初中英语牛津译林版 九年级上册 Unit 2 Period 3 Grammar(共50张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 初中英语牛津译林版 九年级上册 Unit 2 Period 3 Grammar(共50张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.4MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津译林版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-05-16 17:14:56 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共50张PPT)
Period 3 Grammar
Unit 2 Colours
课文呈现
Grammar
A. Object clauses introduced by that
An object clause functions as the object of a sentence. We use that to introduce an object clause that is a statement.
An object clause can be put after verbs such as know, think, believe, hope and mean.
Some people believe that colours can influence our moods.
She hopes that yellow can bring her success.
课文呈现
An object clause can also follow adjectives such as certain, sure and glad.
He is glad that the walls in his room are blue.
She is sure that yellow can bring her good luck.
In informal English we often drop that.
I think (that) blue is better than pink.
“I’m feeling blue” means(that) “I’m feeling sad”. “I’m feeling blue”
Do you think(that) your favourite colour matches your characteristics
课文呈现
Talking about room colours
Sandy is chatting online with Millie about room colours. Try to add that to each object clause.
Millie: Did you know there is a relationship between colours and moods ①
Sandy: Certainly. ② I think colours influence our everyday lives in many ways. ③
Millie : How should we choose the colours for the rooms of a house
温馨提示:此符号表示“考点精讲点拨”链接。
课文呈现
Sandy: Most people think light colours are better than dark ones.
Millie: Yes. I notice light colours make rooms seem larger.
Sandy: Sure. I also know blue can make us feel relaxed.
Millie : Yes. My mum says blue is suitable for bedrooms. I also find some people prefer orange for their dining rooms.
Sandy: True, but it depends on personal taste. Anyway, we should choose the colour which makes us feel comfortable.
personal 常在名词前作定语,由“person (n.) 人+-al(形容词后缀) ”构成。
具有审视和选择意识,能够根据不同情境和自身实际,选择适合自己的生存环境。
课文呈现
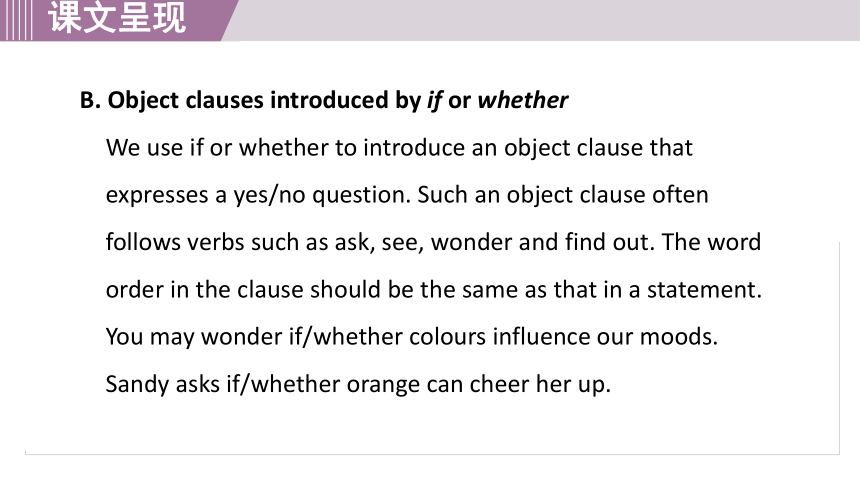
B. Object clauses introduced by if or whether
We use if or whether to introduce an object clause that expresses a yes/no question. Such an object clause often follows verbs such as ask, see, wonder and find out. The word order in the clause should be the same as that in a statement.
You may wonder if/whether colours influence our moods.
Sandy asks if/whether orange can cheer her up.
课文呈现
Problems about shopping
B1. The Class 1, Grade 9 students are plete the sentences by using if or whether to make object clauses.
1. Should I choose the red dress
Kitty cannot decide _____________________________________.
2. Do white clothes suit me
Sandy does not know ______________________________.
if/whether she should choose the red dress
if/whether white clothes suit her
课文呈现
3. Is the sports bag made of cotton
Amy is asking ____________________________________________.
4. Does the green T-shirt match my trousers
Simon is not sure _________________________________________.
5. Should I stay at home instead of going shopping with my classmates ④
Daniel often wonders _____________________________________
_______________________________________________________.
if/whether the sports bag is made of cotton
if/whether the green T-shirt matches his trousers
if/whether he should stay at home instead
going shopping with his classmates
课文呈现
How much do you know about colours
B2. Daniel wants to tell his online friend Tommy about colours. Help him complete his email using that, if or whether.
