中考英语二轮语法专项复习课件 第11讲动词时态
文档属性
| 名称 | 中考英语二轮语法专项复习课件 第11讲动词时态 |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.2MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 鲁教版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-12-25 22:32:44 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共61张PPT)
第十一讲 动 词 时 态
中考英语专项复习
1.能够动词的基本变化形式及英语的时态;
2.掌握中考常考时态的应用。
学习目标
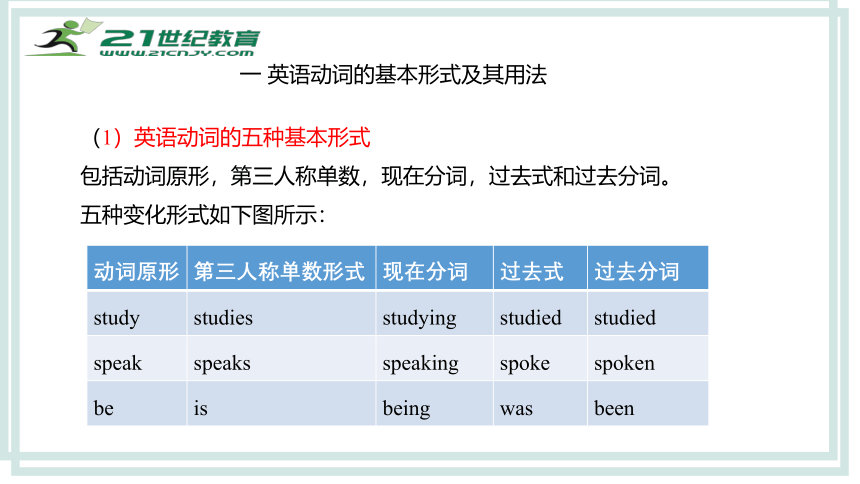
一 英语动词的基本形式及其用法
(1)英语动词的五种基本形式
包括动词原形,第三人称单数,现在分词,过去式和过去分词。
五种变化形式如下图所示:
动词原形 第三人称单数形式 现在分词 过去式 过去分词
study studies studying studied studied
speak speaks speaking spoke spoken
be is being was been
(2) 动词的五种基本形式的使用
基本形式 用法 例句
动词原形 (1)放于不定式to的后面 (2)在do, does, did等助动词的后面 (3)放在情态动词的后面。 (4)用于一般现在时(除第三人称单数外) I want to leave here.
Does she live here
He did’t catch the early bus yesteray.
You can go now.
I play football after shool every day.
第三人称单数形式 用于主语为第三人称单数的一般现在时 Mary often goes to school by bus.
现在分词 构成进行时态,包括现在进行时和过去进行时 They are playing basketball now.
I was sleeping when the rainstorm came.
基本形式 用法 例句
过去式 通常用于一般过去时 They went to the park two days ago
He was late for work yesterday.
过去分词 用于被动语态和完成时 A bridge was built last year.
被动语态
Have you read the book yet?
现在完成时
When I woke up,it had already stopped raining.
过去完成时
二 时 态
初中阶段共出现了八种时态,包括:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时和过去将来时。
(1) 一般现在时的谓语构成及句式变化
一般现在时的谓语构成:是由主语+“动词原形”或“动词第三人称单数形式”(当主语为第三人称单数)或 主语+“be动词(am/is/are)”构成。
句式变化及回答:
①否定形式是在动词前加don’t或doesn’t(第三人称单数的时候注意变成原形)。如果是be动词,则直接在be后加not。
②一般疑问句要借助do或does,注意后面的动词如果时第三人称单数形式则变回原形。如果是be动词,则把be动词放到句首。原句第一人称变一般疑问句要转为第二人称。
1、一 般 现 在 时
① She is a teacher. // She is not a teacher.
---- Is she a teacher --- Yes, he is. (No, he isn’t.)
② I go to school on foot. // I don’t go to school on foot.
---- Do you go to school on foot ---- Yes, I do. (No, I don’t.)
③ He eats an egg at breakfast. // He doesn’t eat an egg at breakfast.
---- Does he eat an egg at breakfast ---- Yes, he does. (No, he doesn’t)
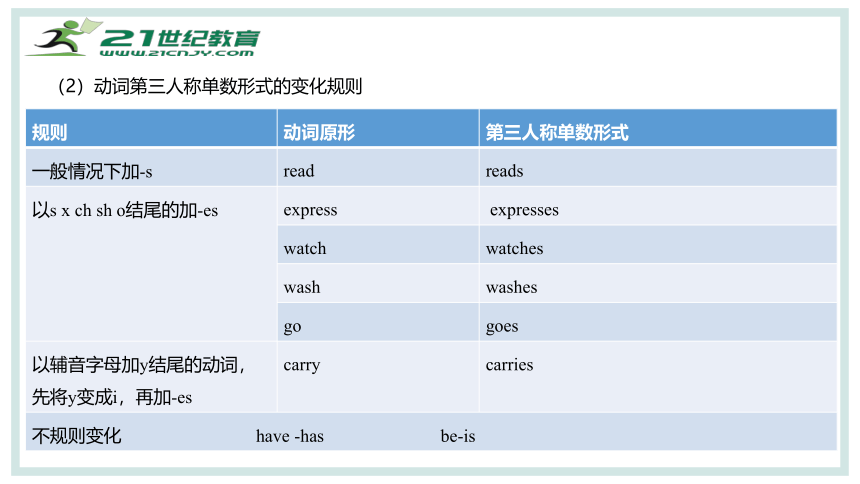
(2)动词第三人称单数形式的变化规则
规则 动词原形 第三人称单数形式
一般情况下加-s read reads
以s x ch sh o结尾的加-es express expresses
watch watches
wash washes
go goes
以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,先将y变成i,再加-es carry carries
不规则变化 have -has be-is
文本信息
(2)一般现在时的基本用法:
①表示经常发生或反复发生的动作。这种用法经常与 always, usually, often, sometimes, every day (week, month, year…), once a week, on Sundays, now and then等时间状语连用。
He usually gets up at 6:30 every day.
Jim often goes to school on foot.
②表示现在的情况或状态
I enjoy computer games
Does Mary live here
③表述客观事实、普遍真理、客观存在、 自然现象、科学事实 、名言、警句或者谚语等。
The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
The earth goes around the sun.
Every dog has its day. 人皆有得意日。
④表示按时间表 ,按计划或规定将要发生的动作,但限于部分动词,如:begin, be,come, leave, go ,arrive, start , stop, return, open, close,move,finish,continue等此时用一般现在时态的句子中可用来表示按计划、规定将要发生的动作。
The meeting begins at seven.
