新概念英语一册语法总复习课件 (共68张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 新概念英语一册语法总复习课件 (共68张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | ppt | ||
| 文件大小 | 790.0KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 新概念英语 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-01-01 09:14:55 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共68张PPT)
时态
一般现在时,现在进行时,一般过去时,现在完成时,一般将来时,过去进行时,过去完成时,过去将来时
1. 一般现在时
表示一般性,经常性的动作或一般性事实。
含有be动词的句子
He is a teacher.
The girl is very beautiful.
Tim and Jack are students.
★变疑问句将be动词移到句首
Is he a teacher
Is the girl very beautiful
Are Tim and Jack students
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, he is. No, he is not.
Yes, she is. No, she is not.
Yes, they are. No, they are not
★变否定句在be动词后面加not
He is not a teacher.
The girl is not very beautiful.
Tim and Jack are not students.
不含有动词的句子,即含有一般动词的句子
第三人称单数及单数名词
He likes books.
She likes him.
The dog likes bones.
★变疑问句在句首加does, 动词变为原型
Does he like books
Does she like him
Does the dog like bones
★变否定句在主语及动词之间加doesn’t, 动词变为原型
He doesn’t like books.
She doesn’t like him.
The dog doesn’t like bones.
★肯定回答及否定回答:
Yes, he does. No, he doesn’t.
Yes, she does. No, she doesn’t
Yes, it does. No, it doesn’t.
注意:第三人称单数形式一般在动词后面加S,不要和名词复数混淆,变否定句或疑问句时名词复数没有任何变化。
其他人称及复数名词
I want to have a bath.
We have some meat.
The students like smart teachers.
★变疑问句在句首加do
Do you want to have a bath ★肯定回答及否定回答
Do we have any meat
Do the students like smart teachers
★变否定句在主语和动词之间加don’t.
You don’t want to have a bath.
We don’t have any meat.
The students don’t like smart teachers.
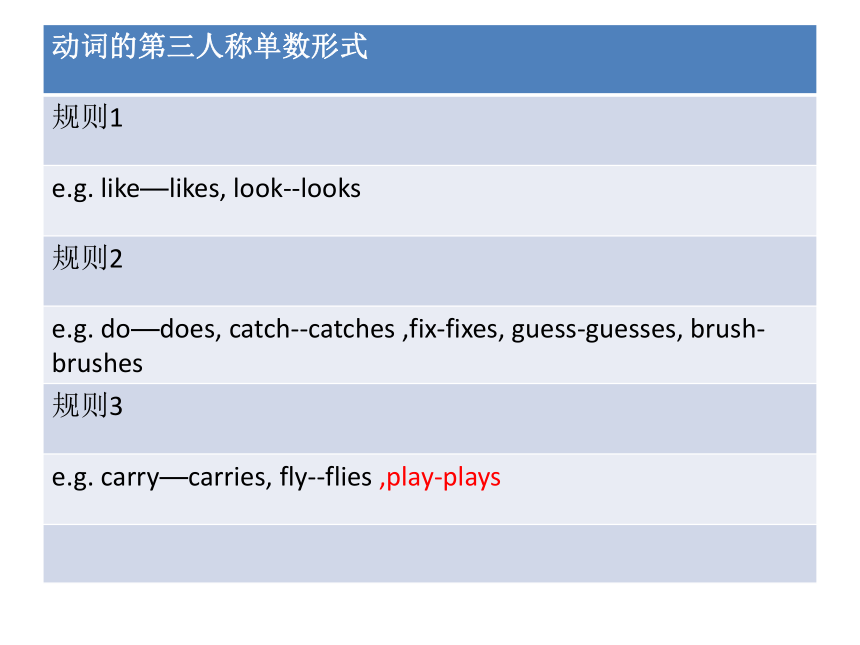
动词的第三人称单数形式
规则1
e.g. like—likes, look--looks
规则2
e.g. do—does, catch--catches ,fix-fixes, guess-guesses, brush-brushes
规则3
e.g. carry—carries, fly--flies ,play-plays
2. 现在进行时
表示现在正在进行的动作。
构成: 主语+be动词+动词的现在分词+其它成分
We are having lunch.
He is reading a book.
The dog is running after a cat.
The boys are swimming across the river.
动词现在分词
规则一
e.g. look—looking, read—reading, play—playing
规则二
e.g. make—making, take—taking, arrive—arriving
规则三
e. g. run—running, sit—sitting, get—getting, swim—swimming, stop--stopping
★变疑问句将be动词移到句首
Are we having lunch
Is he reading a book
Is the dog running after a cat
Are the boys swimming across the river
★变否定句在be动词后面加 not
We are not having lunch.
He is not reading a book.
The dog is not running after a cat.
The boys are swimming across the river.
★特殊疑问句:what, which, how, where, who, etc.
疑问词+动词+主语+现在分词
What are you doing
What is she doing
What is the dog doing
(必背)
没有进行时的动词
表示状态,思想,感情和感觉的动词不能表示正在进行的动作
1. 表示感觉,感官的词
see, hear, like, love, want,
2. have, has当”拥有”讲时没有进行时
3. 一般过去时
表示过去发生的动作或事件, 常和表示过去的时间状语连用,如yesterday, last night, the day before yesterday, 3 days ago,
含有be动词的句子, 将动词变为过去式,am, is的过去式为was,are的过去式为were
I was at the butcher’s.