Dear Tommy,
Have you ever noticed the colours around you Colours are really interesting. A report says(1) ___________ blue can help us feel relaxed because it represents peace. You may wonder (2) ___________ it represents anything else.
that
if/whether
课文呈现
Yes. Blue also means sadness. I do not know(3) ___________ you like green. Some people think(4) ___________ green can give us energy, but it also represents envy. Did you know (5) ___________ red represents good luck in China It is often used for celebrations! ⑤
Please tell me your favourite colour and (6) ___________ you know anything else about colours. Write back soon.
Best wishes,
Daniel
if/whether
that
that
if/whether
celebration为名词,意为“庆祝”。have/hold a celebration “举行庆祝活动”。celebration 的动词形式为celebrate。
课文呈现
B3. Daniel has some questions about colours to ask his dad, but his dad has not come home yet. Help him write a note for his dad.
1. Dad knows a lot about colours.
2. Is red just the colour of heat and power
3. Was yellow once the colour of the rulers in ancient China 4. Did the rulers in ancient Europe like to wear purple
5. Do all the doctors in the world wear white uniforms
课文呈现
I believe(1) ________________________________________________.
I wonder(2) ________________________________________________.
I want to know(3) ___________________________________________
_________________________________________________________.
I do not know(4) ____________________________________________
_________________________________________________________.
I am not certain(5) __________________________________________
_________________________________________________________.
(that) Dad knows a lot about colours
if/whether red is just the colour of heat and power
if/whether yellow was once the colour of the
rulers in ancient China
if/whether the rulers in ancient Europe liked to
wear purple
if/whether all the doctors in the world wear
white uniforms
①Did you know there is a relationship between colours and moods
relationship /r 'le n p/ n. 关系
e.g. He has a good relationship with his classmates.
他和他的同学们关系良好。
The relationship between the father and the son is being improved.
这对父子之间的关系正在得到改善。
考点1
由relation(n.关系)+
-ship(名词后缀)构成
relationship 的常用短语:
① the relationship between A and B
A 与B 之间的关系
② the relationship with sb.
和某人的关系
考题1:We should learn to communicate with our parents actively to keep a good _________________(关系) with them.
relationship
返回
温馨提示:可返回原文
②Certainly.
certainly /'s tnli/ adv. 当然;必定地,无疑地
在肯定句和疑问句中,certainly 用于be 动词、助动词和情态动词之后,行为动词之前。在否定句中,certainly 用于be 动词、助动词和情态动词之前。
考点2
考向
e.g. Several countries certainly hope so.
一些国家肯定希望如此。
We certainly can’t forget that.
我们当然不能忘记那件事。
—Could you help me close the window
帮我把窗户关上好吗?
—Certainly!
当然可以!
certainly 用在答语中表示“当
然可以,没问题”,此时可以与
sure, of course 互换。
考题2:—The game is too hard for me. I will ______ lose.
—You should never say no before you try.
A. well B. certainly
C. carefully D. quickly
B
好 当然
认真地 快速地
返回
③I think colours influence our everyday lives in many ways.
everyday /'evride / adj. 每天的;日常的
考点3
辨析:everyday 与every day
everyday 形容词,在句中作定语
every day 副词短语,在句中作时间状语
e.g. The Internet has become a part of everyday life.
互联网已成为日常生活的一部分。
I eat breakfast every day.
我每天都吃早餐。
一语辨异:
Daniel teaches them everyday English every day.
丹尼尔每天教他们日常英语。
考题3:[ 宜昌] 我们珍惜日常生活中与家人和朋友在一起的时光。(everyday)
We value the time we spend with our family and friends ___________________________________________________.
in (our) everyday life (lives)
返回
④Should I stay at home instead of going shopping with my classmates
instead of 而不是,代替
考点4
辨析:instead of 与instead
instead of 介词短语,意为“代替……;而不是……”,连接否定的内容,常用于句中,后跟名词、代词或动词-ing。
instead 副词,意为“代替;反而”,通常用于句末。上句含有否定意义时,它可用于句首来引出下句并提出相反的情况。
e.g. On Sunday, he likes to stay at home instead of going out.
他周日喜欢待在家里而不喜欢出去。
—Will you go shopping today 今天你去购物吗?