Our trip starts from Beijing tomorrow and finishes up in Huashan Mountain
the day after tomorrow.
⑤在时间状语从句(when, before, after, as soon as, until等引导)和if , as long as等引导的条件状语从句中用来代替一般将来时。(主将从现)
If you come this afternoon, we’ll have a meeting.
As long as it doesn’t rain tomorrow,we will have a trip
⑥用于比赛说明 演示说明 剧情介绍 新闻标题 图片说明中。
Jack throws the ball to John and John cathes it.(比赛说明)
Labor cuts Deals With Investors 削减劳动力,应对投资者(新闻标题)
⑦ 在由here或there引导的倒装句中,用一般现在时替代现在进行时,表示此刻正在发生的动作。
There goes the bell. 铃响了
Here comes the bus. 公交车来了
一般过去时的谓语构成:是由“be动词的过去式(was, were)”或“行为动词的过去式”构成。
句式变化及回答:
①否定形式是在行为动词原形前加didn’t或在was/were后加not,注意同时把动词过去式改为原形
②一般疑问句借助did提问,同时把动词过去式改为原形。如果句子有was/were,则把was/were放到句首。原句第一人称改成第二人称。
2 一般 过 去 时
(1)一般过去时的谓语构成及句式变化
①I wasn’t at home yesterday
---- Were you at home yesterday ---- Yes, I was. (No, I wasn’t.)
②He watched TV last night.
---- Did he watched TV last night ---- Yes, he did. (No, he didn’t.)
(2)动词过去式的变化规则
输入标题文本信息
标题数字等都可以通过点击和重新输入进行更改。文字数字大小颜色参考此模板
规则 动词原形 动词过去式
一般情况加-ed help helped
以不发音的-e结尾的动词加-ed live lived
辅音字母+y结尾的动词把y变为i,再加-ed cry cried
重读闭音节结尾,且词尾只有一个辅音字母的动词,双写辅音字母再加-ed plan planned
不规则变化的动词详见不规则变化表 规则动词的过去式在清辅音后读[t], 在元音和浊辅音后读[d],在辅音[t][d]后面读[ d]
helped [helpt] stayed [ste d] wanted ['w nt d] dicided [d 'sa d d]
标题数字等都可以通过点击和重新输入进行更改。文字数字大小颜色参考此模板
(3)一般过去时的用法:
①表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态。一般带有明确的过去的时间做状语,如:yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week (month, year…), two days (weeks, months, years…) ago, in 2019, just now, once upon a time等.当上下文清楚时可以不带时间状语。
He worked in that factory last year.
②表示过去经常性或习惯性的动作,这时常与always usually often sometimes never等时间状语连用。
I always got up late,and never had enough time for breakfast.
③ 表示过去将来的动作
在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,用一般将来时表示过去将来的动作。
She said she would come if I promised to wait for her
Melissa told me that as soon as she arrived,she would ring me up.
点击此处
输入文本信息
3 一般将来时
一般将来时用来表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,或表示将来反复发生的动作。
(1) 一般将来时的谓语构成及句式变化
一般将来时的谓语构成:是由“be(am/is/are) going to+动词原形”或“will/shall+动词原形”构成。
点击此处
输入文本信息
一般将来时的句式变化及回答:
否定形式是在be, will, shall后直接加not,shall not的缩写shan’t,will not的缩写won’t。一般疑问句是把be, will, shall放到句首。第一人称变第二人称。
I’m going to buy a car this year.
I’m not going to buy a car this year.
---- Are you buy a computer this year ---- Yes, I am. (No, I am not.)
We shall go to the park. We shan’t go to the park.
---- Shall we go to the park ---- Yes, we shall. (No, we shan’t.)
I will play football with you. // I won’t play football with you.
---- Will you play football with us ---- Yes, I will. (No, we won’t.)
(2) 一般将来时的用法
① will/shall+动词原形表将来
此句型表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态,或表示一种倾向或推测。常用的时间状语有:tomorrow, tomorrow morning(afternoon, evening), the day after tomorrow, next day(week, month, year), soon, some day, in the future,“in+一段时间”等。
We will know the result tomorrow.
I shall leave for Canada nex Friday
点击此处
输入文本信息
② be going to do 结构表示将来
表示计划、打算做某事,表示已经决定的、很可能发生的事,也表示说话者主观打算做某事,或客观迹象表明即将发生某事。
I am gong to sell my old house 我打算卖掉我的旧的房子
It is going to rain soon.
【注意】will可用于所有人称;但shall作为will的一种替代形式,表示单纯将来时,一般用于主语为第一人称I和we时。以You and I, some of us, both of us, neither of us作主语时通常用will。
【注意】be going to 既可指主观打算做某事,也可指客观迹象表明要发生某事。而will往往指没有经过计划而临时出现的意图,常伴有说话者的主观意识或表示将来必然发生的事情。
I am going to quit(辞掉) my present job.(现在的打算,事先经过考虑,指向将来)
I will answer the door (未经事先考虑的意图)
I hope it will be fine tomorrow (主观意愿)
The little boy is going to fall over(根据客观迹象来判断的)
③用现在进行时表将来
现在进行时表将来,往往是指计划好或准备好要做的事情。用于部分表示动作位移的的动词,如go come leave start begin move等的进行时表示马上要做某事。
Your mother is coming out soon 你的妈妈很快就出来。
They are leaving for Shanghai tomorrow.
④用一般现在时表将来
按照计划或时刻表要发生的事情
The new library opens next week.
The plane takes off at 3 p.m.
在时间状语从句中(when, before, after, as soon as, until/till等词引导)或条件状语从句(if unless等词引导)中用一般现在时表将来(主将从现)
I will tell her about it when she comes
We’ll start if it doesn‘t rain tomorrow.
⑤ be to do 结构表将来
此结构表示计划中约定的或按照职责 义务和要求必须要去做的事情或即将发生的动作
We are to meet the guests at the station.
I am to get married next year 我明年结婚
⑥ be about to do 结构表将来
表示马上,很快,即将发生的动作。一般不与具体时间状语连用。
The film is about to start. Be quiet
Hurry up. The train is about to leave.
4 现 在 进 行 时
(1)现在进行时的谓语构成及句式变化
谓语构成:由“助动词be(am/is/are) + 现在分词”构成
句式变化及回答:
否定形式是在be(am/is/are)后加not。
一般疑问句是把be(am/is/are)放到句首,第一人称变成第二人称。
如:They aren’t playing football.