You were a student a year ago.
The teacher was very beautiful ten years ago.
★变疑问句将be动词移动到句首
Were you at the butcher’s
Were you a student a year ago
Was the teacher very beautiful ten years ago
★变否定句在be动词后面加not
I was not at the butcher’s.
You were not a student a year ago.
The teacher was not very beautiful ten years ago.
★肯定回答否定回答
Yes, I was. No, I was not.
Yes, you were. No, you were not.
Yes, he/she was. No, he/she was not.
★特殊疑问句:
What did you do
(必背)
不含有be动词的句子,将动词变为过去式,
I finished my homework yesterday.
The boy went to a restaurant.
The Sawyers lived at King Streeta year ago.
King Streeta year ago.
动词过去式
规则动词变化
规则一
e.g. look—looked, watch—watched, play--played
规则二
e.g. make—maked, arrive--arrived
规则三
cry—cried, carry-carried
规则四
stop—stopped,
过去式的读音
在清辅音后面(除外)读/t/
在浊辅音和元音后读/d/
在/t/,/d/后读/id/
e.g. walked, jumped
e.g. washed, watched
e.g. waited, hated
★变疑问句在句首加did, 动词变为原型
Did you finish your homework yesterday
Did the boy go to a restaurant
Did the Sawyers live at King Streeta year ago
King Streeta year ago
★变否定句在主语和动词之间加did not
I did not finish my homework yesterday.
The boy did not go to a restaurant.
The Sawyers did not live at King Streeta year ago.
King Streeta year ago.
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, I did. No, I didn’t.
Yes, he did. No, he didn’t.
Yes, they did. No, they did not.
4. 现在完成时
构成:主语+助动词have, has+过去分词
用法:
1) 表示过去发生的和现在有某种联系的动作,常和just, usually, already, since等时间副词连用
I have just had lunch. (饱了,不用再吃了)
He has had a cup of tea.(不渴了,不用再喝)
They have already had their holiday. (不能再度假了)
The boy has already read the book. (已经知道书的内容了,不用再看了)
2) 表示开始于过去并持续到现在的动作
I have lived in Beijing for twenty years.
I have worked for this school for 1 year.
句型变化:
★变疑问句将助动词移到句首,变否定句在助动词后面加not.
e.g. Have you lost your pen I have not lost my pen.
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, I have. No, I have not.
★特殊疑问句:
What have you done
What has he done
一般过去时与现在完成时的区别:
凡是有明确的表示过去的时间状语的句子为过去时
注意:有些动词表示的动作有一个终点,不能再延续,因此不能和表示一段时间状语连用
错:I’ve left Beijing for 3 days.
对:I left Beijing 3 days ago. I have been away from being for 3 days.
5. 一般将来时
表示将来将要发生的动作, 经常和tomorrow, next year, the day after tomorrow, the year after the next, in five hours’ time, etc. 表示将来的词联用
结构: 主语+助动词will+动词原形
I will go to America tomorrow.
The pilot will fly to Japan the month after the next.
Jack will move into his new house tomorrow morning.
★变疑问句将助动词移到句首
Will you go to America tomorrow
Will the pilot fly to Japan the month after the next
Will Jack move into his new house tomorrow morning
★变否定句在助动词后面加not
I will not go to America tomorrow.
The pilot will not fly to Japan the month after the next.
Jack will not move into his new house tomorrow morning
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, I will. No, I will not.
Yes, he/she will. No, he/she will not.
Yes, he will. No, he will not.
★特殊疑问句:
What will you do
6. 过去完成时:
用法:在过去的时间里,两个动作中,发生在前的哪个动作要用过去完成时。
结构:had+过去分词
After she had finished her homework, she went shopping.
They had sold the car before I asked the price.
The train had left before I arrived at the station.
After/before引导的时间状语从句放在句首要在句子后面加逗号,如果放在主句后则不用加。
★ 变疑问句将助动词移到句首
Had she finished her homework
★ 变否定句在助动词后面加not
She hadn’t finished her homework.
★ 肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, she had. No, she hadn’t.
★ 特殊疑问句:
What had she done
7. 过去进行时
表示过去正在进行的动作,经常用在when, while, as引导的状语从句中。
结构:was/were+doing
When my husband was going into the dining room this morning, he dropped some coins on the floor.
While we were having dinner, my father was watching TV.
8. 过去将来时
结构:would do
She said she would go here the next morning.
句型
1. Be going to 结构
表示打算,准备,计划做某事
★结构:主语+be动词+going to +动词原型
I am going to make a bookcase.
They are going to paint it.
The father is going to give the bookcase to his daughter.
★变疑问句将be动词移到句首
Are you going to make a bookcase
Are they going to paint it
Is the father going to give the bookcase to his daughter
★变否定句在be动词后面加not
I am not going to make a bookcase.
They are going to paint it.
The father is not going to give the bookcase to his daughter.
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, I am. No, I am not.
Yes, they are. No, they are not.
Yes, he is. No, he is not.
★特殊疑问句
What are you going to do
What are they going to do
What is the father going to do
2. There be 句型
表示哪里有什么东西(某处有某物)
There is+单数名词+表示场所的词(一般为介词词组)
There is a book in this room.
