外研版(2019)必修 第一册Unit 5 Into the wild Using language课件(共53张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版(2019)必修 第一册Unit 5 Into the wild Using language课件(共53张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 4.2MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-10-24 14:39:14 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共53张PPT)
Unit 5 Into the wild
Using Language
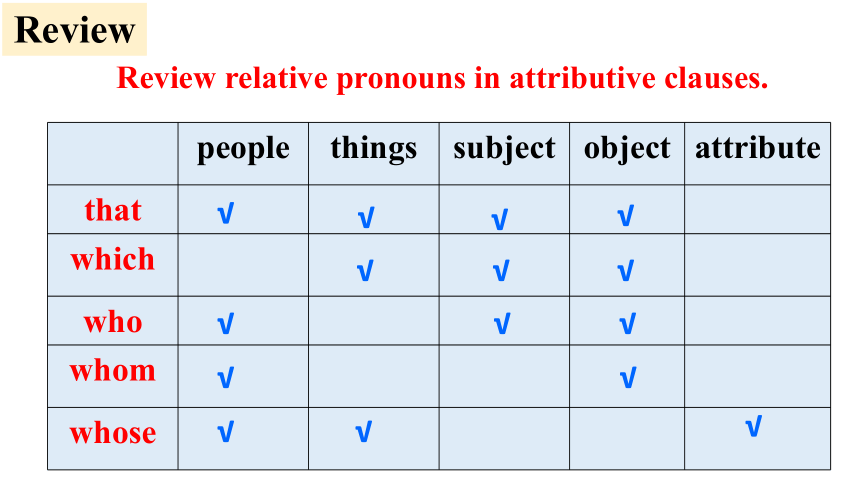
Review relative pronouns in attributive clauses.
people things subject object attribute
that
which
who
whom
whose
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
Review
Review
1. He told me a story yesterday, ________ I thought was interesting.
2. The man ______________ you met just now is my brother.
3. Take the book ____________ is lying on the table.
4. The house ________ windows face north belongs to him.
5. Do you know the things and persons ______ they are talking about
6. You should make eye contact with the person to ______ you are talking.
7. Do you have anything _______ you want to say for yourself
8. This is the very book ______ I’m looking for.
which
that/who/whom
that/which
whose
that
whom
that
that
关系词
关系代词
关系副词
who, which, that, whom, whose
在从句中充当主语、宾语等成分。
where, when, why
在从句中充当状语成分。
The apple I ate yesterday was really sweet.
I ever met a person who was quite famous.
I cannot forget the day when I first entered senior high.
Review
ENGLISH
限制性定语从句
when
1. I still remember the day when I first came to Yuci.
2. You’ve entered into an age when knowledge makes you rich.
当先行词是表示____的名词(如 time, day, year, month, week等), 且从句成分完整时,定语从句用when引导.
1. 关系副词的选择
时间
1. I still remember the time ______ we first met each other.
2. I still remeber the time __________we spent together.
when
which/that
1. Can you tell me the office where he works
2. People are more concerned about the environment where they live.
当先行词是表示_____的名词(如place, room, airport等),且从句成分完整时,定语从句用where引导.
where
1. 关系副词的选择
地点
1. This is the place ___________ we visited last time.
2. This is the place _________ he used to work.
which/that
where
1. They have reached the point ______ they have to break up with each other.
2. It’s helpful to put children in a situation ________ they can see themseves differently.
除地点名词后,where还可用于case, condition, example, situation, stage, point, system, atmosphere, position等表示抽象地点的名词前。
