外研版(2019)必修 第二册Unit 1 Food for thought Using language课件(共35张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版(2019)必修 第二册Unit 1 Food for thought Using language课件(共35张PPT) |
|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 516.5KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-10-25 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共35张PPT)
情态动词
modal
目录
CONTENT
01
情态动词的定义
02
情态动词的选择
概述
情态=情感+态度 表需要、可能、意愿、怀疑等
形式:没有人称和数的变化;
后加动词原型
加be doing表示动作正在进行,
加have done表示动作已经完成。
否定其后加not构成
一般疑问句通常将情态动词提到句首
1. You needn’t try it if you don’t want to.
2. The man can speak two foreign languages.
3. The poor boy had to face the problem bravely.
情态动词_______独立作谓语,只能和_________一起构成谓语,没有数的变化,具有助动词功能。
1. 情态动词的定义
不能
情态动词 (Modal verb)
情感 & 态度
动词原形
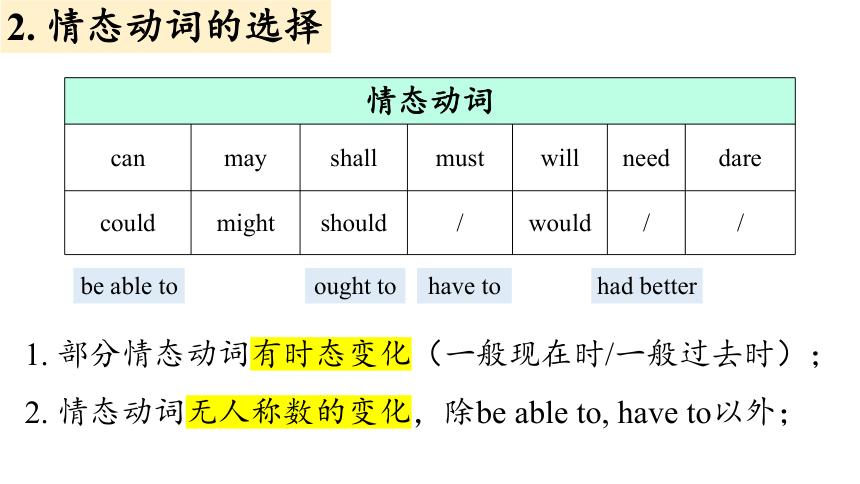
2. 情态动词的选择
情态动词
can may shall must will need dare
could might should / would / /
1. 部分情态动词有时态变化(一般现在时/一般过去时);
2. 情态动词无人称数的变化,除be able to, have to以外;
be able to
had better
ought to
have to
can & could
2. 情态动词的选择
1.表示能力,译为“能够...”
Nobody can stop the development of science.
2. 表示请求建议,用could比can语气更委婉 (could在此并非表示过去式),回答用原形
Could you please wait me a moment, Jenny
Yes, I can.
3. (用于否定句、疑问句或感叹句中)表示猜测(通常否定)或惊诧
How can/could you be here 你怎么会在这儿?
She couldn't/can't be so stupid to do that. 她不可能蠢到去做那种事吧。
can/could与be able to的区别
2. 情态动词的选择
1. The man can/could speak two foreign languages.
2. Yesterday I was able to get home before the heavy rain.
can/could表示_________________,而be able to通常表示通过努力达成的_____________; can/could 主要是一般现在、一般过去时, 而be able to有较为丰富的时态变化。
习惯性具备的能力
一次性的能力
may & might
2. 情态动词的选择
1. 表示请求或允许,译为“可以”。might语气较委婉 (但并非表示过去)。
I wonder if I might ask you a favor
You may tell him this.
2. 表示推测, 译为“可能”。might比may所表示的可能性更小。
That may/might not be true.
3. may/might well (很可能); may/might as well (不妨,还是...为好);
You may well be right. 你很可能是对的。
It’s freezing cold outside. We may as well stay at home.
4. may放在句首,表示祝愿。 May God bless you!
shall & should & ought to
2. 情态动词的选择
Shall
1. shall用于第一人称时,可表示征求对方意见,译为“要不要...”(通常为疑问句);或者表示将要发生的事,译为“将要...”(通常为肯定句)。
Shall we begin our class (表示征求意见)
I shall be in Shanghai this time next week. (表示将来动作)
2. shall用于第二、三人称时, 表示命令规定(通常为肯定句)。译为“应该”。
You shall go to school on time.
4. shall & should
shall
①表征求意见("好不好")
Shall we go camping this weekend.
