【位置】陈述句:通常位于句首;
疑问句:位于系动词、助动词或情态动词之后。
【组成部分】名词、代词、数词、动名词、动词不定式、从句等。
【例句】The apple is red.
Three is enough.
Smoking is bad for you.
2. 谓语
【作用】对主语加以说明,表示主语的行为或状态。
【位置】通常位于主语之后。
【组成部分】动词或动词短语。
【例句】The man borrowed two books.
The plane took off at ten o’clock.
3. 宾语
【作用】动作的对象或承受者。
【位置】动词或介词后。
【组成部分】名词、代词、数词、动名词、动词不定式、名词性从句等,宾语分为直接宾语(指物)和间接宾语(指人)。
【例句】I like China. I want to watch the new movie.
He told me that he would go to college the next year.
He gave me some bananas.
4. 宾语补足语
【作用】对宾语的补充。
【位置】宾语后。
【组成部分】名词、形容词、副词、动词不定式、分词等。
【例句】We elected him monitor.
She found the window broken when she came back home.
5. 表语
【作用】表示主语的性质、状态或特征。
【位置】系动词之后。
【组成部分】名词、数词、代词、形容词、副词、动词不定式、介词短语、形容词化的分词和表语从句等。
【例句】He is a teacher.
All I could do was to wait.
6. 定语
【作用】修饰或限制名词或代词的词、词组或句子。
【位置】单词作定语通常放在所修饰的词之前;短语或从句放在所修饰的成分之后。
【组成部分】名词、名词所有格、代词、数词、形容词、介词短语、现在分词、过去分词、动词不定式短语、定语从句等。
【例句】The woman with a baby in her arms is my sister.
The car parked outside is mine.
7. 状语
【作用】说明时间、地点、方式、原因、目的、结果、条件、程度等,用于修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子。
【位置】位置灵活:一般放在句末,但也可放在句首或句中。
【组成部分】副词、介词短语、动词不定式、分词和分词短语、相当于副词的词或短语、从句等。
【例句】You are quite right.
If you study hard, you will pass the exam.
五大基本句型
句型一:主语+谓语(不及物动词)。
例: It rains.
↓ ↓
主语 谓语
句型二:主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语。
例:①Children often sing this song.
↓ ↓ ↓
主语 谓语 宾语
②He has accepted our invitation.
↓ ↓ ↓
主语 谓语 宾语
句型三:主语+系动词+表语。
例:①The bike is new.
↓ ↓ ↓
主语 系动词 表语
②The milk went sour.
↓ ↓ ↓
主语 系动词 表语
句型四:主语+谓语(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语。
例:She showed her friends all her pictures.
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
主语 谓语 间接宾语 直接宾语
句型五:主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语+宾语补足语。
例:① We keep our classroom clean and tidy.
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
主语 谓语 宾语 宾语补足语
② We have invited all our friends to come.
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
主语 谓语 宾语 宾语补足语
专题一 动词
动词的分类
情态动词(10年7考)
1. 情态动词的基本用法(10年5考)
情态动词 用法 例句
can(2018.38,2014.35) 表示能力,意为“能,会”。 Jim can sing songs.
表示请求、允许,意为“可以”。 Can I play basketball now?
can’t(2016.37) 表示能力,意为“不能,不会”。 I can’t dance.
用于回答表示请求的句子,意为“不可以,不允许”。 —May I play volleyball now —No, you can’t.
could can的过去式,意为“能,会”,表示过去的能力。 Lily could swim at the age of 5.
在疑问句中表示委婉地请求。 Could you please tell me the way to the post office?
couldn’t can’t的过去式,意为“不能,不会”。 I couldn’t hear what they were saying.
must 表示主观看法,意为“必须,一定”。 I must work hard.
mustn’t 意为“一定不要,禁止”。 You mustn’t talk in the library.
have to 意为“不得不”,多表示客观必要。 I have to get up early tomorrow.
need(2019.39) 作情态动词,常用于否定句和疑问句中,其否定式needn’t意为“不必”,常用于回答must的提问。 Need you leave so early Alex needn’t attend the meeting.
may 表示请求、许可,意为“可以”。 May I speak to Amy?
might may的过去式。表示请求、许可,语气比 may 更委婉。 Might I ask you a question?
should/ought to 意为“应该”,表示要求和命令,也可以表示劝告或建议。 You should/ought to come to school on time.
should表示征询意见,常用于疑问句中。 Should I leave at 7:00 p.m.
shouldn’t/ought not to(2013.32) 意为“不应该”。 We shouldn’t/ought not to waste water.
had better 意为“最好”,没有人称和数的变化。 You’d better come back early today.
shall 常用于疑问句,多用于第一、三人称,表示请求或征求对方的意见。 Shall we go to the zoo
will 表示意愿或请求,用于疑问句中,常用于第二人称。 Will you please pass the book to me
would 表示建议或个人意愿,表示建议时,语气较委婉。 Would you please help me with my maths
2. 情态动词表推测的用法(10年2考)
情态动词 用法 例句
must 表示非常有把握的肯定推测,意为“一定,肯定”。 It must be raining outside. My father’s clothes are so wet.
can’t 表示十分有把握的否定推测,意为“一定不,不可能”。 He can’t be having a meeting. I saw him just now.
may(2017.39,2015.44) 表示把握不大的肯定推测,意为“有可能,也许”。 John may come back at 5: 00 p.m.
和not连用,表示把握不大的否定推测,意为“可能不”。 Mandy may not come tonight.
might/could 表示没有把握的肯定推测,意为“有可能,也许”,可能性低于may。 The pencil might/could be Bob’s.
动词的时态(必考:每年1~2道)
常见六种时态的构成及用法:
时态 基本结构及标志词 常见用法及例句
一般现在时(2018.35) 结构 1. 主语+am/is/are(+表语) 2. 主语+动词原形/动词单三形式(+宾语) 1. 表示现阶段经常性、习惯性的动作,常与频度副词连用。 2. 表示客观真理、客观存在或自然现象。如: The earth moves around the sun. (注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是一般过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。) 3. 主将从现:若一个复合句中含有由when, after, before, until, as soon as等引导的时间状语从句或由if, unless, as long as, once等引导的条件状语从句, 主句若用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时表将来。如: I will tell Kate the good news as soon as she comes back. 4. 表示按计划或安排好的将要发生的动作,用一般现在时表将来,但仅限于start, begin, leave, go, come, arrive等动词。如: The train leaves at six tomorrow morning.
标志词 1. 频度副词:always, usually, often, sometimes, seldom, never, hardly 2. 频率词组:once a year, twice a month, three times a day等 3. 其他词组:in the morning, on Sundays, at weekends, every day/year…(every系列)
一般过去时(2014.48) 结构 1. 主语+was/were(+表语) 2. 主语+动词过去式(+宾语) 1. 表示过去某个时间里发生的动作或存在的状态。如: We went to the City Library last week. 2. 表示过去常常或反复发生的动作,常与频度副词连用。如: When I was a child, I often played basketball on the playground. 3. 在since引导的时间状语从句中,主句用现在完成时,从句用一般过去时。
标志词 1. ago及ago词组 2. yesterday及yesterday词组 3. last及last词组 4. just now, in the past, in 1920等 5. at the age of…, used to… 6. one day, long long ago, once upon a time
一般将来时(2022.27,2014.41) 结构 1. 主语+will/shall+动词原形(+表语/宾语) 2. 主语+am/is/are going to+动词原形(+表语/宾语) 1. 表示将来某个时间会发生的动作或存在的状态。如: They are leaving for Shanghai next week. 2. 表示某种必然的趋势。如: Fish will die without water. 3. be going to+动词原形,表示计划、打算做某事,表示已决定的,很可能发生的事,或有某种迹象表明要发生的事情。如: What are you going to do next Sunday?(计划) Look at the dark clouds. There is going to be a storm. (客观迹象) 4. “be about to +动词原形”和“be to +动词原形”结构也可表示即将发生的动作。如: The train is about to leave. 5. 在“祈使句+and/or+陈述句”句型中,陈述 句常用一般将来时。 6. 主将从现。(具体讲解见本表格一般现在时)
标志词 1. tomorrow, soon 2. next week/month(next系列) 3. in a week, in 2024, in+一段时间 4. one day, in the (near) future
现在进行时(2015.37,2013.36) 结构 主语+am/is/are +动词现在分词(+宾语) 1. 表示此时此刻正在进行的动作。如: —What are you doing? —I am reading English. 2. 表示现阶段一直在进行的动作,此刻不一定在进行,常用时间状语有:this/these+表示一段时间的名词。如: They are studying hard this term. 3. be doing表示将来,常用于这种结构的动词有go, come, leave, stay, start, begin, 表示即将发生或安排好要做的事情。如: She is going there tomorrow.
标志词 1. now, right now 2. at present, at this time, at the/this moment 3. these days 4. when, while 5. Look!/Listen!
过去进行时(2016.41) 结构 主语+was/were+动词现在分词(+宾语) 1. 表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作。如: —What were you doing at nine last night? —I was watching TV at that time.
