【期末备考】人教七年级上册重点语法知识梳理【标注重点】
文档属性
| 名称 | 【期末备考】人教七年级上册重点语法知识梳理【标注重点】 |  | |
| 格式 | doc | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.4MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教新目标(Go for it)版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-01-16 16:37:59 | ||
图片预览

文档简介
中小学教育资源及组卷应用平台
【期末备考】人教七上重点语法知识梳理【标注重点】
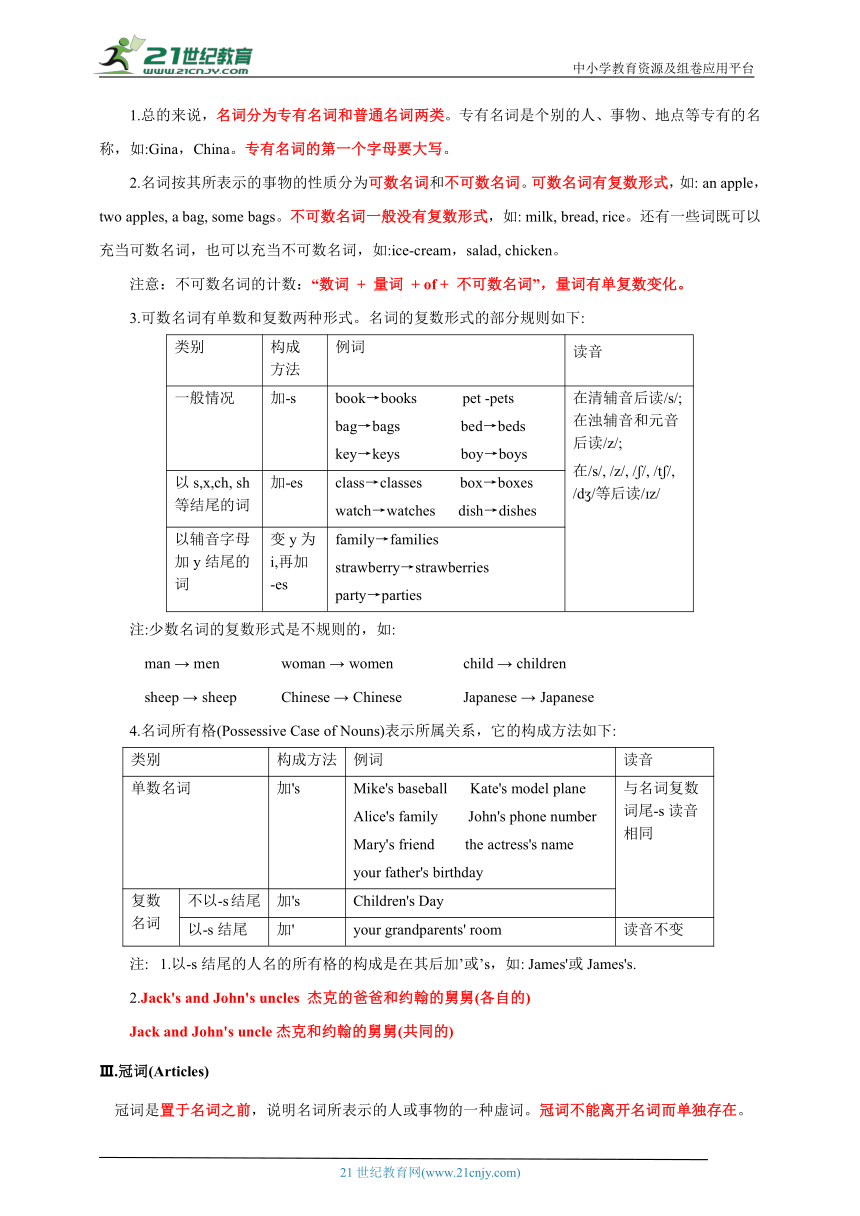
Ⅰ.词类
词类 英语名称 意义 例词 考点解析
名词 Noun (n.) 表示人或事物的名称 vegetable, Chinese, fruit, tennis 1.数(可数名词)2.格(各自有和共同有)3.做定语(man、woman、sport)
冠词 Article(art.) 名词前,帮助说明名词所指的人或事物 a(an), the 1.a和an的选择(根据读音)2.the的用法序数最高专有独乐器类别逢十复
代词 Pronoun(pron.) 代替名词以及起名词作用的短语、分句或句子等 we, that, hers, what 人称(主格:动词前;宾格:动词、介词后)物主(有名则形;无名则名)
形容词 Adjective(adj.) 修饰名词,表示人或事物的特征 red happy, difficult, busy 1.名词前做定语2.be、感官动词、变化动词后做表语3.比较等级
数词 Numeral(num.) 表示数量或顺序 six, thirteen, first, twentieth 基数词表个数序数词表顺序、排名
动词 Verb(v.) 表示动作或状态 be(am,is, are), have, like, go 1.时态2.语态3.固定搭配