---- Are they playing football ---- Yes, they are. (No they aren’t.)
(2)现在分词的变化规则
规则 动词原形 现在分词
一般情况直接加-ing find finding
不发音的-e结尾的,去-e再加-ing ride riding
重读闭音节结尾,且末尾只有一个辅音字母动词, 双写这个辅音字母再加-ing begin beginning
put puting
prefer preferring
少数以ie结尾的动词,变ie为y,再 加-ing die dying
lie lying
tie tying
以-oe -ee -ye结尾的动词,直接加-ing see seeing
(3)现在进行时的用法
①表示说话时正在进行的动作或状态。常见的时间状语有:now,right now,at this moment, at the moment at present等时间状语连用,或从上下文体现出来,或句首出现look, listen, be careful等词,引起人的注意,说明某一动作正在进行
It is snowing hard outside.
Look. Some children are playing basketball over there.
②表示先阶段正在进行的动作
指的是目前一段时间内在做的一件事,但说话时未必正在做。常用的时间状语为these days。
Alisa is writing a book about herself.
③表示将要发生的动作
表示按计划或安排将要发生的动作,此时常与表示将来的时间状语连用,主语通常时人.
They are getting mariied next month
表示马上发生的动作。仅用于动词,如go, come, drive, fly, travel, arrive, leave, start, visit, run, return,begin stop 等,表示马上就.....
Wait a minnute . I am coming
The car is stopping in a few seconds. 汽车几秒内会停下。
④表特定的情感
现在进行时和always, usually, all the time等连用时,表示一种经常、反复的动作,且说话人往往带有某种感彩(如赞扬、生气、厌烦、批评、惊讶、不满等)
She’s always helping others. 她总是乐于助人。(表示赞赏)
You are always talking in class. 你上课老是说话。(表示批评)
⑤ 不能用于进行时的动词
表示心理活动的动词一般不用进行时态,如love like hate know understand
realize remember bilieve want hope wish need agree等
I love you very much.
表示属性或拥有的动词不能用进行时态
此类词have own(拥有) belong to 等
The book belongs to Mary
表示表象 感官的连系动词不能用于进行时态。如seem appear look soud taste等。feel用于进行时态表一时的感觉。
I am not feeling well today 今天感觉不舒服
You seem a little tired. 你看上去有点累。
(d)表行为结果的动词一般不用于进行时
如accept receive allow decide promise 等
I accept you advice
5 过 去 进 行 过
(1)过去进行时的谓语构成及句式变化
谓语构成:由“助动词be的过去形式(was/were)+动词现在分词”。
句式变化及回答:
否定形式是在be(was/were)后加not。
一般疑问句是把be(was/were)放到句首,第一人称变成第二人称
He was not waiting for the bus at that time.
---- Was he waiting for the bus at that time
---- Yes, he was.(No he wasn’t)
(2)过去完成时的用法
①表示过去某一时刻正在发生或进行的动作
此时句中往往有表示过去的时间状语如then .at that moment .at at that time. at this time. this time yesterday等。没有时间状语时,需要根据上下文的语境体会。
I was writing a letter when you phoned.
They were watching TV at nine o’clock last night.
② 表示过去某一段时间内一直在做或持续进行的动作。
He was writing a book last year, but I don’t know if he has finished it
.He was watching TV between 8:00 and 9:00 on Sunday morning.
③在复合句中,若主要动作和背景动作是同时发生的,那么主从句都可用过去进行时
Mary was doing some reading while her younger brother was writing.
④ 表示过去将要发生的动作
即从过去某一时间看将要发生的动作,常表示‘渐渐 快要’的意思。常见的此类动词有come go start begin leave arrive get become turn 等,
He told me that he was leaving for Italy the next day
It was getting dark when we arrived.
⑤与现在进行时相似的使用,过去进行时也通常与 always, forever, continually等副词连用,表示满意、称赞、惊讶、厌恶等感彩。
She was always ringing me up when I was in London.(表示厌烦)
⑥表示礼貌
有时过去进行时并不表示过去的时间,而是表达现在的客气 礼貌或不确定等感情。此类动词主要有hope、
wonder think expect等
I was wondering if we could have dinner together不知是否能一块吃饭
I was hoping that you would help me 真希望你能帮我
(3)when和while的区别:
① 引导时间状语从句时,while 后的从句谓语接延续性动词;而when的从句谓语后既可以是延续性动词也可以是非延续性动词。
When you kocked the door, I was having a bath
It began to rain while we are walking in the park.
② while可以连接两个并列的句子,强调从句的谓语动作和主句的谓语动作同时发生。
While I’m doing my homework, my mother is preparing dinner.
③ when可作特殊疑问词,对时间进行提问;while 不能。
(4)过去进行时和一般过去时的用法比较
① 过去进行时往往表示动作的未完成,而一般过去时则往往表示动作已完成。
②过去进行时侧重说明动作持续时间的长度,而一般过去时侧重说明事实。
She was studying in Canada last year. I don’t know if she has returned
她去年在加拿大学习,不知道是否回来
She studied in Canada last year 她去年在加拿大学习过
6、现 在 完 成 时
(1)现在完成时的谓语构成即句式变化
谓语构成:助动词have/has + 过去分词
have, has可以缩写为’ve或‘s, have not 缩写haven’t, has not 缩写hasn’t
句式变化及回答:
否定形式是在have/has后加not。
一般疑问句是把have/has放到句首。第一人称变为第二人称如:
He has finished the work . // He hasn’t finished the work
//---- Has he finished the work ---- Yes, he has. (No, he hasn’t.)
