北师大版(2019)选择性必修 第四册Unit 11 Conflict And Compromise Lesson3 War Memories 课件(共35张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 北师大版(2019)选择性必修 第四册Unit 11 Conflict And Compromise Lesson3 War Memories 课件(共35张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 3.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 北师大版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-08-30 21:24:29 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
(共35张PPT)
新北师大版高中英语选择性必修四Unit11 Conflict and Compromise
Lesson3 War Memories
How much do you know about the following wars
1) World War I
2) World War II
3) The Vietnam War
World War I (1914-1918)
World War II (1939-1945)
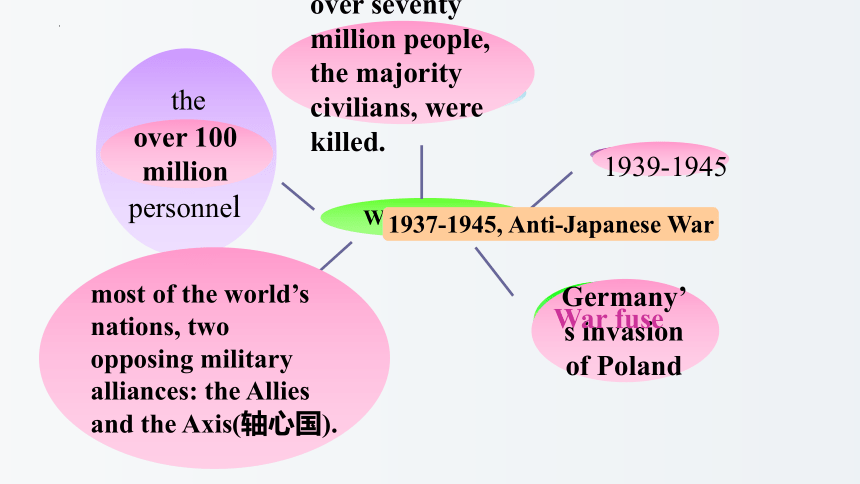
World War Ⅱ
involved
countries
injuries
and deaths
the number
of personnel
Time
over 100 million
Germany’s invasion of Poland
most of the world’s nations, two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis(轴心国).
over seventy million people, the majority civilians, were killed.
1939-1945
War fuse
1937-1945, Anti-Japanese War
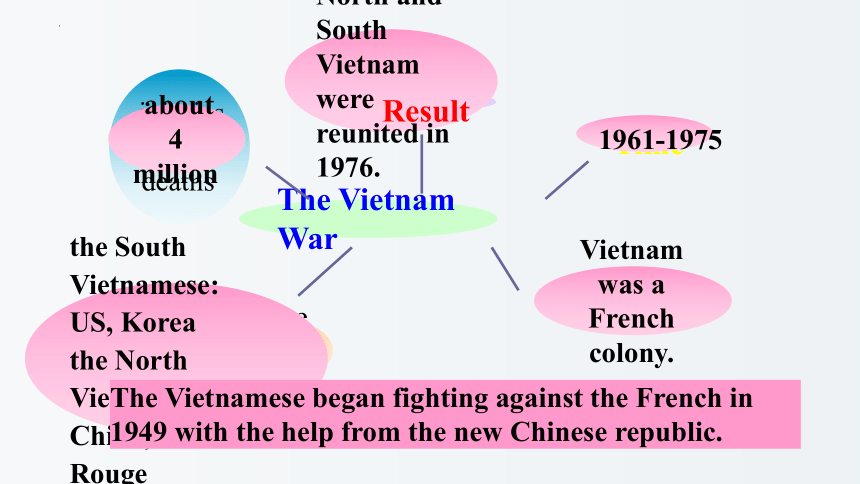
The Vietnam War
(1961-1975)
The Vietnam War
involved
countries
injuries
and deaths
Time
War fuse
Vietnam was a French colony.
North and South Vietnam were reunited in 1976.
about 4 million
the South Vietnamese:
US, Korea
the North Vietnamese: China, Khmer Rouge
1961-1975
The Vietnamese began fighting against the French in 1949 with the help from the new Chinese republic.