副词 Adverb (adv.) 修饰动词、形容词或其他副词 not, too, always, only, here 1.not常和be动词、情态动词和助动词连用,注意缩写形式2.here / there be
介词 Preposition (prep.) 表示名词、代词等与句中其他词的关系 in, on, under, of 1.“某物品在...”句型中不能缺少be动词。2.“在上午” “在某天的上午”介词不同
连词 Conjunction(conj.) 连接词与词、短语与短语或句与句 and, or, but, because, when 1.because和so、although和but2.肯定句变否定或疑问句:and变为or
感叹词 Interjection(interj.) 表示说话时的喜悦、惊讶等情感 oh, hello, well, please
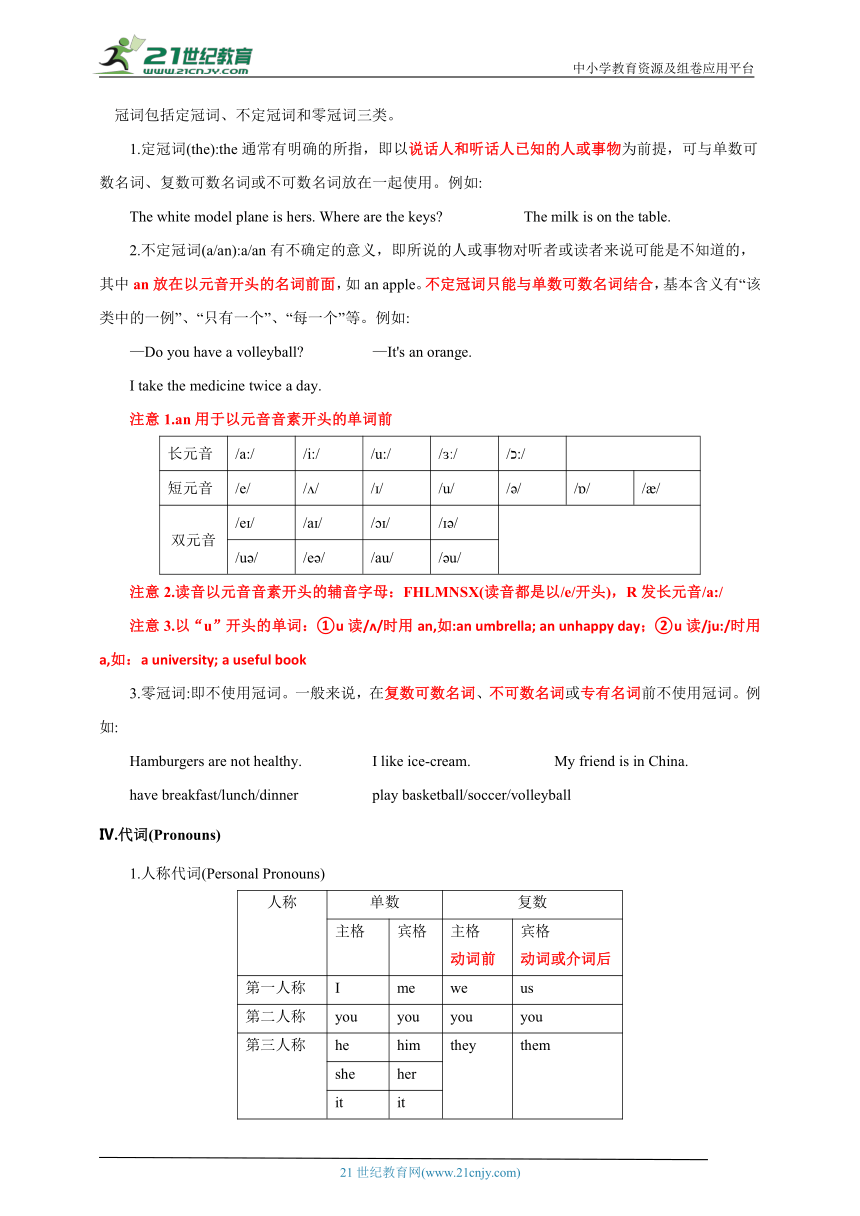
Ⅱ 名词(Nouns) 名词是指人或事物的名称。
1.总的来说,名词分为专有名词和普通名词两类。专有名词是个别的人、事物、地点等专有的名称,如:Gina,China。专有名词的第一个字母要大写。
2.名词按其所表示的事物的性质分为可数名词和不可数名词。可数名词有复数形式,如: an apple,two apples, a bag, some bags。不可数名词一般没有复数形式,如: milk, bread, rice。还有一些词既可以充当可数名词,也可以充当不可数名词,如:ice-cream,salad, chicken。
注意:不可数名词的计数:“数词 + 量词 + of + 不可数名词”,量词有单复数变化。
3.可数名词有单数和复数两种形式。名词的复数形式的部分规则如下:
类别 构成 方法 例词 读音
一般情况 加-s book→books pet -pets bag→bags bed→beds key→keys boy→boys 在清辅音后读/s/;在浊辅音和元音后读/z/;在/s/, /z/, / /, /t /, /d /等后读/ z/