规则 动词原形 动词过去分词
一般情况直接加-ed work worked
以不发音的-e结尾的,加-d liked liked
以辅音字母+y结尾的,变y为i,再加-ed carry carried
以重读闭音节结尾,且词尾只有一个辅音字母时,双向这个辅音字母后再加-ed stop stoped
drop dropped
regret regretted
不规则动词的过去分词详见不规则动词表
(2)动词过去分词的变化规则
(3)现在完成时的用法
①强调过去的动作对现在的影响
表示在说话前已经完成或刚完成的动作,但这个动作的结果对现在仍有影响。常与already, ever, never, just, yet, before 等词连用。
I have already finished all the work 我已经做完所有工作
He has just arrived in Hong Kong 刚到香港
【注意】already, ever, never, just, yet, before的用法辨析
already 意为“已经”
通常用于肯定句中,可放在be 动词 情态动词 助动词之后,实义动词之前,也可以放在句末。在变换句型时,常与yet 互换。
I have already finished the work.我已经完成这项工作了。
改为否定句:I haven’t finished the work yet.我还没有完成这项工作。
改为一般疑问句:Have you finished the work yet
yet 用在疑问句中意为“已经”,用在否定句中意为“还”,常放在句末。
— Have you watched the movie yet
— No. I haven’t watched it yet.
just 意为“刚刚”
表示行为刚刚过去,常放在助动词与过去分词之间。
My father has just finished his work.
ever 意为“曾经”用于疑问句或否定句中,放在助动词与过去分词之间。
Have you ever visited the Great Wall
never 意为“从来没有”多放在助动词与过去分词之间,常与 before 连用。
I have never been to such a beautiful place before.
before 意为“以前”
指过去不确定的某个时间,总是放在句末,不受句型的限制。
I haven’t been to Beijing before.
②表示过去的某一动作或行为一直持续道现在。(how long 提问)
这种用法表示动作发生在过去,但一直持续到现在,并且有可能持续下去。常与表示一段时间的状语连用。此时动词必须是延续性动词(否定句除外)。
如 all my life, all the time ,all day, up to now, so far,in the past /last years ,(ever)since last year,ever since,for a long time.
since + 过去时间点 / 过去时的从句, since + 一段时间 + ago, for + 一段时间
Helen has lived in New York since 2015.
My brother has learned about 500 English words since he was five years old.
They have waited for more than two hours
Jack has played basketball for three years ( since three years ago).
(3)非延续性动词(瞬间性动词)与延续性动词
延续性动词表示能够延续的动作,这种动作可以长时间延续下去或产生持久的影响,如live work等,可以与表示时间段的状语连用;
非延续性动词(瞬间性动词)动词表示不能延续的动作,动作一发生立即结束。如open, die, close, begin,后通常不能跟表示时间段的状语连用。若瞬间性动词要跟时间段,将其转化为延续性动词。
The movie has already begun for ten (错误)
The movie has already begun. (正确)
The movie has already been on for ten (正确)
【注意】 在否定句中非延续动词可与表示一段时间的状语连用。
I haven’t bought anything for one month.
I haven't left here for 3 years.
I haven't heard from him for 3 weeks.
(4)常见非延续性动词(瞬间性动词)与延续性动词的转化
非延续性动词 延续性动词 非延续性动词 延续性动词
arrive in/at / come to be in/at come back be back
begin(start) be on come here be here
borrow keep come to work work
become be die be dead
buy have dress be dressed
close be closed fall asleep be asleep
catch a cold have a cold fall ill be ill
非延续性动词 延续性动词 非延续性动词 延续性动词
finish be over join be in或be a member of
get up be up leave be away (from)
get married /marry be married open be open
go out /come out be out put on wear
go there be there return be back
get a cold have a cold reach be in/at
go back be back stop be over
get to sleep be asleep turn off be off
get/to to be in /at turn on be on
(4)现在完成时与一般过去时的区别
相同的点是两个时态都谈论过去已经发生的事情,但现在完成时表示的动作与现在有关系 ,或者对现在有影响,或谈论现在以前一段时间发生的事情。而一般过去时只是谈论过去的事情,与现在没有关系。
一般过去时表示过去某时发生的动作或单纯叙述过去的事情,强调动作;现在完成时为过去发生的,但强调过去的事情对现在的影响,强调的是影响。
I saw the film yesterday.(强调看的动作发生过了,不涉及现在)
I have seen the film. (强调对现在的影响,电影的内容已经知道了。)
(5)have/has been to, have/has gone to和have/has been in的区别:
have/has gone to+地点。意为“到某地去了”,说话时该人不在现场。一般只用第三人称作主语。
have/has been to+地点。意为“曾经去过某地”,含有“现在已离开那儿”之意,后可接次数(如once,twice,three times等)表示“去过某地几次”,也可和just,never,ever等连用。
have been in+地点。 表示“到某地多长时间了”,常与时间段连用。
Mary has gone to the library 玛丽去图书馆了(现在没回来)
Mary has been to Hong Hong twice 去过香港两次(现在已经回来了)
Mary have been in Canada for ten years 玛丽到加拿大十年了
7 过去将来时
过去将来时表示从过去的某段时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态。这种时态常用于主句是一般过去时的宾语从句中,表示从句的动作发生在主句之后。
过去将来时同一般将来时类似,除了用woud do表示外,还可以用was/were going to do,was/were to do, was/were about to do do及过去进行时(部分单词如come, go, start, move, leave等用过去进行时表将来)等方式表示。
在时间、条件状语从句中用一般过去时表示过去将来时。
Last week he promised that he would come,but he has’t ariived until now.
She was going to sell her old house and buy a new one.
He told me that he was leaving in one hour.
The meeting was to be held the next week
I was about to turn on the power of the computer when the electrity was cut off.
我正要打开电脑的时候断电了
They said they would let us know if they heard any news about him.
8 过去完成时
(1)过去完成时的谓语构成即句式变化
谓语构成:助动词had+ 过去分词。had not 缩写hadn’t
句式变化及回答:
否定形式是在had后加not。
They hadn’t finished the work when we got there.
一般疑问句是把had放到句首。第一人称变为第二人称如:
Had he told you to go there earlier yesterday 他昨天告诉过你早点儿到那儿吗
—Yes, he had. (No, he hadn’t.)
(2)过去完成时的用法
①表示过去某一时间或动作之前已经完成的动作
过去完成时的这种用法表示:过去的过去。这个过去的时刻常用by,before等介词短语或时间状语从句来表示,也可以用一个表示过去的动作或上下文来表示。
He had left before I arrived
I had just finished half the work by yesterday
He had had lunch when I came to his house
②表示从过去的某一个时间开始一直延续到过去另一个时间的动作或状态
He had worked in the factory for five years before he moved here.
By nine o'clock he had worked for ten hours.
③用来表示未曾实现的愿望或打算
动词hope ,wish ,plan, want ,mean,thought,expect等表示打算 计划 希望 认为等的动词用于过去完成时表示过去未曾实现的愿望 ,打算或意图。
I had hoped to be back last night,but I didn’t catch the train.
本希望昨晚回来,但没赶上火车
We had planned to go on a picnic yesterday,but it was raining.
本计划昨天去野餐,但一直下雨,
④ 固定句式中的过去完成时
在表示:一....就....的harldy/scarely...when...., no sooner...than...的句式中。
主句用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时。
We had no sooner arrived than we started singing and dancing.