1. 关系副词的选择
where
where
where
1. Do you know the reason why he was late yesterday
2. This is the reason why he gave up trying in the end.
当先行词是表示原因的名词_______,且从句成分完整时,定语从句用why引导,且只能引导限定性定语从句。
why
1. 关系副词的选择
reason
1. I won’t believe the reason ___________ you have given me.
2. This is the reason _______ she cied.
that/which
why
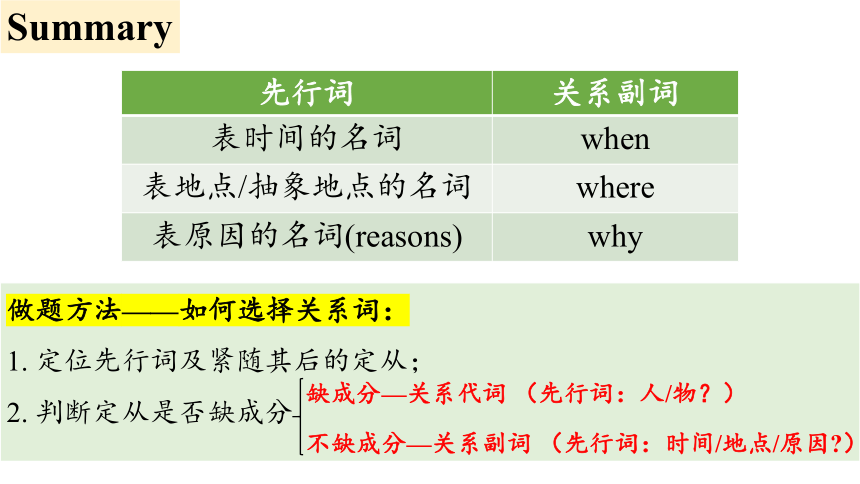
先行词 关系副词
表时间的名词 when
表地点/抽象地点的名词 where
表原因的名词(reasons) why
Summary
做题方法——如何选择关系词:
1. 定位先行词及紧随其后的定从;
2. 判断定从是否缺成分
缺成分—关系代词 (先行词:人/物?)
不缺成分—关系副词 (先行词:时间/地点/原因 )
1. Do you know the teenager ________ you are talking about
2. This is the house _________ I lived in for three years.
2. 介词+关系代词
who/that
which/that
1. Do you know the teenager about ______ you are talking
2. This is the house in _______ I lived for three years.
whom
which
思考:在表示时间、地点和原因状语时,“介词+关系代词”是否可以替换为关系副词“when, where, why”
思考:介词是否可以提前至关系词之前?
1. I still remember the day __________ I lost my money.
2. We visited the yard __________ a famous poet once lived.
3. Patience is a kind of quality, ____________ you can’t work well.
代入法:1. 确定先行词及从句;2. 从句 ? 先行词 (搭配问题)
2. 介词+关系代词
I lost my money ______ the day 根据先行词的搭配
“介词+关系代词”中介词的确定
on
on which
A famous poet once lived ___ the yard 根据从句中动词的搭配
in
in which
You can’t work well _______ patience. 根据意义确定介词
without
without which
1. I like girls ________ hair is black and long.
2. I like books ________ covers are beautiful.
I like books the covers of which are beautiful.
2. 介词+关系代词
I like girls the hair of whom is black and long.
whose = ... of which / of whom
whose
whose
Can you tell me the way ________ you used to solve the problem. problem.
3. “way”作为先行词时
1. 从句缺成分
2. 从句不缺成分
I like the way _______________ you talk to me.
that/in which/省略
that/which
the way作先行词时:
1. 从句缺少成分时,使用关系代词that/which.
2. 从句不缺成分时,可使用that/in which/省略.
ENGLISH
定语从句之关系副词when, where, why
This is the place _____________ we visited last time.
This is the place _____________ we visited the equipment设备 last time.
I still remember the time __________ we spend together.
I still remember the time __________ we first met each other.
This is the reason __________ she gave me.
This is the reason __________ she cried.
(
)
定语从句不完整,先行词在定语从句中做宾语,指物
that/which
(
)
定语从句完整,也不缺定语,缺状语,指地点
where
(
)
定语从句不完整,先行词在定语从句中做宾语,指物
that/which
(
)
定语从句完整,也不缺定语,缺状语,指时间
when
(
(
)
定语从句不完整,先行词在定语从句中做宾语,指物
that/which
)
定语从句完整,也不缺定语,缺状语,指原因
why
ENGLISH
做题步骤
画出定语从句,
看定语从句缺不缺主/宾/表
缺
关系代词
that/which
/who/whom/as
不缺
whose
关系副词
when, where, why
缺定语
缺状语
ENGLISH
非限制性定语从句
ENGLISH
定语从句分类
限制性定语从句
非限制性定语从句
先行词范围很广,用限制性定语从句缩小限定先行词的范围。缺了从句,主句意思会受影响。从句
I'm enjoying the book (that you lent me.)
先行词唯一,非限制性定语从句为主句提供附加信息,补充说明。
缺了从句,主句意思不受影响。
This is my friend Tina, (who is a good girl.)
I met the man (who lives next door.)
I saw Yao Ming, (who is the greatest NBA star.)