Result
What can wars lead to
Use the words and phrases to help you.
Read&discuss
1
Pre-reading
army soldier bomb
officer general trench
enemy bleeding frontier
shooting firing dead body
mass murder losing family members
destroyed cities and villages changing borders
being wounded fleeing homeland
weeping/sobbing/crying peace
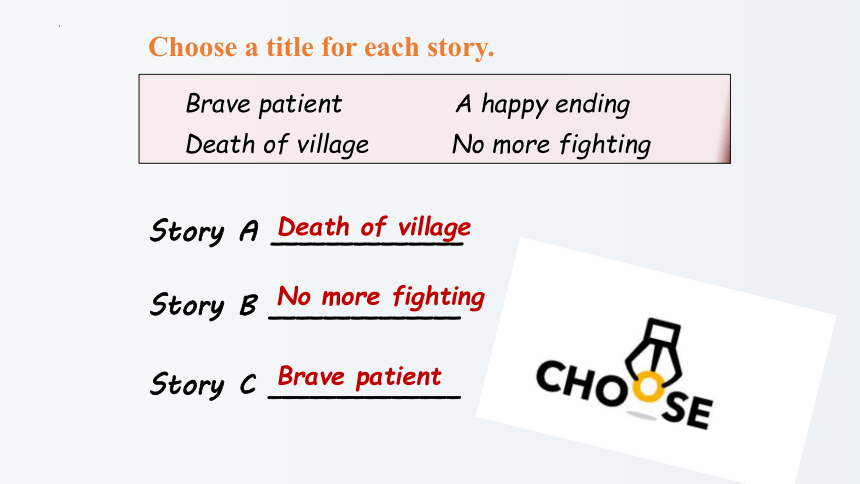
Skim through the three stories to choose a
title for each story.
While-reading
2
Choose a title for each story.
Brave patient A happy ending
Death of village No more fighting
Story A ______________
Story B ______________
Story C ______________
Death of village
No more fighting
Brave patient
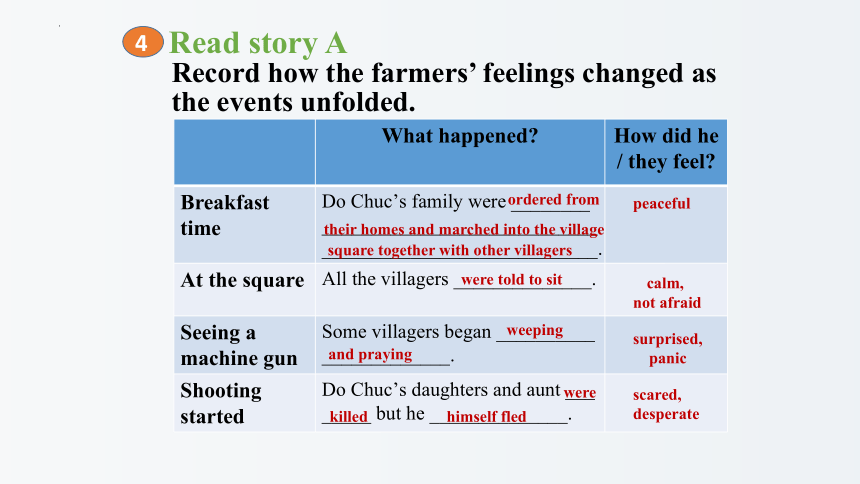
Read story A
Record how the farmers’ feelings changed as
the events unfolded.
4
What happened How did he / they feel
Breakfast time Do Chuc’s family were ________ ________________________________________________________.
At the square All the villagers ______________.
Seeing a machine gun Some villagers began __________ _____________.