过去进行时 标志词 1. then 2. at that time, at ten yesterday, at this time yesterday 3. when/while引导的表示过去时间的状语从句 2. 表示过去某段时间内持续进行的动作。如: What were you doing from seven to nine yesterday 3. 常和always等时间副词连用,表示过去频繁发生的习惯性动作,此时带有一定的感彩。如: Alice was always changing her mind. (表示厌烦)
现在完成时(10年4考) 结构 主语+have/has+动词过去分词(+表语/宾语) 1. 表示过去发生的动作或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响。如: —Have you had your lunch yet? —Yes. I’ve just had it. 2. 表示从过去开始持续到现在的动作或状态,也许还要持续下去,常和for, since连用,动词应用延续性动词。如: We have lived here since 2000. 3. 在“It/This is the+序数词+time that…”句型中,that引导的从句用现在完成时。 4. 特殊用法: (1)have gone to已去某地(未回) have been to曾去过某地(已回) have been in待在某地 (2)It has been+时间段+since+一般过去时的句子
标志词 1. already, ever, never, just, yet, still 2. recently, lately, so far, up till now 3. in the past/last three years/… 4. since 1998, since+一段时间 5. for three years, for+一段时间
动词的语态(10年5考)
1. 被动语态的构成
时态 结构 例句
一般现在时 am/is/are+done(2018.44) My homework is always finished on time. 我的作业总是按时完成。
一般过去时 was/were+done(2017.42, 2016.34) The breakfast was cooked by Linda.早餐是琳达做的。
一般将来时 will/shall/be going to be+done(2019.42) Jim’s room will be cleaned tonight. 今晚,吉姆的房间将被打扫。
情态动词 情态动词+be+done(2013.46) The flower should (not) be watered every day. 这种花(不)应该每天被浇水。
2. 主动语态变被动语态的方法
口诀:宾变主,主变宾,谓语动词用被动。
拓展
主动语态变被动语态的特殊情况
主动语态中有些感官动词(如:hear,see, watch, notice等)和使役动词(如:make, let等)后用不带to的不定式作宾语补足语,变为被动语态时,要把不定式符号to还原,如:
hear/see sb. do sth.→sb. be heard/seen to do sth.
make sb. do sth.→sb. be made to do sth.
3. 主动结构表被动意义的情况
(1)open, lock, write, read, sell, wash, clean, watch, cut, burn, drive 等作不及物动词时,其主语为物,可用主动结构表被动意义。如:
This kind of pen writes very smoothly.
(2)look, sound, taste, smell 等系动词用主动结构表被动意义。如:
Mooncakes taste delicious.
(3)be worth doing 意为“值得做”,用主动结构表被动意义。如:
This book is worth reading.
(4)“need/require+doing”相当于“need/require+to be done”,to be done是不定式的被动结构。如:
Your car needs washing.=Your car needs to be washed.
非谓语动词(近10年未考)
1. 动词不定式
(1)动词不定式的用法
基本形式:①to +动词原形;②(省略不定式符号to的不定式)
否定形式:not to +动词原形
作宾语
接动词不定式作宾语的动词(词组)(v.+to do sth.):
afford负担得起 agree同意 choose选择
dare敢 decide决定 expect期待
fail未能 happen发生 hope/wish希望
learn学习 manage设法完成 offer主动提出
plan计划 prefer更喜欢 prepare准备
pretend假装 promise承诺 refuse拒绝
rush急促 seem似乎 wait等待
can’t wait迫不及待 used to过去常常 want/would like想要
作宾语补足语
①接动词不定式作宾补的动词(词组)(v.+sb.+to do sth.):
advise建议 allow允许 ask要求
encourage鼓励 expect期望 force强迫
invite邀请 order命令 teach教
tell告诉 warn警告 wish希望
want/would like想要 request要求,请求 remind提醒
②接省略to的动词不定式作宾补的动词(词组)(v.+sb.+do sth.):
一感 feel感觉到
一听 hear听到
三看 see看到 watch观看 notice注意到
三使 let让 make使 have让,使
注意:一些使役动词和感官动词后接动词不定式作宾补变被动语态时,要还原to。
作状语
①作目的状语
Jim got up early to cook breakfast for his mother.
②作结果状语
Paul is too excited to say anything.
③作原因状语
I am very happy to talk with you.
作主语
①动词不定式作主语时,常用it作形式主语,真正的主语——动词不定式则被后置。如:
It’s good for you to take exercise.
②若动词不定式位于句首作主语,谓语动词应用第三人称单数形式。如:
To help others makes James happy.
作定语
动词不定式作定语时,要置于被修饰的名词之后,作后置定语。如:
I am not free now. I have lots of things to do.
作表语
动词不定式常位于系动词之后。如:
To see is to believe. 眼见为实/百闻不如一见。
(2)动词不定式的常用句型
①too+adj.+to do sth.太……而不能做某事
②adj.+enough to do sth.足够……做某事
③prefer to do sth. rather than do sth.宁愿做某事而不愿做某事
④It’s+adj.(+for sb.)+to do sth.(对于某人而言,)做某事是……的
⑤It’s+adj.+of sb.+to do sth.某人做某事是……的
⑥It’s time to do sth.该是做某事的时候了
⑦It’s one’s turn to do sth.轮到某人做某事了
⑧It takes/took sb. some time to do sth.某人花费多长时间做某事
⑨find/think/feel it+adj.+to do sth.发现/认为/感到做某事是……的
(3)“疑问词+动词不定式”的用法
①动词不定式与疑问词连用可作主语、宾语或表语。如:
When to go to Beijing hasn’t been decided yet.(作主语)
I haven’t decided when to leave Beijing.(作宾语)
My question is how to go to Beijing. (作表语)
②“疑问词+动词不定式”作宾语时可以转化为宾语从句。如:
Can you tell me where to buy a cup =Can you tell me where I can buy a cup
2. 动名词
(1)动名词(v.-ing)的用法
用法 例句 注意
作宾语 动词宾语 I like playing football very much. 表示一般的习惯、抽象行为或经常性动作
介词宾语 I have no experience in teaching English.
作主语 Getting up early is a good habit. 谓语动词用单数
作表语 His job is teaching Chinese in a school.=Teaching Chinese in a school is his job. 多数情况下,动名词作表语可转换成作主语
作定语 We need a washing machine. 表示它所修饰的词的用途、所属等,置于被修饰词之前
(2)接动名词作宾语的动词(词组)、句型
admit承认 advise建议 avoid避免
complete完成 consider考虑 enjoy喜欢
finish完成 imagine想象 keep坚持
mind介意 miss错过 practic(s)e练习
risk冒险 stop停止 suggest建议
be busy (in) doing sth.忙于做某事
be good at/do well in doing sth.擅长做某事
be interested (in) doing sth.对做某事感兴趣
be worth doing sth.值得做某事
be/get/become used to doing sth.习惯于做某事
can’t/couldn’t help doing sth.情不自禁做某事
feel like doing sth.想要做某事
give up doing sth.放弃做某事
have fun (in) doing sth.做某事很开心
hold on to/stick to doing sth.坚持做某事
look forward to doing sth.期待做某事
pay attention to doing sth.注意做某事
succeed (in) doing sth.成功做某事
【注意】有些动词后面既可接动词不定式,也可接动名词,但意思有区别,常见的有:
begin/start begin/start to do sth.= begin/start doing sth.开始做某事
like like to do sth.= like doing sth.喜欢做某事
love love to do sth.= love doing sth.热爱做某事
prefer prefer to do sth.=prefer doing sth.更喜欢做某事
hate hate to do sth.= hate doing sth.讨厌做某事
continue continue to do sth.继续做另一件事
continue doing sth.继续做同一件事
forget forget to do sth.忘记要做某事(未做)
forget doing sth.忘记做过某事(已做)
remember remember to do sth.记得要做某事(未做)
remember doing sth.记得做过某事(已做)
regret regret to do sth.遗憾要做某事(未做)
regret doing sth.懊悔做过某事(已做)
stop stop to do sth.停下来去做另一件事
stop doing sth.停止正在做的某件事
mean mean to do sth.打算做某事
mean doing sth.意味着做某事
try try to do sth.努力做某事
try doing sth.尝试做某事
need need to do sth.(某人)需要做某事
need doing sth.(某物)需要被……
3. 分词
(1)分词的用法
分词包括现在分词(v.-ing)和过去分词(v.-ed),其常见用法有:
用法 例句
作补足语 现在分词作补足语,被修饰的宾语或主语是它的逻辑主语(即主动关系)。 I hear my sister singing.
过去分词作补足语,被修饰的宾语或主语是它的逻辑宾语(即动宾关系)。 I had my hair cut last night.
作定语 现在分词作定语,所修饰的词是其逻辑主语。 Do you know the boy playing football
过去分词作定语,所修饰的词是其逻辑宾语。 Please hand in your written exercises.
(2)现在分词与过去分词的区别
角度 意义 示例
语态 现在分词表示主动意义 a sleeping girl一个睡着的女孩
过去分词表示被动意义 the moved people被感动的人们
时间 现在分词表示正在进行的动作 the developing country发展中国家
过去分词表示已完成的动作 the developed country发达国家
主谓一致与 There be句型(2015.43)
1. 主谓一致(近10年未考)
(1)语法一致原则
语法一致表示谓语动词与主语在单、复数形式上保持一致。
主语 谓语 例句
不可数名词 单数 Water is important to everyone.
可数名词单数,第三人称单数及it 单数 The young man is from Paris.
名词复数、人称代词复数、第一人称单数I及第二人称单数you 复数 The children were in the classroom two hours ago.
one of+可数名词复数/代词复数 单数 One of the books is boring.
and或both… and…连接的名词 复数 Both Jenny and Kate are my friends.
either, neither, each, every或no +单数名词 单数 Each person has a new book.
