外研版(2019)必修 第一册Unit 1 A new start Using language 课件(共50张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版(2019)必修 第一册Unit 1 A new start Using language 课件(共50张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.4MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-10-21 18:26:16 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共50张PPT)
Unit 1 A new start
Using language
Vocabulary
1. stage
on stage 在舞台上
go on/off stage 登上/走下舞台
take the stage 登上舞台
get to/reach a stage 到达一个阶段
go through a stage 经历一个阶段
a stage of development 发展阶段
at this/that stage 在这个/那个阶段
at an early/a late stage 在初期/后期
练习:The children are at different _______(stage) of development.
stages
Vocabulary
2. argue
argument n. 争论,争吵
argue with sb. 与某人争论/争吵
argue about/over sth. 为某事争论/争吵
argue that … 主张/认为……
argue for/against (doing) sth. 赞成/反对(做)某事
argue sb. into/out of doing sth. 说服某人做/不做某事
have an argument with sb. 为某人争论/争吵
have an argument about/over sth. 为某事争论/争吵
get into an argument 争论/争吵起来
练习:I find it hart _________(argue) with him about the topic.
to argue
Vocabulary
3. investigate
investigation n. 调查
investigate sb. (for sth.) (因为某事)调查某人
investigate an incident 调查一个事件
be called in to investigate 应召前来调查
under investigation 正在调查中
conduct an investigation 进行调查
an investigation into 对……的调查
练习:Many people witnessed the car accident, so it was not difficult ____________(investigate).
to investigate
Vocabulary
4. various
vary v. 不同,变化 in various sizes 大小不一
in various ways 以不同的方式
various styles 各种款式;款式齐全;款式多样
various people 各行各业的人
a variety of = varieties of = various 种类繁多的
vary in 在……方面不同 vary with sth. 随……而变化
vary from…to… 从……到……变化
vary between…and… 在……和……之间变化
vary from person to person 因人而异
练习:There are _______(vary) solutions to your problem.
various
Vocabulary
5. apply
application n. 申请;应用 applied adj. 应用的
applicant n. 申请者 apply for 申请
apply to sb. for sth. 向某人申请……
apply sth. to sth. 把……应用到……
apply oneself to 致力于 a job application 求职信
fill in an application form 填写申请表 a written application 书面申请
college applications 大学(入学)申请
make an application to sb. for… 向某人(某机构)申请……
练习:He graduated with high enough marks to ______ for a university.
apply
Leading in
What basic sentence structures do you know
Using language
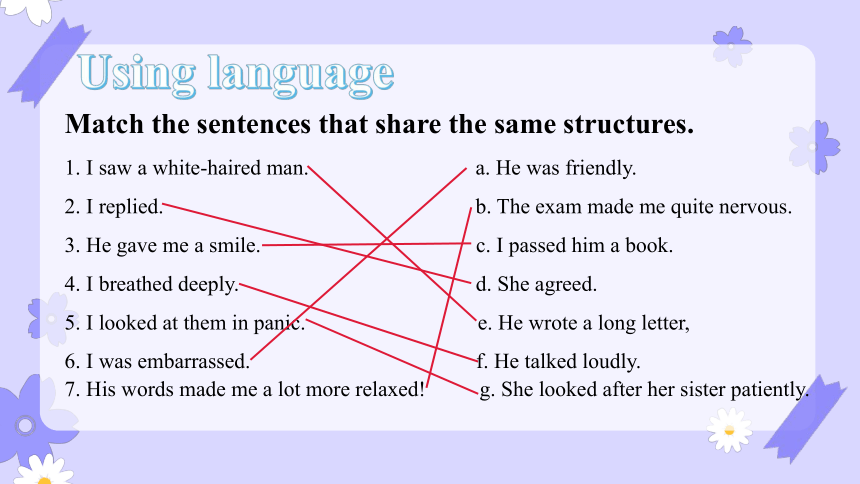
Match the sentences that share the same structures.
1. I saw a white-haired man. a. He was friendly.
2. I replied. b. The exam made me quite nervous.
3. He gave me a smile. c. I passed him a book.
4. I breathed deeply. d. She agreed.
5. I looked at them in panic. e. He wrote a long letter,
6. I was embarrassed. f. He talked loudly.
7. His words made me a lot more relaxed! g. She looked after her sister patiently.
Using language
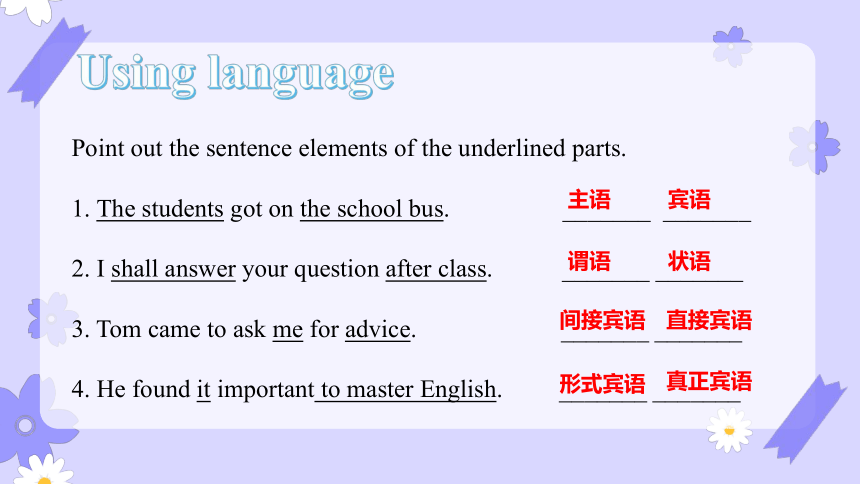
Point out the sentence elements of the underlined parts.