Shooting started Do Chuc’s daughters and aunt ___ _____ but he ______________.
ordered from
their homes and marched into the village
square together with other villagers
peaceful
were told to sit
weeping
and praying
were
killed
himself fled
calm,
not afraid
surprised,
panic
scared,
desperate
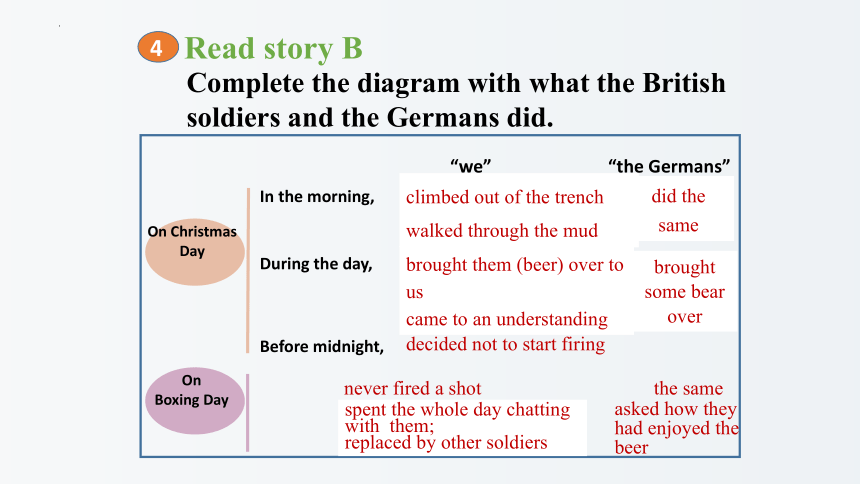
Read story B
Complete the diagram with what the British
soldiers and the Germans did.
4
“we”
“the Germans”
In the morning,
During the day,
Before midnight,
On Christmas Day
On
Boxing Day
stuck up a board
threw their equipment off
climbed out of the trench
walked through the mud
did the same
spent all day with one another
talked about the war
brought them (beer) over to us
came to an understanding
brought some bear over
decided not to start firing
the same
never fired a shot
seemed to be waiting for the other to set the ball rolling;
spent the whole day chatting
with them;
replaced by other soldiers
asked how they had enjoyed the beer
Read story C
Answer the questions.
5
1. What happened in the story Whose memory is it
2. Why was the patient in the hospital
3. Why did the nurse feel turned off when she was
told to clean up the ward for some VIPs’ visit
4. Why did the general come to the hospital
5. Why did the soldier throw back the watch at the general
6. Why did the soldier sob and the nurse cry in the end
Answers
1. A wounded soldier gets an award while in hospital but
feels angry. It’s a nurse’s memory.
2. The patient was in the hospital because he had had
both his legs blown off.
3. Because she probably felt that they had to deal with
all the problems while army VIPs only came for
ceremonies.
4. The general came to the hospital to give an award to a
wounded soldier.
5. The patient threw the watch because he thought it was
not going to help him walk.
6. The nurse cried in the end because she admired the
patient for what he said and the soldier cried because
he felt helpless.
Read the stories again.
Complete the summary for each story.
6
were marched
set up
the shooting
greeted each other
shook hands
fed up to the neck
blown off
was given / was awarded
come through
Group Work:
Think and share.
8
1. What is the turning point of each story
2. For each story, what war memories did each
person have
3. What does the author of each story try to convey
Answers
1. The turning point of each story:
Story A: The American soldiers set up a machine gun and
began to shoot the villagers.
Story B: Two of our men threw their equipment off and
climbed out of the trench with thelr hands above
their heads as representatives. Two of the Germans
did the same.
Story C: The patient threw the watch back at the general.
2. War memories:
In Story A, the person has memories of klling and survival.
In Story B, the person has a memory of an unexpected,
peaceful event between soldiers.
In Story C, the personhas a memory of the effects of war on
a soldier.
Post-reading
3. The authors try to convey the message that war is cruel and hurts everyone, both soldiers and innocent persons .
Express Yourself
Search online for statistics about the death
and destruction caused by World War II.
11
Discuss the ways in which war causes suffering.
What is your opinion on war
Focus on language
Verbs with similar meanings
Put the words in the Word Builder into two groups and explain their difference in usage.
sob chat reply swear greet tell
weep speak shout whisper mention
Verbs with similar meanings
Cry has a similar meaning to: __________
Say has a similar meaning to: ____
sob
chat
weep
reply, swear, greet, whisper, tell, speak, shout, mention
Complete the text by choosing the correct options.