There is a pen on the table
There are+复数名词+表示场所的词(一般为介词词组)
There are two pens on the table.
There are three schools there.
★变疑问句将be动词移到句首
Is there a book in this room
Are there two pens on the table
★变否定句在动词后面加not
There is not a book in this room.
There are not two pens on the table.
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, there is. No, there is not.
Yes, there are. No, there are not.
3. 问句:
一般疑问句,特殊疑问句,选择疑问句,反意疑问句,选择疑问句,否定疑问句
一般疑问句: 助动词/be动词+主语
Are you a teacher Do you want to have a cup of tea
特殊疑问句: 特殊疑问词+一般疑问句
What is your name
选择疑问句: or
Do you want beef or lamb
反意疑问句: 肯定陈述句+否定疑问部分, 否定陈述部分+肯定疑问部分
You don’t need that pen, do you
否定疑问句: 一般疑问句+否定词
Aren’t you lucky Don’t you want have a rest
4、感叹句
1. What + a / an + adj + n
What + adj + n
What + n (What a mess! / What a pity!)
2. How + adj + 主 + 谓
如:The dog is cute.
What a cute dog!
How cute the dog is!
5. 祈使句:
祈使句(第二人称)
祈使句表示请求,命令,建议,邀请等,谓语动词一律用原型,句子中通常不用主语,句末用惊叹好或者句号,用降调
★肯定句 动词原型
例, Come here, please.
Go downstairs, please.
Stand up.
Sit down.
Be quiet.
Be careful.
祈使句中如果有唤语,一定要用逗号隔开,放在句首或者句尾
Come in, Amy.
Sit down here, Tom.
Mary, give me a book please.
★否定:Don't+动词原型
Don't come here.
Don’t sit down.
Don’t stand up.
Don’t give me it.
let sb. do
Let me pass.
Let us have a rest.
Let’s have a rest.
(反意疑问):
Let’s have a walk along the river, shall we
Let us go out for a drink, will you
6. 倒装句:so/neither的倒装
eg.
He can swim. So can I.
I didn’t go to class. Neither did I.
结构:
so/neither+be+ 主语
so/neither+助动词+ 主语
so/neither+情态动词+ 主语
一般现在时, do, does/am, is, are
现在进行时, am, is, are
一般过去时, did
现在完成时, have, has
一般将来时, will, shall,
过去进行时,was, were
过去完成时,had
过去将来时, would
词类
代词及be动词 第一人称 第二人称 第三人称
单数 复数 单数 复数 单数
主格 I we you you she/he/it
宾格 me us you you her/him/it
形容词性物主代词 my our your your her/his/its
名词性物主代词 mine ours yours yours hers/his/its
be动词现在时 Am are are are is
be动词过去时 was were were were was
规则一 一般加-er
e.g. high—higher
规则二 以e结尾加-r
nice—nicer
规则三 以辅音字母加y结尾,变y为i再加-er
busy—busier,
规则四 重读闭音节结尾, 双写辅音字母再加-er
fat—fatter,
形容词和副词的比较级 和 最高级
规则一 一般加-est
e.g. high—highest
规则二 以结尾加-st
nice—nicest
规则三 以辅音字母加y结尾,变y为i再加-est
busy—busiest
规则四 重读闭音节结尾, 双写辅音字母再加--est
fat—fattest
一. 限定词:some, any, many, much
some, any 修饰可数名词或不可数名词,
some用于肯定句,any用于否定句和疑问句,
注意,当期待对方的答案为肯定回答时用some
“许多”
many修饰可数名词,much修饰不可数名词,在口语中表示很多一般不用many, much, 而用a lot of, 在否定句中表示很多用many, much.
I have a lot of money. I don’t have much money.
二. 名词:种类,复数,名词所有格
1.名词分为可数名词和不可数名词
不可数名词
无法分开的东西:water, tea, bread, milk, rice(米)
抽象的东西:love, beauty, coldness(寒冷)
不可数名词有以下特点:
不能用a, an修饰
不能加s
和单数be动词或动词搭配
可数名词:
单数可数名词要用冠词修饰,复数可数名词要在名词后面加s,名词复数共有以下几种变化:
规则1 一般情况+s
e.g. shell→shells book→books
规则2 以s, x, ch, sh结尾+es
e.g. fox→foxes church→churches, bus→buses, watch→watches
规则3 以o结尾+s或+es
e.g. potato→potatoes, Negro→Negroes, hero→heroes, tomato→tomatoes,(口诀:黑人英雄爱吃土豆和西红柿),剩下一般加s, radio→radios
规则4 以f, fe结尾的,变f, fe为ves
e.g. life→lives half→halves, shelf→shelves, city→cities, wife→wives
规则5 以辅音字母+y结尾, 变y为i+es
e.g. sky→skies fly→flies
不规则变化的名词复数形式
单数 man woman foot goose
复数 men women feet geese
单数 child sheep deer mouse
复数 children sheep deer mice
三.副词:用法及形容词变副词的变化
副词可以修饰形容词,动词,副词或整个句子。如:
The book is very good.
He runs fast.
She came here quite early.
Certainly I will go with you.