1. The students got on the school bus. _______ _______
2. I shall answer your question after class. _______ _______
3. Tom came to ask me for advice. _______ _______
4. He found it important to master English. _______ _______
主语
宾语
谓语
状语
间接宾语
直接宾语
形式宾语
真正宾语
Using language
5. Do you have anything else to say _______ _______
6. He became a teacher at the age of twenty one. _______
7. Would you please tell me your address _______ _______
8. It is our duty to keep our classroom clean and tidy.
_______ _______
9. We must keep it a secret. _______ _______
宾语
定语
间接宾语
直接宾语
形式主语
真正主语
表语
宾语
宾语补足语
Using language
一、句子和句子成分
句子是表达一个完整意义的最小单位,也是构成篇章的重要组成部分。学习英语要以句子为基本单位和基本素材。分析并弄懂每个句子的成分、结构、类型是学习语法的目的,更是理解句意的基础。句子是由词或短语构成的,这些词或短语便是句子成分。句子成分是按照该组成部分在句中所起的作用而划分的。一个完整的句子,由主语和谓语两大部分组成。谓语是一个组成部分,是一个整体,它包括谓语动词、宾语和状语。谓语部分的构成,正确的划分是(括号里面是谓语的构成):
Using language
1. 主语+谓语(不及物动词)
2. 主语+谓语(及物动词+宾语)
3. 主语+谓语(及物动词+双宾语)
4. 主语+谓语(及物动词+复合宾语)
5. 主语+谓语(系动词+表语)
Using language
注意:
·用在及物动词之后或者用在介词之后的成分,叫宾语;
·修饰、限定名词或代词的成分,叫定语;
·修饰动词形容词、副词、介词短语或全句的成分,叫状语;
·用在系动词之后的成分,叫表语;
·用来补充说明宾语的成分,叫补足语;
·对一个名词或代词做进一步解释的成分,叫同位语。
Using language
1. 主语
主语是谓语所表示动作或状态的执行者,是一个句子所叙述的主体,表示句子所说的是"谁"或是"什么"。名词(短语)、代词、数词、不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)和从句等都可作主语。主语一般位于句首,但在there be结构、疑问句(特殊疑问词作主语时例外)和倒装句中主语位于谓语、助动词或情态动词后面。
Using language
A light wind woke among the trees.
微风从林间掠过。(名词短语作主语)
No one but yourself can help you.
只有你自己才能帮助你。(代词作主语)
Three plus five is eight.
3加5等于8。(数词作主语)
To drink a cup of cold water in such hot weather is a great pleasure.
在这么热的天喝一杯冷水是一件很愉快的事。(不定式短语作主语)
Using language
Travelling abroad is popular among young people.
出国旅游受年轻人的欢迎。(动名词短语作主语)
The rich are not always happier than the poor.
有钱人并不一定总比穷人更快乐。(名词化的形容词作主语)
Generally speaking, what we can't get seems better than what we have.
一般说来,我们得不到的东西似乎比我们拥有的东西好。(从句作主语)
It is believed that girls are good at language.
人们认为女孩儿更擅长语言。(it作形式主语,that…作真正的主语)
Using language
2. 谓语动词
谓语动词说明主语的行为或具有的特征和状态,由动词充当,位于主语的后面,是句子的基本构成成分。谓语动词有人称、数和时态的变化。谓语动词分为简单谓语动词和复合谓语动词。
(1)简单谓语动词
不论何种时态、语态、语气,凡是由一个动词或动词词组构成的都是简单谓语动词。
Using language
He shows confidence at any time. 他任何时候都表现出自信。
He looked after two orphans. 他照顾两个孤儿。
I have tried three times in this way. 我已经用这种方法试了三次。
Don't get off the bus until it comes to a stop. 公共汽车停稳后再下车。
Our school was built in 1961. 我们学校建于1961年。
Using language
(2)复合谓语动词
由"情态动词或助动词+动词原形"或"连系动词+表语"构成的谓语叫作复合谓语。
He can speak English very well. 他英语说得很好。
The work must be done before three o'clock. 这项工作必须在三点以前完成。
This film is very interesting. 这部电影很有意思。
He seems unhappy. 他似乎不高兴。
Using language
3. 表语
表语说明主语的性质、特征、身份或状态,与连系动词be, look, seem, appear, feel, taste, smell, sound , become, get, grow, turn, remain, keep, stay 等一起构成复合谓语。表语通常由名词、代词、形容词、数词、副词、介词短语、动词不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)、分词(短语)或从句等充当。
These are books. 这些是书本。(名词作表语)
The winner is you. 获胜者是你。(代词作表语)
Julie always looks cheerful. 朱莉看上去总是很高兴。(形容词作表语)
One plus two is three. 1 加2 等于3。(数词作表语)
Using language
The war was over. 战争结束了。(副词作表语)
He is out of condition. 他身体状况不好。(介词短语作表语)
His dream is to explore the outer space. 他的梦想是探索外太空。(不定式短语作表语)
My hobby is playing the piano. 我的爱好是弹钢琴。(动名词短语作表语)
He was quite surprised to see me there.
在那里见到我他感到非常惊讶。(过去分词短语作表语)
This is what he told me yesterday. 这就是他昨天告诉我的。(从句作表语)
Using language
4. 宾语
宾语表示动作的对象或承受者,一般位于及物动词和介词后面。可以用作宾语的有名词、代词、数词、名词化的形容词、不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)、从句等。宾语又分单宾语、双宾语、复合宾语三种。
单宾语
Richard does not like his job. 理查德不喜欢他的工作。(名词作宾语)
I don't know him. 我不认识他。(代词作宾语)
—How many computers do you need 你们需要几台电脑?
—We need five. 我们需要五台。(数词作宾语)
Using language
We donated money and cotton clothes to help the homeless in the flooded area.
我们捐了钱和棉衣帮助洪灾地区无家可归的人。(名词化的形容词作宾语)
Monica decided to solve the problem on her own.