A soldier from World War I tells one of his war memories…
During the war, I had to work on an air base in South Africa. I remember once we had 24 hours off-duty, my friends and I had a night out in the town. We were walking slowly back to the base at about midnight, talking about the evening, when someone mentioned/chatted South Africa’s famous wild animals. We were chatting/swearing about stories we’d heard when suddenly my friend, Bob, begged us to be quiet.
mentioned
chatting
“Be quiet yourself!” somebody greeted/replied. Then I heard them. “No, everyone be quiet,” I whispered/swore. And then we all could hear the lions. “Quick, run!” someone mentioned/ shouted. We all ran towards our base. Everyone made it back except me - I fell into a trench! I stayed there till morning when I climbed out and walked back to the base. My friends
whispered/greeted me like a hero. They thought I’d been eaten! l swore/chatted that I’d never go drinking and then walking in the wild at night again.
replied
whispered
shouted
greeted
swore
1. Then, he watched in surprise as the soldiers set up a machine gun.
in / with surprise 吃惊地,惊奇地
e.g. Bill looked at her in / with surprise, unable to believe his own eyes.
Bill吃惊地看着她,简直不相信他自己的
眼睛。
She looked up in surprise when I shouted.
我叫喊时,她吃惊地抬起头来看。
LanguagePoints
to one’s surprise 使某人惊讶的是
e.g. Much to his surprise, she gave him her phone number. 令他颇感意外的是,她把电话号码给了他。
take / catch sb by surprise 出乎某人意料
e.g. The question took her by surprise.
这个问题使她猝不及防。
come as a surprise (to sb) 出乎(某人)意料, 使(某人)感到突然
e.g. The triumph came as a surprise to many fans.
对很多球迷来说,胜利来得出乎意料。
2. The people began weeping and praying.
weep v. (wept, wept) to cry, especially because you feel very sad (尤因悲伤而)哭泣,流(泪)
e.g. James broke down and wept.
James控制不住感情,哭了起来。
She wept for the loss of her mother.
她因母亲去世而哭泣。
People in the street wept with joy when peace was announced. 当宣布和平来临时,街上的人们喜极而泣。
【拓展】
weepy adj. sad and likely to cry; tearful; to make one weep
悲伤欲哭的; 爱哭的; 含泪的; 催人泪下的, 伤感的
n. = weepie a film or a book which makes people want to cry because it is sad 催人泪下的电影(或书)
e.g. I suddenly felt very weepy. 我突然很想哭。
Weddings always made her feel weepy. 婚礼总让她伤感。
If I were you I’d take some tissues to the cinema — it’s a real weepy. 如果我是你,我会带一些纸巾去看电影 —— 那真是一部感人的电影。
pray v. to speak to God in order to ask for help or give thanks
or to hope for sth very much 祈祷,祈求,强烈地希望
pray (to sb) for… / pray (sb) to do sth / pray that…
e.g. Let us pray for the victims of this terrible disaster.
让我们为这次可怕灾难的受害者祈祷吧。
We pray you to set the prisoner free.
我们恳求你释放这个囚犯。
Paul was praying that no one had noticed his absence.
Paul但愿没有人注意到他的缺席。
3. The calm ended and panic set in.
panic n. a sudden strong feeling of fear or nervousness that makes you unable to think clearly or behave sensibly惶恐,惊恐,惊慌
in (a) panic 惊慌地
get into a panic 惊慌失措
e.g. The children fled in panic.
孩子们惊慌地逃走了。
She got into a panic when she couldn't find the tickets.
她找不到门票,慌了起来。
4. Chuc was wounded in the leg and almost unconscious, but...
表示身体部位受打击(hit)、受伤(wound)等的句式:
“介词(in/on/…)+the+身体部位” (in指嵌入或里面,on指表面)
e.g. She hit him on the head with a book.
她用书打他的头。
Police said Dr Mahgoub had been hit in the head.
警察称Mahgoub医生的头部遭到了击打。
Flying glass wounded her in the face and neck.
