外研版(2019)选择性必修 第四册Unit 3 The world meets China Grammar learning课件(共43张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版(2019)选择性必修 第四册Unit 3 The world meets China Grammar learning课件(共43张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 325.5KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-05-24 10:52:43 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共43张PPT)
Unit 3 The world meets China
Discovering Useful Structures—
Review the adverbial clauses
(复习状语从句)
When the national flag rises, we will feel more than happy and proud. As China is making great progress in many fields, we are playing an increasing important role in international society.
状语从句的魅力
Lead-in
Look at the following sentences from the reading passage, classify the adverbial clauses in the sentences and answer the questions.
a.You can imagine how travelers felt when they saw the oasis of Dunhuang ahead of them.
b. If you look up, you can see the paintings and other artworks…
c.…Dunhuang was not as prosperous as it used to be.
d. Given that the theme of the Expo was to promote cultural exchange…,
Dunhuang was the ideal place.
time
condition
comparison
reason
Lead-in
Lead-in
Look at the following sentences from the reading passage answer the questions.
1.Classify the adverbial clauses in the sentences.
condition comparison reason time
2.What other types of adverbial clause can you think of Give some examples.
As long as you put some effort, you will make progress.
You can do everything as you are told to.
the first time I read it
Now that this dream has come true
More adverbial clauses from the reading passage of this unit.
1.the first time引导时间状语从句
I fell in love with Dream of the Red Chamber _________________,and was determined to translate it into Bulgarian.
我第一次读《红楼梦》时就爱上了它,并决心把它译成保加利亚语。
2.now that引导原因状语从句
,my next goal is to translate The Romance of the Three Kingdoms.
由于这个梦想已经实现,我的下一个目标是翻译《三国演义》。
Lead-in
2.Complete the passage with the clauses in the box.
no matter what culture it comes from
so that people can learn about different cultures
as if they are neighbours
that over 15,000 people each year attend them
as the traditional is mixed with the modern
Yo-yo ma is a French-born Chinese American cellist known for his musical talent. In 1998, Ma founded Silk Road, an organization that explores musical traditions in countries___________________________