形式上:不用逗号隔开主从句
形式上:用逗号隔开主从句
ENGLISH
翻译
My sister (who is a teacher )always encourages me to study hard.
My sister, ( who is a teacher ), always encourages me to study hard.
我的姐姐,她是个老师,总是鼓励我努力学习
(我只有一个姐姐,她的职业是老师)
我那当老师的姐姐总是鼓励我努力学习。(隐含我不止一个姐姐)
ENGLISH
注意事项
1.非限制性定语从句有逗号。从句与主句用逗号分隔开了
My sister (who is a teacher )always encourages me to study hard.
(限制性定语从句,修饰限定,我那当老师的姐姐总是鼓励我努力学习)
My sister, ( who is a teacher ), always encourages me to study hard.
(非限制性定语从句,补充说明,我的姐姐,她是个老师,总是鼓励我努力学习)
ENGLISH
注意事项
2. 修饰对象不同。
限制性定语从句只能修饰从句前面的那个名词,而非限制性定语从句,除了可以修饰它前面的名词,还可以修饰它前面的整个句子,或句子的部分内容,如:
My sister always hits me, which makes me unhappy.
(which引导的从句不再具体修饰哪个名词,而是指代了它前面整个句子,把which的含义翻译出来,就是“这件事……”,指的就是前面姐姐总是打我那件事)
ENGLISH
注意事项
3. 关系词使用不同。
在限制性定语从句中,先行词是人、物或事情时,关系代词都可以用that;而非限制性定语从句绝对不可以用that引导,指物用which替代。
The holiday, which we’re looking forward to, is coming.
指原因不用why,用for which替代
I have told them the reason, for which I changed my mind.
ENGLISH
when引导的非限制性定语从句
when在非限制性定语从句中作时间状语,指代主句中表示时间的词语。
He will put off the picnic until May 1st, when he will be free.
他将把郊游推迟到5月1号,那时他将有空。
where引导的非限制性定语从句
where在非限制性定语从句中作地点状语,指代主句中表示地点的词语。They reached there yesterday, where a party will be held.
他们昨天抵达那里, 有一个关于销售的谈判在那儿举行。
Complete the email with where, when or why. (P53)
where
when
why
where
总结做题方法
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
找先行词确定其性质(人/物)
将先行词代入从句中看做何成分
确定关系代词 /关系副词
抽象地点名词
先行词为表地点含义的抽象名词:situation, case, position, point 等,如从句中缺少状语时,用where引导定于从句。
It's helpful to put children in a situation where they can see themselves differently.
Their relationship has reached to the point where they have to divorece.
Step 4: Language practice
Activity 3
where
when
why
where
3
Exercises from CEE
1.He wrote a letter _____ he explained what had happened in the accident.
2.Sales director is a position _____ communication ability is just as important as sales skills.
3. As the smallest child of his family, Alex is longing for the time______he should be able to be independent.
where
where
when
4.There are many good websites _____ you can check out the latest in the science world.
5.His interest started a few years ago, _____ he was in college and studying wildlife science.
6.Finally, after four hours, they arrived at the campsite(营地) _____ their parents were waiting.
where
when
where
1.Love me, love my dog.
2.Don’t ride the high horse.
3.Never offer to teach fish to swim.
4.Fine feathers make fine birds.
Lead-in
Guess the meanings of the following proverbs about animals.
爱屋及乌。
勿摆架子。
不要班门弄斧。
人凭衣裳马凭鞍。
Animal idioms
Look at the pictures and complete the idioms with animal names.(P54)
as busy as a(n) _______
kill two ________with one stone
bee
birds
忙得不可开交
一石二鸟;一箭双雕;一举两得
When the cat’s away, the _______ will play.
hold your _______
mice
horses
猫儿不在,老鼠翻天;
山中无老虎,猴子称大王
[非正式用语]且慢;请三思
It’s raining _______ and _______ .
cats
dogs
[口语]下倾盆大雨
Find more animal idioms.
Love me, love my dog. 爱屋及乌。
like a cat on hot bricks 像热锅上的蚂蚁
He is a lucky dog. 他是个幸运儿。
dark horse 黑马
Never offer to teach fish to swim.
不要班门弄斧。
A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush.
双鸟在林不如一鸟在手。
Fine feathers make fine birds.
人要衣装,马要鞍。
Cats hide their claws.
知人知面不知心。
Don't count your chickens before they're hatched.
鸡蛋未孵出,先别数小鸡。
A crow is never the whiter for washing herself often.