飞溅的玻璃刮伤她的脸和颈部。
5. …we stuck up a board displaying “A Merry Christmas” on it.
display v. to show sth to people, or put it in a place where people can see it easily 展示,陈列
e.g. The cabinets display seventeenth-century blue-and-white porcelain.
展柜中陈列着17世纪的青花瓷。
All the exam results will be displayed on the noticeboard.所有的考试成绩将公布在布告板上。
【拓展】
display v. to clearly show a feeling, attitude, or quality by what you do or say 显示, 显露(某种情感、态度或特质)
e.g. She displayed no emotion on the witness stand.
她在证人席上面无表情。
display v. if a computer or sth similar displays information, it shows it on its screen 显示(信息)
e.g. I pressed “return” and an error message was displayed.
我按了“回车”键后就显示了一条错误信息。
display n. a collection of objects or pictures arranged for people to look at, or a performance or show for people to watch 陈列品,展览品;陈列,展示,展览;表演
on display 展示;陈列
e.g. A collection of photographs was on display in the hall.
大厅里展出了一辑照片。
display n. when sth is shown electronically such as on a computer screen (电脑屏幕等的)显示
e.g. The display problems might be due to a shortage of disk space. 显示问题可能是硬盘空间不足造成的。
6 … and that he was fed up to the neck with this war and would be glad when it was over.
fed up with: annoyed or bored, and wanting sth to change
受够了;厌烦;对……厌倦
e.g. People get fed up with anyone who brags all the time.
人们讨厌老是自吹自擂的人。
I’m really fed up with this constant rain.
连续下雨我都烦死了。
Anna got fed up with waiting.
Anna都等烦了。
7. Bill distributed the beer among us and we consumed a lot.
distribute v. = give out to share things among a group of people, especially in a planned way
分发,分配,分送
distribute sth among / to…
e.g. Clothes and blankets have been distributed among them.
已经向他们分发了衣服和毯子。
The books will be distributed free to local schools.
这些书将免费发放给当地学校。
8. We’d formed a bond and... to be waiting for the other to set the ball rolling.
set/start/keep the ball rolling: to set an activity in motion; to make a start 着手做,开始做;带头做
e.g. To start the ball rolling, the government was asked to contribute £1 million.
政府被要求出资 100 万英镑作为启动经费。
I decided to set the ball rolling and got up to dance.
我决定带头,就站了起来跳舞。
9. This really turned me off to begin with, “Let’s clean up ...”
turn sb off: to make sb decide they do not like sth
使失去兴趣
e.g. What turns teenagers off science and technology
是什么使青少年对科学技术丧失了兴趣?
Teaching off a blackboard is boring, and undoubtedly turns people off.
照本宣科枯燥乏味,无疑会使人们丧失学习兴趣。
【拓展】
turn sth off
to start going along a different road or path which leads away from it 驶离; 转弯; 拐入旁路
e.g. The truck suddenly turned off the main road.
卡车突然驶离大路。
to stop heat, sound, or water being produced by adjusting the controls 关上; 关掉; 截断, 切断(……的供应)
e.g. Their water was turned off weeks ago without explanation.
他们的水在几周前就毫无理由地被切断了。
10. As the general handed him the watch, … the kid more or less threw the watch back at him.
more or less: almost; mostly; approximately
几乎, 差不多; 主要, 大体; 大约
e.g. I’ve more or less finished the book.
我差不多读完这本书了。
The project was more or less a success.
这项计划大致上成功。
It’s a mile, more or less, from his home to school.
从他家到学校大约有一英里远。
新北师大版高中英语选择性必修四Unit11 Conflict and Compromise
Lesson3 War Memories
How much do you know about the following wars
1) World War I
2) World War II
3) The Vietnam War
World War I (1914-1918)
World War II (1939-1945)
World War Ⅱ
involved
countries
injuries
and deaths
the number
of personnel
Time
over 100 million
Germany’s invasion of Poland
most of the world’s nations, two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis(轴心国).
over seventy million people, the majority civilians, were killed.
1939-1945
War fuse
1937-1945, Anti-Japanese War
The Vietnam War
(1961-1975)
The Vietnam War
involved
countries
injuries
and deaths
Time
War fuse
Vietnam was a French colony.
