Module 1 Unit 1 Wise men in history Listening & Grammar课件+嵌入音频(共49张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | Module 1 Unit 1 Wise men in history Listening & Grammar课件+嵌入音频(共49张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 13.5MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津深圳版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-07-30 10:53:45 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共49张PPT)
初中英语
九年级上 沪教牛津版
Module 1 Geniuses
Unit 1 Wise men in history
Listening & Grammar
Getting ready
Listen to a radio programme about the ancient Olympics.
Learn how to use question tags.
Learn about different types of sentences.
Listening
Grammar
Reading review
Read paragraphs 1 and 2. Then complete the flow chart about the beginning of the story.
King Hiero asked a crown maker
to make him a golden crown.
He was very happy with it.
He began to doubt that
it was a real golden crown.
He sent the crown to Archimedes and asked him to find out the truth.
________________________________
___________
_____________________________
_______________
_____________________
Read paragraphs 3 to 5 and answer the questions.
What did Archimedes think when he received the crown from King Hiero
What happened when Archimedes got into the bath
Why was Archimedes so excited
Some water ran out of the bath/ran over.
He thought it was difficult to solve the problem.
Because he thought that he could solve the king’s problem.
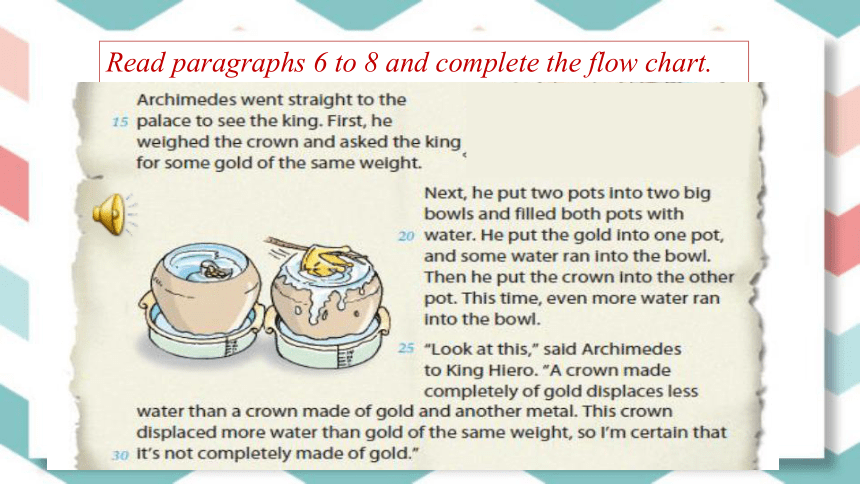
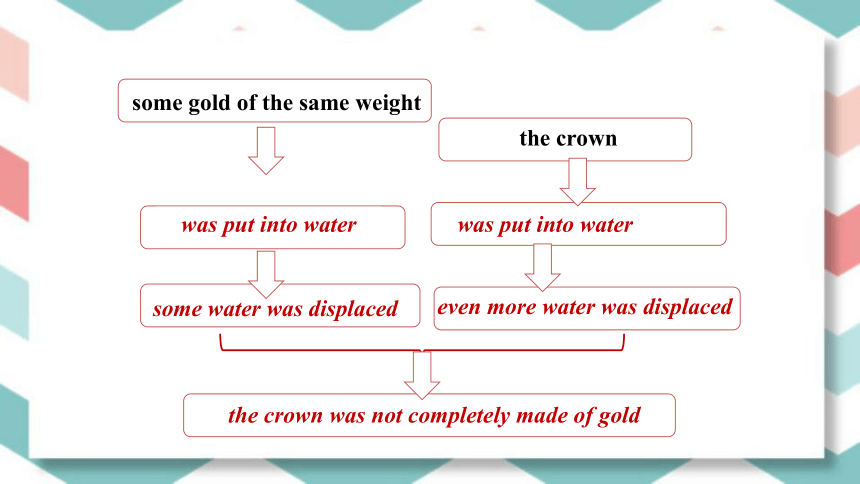
Read paragraphs 6 to 8 and complete the flow chart.
was put into water
some gold of the same weight
some water was displaced
was put into water
even more water was displaced
the crown
the crown was not completely made of gold
A Listen to a radio programme about sports in the ancient Olympics. Match the descriptions with the pictures by writing the numbers 1-4 in the boxes.
