人教版 选择性必修二 Unit 1 Science and Scientists Learning About Language课件(共35张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版 选择性必修二 Unit 1 Science and Scientists Learning About Language课件(共35张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 12.8MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-08-17 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
(共35张PPT)
人教版(2019)选择性必修二
Unit 1 Science and Scientists
Learning About Language
Build up your vocabulary
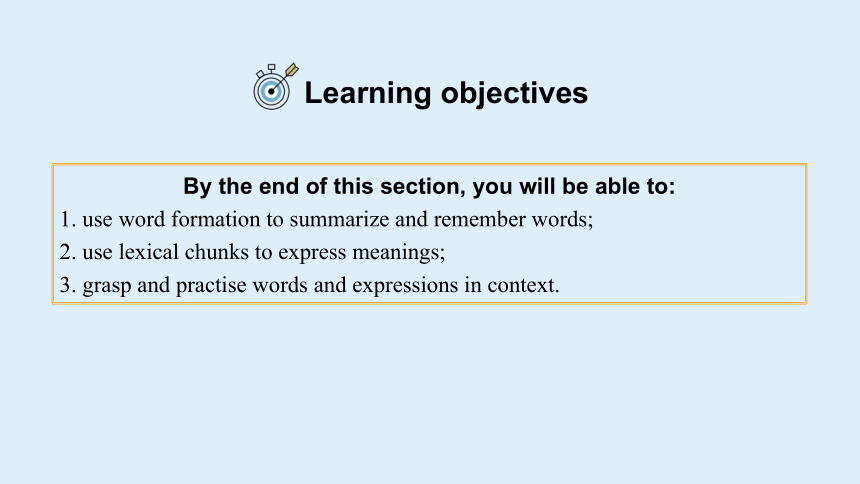
Learning objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
1. use word formation to summarize and remember words;
2. use lexical chunks to express meanings;
3. grasp and practise words and expressions in context.
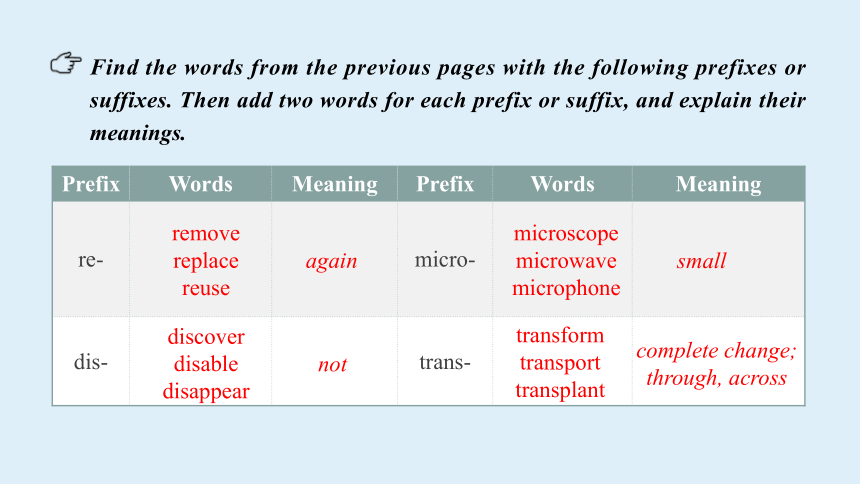
Find the words from the previous pages with the following prefixes or suffixes. Then add two words for each prefix or suffix, and explain their meanings.
Prefix Words Meaning Prefix Words Meaning
re- micro-
dis- trans-
remove
replace
reuse
microscope
microwave
microphone
discover
disable
disappear
transform
transport
transplant
again
not
small
complete change; through, across
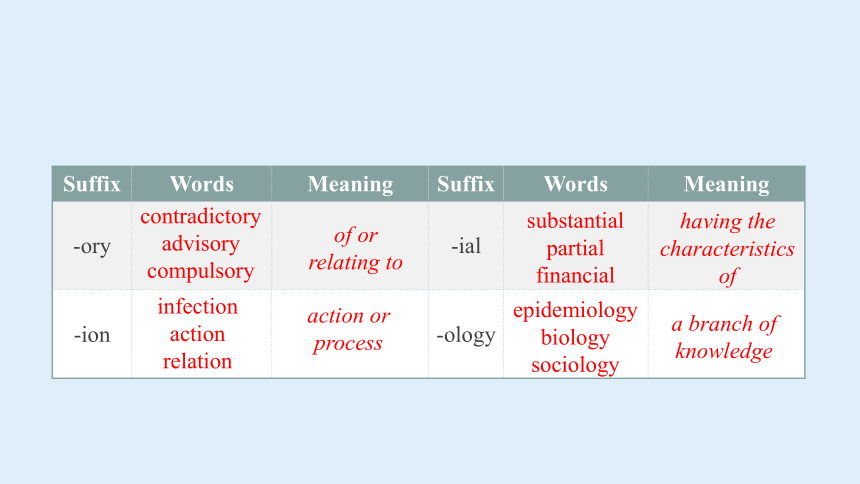
Suffix Words Meaning Suffix Words Meaning
-ory -ial
-ion -ology
contradictory
advisory
compulsory
infection
action
relation
substantial
partial
financial
epidemiology
biology
sociology
of or
relating to
action or process
having the characteristics of
a branch of knowledge
Make phrases by combining the words in the left box with those on the right. Then complete the sentences using these phrases.