以s,x,ch, sh等结尾的词 加-es class→classes box→boxeswatch→watches dish→dishes
以辅音字母加y结尾的词 变y为i,再加-es family→familiesstrawberry→strawberries party→parties
注:少数名词的复数形式是不规则的,如:
man → men woman → women child → children
sheep → sheep Chinese → Chinese Japanese → Japanese
4.名词所有格(Possessive Case of Nouns)表示所属关系,它的构成方法如下:
类别 构成方法 例词 读音
单数名词 加's Mike's baseball Kate's model planeAlice's family John's phone numberMary's friend the actress's nameyour father's birthday 与名词复数词尾-s读音相同
复数名词 不以-s结尾 加's Children's Day
以-s结尾 加' your grandparents' room 读音不变
注: 1.以-s结尾的人名的所有格的构成是在其后加’或’s,如: James'或James's.
2.Jack's and John's uncles 杰克的爸爸和约翰的舅舅(各自的)
Jack and John's uncle杰克和约翰的舅舅(共同的)
Ⅲ.冠词(Articles)
冠词是置于名词之前,说明名词所表示的人或事物的一种虚词。冠词不能离开名词而单独存在。
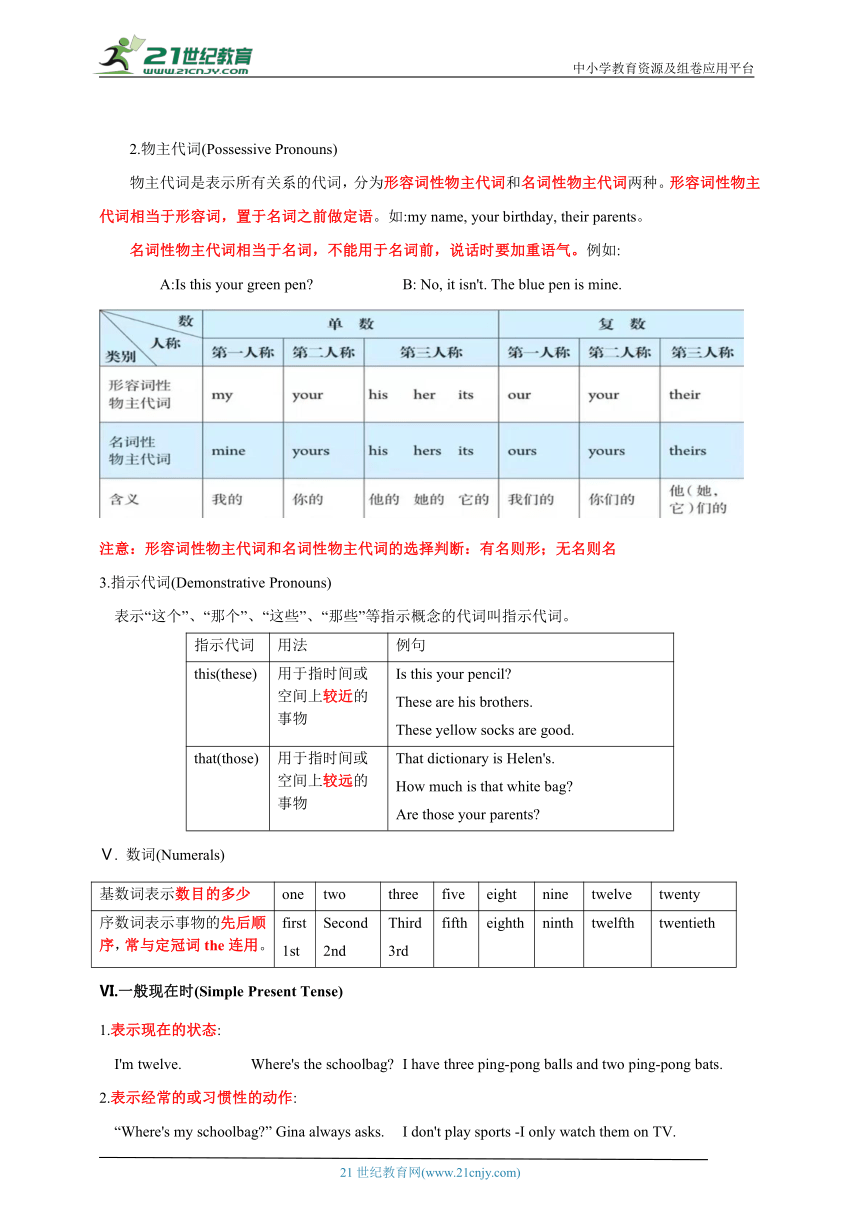
冠词包括定冠词、不定冠词和零冠词三类。
1.定冠词(the):the通常有明确的所指,即以说话人和听话人已知的人或事物为前提,可与单数可数名词、复数可数名词或不可数名词放在一起使用。例如:
The white model plane is hers. Where are the keys The milk is on the table.