—No, I’ll stay at home instead. 不,我就待在家里。
考题4:[连云港改编] For a green life, we’d better ride bicycles ______________(而不是) driving.
instead of
返回
⑤It is often used for celebrations!
be used for 被用来……
e.g. This cup is used for drinking wine.
这个杯子是用来喝酒的。
Elsilbo can be used for all kinds of messages, including greetings and announcements.
Elsilbo 可以用于各种信息,包括问候语和公告。
考点5
be used for doing sth.
被用来做某事
used 的常用短语:
① be used to do sth. 被用来做某事
② be used to doing sth. 习惯于做某事
③ used to do sth. 过去常常做某事
考题5:[辽阳]这个新产品是用来快速加热食物的。
This new product ______________ heating food quickly.
【点拨】由句意可知本题用be used for 短语,句中主语是“This new product”,且句子叙述的是现在的情况,因此be 动词用is。故填is used for。
is used for
返回
that 和if/whether 引导的宾语从句
that 和if/whether 引导的 宾语从句 that 引导的宾语从句 当由陈述句充当宾语从句时,用that 引导,that无词义,在口语或非正式文体中常被省略。①
if 或whether 引导的宾语 从句 当从句部分的语义由一般疑问句充当宾语从句时,用if 或whether 引导,意为“是否”。②
if 或whether 引导宾语从句时,作“是否”讲,常放在动词ask, see, wonder 和know 等后面。一般情况下,两者常可换用,在口语中多用if。
宾语从句是指一个句子充当宾语,在主句与从句之间有一个引导词。
1 e.g. I’m glad (that) you can come for dinner.
我很开心你能来吃晚餐。
引导词本身的省略
连词that 引导宾语从句,只起连接主、从句的作用,它本身无意义,在口语或非正式文体中常省略。
e.g. He says (that) he is a Young Pioneer.
他说他是一名少先队员。
考点1
何时使用that 引导的宾语从句that 引导的宾语从句表示陈述一件事,即由陈述句转化而来。
e.g. He says. He is listening to the weather report.
(合并成主从句)
→He says (that) he is listening to the weather report.
他说他正在听天气预报。
考点2
主句的谓语动词是think, hear, hope, wish, remember, forget, know, say, guess 等时,常接that 引导的宾语从句。
e.g. I hope (that) he will be fine soon.
我希望他会很快好起来。
考向1
主句是由“连系动词+形容词”构成的系表结构,常接that 引导的宾语从句。这类形容词多表示感情,如:happy, glad, pleased, sad, afraid 等。
e.g. I’m afraid (that) he can’t come. 恐怕他不能来了。
考向2
that 引导宾语从句的相关内容
语序
宾语从句用陈述语序,即“主语+ 谓语+其他”。
e.g. Do you think The radio is too noisy.
(合并成主从句)
→Do you think (that) the radio is too noisy
你认为收音机太吵吗?
考点3
考向1
时态
(1) that 引导的宾语从句,主句用一般现在时,从句可以用符合句意要求的任意时态。
e.g. He says (that) they have already returned.
他说他们已经回来了。
He tells me that he was born in 1985.
他告诉我他生于1985 年。
考向2
(2) 如果主句用一般过去时,从句要用过去时态的某种形式(一般过去时、过去进行时、过去将来时、过去完成时等) 。
e.g. He said (that) he had bought a new dictionary.
他说他买了本新词典。
I knew (that) they were studying English.
我知道他们正在学英语。
特别提醒:
如果从句表达的是客观事实、真理、自然现象、名言、警句、格言、谚语等,尽管主句用一般过去时,从句也要用一般现在时。
e.g. He said that time is life. 他说时间就是生命。
考题1:[龙东] In the past, people didn’t know that light _______ faster than sound.
A. travels B. travelled C. travel
A
【点拨】本题用语法判定法。宾语从句中,从句是客观规律时不受主句时态的限制,依然使用一般现在时。
考题2:[扬州]我希望今年暑假我们能和朋友共度更多的时光。
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
【点拨】本题是一个宾语从句,主句 I hope that... 表示“我希望……”,后加宾语从句,that 可以省略。
I hope we can spend more time with friends this summer
vacation/holiday.
返回
2 e.g. Nobody knows whether /if it will rain tomorrow.
没有人知道明天是否会下雨。
Lucy asked whether /if they had cotton coats.
