外研版(三起)英语六年级下册 期末语法总结(知识清单)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版(三起)英语六年级下册 期末语法总结(知识清单) |  | |
| 格式 | docx | ||
| 文件大小 | 83.4KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(三年级起点) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-01-04 11:46:01 | ||
图片预览


文档简介
中小学教育资源及组卷应用平台
2024外研社小学英语总复习-语法总结
名词有可数名词和不可数名词之分。可数名词可用数字来计算,有单、复数形式,不可数名词不能用数字来计算,没有复数形式。
一、可数名词单数变复数规则
1.一般情况,直接在名词后加-s,如:book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats
2.以s. x. sh. ch结尾的词,在词尾加-es,
如:bus-buses, box-boxes, watch-watches
3.以“辅音字母+y”结尾得词,变y为i, 再加-es,
如:family-families, baby-babies
4.以“f或fe”结尾,变f或fe为v, 再加-es,
如:knife-knives,wife-wives
5.不规则名词复数:
man-men, woman-women, policeman-policemen, policewoman-policewomen, mouse-mice,child-children, foot-feet, tooth-teeth, fish-fish, sheep-sheep people-people, Chinese-Chinese, Japanese-Japanese
1. at
(1)表示时间概念的某一个点。(在具体的某一时刻和时段等)。
at night at 6:00
(2)表示在某一具体地点(小地点)。如at the bus stop , at home
2. on
(1) 在······上面(表面接触;长在上面)。如on the chair, on the tree
(2)在某天的上午、下午或晚上。如:on Monday, on Tuesday morning
3.in
(1)在······里面。如:in the box
(2)在一段时间里。如:in the morning
(3)在某一年份、季节、月份。如:in 2014,in October, in summer
(4)在······上(外来)如:There is a cat in the tree.
4.after
(1)在······之后(时间)。如:I often play football at school.
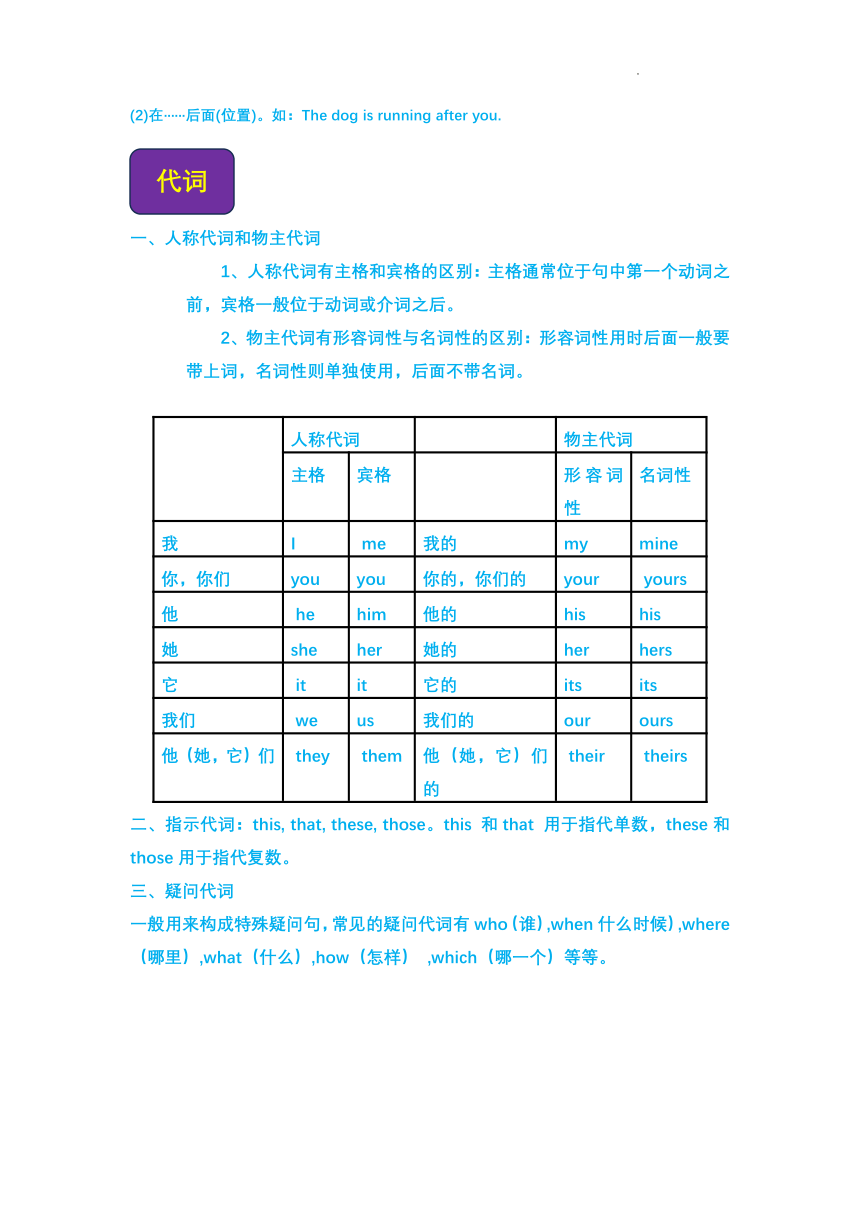
(2)在······后面(位置)。如:The dog is running after you.