复合不定代词 单数 Everybody has a chance to win.
主语后面跟有with, together with, except, but, like, as well as, rather than, including等 取决于主语的数 The mother together with her three sons was happy.
分数/百分数+of+名词 取决于名词的数 60%of the students in our class are girls.
a lot of/lots of/plenty of/the rest of+名词
A lot of people are in the classroom.
动词不定式短语、动名词短语或从句 单数 What he said is very meaningful.
a number of+可数名词复数 复数 A number of books were given to the poor students.
the number of+可数名词复数 单数 The number of the apples is 12.
(2)意义一致原则
意义一致就是概念一致,即谓语动词的形式要和主语所表达的概念一致。
主语 谓语 例句
表示重量、度量、时间、长度、价格等的词或短语 单数 Two meters is not as high as you think.
the+姓氏名词复数,表示“……一家人;……夫妇” 复数 The Smiths have decided to go to Kunming for holiday.
the+形容词,表示一类人 复数 The young are energetic.
集体名词(如:family /class /team/group等) 整体看待→单数 强调成员→复数 His family is going to move to Beijing. The whole family are looking forward to the holiday.
由(both…)and连接的两个名词指代同一个人 单数 The writer and actor has come.
(3)就近原则
就近原则指谓语动词的形式不与主语一致,而是和靠近它的名词或代词保持一致。
主语 谓语 例句
由either… or…, neither… nor…, not only… but(also)…, not… but… 或 or连接的两个并列主语 和距其较近的主语在数上保持一致 Either Jimmy or I am going to give a speech.
There/Here be…句型中 be动词与距其最近的主语在数上保持一致 Here is a book and two notebooks for you.
2. There be句型(2015.43)
“There be+ sb./sth.+地点状语”表示“某地有某人/某物”。
(1)基本结构
句式 结构 例句
肯定 There be+ sb./sth.+其他 There is a dog in the room.
否定 There be+ not/not any/no+ sb./sth.+其他 There is no water in the bottle.
疑问 Be there+sb./sth.+其他 Is there water in the bottle
(2)时态
时态 There be句型结构
一般现在时 There is/are…
一般过去时 There was/were…
一般将来时 There will be…/There is/are going to be…
现在完成时 There has/have been…
“There be句型”还可以和助动词或情态动词连用。如:
There will be/There is going to be a new film on Monday.
There must be a mistake somewhere.
(3)be动词的单复数:be动词的单复数必须和其后所接的名词的数保持一致。若be动词后接两个或两个以上的并列名词时,be动词和距其最近的名词的数保持一致,即遵循“就近原则”。如:
There is a girl and two boys in the classroom.
(4)答语
回答“Be there+其他”时,常用“Yes/No, there+be动词(not)”。其中, be动词的数和时态与问句保持一致。如:
—Was there a park in your city 20 years ago?
—Yes, there was.
注意
“There be句型”强调某地有某物,不表示所属关系,故其不能和“have(有)”同时使用。如:
There is going to have a basketball game this afternoon.(×)
There is going to be a basketball game this afternoon.(√)
动词填空(必考:每年1~2道)
1. 考查方式
2. 解题技巧
先判定空格处是否填动词
(1)根据括号内的汉语提示词和首字母直接判断;
(2)若括号内的汉语提示表明所填词既可作名词,又可作动词,则需根据题干的句子成分判断所填词在句中作什么成分;如果句中缺谓语,则可判定此处应填动词。
再确定动词是否需要变形
(1)填动词原形(10年7考)
①位于情态动词或其否定形式之后;
②位于动词不定式符号to之后;
③祈使句中以动词原形开头;
④当时态为一般现在时且主语为可数名词复数、复数人称代词或I;
⑤位于助动词(do/does/did/will)或其否定形式之后。
(2)填单三形式(10年6考)
若句子用一般现在时,在以下情况中,谓语动词用单三形式:
①不可数名词作主语;
②“a/an/the+可数名词单数”作主语;
③人称代词第三人称he, she, it 作主语;
④单个人名、地名作主语;
⑤不定代词(every系列/some系列/any系列/no系列)作主语;
⑥指示代词(this/that/it)作主语;
⑦非谓语动词(动词不定式/动名词) 作主语;
⑧主谓一致【见P51的讲解】。
(3)填现在分词(2017.93)
用于现在/过去进行时(am/is/are/was/were+doing)结构中。
(4)填过去式(2021.77)
①有明显的表示过去的时间标志词。如: yesterday, just now, two days ago, last night/week/month/year等;
②过去式+ and/or +过去式;
③主从复合句中,若从句用一般过去时,主句通常也用过去的某种时态;
④根据上下文语境和时态判断。
【拓展】
1. 动词的基本形式变化表
类别 构成方法 例词
原形 没有任何形式变化的动词 do, dance,leave
第三人称单数 一般在动词原形后直接加-s work→works read→reads
以s, o, x, sh, ch结尾的动词,后加-es go→goes wash→washes
辅音字母加y结尾的动词,应将y改为i再加-es fly→flies study→studies
过去式与过去分词 一般在动词原形后直接加-ed work→worked stay→stayed
以e结尾的动词后只加-d close→closed like→liked
以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,应将y改为i再加-ed study→studied carry→carried
以重读闭音节结尾且末尾只有一个辅音字母的动词,双写此辅音字母再加-ed stop→stopped plan→planned
现在分词 一般在动词原形后直接加-ing sleep→sleeping wait→waiting
以不发音的e结尾的动词,去e再加-ing smile→smiling move→moving
以重读闭音节结尾且末尾只有一个辅音字母的动词,双写此辅音字母再加-ing sit→sitting dig→digging plan→planning
少数以ie结尾的动词,变ie为y,再加-ing die→dying lie→lying tie→tying
2. 动词过去式和过去分词的不规则变化
①AAA型
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
cost cost cost 花费
cut cut cut 切;割
hit hit hit 撞;击
hurt hurt hurt 受伤
let let let 让
put put put 放
read read read 读
set set set 设置
shut shut shut 关闭
spread spread spread 传播
②ABA型
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
become became become 成为
come came come 来
run ran run 跑
③ABB型
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
bring brought brought 带来
build built built 建造
buy bought bought 买
catch caught caught 捉;抓
deal dealt dealt 处理
dig dug dug 挖(洞);凿(孔)
feed fed fed 喂
feel felt felt 感到
fight fought fought 打架
find found found 发现
get got got/gotten 得到
hang hung hung 悬挂
have had had 有
hear heard heard 听见
hold held held 握住
keep kept kept 保持
lay laid laid 放置
lead led led 导致
leave left left 离开
lend lent lent 借给
lose lost lost 丢失
make made made 制造
mean meant meant 意思是
meet met met 遇到
pay paid paid 付钱
say said said 说
sell sold sold 卖
send sent sent 送;寄
shine shone shone 发光;照耀
sit sat sat 坐
sleep slept slept 睡
speed sped sped 加速
spend spent spent 花费
stand stood stood 站
stick stuck stuck 粘贴;将……刺入
teach taught taught 教
tell told told 告诉
think thought thought 想;认为
understand understood understood 理解
win won won 赢
④ABC型
原形→ew→own
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
blow blew blown 吹
fly flew flown 飞
grow grew grown 生长
know knew known 知道
i→a→u
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
begin began begun 开始
drink drank drunk 喝
ring rang rung 打电话
sing sang sung 唱
swim swam swum 游泳
原形→过去式→过去式+(e)n/过去式去掉字母e+n/过去式双写末尾字母+en
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
bear bore born 负担;忍受
break broke broken 破;裂;碎
choose chose chosen 选择
forget forgot forgotten 忘记
hide hid hidden 藏
speak spoke spoken 说
steal stole stolen 偷
wake woke woken 醒来
wear wore worn 穿
原形→过去式→原形+(e)n
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
draw drew drawn 画
drive drove driven 开车
eat ate eaten 吃
fall fell fallen 落下
give gave given 给
mistake mistook mistaken 误会
rise rose risen 升起;增加;提高
see saw seen 看见
shake shook shaken 摇动;抖动
show showed shown/showed 展示;给……看
take took taken 买下;拿;取
throw threw thrown 扔掉
⑤有两种形式
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
burn burned burned 燃烧
burnt burnt
dream dreamed dreamed 做梦;梦想
dreamt dreamt
learn learned learned 学
learnt learnt
lie lied lied 说谎
lay lain 躺;位于
light lighted lighted 照亮
lit lit
smell smelled smelled 闻
smelt smelt
spell spelled spelled 拼写
spelt spelt
⑥其他形式
原形 过去式 过去分词 释义
be(am, is, are) was, were been 是
beat beat beaten 敲打;打败
do did done 做
go went gone 去;走
ride rode ridden 骑
write wrote written 写
can could / 能;会
may might / 也许;可能;可以
must must / 必须
shall should / 将要;将会
will would / 将要;会
专题二 名词填空(必考:每年1~3道)
1. 考查方式
2. 解题技巧
先判断空格处是否填名词
(1)根据题干所给汉语提示词和首字母判断。如:2021年78题,汉语提示词为“英雄”,考生可直接确定空处填名词;
(2)根据语境和句子结构判断。具体方法如下:
①位于系动词后作表语;
②位于冠词、数词、形容词性物主代词、名词所有格后;
③位于动词或介词后作宾语;
④位于形容词后;
⑤位于句首,在句中作主语;
⑥位于限定词this, these, that, those, many, some, any, a lot of等后。
判断所填名词是可数名词还是不可数名词
类型 特点
可数名词 ①有单数和复数两种形式,表示一个或者多个,如:a desk→two desks;
可数名词 ②前面可以被不定冠词(a/an)、基数词、序数词、指示代词、 many、 a few 等词直接修饰,如:an egg, three girls, many singers。
不可数名词 ①没有复数形式,如:beef, ice,作主语时,谓语动词用单数; ②前面可用much, little等词修饰,不可以被不定冠词(a/an)、基数词、序数词、指示代词, many, a few 等词直接修饰。 ③若表示具体的量,可用量词来修饰,如:a piece of cake, two cups of coffee。
(1)若判断所给名词为不可数名词,无需变形(不可数名词没有复数形式)。常见的不可数名词主要有三类:专有名词、物质名词和抽象名词。
(2)若判断所给名词是可数名词,要考虑是否需要变形。
注意:英语中有一些名词既可以作可数名词,也可以作不可数名词,但含义不同,常见的有:
名词 可数 不可数 名词 可数 不可数
chicken 小鸡 鸡肉 orange 橙子 橙汁
experience 经历 经验 paper 试卷;论文 纸
exercise 练习 锻炼 radio 收音机 无线电
glass 玻璃杯 玻璃 room 房间 空间
iron 熨斗 铁 time 次数;倍数 时间
life 生命 生活 wood 树林 木头;木材
light 电灯 光;光线 work 作品 工作
拓展
可数名词和不可数名词的常见修饰语
1. 只修饰可数名词的修饰语:
few很少;几乎没有 a few一些;几个
several几个 different不同的
a couple of两个 many (a) 很多
a number of若干;许多
a great/large number of许多
2. 只修饰不可数名词的修饰语:
little很少;几乎没有
a little一点儿;少量
much很多
a good/great deal of很多
a bit of有一点儿
a large amount of大量的
3. 既可修饰可数名词又可修饰不可数名词的修饰语:
some一些 a lot of很多
lots of很多 plenty of充足的
most大多数的 all全部的
the rest of剩下的
判断可数名词是否需要变形
(1)填单数名词的判定方法
①a/an/this/that/every/each/another/either/one/序数词/any other+可数名词单数。如:
a clear idea(2019.91)
has a role to play(2018.92)
②可数名词单数(主语)+be动词单数形式/谓语动词的单三形式。如:
My main task was to prepare for the meeting.