2.不定冠词(a/an):a/an有不确定的意义,即所说的人或事物对听者或读者来说可能是不知道的,其中an放在以元音开头的名词前面,如an apple。不定冠词只能与单数可数名词结合,基本含义有“该类中的一例”、“只有一个”、“每一个”等。例如:
—Do you have a volleyball —It's an orange.
I take the medicine twice a day.
注意1.an用于以元音音素开头的单词前
长元音 /a:/ /i:/ /u:/ / / / :/
短元音 /e/ / / / / /u/ / / / / / /
双元音 /e / /a / / / / /
/u / /e / /au/ / u/
注意2.读音以元音音素开头的辅音字母:FHLMNSX(读音都是以/e/开头),R发长元音/a:/
注意3.以“u”开头的单词:①u读/ /时用an,如:an umbrella; an unhappy day;②u读/ju:/时用a,如:a university; a useful book
3.零冠词:即不使用冠词。一般来说,在复数可数名词、不可数名词或专有名词前不使用冠词。例如:
Hamburgers are not healthy. I like ice-cream. My friend is in China.
have breakfast/lunch/dinner play basketball/soccer/volleyball
Ⅳ.代词(Pronouns)
1.人称代词(Personal Pronouns)
人称 单数 复数
主格 宾格 主格动词前 宾格动词或介词后
第一人称 I me we us
第二人称 you you you you
第三人称 he him they them
she her
it it
2.物主代词(Possessive Pronouns)
物主代词是表示所有关系的代词,分为形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词两种。形容词性物主代词相当于形容词,置于名词之前做定语。如:my name, your birthday, their parents。
名词性物主代词相当于名词,不能用于名词前,说话时要加重语气。例如:
A:Is this your green pen B: No, it isn't. The blue pen is mine.
注意:形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词的选择判断:有名则形;无名则名
3.指示代词(Demonstrative Pronouns)
表示“这个”、“那个”、“这些”、“那些”等指示概念的代词叫指示代词。
指示代词 用法 例句
this(these) 用于指时间或空间上较近的事物 Is this your pencil These are his brothers.These yellow socks are good.
that(those) 用于指时间或空间上较远的事物 That dictionary is Helen's.How much is that white bag Are those your parents
Ⅴ. 数词(Numerals)
基数词表示数目的多少 one two three five eight nine twelve twenty
序数词表示事物的先后顺序,常与定冠词the连用。 first1st Second2nd Third3rd fifth eighth ninth twelfth twentieth
Ⅵ.一般现在时(Simple Present Tense)
1.表示现在的状态:
I'm twelve. Where's the schoolbag I have three ping-pong balls and two ping-pong bats.
2.表示经常的或习惯性的动作:
“Where's my schoolbag ” Gina always asks. I don't play sports -I only watch them on TV.