一、人称代词和物主代词
人称代词有主格和宾格的区别:主格通常位于句中第一个动词之前,宾格一般位于动词或介词之后。
2、物主代词有形容词性与名词性的区别:形容词性用时后面一般要带上词,名词性则单独使用,后面不带名词。
人称代词 物主代词
主格 宾格 形容词性 名词性
我 I me 我的 my mine
你,你们 you you 你的,你们的 your yours
他 he him 他的 his his
她 she her 她的 her hers
它 it it 它的 its its
我们 we us 我们的 our ours
他(她,它)们 they them 他(她,它)们的 their theirs
二、指示代词:this, that, these, those。this 和that 用于指代单数,these和 those用于指代复数。
三、疑问代词
一般用来构成特殊疑问句,常见的疑问代词有who(谁),when什么时候),where(哪里),what(什么),how(怎样) ,which(哪一个)等等。
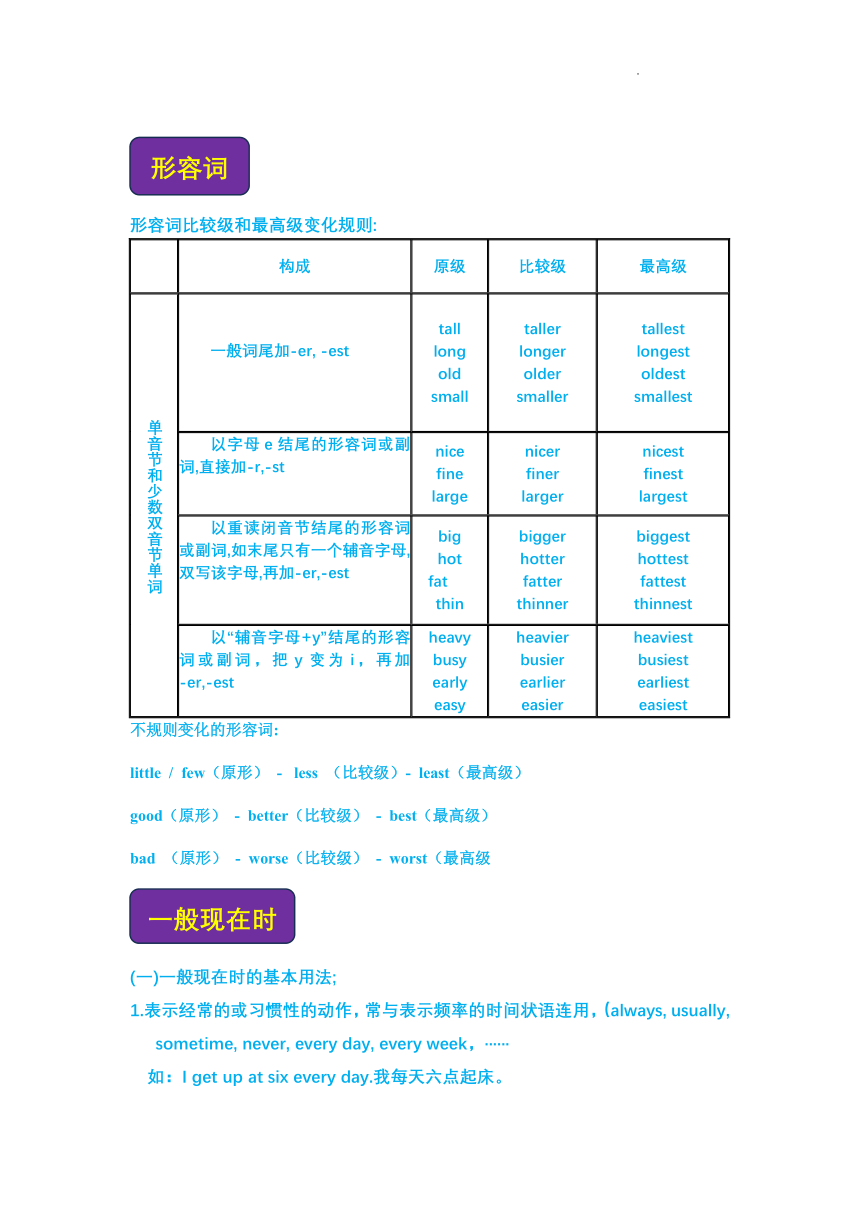
形容词比较级和最高级变化规则:
构成 原级 比较级 最高级
单音节和少数双音节单词 一般词尾加-er, -est tall long old small taller longer older smaller tallest longest oldest smallest
以字母e结尾的形容词或副词,直接加-r,-st nice fine large nicer finer larger nicest finest largest
以重读闭音节结尾的形容词或副词,如末尾只有一个辅音字母,双写该字母,再加-er,-est big hot fat thin bigger hotter fatter thinner biggest hottest fattest thinnest
以“辅音字母+y”结尾的形容词或副词,把y变为i,再加-er,-est heavy busy early easy heavier busier earlier easier heaviest busiest earliest easiest
不规则变化的形容词:
little / few(原形) - less (比较级)- least(最高级)
good(原形) - better(比较级) - best(最高级)
bad (原形) - worse(比较级) - worst(最高级
(一)一般现在时的基本用法;
1.表示经常的或习惯性的动作,常与表示频率的时间状语连用,(always, usually, sometime, never, every day, every week,······
如:I get up at six every day.我每天六点起床。
2.表示客观现实和普遍的真理。如:The earth moves around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。
3.表示主语的特征、能力、职业、性格。
如:The sky is blue.天空是蓝色的。My mother is a teacher .我妈妈是位老师。
