2015中考英语专题突破课标版专题精讲九 简单句和并列句
文档属性
| 名称 | 2015中考英语专题突破课标版专题精讲九 简单句和并列句 |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2015-04-28 21:36:15 | ||
图片预览






文档简介
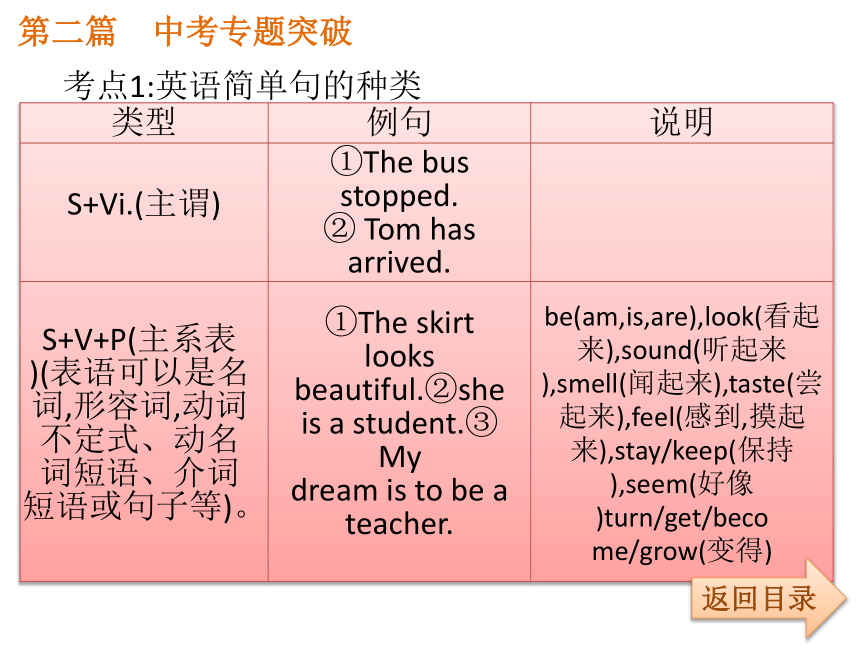
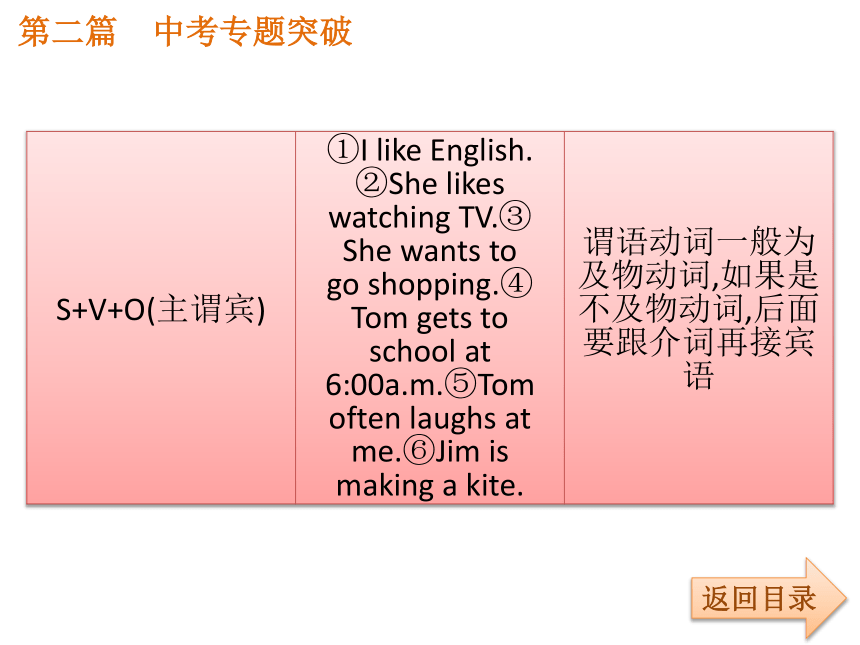
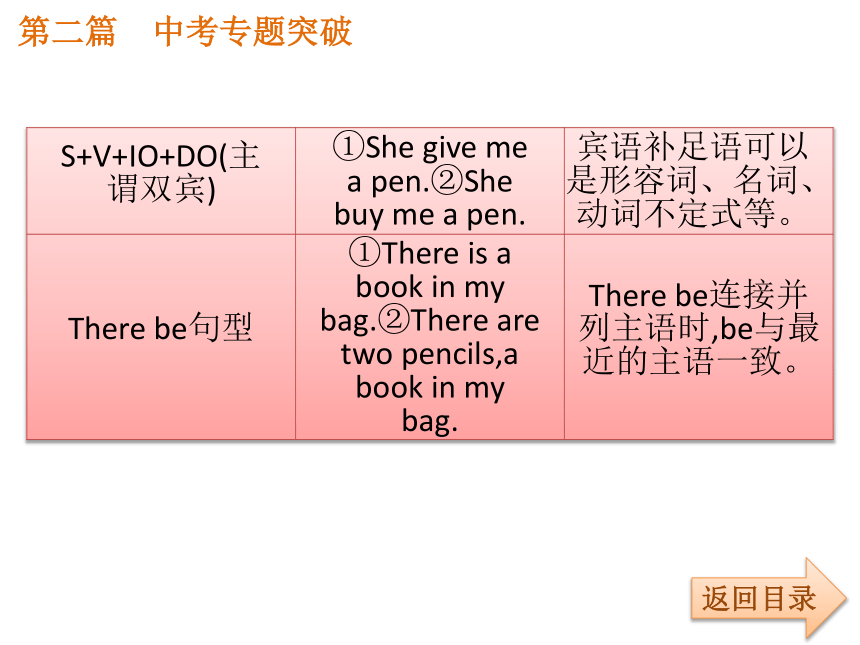
课件35张PPT。第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录专题精讲九 简单句和并列句第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破考点1:英语简单句的种类返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录【注意】(1)直接宾语与间接宾语位置互换时,间接宾语前加介词to的动词有:
send(寄给) write(写给) show(出示)
return(还给) bring(带来) pass(递给)
leave(留给) offer(提供) tell(告诉)
lend(借给) give(给) sell(卖) teach(教)
(2)间接宾语前加介词for的动词有:
choose(选择) order(订购) get(弄到)
sing(唱歌) play(演奏) make(做)
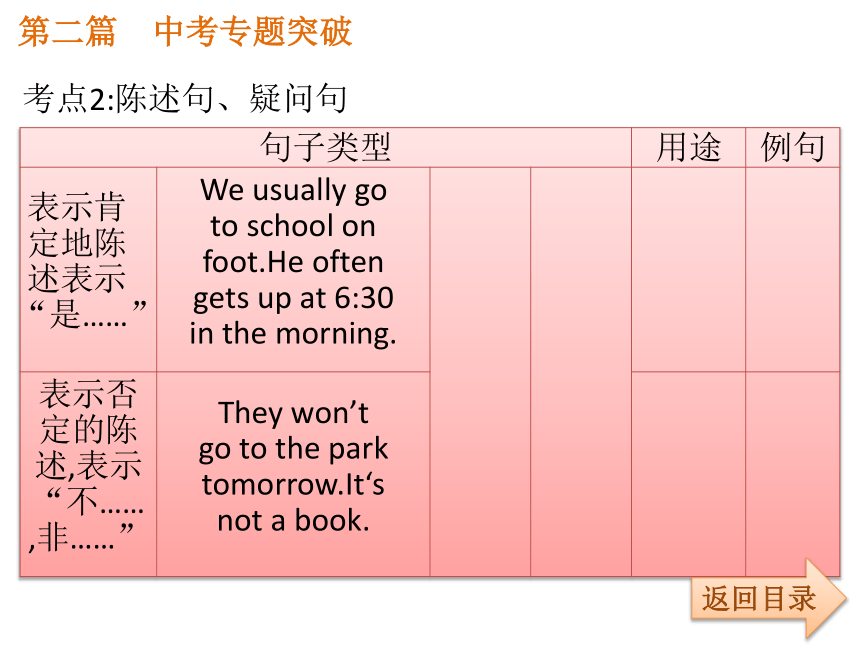
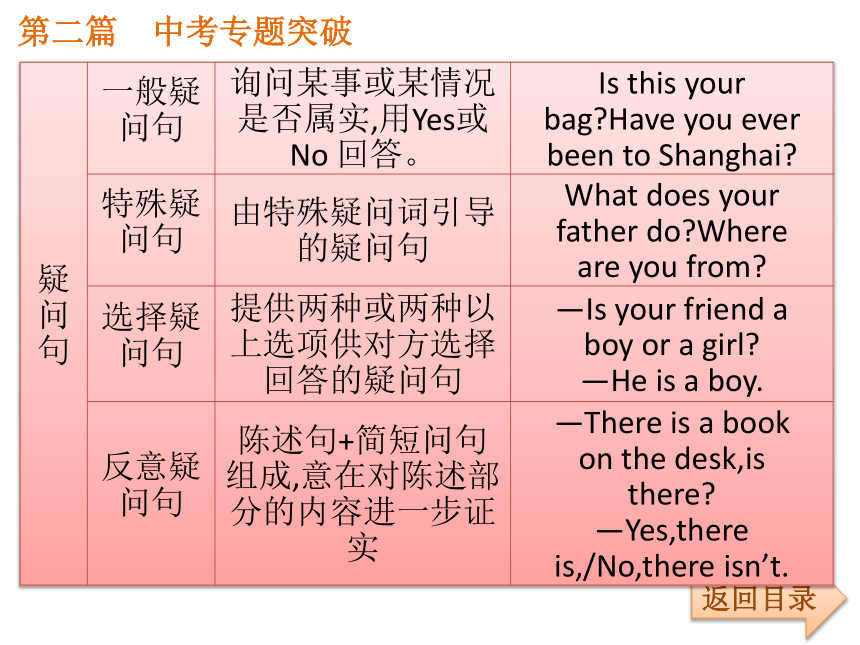
buy(买) do(做)第二篇 中考专题突破考点2:陈述句、疑问句返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录考点3:选择疑问句
1.构成:
(1)一般疑问句+or+第二选项?
(2)特殊疑问句+第一选项(+第二选项)+or+第三选项?
2.选择疑问句的结构与特殊疑问句相同,即要具体回答,不可以用Yes/No回答。如:
①—Is your friend a boy or a girl?—A girl.
②—Which do you prefer,coffee or tea?—Tea,please.
③—Which do you like best,singing,dancing or skating?—Dancing,of course.第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录考点4:反意疑问句
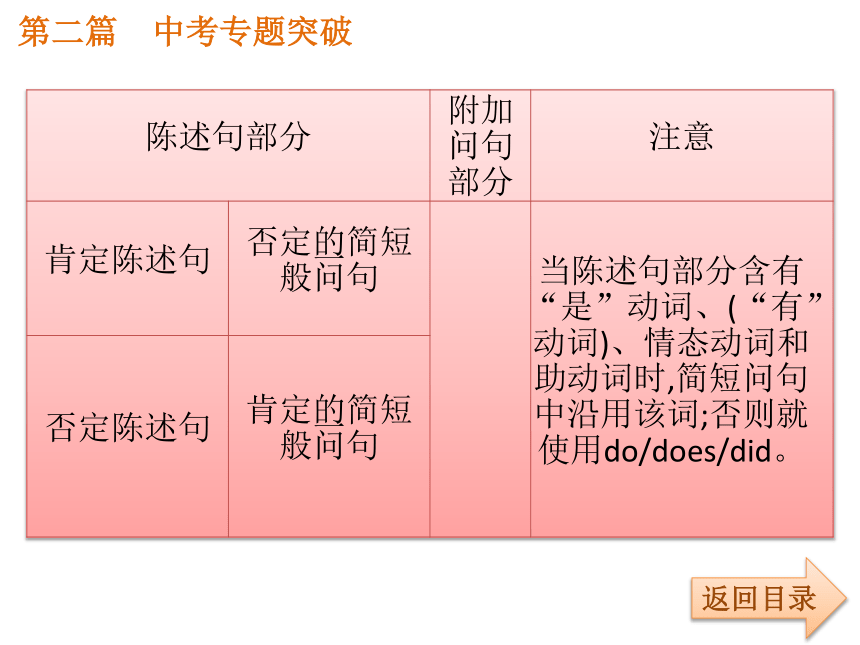
1.构成:由两部分组成:前者是陈述部分,后者是疑问部分(它是由be,have,助动词或情态动词+主语构成)。如果陈述部分是肯定结构,反意疑问句须用否定结构;反之,陈述部分如果是否定结构,反意疑问句须用肯定结构。反意疑问句的两部分,必须保持人称和时态的一致;反意疑问句的回答有时会和汉语不同。第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录如:(1)He is old,isn’t he?(他老了,不是吗?)