______________.
The fundamental purpose of Silk Road is to bring people from across the globe together to play and listen to music. Instruments and styles are blended together to create music that is surprising, rich and completely original, ______________________________. What’s more, _________
_____________________________, people can learn about the development of culture as a whole.
no matter what culture it comes from
as the
traditional is mixed with the modern
so that people can learn about
different cultures
The events that Silk Road organizes are either performances, workshops or mixed musical-artistic displays. It is so successful ___________________
_____________________.
People meet as strangers, but they leave ________________________,
learning that different cultures have more in common than they imagined.
as if they are neighbors
each year attend them
that over 15,000 people
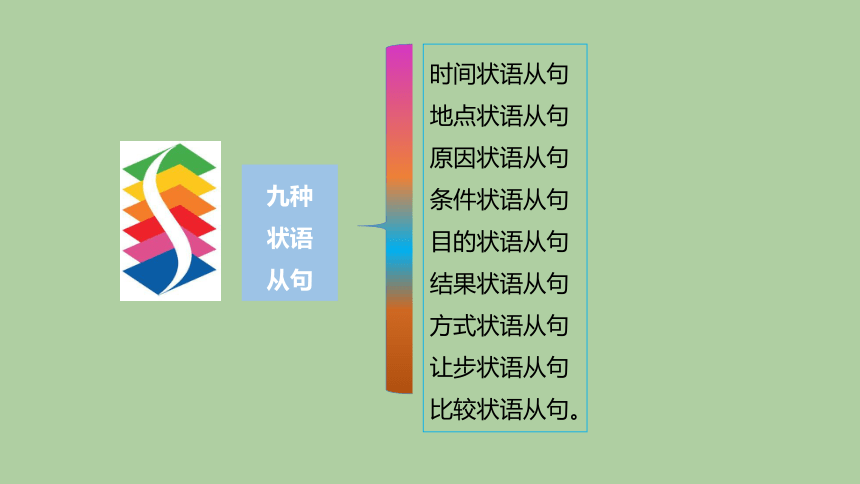
时间状语从句
地点状语从句
原因状语从句
条件状语从句
目的状语从句
结果状语从句
方式状语从句
让步状语从句
比较状语从句。
九种状语从句
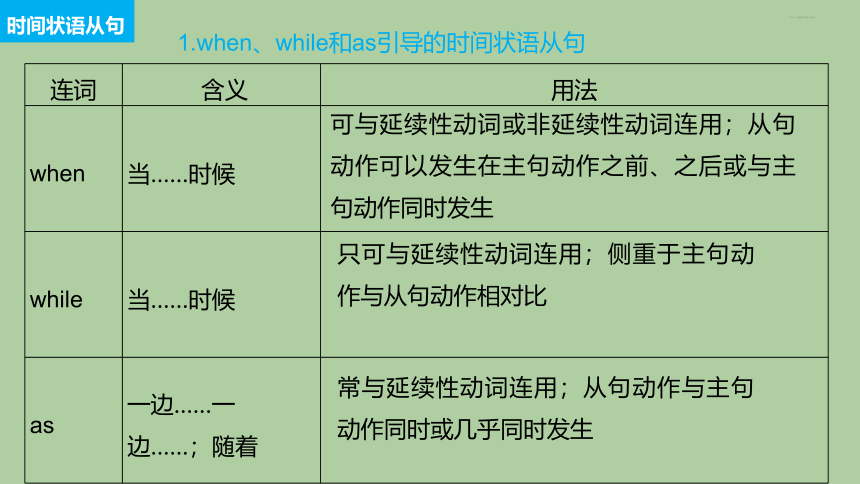
连词 含义 用法
when 当……时候
while 当……时候
as 一边……一 边……;随着
可与延续性动词或非延续性动词连用;从句动作可以发生在主句动作之前、之后或与主句动作同时发生
只可与延续性动词连用;侧重于主句动作与从句动作相对比
常与延续性动词连用;从句动作与主句动作同时或几乎同时发生
时间状语从句
1.when、while和as引导的时间状语从句
【温馨提示】
如果主句表示的是非延续性动作,而从句用延续性动词的进行时态表示在一段时间内正在进行的动作,则when、while与as可互换使用。
When/While/As I was walking down the street, I came across an old friend.
当我在街上走的时候,碰巧遇到了我的一个老朋友。
时间状语从句
2.表示“一……就……”含义的词或短语引导的时间状语从句
(1)有的名词短语或副词可引导时间状语从句,如:the moment,the minute,the second,the instant,immediately,directly,instantly等。另外as soon as也可引导时间状语从句,从句中用一般时态代替将来时态。
(2)在hardly/scarcely...when...和no sooner...than...结构中,主句用过去完成时,than或when所在的从句用一般过去时。
时间状语从句
【温馨提示】
在hardly/scarcely...when...与no sooner...than...结构中,当hardly,scarcely或no sooner位于句首时,主句要用部分倒装。
They had hardly reached Edinburgh when they were ordered to return to London.
=Hardly had they reached Edinburgh when they were ordered to return to London.
他们刚抵达爱丁堡就接到了回伦敦的命令。
时间状语从句
3.till,until和 not...until/till的用法
until与till两者均表示“直到……为止”,引导时间状语从句。肯定句中,其主句谓语动词必须为延续性动词,表示某动作一直延续到某时间为止。not...until...与not...till...两者均表示“直到……才……”,not 所在的主句的谓语动词必须为非延续性动词,表示某动作直到某时间才开始。until可用于句首,而till不可放在句首,till一般不用于强调句型。
时间状语从句
4.after、before引导的时间状语从句
after表示“在……之后”;before表示“在……之前;还没来得及……就……”。
He changed his name after he left his hometown.
离开家乡后他把名字改了。
Before modern medicine changed the laws of nature, many children died of common childhood diseases.