莫妮卡决定自己解决这个问题。(不定式短语做宾语)
The young man risked losing his life to save the girl.
那个年轻人冒着生命危险去救那个女孩。(动名词短语作宾语)
Miya said that she would return soon. 米娅说她会很快回来的。(从句作宾语)
Using language
同源宾语
同源宾语指由同源动词之名词所作的宾语,前面常有不定冠词a和形容词修饰语。
live a happy life 过着幸福的生活 die a worthy death 死得有价值
laugh a good laugh 大笑 blow a heavy blow 沉重地一击
smile a gentle smile 微微一笑 sing a sweet song 唱一首甜美的歌
dream a terrible dream 做一个噩梦 die a glorious death 光荣牺牲
Using language
(2) 双宾语
双宾语是指动词后带有两个宾语,一个是间接宾语,一个是直接宾语。直接宾语表示动作的承受者或结果,通常指物;间接宾语表示动作是对谁做的,为谁做的,通常指人。间接宾语一般位于直接宾语之前,也可位于其后。但位于后面时在它的前面须加介词to 或 for.
They offered me the job. — They offered the job to me.
他们给我提供了那份工作。(me 为间接宾语,the job为直接宾语)
Please show me your passport. — Please show your passport to me.
请向我出示你的护照。(me 为间接宾语,your passport为直接宾语)
Cora played us some light music. — Cora played some light music for us.
科拉给我们演奏了一些轻音乐。(us 为间接宾语,some light music为直接宾语)
Using language
(3)复合宾语
有些动词除了带有宾语外,还需要另外一个成分来说明宾语的情况,以补充意义上的不足,让宾语的意义完整。这种起补充说明作用的词或短语叫作宾语补足语。宾语和补足语之间存在着逻辑上的主谓关系,二者一起构成复合宾语。能作宾语补足语的有名词、形容词、介词短语、不定式短语、分词短语、副词等。判断某个成分是否为宾补,这跟谓语动词的性质有关。宾补是谓语动词作用于宾语的结果。如谓语动词具有"使令""指使""影响"宾语做某事的作用,谓语动词使宾语怎么样,成为什么,变成什么(如cause 类,make 类)。谓语动词具有感官性能,对宾语的动作具有感知作用(如 see, hear, find 类)。
We all find Josie a good girl.
我们都发现乔茜是一个好女孩。(Josie 为宾语,a good girl 为宾语补足语)
Using language
Don't force such a little baby to learn.
不要逼这样小的孩子学习。(a little baby 为宾语,to learn为宾语补足语)
He made himself known to them first.
他先向他们做了自我介绍。(himself 为宾语,known to them为宾语补足语)
We must keep it a secret.
我们必须对此保密。(it为宾语,a secret 为宾语补足语)
Please make yourself at home.
请随便一点。(yourself为宾语,at home为宾语补足语)
Please keep the dog out.
请把狗关在外面。(the dog 为宾语,out 为宾语补足语)
Using language
5. 定语
修饰或限定名词或代词的成分叫作定语。定语是用来描述名词或代词的修饰语,它常和名词构成名词短语。定语分为前置定语和后置定语两种。
前置定语
可以充当前置定语的有形容词、代词、数词、名词或名词所有格、动名词、分词等。一般而言,单个的词语作定语都是前置定语。
This is a heated argument.
这是一场激烈的辦论。(形容词作定语)
The doctor told me to open my mouth and put out my tongue.
医生让我张开嘴巴伸出舌头。(代词作定语)
He drank three whole glasses. 他喝了满满三杯。(数词作定语)
Using language
He works in a shoe factory. 他在一家鞋厂上班。(名词作定语)
Do you know Vela's mother 你认识维拉的妈妈吗?(名词所有格作定语)
Books can't be taken away from the reading room.
书籍不可以从阅览室中带走。(动名词作定语)
We should adapt to the changing situation quickly.
我们应该迅速地适应变化的形势。(现在分词作定语)
Is there any difference between spoken English and written English?
英语口语和书面语之间存在什么不同吗?(过去分词作定语)
Using language
(2) 后置定语
可以充当后置定语的有形容词短语、介词短语、地点方位副词、不定式短语、分词短语、从句等。词组或从句作定语都是后置定语。
The lady was carrying a basket full of vegetables.
那位女士提着一只盛满蔬菜的篮子。(形容词短语作定语)
The girl in white is his sister.
穿白衣服的女孩是他妹妹。(介词短语作定语)
Fill in the blanks in the sentences below.
在下面的句子中填空。(地点方位副词作定语)
Using language
Now is your chance to talk to him.
马上就是你和他谈话的机会了。(不定式短语作定语)
Do you know the man speaking to our headmaster
你认识正在跟我们的校长说话的那个人吗?(现在分词短语作定语)
Most of the people invited to the conference are from Europe.
应遊出席会议的人大多来自政洲。(过去分词短语作定语)
Do you know the man who spoke just now
你认识刚才发言的那个人吗?(从句作定语)
Using language
6. 状语
状语是用来修饰动词、形容词、副词或句子的一种成分。它可以表示时间、地点、方式、程度、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步或比较等。通常由副词、介词短语、不定式(短语)、分词(短语)、形容词、名词、从句等充当。
Jennifer runs very fast. 珍妮弗跑得很快。(副词作状语)
I'll be back in a while. 我一会儿就回来。(介词短语作状语)
He waited to see the result of the game.
他等着看比赛结果。(不定式短语作状语)
Living in the country, they have few amusements.
因为住在农村,他们没有什么娱乐活动。(现在分词短语作状语)
Using language
Given more time and money, we would have done the work better.
如果给予更多的时间和钱的话,我们会把工作做得更好。(过去分词短语作状语)
She sat there, silent.
她坐在那儿,一声不吭。(形容词作状语)
Wait a moment, I'll come.等一会儿,我就来。(名词作状语)
It rained so hard that they had to put off the sports meeting.