江山易改,本性难移。
Every dog has his day. 人人皆有得意时。
Let sleeping dogs lie. 勿惹是生非。
The frog in the well knows nothing of the great ocean.
井底之蛙,不知大海。
The fox preys farthest from his hole.
兔子不吃窝边草。
Complete the paragraph with the animal idioms. (P54)
English idioms are a way of adding colour to the language. For example, instead of saying “It’s raining heavily”, you could say “1_____________________”. Another reason to use idioms is that they are concise. For example, to describe someone who is always working or busy doing something, we can say they are 2 ________________ .
It’s raining cats and dogs
as busy as a bee
concise adj. 简明的;简练的
If they’re rushing into something and should wait and be patient, you could say “3 ______________ ”. Learning idioms can be fun, especially when we compare them to Chinese equivalents. Take, for example, “4 ___________
_____________________ ” (people do what they want and have fun when someone in authority is absent) and
“5 ________________________ ” (solve two problems with one action) – are there corresponding idioms in Chinese
hold your horses
equivalent n. 对应词
When the cat’s
away, the mice will play
kill two birds with one stone
corresponding adj. 相应的;相关的
A: She’s as busy as a bee.
B: What makes you say that
A: She is currently doing three part-time jobs. I
haven’t seen her for three months.
Vocabulary building: Animal idioms
Work in pairs. Find more animal idioms. Choose an idiom and describe a situation with it.
sample
Dogs were first domesticated over 14,000 years ago. Sheep, cows and pigs have been kept at home as sources of food for around 7,000 years.
The oldest zoo in the world is in Vienna, opened in 1752. The oldest zoo in China is Beijing Zoo, which was founded in 1906.
Pre-listening: Learn words and expressions
1.zookeeper
2.Keep Wild Animals Wild
3.in danger of
4.die out
5.programme
6.fail-failure
7.admit
8.totally
9.allow sb. to do sth
10.as much as possible
11.educate
12.observe
13.be similar to
14.natural environment
15.offer
16.a huge amount of
17.on the whole
18.do good for
19.continue
20.after a short break
动物园管理员
处于…危险之中
灭亡;逐渐消失
计划,方案; 节目
承认; 招供
与…相似
提供
大量的
大体上,基本上
行善
继续
短暂休息后
Analyze long and difficult sentences
1.We have seen a lot of examples where the animals start to depend too much on humans, and are unable to live on their own when returned to the wild.
2.I totally agree that people should lean as much as possible about animals because we share the planet with them.
3.They are here to discuss whether we should keep wild animals in zoo.
While-listening
Activity 7 Listen to the TV debate and choose the correct topic
Can zoo animals survive in the wild
Can zoos offer animals their natural environment
Should we keep wild animals in the zoo
Should we educate people more about animals
Listen to find out the main idea
Listening tips:
In a debate, first listen out the main topic. The main topic is usually a statement or a question at the very start of the debate.
While-listening
Activity 8 Listen again and complete the mind map
1. in danger of dying out
2. educate people about animals
3. natural environment
4. depend too much on humans
5. as good as
6. do more good for
Post-listening
Look at your listening material and talk about how the speakers express agreement and disagreement.
Disagreeing:
1.I am afraid I don't agree that these programme are always successful.
2. But you must admit that there are successful ones.
3. I'm sorry, but that's not true.
Agreeing:
1.I totally agree that people should learn as much as possible about animals.
2. Exactly!
Post-listening
Activity 9 Work in pairs. Hold a debate on whether we should keep animals as pets.
Student A: Turn to Page 83. (agree)
Student B: Turn to Page 86. (disagree)
Student A: Turn to Page 83. (agree)
You are in favor of keeping animals as pets. You have the following arguments:
1. Keeping pets develops a kind and caring attitude towards animals.
2. Keeping pets is good for people's physical and mental health.
3. Keeping pets helps people know more about animals.
Student B: Turn to Page 86. (disagree)
You are against keeping pets as pets. You have the following arguements:
1. Caring for other people is more important than caring for animals.
2. It is bad for animals's physical and mental health to be kept as pets.
3.Animals kept at home can cause trouble for neighbours.