(二)一般现在时的构成:
1. be动词:
①肯定句:主语+be(am, is, are)+其它。如: I am a boy. 我是一个男孩。
②否定句:主语+ be + not +其它。 如:He is not a worker.他不是工人。
③一般疑问句:Be +主语+其它。 如:-Are you a student -Yes. I am. / No, I'm not.
2. 行为动词:
①肯定句:主语+行为动词(+其它)。
(当主语为第三人称单数(he, she, it)时,要在动词后加"-s"或"-es"。如:Mary likes Chinese.玛丽喜欢汉语)
②否定句:主语+ don't( doesn't ) +动词原形(+其它)。
(当主语为第三人称单数时,要用doesn't构成否定句。
③一般疑问句:Do( Does ) +主语+动词原形+其它。
(三)一般现在时动词第三人称单数形式变化规则:
1.一般情况下,直接加-s,如:look-looks, play--plays
2.以s. x. sh. ch. o结尾,加-es,
如: wash-washes, watch-watches, go-goes
3.以“辅音字母+y”结尾,变y为i, 再加-es,如:study-studies, fly--flies【注意】have—has
现在进行时
现在进行时表示现在正在进行或发生的动作,也可表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作。
现在进行时由be+动词ing构成
①肯定句 基本结构:主语+be+ 动词ing.
②否定句 基本结构:主语+be not + 动词ing.
③一般疑问句 基本结构: be动词 +主语 +动词ing
④特殊疑问句 基本结构:疑问词+ be +主语+动词ing
【注意】疑问词当主语时,结构为:疑问词+ be + 动词ing
如:Who is watching TV
动词加ing(动词现在分词)的变化规则
动词现在分词构成:动词原形+ing,规则如下:
① 直接加ing
think-thinking sleep-sleeping
②以不发音的字母e结尾的单词,去掉字母e,再加ing
come-coming make-making
③ 以重读闭音节(重读闭音节即两个辅音中间夹一个元音并且重读的音节)结尾,先双写末尾的辅音字母,再加ing
stop-stopping sit-sitting
一般将来时
表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,也可以表示打算、计划或准备做某事。
常与一般将来时连用的时间状语有:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon, the day after tomorrow(后天)等。
一般将来时的用法和结构;
⑴肯定句:
①主语+will+ 动词原形+其它.
②主语+be going to + 动词原形+其它 be going to = will
e.g. I will go to the park tomorrow. = I am going to go to the park tomorrow.