North and South Vietnam were reunited in 1976.
about 4 million
the South Vietnamese:
US, Korea
the North Vietnamese: China, Khmer Rouge
1961-1975
The Vietnamese began fighting against the French in 1949 with the help from the new Chinese republic.
Result
What can wars lead to
Use the words and phrases to help you.
Read&discuss
1
Pre-reading
army soldier bomb
officer general trench
enemy bleeding frontier
shooting firing dead body
mass murder losing family members
destroyed cities and villages changing borders
being wounded fleeing homeland
weeping/sobbing/crying peace
Skim through the three stories to choose a
title for each story.
While-reading
2
Choose a title for each story.
Brave patient A happy ending
Death of village No more fighting
Story A ______________
Story B ______________
Story C ______________
Death of village
No more fighting
Brave patient
Read story A
Record how the farmers’ feelings changed as
the events unfolded.
4
What happened How did he / they feel
Breakfast time Do Chuc’s family were ________ ________________________________________________________.
At the square All the villagers ______________.
Seeing a machine gun Some villagers began __________ _____________.
Shooting started Do Chuc’s daughters and aunt ___ _____ but he ______________.
ordered from
their homes and marched into the village
square together with other villagers
peaceful
were told to sit
weeping
and praying
were
killed
himself fled
calm,
not afraid
surprised,
panic
scared,
desperate
Read story B
Complete the diagram with what the British
soldiers and the Germans did.
4
“we”
“the Germans”
In the morning,
During the day,
Before midnight,
On Christmas Day
On
Boxing Day
stuck up a board
threw their equipment off
climbed out of the trench
walked through the mud
did the same
spent all day with one another
talked about the war
brought them (beer) over to us
came to an understanding
brought some bear over
decided not to start firing
the same
never fired a shot
seemed to be waiting for the other to set the ball rolling;
spent the whole day chatting
with them;
replaced by other soldiers
asked how they had enjoyed the beer
Read story C
Answer the questions.
5
1. What happened in the story Whose memory is it
2. Why was the patient in the hospital
3. Why did the nurse feel turned off when she was
told to clean up the ward for some VIPs’ visit
4. Why did the general come to the hospital
5. Why did the soldier throw back the watch at the general
6. Why did the soldier sob and the nurse cry in the end
Answers
1. A wounded soldier gets an award while in hospital but
feels angry. It’s a nurse’s memory.
2. The patient was in the hospital because he had had
both his legs blown off.
3. Because she probably felt that they had to deal with
all the problems while army VIPs only came for
ceremonies.
4. The general came to the hospital to give an award to a
wounded soldier.
5. The patient threw the watch because he thought it was
not going to help him walk.
6. The nurse cried in the end because she admired the
patient for what he said and the soldier cried because
he felt helpless.
Read the stories again.
Complete the summary for each story.
6
were marched
set up
the shooting
greeted each other
shook hands
fed up to the neck
blown off
was given / was awarded
come through
Group Work:
Think and share.
8
1. What is the turning point of each story
2. For each story, what war memories did each
person have
3. What does the author of each story try to convey
Answers
1. The turning point of each story:
Story A: The American soldiers set up a machine gun and
began to shoot the villagers.
Story B: Two of our men threw their equipment off and
climbed out of the trench with thelr hands above
their heads as representatives. Two of the Germans
did the same.
Story C: The patient threw the watch back at the general.
2. War memories:
In Story A, the person has memories of klling and survival.
In Story B, the person has a memory of an unexpected,
peaceful event between soldiers.
In Story C, the personhas a memory of the effects of war on
a soldier.
Post-reading
3. The authors try to convey the message that war is cruel and hurts everyone, both soldiers and innocent persons .
Express Yourself
Search online for statistics about the death
and destruction caused by World War II.
11
Discuss the ways in which war causes suffering.
What is your opinion on war
Focus on language
Verbs with similar meanings
Put the words in the Word Builder into two groups and explain their difference in usage.
sob chat reply swear greet tell
weep speak shout whisper mention
Verbs with similar meanings
Cry has a similar meaning to: __________
Say has a similar meaning to: ____
sob
chat
weep
reply, swear, greet, whisper, tell, speak, shout, mention
Complete the text by choosing the correct options.