雨下得很大,他们不得不推迟运动会。(从句作状语)
He was absent from the lecture yesterday because he was ill.
昨天他没参加讲座,是因为病了。(从句作状语)
Using language
7. 补足语
补足语是用来说明宾语的性质、状态等的一种句子成分。宾语和宾语补足语构成了复合宾语,它们在逻辑上有主谓关系。名词、形容词、副词、介词短语、现在分词、过去分词、不定式(短语)等皆可作补足语。含有宾语补足语的句子在变为被动句时,宾语补足语便成了主语补足语。
She was appointed manager of the company.
她被任命为公司经理。(名词短语作补足语)
We should keep our classroom clean and tidy.
我们应该保持教室干净整洁。(形容词短语作补足语)
Using language
Miranda likes sleeping with the light on.
米兰达喜欢开着灯睡觉。(副词作补足语)
When she woke up, she found herself in a hospital.
当她醒来时,她发现自己在一家医院里。(介词短语作补足语)
Her mother doesn't allow her to go out alone at night.
她妈妈不允许她晚上一个人出去。(不定式短语作补足语)
Our English teacher always has us reading and reciting.
我们的英语老师总是让我们读和背。(现在分词短语作补足语)
He always kept us greatly surprised.
他总是让我们大吃一惊。(过去分词作补足语)
Using language
8. 同位语
对句子中某一成分作进一步解释说明,与该成分在语法上处于同等地位的句子成分叫作同位语。可以用作同位语的有名词、代词、数词或从句等。
This is Mr. Li, our headmaster.
这是我们的校长李老师。(名词短语作同位语)
We each have a cellphone now.
现在我们每个人都有手机了。(代词作同位语)
Are you two ready to start out now
你们两个人都准备好现在出发了吗?(数词作同位语)
The news that our team has won again is true.
我们队又赢了的消息是真的。(从句作同位语)
Using language
名称 英语全称 简称
主语+谓语动词 Subject + Verb S+V
主语+谓语动词+宾语 Subject + Verb + Object S+V+O
主语+连系动词+表语 Subject + Verb + Predicative S+V+P
主语+谓语动词+间接宾语+直接宾语 Subject + Verb + Indirect Object + Direct Object S+V+IO+DO
主语+谓语动词+宾语+宾语补足语 Subject + Verb + Object + Complement S+V+O+C
主语+谓语动词+状语 Subject + Verb + Adverbial S+V+A
主语+谓语动词+宾语+状语 Subject + Verb + Object + Adverbial S+V+O+A
存在句 There be There be
二、八种基本句型
不同的句子成分构成了英语中各式各样的句子。所有句子中,归纳起来共有八种最基本的句型。其他的各种句型都是由这八种基本句型扩展而来的。
Using language
S+V 句式
这种句型中的 V 是指不及物动词。
在英语中大多数动词既可作及物动词又可作不及物动词,纯粹不及物动词数量较少。常见的有 apologize, appear, arrive, come, die, disappear, dive, exist, fall, flow, happen, rise 等。
Things changed. 情况有了变化。
The bell has rung. 铃声响过了。
What happened over there 那儿发生了什么事?
Kevin apologized to his mother for his rudeness.
凯文为他的粗鲁向他母亲道了歉。
Using language
2. S+V+O句式
英语中绝大多数及物动词都是只带一个宾语的动词。
Farmers in our county grow all kinds of vegetables.
我们县的农民种植各种各样的蔬菜。
Danny runs a big clothes factory. 丹尼经营一家大型服装厂。
Using language
3. S+V+P句式
这种句型结构主要指谓语动词为连系动词的情况。连系动词除 be 外,还有 look, seem, appear, feel, taste, smell, ssound, become, get, grow, turn, remain, keep, stay 等。作表语的可以是名词、形容词、代词、副词、介词短语、不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)、从句等。
Jackson is a common English name. 杰克逊是常见的英语人名。
The weather is becoming colder and colder. 天气变得越来越冷。
It looks like a made-up word. 这看起来像是一个杜撰的词。
Her job is looking after children.她的工作是照料小孩。
Using language
4. S+V+IO+DO 句式
这是带双宾语的向式结构,IO为间接宾语,DO 为直接宾语。直接宾语一般是指物的名词或代词,间接宾语一般是指人的名词或代词。
Her friend promised her a birthday gift. 她的朋友答应她给她一份生日礼物。
Father made me a wooden gun. 爸爸给我做了一把木头手枪。
Who'd like to fetch me some chalks 谁愿意给我取些粉笔来?
The rescued miners told us a lot about their adventures.
被营救的矿工告诉了我们很多他们的冒险经历。
Using language
5. S+V+O+C 句式
"主语+动词+宾语+宾语补足语"是英语句子中较为常见的句式。可作宾语补足语的有名词、形容词、副词、介词短语、不定式(短语)、分词(短语)等。
We have made our city a beautiful garden.
我们已把我们的城市变成了一座美丽的花园。
I painted the fence dark green. 我把栅栏漆成了深绿色。
Sara would like me to accompany her. 萨拉想让我陪伴着她。
Using language
6. S+V+A 句式
有时候在谓语动词之后,必须加上一个状语,否则句子就没有意义或意思不完整,这叫作"必具性状语"。
He lives in the countryside. 他住在乡下。
She always walks fast. 他总是走路很快。
Using language
7. S+V+O+A 句式
有时候在宾语之后,也要加上一个"必具性状语",否则向子就没有意义或意思不完整。
Mary put her book on the desk. 玛丽把书放在桌子上。
They treat me very well. 他们待我很好。
Using language
8. There be 存在句
There be 句型是英语中最常用的句型之一,此句型是由"there + be + 主语 + 状语"构成,表示"存在〞,意为"(在….)有……"。它其实是由 there 引导的倒装句的一种,主语位于谓语动词 be 之后,there 仅为引导词,并无实际意义。
There's a restaurant around the corner. 拐角处有一家餐馆。
There are two people waiting outside. 有两个人正在外面等候。
此句型有时不用be 动词,而用不及物动词 live, stand, come, go, lie, remain, exist 等。如:
There stands a hill in the middle of the park.