Agreeing
1. Exactly!
2. I agree.
3. That is true.
4. I see your point.
5. No doubt about it.
6. I suppose so.
Disagreeing
1. I don’t agree.
2. That’s just not true.
3. I’m afraid I totally disagree.
4. I’m not so sure about that.
5. I don’t think so.
6. That’s not always the same.
Topic: Whether we should keep animals as pets
A:_______________(我方支持把动物当宠物养),because I have seen that keeping pets develops a kind and caring attitude towards animals. _____________________(例如,那些把动物当宠物养的人每天都会悉心照顾他们宠物,比如,每天为他们洗澡,陪他们玩耍等等)。They love their animals very much.
B: ________________(恐怕,我不同意你的观点。并不是所有人都爱他们的宠物。有时候我们会发现,有的宠物,比如狗,会被主人遗弃在街道上。)From this point, I think it is bad for animals' physical and mental health to be kept as pets.
A:_____________________(但是你必须承认很多人是爱他们的宠物的!他们把宠物当成自己的家人。宠物也会让人们感到快乐)。Therefore, keeping pets is not only good for people's physical and mental health, but also helps people know more about animals.
B:_________________(抱歉,但那是不正确的。动物应该属于大自然环境)。So, animals kept at home can cause trouble for neighbours and it is bad for animals physical and mental health.
I agree that we should keep animals as pets because ……
I don’t agree that we should keep animals as pets because ……
FOR
AGAINST
Keeping pets develops a kind and caring attitude towards animals.
Keeping pets is good for people’s physical and mental health.
Keeping pets helps people know more about animals.
…
Caring for other people is more important than caring for animals.
It’s bad for animals’ physical and mental health to be kept as pets.
Animals kept at home can cause trouble for neighbors.
…
Unit 5 Into the wild
Using Language
Review relative pronouns in attributive clauses.
people things subject object attribute
that
which
who
whom
whose
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
Review
Review
1. He told me a story yesterday, ________ I thought was interesting.
2. The man ______________ you met just now is my brother.
3. Take the book ____________ is lying on the table.
4. The house ________ windows face north belongs to him.
5. Do you know the things and persons ______ they are talking about
6. You should make eye contact with the person to ______ you are talking.
7. Do you have anything _______ you want to say for yourself
8. This is the very book ______ I’m looking for.
which
that/who/whom
that/which
whose
that
whom
that
that
关系词
关系代词
关系副词
who, which, that, whom, whose
在从句中充当主语、宾语等成分。
where, when, why
在从句中充当状语成分。
The apple I ate yesterday was really sweet.
I ever met a person who was quite famous.
I cannot forget the day when I first entered senior high.
Review
ENGLISH
限制性定语从句
when
1. I still remember the day when I first came to Yuci.
2. You’ve entered into an age when knowledge makes you rich.
当先行词是表示____的名词(如 time, day, year, month, week等), 且从句成分完整时,定语从句用when引导.
1. 关系副词的选择
时间
1. I still remember the time ______ we first met each other.
2. I still remeber the time __________we spent together.
when
which/that
1. Can you tell me the office where he works
2. People are more concerned about the environment where they live.
当先行词是表示_____的名词(如place, room, airport等),且从句成分完整时,定语从句用where引导.
where
1. 关系副词的选择
地点
1. This is the place ___________ we visited last time.
2. This is the place _________ he used to work.
which/that
where
1. They have reached the point ______ they have to break up with each other.
2. It’s helpful to put children in a situation ________ they can see themseves differently.
除地点名词后,where还可用于case, condition, example, situation, stage, point, system, atmosphere, position等表示抽象地点的名词前。
1. 关系副词的选择
where
where
where
1. Do you know the reason why he was late yesterday
2. This is the reason why he gave up trying in the end.
当先行词是表示原因的名词_______,且从句成分完整时,定语从句用why引导,且只能引导限定性定语从句。
why
1. 关系副词的选择
reason
1. I won’t believe the reason ___________ you have given me.
2. This is the reason _______ she cied.
that/which
why
先行词 关系副词
表时间的名词 when
表地点/抽象地点的名词 where
表原因的名词(reasons) why
Summary
做题方法——如何选择关系词:
1. 定位先行词及紧随其后的定从;
2. 判断定从是否缺成分
缺成分—关系代词 (先行词:人/物?)
不缺成分—关系副词 (先行词:时间/地点/原因 )
1. Do you know the teenager ________ you are talking about
2. This is the house _________ I lived in for three years.
2. 介词+关系代词
who/that
which/that
1. Do you know the teenager about ______ you are talking
2. This is the house in _______ I lived for three years.
whom
which
思考:在表示时间、地点和原因状语时,“介词+关系代词”是否可以替换为关系副词“when, where, why”
思考:介词是否可以提前至关系词之前?
