外研版(2019)必修 第一册Unit 2 Exploring English Understanding ideas 课文分析课件(共26张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版(2019)必修 第一册Unit 2 Exploring English Understanding ideas 课文分析课件(共26张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 27.2MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-11-29 22:21:35 | ||
图片预览






文档简介
(共26张PPT)
Unit 2 Exploring English
Understanding ideas
Exploring English
History of English
English word formation
Difference between AmE&BrE
Misunderstand-ing in English
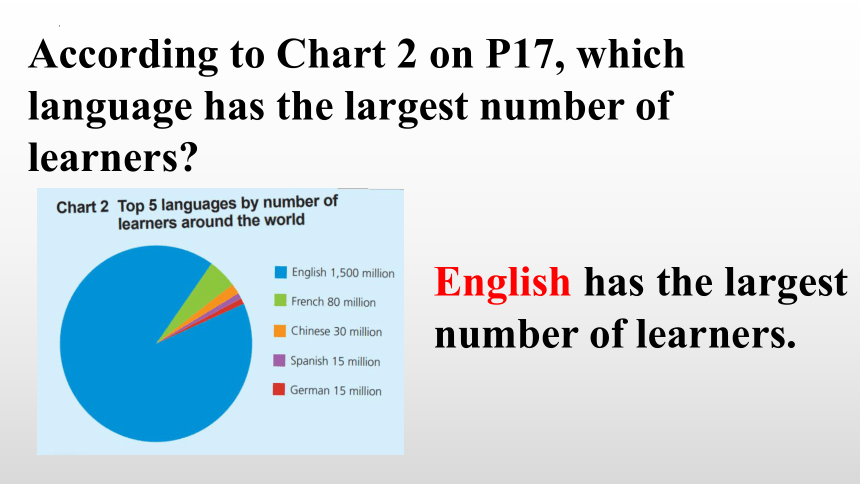
According to Chart 2 on P17, which language has the largest number of learners
English has the largest number of learners.
Which countries mentioned in the video have English as their first language
The UK, Ireland, the USA, Canada, New Zealand and Australia.
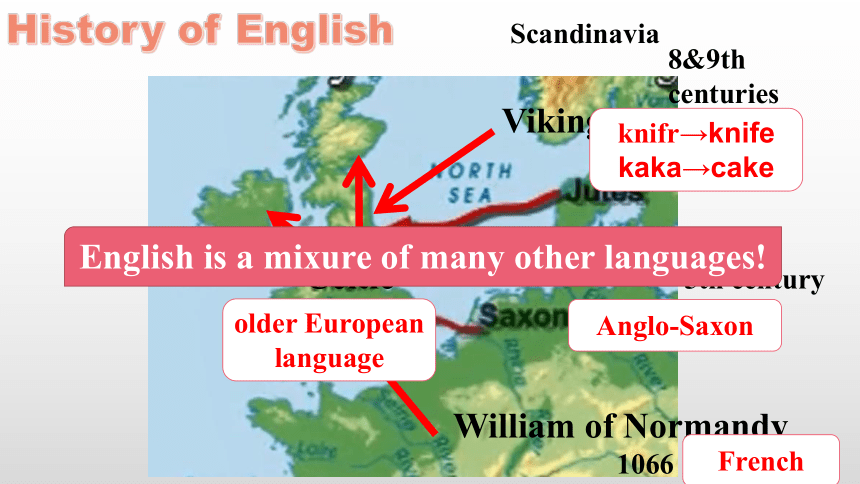
History of English
Celtic
Vikings
5th century
8&9th centuries
Scandinavia
William of Normandy
1066
older European language
Anglo-Saxon
French
knifr→knife
kaka→cake
English is a mixure of many other languages!
Look at the title of the passage and the pictures. Guess what the passage is about. (P18-19)
food
cooking
words
plants
fruit
Read the passage and answer the questions.
What is the passage about
food
cooking
words
plants
fruit
Read the passage and choose the right answer.
What is the author’s purpose in writing the passage
A. To tell us that English is difficult to learn.
B. To give advice on how to learn English.
C. To show that English is interesting and creative.
D. To explain how English was created.
Skim the passage and fill in the blanks.
hamburger
take
opposing
homesick
reflects
Read the passage quickly and match each part with its main idea.