在公园中央有一座小山。
Once upon a time there lived an old king in the town.
从前镇上住着一位年老的国王。
Using language
练习:请写出加黑词在句中所属的句子成分
1. His words made me confident. _________
2. The old man breathed deeply in the clean yard. _________
3. The challenges in our life must be various. _________
4. These doctors and nurses are fighting against COVID-19 bravely. _________
5. The baby smiled. _________
6. The person told us a white lie. _________
7. She has found her wallet. _________
宾语补足语
状语
表语
宾语
谓语
直接宾语
宾语
Using language
Discuss in groups and complete Activity 2 in page 5.
Mike was playing basketball in the classroom excitedly when the ball slipped from his hand and it hit Mary's smart phone. The phone fell off the desk and the screen of the smart phone was broken. Mike was rather worried. He thought Mary must be very angry. When Mary came back to the classroom, Mike told Mary the truth. To his surprise, Mary was not so angry as he had imagined. Mary said it was also her fault to take the smart phone to school and put it on the desk.
Using language
Complete the posters with the correct form of the words in the box on Page 6.
Badminton
gym
Drama
stage
piano
band
Using language
Complete the posters with the correct form of the words in the box on Page 6.
Debate
Science
Photograph
Thank you
Unit 1 A new start
Using language
Vocabulary
1. stage
on stage 在舞台上
go on/off stage 登上/走下舞台
take the stage 登上舞台
get to/reach a stage 到达一个阶段
go through a stage 经历一个阶段
a stage of development 发展阶段
at this/that stage 在这个/那个阶段
at an early/a late stage 在初期/后期
练习:The children are at different _______(stage) of development.
stages
Vocabulary
2. argue
argument n. 争论,争吵
argue with sb. 与某人争论/争吵
argue about/over sth. 为某事争论/争吵
argue that … 主张/认为……
argue for/against (doing) sth. 赞成/反对(做)某事
argue sb. into/out of doing sth. 说服某人做/不做某事
have an argument with sb. 为某人争论/争吵
have an argument about/over sth. 为某事争论/争吵
get into an argument 争论/争吵起来
练习:I find it hart _________(argue) with him about the topic.
to argue
Vocabulary
3. investigate
investigation n. 调查
investigate sb. (for sth.) (因为某事)调查某人
investigate an incident 调查一个事件
be called in to investigate 应召前来调查
under investigation 正在调查中
conduct an investigation 进行调查
an investigation into 对……的调查
练习:Many people witnessed the car accident, so it was not difficult ____________(investigate).
to investigate
Vocabulary
4. various
vary v. 不同,变化 in various sizes 大小不一
in various ways 以不同的方式
various styles 各种款式;款式齐全;款式多样
various people 各行各业的人
a variety of = varieties of = various 种类繁多的
vary in 在……方面不同 vary with sth. 随……而变化
vary from…to… 从……到……变化
vary between…and… 在……和……之间变化
vary from person to person 因人而异
练习:There are _______(vary) solutions to your problem.
various
Vocabulary
5. apply
application n. 申请;应用 applied adj. 应用的
applicant n. 申请者 apply for 申请
apply to sb. for sth. 向某人申请……
apply sth. to sth. 把……应用到……
apply oneself to 致力于 a job application 求职信
fill in an application form 填写申请表 a written application 书面申请
college applications 大学(入学)申请
make an application to sb. for… 向某人(某机构)申请……
练习:He graduated with high enough marks to ______ for a university.
apply
Leading in
What basic sentence structures do you know
Using language
Match the sentences that share the same structures.
1. I saw a white-haired man. a. He was friendly.
2. I replied. b. The exam made me quite nervous.
3. He gave me a smile. c. I passed him a book.
4. I breathed deeply. d. She agreed.
5. I looked at them in panic. e. He wrote a long letter,
6. I was embarrassed. f. He talked loudly.
7. His words made me a lot more relaxed! g. She looked after her sister patiently.
Using language
Point out the sentence elements of the underlined parts.
1. The students got on the school bus. _______ _______
2. I shall answer your question after class. _______ _______
3. Tom came to ask me for advice. _______ _______
4. He found it important to master English. _______ _______
主语
宾语
谓语
状语
间接宾语
直接宾语
形式宾语
真正宾语
Using language
5. Do you have anything else to say _______ _______
6. He became a teacher at the age of twenty one. _______
7. Would you please tell me your address _______ _______
8. It is our duty to keep our classroom clean and tidy.
_______ _______
9. We must keep it a secret. _______ _______
宾语
定语
间接宾语
直接宾语
形式主语
真正主语
表语
宾语
宾语补足语
Using language
一、句子和句子成分
句子是表达一个完整意义的最小单位,也是构成篇章的重要组成部分。学习英语要以句子为基本单位和基本素材。分析并弄懂每个句子的成分、结构、类型是学习语法的目的,更是理解句意的基础。句子是由词或短语构成的,这些词或短语便是句子成分。句子成分是按照该组成部分在句中所起的作用而划分的。一个完整的句子,由主语和谓语两大部分组成。谓语是一个组成部分,是一个整体,它包括谓语动词、宾语和状语。谓语部分的构成,正确的划分是(括号里面是谓语的构成):
Using language
1. 主语+谓语(不及物动词)
2. 主语+谓语(及物动词+宾语)
3. 主语+谓语(及物动词+双宾语)
4. 主语+谓语(及物动词+复合宾语)
5. 主语+谓语(系动词+表语)
Using language
注意:
·用在及物动词之后或者用在介词之后的成分,叫宾语;
·修饰、限定名词或代词的成分,叫定语;
·修饰动词形容词、副词、介词短语或全句的成分,叫状语;
·用在系动词之后的成分,叫表语;
·用来补充说明宾语的成分,叫补足语;
·对一个名词或代词做进一步解释的成分,叫同位语。
Using language
1. 主语
主语是谓语所表示动作或状态的执行者,是一个句子所叙述的主体,表示句子所说的是"谁"或是"什么"。名词(短语)、代词、数词、不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)和从句等都可作主语。主语一般位于句首,但在there be结构、疑问句(特殊疑问词作主语时例外)和倒装句中主语位于谓语、助动词或情态动词后面。
Using language
A light wind woke among the trees.