Many scientists _____________ the view that it is human activity that has caused global warming.
He was to ___________ the accident because he drove on the wrong side of the road.
The man _____________ being behind the robbery was seen crossing the street.
Since heart disease is often ___________ our lifestyle choices, we need to make healthy living an important part of our lives.
to of for
subscribe suspect blame link
subscribe to
blame for
suspected of
linked to
Replace the underlined parts with suitable words from the box.
It is not unusual for an athlete to be well known while he is active, and quickly forgotten when his athletic career is over.
I’m sure she’ll deal with the changes very well because she’s very adaptable.
He was ready to serve dinner to his friends when he realised that he had forgotten to turn on the oven and the meat was not cooked yet.
He used his great influence to change the thinking of the scientific community on this issue.
Scientists have collected more data than expected to prove the theory.
raw a household name substantial statistics handle
raw
substantial
statistics
a household name
handle
Read this passage about medical plete it using the words below.
British scientists believe they may have found a way to fight the common cold. It blocks a key protein in the body’s cells that is to _______ for the spread of cold-causing virus. Targeting the host rather than the _________ was a bit non-traditional but made sense because it was tricky to target the virus. Cold-causing virus are not only of _________ kinds, they also ___________ rapidly, meaning they can quickly develop resistance to medicine. Researchers are working on making a form of medicine that can be taken directly into one’s lungs, to _________ the chance of side effects. Though these scientists have made __________ advances in their research, further _______ is needed to make sure such drugs are not so _________ that they harm the body.
infection multiple decrease severe
transform proof blame substantial
infection
multiple
transform
blame
decrease
substantial
proof
severe
Discover useful structures
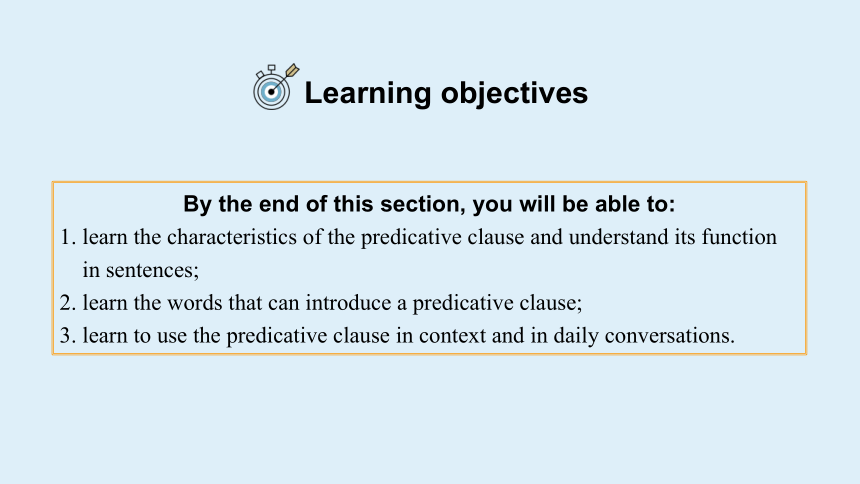
Learning objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
1. learn the characteristics of the predicative clause and understand its function
in sentences;
2. learn the words that can introduce a predicative clause;
3. learn to use the predicative clause in context and in daily conversations.