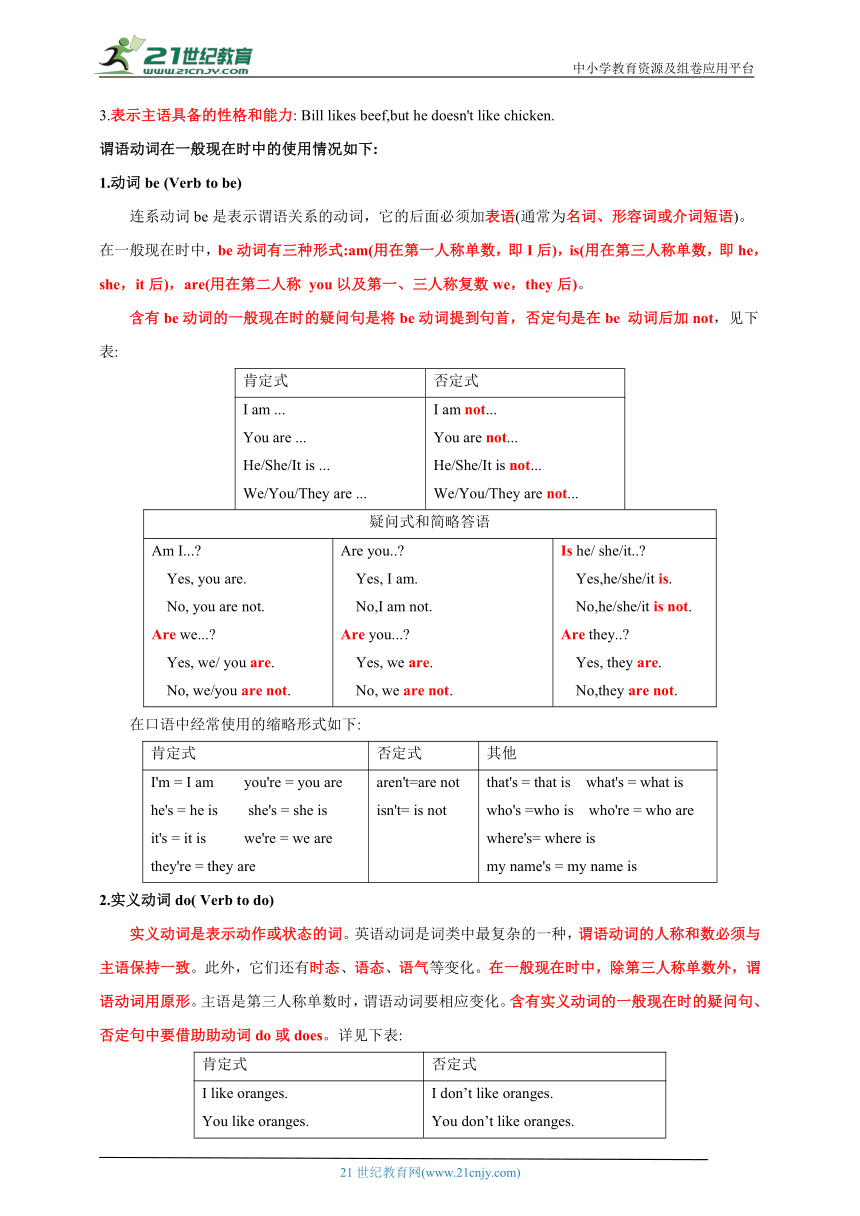
3.表示主语具备的性格和能力: Bill likes beef,but he doesn't like chicken.
谓语动词在一般现在时中的使用情况如下:
1.动词be (Verb to be)
连系动词be是表示谓语关系的动词,它的后面必须加表语(通常为名词、形容词或介词短语)。在一般现在时中,be动词有三种形式:am(用在第一人称单数,即I后),is(用在第三人称单数,即he,she,it后),are(用在第二人称 you以及第一、三人称复数we,they后)。
含有be动词的一般现在时的疑问句是将be动词提到句首,否定句是在be 动词后加not,见下表:
肯定式 否定式
I am ...You are ...He/She/It is ...We/You/They are ... I am not...You are not...He/She/It is not...We/You/They are not...
疑问式和简略答语
Am I... Yes, you are. No, you are not.Are we... Yes, we/ you are. No, we/you are not. Are you.. Yes, I am. No,I am not.Are you... Yes, we are. No, we are not. Is he/ she/it.. Yes,he/she/it is. No,he/she/it is not.Are they.. Yes, they are. No,they are not.
在口语中经常使用的缩略形式如下:
肯定式 否定式 其他
I'm = I am you're = you arehe's = he is she's = she isit's = it is we're = we arethey're = they are aren't=are not isn't= is not that's = that is what's = what iswho's =who is who're = who arewhere's= where ismy name's = my name is
2.实义动词do( Verb to do)
实义动词是表示动作或状态的词。英语动词是词类中最复杂的一种,谓语动词的人称和数必须与主语保持一致。此外,它们还有时态、语态、语气等变化。在一般现在时中,除第三人称单数外,谓语动词用原形。主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词要相应变化。含有实义动词的一般现在时的疑问句、否定句中要借助助动词do或does。详见下表:
肯定式 否定式
I like oranges.You like oranges.He/She likes oranges.We/ You/They like oranges. I don’t like oranges.You don’t like oranges.He/She doesn’t like oranges.We/ You/They don’t like oranges.
疑问式和简略答语
Do I like oranges Yes, you do. No, you do not.Do we like oranges Yes, we/ you do. No, we/you do not. Do you like oranges Yes,I do. No,I do not.Do you like oranges Yes, we do. No, we do not. Does he/ she like oranges Yes, he/she does. No,he/she does not.Do they like oranges Yes, they do. No, they do not.