③结合上下文语境或者句中对应的提示词,如:it, its。
My father’s T-shirt has completely lost its shape.(2017.92)
④专有名词,如:the Great Wall。
(2)填复数名词的判定方法
①these/those/普通不定代词(many/some/several/few/a few/both/all/other 等)/大于1的基数词/one of(+形容词最高级)/quite a few/a pair of/a couple of/a (great/large) number of/different kinds of/all kinds of+可数名词复数;
②both/either/neither/all/none of+可数名词复数;
③可数名词复数(主语)+be 动词复数形式/动词原形;
④结合上下文语境或句中对应的提示词,如:them, their;
⑤通常用复数或只有复数形式的名词:chopsticks 筷子,clothes 衣服,glasses 眼镜, scissors 剪刀, socks 袜子, trousers 裤子。
【拓展】
1. 可数名词单数变复数的规则变化表
构成方法 示例
一般情况加 -s star→stars gift→gifts invention→inventions
以字母s, x, sh, ch结尾的词加 -es class→classes box→boxes brush→brushes watch→watches 特例:stomach→stomachs
以f或fe结尾的词变f或fe为v再加 -es leaf→leaves knife→knives shelf→shelves wife→wives 特例:roof→roofs proof→proofs belief→beliefs
以辅音字母加y结尾的词先变y为i,再加 -es party →parties baby→babies story→stories family →families
以元音字母加y结尾的词加 -s key→keys holiday→holidays monkey→monkeys
以ce, se, ze, ge等结尾的词加 -s face→faces license→licenses prize→prizes orange→oranges
以o结尾有生命的加 -es, 无生命的加 -s tomato→tomatoes hero→heroes potato→potatoes photo→photos piano→pianos
2. 可数名词单数变复数的不规则变化表
构成方法 示例
a→e型 man→men woman→women fireman→firemen postman→postmen gentleman→gentlemen policeman→policemen policewoman→policewomen 特例:human→humans
oo→ee型 foot→feet tooth→teeth 特例:boot→boots
“某国人”变化口诀 ①中日永不变 Chinese→Chinese Japanese→Japanese ②英法a变e Englishman→Englishmen Frenchman→Frenchmen ③其余s加后面 American→Americans Canadian→Canadians German→Germans Indian→Indians Russian→Russians
单复数同形 deer→deer sheep→sheep
合成词:将主体词变为复数 passer-by→passers-by toothbrush→toothbrushes
其他 mouse→mice child→children
专题三 形容词和副词
形容词和副词的比较等级(10年2考)
1. 标志词
原级:(not)as… as…
比较级:than;the+比较级,the+比较级;比较级+and+比较级
最高级:one of…;含有among, in或of等短语表示的范围
2. 原级的用法
用法 例句
描述人物或事物性质,如:“so/very/too/quite+原级”表示“如此/非常/太/相当……”。 The story is quite interesting.
“A+be动词/实义动词+as+原级+as+B”表示“A和B一样……”。 Is Fuyang as big as Hefei
“A+be动词/实义动词(否定)+so/as+原级+as+B”表示“A不如B……”。 Jack is not as tall as Jim.
“A+实义动词+as+much/many+名词+as+B”表示“A和B的……数量相同”。 Linda has as many books as Lily.
“A+be动词/实义动词+倍数+as+原级+as+B”表示“A是B的……倍”。 My room is twice as big as his.
3. 比较级的用法(2020.46,2017.35)
用法 例句
“the+比较级,the +比较级”表示“越……,就越……”。 The harder we study, the better grades we’ll get.
“比较级+and+比较级/more and more+多音节形容词/副词”表示“越来越……”。 This song is becoming more and more popular.
“A+be动词/实义动词+比较级+than+B”表示“A比B……”。 The blue cup is bigger than the green one.
“A+be动词/实义动词+less+多音节形容词/副词原级+than+B”表示“A不及B……”。 I am less careful than you.
“Which/Who+be动词/实义动词+比较级,A or B ”表示“A、B两者中哪一个/谁更……” Who is taller, you or Tom?
“A+be动词/实义动词+比较级+than+any other+可数名词单数”/“A+be动词/实义动词+比较级+than+the other+可数名词复数”表示“A比其他任何一个都……”(比较级结构表示最高级含义)。 He is taller than any other boy in his class.=He is taller than the other boys in his class.
“A+be动词/实义动词+倍数+比较级+than+B”表示“A是B的……倍……”。 This box is three times bigger than that box.
注意
1. 当形容词或副词由表示程度的副词(词组)a little, a bit, a lot, much, even, far等修饰时, 常用该形容词或副词的比较级形式。如:
It is even colder today. 今天甚至更冷了。
2. 表示“(两者之中)较……的一个”时, 常用“the+比较级”结构。如:
My brother is the taller one of the two. 我哥哥/弟弟是这两个人中较高的那一个。
4. 最高级的用法
用法 例句
“A+be动词/实义动词(+the)+最高级+范围”表示“A是……中最……”。 I am the tallest student in our class.
“A+be动词/实义动词+one of the+最高级+可数名词复数”表示“A是最……的……之一”。 Lang Ping is one of the most famous volleyball coaches in the world.
“Which/Who+be动词/实义动词(+the)+最高级, A, B or C ”表示“A、B、C三者中,哪个/谁最……”。 Which is the biggest, the sun, the moon or the earth
“A+be动词/实义动词+the+序数词+最高级+名词+范围”表示“A是……中第几……”。 The Yellow River is the second longest river in China.
注意
1. 形容词最高级前必须加定冠词the, 副词最高级前可以不加the。如:
This picture is the best of all.
He draws (the) most wonderfully.
2. 形容词最高级前面有物主代词、指示代词、名词所有格等修饰时, 不再加定冠词the。如:
She is my best friend.
形容词和副词填空(必考:每年1~3道)
1. 读汉语,定词性
在单词拼写中,所填形容词和副词均为原形,没有任何变形,因此考生根据题干所给汉语提示和首字母即可联想到所填词。
2. 读语境,定单词
对于根据汉语提示不能确定词性的单词,考生可分析语境和句子结构,再次判断词性,并进一步确定单词。
(1)填形容词的判定方法
①所填词位于名词前作定语;
②所填词位于be动词后作表语;
③所填词位于形容词短语中,其结构为:be动词+形容词+介词;
④所填词位于感官动词和连系动词look, sound, smell, taste, feel, seem, become, grow, get, turn, keep, remain之后;
⑤所填词位于复合不定代词后作后置定语;
⑥所填词位于定冠词the后表示一类人;
⑦所填词位于固定句型It is+adj.(+for/of sb.)+to do sth.中;
⑧所填词位于“形容词+ and/or+形容词”结构中;
⑨所填词位于宾语之后作宾补,常与make, leave, keep等动词连用;
⑩在as… as… 结构中,且空前有系动词。
(2)填副词的判定方法
①所填词修饰动词或动词短语;
②所填词修饰形容词或其他副词;
③所填词修饰介词短语;
④所填词位于句首,作状语,修饰整个句子;
⑤在as…as结构中,且谓语动词为实义动词。
专题四 代词
人称代词、物主代词与反身代词(10年2考)
1. 人称代词、物主代词与反身代词一览表
类别 人称 人称代词 物主代词 反身代词
主格 宾格 形容词性 名词性
第一人称 单数 I me my mine myself
复数 we us our ours ourselves
第二人称 单数 you you your yours yourself
复数 you you your yours yourselves
第三人称 单数 he him his his himself
she her her hers herself
it it its its itself
复数 they them their theirs themselves
2. 人称代词的用法以及所作的成分(2015.51)
类别 用法 成分 例句
主格 用在动词/系动词/情态动词之前。 作主语 They all like sports.