4
3
1
2
The ancient Olympics
Listening
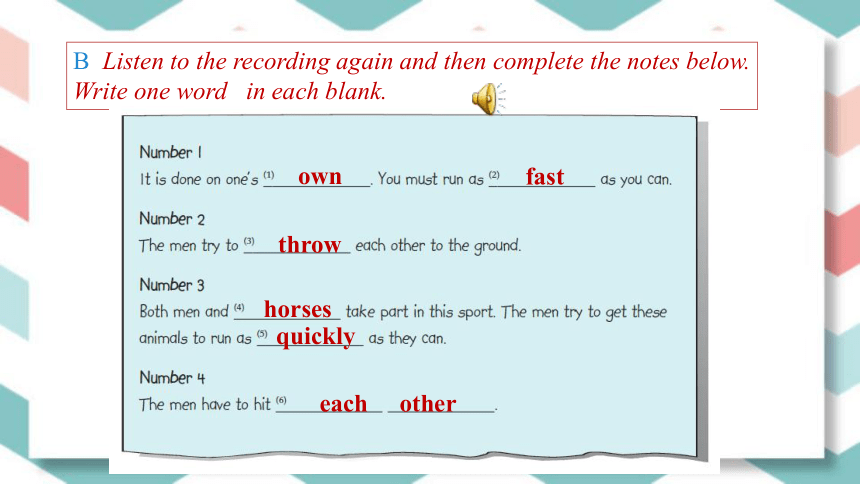
B Listen to the recording again and then complete the notes below. Write one word in each blank.
own
fast
throw
horses
quickly
each other
Show time
Retell a story about a clever kid in Chinese history.
Sima Guang breaks the rain barrel
Kuang Heng bores a hole in the wall for light
Cao Zhi composes a poem within seven paces
Ti Ying saves her father
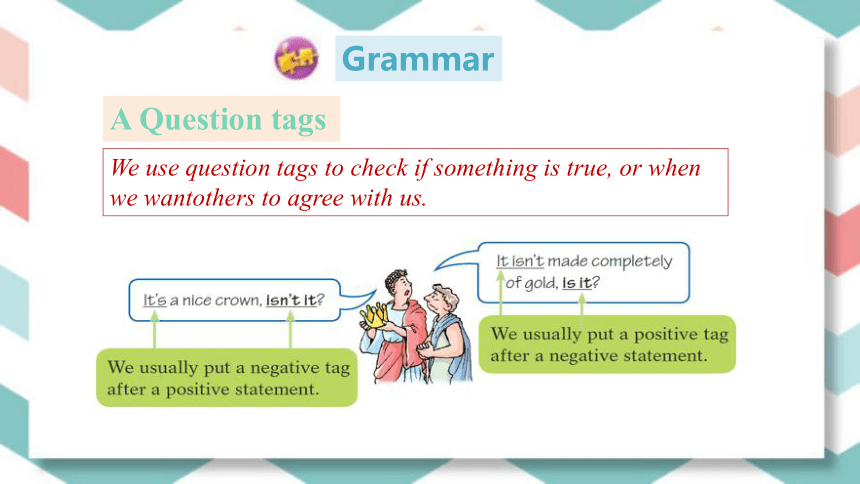
A Question tags
We use question tags to check if something is true, or when we wantothers to agree with us.
Grammar
A Question tags
We use question tags to check if something is true, or when we wantothers to agree with us.
have
Grammar
概念
反意疑问句(Question tags)即附加疑问句。它表示提问人的看法,没有把握,需要对方证实。翻译为“是吗”。
结构
反意疑问句由两部分组成(该两部分的人称时态应保持一致) :陈述句+简短问句。两部分之间用逗号隔开。
反意疑问句
陈述部分肯定式+疑问部分否定式
陈述部分否定式+疑问部分肯定式
主要形式
读法规则
反义疑问句陈述部分用降调,问句部分可升可降。提问者对陈述部分把握较大时,问句部分用降调;反之用升调。
速记方法
前肯后否,前否后肯,前be后be,前情态后情态,前无be或情态后加助,并改为否定,时态一致。
回答
对反意疑问句的回答,无论问题的提法如何,如果事实是肯定的,就用yes,事实是否定的,就要用no。但是,翻译成汉语意思刚好相反,这种回答的yes要译成“不”,no要译成“是”。
—He likes playing football, doesn’t he
他喜欢踢足球,不是吗?