变化:
1. 直接在形容词后加-ly,
careful-carefully, slow-slowly,
2. 以辅音字母加y结尾的形容词,把y变I, 加-ly,
happy-happily, lucky-luckily
3. 有些词形容词和副词的形式相同,不需要做任何变化
fast, hard, late
4. 有些词加上-ly后意思与原词相差很远:
neary-nearly, high-highly, late-lately,
四. 情态动词的使用:can, must, may, might, need,
1.情态动词can(能够), must(必须), may(可以)
结构:主语+can/must/may+动词原型
He can make the tea.
Sally can air the room.
We can speak English.
★变疑问句将情态动词移到句首
Can he make the tea
Can Sally air the room
Can we speak English
★变否定句在情态动词后面加not
He cannot make the tea.
Sally cannot air the room.
We cannot speak English.
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, he can. No, he cannot.
Yes, she can. No, she cannot.
Yes, we can. No, we cannot.
★特殊疑问句:
What can you do
(必背)
注意:情态动词的句子没有第三人称单数的变化,不要在情态动词或动词后面加S。
2.Must/have to的区别
must 表示必须,是主观上觉得应该做,have to是不得不,是由于客观条件逼迫的必要要做
must 只能用在表示现在和将来的句子里,而have to do可以用在任何时态
3.must, may, might表示猜测:
must do 表示对现在事实的猜测
must have done表示对过去事实的猜测
must have been doing 表示对过去正在进行的事实的猜测
may/might do, may/might have done表示没有任何事实依据的猜测,might的可能性更小。
can’t/couldn’t 表示不可能
4.need 用法:
表示“需要”时为实意动词,后面可以加名词,也可以加不定式:
I need a pen. Do you need any beer No, I don’t.
I need to have a rest.
Need在否定时做情态动词使用
You needn’t go so early. =You don’t need to go so early.
Must I clean the desk right now No, you needn’t.
从句
一. 直接引语/间接引语
如果引语的主句所用动词为过去时,那么间接引语要做相应变化:时态,人称,时间地点及指示词
时态变化:
一般现在时——一般过去时
现在进行时——过去进行时
一般过去时——过去完成时
现在完成时——过去完成时
一般将来时——过去将来时
be going to——was/were going to/would
can----------------could
may---------------might
时间地点及指示词的变化:
here—there, tomorrow—the next day, the following day, this—that…
人称变化:一随主,二随宾,第三人称不更新
二、宾语从句
在句中作宾语,一般用that引导,但在口语中经常省略掉that。
可用在say,think,believe,hope,know,understand,suppose等动词之后;也可用在某些描写感情的形容词之后,如afraid,sure,sorry,glad等之后。
时态
1.如果主句是一般现在时 ,从句的时态可根
据实际情况而定
I know he lives here .
I know he lived here ten years ago .
I have heard that he will come tomorrow .
2.如果主句一般过去时,从句的时态一定要用过去的某种时态(包括一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时, 过去完成时)
I knew who lived here.
I saw she was talking with her mother.
He asked whether his father would come back
tomorrow.
He said that he had seen it .
3.当从句是客观真理,定义,公理,定理
时用一般现在时。
The teacher said that the earth goes
around the sun.
连词(引导词)
1.陈述句
that
2. 当宾语从句是一般疑问句时,由连词whether或if引导(口语中常用if),因为if/whether翻译成:“是否”,具有一定的意义,所以不能省略
Lily wanted to know if /whether her grandma
liked the handbag .
Let’s see if /whether he can eat all these burgers.
如果从句中含有or或or not时,只能
用whether而不用if
Could you tell me whether that’s a fast
train or not
Do you know whether he is right or not
I don’t care whether he’ll stay here or not .
3. 当宾语从句是特殊疑问句时,由连接代词(what, who, whom, which, whose)或连接副词(when, where, how, why)引导,因为连接代词
或连接副词在从句中担任一定的句子成分,具
有一定的意义,所以不可以省略
Do you know what he said just now
I don’t remember when we arrived .
I asked him where I could get so much money .
Please tell me who (whom) we have to see .
三、定语从句
修饰前面某一名词或代词的从句叫定语从句。
结构: 先行词 + 关系词 + 句子
关系代词who, that, whom引导的定语从句:
如果先行词是表示人的名词或代词,关系代词应用who, that (作主语或宾语)
whom (作宾语)
who / whom / that 作宾语:( 可省略)
The man is a famous writer.
He described the man just now.
The man ( who/ whom/ that ) he described just now is a famous writer. (作宾语)
The boy who(m) I ‘m looking for is my friend.
The thief has been sent to prison.
The police caught the thief last night.
The thief whom the police caught last night has been sent to prison.
关系代词that, which引导的定语从句:
如果先行词是表示物的名词或代词,关系代词应用that、which. (作主语或宾语)
which / that 作宾语 : (可省略)
This is the card.
I’ve just received the card.
This is the card which / that I’ve just received.
Practise:
This is the mistake which /that I always make.
I still keep the letters which she wrote to me.
I lost the pen which my father bought me.
( )
(作宾语)
特殊情况
关系词只能用that的情况
序数词修饰先行词
最高级修饰先行词
That is the most interesting book that I have ever read.