在口语中,do not经常缩略为don't,does not经常缩略为doesn't。
当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词有下列几种变化形式:
类别 构成 方法 例词 读音
一般情况 加-s help→helps like→likescome→comes know→knowsplay→plays get→getsfind→finds 在清辅音后读/s/;在浊辅音和元音后读/z/;在/s/, /z/, / /, /t /, /d /等后读/ z/
以s,x,ch, sh等结尾的词 加-es guess→guesses fix→fixesteach→teaches finish→finishes
以辅音字母加y结尾的词 变y为i,再加-es study→studies
Ⅶ.介词(Prepositions)
介词一般用于名词或代词前,表示该词与句子其他成分的关系。介词后面的名词或代词称为介词宾语。介词和介词宾语一起构成介词短语。
在本册书中出现的含有介词的主要短语如下:
about: what about doing how about doing think about doing 考虑做...
after: after class after dinner
at: at school at three (o’clock) e-mail me at + 电子邮箱地址
call me at + 电话号码 sell ... at good prices 以...价格出售
For :Thank you for your help. thanks for for boys
ask the teacher for it for two hours (用特殊疑问词How long提问)
have...for breakfast/lunch/dinner 早饭/午饭/晚饭吃...
from:from 12:00 to 1:00
in: in the schoolbag in your grandparents' room in purple 穿着紫色的衣服
in the photo in July in my family
in China in the afternoon in English 用英语
of: a photo of my family the name of my dog
on: on the table on January fifth
on TV/radio/internet 在电视/收音机/互联网上
on your head on Saturday
under: under the desk under your bed
with: play with our friends
Ⅷ.句子种类(Sentence Types)
英语句子按照用途可分为以下四类:
种类 用途 例句
陈述句 用于说明事实或说话人的看法 My name is Jenny Green.I like him because he always plays games with us.Hamburgers are not healthy.I think history is interesting.
疑问句 用于提出问题 Are you Jenny Do you like ice-cream How much are those yellow socks When is your mother's birthday
祈使句 用于表示请求、命令、劝告、建议等 Spell it, e and buy your clothes at our great sale!Let's play basketball.Please come next week.
感叹句 用于表达强烈的感情 What a fine day it is!How clean the classroom is!Have a good day, Jane!
陈述句包括肯定结构和否定结构,在肯定结构中,谓语动词不含否定词,否定结构在be动词、助动词或情态动词后加not,常用缩略形式。陈述句句末用句号。
疑问句包括一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句、附加疑问句等。其中一般疑问句和特殊疑问句的解释见下页,其他疑问句将在后面的册次学习。疑问句句末用问号。
祈使句的结构与陈述句一样,但主语常常省略,谓语动词用原形。祈使句的否定结构用don't加动词原形形式,句末用句号或感叹号。
感叹句句末常用感叹号。将感叹词what或how及其所修饰的词置于句首,即可构成感叹句。what后接名词,how后接形容词或副词,其他部分用陈述句语序。陈述句句末加感叹号,朗读时加强语气亦可构成感叹句。
注:陈述语序:主语+谓语+其他 主语+连系动词+表语
疑问语序:be/情态动词/助动词+主语+谓语+其他 be动词+主语+表语
疑问句(Questions)
1.一般疑问句(Yes/No-Questions)
一般疑问句是在句子中用提问的方式提供一些信息,要求对方用Yes 或No 回答的疑问句。在答语中通常重复问句里的be动词、助动词或情态动词,完全否定时口语中通常使用缩略词,例如: aren't, doesn't。例句如下:
A: Is this your pencil B: Yes,it is./No, it isn't.
A: Do you have a soccer ball B: Yes, 1I do./No, I don't.
A: Does she like tomatoes B: Yes, she does./No, she doesn't.
当然,一般疑问句的回答有时可以省去Yes 或No,或者补充更多信息,例如:
A: Do you like salad B: Yes, I really like it.
A: Do you have a tennis ball Jane B: Sorry, 1 don't.
2.特殊疑问句(Wh-Questions) 【特殊疑问句 = 特殊疑问词 + 一般疑问句】
特殊疑问句是以特殊疑问词开始的以寻求信息为目的的疑问句。
常见的特殊疑问词包括:what(什么),who(谁),where(在哪里),when(何时),why(为什么),how(如何)等。例句如下:
A: What's your name B: My name's Alan.
A: What's your favorite subject B: My favorite subject is PE.
A: Who're they B: They're my grandparents,
A: Who's your PE. teacher B: Mr. Hu.
A: Where are my books B: They're on the sofa.
A: When is your birthday, Linda B: It's on May 2nd.
A:When is Sally's birthday party B:It's on October 5th
A: When s the class B: On Monday and Wednesday:
A: Why do you like PE B: Because it's fun.
A: How much is this T-shirt B:It's seven dollars.
(=What’s the price of ... )
A: How old are you B: I'm thirteen.