⑵否定句:
在be动词(am, is, are)后加not,情态动词will后加not(will not=won’t)。e.g. I will have a picnic this afternoon.→ I won’t going to have a picnic this afternoon.
⑶一般疑问句:
把be或will提到句首,some改为any, and改为or,第一二人称互换。
e.g. I will go to the park tomorrow. -Will you go to the park tomorrow
特殊疑问句
1、问人疑问词为(Who)
e.g. I’m going to New York soon. →Who’s going to New York soon.
2. 问某人要去干什么疑问词为(What).
e.g. My father is going to watch TV this afternoon. →What is your father going to do this afternoon
3. 问某人去哪里疑问词为(where)
He’s going to have a picnic in the park.
- Where is he going to have a picnic
4.问某人什么时候去疑问词为(when)
e.g. She’s going to go to bed at nine. →When is she going to bed
一般过去式
一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示过去经常或反复发生的动作。
常用的表示过去的时间状语有:yesterday, last year /month/week/night, just now, ago.
一般过去时的句型结构;
⑴谓语动词为be动词的句型结构
肯定句:主语+be动词过去式+其它
②否定句:主语+be动词过去式+not+其它 如:
③be动词过去式+主语+其它
⑵一般过去时be动词的变化:
①am 和is在一般过去时中变为was。(was not=wasn’t)
②are在一般过去时中变为were。(were not=weren’t)
③带有was或were的句子,其否定、疑问的变化和is, am, are一样,即否定句在was或were后加not,一般疑问句把was或were调到句首。
⑵谓语动词是实义动词的句型结构
①肯定句:主语+动词过去式+其它 如: Jim went home yesterday.
②否定句:主语+didn’t +动词原形? 如:Jim didn’t go home yesterday.
③一般疑问句: Did+主语+动词原形? 如:Did Jim go home yesterday
④ 特殊疑问句:疑问词+did+主语+动词原形?
如: What did Jim do yesterday
当疑问词做主语时:疑问词+动词过去式?如:Who went home yesterday
动词过去式变化规则:
1.一般在动词末尾加-ed,如:play—played, cook-cooked
2.结尾是e加d,如:like—liked
3.以重读闭音节结尾,先双写末尾的辅音字母,在加-ed,如:stop-stopped
4.以“辅音字母+y”结尾的,变y为i, 再加-ed,如:study-studied
5.不规则动词过去式:
am, is-was, are-were, do-did, see-saw, say-said, give-gave, get-got, go-went, come-came, have-had, eat-ate, take-took, run-ran, sing-sang, put-put, make-made, read-read, write-wrote, draw-drew, drink-drank, fly-flew, ride-rode, speak-spoke, sweep-swept, swim-swam, sit-sat
1、There be 句型表示:在某地有某物(或人)
2、在there be 句型中,主语是单数,be 动词用is ; 主语是复数,be 动词用are ; 如有几件物品,be 动词根据最近be 动词的那个名词决定(就近原则0。
3、there be 句型的否定句在be 动词后加not , 一般疑问句把be 动词调到句首。
4、there be句型与have(has) 的区别:there be 表示在某地有某物(或人);have(has) 表示某人拥有某物。
5、some 和any 在there be 句型中的运用:some 用于肯定句, any 用于否定句或疑问句。
6、and 和or 在there be句型中的运用:and 用于肯定句, or 用于否定句或疑问句。
7、针对数量提问的特殊疑问句的基本结构是:
How many + 名词复数 + are there + 介词短语?
How much + 不可数名词 + is there + 介词短语?
学科(北京)股份有限公司
2024外研社小学英语总复习-语法总结
名词有可数名词和不可数名词之分。可数名词可用数字来计算,有单、复数形式,不可数名词不能用数字来计算,没有复数形式。
一、可数名词单数变复数规则
1.一般情况,直接在名词后加-s,如:book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats
2.以s. x. sh. ch结尾的词,在词尾加-es,
如:bus-buses, box-boxes, watch-watches
3.以“辅音字母+y”结尾得词,变y为i, 再加-es,
如:family-families, baby-babies
4.以“f或fe”结尾,变f或fe为v, 再加-es,
如:knife-knives,wife-wives
5.不规则名词复数:
man-men, woman-women, policeman-policemen, policewoman-policewomen, mouse-mice,child-children, foot-feet, tooth-teeth, fish-fish, sheep-sheep people-people, Chinese-Chinese, Japanese-Japanese
1. at
(1)表示时间概念的某一个点。(在具体的某一时刻和时段等)。
at night at 6:00
(2)表示在某一具体地点(小地点)。如at the bus stop , at home
2. on
(1) 在······上面(表面接触;长在上面)。如on the chair, on the tree
(2)在某天的上午、下午或晚上。如:on Monday, on Tuesday morning
3.in
(1)在······里面。如:in the box
(2)在一段时间里。如:in the morning
(3)在某一年份、季节、月份。如:in 2014,in October, in summer
(4)在······上(外来)如:There is a cat in the tree.