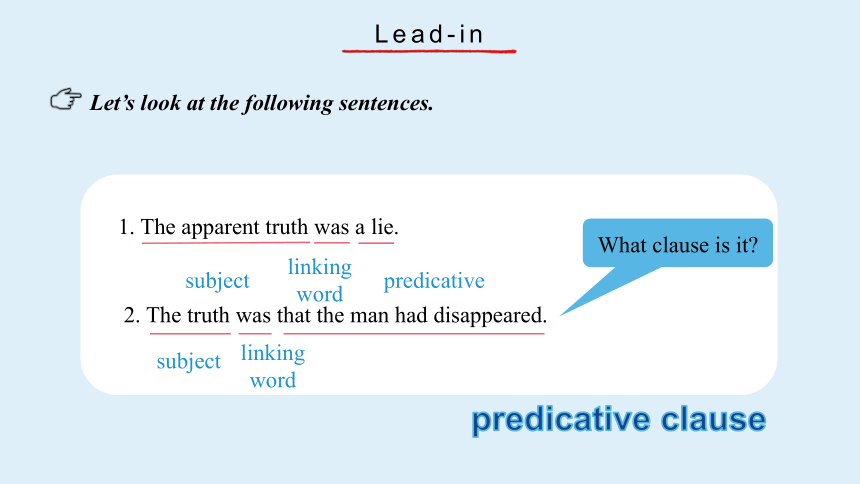
1. The apparent truth was a lie.
2. The truth was that the man had disappeared.
Let’s look at the following sentences.
Lead-in
subject
linking
word
predicative clause
What clause is it
subject
linking
word
predicative
Underline all the examples in the reading passage where noun clauses are used as the predicative. Then state their meaning and functions.
One theory was that bad air caused the disease.
Another was that cholera was caused by an infection from germs in food or water.
It seemed that the woman liked the water from the pump so much that she had it delivered to her house every day.
The truth was that the water from the Broad Street pump had been infected by waste.
Presentation
Predicative Clauses
( 表语从句)
定义
在复合句中作表语的从句叫作表语从句。表语从句经常位于主句的系动词之后,对主语进行解释、说明,使主语的内容具体化。与宾语从句和主语从句一样,表语从句也是一种名词性从句。
e.g. The question is who broke the vase.
My suggestion is that we (should) start early tomorrow.
连
系
动
词
状态类: be动词, seem, appear, keep, remain, stay…
变化类: become, get, turn, grow, fall, come, go …
感官类: look, smell, taste, sound, feel …
连接词 连词 在从句中不作成分 that, whether, as if, as though, because …
连接代词 在从句中作主语、宾语、表语、定语 what, who, whom, whose, which, whatever, whoever, whichever …
连接副词 在从句中作状语 when, where, how, why …
表语从句的引导词
表语从句要点归纳
1. 表语从句一定要用陈述语序。
e.g. What I want to know is when she will be back.
Raw material is what we are badly in need of.
2. that引导表语从句时,在句中只起连接作用,不充当句子成分,无实
际意义,有时省略。
e.g. The fact is (that) she never liked him.
The trouble is that I have lost his address.
One theory was that bad air caused the disease.
3. whether引导表语从句时,起连接作用,意为“是否,到底”,在句
中不作任何成分。 if不能引导表语从句。
e.g. The question is whether your uncle will offer help to us.
Her confusion is whether she should stick to her own way of life or
follow the American way.
4. 连接代词who, whom, whose, what, which, whoever, whatever,
whichever等除在句中起连接作用外,在从句中还充当主语、宾语、
表语或定语,本身具有词义。
e.g. The question is who will be the successful applicant for the summer job
at the law firm.
Taking a year off from school to travel abroad is what is generally called
a gap year.
5. 连接副词where, when, why, how等除在句中起连接作用,在从句中
还充当地点、时间、原因、方式状语,本身具有词义。
e.g. The question is when they will start the project.
The question is how he did it.
What John Snow was determined to find out was why the 1854
outbreak of cholera in London had caused over 500 deaths
within ten days.
6. That is because ... 指原因或理由;
That is why ... 指由于某种原因所造成的后果。
e.g. Bruce did not watch the game last night. That was because he had to
help his little sister with her homework.
Bob had seen the film before. That was why he did not see it yesterday.
7. 需使用虚拟语气的表语从句
在advice, suggestion, order, proposal等表示建议、劝告、命令等含义的名词后的表语从句中,谓语动词需用“should +动词原形”形式,should可省略。
e.g. My suggestion is that we (should) start early tomorrow.
Our decision is that the school remain closed.
Answer the following questions using the information from the reading passage as well as the predicative clauses.
Example
What was it that John Snow showed to the world
→What John Snow showed to the world was how cholera could be overcome.