② 表允诺、威胁、警告、命令
Don’t worry, you shall get the answer this afternoon. ③ 表规章、法令、预言:"必须"
Passengers shall not talk with the driver while the bus is moving.
4. shall & should
Should
① 责任,义务或要求
You should pay more attention to what your teacher says.
② 推测和可能性,是" (按理说)应该”
He should be around sixty years old.
If things should change suddenly, please let me know. ③ 用于疑问句或感叹句中,表示意外、惊异,意为“竟会”
Don’t ask me. How should I know
shall & should & ought to
2. 情态动词的选择
Should/Ought to
1. 表示义务或责任, 译为为“应该”。
We should/ought to learn from each other.
2. 表示建议或劝告,译为为“可以,应该”。
You should/ought to try your best to better your performance.
3. 表示推断, 译为”应该”, “可能”, “按道理会”。
They should/ought to be there by now.
4. should表示意外或惊讶,译为“竟然”。
It's strange that he should come so late.
must & have to
2. 情态动词的选择
Must
1. must表示“必须”(侧重于主观意愿); mustn’t表示“禁止”。
Must I do my homework now You mustn't smoke here.
2. must表示推测,译为“准是,一定是”(只用于肯定句)。若用于否定句或疑问句,则用can’t (一定不是)。
That can't be the only way. There must be other ways of solving the problem.
Have to
表示客观上的需要,强调被迫性,有“不得不”的含义。
Sorry, I have to leave now.
will & would
2. 情态动词的选择
1. 表示意愿,译为“愿意”。will指现在的意愿,would指过去的意愿。
I will read the letter for you, if you want.
He asked if I would show him the way.
2. 表示委婉语气,译为“好吗?” 。would较will而言更加委婉。
Will/Would you please pass me the salt
Would you like a cup of tea
3. 表示习惯或倾向,译为“一般,总会”。will表示现在,would表示过去。
He would always complain if he got the opportunity.
Wherever he goes, he will take an umbrella with him.
need
2. 情态动词的选择
1. need用作情态动词,表示“需要”(无时态与人称的变化)。
I need your help.
She need not any help. (否定时,直接在情态动词后+not)
2. need用作实义动词,通常为“need to do sth”结构或“need+n” (有时态与人称的变化)。need to be done=need V-ing
Lily needs more money to pay for that book. (时态变化)
Lily needed more money to pay for that book at that time. (人称数的变化)
Lily doesn’t need any more money to pay for that book. (否定,添加助动词)
dare
2. 情态动词的选择
1. 作情态动词,译为“敢”,通常只用于否定句、疑问句以及if或whether之后,一般不用于肯定句。(无人称变化,有过去式dared)
Dare you tell her the truth
I daren't ask her this question.
2. 作实义动词,译为“敢于”,通常为“dare to do sth” (有人称与时态的变化)
She dares to go alone.
She doesn’t dare to go alone.
She didn’t dare to go alone.
情态动词表推测
2. 情态动词的选择
“情态动词+have+过去分词”表示对过去动作或状态的推测、假设
(1)must have done “过去一定做了某事”?
(2)can’t/couldn’t have done “过去不可能做了某事”?
(3)may/might have done “过去可能做了某事”?
(4)needn’t have done “过去本来没有必要做而做了某事”
(5)need have done “过去本需要做某事而实际未做” ??
(6)should/ought to have done “过去本来应该做某事而没有做”?
(7)shouldn’t/oughtn’t to have done “过去本来不应该做某事而做了”?
情态动词表推测
2. 情态动词的选择
1. He is right.
2. He must be right.
3. He will be right.
4. He would be right.
5. He ought to be right.
6. He should be right.
7. He may be right.
8. He could be right.
9. He might be right.
certain
almost certain
uncertain
study
1. dare
① Dare作情态动词时,敢于, 主要用于疑问句、否定句和条件从句中,一般不用在肯定句中。
—Dare you tell her the truth
—Yes, I dare. /No, I daren’t.
How dare you accuse me of lying!
He daren’t admit this.
② Dare作实义动词时,在肯定句中,dare后接带to的不定式
Only a few journalists dared to cover the story.
He doesn’t dare (to) go there alone.
Don’t you dare (to) touch it
practice
How_______ you accuse me of cheating in the exam!
He_______ admit that he spending all his money in gambling.
If you _______ do such a thing, you are sure to be punished.
If he_______ say such a thing again, I shall knock him down.
dare
daren’t
dare
dare
2. need
① 作情态动词时,需要、必须, 主要用于疑问句、否定句
You need not admit the entire truth.
Need I do my homework now
-Yes, you must.