在现代医学改变自然法则之前,许多孩子死于一些常见的儿童疾病。
时间状语从句
5.since引导的时间状语从句
since意为“自从……以来”,从句的谓语动词一般是非延续性动词,主句的谓语动词一般是延续性动词。since从句的时态若是一般过去时,主句常用现在完成时或现在完成进行时。
They have been friends since they met for the first time in London.
自从在伦敦第一次见面以来,他们一直是朋友。
It has been three years since the war ended.
战争已经结束三年了。
时间状语从句
6.其他常见名词短语引导的时间状语从句
every time每次、each time每次、any time任何时候、next time下次、the first/last time第一次/最后一次。
Every time I meet her I always forget her name.
每次我见到她时,我总记不起她的名字。
The first time I met her, I thought her nice and honest.
我第一次遇见她时,就觉得她友好又诚实。
时间状语从句
1.The father waited until his daughter finished her homework.
那位父亲一直等到他的女儿做完家庭作业。
2.The baby didn’t go to bed until/till his mother returned.
这个婴儿直到他的妈妈回来才睡觉。
3.I had hardly told him the news when he stopped listening.
我刚告诉他那则消息他就不听了。
读一读,译一译
时间状语从句
4.He had no sooner finished his speech than the students started cheering.
他一完成演讲,学生就开始欢呼起来。
5.Researchers in Britain found that when French music was played, sales of French wines went up.
英国的研究者发现,播放法国音乐时,法国葡萄酒的销量会增加。
6.While watching TV, children do not merely absorb words and images.
孩子们在看电视的时候,接收的不只是文字和图像信息。
读一读,译一译
时间状语从句
7.As he grew older, he became less active.
随着他逐渐长大,他变得不那么活泼了。
8.For example, the moment you get on the airplane, start adjusting your biological clock to the destination’s time.
例如,你一上飞机,就开始按照目的地的时间调整你的生物钟。
9.The boy ran off the minute he saw the owner of the orchard.
那个男孩一见到果园的主人就跑开了。
读一读,译一译
时间状语从句
连词 区别
位置 内涵 能否回答 why问句 能否被强调
because 主句前或后 直接原因 能 能
as 主句前或后 双方都知 道的原因 否 否
since/now that 主句前
原因状语从句
1.原因状语从句通常由because、since、as、now that等连词引导。
2.seeing that...(由于;鉴于)、considering that...(考虑到;鉴于)
也可引导原因状语从句。
Seeing (that) the weather is bad, we’ll stay at home.
鉴于天气不好,我们要待在家里了。
Considering (that) it is hand-made, the price seems reasonable.
考虑到它是手工制作,价格还算合理。
原因状语从句
1.Now that you’ve got a chance, you might as well make full use of it.
既然你得到了机会,那么你不妨充分利用它。
2.We had better hurry as it’s getting dark.
天快要黑了,所以我们最好快点。
读一读,译一译
原因状语从句
1.引导条件状语从句的常见从属连词(短语)有:if, unless, as/so long as, in case (万一), once, on condition that, provided/providing (that), supposing/suppose (that), assuming that (假设)等。
You’ll fail the exam unless you study hard.
除非你努力学习,否则你会考试不及格。
条件状语从句
They agreed to lend us the car on condition that we returned it before the weekend.
他们同意把车借给我们,条件是我们必须在周末前归还。
My parents don’t mind what job I do as long as I am happy.
我的父母不在意我从事什么工作,只要我高兴就好。
条件状语从句
2.only if和if only的区别
only if意为“只有;只要……就”,置于句首时主句要用部分倒装结构。
if only意为“但愿;要是……就好了”,引导的从句要用虚拟语气:
与现在的情况相反时,从句用一般过去时;与过去的情况相反时,从句用过去完成时;与将来的情况相反时,谓语用“would/could+动词原形”。
Only if you try your best will you feel relieved.
只要你尽力了,你就会感到欣慰。
If only I had seen you yesterday.
要是我昨天看到你就好了。
条件状语从句
1.他只有更加努力学习才能赶上其他人。
Only if he studies harder can he catch up with others.
2.但愿雨会停!
If only it would stop raining!
3.要是我是一只小鸟就好了。
If only I were a bird.