(2)Your father went to Japan,didn’t he?(你爸爸去了日本,不是吗?)
(3)He isn’t old,is he?(他不老,是吗?)
(4)He seldom plays football,does he?(他很少踢足球,是吗?)
★(5)Tom has been to Japan,hasn’t he?
比较:Tom has to do housework,doesn’t he?
(6)There is little water,is there?
(7)Kate hardly speaks Chinese,does she?
(8)Please open the door,will you?第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录★(除Let’s外的祈使句的反意疑问句用will you)
★(Let’s开头的祈使句的反意疑问句用shall we)
(9)Let us go swimming,will you?
(10)Let’s go swimming,shall we?
(11)Everyone is here,aren’t they?(everyone指人)
(12)Everything is ready,isn’t it? (everything指物)
(13)I don’t think Tom has done that,has he?(主要看宾语从句:I/we think/believe 引导宾从时否定前移)
(14)She thinks Tom hasn’t done that,doesn’t she?(主要看主句)第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录2.反意问句的回答:无论哪种形式的反意问句,回答时要遵循:“Yes,+肯定式”或者“No,+否定式”
如:(1)—The man went away,didn’t he?(那人走开了,不是吗?)
—Yes,he did.(是的,他走了。)/No,he didn’t.(不,他没有走。)
(2)—Tom didn’t go there,did he?(Tom没去那里,是吗?)
—Yes,he did.(不,他去了。)/No,he didn’t.(是的,他没去。)第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录考点5:祈使句
祈使句用来表示请求、命令等。它的主语you往往不说出。
▲祈使句的肯定式:动词(原形)+其他
如:Please give me a hand.(请帮忙)
Shut up!(住嘴!)
▲祈使句的否定式:Don’t+动词原形+其他
如:Please don’t talk in low voice.(请不要低声讲话。)Don’t look back!(不要掉头看。)第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录【注意】以“let’s”引出的祈使句的否定结构,“not”应放在“let’s”后面。如:Let’s not trouble him.(我们不要打扰他。)
▲肯定祈使句前可以用助动词来强调语气。
如:Please do help me!(请千万帮帮我。)(do起强调作用)
▲祈使句在复合句和其它一些情况下看作将来时。
如:Please call me when she comes back.(当她回来时给我打个电话。)
—Don’t bring it here tomorrow.—OK,I won’t.第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录考点6:感叹句
感叹句用来表示喜怒哀乐等强烈感情。句末常用“!”
1.what感叹名词。对含有形容词的名词短语感叹的结构通常是:
★What+(a/an)+(形容词)+名词+陈述句结构!
(主谓)
(1)感叹可数名词单数。
如:①What a kind girl (she is)! (她是多么善良的一个女孩啊!)
②What a tall tree (it is)! (它是多高的一棵树啊!)第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录(2)感叹可数名词复数。
如:①What kind girls (they are)! (她们是多么善良的女孩啊!)
②What tall trees (they are)! (它们是多高的树啊!)第二篇 中考专题突破(3)感叹不可数名词。如:
①What delicious food (it is)!
②What bad/good weather (it is)!
③What good news (it is)!
④What useful information (it is)!
⑤What good advice (it is)!
⑥What hard work (it is)!
⑦What great fun (they had)!
(have fun词组)
★特例:What a good time (they are having)! (have a good time词组)
★技巧:what引导的感叹句中的形容词后肯定直接有一个名词。返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录2.how对形容词或副词进行感叹:★结构通常是:How+形容词/副词+陈述句结构(主谓语),用来强调句子中的形容词、副词或动词。
(1)how感叹形容词时,可以与what 感叹句相互转化。
①How kind the girl is! (那个女孩多么善良啊!)
②How tall the tree is! (那棵树多高啊!)
(2)how感叹副词时,不可以与what 感叹句相互转化。
①How carefully the old man walks!(这老人走路真小心!)