1. What was Snow’s discovery in two particular streets in London
Snow’s discovery in two particular streets in London was that _____________
_______________________________________________________________.
the cholera
outbreak was so severe that more than 500 people died in ten days
2. What was Snow determined to find out during the 1854 outbreak of cholera in
London
What Snow was determined to find out was why ________________________
_________________________________.
3. What were the exact places Snow marked on the map
The exact places Snow marked on the map were where ___________________
__________.
4. What was the finding that Snow announced
Snow’s finding was that _________________________________________.
the outbreak of cholera had
caused over 500 deaths within ten days
all those who died
the pump water carried cholera germs
had lived
as if that what who when how why whose which whether
A Absolutely. You may not believe it, but that was ________ happened at the initial stage of our
group’s research on developing a vaccine for malaria.
B Yes, it is. And it seemed _______ all the theories were useful, but the fact was _________ we
couldn’t persuade one another that one theory was better than another.
C Exactly. The problem was not about ___________ all our theories were equally good, but in
deciding __________________ theory to depend upon.
D We realised that what we cared about was not __________ aspect we needed to develop a
theory in, but rather ______ we can reduce the cost of a vaccine without reducing its effect!
E You’re right. At last, we became focused on the key issue, which was ______ we had to carry
out the research in the first place.
David is talking to Maria about their scientific research project. First complete David’s lines (A-E), using the words in the box. Then put David’s lines in the correct order and practise the conversation.
Practice
what
as if
that
which/what
which/ what/ whose
how
why
whether
Maria: This mix of theory and data is one of the key characteristics of what we call science.
David: ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Maria: With your theoretical framework
David: ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Maria: Deciding on a theory is definitely of critical importance.
David: ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Maria: This was when you should have calmed down and got down to doing some solid work.
David: ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Maria: So what happened in the end
David: ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
C Exactly. The problem was not about whether all our theories were equally good, but in
deciding which/ what/ whose theory to depend upon.
A Absolutely. You may not believe it, but that was what happened at the initial stage of our
group’s research on developing a vaccine for malaria.
D We realised that what we cared about was not which/what aspect we needed to develop a
theory in, but rather how we can reduce the cost of a vaccine without reducing its effect!
B Yes, it is. And it seemed as if all the theories were useful, but the fact was that we
couldn’t persuade one another that one theory was better than another.
E You’re right. At last, we became focused on the key issue, which was why we had to carry
out the research in the first place.
Complete the following ideas by famous scientists with a word or expression that introduces a predicative clause.
1. Research is __________ I’m doing when I don’t know what I’m doing.
(Werner von Braun)
2. The saddest aspect of life right now is __________ science gathers knowledge faster
than society gathers wisdom.
(Isaac Asimov)
3. An expert can be __________ has made all the mistakes that can be made in a very
narrow field.
(Niels Bohr)
what
that
Workbook
as though because that what whoever why
whoever
4. ... when different experiments give you the same result, it is no longer subject to
your opinion. That’s the good thing about science: It’s true whether or not you
believe in it. That’s __________ it works.
(Neil deGrasse Tyson)
5. This applied science, which saves work and makes life easier, brings us little
happiness. That is __________ we have not yet learnt to make sensible use of it!
(Albert Einstein)
6. There are only two ways to live your life. One is __________ nothing is a miracle.
The other is __________ everything is a miracle.
(Albert Einstein)
why
because
as though because that what whoever why
as though
as though
Workbook
Complete the conversations using noun clauses as the predicative.
1. A: Papermaking, printing, gunpowder, and the compass are the four great inventions
of ancient China. They are significant contributions of the Chinese nation to the
world.
B: Sure, they are. What I want to know though is ____________________________
___________________________________________.
2. A: The ancient Chinese were the first to invent paper and printing. Then they went
on to invent books and had opened bookshops in many cities.
B: What I’m curious about is ____________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________.
which one is the greatest in how
these inventions have changed China and the world
who invented paper/how people made the first paper/
when ink was invented/ what paper was made from/ when and how printing spread
to the rest of the world/ how records were kept before the invention of paper
Workbook
3. A: The compass is a special invention of ancient China, dating back to as early as
the Warring States Period.
B: Yes. It seems ______________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
___________________________.
4. A: Gunpowder was originally used for making fireworks.
B: But what surprises me is _____________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________.
that the compass was particularly useful/ as if people had to depend on the positions of the sun, the moon, and so on when they were at sea before the compass was invented/ that ancient Chinese had developed a good knowledge of magnetism
that gunpowder was not used initially for firearms/
how it is so unexpectedly used today/ how heavily mining depends upon it/
that it has been generally used not only in industries but in wars across the world
Workbook
5. A: After the discovery of medicine, acupuncture was invented in China,
acupuncture is a treatment which doesn’t involve any drugs. Very thin needles
are put in certain parts of a person’s body.