不定代词做先行词
当先行词是 all, any, few, little, none,
anything, everything, nothing , everybody,
nobody, everyone, no one 或被它们修饰时。
That’s all that I know.
Is there anything that I can do for you
He answered few questions that the teacher asked.
先行词被强调
当先行词有the very, the only, the same等修饰时。
That’s the only thing that I can do now.
These are the very words that he used.
He is looking at the children and the bags that his daughter brought here.
先行词既是人又是物
Who is the girl that spoke to you just now
Which is the pen that you lost
当主句是who或which 引导的特殊疑问句,而中心词指人或物时,关系代词只能用that.
关系词只能用which的情况
1有逗号,用which
2.介词后用which/whom
It will be sunny tomorrow.
We will have a trip tomorrow.
We will have a trip if it is sunny tomorrow.
If在此引导一个条件状语从句。当主句是一般将来时,if引导的从句必须用现在时来表示将来可能发生的动作或存在的状态。
If从句一般现在时,主句用may/might/can
If you feel better, you can get up.
If he sells that car, he can buy a new one.
If it stops raining , we can/may/might go out.
时态
一般现在时,现在进行时,一般过去时,现在完成时,一般将来时,过去进行时,过去完成时,过去将来时
1. 一般现在时
表示一般性,经常性的动作或一般性事实。
含有be动词的句子
He is a teacher.
The girl is very beautiful.
Tim and Jack are students.
★变疑问句将be动词移到句首
Is he a teacher
Is the girl very beautiful
Are Tim and Jack students
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, he is. No, he is not.
Yes, she is. No, she is not.
Yes, they are. No, they are not
★变否定句在be动词后面加not
He is not a teacher.
The girl is not very beautiful.
Tim and Jack are not students.
不含有动词的句子,即含有一般动词的句子
第三人称单数及单数名词
He likes books.
She likes him.
The dog likes bones.
★变疑问句在句首加does, 动词变为原型
Does he like books
Does she like him
Does the dog like bones
★变否定句在主语及动词之间加doesn’t, 动词变为原型
He doesn’t like books.
She doesn’t like him.
The dog doesn’t like bones.
★肯定回答及否定回答:
Yes, he does. No, he doesn’t.
Yes, she does. No, she doesn’t
Yes, it does. No, it doesn’t.
注意:第三人称单数形式一般在动词后面加S,不要和名词复数混淆,变否定句或疑问句时名词复数没有任何变化。
其他人称及复数名词
I want to have a bath.
We have some meat.
The students like smart teachers.
★变疑问句在句首加do
Do you want to have a bath ★肯定回答及否定回答
Do we have any meat
Do the students like smart teachers
★变否定句在主语和动词之间加don’t.
You don’t want to have a bath.
We don’t have any meat.
The students don’t like smart teachers.
动词的第三人称单数形式
规则1
e.g. like—likes, look--looks
规则2
e.g. do—does, catch--catches ,fix-fixes, guess-guesses, brush-brushes
规则3
e.g. carry—carries, fly--flies ,play-plays
2. 现在进行时
表示现在正在进行的动作。
构成: 主语+be动词+动词的现在分词+其它成分
We are having lunch.
He is reading a book.
The dog is running after a cat.
The boys are swimming across the river.
动词现在分词
规则一
e.g. look—looking, read—reading, play—playing
规则二
e.g. make—making, take—taking, arrive—arriving
规则三
e. g. run—running, sit—sitting, get—getting, swim—swimming, stop--stopping
★变疑问句将be动词移到句首
Are we having lunch
Is he reading a book
Is the dog running after a cat
Are the boys swimming across the river
★变否定句在be动词后面加 not
We are not having lunch.
He is not reading a book.
The dog is not running after a cat.
The boys are swimming across the river.
★特殊疑问句:what, which, how, where, who, etc.
疑问词+动词+主语+现在分词
What are you doing
What is she doing
What is the dog doing
(必背)
没有进行时的动词
表示状态,思想,感情和感觉的动词不能表示正在进行的动作
1. 表示感觉,感官的词
see, hear, like, love, want,
2. have, has当”拥有”讲时没有进行时
3. 一般过去时
表示过去发生的动作或事件, 常和表示过去的时间状语连用,如yesterday, last night, the day before yesterday, 3 days ago,
含有be动词的句子, 将动词变为过去式,am, is的过去式为was,are的过去式为were
I was at the butcher’s.
You were a student a year ago.
The teacher was very beautiful ten years ago.
★变疑问句将be动词移动到句首
Were you at the butcher’s
Were you a student a year ago
Was the teacher very beautiful ten years ago
★变否定句在be动词后面加not
I was not at the butcher’s.
You were not a student a year ago.
The teacher was not very beautiful ten years ago.
★肯定回答否定回答
Yes, I was. No, I was not.
Yes, you were. No, you were not.
Yes, he/she was. No, he/she was not.
★特殊疑问句:
What did you do
(必背)
不含有be动词的句子,将动词变为过去式,
I finished my homework yesterday.
The boy went to a restaurant.
The Sawyers lived at King Streeta year ago.
King Streeta year ago.