露西问他们是否有棉外套。
考题3:[贵港]—I wonder ______.
—I am not sure. Maybe yes.
A. if has Dave got his driver’s license
B. how long has Dave got his driver’s license
C. if Dave has got his driver’s license
D. how long Dave has got his driver’s license
【点拨】本题用语法判定法。句意: —我想知道Dave 是否有驾照。—我不确定,可能有吧。宾语从句用陈述语序,排除A、B 两项;由句意可知选C。
C
考题4:[荆州] —I am worried _______ I can enter a good high school or not.
—Work hard and trust in yourself.
A. why B. what
C. whether D. where
【点拨】本题用语法判定法。why为什么;what 什么;whether 是否;where 哪里。根据句中的or not 可知应选whether。故选C。
C
拓展:(1) if 或whether 引导宾语从句时,要注意三个方面,即连接词、语序和时态。
if 或whether 不能和that 或其他连接词同时使用,也不能省去。
e.g. (误) I don’t know that if/whether he will come here today.
(正) I don’t know if/whether he will come here today.
我不知道他今天是否会来这里。
(误) He came to see what if /whether there was something wrong with his cat.
(正) He came to see if /whether there was something wrong with his cat. 他走过来看看他的猫是否有毛病。
考向1
if 或whether 引导宾语从句时,虽具有疑问意义,但从句仍用陈述语序。
e.g. Did you know the way to the hospital The old woman asked me. (合并成主从句)
→The old woman asked me if /whether I knew the way to the hospital.
这位老妇人问我是否知道去医院的路。
考向2
if 或whether 引导的宾语从句应和主句的时态保持一致。即主句为一般现在时,从句用符合句意要求的任意时态;主句为一般过去时,从句则用与过去相关的某种时态。
e.g. I don’t know if / whether he has come here.
我不知道他是否已经来这儿了。
Tom asked if /whether I had read the book.
汤姆问我是否看过这本书。
考向3
在动词不定式之前只能用whether。
e.g. I can’t decide whether to stay. 我不能决定是否留下。
在whether... or not 的固定搭配中,只能用whether。
e.g. I want to know whether it’s good news or not.
我想知道它是否是好消息。
考向1
(2) if 和whether 的区别:
考向2
在介词后,只能用whether。
e.g. The father is worried about whether he will lose his work.
这位父亲担心他是否会失去他的工作。
考向3
考题5:[广州] 凯特想知道她是否能为科学日做些事。
Kate wondered _________ _________ _________ _________ something for the Science Day.
if she could do
考题6:[达州] “Do you have a good time at the amusement park ” He asked me. (合并为含有宾语从句的复合句)
He asked me ______________ I ________ a good time at the amusement park.
【点拨】空处所在句意为“他问我在游乐园玩得是否开心”,用 whether/if 引导宾语从句,因主句是一般过去时,从句动词应用过去式had。故填whether/if;had。
whether/if had
返回
本节课主要学习了:
重点单词:relationship , certainly , everyday , personal , ancient
重点短语:influence our everyday lives in many ways
Period 3 Grammar
Unit 2 Colours
课文呈现
Grammar
A. Object clauses introduced by that
An object clause functions as the object of a sentence. We use that to introduce an object clause that is a statement.
An object clause can be put after verbs such as know, think, believe, hope and mean.
Some people believe that colours can influence our moods.
She hopes that yellow can bring her success.
课文呈现
An object clause can also follow adjectives such as certain, sure and glad.
He is glad that the walls in his room are blue.
She is sure that yellow can bring her good luck.
In informal English we often drop that.
I think (that) blue is better than pink.
“I’m feeling blue” means(that) “I’m feeling sad”. “I’m feeling blue”
Do you think(that) your favourite colour matches your characteristics
课文呈现
Talking about room colours
Sandy is chatting online with Millie about room colours. Try to add that to each object clause.
Millie: Did you know there is a relationship between colours and moods ①
Sandy: Certainly. ② I think colours influence our everyday lives in many ways. ③
Millie : How should we choose the colours for the rooms of a house
温馨提示:此符号表示“考点精讲点拨”链接。
课文呈现
Sandy: Most people think light colours are better than dark ones.
Millie: Yes. I notice light colours make rooms seem larger.
Sandy: Sure. I also know blue can make us feel relaxed.
Millie : Yes. My mum says blue is suitable for bedrooms. I also find some people prefer orange for their dining rooms.