我们一到就开始唱歌跳舞。
当hardly,scarely,no sooner放于居首时,句中要用部分倒装,
Scarely had Rosa heard the news when she burst into tears
Rosa 一听到消息就哭了(注意倒装)
(3)过去完成时的时间状语
by last week, by then, by the end of (last…) ,before that time,before that year,long
before (很久以前)或者由when, before等引出状语从句。如before I arrived,whe I airrived.
有时句子中会有already, just, once, ever, never等词语,也会有for… 或since…构成的时间状语。如:
The woman had left before he realized she was a thief.
He had already finished cleaning the room when his teacher came.
三 实战演练
1.(2023·江苏宿迁·统考中考真题)— My father and I ________ a lot of photos at the same place in the past ten years.
— Those photos must be your valuable memories.
A.have taken B.will take C.take D.were taking
A
2.(2023·辽宁抚顺·统考中考真题)Look! There ________ some information about traffic safety in this book.
A.is B.are C.was D.were
A
3.(2023·辽宁丹东·统考中考真题)— Where’s your brother, Bob
— Look! He ________ the car in the yard.
A.is cleaning B.cleaned C.cleans D.will clean
A
4.(2023·北京·统考中考真题)The Shenzhou-15 astronauts ________ to Earth safely on June 4, 2023.
A.return B.returned C.will return D.have returned
B
谢谢
21世纪教育网(www.21cnjy.com)
中小学教育资源网站
兼职招聘:
https://www.21cnjy.com/recruitment/home/admin
第十一讲 动 词 时 态
中考英语专项复习
1.能够动词的基本变化形式及英语的时态;
2.掌握中考常考时态的应用。
学习目标
一 英语动词的基本形式及其用法
(1)英语动词的五种基本形式
包括动词原形,第三人称单数,现在分词,过去式和过去分词。
五种变化形式如下图所示:
动词原形 第三人称单数形式 现在分词 过去式 过去分词
study studies studying studied studied
speak speaks speaking spoke spoken
be is being was been
(2) 动词的五种基本形式的使用
基本形式 用法 例句
动词原形 (1)放于不定式to的后面 (2)在do, does, did等助动词的后面 (3)放在情态动词的后面。 (4)用于一般现在时(除第三人称单数外) I want to leave here.
Does she live here
He did’t catch the early bus yesteray.
You can go now.
I play football after shool every day.
第三人称单数形式 用于主语为第三人称单数的一般现在时 Mary often goes to school by bus.
现在分词 构成进行时态,包括现在进行时和过去进行时 They are playing basketball now.
I was sleeping when the rainstorm came.
基本形式 用法 例句
过去式 通常用于一般过去时 They went to the park two days ago
He was late for work yesterday.
过去分词 用于被动语态和完成时 A bridge was built last year.
被动语态
Have you read the book yet?
现在完成时
When I woke up,it had already stopped raining.
过去完成时
二 时 态
初中阶段共出现了八种时态,包括:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时和过去将来时。
(1) 一般现在时的谓语构成及句式变化
一般现在时的谓语构成:是由主语+“动词原形”或“动词第三人称单数形式”(当主语为第三人称单数)或 主语+“be动词(am/is/are)”构成。
句式变化及回答:
①否定形式是在动词前加don’t或doesn’t(第三人称单数的时候注意变成原形)。如果是be动词,则直接在be后加not。
②一般疑问句要借助do或does,注意后面的动词如果时第三人称单数形式则变回原形。如果是be动词,则把be动词放到句首。原句第一人称变一般疑问句要转为第二人称。
1、一 般 现 在 时
① She is a teacher. // She is not a teacher.
---- Is she a teacher --- Yes, he is. (No, he isn’t.)
② I go to school on foot. // I don’t go to school on foot.
---- Do you go to school on foot ---- Yes, I do. (No, I don’t.)
③ He eats an egg at breakfast. // He doesn’t eat an egg at breakfast.
---- Does he eat an egg at breakfast ---- Yes, he does. (No, he doesn’t)
(2)动词第三人称单数形式的变化规则
规则 动词原形 第三人称单数形式
一般情况下加-s read reads
以s x ch sh o结尾的加-es express expresses
watch watches
wash washes
go goes
以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,先将y变成i,再加-es carry carries
不规则变化 have -has be-is
文本信息
(2)一般现在时的基本用法:
①表示经常发生或反复发生的动作。这种用法经常与 always, usually, often, sometimes, every day (week, month, year…), once a week, on Sundays, now and then等时间状语连用。
He usually gets up at 6:30 every day.
Jim often goes to school on foot.
②表示现在的情况或状态
I enjoy computer games
Does Mary live here
③表述客观事实、普遍真理、客观存在、 自然现象、科学事实 、名言、警句或者谚语等。
The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
The earth goes around the sun.
Every dog has its day. 人皆有得意日。
④表示按时间表 ,按计划或规定将要发生的动作,但限于部分动词,如:begin, be,come, leave, go ,arrive, start , stop, return, open, close,move,finish,continue等此时用一般现在时态的句子中可用来表示按计划、规定将要发生的动作。
The meeting begins at seven.
Our trip starts from Beijing tomorrow and finishes up in Huashan Mountain
the day after tomorrow.
⑤在时间状语从句(when, before, after, as soon as, until等引导)和if , as long as等引导的条件状语从句中用来代替一般将来时。(主将从现)
If you come this afternoon, we’ll have a meeting.
As long as it doesn’t rain tomorrow,we will have a trip
⑥用于比赛说明 演示说明 剧情介绍 新闻标题 图片说明中。
Jack throws the ball to John and John cathes it.(比赛说明)
Labor cuts Deals With Investors 削减劳动力,应对投资者(新闻标题)
⑦ 在由here或there引导的倒装句中,用一般现在时替代现在进行时,表示此刻正在发生的动作。
There goes the bell. 铃响了
Here comes the bus. 公交车来了
一般过去时的谓语构成:是由“be动词的过去式(was, were)”或“行为动词的过去式”构成。
句式变化及回答:
①否定形式是在行为动词原形前加didn’t或在was/were后加not,注意同时把动词过去式改为原形
②一般疑问句借助did提问,同时把动词过去式改为原形。如果句子有was/were,则把was/were放到句首。原句第一人称改成第二人称。
2 一般 过 去 时
(1)一般过去时的谓语构成及句式变化
①I wasn’t at home yesterday
---- Were you at home yesterday ---- Yes, I was. (No, I wasn’t.)
②He watched TV last night.