(=What’s your age )
在特殊疑问句中,疑问词与后面的be动词或助动词常用缩略形式,例如: what’s,where’s.特殊疑问句既可以使用完整答语,其中名词常用代词替代,也可以只回答提问部分。
例如:
A:What's your phone number B:It's 587-6275.
A: How much are they B: Thirty-nine dollars.
21世纪教育网 www.21cnjy.com 精品试卷·第 2 页 (共 2 页)
HYPERLINK "http://21世纪教育网(www.21cnjy.com)
" 21世纪教育网(www.21cnjy.com)
【期末备考】人教七上重点语法知识梳理【标注重点】
Ⅰ.词类
词类 英语名称 意义 例词 考点解析
名词 Noun (n.) 表示人或事物的名称 vegetable, Chinese, fruit, tennis 1.数(可数名词)2.格(各自有和共同有)3.做定语(man、woman、sport)
冠词 Article(art.) 名词前,帮助说明名词所指的人或事物 a(an), the 1.a和an的选择(根据读音)2.the的用法序数最高专有独乐器类别逢十复
代词 Pronoun(pron.) 代替名词以及起名词作用的短语、分句或句子等 we, that, hers, what 人称(主格:动词前;宾格:动词、介词后)物主(有名则形;无名则名)
形容词 Adjective(adj.) 修饰名词,表示人或事物的特征 red happy, difficult, busy 1.名词前做定语2.be、感官动词、变化动词后做表语3.比较等级
数词 Numeral(num.) 表示数量或顺序 six, thirteen, first, twentieth 基数词表个数序数词表顺序、排名
动词 Verb(v.) 表示动作或状态 be(am,is, are), have, like, go 1.时态2.语态3.固定搭配
副词 Adverb (adv.) 修饰动词、形容词或其他副词 not, too, always, only, here 1.not常和be动词、情态动词和助动词连用,注意缩写形式2.here / there be
介词 Preposition (prep.) 表示名词、代词等与句中其他词的关系 in, on, under, of 1.“某物品在...”句型中不能缺少be动词。2.“在上午” “在某天的上午”介词不同
连词 Conjunction(conj.) 连接词与词、短语与短语或句与句 and, or, but, because, when 1.because和so、although和but2.肯定句变否定或疑问句:and变为or
感叹词 Interjection(interj.) 表示说话时的喜悦、惊讶等情感 oh, hello, well, please
Ⅱ 名词(Nouns) 名词是指人或事物的名称。
1.总的来说,名词分为专有名词和普通名词两类。专有名词是个别的人、事物、地点等专有的名称,如:Gina,China。专有名词的第一个字母要大写。
2.名词按其所表示的事物的性质分为可数名词和不可数名词。可数名词有复数形式,如: an apple,two apples, a bag, some bags。不可数名词一般没有复数形式,如: milk, bread, rice。还有一些词既可以充当可数名词,也可以充当不可数名词,如:ice-cream,salad, chicken。
注意:不可数名词的计数:“数词 + 量词 + of + 不可数名词”,量词有单复数变化。
3.可数名词有单数和复数两种形式。名词的复数形式的部分规则如下:
类别 构成 方法 例词 读音
一般情况 加-s book→books pet -pets bag→bags bed→beds key→keys boy→boys 在清辅音后读/s/;在浊辅音和元音后读/z/;在/s/, /z/, / /, /t /, /d /等后读/ z/
以s,x,ch, sh等结尾的词 加-es class→classes box→boxeswatch→watches dish→dishes
以辅音字母加y结尾的词 变y为i,再加-es family→familiesstrawberry→strawberries party→parties
注:少数名词的复数形式是不规则的,如:
man → men woman → women child → children
sheep → sheep Chinese → Chinese Japanese → Japanese
4.名词所有格(Possessive Case of Nouns)表示所属关系,它的构成方法如下:
类别 构成方法 例词 读音
单数名词 加's Mike's baseball Kate's model planeAlice's family John's phone numberMary's friend the actress's nameyour father's birthday 与名词复数词尾-s读音相同
复数名词 不以-s结尾 加's Children's Day
以-s结尾 加' your grandparents' room 读音不变
注: 1.以-s结尾的人名的所有格的构成是在其后加’或’s,如: James'或James's.
2.Jack's and John's uncles 杰克的爸爸和约翰的舅舅(各自的)
Jack and John's uncle杰克和约翰的舅舅(共同的)
Ⅲ.冠词(Articles)
冠词是置于名词之前,说明名词所表示的人或事物的一种虚词。冠词不能离开名词而单独存在。
冠词包括定冠词、不定冠词和零冠词三类。
1.定冠词(the):the通常有明确的所指,即以说话人和听话人已知的人或事物为前提,可与单数可数名词、复数可数名词或不可数名词放在一起使用。例如:
The white model plane is hers. Where are the keys The milk is on the table.