1. I still remember the day __________ I lost my money.
2. We visited the yard __________ a famous poet once lived.
3. Patience is a kind of quality, ____________ you can’t work well.
代入法:1. 确定先行词及从句;2. 从句 ? 先行词 (搭配问题)
2. 介词+关系代词
I lost my money ______ the day 根据先行词的搭配
“介词+关系代词”中介词的确定
on
on which
A famous poet once lived ___ the yard 根据从句中动词的搭配
in
in which
You can’t work well _______ patience. 根据意义确定介词
without
without which
1. I like girls ________ hair is black and long.
2. I like books ________ covers are beautiful.
I like books the covers of which are beautiful.
2. 介词+关系代词
I like girls the hair of whom is black and long.
whose = ... of which / of whom
whose
whose
Can you tell me the way ________ you used to solve the problem. problem.
3. “way”作为先行词时
1. 从句缺成分
2. 从句不缺成分
I like the way _______________ you talk to me.
that/in which/省略
that/which
the way作先行词时:
1. 从句缺少成分时,使用关系代词that/which.
2. 从句不缺成分时,可使用that/in which/省略.
ENGLISH
定语从句之关系副词when, where, why
This is the place _____________ we visited last time.
This is the place _____________ we visited the equipment设备 last time.
I still remember the time __________ we spend together.
I still remember the time __________ we first met each other.
This is the reason __________ she gave me.
This is the reason __________ she cried.
(
)
定语从句不完整,先行词在定语从句中做宾语,指物
that/which
(
)
定语从句完整,也不缺定语,缺状语,指地点
where
(
)
定语从句不完整,先行词在定语从句中做宾语,指物
that/which
(
)
定语从句完整,也不缺定语,缺状语,指时间
when
(
(
)
定语从句不完整,先行词在定语从句中做宾语,指物
that/which
)
定语从句完整,也不缺定语,缺状语,指原因
why
ENGLISH
做题步骤
画出定语从句,
看定语从句缺不缺主/宾/表
缺
关系代词
that/which
/who/whom/as
不缺
whose
关系副词
when, where, why
缺定语
缺状语
ENGLISH
非限制性定语从句
ENGLISH
定语从句分类
限制性定语从句
非限制性定语从句
先行词范围很广,用限制性定语从句缩小限定先行词的范围。缺了从句,主句意思会受影响。从句
I'm enjoying the book (that you lent me.)
先行词唯一,非限制性定语从句为主句提供附加信息,补充说明。
缺了从句,主句意思不受影响。
This is my friend Tina, (who is a good girl.)
I met the man (who lives next door.)
I saw Yao Ming, (who is the greatest NBA star.)
形式上:不用逗号隔开主从句
形式上:用逗号隔开主从句
ENGLISH
翻译
My sister (who is a teacher )always encourages me to study hard.
My sister, ( who is a teacher ), always encourages me to study hard.
我的姐姐,她是个老师,总是鼓励我努力学习
(我只有一个姐姐,她的职业是老师)
我那当老师的姐姐总是鼓励我努力学习。(隐含我不止一个姐姐)
ENGLISH
注意事项
1.非限制性定语从句有逗号。从句与主句用逗号分隔开了
My sister (who is a teacher )always encourages me to study hard.
(限制性定语从句,修饰限定,我那当老师的姐姐总是鼓励我努力学习)
My sister, ( who is a teacher ), always encourages me to study hard.
(非限制性定语从句,补充说明,我的姐姐,她是个老师,总是鼓励我努力学习)
ENGLISH
注意事项
2. 修饰对象不同。
限制性定语从句只能修饰从句前面的那个名词,而非限制性定语从句,除了可以修饰它前面的名词,还可以修饰它前面的整个句子,或句子的部分内容,如:
My sister always hits me, which makes me unhappy.
(which引导的从句不再具体修饰哪个名词,而是指代了它前面整个句子,把which的含义翻译出来,就是“这件事……”,指的就是前面姐姐总是打我那件事)
ENGLISH
注意事项
3. 关系词使用不同。
在限制性定语从句中,先行词是人、物或事情时,关系代词都可以用that;而非限制性定语从句绝对不可以用that引导,指物用which替代。
The holiday, which we’re looking forward to, is coming.