②How beautifully Lily is singing!第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录▲有时,陈述句、祈使句、疑问句、一个词或词组,也带有一定的感彩,也可以成为感叹句,此时未必使用感叹句型。He is sitting on a tiger’s back!(他坐在老虎的背上!)/A nice shot!(漂亮一击!)/Good goal!(好球!)第二篇 中考专题突破考点7:There be句型
(1)There be(is/are/was/were)+sb./sth.+地点状语。意为“某处有(存在)某人或某物”。be 必须与其后的主语保持人称和数的一致;如果是并列主语,be 应该和临近的主语保持一致。
(2)There be结构的一般疑问句变化只需把be动词移到句首,再在句尾加上问号即可。
(3)there be 结构有不同的时态,可与多种助动词或情态动词连用。如:
There must be a pen in the box.There happened to be some money in my pocket.There is going to be a meeting tonight.There has been a big tree on the top of the hill.There used to be a church across from the bank.返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破(4)There be句型否定句式的构成和含有be动词的其它句型一样,在be后加上“not”。也可用“no”来表示。即:no+n.(名词)=not a/an/any+n.(名词)。注意:no+n.(可数名词单数)=not a/an+n.(可数名词单数);no+n.(可数名词复数)=not any+n.(可数名词复数);no+n.(不可数名词)=not any+n.(不可数名词)。如:
① There is an orange in her bag.
→There isn’t an orange in her bag.=There is no orange in her bag.
② There are some oranges in her bag.
→There aren’t any oranges in her bag.=There are no oranges in her bag.返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录(5)There be句型的特殊疑问句有以下三种形式:
①对主语提问:当主语是人时,用“Who’s+介词短语?”;当主语是物时,用“What’s+介词短语?”。其中there在口语中常常省略。
【注意】无论原句的主语是单数还是复数,对其提问时一般都用be的单数形式(回答时却要根据实际情况来决定)。如:
There is a bird in the tree.→What’s in the tree?
There are some bikes over there.→What’s over there?
There is a little girl in the room.→Who is in the room?第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录②对地点状语提问:用“Where is/are+主语?”表示(注意其答语变化):如:
There is a computer in my office.
→Where is the computer?—It’s in my office.
There are four children in the classroom.
→Where are the four children?—They’ re in the classroom.第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录③对数量提问:一般有两种提问方式:如果主语是可数名词,无论是单数还是复数,都用“How many+可数名词复数+are there+介词短语?”表示;如果主语是不可数名词,则用“ How much+不可数名词+is there+介词短语?”表示。
There are twelve months in a year.
→How many months are there in a year?
There is some bread in my bag.→How much bread is there in your bag?第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录(6)反意疑问句:There
be或There加其它动词,其反意疑问句一律用…there?如:There is a beautiful girl in the garden,isn’t there?There used to be no school here,used there/did there?
(7)There be句型和have/has的区别:There be句型表示“存在有”,have/has表示“拥有”“所有”,两者不能同时使用。如:桌子上有三本书。There are three books on the desk.我有三本书。I have three books.
(8)There be+主语+doing+介词短语。如:There is a truck collecting rubbish outside.There is a wallet lying on the ground.第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录考点8:倒装句
(1)so引导的倒装句
完全倒装:so+be/助词/情态动词+主语。该倒装句意为“某人也一样”,上下句是不同的两个人或物,但发生同样的行为或状况,是表示肯定的倒装。如:—I have finished my homework.我已经做完作业了。—So has he.他也做完了。
易混句式:so+主语+be/助词/情态动词。该句式表示对前面所描述的事实加以肯定,上下句中所指的是相同人或物。如:—Lucy dances very well.露西舞跳得很好。—So she does.的确如此。第二篇 中考专题突破(2)neither/nor+be/助词/情态动词+主语。该句式表示“某人(物)也不怎么样”,上下句中是不同的两个人或物,他们的行为和状况都一样,是表示否定的倒装。如:—I haven’t seen that film.我没看过那部电影。—Neither(Nor)have I.我也没有。
①存在句(there be/live/stand/lie/seem等)需要全部倒装。如:There once lived an old hunter in the house.这所房子里曾住过一位老猎人。There seems to be many listeners.似乎有很多听众。
②here,there,out,in,down,up,away,now,then等副词置于句首也可构成倒装句,有两种结构:副词+动词+主语(完全倒装);副词+代词+动词 (部分倒装)返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录【注意】谓语动词的单复数由他们后面的名词或代词的单复数决定。如:Here comes the bus.公共汽车来了。Now comes your turn.现在轮到你了。第二篇 中考专题突破考点9:常见的并列句:
(1)用来连接两个并列概念的连接词有and,not only…but also…,neither…nor…,as well as等,and所连接的前后分句往往表示平行关系、顺接关系、对照关系、先后关系、递进关系。前后分句的时态往往保持一致关系,若第一个分句是祈使句,那么第二个分句用将来时。
①He likes playing football and he plays well.他喜欢踢足球,并且踢得很好。
②Hurry up,and you will catch the early bus.