宾格 用在动词/介词之后。 作宾语 My mother will take me to the park. Let’s go and look for him.
用在系动词之后。 作表语 The boy in the picture is me.
3. 物主代词的用法以及所作的成分
类别 用法 成分 示例
形容词性物主代词 相当于形容词,用在名词之前。 作定语 This is my pet cat.
固定搭配中(特例) try one’s best
名词性物主代词 等同于形容词性物主代词+名词,其后不能接 名 词。 用在动词/系动词之前。 作主语 That’s her eraser. Mine is on the desk.
用在动词/介词之后。 作宾语 I left my dictionary at home. Can you lend yours to me
用在系动词之后。 作表语 This pencil is his.
4. 反身代词的用法以及所作的成分(2013.64)
用法 成分 例句
用在动词/介词之后。 作宾语 The little girl can’t dress herself. Charles said to himself, “I must work hard.”
用在系动词之后。 作表语 The man in the story was myself.
用在名词/代词之后或句末。 作同位语 The boy/He himself finished the task.=The boy/He finished the task himself.
普通不定代词
1. both, either, neither, all与none(10年3考)
普通不定代词 含义 谓语形式 短语
both 两者都 复数 both… and………和……都both of… ……都
either(2014.45) 两者中的任意一个 单数 either… or…或者……或者…… either of…两者中的任意一个……
neither(2016.33) 两者都不 单数 neither…nor… ……和……都不neither of………都不
all 三者或三者以上都 根据它所指代或修饰的名词的数来决定 all of………都
none 三者或三者以上都不 根据它所指代或修饰的名词的数来决定 none of… ……都不
2. a little, little, a few与few
肯定含义 否定含义 所跟名词
a little一点儿 little几乎没有 不可数名词
a few一些;几个 few几乎没有 可数名词复数
3. many与much
普通不定代词 相同点 不同点
many 都意为“很多”,可单独使用,也可跟of短语,也可与表示程度的副词so或too连用。 指代或修饰可数名词复数。
much 指代或修饰不可数名词。
4. some与any
普通不定代词 相同点 不同点
some 意为“一些”,均可指代或修饰可数名词复数或不可数名词。 一般用于肯定句中,也可用于表建议或请求的疑问句中,表示说话人希望得到肯定的回答。
any 意为“一些”,均可指代或修饰可数名词复数或不可数名词。 一般用于肯定句中,也可用于表建议或请求的疑问句中,表示说话人希望得到肯定的回答。
5. every与each
普通不定代词 every each
不同点 修饰名词单数,不可单独使用。 既可修饰名词单数也可单独使用。
指三者或三者以上的人或事物中的“每一个”。 指两者或两者以上的人或事物中的“每一个”。
后不可跟of短语。 后可跟of短语。
相同点 “every/each+名词单数”作主语时,谓语动词要用单数形式。
6. other, others, the other, the others与another
普通不定代词 含义 用法
other 其他的;另外的 常接名词复数,表示除去一部分以外的另外的部分,但不是剩下的全部。
others 泛指别的人或物 =other+可数名词复数,表示除去一部分以外另外的部分,但不是剩下的全部。
the other 两者中的另一个。 后接可数名词单数,常用短语:one… the other…
两部分中的另外一部分。 后接可数名词复数,表示其余的全部,常用短语:some… the other…
the others 特指其余的人或物。 =the other+可数名词复数,表示其余的全部。
another(2015.32) 任何一个;另一个。 后接可数名词单数,表示“另一个……”
不接名词,指代三者或三者以上中的另一个。
another +数词 +可数名词复数 = 数词+ more +可数名词复数
复合不定代词(10年6考)
1. 初中常见的复合不定代词如下表:
词缀 词根 -one/-body(指人) -thing(指物)
some-(肯定) someone/somebody某人 something某事,某物
any-(否定/肯定) anyone/anybody任何人 anything任何事
every-(肯定) everyone/everybody每个人 everything每件事,一切
no-(否定) no one/nobody没有人 nothing什么都没有
2. 复合不定代词的用法
(1)由some- 和any- 构成的复合不定代词,其区别同some和any。
(2)当形容词或else修饰复合不定代词时, 形容词或else必须放在复合不定代词之后。如:
Is there anything interesting in this book
(3)复合不定代词可作主语、宾语和表语,不能作定语。作主语时, 谓语动词通常用单数。如:
Everyone is happy to hear the news.
(4)somebody还可意为 “大人物,重要人物”;nobody还可意为 “小人物,无名小卒”。如:
I’d like to be somebody.
3. 含复合不定代词的常用句型
(1)There is something/nothing wrong with… ……出问题了/没有问题。
(2)have something/nothing to do with…和……有关/无关。
(3)sb. can do nothing but… 某人什么都不能做,只能……
指示代词(10年3考)
1. 初中常见的指示代词的用法如下表:
单词 用法
this(复数式:these) ①近指,指时间或空间上离说话人较近的人或物 ②指代下文要提到的人或物 ③在电话用语中,常用this介绍自己是谁
that(复数式:those) ①指时间或空间上离说话人较远的人或物 ②指前面刚提到过的事情或已经完成的事情 ③在电话用语中, 常用that询问对方是谁 ④常用于比较结构中,代替前面提到的名词,以避免重复。当前面的名词为可数名词单数或不可数名词时用that,为可数名词复数时用those。
2. 辨析it与one(10年3考)
代词 用法
it(复数是them)(2017.32) 特指上文提到的同一事物(同类同物)。
one(复数是ones)(2018.33,2013.38) 泛指上文提到的同类人或事物中的一个(同类而不同物)。
拓展
it的特殊用法
1. it作形式主语时, 常用于下列句型中:
(1)It’s+adj.(+for/of sb.)+to do sth.做某事(对某人来说)是……/(某人)做某事真是……。
(2)It’s time to do sth./for sth./that… 是(做)……的时候了。
(3)It’s one’s turn to do sth.轮到某人做某事。
(4)It seems that… 好像/似乎……
(5)It’s+adj.+that从句 ……是……
(6)It takes (sb.)+一段时间+to do sth.做某事花费(某人)多长时间。
2. it作形式宾语时, 代替由动词不定式或从句等表示的真正宾语, 常用在find, think, make, consider, feel等动词之后。如:
Do you think it important to protect our environment
I find it necessary that we do some exercise every day.
3. 指代婴儿或身份不明的人。如:
There is a knock on the door. It must be the postman. 有人在敲门,一定是邮递员。
专题五 介词(10年13考)
1. 介词in, on与at的用法
介词 类别 用法 示例/例句
in(2015.33) 时间介词 后接较长的一段时间(如世纪、年份、季节、月份等)。 in the 21st century in 2009 in summer in July
用在泛指的上午、下午、晚上前。 in the morning/afternoon/evening
表示多长时间或多久以后,常用于一般将来时。 in an hour in two days
方位介词 某人或某物在某地点。 Xiaoming is in the room now.
某一小地点在另一大地点之内。 Japan lies in the east of Asia.
用于较大的地方前(如:国家、城市、乡镇、水域等)。 in China in Lijiang River
方式介词 使用,后接某种语言或声音等。 in Chinese in a high/low voice
其他介词 穿着;戴着。 Lily was in a beautiful dress.
on 时间介词 用在具体的某天或某天的上午、下午、晚上或节日前。 on Tuesday on September 1st on a cold morning on National Day
方位介词 在……表面上(意指接触物体表面)。 There is a book on the desk.
在广阔的平面上。 on the lake
两地不在同一范围内,但接壤。 India is on the southwest of China.
方式介词 “on+通讯工具/电子产品”意为“通过……”。 on TV/the radio talk on the phone
其他介词 关于。 a movie on South Africa
at 时间介词 用在某个时刻或黎明、正午、黄昏、午夜前。 at 7:00 at noon at midnight
方位介词 用于某个较小的地方(如:建筑物、公共机关、机场、街道等)。 She works at the post office.
向;朝。 look at
其他介词 在……岁时。 She got married at 25.
2. 时间介词
介词 用法 示例/例句
from 从……开始,常和表示时间的介词to(到……,至……)连用。 from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. from Monday to Sunday from 1987 to 2018
before 在……之前。 Annie was born a few weeks before Christmas.
after(2014.32) ……之后,与一般将来时连用时,后接时间点。 He’ll come back after two o’clock.