练一练
条件状语从句
1.although、though、as与while引导的让步状语从句
【温馨提示】
while也可以引导让步状语从句,但只能放在句首,意为“虽然;尽管”。
2.even if与even though引导的让步状语从句
even if与even though表示“即使,纵然”,引导让步状语从句时,可用虚拟语气,也可以用陈述语气。
让步状语从句
3.“疑问词+-ever”引导的让步状语从句
however、whatever、whoever、whenever等引导的让步状语从句相当于“no matter+疑问词”,意为“无论……”。
4.whether...or...引导的让步状语从句
让步状语从句
1.Although he is considered a great writer, his works are not widely read.
虽然他被认为他是一个大作家,但是他的作品还没有被广泛阅读。
2.Although this may sound like a simple task, great care is needed.
尽管这听上去像是一个简单的任务,但是你要非常谨慎。
3.While he loves his students, he is very strict with them.
虽然他爱他的学生,但是他对他们很严格。
让步状语从句
4.I’ll do it, even if it takes me all afternoon.
我要做这件事,即使它将花去我整个下午的时间。
5.Even if I were in your place, I wouldn’t take the job.
即使我处于你的位置,我也不会接受这份工作。
6.Wherever/No matter where you go, I would keep you company.
不管你到哪儿去,我都会陪着你。
7.Whether or not he will stay, I really don’t care.
他要留下来还是要走,我真的不在意。
让步状语从句
引导方式状语从句的从属连词有: as(正如,按照)、as if/though(好像,仿佛)。
as if或as though引导的从句与事实相反时,通常用虚拟语气:
与现在事实相反时,从句用一般过去时;
与过去事实相反时,从句谓语用“had+过去分词”;
与将来事实相反时,从句谓语用“would/could/might+动词原形”。从句内容与事实相符或可能成为事实时,则用陈述句语气。
方式状语从句
1.Please do as the teacher tells you to do.
请按照老师告诉你的做。
2.They treat her as though she were their daughter.
他们待她如亲生女儿一样。
3.Look at the clouds! It looks as if it is going to rain.
看那些云!看起来好像要下雨了。
方式状语从句
比较状语从句一般位于句尾,常用as...as、not as/so...as、比较级+than引导。
He is taller than any other student in our school.
他比我们学校的其他任何一个学生都高。
John plays football as well as, if not better than, David.
如果说约翰踢足球踢得不比大卫好,至少他和大卫踢得一样好。
比较状语从句
引导结果状语从句的从属连词有:so that(因此)
so...that...(如此……以至于……);such...that...(如此……以至于……)等。
so...that...与such...that...引导结果状语从句的结构形式为:
so+形容词/副词+that从句
so+形容词+a/an+可数名词单数+that从句
so+many/much/few/little(少)+名词+that从句
such+a/an+形容词+可数名词单数+that从句
such+形容词+可数名词复数/不可数名词+that从句
such+a lot of/lots of+名词+that从句
结果状语从句
He is so experienced a worker that we all believe him.
=He is such an experienced worker that we all believe him.
他是一位经验丰富的工人,我们都相信他。
【温馨提示】在so...that...和such...that...结构中,当“so+adj./adv.”或“such+n.”置于句首时,主句要部分倒装。
他跑得那么快,我抓不住他。
He ran so fast that I I couldn’t catch him.
So fast did he run that I couldn’t catch him.
结果状语从句
1.in order that与so that引导的目的状语
意思是“以便……;为了……”;
状语从句中谓语应用“could/should/might/would+动词原形”。in order that比so that正式,其引导的状语从句可置于主句之前或之后;而so that引导的从句只能置于主句之后。
2.for fear that与in case引导的目的状语从句
for fear that表示“唯恐,生怕”;in case表示“以免,以防”。
目的状语从句
1.Speak louder so that/in order that the people in the hall can all hear you.
大点声讲,以便大厅里的人都能听见。
2.In order that we might get there on time, we should set out early.
为了准时赶到那里,我们应该早点出发。
3.Leave your key with your neighbour in case you lock yourself out one day.