4.after
(1)在······之后(时间)。如:I often play football at school.
(2)在······后面(位置)。如:The dog is running after you.
一、人称代词和物主代词
人称代词有主格和宾格的区别:主格通常位于句中第一个动词之前,宾格一般位于动词或介词之后。
2、物主代词有形容词性与名词性的区别:形容词性用时后面一般要带上词,名词性则单独使用,后面不带名词。
人称代词 物主代词
主格 宾格 形容词性 名词性
我 I me 我的 my mine
你,你们 you you 你的,你们的 your yours
他 he him 他的 his his
她 she her 她的 her hers
它 it it 它的 its its
我们 we us 我们的 our ours
他(她,它)们 they them 他(她,它)们的 their theirs
二、指示代词:this, that, these, those。this 和that 用于指代单数,these和 those用于指代复数。
三、疑问代词
一般用来构成特殊疑问句,常见的疑问代词有who(谁),when什么时候),where(哪里),what(什么),how(怎样) ,which(哪一个)等等。
形容词比较级和最高级变化规则:
构成 原级 比较级 最高级
单音节和少数双音节单词 一般词尾加-er, -est tall long old small taller longer older smaller tallest longest oldest smallest
以字母e结尾的形容词或副词,直接加-r,-st nice fine large nicer finer larger nicest finest largest
以重读闭音节结尾的形容词或副词,如末尾只有一个辅音字母,双写该字母,再加-er,-est big hot fat thin bigger hotter fatter thinner biggest hottest fattest thinnest
以“辅音字母+y”结尾的形容词或副词,把y变为i,再加-er,-est heavy busy early easy heavier busier earlier easier heaviest busiest earliest easiest
不规则变化的形容词:
little / few(原形) - less (比较级)- least(最高级)
good(原形) - better(比较级) - best(最高级)
bad (原形) - worse(比较级) - worst(最高级
(一)一般现在时的基本用法;
1.表示经常的或习惯性的动作,常与表示频率的时间状语连用,(always, usually, sometime, never, every day, every week,······
如:I get up at six every day.我每天六点起床。
2.表示客观现实和普遍的真理。如:The earth moves around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。
3.表示主语的特征、能力、职业、性格。
如:The sky is blue.天空是蓝色的。My mother is a teacher .我妈妈是位老师。
(二)一般现在时的构成:
1. be动词:
①肯定句:主语+be(am, is, are)+其它。如: I am a boy. 我是一个男孩。
②否定句:主语+ be + not +其它。 如:He is not a worker.他不是工人。
③一般疑问句:Be +主语+其它。 如:-Are you a student -Yes. I am. / No, I'm not.
2. 行为动词:
①肯定句:主语+行为动词(+其它)。
(当主语为第三人称单数(he, she, it)时,要在动词后加"-s"或"-es"。如:Mary likes Chinese.玛丽喜欢汉语)
②否定句:主语+ don't( doesn't ) +动词原形(+其它)。
(当主语为第三人称单数时,要用doesn't构成否定句。
③一般疑问句:Do( Does ) +主语+动词原形+其它。
(三)一般现在时动词第三人称单数形式变化规则:
1.一般情况下,直接加-s,如:look-looks, play--plays
2.以s. x. sh. ch. o结尾,加-es,
如: wash-washes, watch-watches, go-goes
3.以“辅音字母+y”结尾,变y为i, 再加-es,如:study-studies, fly--flies【注意】have—has
现在进行时
现在进行时表示现在正在进行或发生的动作,也可表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作。
现在进行时由be+动词ing构成
①肯定句 基本结构:主语+be+ 动词ing.
②否定句 基本结构:主语+be not + 动词ing.