微风从林间掠过。(名词短语作主语)
No one but yourself can help you.
只有你自己才能帮助你。(代词作主语)
Three plus five is eight.
3加5等于8。(数词作主语)
To drink a cup of cold water in such hot weather is a great pleasure.
在这么热的天喝一杯冷水是一件很愉快的事。(不定式短语作主语)
Using language
Travelling abroad is popular among young people.
出国旅游受年轻人的欢迎。(动名词短语作主语)
The rich are not always happier than the poor.
有钱人并不一定总比穷人更快乐。(名词化的形容词作主语)
Generally speaking, what we can't get seems better than what we have.
一般说来,我们得不到的东西似乎比我们拥有的东西好。(从句作主语)
It is believed that girls are good at language.
人们认为女孩儿更擅长语言。(it作形式主语,that…作真正的主语)
Using language
2. 谓语动词
谓语动词说明主语的行为或具有的特征和状态,由动词充当,位于主语的后面,是句子的基本构成成分。谓语动词有人称、数和时态的变化。谓语动词分为简单谓语动词和复合谓语动词。
(1)简单谓语动词
不论何种时态、语态、语气,凡是由一个动词或动词词组构成的都是简单谓语动词。
Using language
He shows confidence at any time. 他任何时候都表现出自信。
He looked after two orphans. 他照顾两个孤儿。
I have tried three times in this way. 我已经用这种方法试了三次。
Don't get off the bus until it comes to a stop. 公共汽车停稳后再下车。
Our school was built in 1961. 我们学校建于1961年。
Using language
(2)复合谓语动词
由"情态动词或助动词+动词原形"或"连系动词+表语"构成的谓语叫作复合谓语。
He can speak English very well. 他英语说得很好。
The work must be done before three o'clock. 这项工作必须在三点以前完成。
This film is very interesting. 这部电影很有意思。
He seems unhappy. 他似乎不高兴。
Using language
3. 表语
表语说明主语的性质、特征、身份或状态,与连系动词be, look, seem, appear, feel, taste, smell, sound , become, get, grow, turn, remain, keep, stay 等一起构成复合谓语。表语通常由名词、代词、形容词、数词、副词、介词短语、动词不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)、分词(短语)或从句等充当。
These are books. 这些是书本。(名词作表语)
The winner is you. 获胜者是你。(代词作表语)
Julie always looks cheerful. 朱莉看上去总是很高兴。(形容词作表语)
One plus two is three. 1 加2 等于3。(数词作表语)
Using language
The war was over. 战争结束了。(副词作表语)
He is out of condition. 他身体状况不好。(介词短语作表语)
His dream is to explore the outer space. 他的梦想是探索外太空。(不定式短语作表语)
My hobby is playing the piano. 我的爱好是弹钢琴。(动名词短语作表语)
He was quite surprised to see me there.
在那里见到我他感到非常惊讶。(过去分词短语作表语)
This is what he told me yesterday. 这就是他昨天告诉我的。(从句作表语)
Using language
4. 宾语
宾语表示动作的对象或承受者,一般位于及物动词和介词后面。可以用作宾语的有名词、代词、数词、名词化的形容词、不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)、从句等。宾语又分单宾语、双宾语、复合宾语三种。
单宾语
Richard does not like his job. 理查德不喜欢他的工作。(名词作宾语)
I don't know him. 我不认识他。(代词作宾语)
—How many computers do you need 你们需要几台电脑?
—We need five. 我们需要五台。(数词作宾语)
Using language
We donated money and cotton clothes to help the homeless in the flooded area.
我们捐了钱和棉衣帮助洪灾地区无家可归的人。(名词化的形容词作宾语)
Monica decided to solve the problem on her own.
莫妮卡决定自己解决这个问题。(不定式短语做宾语)
The young man risked losing his life to save the girl.
那个年轻人冒着生命危险去救那个女孩。(动名词短语作宾语)
Miya said that she would return soon. 米娅说她会很快回来的。(从句作宾语)
Using language
同源宾语
同源宾语指由同源动词之名词所作的宾语,前面常有不定冠词a和形容词修饰语。
live a happy life 过着幸福的生活 die a worthy death 死得有价值
laugh a good laugh 大笑 blow a heavy blow 沉重地一击
smile a gentle smile 微微一笑 sing a sweet song 唱一首甜美的歌
dream a terrible dream 做一个噩梦 die a glorious death 光荣牺牲
Using language
(2) 双宾语
双宾语是指动词后带有两个宾语,一个是间接宾语,一个是直接宾语。直接宾语表示动作的承受者或结果,通常指物;间接宾语表示动作是对谁做的,为谁做的,通常指人。间接宾语一般位于直接宾语之前,也可位于其后。但位于后面时在它的前面须加介词to 或 for.
They offered me the job. — They offered the job to me.
他们给我提供了那份工作。(me 为间接宾语,the job为直接宾语)
Please show me your passport. — Please show your passport to me.
请向我出示你的护照。(me 为间接宾语,your passport为直接宾语)
Cora played us some light music. — Cora played some light music for us.