……之后,与一般过去时连用时,后接时间段。 He came back from Canada after three weeks.
since “since+时间点/since+一段时间+ago”意为“自……以来”,表示从过去某时直至现在,主句用现在完成时或过去完成时。 I have been here since 1989. She has lived in this city since five years ago.
for “for+时间段”表示动作的延续,主句常用现在完成时或过去完成时。 I have studied in the school for 2 years.
by 不迟于某时,包括某时在内。 I will finish the work by Friday.
until 直到……,到……为止,后常接时间点。 My mother didn’t get home until 9:00 p.m.
3. 方位介词
介词 用法 示例/例句
to 到;去;向;朝。有一定的方向性。 I went to the park this morning.
表示在某一地域之外且不接壤。 Japan lies to the east of China.
below 在……下方(两者不接触,也不一定垂直)。 There is a chair below the window.
under 在……正下方(两者不接触)。 A dog is sitting under the tree.
above 在……上方(两者不接触,也不一定垂直)。 He lifted his hands above his head.
over(2013.37) 在……正上方(两者不接触)。 They will build a bridge over the river.
在……上面,表示部分覆盖或全部覆盖。 She put a blanket over the sleeping child.
behind(2017.38,2016.53) 在……后面。 There is a cat behind the door.
beside 在……旁边。 Mary sat beside me.
outside 在……外面。 You can park your car outside our house.
against 紧靠;倚。 Place the ladder against the wall.
along 顺着;沿着。 Walk along the road, and you will see a bank on the left.
around 四周;在……周围。 Would you like to walk around the factory this afternoon
by(2019.38) 在……旁边;靠近。 There is a piano by the window.
near 在……附近。 Do you live near here
next to 紧挨着……。 My home is next to the bank.
4. 方式介词
介词 用法 示例/例句
by 通过某种方式或手段,后常跟动名词、名词。 I learn English by using the iPad.
“by+交通工具”意为“乘……”。 by bike/bus
with 使用,后接具体有形的工具。 He broke the window with a stone.
through 以;凭借;通过。 He won what he wanted through hard work.
5. 其他常见介词
介词 用法 示例/例句
for 为了(表目的)。 What can I do for you?
支持。 We are for the idea.
给;对。 It’s a book for children.
without 没有;缺乏。 We got there without any trouble.
不和……在一起;无……相伴。 Don’t go without me.
不(做某事)。 He left without saying anything.
with 和……在一起。 I like staying with my parents.
带有;具有。 I have no money with me.
about 关于。 Could you tell me about your life
against(2018.36) 碰;撞。 The rain is beating against the window.
反对,其反义词是for。 He is against your ideas.
对抗;和……竞争。 Our team will play against yours this afternoon.
as 作为;以……身份。 He came to China as a tourist five years ago.
像;如同;跟……一样。 She describes herself as a reporter.
from 来自(表示来源)。 Where are you from
like 像;与……相似。 Tom looks like his mother.
……怎么样。 What is she like
例如。 I like reading English novels like Little Women and Three Days to See.
of 属于(某人或某物);关于(某人或某物)。 the window of the room a photo of my dog
except 除……之外(其他的都) Everyone is happy except John.
besides 除……之外(其他的也) I learn English and math besides Chinese.
6. 常见介词短语(10年4考)——见背面《晨读核心词句篇》P57;
常见介词与形容词的固定搭配(2015.50)——见背面《晨读核心词句篇》P55;
常见介词与动词的固定搭配(2021.24)——见背面《晨读核心词句篇》P50。
专题六 数词(近10年未考)
基数词与序数词
1. 基数词和序数词的构成
1~9 11~19 10~90(整十数) ≥100
基数词 序数词 基数词 序数词 基数词 序数词 基数词 序数词
one first eleven eleventh ten tenth hundred hundredth
two second twelve twelfth twenty twentieth thousand thousandth
three third thirteen thirteenth thirty thirtieth million millionth
four fourth fourteen fourteenth forty fortieth billion billionth
five fifth fifteen fifteenth fifty fiftieth
six sixth sixteen sixteenth sixty sixtieth
seven seventh seventeen seventeenth seventy seventieth
eight eighth eighteen eighteenth eighty eightieth
nine ninth nineteen nineteenth ninety ninetieth
2. 基数词的用法
(1)表示数量。表示事物或人物的确切数量,用“基数词+可数名词单数/复数”。如:
one apple一个苹果;two pears两个梨。
(2)表示时刻。
①表示“……点”用“基数词+o’clock”。如:nine o’clock 九点钟;
②表示“……点过……分”时,若分钟数小于或等于30分钟,用“基数词+past+基数词”。如:
twenty past three三点二十分;
③表示“差……分到……点”时,若分钟数小于30分钟,用“基数词+to+基数词”。如:twenty to three 两点四十分。
(3)表示年份。如:in 2019在2019年;
(4)表示年代。“in the+年份后加-s”表示“在……世纪……年代”。如:
in the 1860s 在十九世纪六十年代。
(5)表达年龄。
①用基数词(+year/years old)表达。如:twenty (years old) 二十岁;
②at the age of+基数词。如:
at the age of twenty在二十岁的时候;
③表示不确切的岁数时,常用几十的复数形式。如:
in his thirties在他三十多岁时。
(6)表示电话号码。数字可单个读,重复的数字也可以读“double+数字”。如:53882069 读作:five three double eight two zero six nine。
(7)表示长、宽、高等。用基数词+单位词(meter, kilogram等)+形容词(long, wide, high等)表示。如:three meters long 三米长;four meters high四米高。
(8)表示时间、距离。使用含基数词的名词所有格形式作定语。如:twenty years’ time二十年的时间;five minutes’ walk 步行五分钟的路程。
(9)“基数词+名词(+形容词)”复合结构作定语:名词用单数形式,各部分间要用连字符“-”来连接。如:a fifteen-minute drive十五分钟的车程;a sixteen-year-old girl一个十六岁的女孩。
3. 序数词的用法
(1)序数词前通常加the,其后接名词单数,但当序数词前有形容词性物主代词、名词所有格等限定词时,不能加the。如:
I like the third photo.我喜欢第三张照片。
It is my second time to visit Hefei. 这是我第二次游览合肥。
(2)序数词前面有不定冠词a或an,表示“又一,再一”。如:
I have read this novel three times, but I
want to read it a fourth time. 这本小说我已经读了三遍了,但是我还想再读一遍。
(3)“the+序数词+形容词最高级+名词单数”表示“第几……”。如:
The Yellow River is the second longest river in China. 黄河是中国第二长河。
(4)表示日期、年和月用基数词,日用序数词。如:
on Sept.12th, 2021 2021年9月12日。
注意
1. 在表示顺序和编号时,既可以用序数词,也可以用基数词。如:
the eighth lesson=Lesson Eight第八课;
the twelfth page=Page Twelve第十二页。
2. one的副词是once (一次),two的副词是twice (两次),都常用来表示频率。如:
once a day一天一次;
twice a week一周两次。
确数词与概数词
确数词与概数词的具体用法如下:
类别 含义 用法 示例
确数词 表示确切的数字 基数词+hundred/thousand/million/billion (+可数名词复数) three hundred 三百 five thousand years 五千年
概数词 表示不确切的数字 hundreds/thousands/millions/billions+of+可数名词复数 hundreds of animals 成百上千只动物
专题七 冠词(近10年未考)
不定冠词a/an
1. 基本用法
用法 例句
用于第一次提到的某人或某物前。 A little girl is smiling at me.
指一类人、一类事物或某一类中的某一个。 An ant is much smaller than an elephant. I want to be a nurse when I grow up.
用于序数词前,表示“又一; 再一”。 The cake is delicious, and I’d like a second one.
用于表示时间、速度、价格等意义的名词前, 表示“每一”。 I go skiing once a week.
用于可视为一个整体的两个名词前。 Please give me a knife and fork.
2. a和an的区别
(1)a用在以辅音音素开头的单词前;an用在以元音音素开头的单词前。如:a big house一所大房子;an old man一位老人。
(2)初中常见的前面用an的单词如下表所示:
类别 示例
前面用an的名词 actor; actress; airport; apple; artist; aunt; earthquake; egg; hour; idea; invention; orange; opinion; umbrella
前面用an的形容词 American;Asian;English;exciting;expensive;excellent;honest;important; interesting; old; outgoing; unusual; unhappy; ugly
前面用an的数词 eight(h); eleven(th); eighteen(th); eighty; eightieth
注意
以元音字母开头,但以辅音音素开头的单词前面要用a,初中常见的这类单词有:university; useful; usual; European; UFO。
3. 固定搭配
a couple of两个;一对;几个 a few一些;少数
a little一点儿;少量
a little bit有点儿;稍微
a lot of/a number of许多
a piece of一片/块/条
all of a sudden突然;猛地
as a result结果;因此
come to an end结束
go to a doctor去看医生
give sb. a hand帮助某人
have a good time玩得愉快
have/take a look看一看 have a point有道理
have a rest休息 take a break 休息
have a try试一试 in a word总而言之
in a hurry匆忙地
make a decision做决定
make a difference有影响
make an effort付出努力
make a living谋生
make a mess弄得一团糟
make a mistake犯错误 make a wish许愿
once in a while偶尔;间或
once upon a time从前
pay a visit to sb.拜访某人
quite a few相当多
ride a bike骑自行车
take a message捎个口信
take a risk冒险
take a shower洗淋浴
take a trip去旅游 take a walk散步
play a role/part in… 在……中发挥作用
catch/have a cold/fever/headache/stomachache感冒/发烧/头疼/胃疼
take a bus/car/plane/ship乘公交车/汽车/飞机/轮船
定冠词the
1. 基本用法
用法 示例
用在上文已提及的人或事物前。 I saw a film yesterday. The film was very interesting.