Sandy: True, but it depends on personal taste. Anyway, we should choose the colour which makes us feel comfortable.
personal 常在名词前作定语,由“person (n.) 人+-al(形容词后缀) ”构成。
具有审视和选择意识,能够根据不同情境和自身实际,选择适合自己的生存环境。
课文呈现
B. Object clauses introduced by if or whether
We use if or whether to introduce an object clause that expresses a yes/no question. Such an object clause often follows verbs such as ask, see, wonder and find out. The word order in the clause should be the same as that in a statement.
You may wonder if/whether colours influence our moods.
Sandy asks if/whether orange can cheer her up.
课文呈现
Problems about shopping
B1. The Class 1, Grade 9 students are plete the sentences by using if or whether to make object clauses.
1. Should I choose the red dress
Kitty cannot decide _____________________________________.
2. Do white clothes suit me
Sandy does not know ______________________________.
if/whether she should choose the red dress
if/whether white clothes suit her
课文呈现
3. Is the sports bag made of cotton
Amy is asking ____________________________________________.
4. Does the green T-shirt match my trousers
Simon is not sure _________________________________________.
5. Should I stay at home instead of going shopping with my classmates ④
Daniel often wonders _____________________________________
_______________________________________________________.
if/whether the sports bag is made of cotton
if/whether the green T-shirt matches his trousers
if/whether he should stay at home instead
going shopping with his classmates
课文呈现
How much do you know about colours
B2. Daniel wants to tell his online friend Tommy about colours. Help him complete his email using that, if or whether.
Dear Tommy,
Have you ever noticed the colours around you Colours are really interesting. A report says(1) ___________ blue can help us feel relaxed because it represents peace. You may wonder (2) ___________ it represents anything else.
that
if/whether
课文呈现
Yes. Blue also means sadness. I do not know(3) ___________ you like green. Some people think(4) ___________ green can give us energy, but it also represents envy. Did you know (5) ___________ red represents good luck in China It is often used for celebrations! ⑤
Please tell me your favourite colour and (6) ___________ you know anything else about colours. Write back soon.
Best wishes,
Daniel
if/whether
that
that
if/whether
celebration为名词,意为“庆祝”。have/hold a celebration “举行庆祝活动”。celebration 的动词形式为celebrate。
课文呈现
B3. Daniel has some questions about colours to ask his dad, but his dad has not come home yet. Help him write a note for his dad.
1. Dad knows a lot about colours.
2. Is red just the colour of heat and power
3. Was yellow once the colour of the rulers in ancient China 4. Did the rulers in ancient Europe like to wear purple
5. Do all the doctors in the world wear white uniforms
课文呈现
I believe(1) ________________________________________________.
I wonder(2) ________________________________________________.
I want to know(3) ___________________________________________
_________________________________________________________.
I do not know(4) ____________________________________________
_________________________________________________________.
I am not certain(5) __________________________________________
_________________________________________________________.
(that) Dad knows a lot about colours
if/whether red is just the colour of heat and power
if/whether yellow was once the colour of the
rulers in ancient China
if/whether the rulers in ancient Europe liked to
wear purple
if/whether all the doctors in the world wear
white uniforms
①Did you know there is a relationship between colours and moods
relationship /r 'le n p/ n. 关系
e.g. He has a good relationship with his classmates.
他和他的同学们关系良好。
The relationship between the father and the son is being improved.
这对父子之间的关系正在得到改善。
考点1
由relation(n.关系)+
-ship(名词后缀)构成
relationship 的常用短语:
① the relationship between A and B
A 与B 之间的关系
② the relationship with sb.
和某人的关系
考题1:We should learn to communicate with our parents actively to keep a good _________________(关系) with them.
relationship
返回
温馨提示:可返回原文
②Certainly.
certainly /'s tnli/ adv. 当然;必定地,无疑地
在肯定句和疑问句中,certainly 用于be 动词、助动词和情态动词之后,行为动词之前。在否定句中,certainly 用于be 动词、助动词和情态动词之前。
考点2
考向
e.g. Several countries certainly hope so.
一些国家肯定希望如此。
We certainly can’t forget that.
我们当然不能忘记那件事。
—Could you help me close the window
帮我把窗户关上好吗?
—Certainly!
当然可以!
certainly 用在答语中表示“当
然可以,没问题”,此时可以与
sure, of course 互换。
考题2:—The game is too hard for me. I will ______ lose.