—Yes, he does. / No, he doesn’t.
是的。/ 不是。
—His sister didn’t attend the meeting, did she
他妹妹没有参加会议,是吗?
—Yes, she did. / No, she didn’t.
不,她参加了。/ 是的,她没参加。
用法:
当陈述句中含有be动词,助动词,或是情态动词时,反问句部分由这些词加上主语人称代词构成,
Be动词包括: am, is, are, was, were
助动词有:do, does, did, have/has(用在现在完成时)
情态动词有:can, could, may, might, must,
will, would, shall, should
2. 反意疑问句的陈述部分带有little, few, never, hardly, seldom, nobody, nothing等否定意义的词时,问句部分用肯定式。
如:
①She never tells a lie, does she
(不用doesn’t she )
②He was seldom late, was he
(不用wasn’t he )
3. 祈使句用于反意疑问句中
a. 肯定的祈使句, 用will you(表示请求) / won’t you(表示提醒)。
Listen to me, will you (won’t you)
b. 否定的祈使句, 用will you。
Don’t play with fire, will you
c. Let’s 和 Let us的祈使句:
Let’s go to school, shall we
Let us help you, will you
Let’s …, shall we
Let us …, will you
Things to remember
When we answer tag questions, we use yes or no according to the facts.
The runner didn’t win the race, did he
Yes, he did. (He won the race.)
No, he didn’t. (He did not win the race.)
Pay attention to the following special question tags.
Take out your books, will you
Let’s get out of here, shall we
You’re never late, are you
We put a comma (,) before a question tag.
陈述句是陈述一个事实或者说话人的看法的,陈述句分为肯定句和否定句。
陈述句句末用句号(。),朗读时用降调。
定义:
陈述句
结构:
陈述句的肯定式
1.主语+系动词+表语
Tina is my friend.
2. 主语+不及物动词
The river is flooded.
3.主语+及物动词+宾语
He bought an umbrella.
4.主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语
He passed me a cup of tea.
5.主语+及物动词+宾语+宾语补足语
She told me to buy a ticket.
II. 陈述句的否定式
主语+be+not+表语
He is not a teacher.
主语+助动词/情态动词+not+谓语动词+其他
I don't think you are right.
He hasn't yet paid the money. 他尚未付钱。
使用“not”以外的否定词:
副词:never, seldom, hardly, little,neither等。
She seldom comes to see me.
她不常来看我。
b. 形容词:no, few, little等。
He has few friends in Hong Kong.
他在香港几乎没有朋友。
c. 代词:nothing, nobody, none等。
I found nobody in that house.
在那栋房子里我没看到任何人。
疑问句的主要交际功能是提出问题,询问情况。分为一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
疑问句句末用问号( )。
定义:
疑问句
一般疑问句通常用来询问一件事情是否属实。答句通常是"yes或no"。
句型一:Be +主语+ …
Are these books on the desk 这些书在桌子上吗?
句型二:Do/Does/Did+主语+谓语+…
Do you like English 你喜欢英语吗?
句型三:情态动词+主语+谓语+…
Must I finish my homework now
我必须现在完成我的家庭作业吗?
一般疑问句
句型四:Have/Has+主语+过去分词+…
Have you heard from him
你收到他的来信吗?
另外,还有以be动词、助动词或情态动词的否定缩写形式开头的一般疑问句,这种句子一般表示请求、惊讶和对事物的看法等,回答时所用的yes和no表达的意思和汉语的习惯不同。例如:
-- Isn't he tall 难道他不高吗?
-- Yes, he is. 不,他很高。
对句中某一成分提问的句子叫特殊疑问句。特殊疑问句以疑问词开头。
常用的疑问词有:what、who、whose、which、when、where、how、why等。不能用yes或no回答。朗读时用降调。
例如:
Who is singing in the room
What class are you in
特殊疑问句
句式: 特殊疑问词 + 一般疑问句
疑问词分为三类
疑问代词: what, who, which, whose, who
疑问词组: what(which, whose)+名词
疑问副词: when, where, why, how
We use ‘Wh-’ questions to ask for information about someone or something.