B: Really What puzzles me is __________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
____________.
6. A: High-speed trains, mobile payments, the bike-sharing system, and online
shopping are considered by some as the new “four inventions” of China.
B: Is that so I feel/ It seems ____________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________.
who first started this practice/ for whom this practice was first done/ why anyone would stick a needle in their body, even to become well
that these inventions have really made our lives easier/
that every Chinese is proud of the new “four inventions”/ as if I could not live without them, especially when it comes to online shopping/ that we all benefit from all these things/ that we may have to remember that every coin has two sides
Workbook
Complete the following conversation using an appropriate word below.
Exercise
Tom: Hi, Jane. I want to become a scientist. My question is ________ scientists work
and what I need to do in order to become a scientist. First of all, I’d like to know
how long I have to study to become a scientist.
Jane: Well, that depends. Usually, a scientist must have at least a Bachelor’s degree, so
that means about four years in college. Nowadays, most scientists need a Master’s
degree, too.
Tom: My second question is ________ courses or major should I choose.
Jane: Again, that depends on what you want to study in the future. You will need to
study maths. If you want to be a successful scientist, you must understand the
basics of physics, chemistry and biology.
that which how what whether
what
how
Tom: Wow, that’s a lot. What puzzled me was ________ branch of science I should
choose
Jane: Well, I think the best way is ______ you should get some practical experience.
Visit scientists and laboratories to see what the life of a scientist is like. Ask
scientists to tell you about their work. You should also try to find out which
branch of science you like and are good at.
Tom: I like physics, but the question is _________ my parents will allow me to major in it.
Jane: That’s unbelievable. My first advice is ______ you should make your own decision.
Tom: I think so. Do you have any other advice for me
Jane: Yes. I think a good scientist should be careful, curious and creative and that he or
she should like to ask a lot of questions and solve problems.
which
that
that
whether
that which how what whether
Words and Expressions
He used his great influence to change the thinking of the scientific community on this
issue. (P4)
他利用自己的巨大影响力改变了科学界对这个问题的看法。
thinking / θ k / n. 想法,看法;态度;思想;思维;见解
搭配
clear/critical thinking 清晰的思维/批判性的思维 lateral thinking 横向思维
put on your thinking cap 动脑筋,通过思考解决问题
例句
My father is very rigid in his thinking.
我父亲的思想非常顽固。
His thinking on social issues has changed considerably over the years.
这些年来,他对社会问题的见解有了很大改变。
1
It blocks a key protein in the body’s cells that is to blame for the spread of cold-
causing virus. (P4)
它阻断了人体细胞中的一种关键蛋白质,这种蛋白质导致了感冒病毒的传播。
cell /sel/ n. 细胞;小房间;单间牢房
搭配
brain/nerve cell 脑细胞/神经细胞 cell division 细胞分裂
prison cell 囚室
例句
All living things are composed of cells.
所有的生物都由细胞组成。
They keep her locked up in one of these little cells.
她关在其中一个小房间里。
2
What was the finding that Snow announced (P5)
斯诺宣布了什么发现?
finding / fa nd / n. 发现;调查结果;(法律)判决
例句
The findings caught Carli off guard.
这些发现让卡利措手不及。
The findings have been published in the journal Nature Geoscience.
研究结果已在《自然地球科学》期刊上发表。
The government hopes the court will announce its findings before the end of the month.
政府希望法庭能在月底前宣布其判决结果。
3
Try to summarize more prefixes and suffixes and understand their meanings;
Practise using the predicative clause.
Homework
人教版(2019)选择性必修二
Unit 1 Science and Scientists
Learning About Language
Build up your vocabulary
Learning objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
1. use word formation to summarize and remember words;
2. use lexical chunks to express meanings;
3. grasp and practise words and expressions in context.
Find the words from the previous pages with the following prefixes or suffixes. Then add two words for each prefix or suffix, and explain their meanings.
Prefix Words Meaning Prefix Words Meaning
re- micro-
dis- trans-
remove
replace
reuse
microscope
microwave
microphone
discover
disable
disappear
transform
transport
transplant
again
not
small
complete change; through, across
Suffix Words Meaning Suffix Words Meaning
-ory -ial
-ion -ology
contradictory
advisory
compulsory
infection
action
relation
substantial
partial
financial
epidemiology
biology
sociology
of or
relating to
action or process
having the characteristics of
a branch of knowledge
Make phrases by combining the words in the left box with those on the right. Then complete the sentences using these phrases.