③一般疑问句 基本结构: be动词 +主语 +动词ing
④特殊疑问句 基本结构:疑问词+ be +主语+动词ing
【注意】疑问词当主语时,结构为:疑问词+ be + 动词ing
如:Who is watching TV
动词加ing(动词现在分词)的变化规则
动词现在分词构成:动词原形+ing,规则如下:
① 直接加ing
think-thinking sleep-sleeping
②以不发音的字母e结尾的单词,去掉字母e,再加ing
come-coming make-making
③ 以重读闭音节(重读闭音节即两个辅音中间夹一个元音并且重读的音节)结尾,先双写末尾的辅音字母,再加ing
stop-stopping sit-sitting
一般将来时
表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,也可以表示打算、计划或准备做某事。
常与一般将来时连用的时间状语有:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon, the day after tomorrow(后天)等。
一般将来时的用法和结构;
⑴肯定句:
①主语+will+ 动词原形+其它.
②主语+be going to + 动词原形+其它 be going to = will
e.g. I will go to the park tomorrow. = I am going to go to the park tomorrow.
⑵否定句:
在be动词(am, is, are)后加not,情态动词will后加not(will not=won’t)。e.g. I will have a picnic this afternoon.→ I won’t going to have a picnic this afternoon.
⑶一般疑问句:
把be或will提到句首,some改为any, and改为or,第一二人称互换。
e.g. I will go to the park tomorrow. -Will you go to the park tomorrow
特殊疑问句
1、问人疑问词为(Who)
e.g. I’m going to New York soon. →Who’s going to New York soon.
2. 问某人要去干什么疑问词为(What).
e.g. My father is going to watch TV this afternoon. →What is your father going to do this afternoon
3. 问某人去哪里疑问词为(where)
He’s going to have a picnic in the park.
- Where is he going to have a picnic
4.问某人什么时候去疑问词为(when)
e.g. She’s going to go to bed at nine. →When is she going to bed
一般过去式
一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示过去经常或反复发生的动作。
常用的表示过去的时间状语有:yesterday, last year /month/week/night, just now, ago.
一般过去时的句型结构;
⑴谓语动词为be动词的句型结构
肯定句:主语+be动词过去式+其它
②否定句:主语+be动词过去式+not+其它 如:
③be动词过去式+主语+其它
⑵一般过去时be动词的变化:
①am 和is在一般过去时中变为was。(was not=wasn’t)
②are在一般过去时中变为were。(were not=weren’t)
③带有was或were的句子,其否定、疑问的变化和is, am, are一样,即否定句在was或were后加not,一般疑问句把was或were调到句首。
⑵谓语动词是实义动词的句型结构
①肯定句:主语+动词过去式+其它 如: Jim went home yesterday.
②否定句:主语+didn’t +动词原形? 如:Jim didn’t go home yesterday.
③一般疑问句: Did+主语+动词原形? 如:Did Jim go home yesterday
④ 特殊疑问句:疑问词+did+主语+动词原形?
如: What did Jim do yesterday
当疑问词做主语时:疑问词+动词过去式?如:Who went home yesterday
动词过去式变化规则:
1.一般在动词末尾加-ed,如:play—played, cook-cooked
2.结尾是e加d,如:like—liked
3.以重读闭音节结尾,先双写末尾的辅音字母,在加-ed,如:stop-stopped
4.以“辅音字母+y”结尾的,变y为i, 再加-ed,如:study-studied
5.不规则动词过去式:
am, is-was, are-were, do-did, see-saw, say-said, give-gave, get-got, go-went, come-came, have-had, eat-ate, take-took, run-ran, sing-sang, put-put, make-made, read-read, write-wrote, draw-drew, drink-drank, fly-flew, ride-rode, speak-spoke, sweep-swept, swim-swam, sit-sat
1、There be 句型表示:在某地有某物(或人)
2、在there be 句型中,主语是单数,be 动词用is ; 主语是复数,be 动词用are ; 如有几件物品,be 动词根据最近be 动词的那个名词决定(就近原则0。
3、there be 句型的否定句在be 动词后加not , 一般疑问句把be 动词调到句首。
4、there be句型与have(has) 的区别:there be 表示在某地有某物(或人);have(has) 表示某人拥有某物。
5、some 和any 在there be 句型中的运用:some 用于肯定句, any 用于否定句或疑问句。
6、and 和or 在there be句型中的运用:and 用于肯定句, or 用于否定句或疑问句。
7、针对数量提问的特殊疑问句的基本结构是:
How many + 名词复数 + are there + 介词短语?
How much + 不可数名词 + is there + 介词短语?
学科(北京)股份有限公司
同课章节目录