‘Wh-’ word Use in questions
What To find out sth.
Who To find out about person
When To ask about time
Where To ask about place
Why To ask about the reason
How To find out “in what way’
How long To talk about “the degree”
Ⅰ. what
问姓名;问物品;问职业;
what about 用来征求意见或询问消息,相当于how about
what colour 问颜色;
what class 问哪个班级;
what size 问尺寸
Ⅱ. who---Person (对人提问)
-- Who will visit you tomorrow
-- My father.
Ⅲ. when---Time (对时间提问)
-- When will you finish your homework
-- Tomorrow.
Ⅴ. why---Reason (对原因提问)
-- Why are you late
-- Because I missed the bus.
Ⅳ. where---Place (询问地点、场所)
Where do you live?
Where are you going?
- How do you go to school?(问方式)
- I go to school by bus.
- How are you?(问健康)
-I’m fine. Thank you!
How is the weather today?(问天气)
(2) How+形容词(副词)~? 询问年龄、身高、数量、次数、距离……
How much are they (问价格)
Ⅵ. how
(1) How… 询问做某事的方法、手段及健康、天气……
词组 词义 例句
How many 多少(可数) How many apples do you want
How much 多少(不可数) How much meat shall I buy
How old 多大(岁数) How old are you
How long 多长时间 (多久) How long will you stay here
多长(长度) How long is the river
How often 多久(频率) How often do you visit your grandma
How soon 多快(时间) How soon will he be back
How far 多远(距离) How far is it from A to B
选择疑问句
定义:
提出两种或两种以上的情况,要求对方选择一种情况回答的问句。两种情况之间用or连接。
回答:
回答不用yes/no,用一个完整的句子或其省略形式。语调前升后降。
分类:
一般选择疑问句和特殊选择疑问句
一般选择疑问句:
一般疑问句+or+被选择部分?
-- Do you like apples or pears
-- I like pears.
2. 特殊选择疑问句:特殊疑问句, +A or B
-- Which would you like better, tea or coffee
-- I like coffee.
祈使句的结构及用法
祈使句表示命令、请求、建议、或劝告等等。主语通常被省略,谓语动词用原形,句末用感叹号或句号,读降调。
祈使句
1.肯定的祈使句
1) 句型:以动词原形开头(省略主语)
Come in!
2) 动词前加do, 加强语气。表“务必,一定”
Do come on time! 一定要准时来!
Do look out! 一定要小心!
2. 否定祈使句
1) Don‘t +动词原形 Don't be late!
2) Let‘s + not + 动词原形 Let's not speak loudly!
1.由what引导的感叹句
What + a/an +形容词 + 可数名词的单数+ 主语 + 谓语!
What a beautiful girl she is!
2) What + 形容词 + 可数名词复数 + 主语 +谓语!
What important jobs they have done!
3) What+形容词+不可数名词+主语+谓语!
What sweet water it is!
感叹句
2.由how引导的感叹词
1) How+形容词或副词+主语+谓语!
How interesting the dog is!
2) How+形容词+a/an+可数名词的单数形式+主语+谓语!
How useful a subject it is!
3) How+主语+谓语!
How time flies!
3.一些特殊形式
陈述句、疑问句或祈使句+感叹号,表示某种强烈的感情
He runs so fast!
2) 一个词或词组
Wonderful! \ Look out! \ Great!
3) 以there \ here 等副词开头
There she is!
There goes the bell!
4. 如何判断用what还是用how来引导感叹句
方法一:凡是用a\an开头的,多用what
方法二:凡是形容词+名词,多用what
方法三:其他一般用how
There are four types of sentences.
Positive statement
Statements
One day in ancient Greece, King Hiero asked
a crown maker to make him a golden crown.
Negative statement
It was not a real golden crown.
A statement talks about a certain person or thing.
It usually ends with a full stop (.).
B Sentence types
We use questions to ask for information.
A question ends with a question mark ( ).
Questions
Is it made completely of gold
It’s a nice crown, isn’t it
Yes/No questions
Wh-question
What should I do
Alternative
question
Tag question
What is the crown made of,
gold or something else
When we want to give commands or make requests or suggestions, we use the imperatives. An imperative sentence ends with a full stop (.) or an exclamation mark (!).