用在由限制性定语所修饰的人或事物前。 The notebook on the desk isn’t mine.
用在谈话双方都知道的人或事物前。 Can you give me the pencil
用在序数词、形容词或副词的最高级之前(副词最高级前的the也可以省略)。 the second floor the tallest boy
用在表示西洋乐器的名词之前。 play the piano/violin/ drums
用在某些形容词前,表示某一类人或事物。 the poor the rich
用在可数名词单数前,表示某一类人或事物。 The elephant is my favorite animal.
用在专有名词前。 the Terracotta Army the Great Wall
用在表示具体的方位、时间前。 on the left in the evening
用在世界上独一无二的事物前。 the sun the moon
2. 固定搭配
all the time一直
all (the) year round一年到头
around the world全世界
at the age of在……岁时
at the beginning of在……开始
at the end of在……的末尾
at the same time同时
at the top of在……顶部
by the way顺便说/提一下
do the dishes清洗餐具
go to the doctor去看医生
go to the movies去看电影
in the countryside在农村
in the end最后
in the future在未来
in the middle of在……的中间
in the morning/in the afternoon/in the evening在早上/在下午/在晚上
in the past在过去
on the Internet在网上
the day after tomorrow后天
the day before yesterday前天
the Olympic Games奥林匹克运动会
the same as和……相同
by the end of在……(某时间点)以前
get in the way of挡……的路;妨碍
in the face of面对(问题、困难等)
make the soccer team加入足球队
on (the) one hand… on the other hand… 一方面……另一方面……
the more… the more… 越……,就越……
with the help of在……的帮助下
零冠词
用法 示例
三餐、球类、棋类、学科和语言前不用冠词。 have breakfast play basketball play chess learn English
by与交通工具连用时不用冠词。 by bike/bus/car/plane/ship/taxi/train
节日、季节、月份、星期前不用冠词。 on Mother’s Day in summer in February on Monday
名词前有物主代词、指示代词、不定代词、疑问代词或名词所有格修饰时不用冠词。 her daughter that book both sweaters which school Jason’s computer
不可数名词或名词复数表示泛指时,其前不用冠词。 Students should study hard.
某些专有名词(如:人名、地名、国名)前不用冠词。 in London go to Canada 特例:the US the UK the UN
街名、路名、山名等词前不用冠词。 Hainan Island Nanjing Road
专题八 简单句
疑问句(10年3考)
1. 一般疑问句:能用yes或no来回答的疑问句。
形式 答语
Be+主语+其他? Yes(,主语+be)./No(,主语+be+not).
情态动词+主语+动词原形+其他? Yes(,主语+情态动词)./No(,主语+情态动词+not).
助动词(Do/Does/Did/Have/Has/Had)+主语+动词原形/过去分词+其他? Yes(,主语+助动词)./No(,主语+助动词+not).
2. 特殊疑问句:用特殊疑问词引导的疑问句。其不能用yes或no来回答。
疑问词(组) 含义及用法 答语
what(2015.31) 什么,询问物品、职业或身份。 根据实际情况作答。
who/whom 谁,询问人物。
which 哪一个,询问特定范围内的人或物。
whose 谁的,询问所属。
when 什么时候,询问时间。
why(2013.40) 为什么,询问原因。
where 哪里,询问地点或位置。
how 如何,询问方式。
how much 多少,询问不可数名词的量。 冠词/数词+单位名词+of+不可数名词。
多少钱,询问价格。 根据实际情况作答。
how many 多少,询问可数名词的数量。 数词(+单位名词+of+可数名词复数).
how often 多久一次,询问频率。 次数+a(n)/one+表示时间的名词.
how long 多长,询问物体长度。 数词+单位名词+long.
多长时间,询问时间长短。 For+时间段.
how soon(2013.34) 多久以后。 In+时间段.
how far 多远,询问距离。 根据实际情况作答。
3. 反意疑问句
形式 例句
肯定陈述句+否定疑问句 Jack is waiting for you, isn’t he
否定陈述句+肯定疑问句? Max didn’t play basketball yesterday, did he
Let’s+do sth., shall we Let’s make our weekend plan, shall we
Let us +do sth., will you Let us check the answer again, will you
肯定祈使句,will/won’t you Stand up, will/won’t you?
否定祈使句, will you? Don’t be late again, will you
注意
回答反意疑问句时,不论陈述部分是肯定句还是否定句, 若事实是肯定的, 答语就要用yes;若事实是否定的, 答语就要用no。注意在“前否后肯”的反意疑问句的答语中, yes意为“不”, no意为“是的”。如:
—Mike didn’t come to your party last night, did he 迈克昨晚没有来你的聚会,是吗?
—Yes, he did./No, he didn’t.不,他来了。/是的,他没来。
感叹句(近10年未考)
引导词 结构 例句
what What+ a/an+形容词+可数名词单数(+主语+谓语)! What a kind girl(she is)!
What+形容词+可数名词复数(+主语+谓语)! What beautiful dresses (they are)!
What+形容词+不可数名词(+主语+谓语)! What good news (it is)!
how How+形容词/副词(+主语+谓语)! How fine the weather is!
How+形容词+a/an+可数名词单数(+主语+谓语)! How beautiful a present (it is)!
How+主语+谓语! How time flies!
祈使句(近10年未考)
形式 结构 例句
肯定形式 动词原形/Be+其他. Open the door, please. Be happy.
Let’s+动词原形+其他. Let’s go swimming.
否定形式 Don’t+动词原形+其他. Don’t play with fire.
否定形式 Let’s+not+动词原形+其他. Let’s not play games here.
No+名词/动名词. No photos! No parking!
Never+动词原形. Never give up!
专题九 并列复合句(10年7考)
1. 并列连词
并列连词 含义及用法 例句
and(2019.36,2013.35) 和,又,表并列或顺承关系。 My aunt bought me a dictionary, and I like it very much.
用于“祈使句, and+陈述句”结构。 Work hard, and you will make much progress.
but(2018.41,2016.48,2015.40) 但是,表转折关系,不能与though和although连用。 I failed again, but I won’t give up.
or(2017.36,2014.47) 或者,表选择关系。 Does he work at school or in the hospital
否则,表条件。 Study hard, or your math will be worse.
so 所以,因此,表因果关系。 I have a cold, so I have to see a doctor.
2. 并列连词短语
连词短语 含义及用法 例句
not only…but also… 不但……而且……,连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词遵循“就近原则”。 Not only you but also he does well in French.
both… and… ……和……都,连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词用复数。 Both he and I want to go skating.
neither…nor… ……和……都不,连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词遵循“就近原则”。 Neither she nor her children like beef.
either… or… 或者……或者……,连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词遵循“就近原则”。 Either you or I am going to the party.
专题十 主从复合句
宾语从句(10年8考)
三要素 构成及用法 例句
引导词 that 在从句中无意义,不充当句子成分,在口语中常可省略。 I believe (that) you will succeed.
连接代词(what/which/who/whom/whose) 在从句中作一定的成分,如主语、宾语、定语等。 Lisa wonders what she should do next. Do you know whose coat it is?
连接副词(where/when/why/how/how词组)(10年7考) 在从句中作状语。 Jessie hasn’t decided when she will leave for Paris.
if/whether(2021.28) 意为“是否”,不作句子成分,但不能省略。 I don’t know if/whether my sister will come to the party.
语序 陈述句语序:主语+谓语+其他。 I wonder how Jim came to school this morning.
时态 主句:现在的某种时态; 从句:根据实际情况使用相应时态。 I remember Linda came here two days ago.
主句:过去的某种时态; 从句:过去的某种时态。 John told me he had finished his homework.
从句若为客观事实、真理、自然现象等,不管主句使用什么时态,从句都用一般现在时。 Our geography teacher told us that the earth travels around the sun.
拓展
1. 在介词之后、动词不定式之前或与or not连用时,只能用whether,不用if。除此之外,whether引导的从句可以放在句首,if不可以。如:
I can’t decide whether to buy this bike or not.
2. 宾语从句的否定前移
在宾语从句中,当主语为第一人称,主句的谓语动词为think, believe, expect, imagine, suppose等且无其他修饰语时, 从句中表示否定意义的not应移到这些词之前。如:
I don’t think you are right.我认为你是不对的。
3. 如果复合句中的宾语从句很长, 那么可以用it作形式宾语, 以免句子头重脚轻。如:
He made it quite clear that he preferred to study English.
定语从句(2013.49)
1. 关系代词
(1)结构图示
(2)用法
关系代词 成分 先行词 例句
that(2013.49) 主语、宾语(可省)、表语 人、物 A dictionary is a book that gives the meanings of words.(作主语)
which 主语、宾语(可省)、表语 物 I’ll never forget the days (which) we spent together.(作宾语)
who 主语、宾语(可省) 人 Do you know the girl who often comes here (作主语)
whom 宾语(可省) 人 He’s the boy(whom) I talked with just now.(作宾语)
whose 定语 人、物 He is the writer whose name is Jerry.(作定语)
(3)特殊情况
①只能用that的情况:
1)先行词为不定代词anything, nothing, all, much, few, any, little等或the one时。如:
Is there anything that I can do for you
2)先行词被序数词、形容词最高级修饰时。如:
This is the first book that I bought.