科拉给我们演奏了一些轻音乐。(us 为间接宾语,some light music为直接宾语)
Using language
(3)复合宾语
有些动词除了带有宾语外,还需要另外一个成分来说明宾语的情况,以补充意义上的不足,让宾语的意义完整。这种起补充说明作用的词或短语叫作宾语补足语。宾语和补足语之间存在着逻辑上的主谓关系,二者一起构成复合宾语。能作宾语补足语的有名词、形容词、介词短语、不定式短语、分词短语、副词等。判断某个成分是否为宾补,这跟谓语动词的性质有关。宾补是谓语动词作用于宾语的结果。如谓语动词具有"使令""指使""影响"宾语做某事的作用,谓语动词使宾语怎么样,成为什么,变成什么(如cause 类,make 类)。谓语动词具有感官性能,对宾语的动作具有感知作用(如 see, hear, find 类)。
We all find Josie a good girl.
我们都发现乔茜是一个好女孩。(Josie 为宾语,a good girl 为宾语补足语)
Using language
Don't force such a little baby to learn.
不要逼这样小的孩子学习。(a little baby 为宾语,to learn为宾语补足语)
He made himself known to them first.
他先向他们做了自我介绍。(himself 为宾语,known to them为宾语补足语)
We must keep it a secret.
我们必须对此保密。(it为宾语,a secret 为宾语补足语)
Please make yourself at home.
请随便一点。(yourself为宾语,at home为宾语补足语)
Please keep the dog out.
请把狗关在外面。(the dog 为宾语,out 为宾语补足语)
Using language
5. 定语
修饰或限定名词或代词的成分叫作定语。定语是用来描述名词或代词的修饰语,它常和名词构成名词短语。定语分为前置定语和后置定语两种。
前置定语
可以充当前置定语的有形容词、代词、数词、名词或名词所有格、动名词、分词等。一般而言,单个的词语作定语都是前置定语。
This is a heated argument.
这是一场激烈的辦论。(形容词作定语)
The doctor told me to open my mouth and put out my tongue.
医生让我张开嘴巴伸出舌头。(代词作定语)
He drank three whole glasses. 他喝了满满三杯。(数词作定语)
Using language
He works in a shoe factory. 他在一家鞋厂上班。(名词作定语)
Do you know Vela's mother 你认识维拉的妈妈吗?(名词所有格作定语)
Books can't be taken away from the reading room.
书籍不可以从阅览室中带走。(动名词作定语)
We should adapt to the changing situation quickly.
我们应该迅速地适应变化的形势。(现在分词作定语)
Is there any difference between spoken English and written English?
英语口语和书面语之间存在什么不同吗?(过去分词作定语)
Using language
(2) 后置定语
可以充当后置定语的有形容词短语、介词短语、地点方位副词、不定式短语、分词短语、从句等。词组或从句作定语都是后置定语。
The lady was carrying a basket full of vegetables.
那位女士提着一只盛满蔬菜的篮子。(形容词短语作定语)
The girl in white is his sister.
穿白衣服的女孩是他妹妹。(介词短语作定语)
Fill in the blanks in the sentences below.
在下面的句子中填空。(地点方位副词作定语)
Using language
Now is your chance to talk to him.
马上就是你和他谈话的机会了。(不定式短语作定语)
Do you know the man speaking to our headmaster
你认识正在跟我们的校长说话的那个人吗?(现在分词短语作定语)
Most of the people invited to the conference are from Europe.
应遊出席会议的人大多来自政洲。(过去分词短语作定语)
Do you know the man who spoke just now
你认识刚才发言的那个人吗?(从句作定语)
Using language
6. 状语
状语是用来修饰动词、形容词、副词或句子的一种成分。它可以表示时间、地点、方式、程度、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步或比较等。通常由副词、介词短语、不定式(短语)、分词(短语)、形容词、名词、从句等充当。
Jennifer runs very fast. 珍妮弗跑得很快。(副词作状语)
I'll be back in a while. 我一会儿就回来。(介词短语作状语)
He waited to see the result of the game.
他等着看比赛结果。(不定式短语作状语)
Living in the country, they have few amusements.
因为住在农村,他们没有什么娱乐活动。(现在分词短语作状语)
Using language
Given more time and money, we would have done the work better.
如果给予更多的时间和钱的话,我们会把工作做得更好。(过去分词短语作状语)
She sat there, silent.
她坐在那儿,一声不吭。(形容词作状语)
Wait a moment, I'll come.等一会儿,我就来。(名词作状语)
It rained so hard that they had to put off the sports meeting.
雨下得很大,他们不得不推迟运动会。(从句作状语)
He was absent from the lecture yesterday because he was ill.
昨天他没参加讲座,是因为病了。(从句作状语)
Using language
7. 补足语
补足语是用来说明宾语的性质、状态等的一种句子成分。宾语和宾语补足语构成了复合宾语,它们在逻辑上有主谓关系。名词、形容词、副词、介词短语、现在分词、过去分词、不定式(短语)等皆可作补足语。含有宾语补足语的句子在变为被动句时,宾语补足语便成了主语补足语。
She was appointed manager of the company.
她被任命为公司经理。(名词短语作补足语)
We should keep our classroom clean and tidy.
我们应该保持教室干净整洁。(形容词短语作补足语)
Using language
Miranda likes sleeping with the light on.
米兰达喜欢开着灯睡觉。(副词作补足语)
When she woke up, she found herself in a hospital.
当她醒来时,她发现自己在一家医院里。(介词短语作补足语)
Her mother doesn't allow her to go out alone at night.
她妈妈不允许她晚上一个人出去。(不定式短语作补足语)
Our English teacher always has us reading and reciting.
我们的英语老师总是让我们读和背。(现在分词短语作补足语)
He always kept us greatly surprised.
他总是让我们大吃一惊。(过去分词作补足语)
Using language
8. 同位语
对句子中某一成分作进一步解释说明,与该成分在语法上处于同等地位的句子成分叫作同位语。可以用作同位语的有名词、代词、数词或从句等。
This is Mr. Li, our headmaster.