Imperatives
Look at this.
Please give me some gold of the same weight.
Watch out!
Keep quiet!
When we want to express strong feelings, we use exclamations.
An exclamation usually ends with an exclamation mark (!).
Exclamations
How excited Archimedes was!
What a bad man the crown maker is!
B2 Look at the sentences below and label the sentence types.
Imperative
Tag question
Positive statement
Exclamation
Yes/No question
Negative statement
1 How can I find out___ 5 Please close the window___
2 The crown is nice___ 6 What a nice crown___
3 How wonderful___ 7 This is difficult, isn’t it___
4 The king was not happy___ 8 Leave me alone___
B1 Add a full stop (.), a question mark ( ) or an exclamation mark (!) to the end of the following sentences.
.
!
.
./!
!
./!
Homework
背诵课文。
H
初中英语
九年级上 沪教牛津版
Module 1 Geniuses
Unit 1 Wise men in history
Listening & Grammar
Getting ready
Listen to a radio programme about the ancient Olympics.
Learn how to use question tags.
Learn about different types of sentences.
Listening
Grammar
Reading review
Read paragraphs 1 and 2. Then complete the flow chart about the beginning of the story.
King Hiero asked a crown maker
to make him a golden crown.
He was very happy with it.
He began to doubt that
it was a real golden crown.
He sent the crown to Archimedes and asked him to find out the truth.
________________________________
___________
_____________________________
_______________
_____________________
Read paragraphs 3 to 5 and answer the questions.
What did Archimedes think when he received the crown from King Hiero
What happened when Archimedes got into the bath
Why was Archimedes so excited
Some water ran out of the bath/ran over.
He thought it was difficult to solve the problem.
Because he thought that he could solve the king’s problem.
Read paragraphs 6 to 8 and complete the flow chart.
was put into water
some gold of the same weight
some water was displaced
was put into water
even more water was displaced
the crown
the crown was not completely made of gold
A Listen to a radio programme about sports in the ancient Olympics. Match the descriptions with the pictures by writing the numbers 1-4 in the boxes.
4
3
1
2
The ancient Olympics
Listening
B Listen to the recording again and then complete the notes below. Write one word in each blank.
own
fast
throw
horses
quickly
each other
Show time
Retell a story about a clever kid in Chinese history.
Sima Guang breaks the rain barrel
Kuang Heng bores a hole in the wall for light
Cao Zhi composes a poem within seven paces
Ti Ying saves her father
A Question tags
We use question tags to check if something is true, or when we wantothers to agree with us.
Grammar
A Question tags
We use question tags to check if something is true, or when we wantothers to agree with us.
have
Grammar
概念
反意疑问句(Question tags)即附加疑问句。它表示提问人的看法,没有把握,需要对方证实。翻译为“是吗”。
结构
反意疑问句由两部分组成(该两部分的人称时态应保持一致) :陈述句+简短问句。两部分之间用逗号隔开。
反意疑问句
陈述部分肯定式+疑问部分否定式
陈述部分否定式+疑问部分肯定式
主要形式
读法规则
反义疑问句陈述部分用降调,问句部分可升可降。提问者对陈述部分把握较大时,问句部分用降调;反之用升调。
速记方法
前肯后否,前否后肯,前be后be,前情态后情态,前无be或情态后加助,并改为否定,时态一致。
回答
对反意疑问句的回答,无论问题的提法如何,如果事实是肯定的,就用yes,事实是否定的,就要用no。但是,翻译成汉语意思刚好相反,这种回答的yes要译成“不”,no要译成“是”。
—He likes playing football, doesn’t he
他喜欢踢足球,不是吗?
—Yes, he does. / No, he doesn’t.
是的。/ 不是。
—His sister didn’t attend the meeting, did she
他妹妹没有参加会议,是吗?
—Yes, she did. / No, she didn’t.