动词过去式
规则动词变化
规则一
e.g. look—looked, watch—watched, play--played
规则二
e.g. make—maked, arrive--arrived
规则三
cry—cried, carry-carried
规则四
stop—stopped,
过去式的读音
在清辅音后面(除外)读/t/
在浊辅音和元音后读/d/
在/t/,/d/后读/id/
e.g. walked, jumped
e.g. washed, watched
e.g. waited, hated
★变疑问句在句首加did, 动词变为原型
Did you finish your homework yesterday
Did the boy go to a restaurant
Did the Sawyers live at King Streeta year ago
King Streeta year ago
★变否定句在主语和动词之间加did not
I did not finish my homework yesterday.
The boy did not go to a restaurant.
The Sawyers did not live at King Streeta year ago.
King Streeta year ago.
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, I did. No, I didn’t.
Yes, he did. No, he didn’t.
Yes, they did. No, they did not.
4. 现在完成时
构成:主语+助动词have, has+过去分词
用法:
1) 表示过去发生的和现在有某种联系的动作,常和just, usually, already, since等时间副词连用
I have just had lunch. (饱了,不用再吃了)
He has had a cup of tea.(不渴了,不用再喝)
They have already had their holiday. (不能再度假了)
The boy has already read the book. (已经知道书的内容了,不用再看了)
2) 表示开始于过去并持续到现在的动作
I have lived in Beijing for twenty years.
I have worked for this school for 1 year.
句型变化:
★变疑问句将助动词移到句首,变否定句在助动词后面加not.
e.g. Have you lost your pen I have not lost my pen.
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, I have. No, I have not.
★特殊疑问句:
What have you done
What has he done
一般过去时与现在完成时的区别:
凡是有明确的表示过去的时间状语的句子为过去时
注意:有些动词表示的动作有一个终点,不能再延续,因此不能和表示一段时间状语连用
错:I’ve left Beijing for 3 days.
对:I left Beijing 3 days ago. I have been away from being for 3 days.
5. 一般将来时
表示将来将要发生的动作, 经常和tomorrow, next year, the day after tomorrow, the year after the next, in five hours’ time, etc. 表示将来的词联用
结构: 主语+助动词will+动词原形
I will go to America tomorrow.
The pilot will fly to Japan the month after the next.
Jack will move into his new house tomorrow morning.
★变疑问句将助动词移到句首
Will you go to America tomorrow
Will the pilot fly to Japan the month after the next
Will Jack move into his new house tomorrow morning
★变否定句在助动词后面加not
I will not go to America tomorrow.
The pilot will not fly to Japan the month after the next.
Jack will not move into his new house tomorrow morning
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, I will. No, I will not.
Yes, he/she will. No, he/she will not.
Yes, he will. No, he will not.
★特殊疑问句:
What will you do
6. 过去完成时:
用法:在过去的时间里,两个动作中,发生在前的哪个动作要用过去完成时。
结构:had+过去分词
After she had finished her homework, she went shopping.
They had sold the car before I asked the price.
The train had left before I arrived at the station.
After/before引导的时间状语从句放在句首要在句子后面加逗号,如果放在主句后则不用加。
★ 变疑问句将助动词移到句首
Had she finished her homework
★ 变否定句在助动词后面加not
She hadn’t finished her homework.
★ 肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, she had. No, she hadn’t.
★ 特殊疑问句:
What had she done
7. 过去进行时
表示过去正在进行的动作,经常用在when, while, as引导的状语从句中。
结构:was/were+doing
When my husband was going into the dining room this morning, he dropped some coins on the floor.
While we were having dinner, my father was watching TV.
8. 过去将来时
结构:would do
She said she would go here the next morning.
句型
1. Be going to 结构
表示打算,准备,计划做某事
★结构:主语+be动词+going to +动词原型
I am going to make a bookcase.
They are going to paint it.
The father is going to give the bookcase to his daughter.
★变疑问句将be动词移到句首
Are you going to make a bookcase
Are they going to paint it
Is the father going to give the bookcase to his daughter
★变否定句在be动词后面加not
I am not going to make a bookcase.
They are going to paint it.
The father is not going to give the bookcase to his daughter.
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, I am. No, I am not.
Yes, they are. No, they are not.
Yes, he is. No, he is not.
★特殊疑问句
What are you going to do
What are they going to do
What is the father going to do
2. There be 句型
表示哪里有什么东西(某处有某物)
There is+单数名词+表示场所的词(一般为介词词组)
There is a book in this room.
There is a pen on the table
There are+复数名词+表示场所的词(一般为介词词组)
There are two pens on the table.
There are three schools there.
★变疑问句将be动词移到句首
Is there a book in this room
Are there two pens on the table
★变否定句在动词后面加not
There is not a book in this room.
There are not two pens on the table.
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, there is. No, there is not.
Yes, there are. No, there are not.
3. 问句:
一般疑问句,特殊疑问句,选择疑问句,反意疑问句,选择疑问句,否定疑问句
一般疑问句: 助动词/be动词+主语
Are you a teacher Do you want to have a cup of tea
特殊疑问句: 特殊疑问词+一般疑问句
What is your name
选择疑问句: or
Do you want beef or lamb
反意疑问句: 肯定陈述句+否定疑问部分, 否定陈述部分+肯定疑问部分
You don’t need that pen, do you
否定疑问句: 一般疑问句+否定词
Aren’t you lucky Don’t you want have a rest
4、感叹句
1. What + a / an + adj + n
What + adj + n
What + n (What a mess! / What a pity!)