指原因不用why,用for which替代
I have told them the reason, for which I changed my mind.
ENGLISH
when引导的非限制性定语从句
when在非限制性定语从句中作时间状语,指代主句中表示时间的词语。
He will put off the picnic until May 1st, when he will be free.
他将把郊游推迟到5月1号,那时他将有空。
where引导的非限制性定语从句
where在非限制性定语从句中作地点状语,指代主句中表示地点的词语。They reached there yesterday, where a party will be held.
他们昨天抵达那里, 有一个关于销售的谈判在那儿举行。
Complete the email with where, when or why. (P53)
where
when
why
where
总结做题方法
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
找先行词确定其性质(人/物)
将先行词代入从句中看做何成分
确定关系代词 /关系副词
抽象地点名词
先行词为表地点含义的抽象名词:situation, case, position, point 等,如从句中缺少状语时,用where引导定于从句。
It's helpful to put children in a situation where they can see themselves differently.
Their relationship has reached to the point where they have to divorece.
Step 4: Language practice
Activity 3
where
when
why
where
3
Exercises from CEE
1.He wrote a letter _____ he explained what had happened in the accident.
2.Sales director is a position _____ communication ability is just as important as sales skills.
3. As the smallest child of his family, Alex is longing for the time______he should be able to be independent.
where
where
when
4.There are many good websites _____ you can check out the latest in the science world.
5.His interest started a few years ago, _____ he was in college and studying wildlife science.
6.Finally, after four hours, they arrived at the campsite(营地) _____ their parents were waiting.
where
when
where
1.Love me, love my dog.
2.Don’t ride the high horse.
3.Never offer to teach fish to swim.
4.Fine feathers make fine birds.
Lead-in
Guess the meanings of the following proverbs about animals.
爱屋及乌。
勿摆架子。
不要班门弄斧。
人凭衣裳马凭鞍。
Animal idioms
Look at the pictures and complete the idioms with animal names.(P54)
as busy as a(n) _______
kill two ________with one stone
bee
birds
忙得不可开交
一石二鸟;一箭双雕;一举两得
When the cat’s away, the _______ will play.
hold your _______
mice
horses
猫儿不在,老鼠翻天;
山中无老虎,猴子称大王
[非正式用语]且慢;请三思
It’s raining _______ and _______ .
cats
dogs
[口语]下倾盆大雨
Find more animal idioms.
Love me, love my dog. 爱屋及乌。
like a cat on hot bricks 像热锅上的蚂蚁
He is a lucky dog. 他是个幸运儿。
dark horse 黑马
Never offer to teach fish to swim.
不要班门弄斧。
A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush.
双鸟在林不如一鸟在手。
Fine feathers make fine birds.
人要衣装,马要鞍。
Cats hide their claws.
知人知面不知心。
Don't count your chickens before they're hatched.
鸡蛋未孵出,先别数小鸡。
A crow is never the whiter for washing herself often.
江山易改,本性难移。
Every dog has his day. 人人皆有得意时。
Let sleeping dogs lie. 勿惹是生非。
The frog in the well knows nothing of the great ocean.
井底之蛙,不知大海。
The fox preys farthest from his hole.
兔子不吃窝边草。
Complete the paragraph with the animal idioms. (P54)
English idioms are a way of adding colour to the language. For example, instead of saying “It’s raining heavily”, you could say “1_____________________”. Another reason to use idioms is that they are concise. For example, to describe someone who is always working or busy doing something, we can say they are 2 ________________ .
It’s raining cats and dogs
as busy as a bee
concise adj. 简明的;简练的
If they’re rushing into something and should wait and be patient, you could say “3 ______________ ”. Learning idioms can be fun, especially when we compare them to Chinese equivalents. Take, for example, “4 ___________
_____________________ ” (people do what they want and have fun when someone in authority is absent) and
“5 ________________________ ” (solve two problems with one action) – are there corresponding idioms in Chinese
hold your horses
equivalent n. 对应词
When the cat’s
away, the mice will play
kill two birds with one stone
corresponding adj. 相应的;相关的
A: She’s as busy as a bee.
B: What makes you say that
A: She is currently doing three part-time jobs. I
haven’t seen her for three months.
Vocabulary building: Animal idioms
Work in pairs. Find more animal idioms. Choose an idiom and describe a situation with it.
sample
Dogs were first domesticated over 14,000 years ago. Sheep, cows and pigs have been kept at home as sources of food for around 7,000 years.