Many scientists _____________ the view that it is human activity that has caused global warming.
He was to ___________ the accident because he drove on the wrong side of the road.
The man _____________ being behind the robbery was seen crossing the street.
Since heart disease is often ___________ our lifestyle choices, we need to make healthy living an important part of our lives.
to of for
subscribe suspect blame link
subscribe to
blame for
suspected of
linked to
Replace the underlined parts with suitable words from the box.
It is not unusual for an athlete to be well known while he is active, and quickly forgotten when his athletic career is over.
I’m sure she’ll deal with the changes very well because she’s very adaptable.
He was ready to serve dinner to his friends when he realised that he had forgotten to turn on the oven and the meat was not cooked yet.
He used his great influence to change the thinking of the scientific community on this issue.
Scientists have collected more data than expected to prove the theory.
raw a household name substantial statistics handle
raw
substantial
statistics
a household name
handle
Read this passage about medical plete it using the words below.
British scientists believe they may have found a way to fight the common cold. It blocks a key protein in the body’s cells that is to _______ for the spread of cold-causing virus. Targeting the host rather than the _________ was a bit non-traditional but made sense because it was tricky to target the virus. Cold-causing virus are not only of _________ kinds, they also ___________ rapidly, meaning they can quickly develop resistance to medicine. Researchers are working on making a form of medicine that can be taken directly into one’s lungs, to _________ the chance of side effects. Though these scientists have made __________ advances in their research, further _______ is needed to make sure such drugs are not so _________ that they harm the body.
infection multiple decrease severe
transform proof blame substantial
infection
multiple
transform
blame
decrease
substantial
proof
severe
Discover useful structures
Learning objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
1. learn the characteristics of the predicative clause and understand its function
in sentences;
2. learn the words that can introduce a predicative clause;
3. learn to use the predicative clause in context and in daily conversations.
1. The apparent truth was a lie.
2. The truth was that the man had disappeared.
Let’s look at the following sentences.
Lead-in
subject
linking
word
predicative clause
What clause is it
subject
linking
word
predicative
Underline all the examples in the reading passage where noun clauses are used as the predicative. Then state their meaning and functions.
One theory was that bad air caused the disease.
Another was that cholera was caused by an infection from germs in food or water.
It seemed that the woman liked the water from the pump so much that she had it delivered to her house every day.
The truth was that the water from the Broad Street pump had been infected by waste.
Presentation
Predicative Clauses
( 表语从句)
定义
在复合句中作表语的从句叫作表语从句。表语从句经常位于主句的系动词之后,对主语进行解释、说明,使主语的内容具体化。与宾语从句和主语从句一样,表语从句也是一种名词性从句。
e.g. The question is who broke the vase.
My suggestion is that we (should) start early tomorrow.
连
系
动
词
状态类: be动词, seem, appear, keep, remain, stay…
变化类: become, get, turn, grow, fall, come, go …
感官类: look, smell, taste, sound, feel …
连接词 连词 在从句中不作成分 that, whether, as if, as though, because …
连接代词 在从句中作主语、宾语、表语、定语 what, who, whom, whose, which, whatever, whoever, whichever …
连接副词 在从句中作状语 when, where, how, why …
表语从句的引导词
表语从句要点归纳
1. 表语从句一定要用陈述语序。
e.g. What I want to know is when she will be back.
Raw material is what we are badly in need of.
2. that引导表语从句时,在句中只起连接作用,不充当句子成分,无实
际意义,有时省略。
e.g. The fact is (that) she never liked him.
The trouble is that I have lost his address.
One theory was that bad air caused the disease.
3. whether引导表语从句时,起连接作用,意为“是否,到底”,在句
中不作任何成分。 if不能引导表语从句。
e.g. The question is whether your uncle will offer help to us.
Her confusion is whether she should stick to her own way of life or
follow the American way.
4. 连接代词who, whom, whose, what, which, whoever, whatever,
whichever等除在句中起连接作用外,在从句中还充当主语、宾语、
表语或定语,本身具有词义。
e.g. The question is who will be the successful applicant for the summer job
at the law firm.
Taking a year off from school to travel abroad is what is generally called
a gap year.
5. 连接副词where, when, why, how等除在句中起连接作用,在从句中
还充当地点、时间、原因、方式状语,本身具有词义。
e.g. The question is when they will start the project.
The question is how he did it.
What John Snow was determined to find out was why the 1854
outbreak of cholera in London had caused over 500 deaths
within ten days.