不,她参加了。/ 是的,她没参加。
用法:
当陈述句中含有be动词,助动词,或是情态动词时,反问句部分由这些词加上主语人称代词构成,
Be动词包括: am, is, are, was, were
助动词有:do, does, did, have/has(用在现在完成时)
情态动词有:can, could, may, might, must,
will, would, shall, should
2. 反意疑问句的陈述部分带有little, few, never, hardly, seldom, nobody, nothing等否定意义的词时,问句部分用肯定式。
如:
①She never tells a lie, does she
(不用doesn’t she )
②He was seldom late, was he
(不用wasn’t he )
3. 祈使句用于反意疑问句中
a. 肯定的祈使句, 用will you(表示请求) / won’t you(表示提醒)。
Listen to me, will you (won’t you)
b. 否定的祈使句, 用will you。
Don’t play with fire, will you
c. Let’s 和 Let us的祈使句:
Let’s go to school, shall we
Let us help you, will you
Let’s …, shall we
Let us …, will you
Things to remember
When we answer tag questions, we use yes or no according to the facts.
The runner didn’t win the race, did he
Yes, he did. (He won the race.)
No, he didn’t. (He did not win the race.)
Pay attention to the following special question tags.
Take out your books, will you
Let’s get out of here, shall we
You’re never late, are you
We put a comma (,) before a question tag.
陈述句是陈述一个事实或者说话人的看法的,陈述句分为肯定句和否定句。
陈述句句末用句号(。),朗读时用降调。
定义:
陈述句
结构:
陈述句的肯定式
1.主语+系动词+表语
Tina is my friend.
2. 主语+不及物动词
The river is flooded.
3.主语+及物动词+宾语
He bought an umbrella.
4.主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语
He passed me a cup of tea.
5.主语+及物动词+宾语+宾语补足语
She told me to buy a ticket.
II. 陈述句的否定式
主语+be+not+表语
He is not a teacher.
主语+助动词/情态动词+not+谓语动词+其他
I don't think you are right.
He hasn't yet paid the money. 他尚未付钱。
使用“not”以外的否定词:
副词:never, seldom, hardly, little,neither等。
She seldom comes to see me.
她不常来看我。
b. 形容词:no, few, little等。
He has few friends in Hong Kong.
他在香港几乎没有朋友。
c. 代词:nothing, nobody, none等。
I found nobody in that house.
在那栋房子里我没看到任何人。
疑问句的主要交际功能是提出问题,询问情况。分为一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
疑问句句末用问号( )。
定义:
疑问句
一般疑问句通常用来询问一件事情是否属实。答句通常是"yes或no"。
句型一:Be +主语+ …
Are these books on the desk 这些书在桌子上吗?
句型二:Do/Does/Did+主语+谓语+…
Do you like English 你喜欢英语吗?
句型三:情态动词+主语+谓语+…
Must I finish my homework now
我必须现在完成我的家庭作业吗?
一般疑问句
句型四:Have/Has+主语+过去分词+…
Have you heard from him
你收到他的来信吗?
另外,还有以be动词、助动词或情态动词的否定缩写形式开头的一般疑问句,这种句子一般表示请求、惊讶和对事物的看法等,回答时所用的yes和no表达的意思和汉语的习惯不同。例如:
-- Isn't he tall 难道他不高吗?
-- Yes, he is. 不,他很高。
对句中某一成分提问的句子叫特殊疑问句。特殊疑问句以疑问词开头。
常用的疑问词有:what、who、whose、which、when、where、how、why等。不能用yes或no回答。朗读时用降调。
例如:
Who is singing in the room
What class are you in
特殊疑问句
句式: 特殊疑问词 + 一般疑问句
疑问词分为三类
疑问代词: what, who, which, whose, who
疑问词组: what(which, whose)+名词
疑问副词: when, where, why, how
We use ‘Wh-’ questions to ask for information about someone or something.
‘Wh-’ word Use in questions
What To find out sth.
Who To find out about person
When To ask about time
Where To ask about place
Why To ask about the reason
How To find out “in what way’
How long To talk about “the degree”
Ⅰ. what
问姓名;问物品;问职业;
what about 用来征求意见或询问消息,相当于how about
what colour 问颜色;
what class 问哪个班级;
what size 问尺寸
Ⅱ. who---Person (对人提问)
-- Who will visit you tomorrow
-- My father.
Ⅲ. when---Time (对时间提问)
-- When will you finish your homework
-- Tomorrow.
Ⅴ. why---Reason (对原因提问)
-- Why are you late
-- Because I missed the bus.
Ⅳ. where---Place (询问地点、场所)
Where do you live?
Where are you going?