The oldest zoo in the world is in Vienna, opened in 1752. The oldest zoo in China is Beijing Zoo, which was founded in 1906.
Pre-listening: Learn words and expressions
1.zookeeper
2.Keep Wild Animals Wild
3.in danger of
4.die out
5.programme
6.fail-failure
7.admit
8.totally
9.allow sb. to do sth
10.as much as possible
11.educate
12.observe
13.be similar to
14.natural environment
15.offer
16.a huge amount of
17.on the whole
18.do good for
19.continue
20.after a short break
动物园管理员
处于…危险之中
灭亡;逐渐消失
计划,方案; 节目
承认; 招供
与…相似
提供
大量的
大体上,基本上
行善
继续
短暂休息后
Analyze long and difficult sentences
1.We have seen a lot of examples where the animals start to depend too much on humans, and are unable to live on their own when returned to the wild.
2.I totally agree that people should lean as much as possible about animals because we share the planet with them.
3.They are here to discuss whether we should keep wild animals in zoo.
While-listening
Activity 7 Listen to the TV debate and choose the correct topic
Can zoo animals survive in the wild
Can zoos offer animals their natural environment
Should we keep wild animals in the zoo
Should we educate people more about animals
Listen to find out the main idea
Listening tips:
In a debate, first listen out the main topic. The main topic is usually a statement or a question at the very start of the debate.
While-listening
Activity 8 Listen again and complete the mind map
1. in danger of dying out
2. educate people about animals
3. natural environment
4. depend too much on humans
5. as good as
6. do more good for
Post-listening
Look at your listening material and talk about how the speakers express agreement and disagreement.
Disagreeing:
1.I am afraid I don't agree that these programme are always successful.
2. But you must admit that there are successful ones.
3. I'm sorry, but that's not true.
Agreeing:
1.I totally agree that people should learn as much as possible about animals.
2. Exactly!
Post-listening
Activity 9 Work in pairs. Hold a debate on whether we should keep animals as pets.
Student A: Turn to Page 83. (agree)
Student B: Turn to Page 86. (disagree)
Student A: Turn to Page 83. (agree)
You are in favor of keeping animals as pets. You have the following arguments:
1. Keeping pets develops a kind and caring attitude towards animals.
2. Keeping pets is good for people's physical and mental health.
3. Keeping pets helps people know more about animals.
Student B: Turn to Page 86. (disagree)
You are against keeping pets as pets. You have the following arguements:
1. Caring for other people is more important than caring for animals.
2. It is bad for animals's physical and mental health to be kept as pets.
3.Animals kept at home can cause trouble for neighbours.
Agreeing
1. Exactly!
2. I agree.
3. That is true.
4. I see your point.
5. No doubt about it.
6. I suppose so.
Disagreeing
1. I don’t agree.
2. That’s just not true.
3. I’m afraid I totally disagree.
4. I’m not so sure about that.
5. I don’t think so.
6. That’s not always the same.
Topic: Whether we should keep animals as pets
A:_______________(我方支持把动物当宠物养),because I have seen that keeping pets develops a kind and caring attitude towards animals. _____________________(例如,那些把动物当宠物养的人每天都会悉心照顾他们宠物,比如,每天为他们洗澡,陪他们玩耍等等)。They love their animals very much.
B: ________________(恐怕,我不同意你的观点。并不是所有人都爱他们的宠物。有时候我们会发现,有的宠物,比如狗,会被主人遗弃在街道上。)From this point, I think it is bad for animals' physical and mental health to be kept as pets.
A:_____________________(但是你必须承认很多人是爱他们的宠物的!他们把宠物当成自己的家人。宠物也会让人们感到快乐)。Therefore, keeping pets is not only good for people's physical and mental health, but also helps people know more about animals.
B:_________________(抱歉,但那是不正确的。动物应该属于大自然环境)。So, animals kept at home can cause trouble for neighbours and it is bad for animals physical and mental health.
I agree that we should keep animals as pets because ……
I don’t agree that we should keep animals as pets because ……
FOR
AGAINST
Keeping pets develops a kind and caring attitude towards animals.
Keeping pets is good for people’s physical and mental health.
Keeping pets helps people know more about animals.
…
Caring for other people is more important than caring for animals.
It’s bad for animals’ physical and mental health to be kept as pets.
Animals kept at home can cause trouble for neighbors.
…