-No, you needn’t/don’t have to.
②作实义动词时,后接带to的不定式
I need to know the truth.
He needs to practice more.
Your car needs washing
= Your car needs to be washed.
You needn’t have told him this news. He knew it already.
归纳拓展:
sb needs sth表示”某人需要某物”
sb needs to do sth,表示”某人需要去做某事”
sth need doing. 某事需要被做
= need to be done
need/needn’t+动词完成式,表示过去”需要但实际未做“或”过去不需要,但却做了
practice
I didn’t _______ to buy the dictionary. I had a copy at home.
The team _______ to finish their project before this year.
You needn't ___________ (take)it seriously yesterday.
They needed _______(help) others with the difficulty.
need
needs
have taken
to help
3. be able to 能够
You don't have to tell him about the sad news.
He was able to flee Europe before the war broke out.
They will be able to tell you the news soon.
Are you able to finish the task this morning
Lingling has been able to play the piano for over 2 years.
The fire was very big, but most people were able to escape from the building.
4. have to 不得不
The young man has to work for 16 hours a day to earn enough money.
He doesn't have to do the homework now.
He had to look after his sister last week.
We didn't have to answer the question yesterday.
Do I have to go there now
—Yes, you do.
—No, you don't have to.
4. have to VS must
①have to则往往强调客观需要, 而must表示的是说话人的主观看法。
I had to work when I was your age.
The play is not interesting. I really must go now.
② have有更多的时态形式, must一般只表现在一般现在时。
③ 二者的否定意义不大相同。
You don't have to go. 你不必去。
You mustn't go. 你可不要去。
5. had better 最好
① had better 只有一种形式,它后面要跟动词原形。
had better do sth had better not do sth
It is pretty cold outside. You'd better put on your coat.
He just left, you had better have come earlier.
You had better not smoke for there are some babies.
Hadn't we better stop now
have a test
1. Nothing is hard in the world, if you _______scale the heights.
2. You_______ have watered the plants, for it is going to rain.
3. He _______ speak English before such a crowd, dare he
4. Do they _______ pay their bill before the end of the month
5. I’ve always wanted to _______speak fluent English.
dare
needn’t
daren’t
have to
be able to
have a test
6. He _______ go because of somebody's calling him that day.
7. In order to take the exam, we_______ finish the whole book by the end of this month .
8. It's dark already, we _______ go back homework.
9. My brother was very ill, so I _______ call the doctor in the middle of the night.
10. Those bags look really heavy, are you sure you_______ to carry them on your own
had to
will have to
had better
had to
will be able
have a test
11. You _______ sit here and have a rest before having next try.
12. I _______ leave school because my family is poor now.
13. I wonder if we ___________ take sleeping bag.
14. If he _______ say such a thing again, I shall knock him down.
15. After the accident it was a long time before she _______ walk again.
had better
have to
need
dare
was able to
口诀:
情态动词两特点
动词原形接后面,说话语气较委婉。
can "能力"may"许可",must"责任"或"义务"。
否定回答needn't换,"需要"need, dare"敢"。
should"应该",would"愿",have to"被迫"表客观。
情态动词
modal
目录
CONTENT
01
情态动词的定义
02
情态动词的选择
概述
情态=情感+态度 表需要、可能、意愿、怀疑等
形式:没有人称和数的变化;
后加动词原型
加be doing表示动作正在进行,
加have done表示动作已经完成。
否定其后加not构成
一般疑问句通常将情态动词提到句首
1. You needn’t try it if you don’t want to.
2. The man can speak two foreign languages.
3. The poor boy had to face the problem bravely.
情态动词_______独立作谓语,只能和_________一起构成谓语,没有数的变化,具有助动词功能。
1. 情态动词的定义
不能
情态动词 (Modal verb)
情感 & 态度
动词原形
2. 情态动词的选择
情态动词
can may shall must will need dare
could might should / would / /
1. 部分情态动词有时态变化(一般现在时/一般过去时);
2. 情态动词无人称数的变化,除be able to, have to以外;
be able to
had better
ought to
have to
can & could
2. 情态动词的选择
1.表示能力,译为“能够...”
Nobody can stop the development of science.
2. 表示请求建议,用could比can语气更委婉 (could在此并非表示过去式),回答用原形
Could you please wait me a moment, Jenny
Yes, I can.
3. (用于否定句、疑问句或感叹句中)表示猜测(通常否定)或惊诧
How can/could you be here 你怎么会在这儿?