6. That is because ... 指原因或理由;
That is why ... 指由于某种原因所造成的后果。
e.g. Bruce did not watch the game last night. That was because he had to
help his little sister with her homework.
Bob had seen the film before. That was why he did not see it yesterday.
7. 需使用虚拟语气的表语从句
在advice, suggestion, order, proposal等表示建议、劝告、命令等含义的名词后的表语从句中,谓语动词需用“should +动词原形”形式,should可省略。
e.g. My suggestion is that we (should) start early tomorrow.
Our decision is that the school remain closed.
Answer the following questions using the information from the reading passage as well as the predicative clauses.
Example
What was it that John Snow showed to the world
→What John Snow showed to the world was how cholera could be overcome.
1. What was Snow’s discovery in two particular streets in London
Snow’s discovery in two particular streets in London was that _____________
_______________________________________________________________.
the cholera
outbreak was so severe that more than 500 people died in ten days
2. What was Snow determined to find out during the 1854 outbreak of cholera in
London
What Snow was determined to find out was why ________________________
_________________________________.
3. What were the exact places Snow marked on the map
The exact places Snow marked on the map were where ___________________
__________.
4. What was the finding that Snow announced
Snow’s finding was that _________________________________________.
the outbreak of cholera had
caused over 500 deaths within ten days
all those who died
the pump water carried cholera germs
had lived
as if that what who when how why whose which whether
A Absolutely. You may not believe it, but that was ________ happened at the initial stage of our
group’s research on developing a vaccine for malaria.
B Yes, it is. And it seemed _______ all the theories were useful, but the fact was _________ we
couldn’t persuade one another that one theory was better than another.
C Exactly. The problem was not about ___________ all our theories were equally good, but in
deciding __________________ theory to depend upon.
D We realised that what we cared about was not __________ aspect we needed to develop a
theory in, but rather ______ we can reduce the cost of a vaccine without reducing its effect!
E You’re right. At last, we became focused on the key issue, which was ______ we had to carry
out the research in the first place.
David is talking to Maria about their scientific research project. First complete David’s lines (A-E), using the words in the box. Then put David’s lines in the correct order and practise the conversation.
Practice
what
as if
that
which/what
which/ what/ whose
how
why
whether
Maria: This mix of theory and data is one of the key characteristics of what we call science.
David: ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Maria: With your theoretical framework
David: ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Maria: Deciding on a theory is definitely of critical importance.
David: ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Maria: This was when you should have calmed down and got down to doing some solid work.
David: ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Maria: So what happened in the end
David: ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
C Exactly. The problem was not about whether all our theories were equally good, but in
deciding which/ what/ whose theory to depend upon.
A Absolutely. You may not believe it, but that was what happened at the initial stage of our
group’s research on developing a vaccine for malaria.
D We realised that what we cared about was not which/what aspect we needed to develop a
theory in, but rather how we can reduce the cost of a vaccine without reducing its effect!
B Yes, it is. And it seemed as if all the theories were useful, but the fact was that we
couldn’t persuade one another that one theory was better than another.
E You’re right. At last, we became focused on the key issue, which was why we had to carry
out the research in the first place.
Complete the following ideas by famous scientists with a word or expression that introduces a predicative clause.
1. Research is __________ I’m doing when I don’t know what I’m doing.
(Werner von Braun)
2. The saddest aspect of life right now is __________ science gathers knowledge faster
than society gathers wisdom.
(Isaac Asimov)
3. An expert can be __________ has made all the mistakes that can be made in a very
narrow field.
(Niels Bohr)
what
that
Workbook
as though because that what whoever why
whoever
4. ... when different experiments give you the same result, it is no longer subject to
your opinion. That’s the good thing about science: It’s true whether or not you
believe in it. That’s __________ it works.
(Neil deGrasse Tyson)
5. This applied science, which saves work and makes life easier, brings us little
happiness. That is __________ we have not yet learnt to make sensible use of it!
(Albert Einstein)
6. There are only two ways to live your life. One is __________ nothing is a miracle.
The other is __________ everything is a miracle.
(Albert Einstein)
why
because
as though because that what whoever why
as though
as though
Workbook
Complete the conversations using noun clauses as the predicative.
1. A: Papermaking, printing, gunpowder, and the compass are the four great inventions
of ancient China. They are significant contributions of the Chinese nation to the
world.
B: Sure, they are. What I want to know though is ____________________________
___________________________________________.
2. A: The ancient Chinese were the first to invent paper and printing. Then they went
on to invent books and had opened bookshops in many cities.