③as well as是英语中常用的连接词(并列连词),侧重于前项。The child is lively as well as healthy.这孩子既健康又活泼。=The child is not only lively but also healthy.返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录(2)表示在两者之间选择一个,常用的连接词有or,either…or…等,前后分句的时态往往保持一致关系,若第一个分句是祈使句,那么第二个分句用将来时。
①Now you can have a rest or you can go to the cinema.(or译为:或者)
②Hurry up,or you will miss the early bus.(or译为:否则)第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录(3)表明两个概念彼此有矛盾、相反或者转折,常用的连接词有but,yet,still,however,while(而)等,前后分句时态一致。
①It has no mouth,but it can talk.它没有嘴巴,但是它会说话。(前后彼此矛盾,表示转折)
②School is over,yet all the teachers are still working.学校放学了,可是老师们仍然在工作。(前后彼此矛盾,表示转折)
③He wants to be a writer,while I want to be a scientist.他想当作家,而我则想当科学家。(前后不矛盾,只是表示转折)第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录(4)说明原因或理由,用连接词for,前后分句时态一致。如:He has many good friends,for he is an honest man。他有许多好朋友,因为他是个诚实的男子汉。
(5)表示结果,用连接词so,前后分句时态一致。如:Mr.Li went to his hometown,so Mr.Wang was taking his class instead.李老师回老家去了,所以王老师代他的课。
send(寄给) write(写给) show(出示)
return(还给) bring(带来) pass(递给)
leave(留给) offer(提供) tell(告诉)
lend(借给) give(给) sell(卖) teach(教)
(2)间接宾语前加介词for的动词有:
choose(选择) order(订购) get(弄到)
sing(唱歌) play(演奏) make(做)
buy(买) do(做)第二篇 中考专题突破考点2:陈述句、疑问句返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录考点3:选择疑问句
1.构成:
(1)一般疑问句+or+第二选项?
(2)特殊疑问句+第一选项(+第二选项)+or+第三选项?
2.选择疑问句的结构与特殊疑问句相同,即要具体回答,不可以用Yes/No回答。如:
①—Is your friend a boy or a girl?—A girl.
②—Which do you prefer,coffee or tea?—Tea,please.
③—Which do you like best,singing,dancing or skating?—Dancing,of course.第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录考点4:反意疑问句
1.构成:由两部分组成:前者是陈述部分,后者是疑问部分(它是由be,have,助动词或情态动词+主语构成)。如果陈述部分是肯定结构,反意疑问句须用否定结构;反之,陈述部分如果是否定结构,反意疑问句须用肯定结构。反意疑问句的两部分,必须保持人称和时态的一致;反意疑问句的回答有时会和汉语不同。第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录如:(1)He is old,isn’t he?(他老了,不是吗?)
(2)Your father went to Japan,didn’t he?(你爸爸去了日本,不是吗?)
(3)He isn’t old,is he?(他不老,是吗?)
(4)He seldom plays football,does he?(他很少踢足球,是吗?)
★(5)Tom has been to Japan,hasn’t he?
比较:Tom has to do housework,doesn’t he?
(6)There is little water,is there?
(7)Kate hardly speaks Chinese,does she?
(8)Please open the door,will you?第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录★(除Let’s外的祈使句的反意疑问句用will you)
★(Let’s开头的祈使句的反意疑问句用shall we)
(9)Let us go swimming,will you?
(10)Let’s go swimming,shall we?
(11)Everyone is here,aren’t they?(everyone指人)
(12)Everything is ready,isn’t it? (everything指物)
(13)I don’t think Tom has done that,has he?(主要看宾语从句:I/we think/believe 引导宾从时否定前移)
(14)She thinks Tom hasn’t done that,doesn’t she?(主要看主句)第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录2.反意问句的回答:无论哪种形式的反意问句,回答时要遵循:“Yes,+肯定式”或者“No,+否定式”
如:(1)—The man went away,didn’t he?(那人走开了,不是吗?)
—Yes,he did.(是的,他走了。)/No,he didn’t.(不,他没有走。)
(2)—Tom didn’t go there,did he?(Tom没去那里,是吗?)
—Yes,he did.(不,他去了。)/No,he didn’t.(是的,他没去。)第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录考点5:祈使句
祈使句用来表示请求、命令等。它的主语you往往不说出。
▲祈使句的肯定式:动词(原形)+其他
如:Please give me a hand.(请帮忙)
Shut up!(住嘴!)