留一把钥匙给你的邻居,以防哪天你把自己锁在门外。
目的状语从句
地点状语从句可由where、wherever和everywhere引导。
You should make it a rule to leave things where you can find them again.
你应当养成习惯,将东西放在你能找到的地方。
Everywhere they went, the distinguished guests were warmly welcomed.
贵宾每到一处都受到了热烈欢迎。
地点状语从句
【温馨提示】
where既可以引导定语从句,也可以引导地点状语从句。引导定语从句时,从句前应该有一个表示地点的名词作先行词,where可以变为“介词+关系代词”形式;而状语从句前则没有先行词。
Put the book at the place where you took it.(定语从句)
Put the book where you took it.(状语从句)
把书放回原来的地方。
地点状语从句
1. ,we won’t wait for him.
如果他在12点前不来,我们就不等他了。
2.Hardly had he gone to bed .
他刚刚睡下,门铃就响了。
3. ,she failed to pass the exam.
尽管她非常努力,但还是没有通过那次考试。(倒装)
If he doesn’t come before 12 o’clock
when the door bell rang
Hard as/though she tried
练一练
4.______________,please remind me of the appointment.
万一我忘记了,请提醒我这次约会。
5.The boy looked around ____________________________.
那个男孩环顾四周,好像在寻找什么东西似的。
6. ______ there is a will, there is a way.
有志者事竟成。
In case I forget
as if he was in search of something
Where
练一练
1.Go over what we have learnt.
2.Finish the Exercises 2 & 3 on Page29 and
exercises in this unit on workbook.
Homework
Unit 3 The world meets China
Discovering Useful Structures—
Review the adverbial clauses
(复习状语从句)
When the national flag rises, we will feel more than happy and proud. As China is making great progress in many fields, we are playing an increasing important role in international society.
状语从句的魅力
Lead-in
Look at the following sentences from the reading passage, classify the adverbial clauses in the sentences and answer the questions.
a.You can imagine how travelers felt when they saw the oasis of Dunhuang ahead of them.
b. If you look up, you can see the paintings and other artworks…
c.…Dunhuang was not as prosperous as it used to be.
d. Given that the theme of the Expo was to promote cultural exchange…,
Dunhuang was the ideal place.
time
condition
comparison
reason
Lead-in
Lead-in
Look at the following sentences from the reading passage answer the questions.
1.Classify the adverbial clauses in the sentences.
condition comparison reason time
2.What other types of adverbial clause can you think of Give some examples.
As long as you put some effort, you will make progress.
You can do everything as you are told to.
the first time I read it
Now that this dream has come true
More adverbial clauses from the reading passage of this unit.
1.the first time引导时间状语从句
I fell in love with Dream of the Red Chamber _________________,and was determined to translate it into Bulgarian.
我第一次读《红楼梦》时就爱上了它,并决心把它译成保加利亚语。
2.now that引导原因状语从句
,my next goal is to translate The Romance of the Three Kingdoms.
由于这个梦想已经实现,我的下一个目标是翻译《三国演义》。
Lead-in
2.Complete the passage with the clauses in the box.
no matter what culture it comes from
so that people can learn about different cultures
as if they are neighbours
that over 15,000 people each year attend them
as the traditional is mixed with the modern
Yo-yo ma is a French-born Chinese American cellist known for his musical talent. In 1998, Ma founded Silk Road, an organization that explores musical traditions in countries___________________________
______________.
The fundamental purpose of Silk Road is to bring people from across the globe together to play and listen to music. Instruments and styles are blended together to create music that is surprising, rich and completely original, ______________________________. What’s more, _________
_____________________________, people can learn about the development of culture as a whole.
no matter what culture it comes from
as the
traditional is mixed with the modern
so that people can learn about
different cultures
The events that Silk Road organizes are either performances, workshops or mixed musical-artistic displays. It is so successful ___________________
_____________________.
People meet as strangers, but they leave ________________________,
learning that different cultures have more in common than they imagined.