She couldn't/can't be so stupid to do that. 她不可能蠢到去做那种事吧。
can/could与be able to的区别
2. 情态动词的选择
1. The man can/could speak two foreign languages.
2. Yesterday I was able to get home before the heavy rain.
can/could表示_________________,而be able to通常表示通过努力达成的_____________; can/could 主要是一般现在、一般过去时, 而be able to有较为丰富的时态变化。
习惯性具备的能力
一次性的能力
may & might
2. 情态动词的选择
1. 表示请求或允许,译为“可以”。might语气较委婉 (但并非表示过去)。
I wonder if I might ask you a favor
You may tell him this.
2. 表示推测, 译为“可能”。might比may所表示的可能性更小。
That may/might not be true.
3. may/might well (很可能); may/might as well (不妨,还是...为好);
You may well be right. 你很可能是对的。
It’s freezing cold outside. We may as well stay at home.
4. may放在句首,表示祝愿。 May God bless you!
shall & should & ought to
2. 情态动词的选择
Shall
1. shall用于第一人称时,可表示征求对方意见,译为“要不要...”(通常为疑问句);或者表示将要发生的事,译为“将要...”(通常为肯定句)。
Shall we begin our class (表示征求意见)
I shall be in Shanghai this time next week. (表示将来动作)
2. shall用于第二、三人称时, 表示命令规定(通常为肯定句)。译为“应该”。
You shall go to school on time.
4. shall & should
shall
①表征求意见("好不好")
Shall we go camping this weekend.
② 表允诺、威胁、警告、命令
Don’t worry, you shall get the answer this afternoon. ③ 表规章、法令、预言:"必须"
Passengers shall not talk with the driver while the bus is moving.
4. shall & should
Should
① 责任,义务或要求
You should pay more attention to what your teacher says.
② 推测和可能性,是" (按理说)应该”
He should be around sixty years old.
If things should change suddenly, please let me know. ③ 用于疑问句或感叹句中,表示意外、惊异,意为“竟会”
Don’t ask me. How should I know
shall & should & ought to
2. 情态动词的选择
Should/Ought to
1. 表示义务或责任, 译为为“应该”。
We should/ought to learn from each other.
2. 表示建议或劝告,译为为“可以,应该”。
You should/ought to try your best to better your performance.
3. 表示推断, 译为”应该”, “可能”, “按道理会”。
They should/ought to be there by now.
4. should表示意外或惊讶,译为“竟然”。
It's strange that he should come so late.
must & have to
2. 情态动词的选择
Must
1. must表示“必须”(侧重于主观意愿); mustn’t表示“禁止”。
Must I do my homework now You mustn't smoke here.
2. must表示推测,译为“准是,一定是”(只用于肯定句)。若用于否定句或疑问句,则用can’t (一定不是)。
That can't be the only way. There must be other ways of solving the problem.
Have to
表示客观上的需要,强调被迫性,有“不得不”的含义。
Sorry, I have to leave now.
will & would
2. 情态动词的选择
1. 表示意愿,译为“愿意”。will指现在的意愿,would指过去的意愿。
I will read the letter for you, if you want.
He asked if I would show him the way.
2. 表示委婉语气,译为“好吗?” 。would较will而言更加委婉。
Will/Would you please pass me the salt
Would you like a cup of tea
3. 表示习惯或倾向,译为“一般,总会”。will表示现在,would表示过去。
He would always complain if he got the opportunity.
Wherever he goes, he will take an umbrella with him.
need
2. 情态动词的选择
1. need用作情态动词,表示“需要”(无时态与人称的变化)。
I need your help.
She need not any help. (否定时,直接在情态动词后+not)
2. need用作实义动词,通常为“need to do sth”结构或“need+n” (有时态与人称的变化)。need to be done=need V-ing
Lily needs more money to pay for that book. (时态变化)
Lily needed more money to pay for that book at that time. (人称数的变化)
Lily doesn’t need any more money to pay for that book. (否定,添加助动词)
dare
2. 情态动词的选择
1. 作情态动词,译为“敢”,通常只用于否定句、疑问句以及if或whether之后,一般不用于肯定句。(无人称变化,有过去式dared)
Dare you tell her the truth
I daren't ask her this question.
2. 作实义动词,译为“敢于”,通常为“dare to do sth” (有人称与时态的变化)
She dares to go alone.
She doesn’t dare to go alone.
She didn’t dare to go alone.
情态动词表推测
2. 情态动词的选择
“情态动词+have+过去分词”表示对过去动作或状态的推测、假设
(1)must have done “过去一定做了某事”?
(2)can’t/couldn’t have done “过去不可能做了某事”?