▲祈使句的否定式:Don’t+动词原形+其他
如:Please don’t talk in low voice.(请不要低声讲话。)Don’t look back!(不要掉头看。)第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录【注意】以“let’s”引出的祈使句的否定结构,“not”应放在“let’s”后面。如:Let’s not trouble him.(我们不要打扰他。)
▲肯定祈使句前可以用助动词来强调语气。
如:Please do help me!(请千万帮帮我。)(do起强调作用)
▲祈使句在复合句和其它一些情况下看作将来时。
如:Please call me when she comes back.(当她回来时给我打个电话。)
—Don’t bring it here tomorrow.—OK,I won’t.第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录考点6:感叹句
感叹句用来表示喜怒哀乐等强烈感情。句末常用“!”
1.what感叹名词。对含有形容词的名词短语感叹的结构通常是:
★What+(a/an)+(形容词)+名词+陈述句结构!
(主谓)
(1)感叹可数名词单数。
如:①What a kind girl (she is)! (她是多么善良的一个女孩啊!)
②What a tall tree (it is)! (它是多高的一棵树啊!)第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录(2)感叹可数名词复数。
如:①What kind girls (they are)! (她们是多么善良的女孩啊!)
②What tall trees (they are)! (它们是多高的树啊!)第二篇 中考专题突破(3)感叹不可数名词。如:
①What delicious food (it is)!
②What bad/good weather (it is)!
③What good news (it is)!
④What useful information (it is)!
⑤What good advice (it is)!
⑥What hard work (it is)!
⑦What great fun (they had)!
(have fun词组)
★特例:What a good time (they are having)! (have a good time词组)
★技巧:what引导的感叹句中的形容词后肯定直接有一个名词。返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录2.how对形容词或副词进行感叹:★结构通常是:How+形容词/副词+陈述句结构(主谓语),用来强调句子中的形容词、副词或动词。
(1)how感叹形容词时,可以与what 感叹句相互转化。
①How kind the girl is! (那个女孩多么善良啊!)
②How tall the tree is! (那棵树多高啊!)
(2)how感叹副词时,不可以与what 感叹句相互转化。
①How carefully the old man walks!(这老人走路真小心!)
②How beautifully Lily is singing!第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录▲有时,陈述句、祈使句、疑问句、一个词或词组,也带有一定的感彩,也可以成为感叹句,此时未必使用感叹句型。He is sitting on a tiger’s back!(他坐在老虎的背上!)/A nice shot!(漂亮一击!)/Good goal!(好球!)第二篇 中考专题突破考点7:There be句型
(1)There be(is/are/was/were)+sb./sth.+地点状语。意为“某处有(存在)某人或某物”。be 必须与其后的主语保持人称和数的一致;如果是并列主语,be 应该和临近的主语保持一致。
(2)There be结构的一般疑问句变化只需把be动词移到句首,再在句尾加上问号即可。
(3)there be 结构有不同的时态,可与多种助动词或情态动词连用。如:
There must be a pen in the box.There happened to be some money in my pocket.There is going to be a meeting tonight.There has been a big tree on the top of the hill.There used to be a church across from the bank.返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破(4)There be句型否定句式的构成和含有be动词的其它句型一样,在be后加上“not”。也可用“no”来表示。即:no+n.(名词)=not a/an/any+n.(名词)。注意:no+n.(可数名词单数)=not a/an+n.(可数名词单数);no+n.(可数名词复数)=not any+n.(可数名词复数);no+n.(不可数名词)=not any+n.(不可数名词)。如:
① There is an orange in her bag.
→There isn’t an orange in her bag.=There is no orange in her bag.
② There are some oranges in her bag.
→There aren’t any oranges in her bag.=There are no oranges in her bag.返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录(5)There be句型的特殊疑问句有以下三种形式:
①对主语提问:当主语是人时,用“Who’s+介词短语?”;当主语是物时,用“What’s+介词短语?”。其中there在口语中常常省略。
【注意】无论原句的主语是单数还是复数,对其提问时一般都用be的单数形式(回答时却要根据实际情况来决定)。如:
There is a bird in the tree.→What’s in the tree?
There are some bikes over there.→What’s over there?
There is a little girl in the room.→Who is in the room?第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录②对地点状语提问:用“Where is/are+主语?”表示(注意其答语变化):如:
There is a computer in my office.