as if they are neighbors
each year attend them
that over 15,000 people
时间状语从句
地点状语从句
原因状语从句
条件状语从句
目的状语从句
结果状语从句
方式状语从句
让步状语从句
比较状语从句。
九种状语从句
连词 含义 用法
when 当……时候
while 当……时候
as 一边……一 边……;随着
可与延续性动词或非延续性动词连用;从句动作可以发生在主句动作之前、之后或与主句动作同时发生
只可与延续性动词连用;侧重于主句动作与从句动作相对比
常与延续性动词连用;从句动作与主句动作同时或几乎同时发生
时间状语从句
1.when、while和as引导的时间状语从句
【温馨提示】
如果主句表示的是非延续性动作,而从句用延续性动词的进行时态表示在一段时间内正在进行的动作,则when、while与as可互换使用。
When/While/As I was walking down the street, I came across an old friend.
当我在街上走的时候,碰巧遇到了我的一个老朋友。
时间状语从句
2.表示“一……就……”含义的词或短语引导的时间状语从句
(1)有的名词短语或副词可引导时间状语从句,如:the moment,the minute,the second,the instant,immediately,directly,instantly等。另外as soon as也可引导时间状语从句,从句中用一般时态代替将来时态。
(2)在hardly/scarcely...when...和no sooner...than...结构中,主句用过去完成时,than或when所在的从句用一般过去时。
时间状语从句
【温馨提示】
在hardly/scarcely...when...与no sooner...than...结构中,当hardly,scarcely或no sooner位于句首时,主句要用部分倒装。
They had hardly reached Edinburgh when they were ordered to return to London.
=Hardly had they reached Edinburgh when they were ordered to return to London.
他们刚抵达爱丁堡就接到了回伦敦的命令。
时间状语从句
3.till,until和 not...until/till的用法
until与till两者均表示“直到……为止”,引导时间状语从句。肯定句中,其主句谓语动词必须为延续性动词,表示某动作一直延续到某时间为止。not...until...与not...till...两者均表示“直到……才……”,not 所在的主句的谓语动词必须为非延续性动词,表示某动作直到某时间才开始。until可用于句首,而till不可放在句首,till一般不用于强调句型。
时间状语从句
4.after、before引导的时间状语从句
after表示“在……之后”;before表示“在……之前;还没来得及……就……”。
He changed his name after he left his hometown.
离开家乡后他把名字改了。
Before modern medicine changed the laws of nature, many children died of common childhood diseases.
在现代医学改变自然法则之前,许多孩子死于一些常见的儿童疾病。
时间状语从句
5.since引导的时间状语从句
since意为“自从……以来”,从句的谓语动词一般是非延续性动词,主句的谓语动词一般是延续性动词。since从句的时态若是一般过去时,主句常用现在完成时或现在完成进行时。
They have been friends since they met for the first time in London.
自从在伦敦第一次见面以来,他们一直是朋友。
It has been three years since the war ended.
战争已经结束三年了。
时间状语从句
6.其他常见名词短语引导的时间状语从句
every time每次、each time每次、any time任何时候、next time下次、the first/last time第一次/最后一次。
Every time I meet her I always forget her name.
每次我见到她时,我总记不起她的名字。
The first time I met her, I thought her nice and honest.
我第一次遇见她时,就觉得她友好又诚实。
时间状语从句
1.The father waited until his daughter finished her homework.
那位父亲一直等到他的女儿做完家庭作业。
2.The baby didn’t go to bed until/till his mother returned.
这个婴儿直到他的妈妈回来才睡觉。
3.I had hardly told him the news when he stopped listening.
我刚告诉他那则消息他就不听了。
读一读,译一译
时间状语从句
4.He had no sooner finished his speech than the students started cheering.
他一完成演讲,学生就开始欢呼起来。
5.Researchers in Britain found that when French music was played, sales of French wines went up.
英国的研究者发现,播放法国音乐时,法国葡萄酒的销量会增加。
6.While watching TV, children do not merely absorb words and images.
孩子们在看电视的时候,接收的不只是文字和图像信息。
读一读,译一译
时间状语从句
7.As he grew older, he became less active.