---- Did he watched TV last night ---- Yes, he did. (No, he didn’t.)
(2)动词过去式的变化规则
输入标题文本信息
标题数字等都可以通过点击和重新输入进行更改。文字数字大小颜色参考此模板
规则 动词原形 动词过去式
一般情况加-ed help helped
以不发音的-e结尾的动词加-ed live lived
辅音字母+y结尾的动词把y变为i,再加-ed cry cried
重读闭音节结尾,且词尾只有一个辅音字母的动词,双写辅音字母再加-ed plan planned
不规则变化的动词详见不规则变化表 规则动词的过去式在清辅音后读[t], 在元音和浊辅音后读[d],在辅音[t][d]后面读[ d]
helped [helpt] stayed [ste d] wanted ['w nt d] dicided [d 'sa d d]
标题数字等都可以通过点击和重新输入进行更改。文字数字大小颜色参考此模板
(3)一般过去时的用法:
①表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态。一般带有明确的过去的时间做状语,如:yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week (month, year…), two days (weeks, months, years…) ago, in 2019, just now, once upon a time等.当上下文清楚时可以不带时间状语。
He worked in that factory last year.
②表示过去经常性或习惯性的动作,这时常与always usually often sometimes never等时间状语连用。
I always got up late,and never had enough time for breakfast.
③ 表示过去将来的动作
在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,用一般将来时表示过去将来的动作。
She said she would come if I promised to wait for her
Melissa told me that as soon as she arrived,she would ring me up.
点击此处
输入文本信息
3 一般将来时
一般将来时用来表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,或表示将来反复发生的动作。
(1) 一般将来时的谓语构成及句式变化
一般将来时的谓语构成:是由“be(am/is/are) going to+动词原形”或“will/shall+动词原形”构成。
点击此处
输入文本信息
一般将来时的句式变化及回答:
否定形式是在be, will, shall后直接加not,shall not的缩写shan’t,will not的缩写won’t。一般疑问句是把be, will, shall放到句首。第一人称变第二人称。
I’m going to buy a car this year.
I’m not going to buy a car this year.
---- Are you buy a computer this year ---- Yes, I am. (No, I am not.)
We shall go to the park. We shan’t go to the park.
---- Shall we go to the park ---- Yes, we shall. (No, we shan’t.)
I will play football with you. // I won’t play football with you.
---- Will you play football with us ---- Yes, I will. (No, we won’t.)
(2) 一般将来时的用法
① will/shall+动词原形表将来
此句型表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态,或表示一种倾向或推测。常用的时间状语有:tomorrow, tomorrow morning(afternoon, evening), the day after tomorrow, next day(week, month, year), soon, some day, in the future,“in+一段时间”等。
We will know the result tomorrow.
I shall leave for Canada nex Friday
点击此处
输入文本信息
② be going to do 结构表示将来
表示计划、打算做某事,表示已经决定的、很可能发生的事,也表示说话者主观打算做某事,或客观迹象表明即将发生某事。
I am gong to sell my old house 我打算卖掉我的旧的房子
It is going to rain soon.
【注意】will可用于所有人称;但shall作为will的一种替代形式,表示单纯将来时,一般用于主语为第一人称I和we时。以You and I, some of us, both of us, neither of us作主语时通常用will。
【注意】be going to 既可指主观打算做某事,也可指客观迹象表明要发生某事。而will往往指没有经过计划而临时出现的意图,常伴有说话者的主观意识或表示将来必然发生的事情。
I am going to quit(辞掉) my present job.(现在的打算,事先经过考虑,指向将来)
I will answer the door (未经事先考虑的意图)
I hope it will be fine tomorrow (主观意愿)
The little boy is going to fall over(根据客观迹象来判断的)
③用现在进行时表将来
现在进行时表将来,往往是指计划好或准备好要做的事情。用于部分表示动作位移的的动词,如go come leave start begin move等的进行时表示马上要做某事。
Your mother is coming out soon 你的妈妈很快就出来。
They are leaving for Shanghai tomorrow.
④用一般现在时表将来
按照计划或时刻表要发生的事情
The new library opens next week.
The plane takes off at 3 p.m.
在时间状语从句中(when, before, after, as soon as, until/till等词引导)或条件状语从句(if unless等词引导)中用一般现在时表将来(主将从现)
I will tell her about it when she comes
We’ll start if it doesn‘t rain tomorrow.
⑤ be to do 结构表将来
此结构表示计划中约定的或按照职责 义务和要求必须要去做的事情或即将发生的动作
We are to meet the guests at the station.
I am to get married next year 我明年结婚
⑥ be about to do 结构表将来
表示马上,很快,即将发生的动作。一般不与具体时间状语连用。
The film is about to start. Be quiet
Hurry up. The train is about to leave.
4 现 在 进 行 时
(1)现在进行时的谓语构成及句式变化
谓语构成:由“助动词be(am/is/are) + 现在分词”构成
句式变化及回答:
否定形式是在be(am/is/are)后加not。
一般疑问句是把be(am/is/are)放到句首,第一人称变成第二人称。
如:They aren’t playing football.
---- Are they playing football ---- Yes, they are. (No they aren’t.)
(2)现在分词的变化规则
规则 动词原形 现在分词
一般情况直接加-ing find finding
不发音的-e结尾的,去-e再加-ing ride riding
重读闭音节结尾,且末尾只有一个辅音字母动词, 双写这个辅音字母再加-ing begin beginning
put puting
prefer preferring
少数以ie结尾的动词,变ie为y,再 加-ing die dying
lie lying
tie tying
以-oe -ee -ye结尾的动词,直接加-ing see seeing
(3)现在进行时的用法
①表示说话时正在进行的动作或状态。常见的时间状语有:now,right now,at this moment, at the moment at present等时间状语连用,或从上下文体现出来,或句首出现look, listen, be careful等词,引起人的注意,说明某一动作正在进行
It is snowing hard outside.
Look. Some children are playing basketball over there.
②表示先阶段正在进行的动作
指的是目前一段时间内在做的一件事,但说话时未必正在做。常用的时间状语为these days。
Alisa is writing a book about herself.
③表示将要发生的动作
表示按计划或安排将要发生的动作,此时常与表示将来的时间状语连用,主语通常时人.
They are getting mariied next month
表示马上发生的动作。仅用于动词,如go, come, drive, fly, travel, arrive, leave, start, visit, run, return,begin stop 等,表示马上就.....