(3)may/might have done “过去可能做了某事”?
(4)needn’t have done “过去本来没有必要做而做了某事”
(5)need have done “过去本需要做某事而实际未做” ??
(6)should/ought to have done “过去本来应该做某事而没有做”?
(7)shouldn’t/oughtn’t to have done “过去本来不应该做某事而做了”?
情态动词表推测
2. 情态动词的选择
1. He is right.
2. He must be right.
3. He will be right.
4. He would be right.
5. He ought to be right.
6. He should be right.
7. He may be right.
8. He could be right.
9. He might be right.
certain
almost certain
uncertain
study
1. dare
① Dare作情态动词时,敢于, 主要用于疑问句、否定句和条件从句中,一般不用在肯定句中。
—Dare you tell her the truth
—Yes, I dare. /No, I daren’t.
How dare you accuse me of lying!
He daren’t admit this.
② Dare作实义动词时,在肯定句中,dare后接带to的不定式
Only a few journalists dared to cover the story.
He doesn’t dare (to) go there alone.
Don’t you dare (to) touch it
practice
How_______ you accuse me of cheating in the exam!
He_______ admit that he spending all his money in gambling.
If you _______ do such a thing, you are sure to be punished.
If he_______ say such a thing again, I shall knock him down.
dare
daren’t
dare
dare
2. need
① 作情态动词时,需要、必须, 主要用于疑问句、否定句
You need not admit the entire truth.
Need I do my homework now
-Yes, you must.
-No, you needn’t/don’t have to.
②作实义动词时,后接带to的不定式
I need to know the truth.
He needs to practice more.
Your car needs washing
= Your car needs to be washed.
You needn’t have told him this news. He knew it already.
归纳拓展:
sb needs sth表示”某人需要某物”
sb needs to do sth,表示”某人需要去做某事”
sth need doing. 某事需要被做
= need to be done
need/needn’t+动词完成式,表示过去”需要但实际未做“或”过去不需要,但却做了
practice
I didn’t _______ to buy the dictionary. I had a copy at home.
The team _______ to finish their project before this year.
You needn't ___________ (take)it seriously yesterday.
They needed _______(help) others with the difficulty.
need
needs
have taken
to help
3. be able to 能够
You don't have to tell him about the sad news.
He was able to flee Europe before the war broke out.
They will be able to tell you the news soon.
Are you able to finish the task this morning
Lingling has been able to play the piano for over 2 years.
The fire was very big, but most people were able to escape from the building.
4. have to 不得不
The young man has to work for 16 hours a day to earn enough money.
He doesn't have to do the homework now.
He had to look after his sister last week.
We didn't have to answer the question yesterday.
Do I have to go there now
—Yes, you do.
—No, you don't have to.
4. have to VS must
①have to则往往强调客观需要, 而must表示的是说话人的主观看法。
I had to work when I was your age.
The play is not interesting. I really must go now.
② have有更多的时态形式, must一般只表现在一般现在时。
③ 二者的否定意义不大相同。
You don't have to go. 你不必去。
You mustn't go. 你可不要去。
5. had better 最好
① had better 只有一种形式,它后面要跟动词原形。
had better do sth had better not do sth
It is pretty cold outside. You'd better put on your coat.
He just left, you had better have come earlier.
You had better not smoke for there are some babies.
Hadn't we better stop now
have a test
1. Nothing is hard in the world, if you _______scale the heights.
2. You_______ have watered the plants, for it is going to rain.
3. He _______ speak English before such a crowd, dare he
4. Do they _______ pay their bill before the end of the month
5. I’ve always wanted to _______speak fluent English.
dare
needn’t
daren’t
have to
be able to
have a test
6. He _______ go because of somebody's calling him that day.
7. In order to take the exam, we_______ finish the whole book by the end of this month .
8. It's dark already, we _______ go back homework.
9. My brother was very ill, so I _______ call the doctor in the middle of the night.
10. Those bags look really heavy, are you sure you_______ to carry them on your own
had to
will have to
had better
had to
will be able
have a test
11. You _______ sit here and have a rest before having next try.
12. I _______ leave school because my family is poor now.
13. I wonder if we ___________ take sleeping bag.
14. If he _______ say such a thing again, I shall knock him down.
15. After the accident it was a long time before she _______ walk again.
had better
have to
need
dare
was able to
口诀:
情态动词两特点
动词原形接后面,说话语气较委婉。
can "能力"may"许可",must"责任"或"义务"。
否定回答needn't换,"需要"need, dare"敢"。
should"应该",would"愿",have to"被迫"表客观。