这是我们的校长李老师。(名词短语作同位语)
We each have a cellphone now.
现在我们每个人都有手机了。(代词作同位语)
Are you two ready to start out now
你们两个人都准备好现在出发了吗?(数词作同位语)
The news that our team has won again is true.
我们队又赢了的消息是真的。(从句作同位语)
Using language
名称 英语全称 简称
主语+谓语动词 Subject + Verb S+V
主语+谓语动词+宾语 Subject + Verb + Object S+V+O
主语+连系动词+表语 Subject + Verb + Predicative S+V+P
主语+谓语动词+间接宾语+直接宾语 Subject + Verb + Indirect Object + Direct Object S+V+IO+DO
主语+谓语动词+宾语+宾语补足语 Subject + Verb + Object + Complement S+V+O+C
主语+谓语动词+状语 Subject + Verb + Adverbial S+V+A
主语+谓语动词+宾语+状语 Subject + Verb + Object + Adverbial S+V+O+A
存在句 There be There be
二、八种基本句型
不同的句子成分构成了英语中各式各样的句子。所有句子中,归纳起来共有八种最基本的句型。其他的各种句型都是由这八种基本句型扩展而来的。
Using language
S+V 句式
这种句型中的 V 是指不及物动词。
在英语中大多数动词既可作及物动词又可作不及物动词,纯粹不及物动词数量较少。常见的有 apologize, appear, arrive, come, die, disappear, dive, exist, fall, flow, happen, rise 等。
Things changed. 情况有了变化。
The bell has rung. 铃声响过了。
What happened over there 那儿发生了什么事?
Kevin apologized to his mother for his rudeness.
凯文为他的粗鲁向他母亲道了歉。
Using language
2. S+V+O句式
英语中绝大多数及物动词都是只带一个宾语的动词。
Farmers in our county grow all kinds of vegetables.
我们县的农民种植各种各样的蔬菜。
Danny runs a big clothes factory. 丹尼经营一家大型服装厂。
Using language
3. S+V+P句式
这种句型结构主要指谓语动词为连系动词的情况。连系动词除 be 外,还有 look, seem, appear, feel, taste, smell, ssound, become, get, grow, turn, remain, keep, stay 等。作表语的可以是名词、形容词、代词、副词、介词短语、不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)、从句等。
Jackson is a common English name. 杰克逊是常见的英语人名。
The weather is becoming colder and colder. 天气变得越来越冷。
It looks like a made-up word. 这看起来像是一个杜撰的词。
Her job is looking after children.她的工作是照料小孩。
Using language
4. S+V+IO+DO 句式
这是带双宾语的向式结构,IO为间接宾语,DO 为直接宾语。直接宾语一般是指物的名词或代词,间接宾语一般是指人的名词或代词。
Her friend promised her a birthday gift. 她的朋友答应她给她一份生日礼物。
Father made me a wooden gun. 爸爸给我做了一把木头手枪。
Who'd like to fetch me some chalks 谁愿意给我取些粉笔来?
The rescued miners told us a lot about their adventures.
被营救的矿工告诉了我们很多他们的冒险经历。
Using language
5. S+V+O+C 句式
"主语+动词+宾语+宾语补足语"是英语句子中较为常见的句式。可作宾语补足语的有名词、形容词、副词、介词短语、不定式(短语)、分词(短语)等。
We have made our city a beautiful garden.
我们已把我们的城市变成了一座美丽的花园。
I painted the fence dark green. 我把栅栏漆成了深绿色。
Sara would like me to accompany her. 萨拉想让我陪伴着她。
Using language
6. S+V+A 句式
有时候在谓语动词之后,必须加上一个状语,否则句子就没有意义或意思不完整,这叫作"必具性状语"。
He lives in the countryside. 他住在乡下。
She always walks fast. 他总是走路很快。
Using language
7. S+V+O+A 句式
有时候在宾语之后,也要加上一个"必具性状语",否则向子就没有意义或意思不完整。
Mary put her book on the desk. 玛丽把书放在桌子上。
They treat me very well. 他们待我很好。
Using language
8. There be 存在句
There be 句型是英语中最常用的句型之一,此句型是由"there + be + 主语 + 状语"构成,表示"存在〞,意为"(在….)有……"。它其实是由 there 引导的倒装句的一种,主语位于谓语动词 be 之后,there 仅为引导词,并无实际意义。
There's a restaurant around the corner. 拐角处有一家餐馆。
There are two people waiting outside. 有两个人正在外面等候。
此句型有时不用be 动词,而用不及物动词 live, stand, come, go, lie, remain, exist 等。如:
There stands a hill in the middle of the park.
在公园中央有一座小山。
Once upon a time there lived an old king in the town.
从前镇上住着一位年老的国王。
Using language
练习:请写出加黑词在句中所属的句子成分
1. His words made me confident. _________
2. The old man breathed deeply in the clean yard. _________
3. The challenges in our life must be various. _________
4. These doctors and nurses are fighting against COVID-19 bravely. _________
5. The baby smiled. _________
6. The person told us a white lie. _________
7. She has found her wallet. _________
宾语补足语
状语
表语
宾语
谓语
直接宾语
宾语
Using language
Discuss in groups and complete Activity 2 in page 5.
Mike was playing basketball in the classroom excitedly when the ball slipped from his hand and it hit Mary's smart phone. The phone fell off the desk and the screen of the smart phone was broken. Mike was rather worried. He thought Mary must be very angry. When Mary came back to the classroom, Mike told Mary the truth. To his surprise, Mary was not so angry as he had imagined. Mary said it was also her fault to take the smart phone to school and put it on the desk.
Using language
Complete the posters with the correct form of the words in the box on Page 6.
Badminton
gym
Drama
stage
piano
band
Using language
Complete the posters with the correct form of the words in the box on Page 6.
Debate
Science
Photograph
Thank you