—You should never say no before you try.
A. well B. certainly
C. carefully D. quickly
B
好 当然
认真地 快速地
返回
③I think colours influence our everyday lives in many ways.
everyday /'evride / adj. 每天的;日常的
考点3
辨析:everyday 与every day
everyday 形容词,在句中作定语
every day 副词短语,在句中作时间状语
e.g. The Internet has become a part of everyday life.
互联网已成为日常生活的一部分。
I eat breakfast every day.
我每天都吃早餐。
一语辨异:
Daniel teaches them everyday English every day.
丹尼尔每天教他们日常英语。
考题3:[ 宜昌] 我们珍惜日常生活中与家人和朋友在一起的时光。(everyday)
We value the time we spend with our family and friends ___________________________________________________.
in (our) everyday life (lives)
返回
④Should I stay at home instead of going shopping with my classmates
instead of 而不是,代替
考点4
辨析:instead of 与instead
instead of 介词短语,意为“代替……;而不是……”,连接否定的内容,常用于句中,后跟名词、代词或动词-ing。
instead 副词,意为“代替;反而”,通常用于句末。上句含有否定意义时,它可用于句首来引出下句并提出相反的情况。
e.g. On Sunday, he likes to stay at home instead of going out.
他周日喜欢待在家里而不喜欢出去。
—Will you go shopping today 今天你去购物吗?
—No, I’ll stay at home instead. 不,我就待在家里。
考题4:[连云港改编] For a green life, we’d better ride bicycles ______________(而不是) driving.
instead of
返回
⑤It is often used for celebrations!
be used for 被用来……
e.g. This cup is used for drinking wine.
这个杯子是用来喝酒的。
Elsilbo can be used for all kinds of messages, including greetings and announcements.
Elsilbo 可以用于各种信息,包括问候语和公告。
考点5
be used for doing sth.
被用来做某事
used 的常用短语:
① be used to do sth. 被用来做某事
② be used to doing sth. 习惯于做某事
③ used to do sth. 过去常常做某事
考题5:[辽阳]这个新产品是用来快速加热食物的。
This new product ______________ heating food quickly.
【点拨】由句意可知本题用be used for 短语,句中主语是“This new product”,且句子叙述的是现在的情况,因此be 动词用is。故填is used for。
is used for
返回
that 和if/whether 引导的宾语从句
that 和if/whether 引导的 宾语从句 that 引导的宾语从句 当由陈述句充当宾语从句时,用that 引导,that无词义,在口语或非正式文体中常被省略。①
if 或whether 引导的宾语 从句 当从句部分的语义由一般疑问句充当宾语从句时,用if 或whether 引导,意为“是否”。②
if 或whether 引导宾语从句时,作“是否”讲,常放在动词ask, see, wonder 和know 等后面。一般情况下,两者常可换用,在口语中多用if。
宾语从句是指一个句子充当宾语,在主句与从句之间有一个引导词。
1 e.g. I’m glad (that) you can come for dinner.
我很开心你能来吃晚餐。
引导词本身的省略
连词that 引导宾语从句,只起连接主、从句的作用,它本身无意义,在口语或非正式文体中常省略。
e.g. He says (that) he is a Young Pioneer.
他说他是一名少先队员。
考点1
何时使用that 引导的宾语从句that 引导的宾语从句表示陈述一件事,即由陈述句转化而来。
e.g. He says. He is listening to the weather report.
(合并成主从句)
→He says (that) he is listening to the weather report.
他说他正在听天气预报。
考点2
主句的谓语动词是think, hear, hope, wish, remember, forget, know, say, guess 等时,常接that 引导的宾语从句。
e.g. I hope (that) he will be fine soon.
我希望他会很快好起来。
考向1
主句是由“连系动词+形容词”构成的系表结构,常接that 引导的宾语从句。这类形容词多表示感情,如:happy, glad, pleased, sad, afraid 等。
e.g. I’m afraid (that) he can’t come. 恐怕他不能来了。
考向2
that 引导宾语从句的相关内容
语序
宾语从句用陈述语序,即“主语+ 谓语+其他”。
e.g. Do you think The radio is too noisy.
(合并成主从句)
→Do you think (that) the radio is too noisy
你认为收音机太吵吗?
考点3
考向1
时态
(1) that 引导的宾语从句,主句用一般现在时,从句可以用符合句意要求的任意时态。
e.g. He says (that) they have already returned.