随着他逐渐长大,他变得不那么活泼了。
8.For example, the moment you get on the airplane, start adjusting your biological clock to the destination’s time.
例如,你一上飞机,就开始按照目的地的时间调整你的生物钟。
9.The boy ran off the minute he saw the owner of the orchard.
那个男孩一见到果园的主人就跑开了。
读一读,译一译
时间状语从句
连词 区别
位置 内涵 能否回答 why问句 能否被强调
because 主句前或后 直接原因 能 能
as 主句前或后 双方都知 道的原因 否 否
since/now that 主句前
原因状语从句
1.原因状语从句通常由because、since、as、now that等连词引导。
2.seeing that...(由于;鉴于)、considering that...(考虑到;鉴于)
也可引导原因状语从句。
Seeing (that) the weather is bad, we’ll stay at home.
鉴于天气不好,我们要待在家里了。
Considering (that) it is hand-made, the price seems reasonable.
考虑到它是手工制作,价格还算合理。
原因状语从句
1.Now that you’ve got a chance, you might as well make full use of it.
既然你得到了机会,那么你不妨充分利用它。
2.We had better hurry as it’s getting dark.
天快要黑了,所以我们最好快点。
读一读,译一译
原因状语从句
1.引导条件状语从句的常见从属连词(短语)有:if, unless, as/so long as, in case (万一), once, on condition that, provided/providing (that), supposing/suppose (that), assuming that (假设)等。
You’ll fail the exam unless you study hard.
除非你努力学习,否则你会考试不及格。
条件状语从句
They agreed to lend us the car on condition that we returned it before the weekend.
他们同意把车借给我们,条件是我们必须在周末前归还。
My parents don’t mind what job I do as long as I am happy.
我的父母不在意我从事什么工作,只要我高兴就好。
条件状语从句
2.only if和if only的区别
only if意为“只有;只要……就”,置于句首时主句要用部分倒装结构。
if only意为“但愿;要是……就好了”,引导的从句要用虚拟语气:
与现在的情况相反时,从句用一般过去时;与过去的情况相反时,从句用过去完成时;与将来的情况相反时,谓语用“would/could+动词原形”。
Only if you try your best will you feel relieved.
只要你尽力了,你就会感到欣慰。
If only I had seen you yesterday.
要是我昨天看到你就好了。
条件状语从句
1.他只有更加努力学习才能赶上其他人。
Only if he studies harder can he catch up with others.
2.但愿雨会停!
If only it would stop raining!
3.要是我是一只小鸟就好了。
If only I were a bird.
练一练
条件状语从句
1.although、though、as与while引导的让步状语从句
【温馨提示】
while也可以引导让步状语从句,但只能放在句首,意为“虽然;尽管”。
2.even if与even though引导的让步状语从句
even if与even though表示“即使,纵然”,引导让步状语从句时,可用虚拟语气,也可以用陈述语气。
让步状语从句
3.“疑问词+-ever”引导的让步状语从句
however、whatever、whoever、whenever等引导的让步状语从句相当于“no matter+疑问词”,意为“无论……”。
4.whether...or...引导的让步状语从句
让步状语从句
1.Although he is considered a great writer, his works are not widely read.
虽然他被认为他是一个大作家,但是他的作品还没有被广泛阅读。
2.Although this may sound like a simple task, great care is needed.
尽管这听上去像是一个简单的任务,但是你要非常谨慎。
3.While he loves his students, he is very strict with them.
虽然他爱他的学生,但是他对他们很严格。
让步状语从句
4.I’ll do it, even if it takes me all afternoon.
我要做这件事,即使它将花去我整个下午的时间。
5.Even if I were in your place, I wouldn’t take the job.
即使我处于你的位置,我也不会接受这份工作。
6.Wherever/No matter where you go, I would keep you company.
不管你到哪儿去,我都会陪着你。
7.Whether or not he will stay, I really don’t care.