A soldier from World War I tells one of his war memories…
During the war, I had to work on an air base in South Africa. I remember once we had 24 hours off-duty, my friends and I had a night out in the town. We were walking slowly back to the base at about midnight, talking about the evening, when someone mentioned/chatted South Africa’s famous wild animals. We were chatting/swearing about stories we’d heard when suddenly my friend, Bob, begged us to be quiet.
mentioned
chatting
“Be quiet yourself!” somebody greeted/replied. Then I heard them. “No, everyone be quiet,” I whispered/swore. And then we all could hear the lions. “Quick, run!” someone mentioned/ shouted. We all ran towards our base. Everyone made it back except me - I fell into a trench! I stayed there till morning when I climbed out and walked back to the base. My friends
whispered/greeted me like a hero. They thought I’d been eaten! l swore/chatted that I’d never go drinking and then walking in the wild at night again.
replied
whispered
shouted
greeted
swore
1. Then, he watched in surprise as the soldiers set up a machine gun.
in / with surprise 吃惊地,惊奇地
e.g. Bill looked at her in / with surprise, unable to believe his own eyes.
Bill吃惊地看着她,简直不相信他自己的
眼睛。
She looked up in surprise when I shouted.
我叫喊时,她吃惊地抬起头来看。
LanguagePoints
to one’s surprise 使某人惊讶的是
e.g. Much to his surprise, she gave him her phone number. 令他颇感意外的是,她把电话号码给了他。
take / catch sb by surprise 出乎某人意料
e.g. The question took her by surprise.
这个问题使她猝不及防。
come as a surprise (to sb) 出乎(某人)意料, 使(某人)感到突然
e.g. The triumph came as a surprise to many fans.
对很多球迷来说,胜利来得出乎意料。
2. The people began weeping and praying.
weep v. (wept, wept) to cry, especially because you feel very sad (尤因悲伤而)哭泣,流(泪)
e.g. James broke down and wept.
James控制不住感情,哭了起来。
She wept for the loss of her mother.
她因母亲去世而哭泣。
People in the street wept with joy when peace was announced. 当宣布和平来临时,街上的人们喜极而泣。
【拓展】
weepy adj. sad and likely to cry; tearful; to make one weep
悲伤欲哭的; 爱哭的; 含泪的; 催人泪下的, 伤感的
n. = weepie a film or a book which makes people want to cry because it is sad 催人泪下的电影(或书)
e.g. I suddenly felt very weepy. 我突然很想哭。
Weddings always made her feel weepy. 婚礼总让她伤感。
If I were you I’d take some tissues to the cinema — it’s a real weepy. 如果我是你,我会带一些纸巾去看电影 —— 那真是一部感人的电影。
pray v. to speak to God in order to ask for help or give thanks
or to hope for sth very much 祈祷,祈求,强烈地希望
pray (to sb) for… / pray (sb) to do sth / pray that…
e.g. Let us pray for the victims of this terrible disaster.
让我们为这次可怕灾难的受害者祈祷吧。
We pray you to set the prisoner free.
我们恳求你释放这个囚犯。
Paul was praying that no one had noticed his absence.
Paul但愿没有人注意到他的缺席。
3. The calm ended and panic set in.
panic n. a sudden strong feeling of fear or nervousness that makes you unable to think clearly or behave sensibly惶恐,惊恐,惊慌
in (a) panic 惊慌地
get into a panic 惊慌失措
e.g. The children fled in panic.
孩子们惊慌地逃走了。
She got into a panic when she couldn't find the tickets.
她找不到门票,慌了起来。
4. Chuc was wounded in the leg and almost unconscious, but...
表示身体部位受打击(hit)、受伤(wound)等的句式:
“介词(in/on/…)+the+身体部位” (in指嵌入或里面,on指表面)
e.g. She hit him on the head with a book.
她用书打他的头。
Police said Dr Mahgoub had been hit in the head.