- How do you go to school?(问方式)
- I go to school by bus.
- How are you?(问健康)
-I’m fine. Thank you!
How is the weather today?(问天气)
(2) How+形容词(副词)~? 询问年龄、身高、数量、次数、距离……
How much are they (问价格)
Ⅵ. how
(1) How… 询问做某事的方法、手段及健康、天气……
词组 词义 例句
How many 多少(可数) How many apples do you want
How much 多少(不可数) How much meat shall I buy
How old 多大(岁数) How old are you
How long 多长时间 (多久) How long will you stay here
多长(长度) How long is the river
How often 多久(频率) How often do you visit your grandma
How soon 多快(时间) How soon will he be back
How far 多远(距离) How far is it from A to B
选择疑问句
定义:
提出两种或两种以上的情况,要求对方选择一种情况回答的问句。两种情况之间用or连接。
回答:
回答不用yes/no,用一个完整的句子或其省略形式。语调前升后降。
分类:
一般选择疑问句和特殊选择疑问句
一般选择疑问句:
一般疑问句+or+被选择部分?
-- Do you like apples or pears
-- I like pears.
2. 特殊选择疑问句:特殊疑问句, +A or B
-- Which would you like better, tea or coffee
-- I like coffee.
祈使句的结构及用法
祈使句表示命令、请求、建议、或劝告等等。主语通常被省略,谓语动词用原形,句末用感叹号或句号,读降调。
祈使句
1.肯定的祈使句
1) 句型:以动词原形开头(省略主语)
Come in!
2) 动词前加do, 加强语气。表“务必,一定”
Do come on time! 一定要准时来!
Do look out! 一定要小心!
2. 否定祈使句
1) Don‘t +动词原形 Don't be late!
2) Let‘s + not + 动词原形 Let's not speak loudly!
1.由what引导的感叹句
What + a/an +形容词 + 可数名词的单数+ 主语 + 谓语!
What a beautiful girl she is!
2) What + 形容词 + 可数名词复数 + 主语 +谓语!
What important jobs they have done!
3) What+形容词+不可数名词+主语+谓语!
What sweet water it is!
感叹句
2.由how引导的感叹词
1) How+形容词或副词+主语+谓语!
How interesting the dog is!
2) How+形容词+a/an+可数名词的单数形式+主语+谓语!
How useful a subject it is!
3) How+主语+谓语!
How time flies!
3.一些特殊形式
陈述句、疑问句或祈使句+感叹号,表示某种强烈的感情
He runs so fast!
2) 一个词或词组
Wonderful! \ Look out! \ Great!
3) 以there \ here 等副词开头
There she is!
There goes the bell!
4. 如何判断用what还是用how来引导感叹句
方法一:凡是用a\an开头的,多用what
方法二:凡是形容词+名词,多用what
方法三:其他一般用how
There are four types of sentences.
Positive statement
Statements
One day in ancient Greece, King Hiero asked
a crown maker to make him a golden crown.
Negative statement
It was not a real golden crown.
A statement talks about a certain person or thing.
It usually ends with a full stop (.).
B Sentence types
We use questions to ask for information.
A question ends with a question mark ( ).
Questions
Is it made completely of gold
It’s a nice crown, isn’t it
Yes/No questions
Wh-question
What should I do
Alternative
question
Tag question
What is the crown made of,
gold or something else
When we want to give commands or make requests or suggestions, we use the imperatives. An imperative sentence ends with a full stop (.) or an exclamation mark (!).
Imperatives
Look at this.
Please give me some gold of the same weight.
Watch out!
Keep quiet!
When we want to express strong feelings, we use exclamations.
An exclamation usually ends with an exclamation mark (!).
Exclamations
How excited Archimedes was!
What a bad man the crown maker is!
B2 Look at the sentences below and label the sentence types.
Imperative
Tag question
Positive statement
Exclamation
Yes/No question
Negative statement
1 How can I find out___ 5 Please close the window___
2 The crown is nice___ 6 What a nice crown___
3 How wonderful___ 7 This is difficult, isn’t it___
4 The king was not happy___ 8 Leave me alone___
B1 Add a full stop (.), a question mark ( ) or an exclamation mark (!) to the end of the following sentences.
.
!
.
./!
!
./!
Homework
背诵课文。
H