2. How + adj + 主 + 谓
如:The dog is cute.
What a cute dog!
How cute the dog is!
5. 祈使句:
祈使句(第二人称)
祈使句表示请求,命令,建议,邀请等,谓语动词一律用原型,句子中通常不用主语,句末用惊叹好或者句号,用降调
★肯定句 动词原型
例, Come here, please.
Go downstairs, please.
Stand up.
Sit down.
Be quiet.
Be careful.
祈使句中如果有唤语,一定要用逗号隔开,放在句首或者句尾
Come in, Amy.
Sit down here, Tom.
Mary, give me a book please.
★否定:Don't+动词原型
Don't come here.
Don’t sit down.
Don’t stand up.
Don’t give me it.
let sb. do
Let me pass.
Let us have a rest.
Let’s have a rest.
(反意疑问):
Let’s have a walk along the river, shall we
Let us go out for a drink, will you
6. 倒装句:so/neither的倒装
eg.
He can swim. So can I.
I didn’t go to class. Neither did I.
结构:
so/neither+be+ 主语
so/neither+助动词+ 主语
so/neither+情态动词+ 主语
一般现在时, do, does/am, is, are
现在进行时, am, is, are
一般过去时, did
现在完成时, have, has
一般将来时, will, shall,
过去进行时,was, were
过去完成时,had
过去将来时, would
词类
代词及be动词 第一人称 第二人称 第三人称
单数 复数 单数 复数 单数
主格 I we you you she/he/it
宾格 me us you you her/him/it
形容词性物主代词 my our your your her/his/its
名词性物主代词 mine ours yours yours hers/his/its
be动词现在时 Am are are are is
be动词过去时 was were were were was
规则一 一般加-er
e.g. high—higher
规则二 以e结尾加-r
nice—nicer
规则三 以辅音字母加y结尾,变y为i再加-er
busy—busier,
规则四 重读闭音节结尾, 双写辅音字母再加-er
fat—fatter,
形容词和副词的比较级 和 最高级
规则一 一般加-est
e.g. high—highest
规则二 以结尾加-st
nice—nicest
规则三 以辅音字母加y结尾,变y为i再加-est
busy—busiest
规则四 重读闭音节结尾, 双写辅音字母再加--est
fat—fattest
一. 限定词:some, any, many, much
some, any 修饰可数名词或不可数名词,
some用于肯定句,any用于否定句和疑问句,
注意,当期待对方的答案为肯定回答时用some
“许多”
many修饰可数名词,much修饰不可数名词,在口语中表示很多一般不用many, much, 而用a lot of, 在否定句中表示很多用many, much.
I have a lot of money. I don’t have much money.
二. 名词:种类,复数,名词所有格
1.名词分为可数名词和不可数名词
不可数名词
无法分开的东西:water, tea, bread, milk, rice(米)
抽象的东西:love, beauty, coldness(寒冷)
不可数名词有以下特点:
不能用a, an修饰
不能加s
和单数be动词或动词搭配
可数名词:
单数可数名词要用冠词修饰,复数可数名词要在名词后面加s,名词复数共有以下几种变化:
规则1 一般情况+s
e.g. shell→shells book→books
规则2 以s, x, ch, sh结尾+es
e.g. fox→foxes church→churches, bus→buses, watch→watches
规则3 以o结尾+s或+es
e.g. potato→potatoes, Negro→Negroes, hero→heroes, tomato→tomatoes,(口诀:黑人英雄爱吃土豆和西红柿),剩下一般加s, radio→radios
规则4 以f, fe结尾的,变f, fe为ves
e.g. life→lives half→halves, shelf→shelves, city→cities, wife→wives
规则5 以辅音字母+y结尾, 变y为i+es
e.g. sky→skies fly→flies
不规则变化的名词复数形式
单数 man woman foot goose
复数 men women feet geese
单数 child sheep deer mouse
复数 children sheep deer mice
三.副词:用法及形容词变副词的变化
副词可以修饰形容词,动词,副词或整个句子。如:
The book is very good.
He runs fast.
She came here quite early.
Certainly I will go with you.
变化:
1. 直接在形容词后加-ly,
careful-carefully, slow-slowly,
2. 以辅音字母加y结尾的形容词,把y变I, 加-ly,
happy-happily, lucky-luckily
3. 有些词形容词和副词的形式相同,不需要做任何变化
fast, hard, late
4. 有些词加上-ly后意思与原词相差很远:
neary-nearly, high-highly, late-lately,
四. 情态动词的使用:can, must, may, might, need,
1.情态动词can(能够), must(必须), may(可以)
结构:主语+can/must/may+动词原型
He can make the tea.
Sally can air the room.
We can speak English.
★变疑问句将情态动词移到句首
Can he make the tea
Can Sally air the room
Can we speak English
★变否定句在情态动词后面加not
He cannot make the tea.
Sally cannot air the room.
We cannot speak English.
★肯定回答及否定回答
Yes, he can. No, he cannot.
Yes, she can. No, she cannot.
Yes, we can. No, we cannot.