警察称Mahgoub医生的头部遭到了击打。
Flying glass wounded her in the face and neck.
飞溅的玻璃刮伤她的脸和颈部。
5. …we stuck up a board displaying “A Merry Christmas” on it.
display v. to show sth to people, or put it in a place where people can see it easily 展示,陈列
e.g. The cabinets display seventeenth-century blue-and-white porcelain.
展柜中陈列着17世纪的青花瓷。
All the exam results will be displayed on the noticeboard.所有的考试成绩将公布在布告板上。
【拓展】
display v. to clearly show a feeling, attitude, or quality by what you do or say 显示, 显露(某种情感、态度或特质)
e.g. She displayed no emotion on the witness stand.
她在证人席上面无表情。
display v. if a computer or sth similar displays information, it shows it on its screen 显示(信息)
e.g. I pressed “return” and an error message was displayed.
我按了“回车”键后就显示了一条错误信息。
display n. a collection of objects or pictures arranged for people to look at, or a performance or show for people to watch 陈列品,展览品;陈列,展示,展览;表演
on display 展示;陈列
e.g. A collection of photographs was on display in the hall.
大厅里展出了一辑照片。
display n. when sth is shown electronically such as on a computer screen (电脑屏幕等的)显示
e.g. The display problems might be due to a shortage of disk space. 显示问题可能是硬盘空间不足造成的。
6 … and that he was fed up to the neck with this war and would be glad when it was over.
fed up with: annoyed or bored, and wanting sth to change
受够了;厌烦;对……厌倦
e.g. People get fed up with anyone who brags all the time.
人们讨厌老是自吹自擂的人。
I’m really fed up with this constant rain.
连续下雨我都烦死了。
Anna got fed up with waiting.
Anna都等烦了。
7. Bill distributed the beer among us and we consumed a lot.
distribute v. = give out to share things among a group of people, especially in a planned way
分发,分配,分送
distribute sth among / to…
e.g. Clothes and blankets have been distributed among them.
已经向他们分发了衣服和毯子。
The books will be distributed free to local schools.
这些书将免费发放给当地学校。
8. We’d formed a bond and... to be waiting for the other to set the ball rolling.
set/start/keep the ball rolling: to set an activity in motion; to make a start 着手做,开始做;带头做
e.g. To start the ball rolling, the government was asked to contribute £1 million.
政府被要求出资 100 万英镑作为启动经费。
I decided to set the ball rolling and got up to dance.
我决定带头,就站了起来跳舞。
9. This really turned me off to begin with, “Let’s clean up ...”
turn sb off: to make sb decide they do not like sth
使失去兴趣
e.g. What turns teenagers off science and technology
是什么使青少年对科学技术丧失了兴趣?
Teaching off a blackboard is boring, and undoubtedly turns people off.
照本宣科枯燥乏味,无疑会使人们丧失学习兴趣。
【拓展】
turn sth off
to start going along a different road or path which leads away from it 驶离; 转弯; 拐入旁路
e.g. The truck suddenly turned off the main road.
卡车突然驶离大路。
to stop heat, sound, or water being produced by adjusting the controls 关上; 关掉; 截断, 切断(……的供应)
e.g. Their water was turned off weeks ago without explanation.
他们的水在几周前就毫无理由地被切断了。
10. As the general handed him the watch, … the kid more or less threw the watch back at him.
more or less: almost; mostly; approximately
几乎, 差不多; 主要, 大体; 大约
e.g. I’ve more or less finished the book.
我差不多读完这本书了。
The project was more or less a success.
这项计划大致上成功。
It’s a mile, more or less, from his home to school.
从他家到学校大约有一英里远。
同课章节目录
- Unit 10 Connections
- Lesson 1 How Closely Connected Are We?
- Lesson 2 Community Spirit
- Lesson 3 Anne of Green Gables
- Unit 11 Conflict And Compromise
- Lesson 1 Living In a Community
- Lesson 2 Dealing with Conflict
- Lesson 3 War Memories
- Unit 12 Innovation
- Lesson 1 Scientific Breakthroughs
- Lesson 2 Aha Moment
- Lesson 3 Stephen Hawking