他要留下来还是要走,我真的不在意。
让步状语从句
引导方式状语从句的从属连词有: as(正如,按照)、as if/though(好像,仿佛)。
as if或as though引导的从句与事实相反时,通常用虚拟语气:
与现在事实相反时,从句用一般过去时;
与过去事实相反时,从句谓语用“had+过去分词”;
与将来事实相反时,从句谓语用“would/could/might+动词原形”。从句内容与事实相符或可能成为事实时,则用陈述句语气。
方式状语从句
1.Please do as the teacher tells you to do.
请按照老师告诉你的做。
2.They treat her as though she were their daughter.
他们待她如亲生女儿一样。
3.Look at the clouds! It looks as if it is going to rain.
看那些云!看起来好像要下雨了。
方式状语从句
比较状语从句一般位于句尾,常用as...as、not as/so...as、比较级+than引导。
He is taller than any other student in our school.
他比我们学校的其他任何一个学生都高。
John plays football as well as, if not better than, David.
如果说约翰踢足球踢得不比大卫好,至少他和大卫踢得一样好。
比较状语从句
引导结果状语从句的从属连词有:so that(因此)
so...that...(如此……以至于……);such...that...(如此……以至于……)等。
so...that...与such...that...引导结果状语从句的结构形式为:
so+形容词/副词+that从句
so+形容词+a/an+可数名词单数+that从句
so+many/much/few/little(少)+名词+that从句
such+a/an+形容词+可数名词单数+that从句
such+形容词+可数名词复数/不可数名词+that从句
such+a lot of/lots of+名词+that从句
结果状语从句
He is so experienced a worker that we all believe him.
=He is such an experienced worker that we all believe him.
他是一位经验丰富的工人,我们都相信他。
【温馨提示】在so...that...和such...that...结构中,当“so+adj./adv.”或“such+n.”置于句首时,主句要部分倒装。
他跑得那么快,我抓不住他。
He ran so fast that I I couldn’t catch him.
So fast did he run that I couldn’t catch him.
结果状语从句
1.in order that与so that引导的目的状语
意思是“以便……;为了……”;
状语从句中谓语应用“could/should/might/would+动词原形”。in order that比so that正式,其引导的状语从句可置于主句之前或之后;而so that引导的从句只能置于主句之后。
2.for fear that与in case引导的目的状语从句
for fear that表示“唯恐,生怕”;in case表示“以免,以防”。
目的状语从句
1.Speak louder so that/in order that the people in the hall can all hear you.
大点声讲,以便大厅里的人都能听见。
2.In order that we might get there on time, we should set out early.
为了准时赶到那里,我们应该早点出发。
3.Leave your key with your neighbour in case you lock yourself out one day.
留一把钥匙给你的邻居,以防哪天你把自己锁在门外。
目的状语从句
地点状语从句可由where、wherever和everywhere引导。
You should make it a rule to leave things where you can find them again.
你应当养成习惯,将东西放在你能找到的地方。
Everywhere they went, the distinguished guests were warmly welcomed.
贵宾每到一处都受到了热烈欢迎。
地点状语从句
【温馨提示】
where既可以引导定语从句,也可以引导地点状语从句。引导定语从句时,从句前应该有一个表示地点的名词作先行词,where可以变为“介词+关系代词”形式;而状语从句前则没有先行词。
Put the book at the place where you took it.(定语从句)
Put the book where you took it.(状语从句)
把书放回原来的地方。
地点状语从句
1. ,we won’t wait for him.
如果他在12点前不来,我们就不等他了。
2.Hardly had he gone to bed .
他刚刚睡下,门铃就响了。
3. ,she failed to pass the exam.
尽管她非常努力,但还是没有通过那次考试。(倒装)
If he doesn’t come before 12 o’clock
when the door bell rang
Hard as/though she tried
练一练
4.______________,please remind me of the appointment.
万一我忘记了,请提醒我这次约会。
5.The boy looked around ____________________________.
那个男孩环顾四周,好像在寻找什么东西似的。
6. ______ there is a will, there is a way.
有志者事竟成。
In case I forget
as if he was in search of something
Where
练一练
1.Go over what we have learnt.
2.Finish the Exercises 2 & 3 on Page29 and
exercises in this unit on workbook.
Homework