B: What I’m curious about is ____________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________.
which one is the greatest in how
these inventions have changed China and the world
who invented paper/how people made the first paper/
when ink was invented/ what paper was made from/ when and how printing spread
to the rest of the world/ how records were kept before the invention of paper
Workbook
3. A: The compass is a special invention of ancient China, dating back to as early as
the Warring States Period.
B: Yes. It seems ______________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
___________________________.
4. A: Gunpowder was originally used for making fireworks.
B: But what surprises me is _____________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________.
that the compass was particularly useful/ as if people had to depend on the positions of the sun, the moon, and so on when they were at sea before the compass was invented/ that ancient Chinese had developed a good knowledge of magnetism
that gunpowder was not used initially for firearms/
how it is so unexpectedly used today/ how heavily mining depends upon it/
that it has been generally used not only in industries but in wars across the world
Workbook
5. A: After the discovery of medicine, acupuncture was invented in China,
acupuncture is a treatment which doesn’t involve any drugs. Very thin needles
are put in certain parts of a person’s body.
B: Really What puzzles me is __________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
____________.
6. A: High-speed trains, mobile payments, the bike-sharing system, and online
shopping are considered by some as the new “four inventions” of China.
B: Is that so I feel/ It seems ____________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________.
who first started this practice/ for whom this practice was first done/ why anyone would stick a needle in their body, even to become well
that these inventions have really made our lives easier/
that every Chinese is proud of the new “four inventions”/ as if I could not live without them, especially when it comes to online shopping/ that we all benefit from all these things/ that we may have to remember that every coin has two sides
Workbook
Complete the following conversation using an appropriate word below.
Exercise
Tom: Hi, Jane. I want to become a scientist. My question is ________ scientists work
and what I need to do in order to become a scientist. First of all, I’d like to know
how long I have to study to become a scientist.
Jane: Well, that depends. Usually, a scientist must have at least a Bachelor’s degree, so
that means about four years in college. Nowadays, most scientists need a Master’s
degree, too.
Tom: My second question is ________ courses or major should I choose.
Jane: Again, that depends on what you want to study in the future. You will need to
study maths. If you want to be a successful scientist, you must understand the
basics of physics, chemistry and biology.
that which how what whether
what
how
Tom: Wow, that’s a lot. What puzzled me was ________ branch of science I should
choose
Jane: Well, I think the best way is ______ you should get some practical experience.
Visit scientists and laboratories to see what the life of a scientist is like. Ask
scientists to tell you about their work. You should also try to find out which
branch of science you like and are good at.
Tom: I like physics, but the question is _________ my parents will allow me to major in it.
Jane: That’s unbelievable. My first advice is ______ you should make your own decision.
Tom: I think so. Do you have any other advice for me
Jane: Yes. I think a good scientist should be careful, curious and creative and that he or
she should like to ask a lot of questions and solve problems.
which
that
that
whether
that which how what whether
Words and Expressions
He used his great influence to change the thinking of the scientific community on this
issue. (P4)
他利用自己的巨大影响力改变了科学界对这个问题的看法。
thinking / θ k / n. 想法,看法;态度;思想;思维;见解
搭配
clear/critical thinking 清晰的思维/批判性的思维 lateral thinking 横向思维
put on your thinking cap 动脑筋,通过思考解决问题
例句
My father is very rigid in his thinking.
我父亲的思想非常顽固。
His thinking on social issues has changed considerably over the years.
这些年来,他对社会问题的见解有了很大改变。
1
It blocks a key protein in the body’s cells that is to blame for the spread of cold-
causing virus. (P4)
它阻断了人体细胞中的一种关键蛋白质,这种蛋白质导致了感冒病毒的传播。
cell /sel/ n. 细胞;小房间;单间牢房
搭配
brain/nerve cell 脑细胞/神经细胞 cell division 细胞分裂
prison cell 囚室
例句
All living things are composed of cells.
所有的生物都由细胞组成。
They keep her locked up in one of these little cells.
她关在其中一个小房间里。
2
What was the finding that Snow announced (P5)
斯诺宣布了什么发现?
finding / fa nd / n. 发现;调查结果;(法律)判决
例句
The findings caught Carli off guard.
这些发现让卡利措手不及。
The findings have been published in the journal Nature Geoscience.
研究结果已在《自然地球科学》期刊上发表。
The government hopes the court will announce its findings before the end of the month.
政府希望法庭能在月底前宣布其判决结果。
3
Try to summarize more prefixes and suffixes and understand their meanings;
Practise using the predicative clause.
Homework