Para. 1 Para. 2-6 Para. 7
A. Give some examples to discuss the topic.
B. Conclude the topic of the passage.
C. Introduce to the topic of the passage.
C
A
B
Para. 1
(Lead in)
No ham in a hamburger.
No egg in eggplant.
Neither is there pine nor apple in pineapple.
English is a crazy language to learn.
(TOPIC)
How does the author support his/her idea in the passage
A. By listing numbers.
B. By making comparison.
C. By giving examples.
C. By using research results.
Para. 2-6
(Examples)
sculpt a sculpture
paint a painting
BUT take a photo
seasick→sick at sea
airsick→sick in the air
carsick→sick in a car
BUT homesick≠sick at home
hard soft
harmless hameful
BUT hardly and softly are not an opposing pair.
shameless and shameful have the same meaning.
rain→it’s raining.
snow→it’s snowing.
BUT sunshine→it’s sunshining. ( )
The same rule doesn’t always apply to everything!
Para. 2-6
(Examples)
burn up→burn down
fill in a form→fill out a form
Stars are out.→They are visible.
Lights are out.→They are invisible.
I wind up my watch.→It starts.
I wind up the passage.→It ends.
The same words and phrases may have
different meanings in different contexts.
Different words or phrases may have
the same meaning!
Para. 7
(Conclusion)
English is invented by people and reflects the creativity of the human race.
Read the passage carefully and complete the notes with words from the passage. (P21)
Read the passage carefully and complete the notes with words from the passage. (P21)
In order to support his idea, the author uses many examples that show the 1__________ madness of English.
no egg in eggplant no ham in 2.__________ neither pine nor apple in 3. ____________ sculpt a sculpture
paint a(n) 4.__________
BUT take a photo
unique
hamburger
pineapple
painting
We can’t always understand a compound word by adding the meanings of the words it is made up of!
Can you think of similar examples in Chinese
There isn’t fish in “Yu-Shiang Shredded Pork”.
There isn’t a wife in a “Laopobing”.
“Harmless” is the opposite of “harmful”. Shameful and shameless 9_________ are the same. burn up → burn down
fill in a form→ 10 _____ a form
behaviors
fill out
可耻的
无耻的
seasick → sick at sea 5__________→ sick in the air 6________ → sick in a car BUT 7 ________ → sick at home “Hard” is the opposite of “soft”.
“Hardly”and “softly” are not a(n) 8___________ pair.
airsick
carsick
homesick
opposing
几乎不
轻柔地
对立面
Stars are out. → They are visible. Lights are out. → They are 11 __________. I wind up my watch. →It starts.
I wind up the passage. →
It 12________.
The reason is that English was invented by people, and it 13 __________ the creativity of the human race.
invisible
ends
reflects
出现,未被云遮蔽
熄灭
How does the author give examples Can you find the sentence patterns the author uses to give examples
The author gives examples mainly by comparing. He uses the following sentence patterns.
For example, we ..., but we ...(para 2)
If... are..., why are... not... (para 3)
When we..., we can. But when we..., we can’t....(para 4)
Read the following information and answer the questions. (P21)
How did pineapples, hamburgers and eggplants get their names
Eggplants got the name because they used to look
like eggs.
How did pineapples, hamburgers and eggplants get their names
The name of “pineapple” developed from the spanish word “pina”, with “apple” added to show it’s a kind of fruit.
The name of hamburger came from the idea of “Hamburg steak”, and later people reinvented it and called it “hamburger”.
Homework
1. 完成《导学案》语篇研读P30-32 并批改订正
2. 预习《导学案》新知探究P32-38
3. 背生词P22-26,明天听写
Unit 2 Exploring English
Understanding ideas
Exploring English
History of English
English word formation
Difference between AmE&BrE
Misunderstand-ing in English
According to Chart 2 on P17, which language has the largest number of learners
English has the largest number of learners.
Which countries mentioned in the video have English as their first language
The UK, Ireland, the USA, Canada, New Zealand and Australia.
History of English
Celtic
Vikings
5th century
8&9th centuries
Scandinavia
William of Normandy
1066
older European language
Anglo-Saxon
French
knifr→knife
kaka→cake
English is a mixure of many other languages!