→Where is the computer?—It’s in my office.
There are four children in the classroom.
→Where are the four children?—They’ re in the classroom.第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录③对数量提问:一般有两种提问方式:如果主语是可数名词,无论是单数还是复数,都用“How many+可数名词复数+are there+介词短语?”表示;如果主语是不可数名词,则用“ How much+不可数名词+is there+介词短语?”表示。
There are twelve months in a year.
→How many months are there in a year?
There is some bread in my bag.→How much bread is there in your bag?第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录(6)反意疑问句:There
be或There加其它动词,其反意疑问句一律用…there?如:There is a beautiful girl in the garden,isn’t there?There used to be no school here,used there/did there?
(7)There be句型和have/has的区别:There be句型表示“存在有”,have/has表示“拥有”“所有”,两者不能同时使用。如:桌子上有三本书。There are three books on the desk.我有三本书。I have three books.
(8)There be+主语+doing+介词短语。如:There is a truck collecting rubbish outside.There is a wallet lying on the ground.第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录考点8:倒装句
(1)so引导的倒装句
完全倒装:so+be/助词/情态动词+主语。该倒装句意为“某人也一样”,上下句是不同的两个人或物,但发生同样的行为或状况,是表示肯定的倒装。如:—I have finished my homework.我已经做完作业了。—So has he.他也做完了。
易混句式:so+主语+be/助词/情态动词。该句式表示对前面所描述的事实加以肯定,上下句中所指的是相同人或物。如:—Lucy dances very well.露西舞跳得很好。—So she does.的确如此。第二篇 中考专题突破(2)neither/nor+be/助词/情态动词+主语。该句式表示“某人(物)也不怎么样”,上下句中是不同的两个人或物,他们的行为和状况都一样,是表示否定的倒装。如:—I haven’t seen that film.我没看过那部电影。—Neither(Nor)have I.我也没有。
①存在句(there be/live/stand/lie/seem等)需要全部倒装。如:There once lived an old hunter in the house.这所房子里曾住过一位老猎人。There seems to be many listeners.似乎有很多听众。
②here,there,out,in,down,up,away,now,then等副词置于句首也可构成倒装句,有两种结构:副词+动词+主语(完全倒装);副词+代词+动词 (部分倒装)返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录【注意】谓语动词的单复数由他们后面的名词或代词的单复数决定。如:Here comes the bus.公共汽车来了。Now comes your turn.现在轮到你了。第二篇 中考专题突破考点9:常见的并列句:
(1)用来连接两个并列概念的连接词有and,not only…but also…,neither…nor…,as well as等,and所连接的前后分句往往表示平行关系、顺接关系、对照关系、先后关系、递进关系。前后分句的时态往往保持一致关系,若第一个分句是祈使句,那么第二个分句用将来时。
①He likes playing football and he plays well.他喜欢踢足球,并且踢得很好。
②Hurry up,and you will catch the early bus.
③as well as是英语中常用的连接词(并列连词),侧重于前项。The child is lively as well as healthy.这孩子既健康又活泼。=The child is not only lively but also healthy.返回目录第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录(2)表示在两者之间选择一个,常用的连接词有or,either…or…等,前后分句的时态往往保持一致关系,若第一个分句是祈使句,那么第二个分句用将来时。
①Now you can have a rest or you can go to the cinema.(or译为:或者)
②Hurry up,or you will miss the early bus.(or译为:否则)第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录(3)表明两个概念彼此有矛盾、相反或者转折,常用的连接词有but,yet,still,however,while(而)等,前后分句时态一致。
①It has no mouth,but it can talk.它没有嘴巴,但是它会说话。(前后彼此矛盾,表示转折)
②School is over,yet all the teachers are still working.学校放学了,可是老师们仍然在工作。(前后彼此矛盾,表示转折)
③He wants to be a writer,while I want to be a scientist.他想当作家,而我则想当科学家。(前后不矛盾,只是表示转折)第二篇 中考专题突破返回目录(4)说明原因或理由,用连接词for,前后分句时态一致。如:He has many good friends,for he is an honest man。他有许多好朋友,因为他是个诚实的男子汉。
(5)表示结果,用连接词so,前后分句时态一致。如:Mr.Li went to his hometown,so Mr.Wang was taking his class instead.李老师回老家去了,所以王老师代他的课。
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