他说他们已经回来了。
He tells me that he was born in 1985.
他告诉我他生于1985 年。
考向2
(2) 如果主句用一般过去时,从句要用过去时态的某种形式(一般过去时、过去进行时、过去将来时、过去完成时等) 。
e.g. He said (that) he had bought a new dictionary.
他说他买了本新词典。
I knew (that) they were studying English.
我知道他们正在学英语。
特别提醒:
如果从句表达的是客观事实、真理、自然现象、名言、警句、格言、谚语等,尽管主句用一般过去时,从句也要用一般现在时。
e.g. He said that time is life. 他说时间就是生命。
考题1:[龙东] In the past, people didn’t know that light _______ faster than sound.
A. travels B. travelled C. travel
A
【点拨】本题用语法判定法。宾语从句中,从句是客观规律时不受主句时态的限制,依然使用一般现在时。
考题2:[扬州]我希望今年暑假我们能和朋友共度更多的时光。
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
【点拨】本题是一个宾语从句,主句 I hope that... 表示“我希望……”,后加宾语从句,that 可以省略。
I hope we can spend more time with friends this summer
vacation/holiday.
返回
2 e.g. Nobody knows whether /if it will rain tomorrow.
没有人知道明天是否会下雨。
Lucy asked whether /if they had cotton coats.
露西问他们是否有棉外套。
考题3:[贵港]—I wonder ______.
—I am not sure. Maybe yes.
A. if has Dave got his driver’s license
B. how long has Dave got his driver’s license
C. if Dave has got his driver’s license
D. how long Dave has got his driver’s license
【点拨】本题用语法判定法。句意: —我想知道Dave 是否有驾照。—我不确定,可能有吧。宾语从句用陈述语序,排除A、B 两项;由句意可知选C。
C
考题4:[荆州] —I am worried _______ I can enter a good high school or not.
—Work hard and trust in yourself.
A. why B. what
C. whether D. where
【点拨】本题用语法判定法。why为什么;what 什么;whether 是否;where 哪里。根据句中的or not 可知应选whether。故选C。
C
拓展:(1) if 或whether 引导宾语从句时,要注意三个方面,即连接词、语序和时态。
if 或whether 不能和that 或其他连接词同时使用,也不能省去。
e.g. (误) I don’t know that if/whether he will come here today.
(正) I don’t know if/whether he will come here today.
我不知道他今天是否会来这里。
(误) He came to see what if /whether there was something wrong with his cat.
(正) He came to see if /whether there was something wrong with his cat. 他走过来看看他的猫是否有毛病。
考向1
if 或whether 引导宾语从句时,虽具有疑问意义,但从句仍用陈述语序。
e.g. Did you know the way to the hospital The old woman asked me. (合并成主从句)
→The old woman asked me if /whether I knew the way to the hospital.
这位老妇人问我是否知道去医院的路。
考向2
if 或whether 引导的宾语从句应和主句的时态保持一致。即主句为一般现在时,从句用符合句意要求的任意时态;主句为一般过去时,从句则用与过去相关的某种时态。
e.g. I don’t know if / whether he has come here.
我不知道他是否已经来这儿了。
Tom asked if /whether I had read the book.
汤姆问我是否看过这本书。
考向3
在动词不定式之前只能用whether。
e.g. I can’t decide whether to stay. 我不能决定是否留下。
在whether... or not 的固定搭配中,只能用whether。
e.g. I want to know whether it’s good news or not.
我想知道它是否是好消息。
考向1
(2) if 和whether 的区别:
考向2
在介词后,只能用whether。
e.g. The father is worried about whether he will lose his work.
这位父亲担心他是否会失去他的工作。
考向3
考题5:[广州] 凯特想知道她是否能为科学日做些事。
Kate wondered _________ _________ _________ _________ something for the Science Day.
if she could do
考题6:[达州] “Do you have a good time at the amusement park ” He asked me. (合并为含有宾语从句的复合句)
He asked me ______________ I ________ a good time at the amusement park.
【点拨】空处所在句意为“他问我在游乐园玩得是否开心”,用 whether/if 引导宾语从句,因主句是一般过去时,从句动词应用过去式had。故填whether/if;had。
whether/if had
返回
本节课主要学习了:
重点单词:relationship , certainly , everyday , personal , ancient
重点短语:influence our everyday lives in many ways