Look at the title of the passage and the pictures. Guess what the passage is about. (P18-19)
food
cooking
words
plants
fruit
Read the passage and answer the questions.
What is the passage about
food
cooking
words
plants
fruit
Read the passage and choose the right answer.
What is the author’s purpose in writing the passage
A. To tell us that English is difficult to learn.
B. To give advice on how to learn English.
C. To show that English is interesting and creative.
D. To explain how English was created.
Skim the passage and fill in the blanks.
hamburger
take
opposing
homesick
reflects
Read the passage quickly and match each part with its main idea.
Para. 1 Para. 2-6 Para. 7
A. Give some examples to discuss the topic.
B. Conclude the topic of the passage.
C. Introduce to the topic of the passage.
C
A
B
Para. 1
(Lead in)
No ham in a hamburger.
No egg in eggplant.
Neither is there pine nor apple in pineapple.
English is a crazy language to learn.
(TOPIC)
How does the author support his/her idea in the passage
A. By listing numbers.
B. By making comparison.
C. By giving examples.
C. By using research results.
Para. 2-6
(Examples)
sculpt a sculpture
paint a painting
BUT take a photo
seasick→sick at sea
airsick→sick in the air
carsick→sick in a car
BUT homesick≠sick at home
hard soft
harmless hameful
BUT hardly and softly are not an opposing pair.
shameless and shameful have the same meaning.
rain→it’s raining.
snow→it’s snowing.
BUT sunshine→it’s sunshining. ( )
The same rule doesn’t always apply to everything!
Para. 2-6
(Examples)
burn up→burn down
fill in a form→fill out a form
Stars are out.→They are visible.
Lights are out.→They are invisible.
I wind up my watch.→It starts.
I wind up the passage.→It ends.
The same words and phrases may have
different meanings in different contexts.
Different words or phrases may have
the same meaning!
Para. 7
(Conclusion)
English is invented by people and reflects the creativity of the human race.
Read the passage carefully and complete the notes with words from the passage. (P21)
Read the passage carefully and complete the notes with words from the passage. (P21)
In order to support his idea, the author uses many examples that show the 1__________ madness of English.
no egg in eggplant no ham in 2.__________ neither pine nor apple in 3. ____________ sculpt a sculpture
paint a(n) 4.__________
BUT take a photo
unique
hamburger
pineapple
painting
We can’t always understand a compound word by adding the meanings of the words it is made up of!
Can you think of similar examples in Chinese
There isn’t fish in “Yu-Shiang Shredded Pork”.
There isn’t a wife in a “Laopobing”.
“Harmless” is the opposite of “harmful”. Shameful and shameless 9_________ are the same. burn up → burn down
fill in a form→ 10 _____ a form
behaviors
fill out
可耻的
无耻的
seasick → sick at sea 5__________→ sick in the air 6________ → sick in a car BUT 7 ________ → sick at home “Hard” is the opposite of “soft”.
“Hardly”and “softly” are not a(n) 8___________ pair.
airsick
carsick
homesick
opposing
几乎不
轻柔地
对立面
Stars are out. → They are visible. Lights are out. → They are 11 __________. I wind up my watch. →It starts.
I wind up the passage. →
It 12________.
The reason is that English was invented by people, and it 13 __________ the creativity of the human race.
invisible
ends
reflects
出现,未被云遮蔽
熄灭
How does the author give examples Can you find the sentence patterns the author uses to give examples
The author gives examples mainly by comparing. He uses the following sentence patterns.
For example, we ..., but we ...(para 2)
If... are..., why are... not... (para 3)
When we..., we can. But when we..., we can’t....(para 4)
Read the following information and answer the questions. (P21)
How did pineapples, hamburgers and eggplants get their names
Eggplants got the name because they used to look
like eggs.
How did pineapples, hamburgers and eggplants get their names
The name of “pineapple” developed from the spanish word “pina”, with “apple” added to show it’s a kind of fruit.
The name of hamburger came from the idea of “Hamburg steak”, and later people reinvented it and called it “hamburger”.
Homework
1. 完成《导学案》语篇研读P30-32 并批改订正
2. 预习《导学案》新知探究P32-38
3. 背生词P22-26,明天听写