★特殊疑问句:
What can you do
(必背)
注意:情态动词的句子没有第三人称单数的变化,不要在情态动词或动词后面加S。
2.Must/have to的区别
must 表示必须,是主观上觉得应该做,have to是不得不,是由于客观条件逼迫的必要要做
must 只能用在表示现在和将来的句子里,而have to do可以用在任何时态
3.must, may, might表示猜测:
must do 表示对现在事实的猜测
must have done表示对过去事实的猜测
must have been doing 表示对过去正在进行的事实的猜测
may/might do, may/might have done表示没有任何事实依据的猜测,might的可能性更小。
can’t/couldn’t 表示不可能
4.need 用法:
表示“需要”时为实意动词,后面可以加名词,也可以加不定式:
I need a pen. Do you need any beer No, I don’t.
I need to have a rest.
Need在否定时做情态动词使用
You needn’t go so early. =You don’t need to go so early.
Must I clean the desk right now No, you needn’t.
从句
一. 直接引语/间接引语
如果引语的主句所用动词为过去时,那么间接引语要做相应变化:时态,人称,时间地点及指示词
时态变化:
一般现在时——一般过去时
现在进行时——过去进行时
一般过去时——过去完成时
现在完成时——过去完成时
一般将来时——过去将来时
be going to——was/were going to/would
can----------------could
may---------------might
时间地点及指示词的变化:
here—there, tomorrow—the next day, the following day, this—that…
人称变化:一随主,二随宾,第三人称不更新
二、宾语从句
在句中作宾语,一般用that引导,但在口语中经常省略掉that。
可用在say,think,believe,hope,know,understand,suppose等动词之后;也可用在某些描写感情的形容词之后,如afraid,sure,sorry,glad等之后。
时态
1.如果主句是一般现在时 ,从句的时态可根
据实际情况而定
I know he lives here .
I know he lived here ten years ago .
I have heard that he will come tomorrow .
2.如果主句一般过去时,从句的时态一定要用过去的某种时态(包括一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时, 过去完成时)
I knew who lived here.
I saw she was talking with her mother.
He asked whether his father would come back
tomorrow.
He said that he had seen it .
3.当从句是客观真理,定义,公理,定理
时用一般现在时。
The teacher said that the earth goes
around the sun.
连词(引导词)
1.陈述句
that
2. 当宾语从句是一般疑问句时,由连词whether或if引导(口语中常用if),因为if/whether翻译成:“是否”,具有一定的意义,所以不能省略
Lily wanted to know if /whether her grandma
liked the handbag .
Let’s see if /whether he can eat all these burgers.
如果从句中含有or或or not时,只能
用whether而不用if
Could you tell me whether that’s a fast
train or not
Do you know whether he is right or not
I don’t care whether he’ll stay here or not .
3. 当宾语从句是特殊疑问句时,由连接代词(what, who, whom, which, whose)或连接副词(when, where, how, why)引导,因为连接代词
或连接副词在从句中担任一定的句子成分,具
有一定的意义,所以不可以省略
Do you know what he said just now
I don’t remember when we arrived .
I asked him where I could get so much money .
Please tell me who (whom) we have to see .
三、定语从句
修饰前面某一名词或代词的从句叫定语从句。
结构: 先行词 + 关系词 + 句子
关系代词who, that, whom引导的定语从句:
如果先行词是表示人的名词或代词,关系代词应用who, that (作主语或宾语)
whom (作宾语)
who / whom / that 作宾语:( 可省略)
The man is a famous writer.
He described the man just now.
The man ( who/ whom/ that ) he described just now is a famous writer. (作宾语)
The boy who(m) I ‘m looking for is my friend.
The thief has been sent to prison.
The police caught the thief last night.
The thief whom the police caught last night has been sent to prison.
关系代词that, which引导的定语从句:
如果先行词是表示物的名词或代词,关系代词应用that、which. (作主语或宾语)
which / that 作宾语 : (可省略)
This is the card.
I’ve just received the card.
This is the card which / that I’ve just received.
Practise:
This is the mistake which /that I always make.
I still keep the letters which she wrote to me.
I lost the pen which my father bought me.
( )
(作宾语)
特殊情况
关系词只能用that的情况
序数词修饰先行词
最高级修饰先行词
That is the most interesting book that I have ever read.
不定代词做先行词
当先行词是 all, any, few, little, none,
anything, everything, nothing , everybody,
nobody, everyone, no one 或被它们修饰时。
That’s all that I know.
Is there anything that I can do for you
He answered few questions that the teacher asked.
先行词被强调
当先行词有the very, the only, the same等修饰时。
That’s the only thing that I can do now.
These are the very words that he used.
He is looking at the children and the bags that his daughter brought here.
先行词既是人又是物
Who is the girl that spoke to you just now
Which is the pen that you lost
当主句是who或which 引导的特殊疑问句,而中心词指人或物时,关系代词只能用that.
关系词只能用which的情况
1有逗号,用which
2.介词后用which/whom
It will be sunny tomorrow.
We will have a trip tomorrow.
We will have a trip if it is sunny tomorrow.
If在此引导一个条件状语从句。当主句是一般将来时,if引导的从句必须用现在时来表示将来可能发生的动作或存在的状态。
If从句一般现在时,主句用may/might/can
If you feel better, you can get up.
If he sells that car, he can buy a new one.
If it stops raining , we can/may/might go out.
同课章节目录