Wait a minnute . I am coming
The car is stopping in a few seconds. 汽车几秒内会停下。
④表特定的情感
现在进行时和always, usually, all the time等连用时,表示一种经常、反复的动作,且说话人往往带有某种感彩(如赞扬、生气、厌烦、批评、惊讶、不满等)
She’s always helping others. 她总是乐于助人。(表示赞赏)
You are always talking in class. 你上课老是说话。(表示批评)
⑤ 不能用于进行时的动词
表示心理活动的动词一般不用进行时态,如love like hate know understand
realize remember bilieve want hope wish need agree等
I love you very much.
表示属性或拥有的动词不能用进行时态
此类词have own(拥有) belong to 等
The book belongs to Mary
表示表象 感官的连系动词不能用于进行时态。如seem appear look soud taste等。feel用于进行时态表一时的感觉。
I am not feeling well today 今天感觉不舒服
You seem a little tired. 你看上去有点累。
(d)表行为结果的动词一般不用于进行时
如accept receive allow decide promise 等
I accept you advice
5 过 去 进 行 过
(1)过去进行时的谓语构成及句式变化
谓语构成:由“助动词be的过去形式(was/were)+动词现在分词”。
句式变化及回答:
否定形式是在be(was/were)后加not。
一般疑问句是把be(was/were)放到句首,第一人称变成第二人称
He was not waiting for the bus at that time.
---- Was he waiting for the bus at that time
---- Yes, he was.(No he wasn’t)
(2)过去完成时的用法
①表示过去某一时刻正在发生或进行的动作
此时句中往往有表示过去的时间状语如then .at that moment .at at that time. at this time. this time yesterday等。没有时间状语时,需要根据上下文的语境体会。
I was writing a letter when you phoned.
They were watching TV at nine o’clock last night.
② 表示过去某一段时间内一直在做或持续进行的动作。
He was writing a book last year, but I don’t know if he has finished it
.He was watching TV between 8:00 and 9:00 on Sunday morning.
③在复合句中,若主要动作和背景动作是同时发生的,那么主从句都可用过去进行时
Mary was doing some reading while her younger brother was writing.
④ 表示过去将要发生的动作
即从过去某一时间看将要发生的动作,常表示‘渐渐 快要’的意思。常见的此类动词有come go start begin leave arrive get become turn 等,
He told me that he was leaving for Italy the next day
It was getting dark when we arrived.
⑤与现在进行时相似的使用,过去进行时也通常与 always, forever, continually等副词连用,表示满意、称赞、惊讶、厌恶等感彩。
She was always ringing me up when I was in London.(表示厌烦)
⑥表示礼貌
有时过去进行时并不表示过去的时间,而是表达现在的客气 礼貌或不确定等感情。此类动词主要有hope、
wonder think expect等
I was wondering if we could have dinner together不知是否能一块吃饭
I was hoping that you would help me 真希望你能帮我
(3)when和while的区别:
① 引导时间状语从句时,while 后的从句谓语接延续性动词;而when的从句谓语后既可以是延续性动词也可以是非延续性动词。
When you kocked the door, I was having a bath
It began to rain while we are walking in the park.
② while可以连接两个并列的句子,强调从句的谓语动作和主句的谓语动作同时发生。
While I’m doing my homework, my mother is preparing dinner.
③ when可作特殊疑问词,对时间进行提问;while 不能。
(4)过去进行时和一般过去时的用法比较
① 过去进行时往往表示动作的未完成,而一般过去时则往往表示动作已完成。
②过去进行时侧重说明动作持续时间的长度,而一般过去时侧重说明事实。
She was studying in Canada last year. I don’t know if she has returned
她去年在加拿大学习,不知道是否回来
She studied in Canada last year 她去年在加拿大学习过
6、现 在 完 成 时
(1)现在完成时的谓语构成即句式变化
谓语构成:助动词have/has + 过去分词
have, has可以缩写为’ve或‘s, have not 缩写haven’t, has not 缩写hasn’t
句式变化及回答:
否定形式是在have/has后加not。
一般疑问句是把have/has放到句首。第一人称变为第二人称如:
He has finished the work . // He hasn’t finished the work
//---- Has he finished the work ---- Yes, he has. (No, he hasn’t.)
规则 动词原形 动词过去分词
一般情况直接加-ed work worked
以不发音的-e结尾的,加-d liked liked
以辅音字母+y结尾的,变y为i,再加-ed carry carried
以重读闭音节结尾,且词尾只有一个辅音字母时,双向这个辅音字母后再加-ed stop stoped
drop dropped
regret regretted
不规则动词的过去分词详见不规则动词表
(2)动词过去分词的变化规则
(3)现在完成时的用法
①强调过去的动作对现在的影响
表示在说话前已经完成或刚完成的动作,但这个动作的结果对现在仍有影响。常与already, ever, never, just, yet, before 等词连用。
I have already finished all the work 我已经做完所有工作
He has just arrived in Hong Kong 刚到香港
【注意】already, ever, never, just, yet, before的用法辨析
already 意为“已经”
通常用于肯定句中,可放在be 动词 情态动词 助动词之后,实义动词之前,也可以放在句末。在变换句型时,常与yet 互换。
I have already finished the work.我已经完成这项工作了。
改为否定句:I haven’t finished the work yet.我还没有完成这项工作。
改为一般疑问句:Have you finished the work yet
yet 用在疑问句中意为“已经”,用在否定句中意为“还”,常放在句末。
— Have you watched the movie yet
— No. I haven’t watched it yet.
just 意为“刚刚”
表示行为刚刚过去,常放在助动词与过去分词之间。
My father has just finished his work.
ever 意为“曾经”用于疑问句或否定句中,放在助动词与过去分词之间。
Have you ever visited the Great Wall
never 意为“从来没有”多放在助动词与过去分词之间,常与 before 连用。
I have never been to such a beautiful place before.
before 意为“以前”
指过去不确定的某个时间,总是放在句末,不受句型的限制。
I haven’t been to Beijing before.
②表示过去的某一动作或行为一直持续道现在。(how long 提问)
这种用法表示动作发生在过去,但一直持续到现在,并且有可能持续下去。常与表示一段时间的状语连用。此时动词必须是延续性动词(否定句除外)。
如 all my life, all the time ,all day, up to now, so far,in the past /last years ,(ever)since last year,ever since,for a long time.
since + 过去时间点 / 过去时的从句, since + 一段时间 + ago, for + 一段时间
Helen has lived in New York since 2015.
My brother has learned about 500 English words since he was five years old.
They have waited for more than two hours
Jack has played basketball for three years ( since three years ago).