3)先行词被all, any, every, some, no, few, the only, the very, the last等修饰时。如:
The only thing that I want to do is to have a good rest.
4)先行词既有人又有物时。如:
The film star and her film that you just talked about are really well-known.
5)当主句是以which开头的特殊疑问句时。如:
Which is the hotel that you like best
②只能用which的情况:
1)关系代词放在介词之后。如:
This is the company in which I once worked.
2)非限制性定语从句。如:
He made a wonderful discovery, which is important to the development of science.
2. 关系副词
(1)结构图示
(2)用法
关系词 成分 先行词 例句
when 时间状语 时间 I remember the day when we met for the first time.
where 地点状语 地点 This is the town where President Xi Jinping was born.
why 原因状语 原因 I want to know the reason why you didn’t come to school this morning.
状语从句(必考:每年1~3道)
引导词
1. 引导时间状语从句的从属连词(10年5考)
从属连词 含义 用法
when 当……时 具体用法和例句见下面的“何时用when,何时用while的判定方法”。
while
as引导的从句的动作与主句动作同时发生,但不用进行时,多用一般过去时。
as(2018.57)
until/till(2017.53) 直到 until和till通常可以互换,但是till不用于句首;“not…until/till”意为“直到……才……”。
before(2018.54) 在……之前 主句的动作发生在从句动作之前。
after 在……之后 主句的动作发生在从句动作之后。
since(2015.53,2014.34) 自从 从句用一般过去时,主句常用现在完成时。
as soon as 一……就…… 从句动作一发生,主句的动作随即发生,若主句用一般将来时,从句常用一般现在时表将来。
拓展
何时用when,何时用while的判定方法
(1)若主句的动词是短暂性动词,从句的动词是延续性动词,则when和while都可用。如:
Our teacher came into the classroom when/while we were chatting.
(2)若主句和从句表示两个同时进行的持续性动作,则要用while。如:
My mother was cooking dinner while I was reading a book.
(3)若从句的动词是短暂性动词,则要用when。如:
It was raining when she arrived at the station.
(4)若主句和从句的动作不是同时发生,而是有先后顺序,则要用when。如:
I will study abroad when I have enough money.
(5)when可用作并列连词,意为“这时(突然)”,while也可用作并列连词,意为“而,却”。如:
He was ready to leave home when the phone rang.
I like watching action movies while she likes watching comedies.
2. 引导条件状语从句的从属连词(10年4考)
从属连词 含义 用法
if(2016.44) 如果 若主句用一般将来时,从句常用一般现在时表将来。
unless(if…not)(10年3考) 除非
as long as 只要
3. 引导让步状语从句的从属连词(10年5考)
从属连词 含义 用法
although 虽然;尽管 不能与but连用,但是可以与yet或still连用。
though(10年5考)
even though/even if 即使;虽然 不能与but连用,但是可以与yet或still连用。
whenever 无论什么时候 引导让步状语从句时相当于no matter when。
wherever 无论在哪里 引导让步状语从句时相当于no matter where。
whatever 无论什么 引导让步状语从句时相当于no matter what。
whoever 无论谁 引导让步状语从句时相当于no matter who。
4. 引导原因状语从句的从属连词(10年2考)
从属连词 含义 用法
because(2021.34) 因为 表示造成某种情况的直接原因, 用来回答why引导的问句,不能与so同时使用。
since 既然 语气比because弱, 表示众所周知的原因。
as(2022.38) 由于, 因为 语气比since弱, 表示众所周知的原因或者在说话人看来已经很明显的原因, 引导的从句位于主句前后均可。
5. 引导目的状语从句的从属连词
从属连词 含义 用法
so that/in order that 为了;以便 后接句子,可互换使用。
6. 引导结果状语从句的从属连词
从属连词 含义 用法
so…that… 如此……以至于…… so+adj./adv.+ that从句 so+adj.+a/an+n.+that从句
such…that… such+a/an+adj.+可数名词单数+that从句 such+adj.+可数名词复数/不可数名词+that从句
注意
当名词前有many, much, few, little 修饰时,应该用so,不能用such。如:
There were so many people that I couldn’t find a good place to take photos.
Mrs. Smith thought so much that she couldn’t fall asleep the whole night.
时态
1. 主将从现:在含有时间状语从句、条件状语从句的复合句中,若主句为一般将来时,从句用一般现在时表将来。
(1)引导时间状语从句:when, as, while, after, before, until, as soon as等。如:
I’ll call you as soon as I get to Beijing.
(2)引导条件状语从句:if, unless, as long as, in case, once等。如:
If my mother allows me to go to the party, I will be very happy.
2. 若复合句含有由since引导的时间状语从句,从句用一般过去时,主句用现在完成时。如:
Our English teacher has worked in this school since she graduated from Peking University.
3. 主情从现:主句有情态动词,从句使用一般现在时。如:
You can get good grades if you study hard.
4. 主祈从现:主句为祈使句,从句使用一般现在时。如:
Be careful when you cut the fruit.
专题十一 情景交际
话题1 请求(10年4考)
【问句】
Would you mind (not)… (2020.21)
Would/Do you mind if I…
【答句】
表示不介意的回答
(No,)Not at all.
No, go ahead.
Certainly not./Of course not./No, I don’t mind.
表示介意的回答
You’d better not./(Sorry,)I’m afraid you can’t./I’m sorry, but…
Sorry, we’ll go and play in the park.
【问句】
Can/Could/May I… (2018.31, 2017.45, 2014.33)
I wonder if I can/could…
【答句】
表示同意的回答
Sure./Of course./Certainly.(2017.45)
Feel free./Yes, please./Go ahead, please./Sure, no problem./Here you are(2018.31, 2014.33)
表示不同意的回答
You’d better not./I’m afraid you can’t./I’m sorry, but you can’t … /No, you can’t./No, you mustn’t./No, please don’t.
【问句】
Can/Could/Will/Would you (please)…
【答句】
表示同意的回答
Sure./Certainly./Of course.
Yes, I’ll do it right away./No problem./With pleasure./All right./OK.
表示不同意的回答
(Sorry,)I’m afraid not./(Sorry,)I’m afraid I can’t.
话题2 观点(10年4考)
【问句】
What do you think of… /How do you like…
How is/was…
【答句】
I don’t mind them.
I love/like…(very much).
I don’t love/like…
Great!/Wonderful!/Excellent!/Very good!
It is great/interesting/exciting/boring …/It’s worth …/I can’t stand them.
【问句】Do you think…
【答句】Yes, I think so./No, I don’t think so.
【表达观点】
Reading a good book makes me happy.
This is really a wonderful movie.
We should try our best to protect the environment.
I think…/In my opinion,…/As far as I’m concerned,…/From my point of view, …
【回应观点】
表示同意的回答
I think so.
I agree(with you)./I can’t/couldn’t agree more./That’s true.(2022.30, 2021.30, 2016.45)
表示不同意的回答
I disagree./I don’t agree(with you)./I don’t think so.
表示不完全同意的回答
That depends./You may be right./Yes, maybe.(2018.45)
【表达观点】
I want to play basketball after school.
I am going to join the table tennis club next week.
【回应观点】
So do I./So am I./Me, too.
【表达观点】
I don’t feel like going out this evening.
I’m not sure if the idea is right.
【回应观点】
Neither do I./Neither am I./Me, neither.
话题3 鼓励(10年3考)
【描述担心】
I feel/am nervous about…
I’m anxious/worried about…
【鼓励】
Take it easy.(2017.31, 2013.42)
Don’t worry./There is nothing to worry about.
【描述担心】
I’m afraid. it’s too hard.
I am afraid I have to give up my dream of being a doctor.It’s too difficult.
… is too difficult for me. I will certainly lose.
【鼓励】
Come on./Cheer up. You can do it.(2014.50)
Don’t lose heart. I believe your dream can come true.
【表达伤心】
We lost the soccer game. I feel so sad.
I am so sad.I’ve failed my math exam.
【鼓励】
Cheer up.
话题4 赞美(2019.31)
【表达赞美】
You look so cool with your sunglasses.
You have done such a good job in…
Your dress is beautiful!
You look so beautiful (in this dress/sweater…).
Very good!/Well done!/Wonderful!/Excellent!(2019.31)
Perfect!/Good job!
【回应赞美】
Thank you (very much).
Thanks a lot./Many thanks.
话题5 问候与介绍(2016.31)
【问候】
How is it going(with you) /How’s everything(going with you)
How are you /How are you doing
【答句】
Pretty good!
Very well, thank you./Fine, thanks. And you /Not bad./I’m OK./Everything is OK.
【问候】How do you do
【答句】How do you do
【问候】Good morning/Good afternoon/Good evening.
【答句】Good morning/Good afternoon/Good evening.
【问候】Nice to meet you./Glad to see you./Pleased to meet you all.(2016.31)
【答句】Nice to meet you, too./Glad to see you, too.
【介绍】
Kelly, this is Tom. He is my new friend.
Hello, I’m Steven. I am a new student here.
【答句】
Nice to meet you./It’s a pleasure to know you./I’m pleased to know you.
话题6 建议、提醒或劝告(2014.42)
【建议】
S
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