(3)非延续性动词(瞬间性动词)与延续性动词
延续性动词表示能够延续的动作,这种动作可以长时间延续下去或产生持久的影响,如live work等,可以与表示时间段的状语连用;
非延续性动词(瞬间性动词)动词表示不能延续的动作,动作一发生立即结束。如open, die, close, begin,后通常不能跟表示时间段的状语连用。若瞬间性动词要跟时间段,将其转化为延续性动词。
The movie has already begun for ten (错误)
The movie has already begun. (正确)
The movie has already been on for ten (正确)
【注意】 在否定句中非延续动词可与表示一段时间的状语连用。
I haven’t bought anything for one month.
I haven't left here for 3 years.
I haven't heard from him for 3 weeks.
(4)常见非延续性动词(瞬间性动词)与延续性动词的转化
非延续性动词 延续性动词 非延续性动词 延续性动词
arrive in/at / come to be in/at come back be back
begin(start) be on come here be here
borrow keep come to work work
become be die be dead
buy have dress be dressed
close be closed fall asleep be asleep
catch a cold have a cold fall ill be ill
非延续性动词 延续性动词 非延续性动词 延续性动词
finish be over join be in或be a member of
get up be up leave be away (from)
get married /marry be married open be open
go out /come out be out put on wear
go there be there return be back
get a cold have a cold reach be in/at
go back be back stop be over
get to sleep be asleep turn off be off
get/to to be in /at turn on be on
(4)现在完成时与一般过去时的区别
相同的点是两个时态都谈论过去已经发生的事情,但现在完成时表示的动作与现在有关系 ,或者对现在有影响,或谈论现在以前一段时间发生的事情。而一般过去时只是谈论过去的事情,与现在没有关系。
一般过去时表示过去某时发生的动作或单纯叙述过去的事情,强调动作;现在完成时为过去发生的,但强调过去的事情对现在的影响,强调的是影响。
I saw the film yesterday.(强调看的动作发生过了,不涉及现在)
I have seen the film. (强调对现在的影响,电影的内容已经知道了。)
(5)have/has been to, have/has gone to和have/has been in的区别:
have/has gone to+地点。意为“到某地去了”,说话时该人不在现场。一般只用第三人称作主语。
have/has been to+地点。意为“曾经去过某地”,含有“现在已离开那儿”之意,后可接次数(如once,twice,three times等)表示“去过某地几次”,也可和just,never,ever等连用。
have been in+地点。 表示“到某地多长时间了”,常与时间段连用。
Mary has gone to the library 玛丽去图书馆了(现在没回来)
Mary has been to Hong Hong twice 去过香港两次(现在已经回来了)
Mary have been in Canada for ten years 玛丽到加拿大十年了
7 过去将来时
过去将来时表示从过去的某段时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态。这种时态常用于主句是一般过去时的宾语从句中,表示从句的动作发生在主句之后。
过去将来时同一般将来时类似,除了用woud do表示外,还可以用was/were going to do,was/were to do, was/were about to do do及过去进行时(部分单词如come, go, start, move, leave等用过去进行时表将来)等方式表示。
在时间、条件状语从句中用一般过去时表示过去将来时。
Last week he promised that he would come,but he has’t ariived until now.
She was going to sell her old house and buy a new one.
He told me that he was leaving in one hour.
The meeting was to be held the next week
I was about to turn on the power of the computer when the electrity was cut off.
我正要打开电脑的时候断电了
They said they would let us know if they heard any news about him.
8 过去完成时
(1)过去完成时的谓语构成即句式变化
谓语构成:助动词had+ 过去分词。had not 缩写hadn’t
句式变化及回答:
否定形式是在had后加not。
They hadn’t finished the work when we got there.
一般疑问句是把had放到句首。第一人称变为第二人称如:
Had he told you to go there earlier yesterday 他昨天告诉过你早点儿到那儿吗
—Yes, he had. (No, he hadn’t.)
(2)过去完成时的用法
①表示过去某一时间或动作之前已经完成的动作
过去完成时的这种用法表示:过去的过去。这个过去的时刻常用by,before等介词短语或时间状语从句来表示,也可以用一个表示过去的动作或上下文来表示。
He had left before I arrived
I had just finished half the work by yesterday
He had had lunch when I came to his house
②表示从过去的某一个时间开始一直延续到过去另一个时间的动作或状态
He had worked in the factory for five years before he moved here.
By nine o'clock he had worked for ten hours.
③用来表示未曾实现的愿望或打算
动词hope ,wish ,plan, want ,mean,thought,expect等表示打算 计划 希望 认为等的动词用于过去完成时表示过去未曾实现的愿望 ,打算或意图。
I had hoped to be back last night,but I didn’t catch the train.
本希望昨晚回来,但没赶上火车
We had planned to go on a picnic yesterday,but it was raining.
本计划昨天去野餐,但一直下雨,
④ 固定句式中的过去完成时
在表示:一....就....的harldy/scarely...when...., no sooner...than...的句式中。
主句用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时。
We had no sooner arrived than we started singing and dancing.
我们一到就开始唱歌跳舞。
当hardly,scarely,no sooner放于居首时,句中要用部分倒装,
Scarely had Rosa heard the news when she burst into tears
Rosa 一听到消息就哭了(注意倒装)
(3)过去完成时的时间状语
by last week, by then, by the end of (last…) ,before that time,before that year,long
before (很久以前)或者由when, before等引出状语从句。如before I arrived,whe I airrived.
有时句子中会有already, just, once, ever, never等词语,也会有for… 或since…构成的时间状语。如:
The woman had left before he realized she was a thief.
He had already finished cleaning the room when his teacher came.
三 实战演练
1.(2023·江苏宿迁·统考中考真题)— My father and I ________ a lot of photos at the same place in the past ten years.
— Those photos must be your valuable memories.
A.have taken B.will take C.take D.were taking
A
2.(2023·辽宁抚顺·统考中考真题)Look! There ________ some information about traffic safety in this book.
A.is B.are C.was D.were
A
3.(2023·辽宁丹东·统考中考真题)— Where’s your brother, Bob
— Look! He ________ the car in the yard.
A.is cleaning B.cleaned C.cleans D.will clean
A
4.(2023·北京·统考中考真题)The Shenzhou-15 astronauts ________ to Earth safely on June 4, 2023.
A.return B.returned C.will return D.have returned
B
谢谢
21世纪教育网(www.21cnjy.com)
中小学教育资源网站
兼职招聘:
https://www.21cnjy.com/recruitment/home/admin
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