2.不定冠词(a/an):a/an有不确定的意义,即所说的人或事物对听者或读者来说可能是不知道的,其中an放在以元音开头的名词前面,如an apple。不定冠词只能与单数可数名词结合,基本含义有“该类中的一例”、“只有一个”、“每一个”等。例如:
—Do you have a volleyball —It's an orange.
I take the medicine twice a day.
注意1.an用于以元音音素开头的单词前
长元音 /a:/ /i:/ /u:/ / / / :/
短元音 /e/ / / / / /u/ / / / / / /
双元音 /e / /a / / / / /
/u / /e / /au/ / u/
注意2.读音以元音音素开头的辅音字母:FHLMNSX(读音都是以/e/开头),R发长元音/a:/
注意3.以“u”开头的单词:①u读/ /时用an,如:an umbrella; an unhappy day;②u读/ju:/时用a,如:a university; a useful book
3.零冠词:即不使用冠词。一般来说,在复数可数名词、不可数名词或专有名词前不使用冠词。例如:
Hamburgers are not healthy. I like ice-cream. My friend is in China.
have breakfast/lunch/dinner play basketball/soccer/volleyball
Ⅳ.代词(Pronouns)
1.人称代词(Personal Pronouns)
人称 单数 复数
主格 宾格 主格动词前 宾格动词或介词后
第一人称 I me we us
第二人称 you you you you
第三人称 he him they them
she her
it it
2.物主代词(Possessive Pronouns)
物主代词是表示所有关系的代词,分为形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词两种。形容词性物主代词相当于形容词,置于名词之前做定语。如:my name, your birthday, their parents。
名词性物主代词相当于名词,不能用于名词前,说话时要加重语气。例如:
A:Is this your green pen B: No, it isn't. The blue pen is mine.
注意:形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词的选择判断:有名则形;无名则名
3.指示代词(Demonstrative Pronouns)
表示“这个”、“那个”、“这些”、“那些”等指示概念的代词叫指示代词。
指示代词 用法 例句
this(these) 用于指时间或空间上较近的事物 Is this your pencil These are his brothers.These yellow socks are good.
that(those) 用于指时间或空间上较远的事物 That dictionary is Helen's.How much is that white bag Are those your parents
Ⅴ. 数词(Numerals)
基数词表示数目的多少 one two three five eight nine twelve twenty
序数词表示事物的先后顺序,常与定冠词the连用。 first1st Second2nd Third3rd fifth eighth ninth twelfth twentieth
Ⅵ.一般现在时(Simple Present Tense)
1.表示现在的状态:
I'm twelve. Where's the schoolbag I have three ping-pong balls and two ping-pong bats.
2.表示经常的或习惯性的动作:
“Where's my schoolbag ” Gina always asks. I don't play sports -I only watch them on TV.
3.表示主语具备的性格和能力: Bill likes beef,but he doesn't like chicken.
谓语动词在一般现在时中的使用情况如下:
1.动词be (Verb to be)
连系动词be是表示谓语关系的动词,它的后面必须加表语(通常为名词、形容词或介词短语)。在一般现在时中,be动词有三种形式:am(用在第一人称单数,即I后),is(用在第三人称单数,即he,she,it后),are(用在第二人称 you以及第一、三人称复数we,they后)。
含有be动词的一般现在时的疑问句是将be动词提到句首,否定句是在be 动词后加not,见下表:
肯定式 否定式
I am ...You are ...He/She/It is ...We/You/They are ... I am not...You are not...He/She/It is not...We/You/They are not...
疑问式和简略答语
Am I... Yes, you are. No, you are not.Are we... Yes, we/ you are. No, we/you are not. Are you.. Yes, I am. No,I am not.Are you... Yes, we are. No, we are not. Is he/ she/it.. Yes,he/she/it is. No,he/she/it is not.Are they.. Yes, they are. No,they are not.
在口语中经常使用的缩略形式如下:
肯定式 否定式 其他
I'm = I am you're = you arehe's = he is she's = she isit's = it is we're = we arethey're = they are aren't=are not isn't= is not that's = that is what's = what iswho's =who is who're = who arewhere's= where ismy name's = my name is
2.实义动词do( Verb to do)
实义动词是表示动作或状态的词。英语动词是词类中最复杂的一种,谓语动词的人称和数必须与主语保持一致。此外,它们还有时态、语态、语气等变化。在一般现在时中,除第三人称单数外,谓语动词用原形。主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词要相应变化。含有实义动词的一般现在时的疑问句、否定句中要借助助动词do或does。详见下表:
肯定式 否定式
I like oranges.You like oranges.He/She likes oranges.We/ You/They like oranges. I don’t like oranges.You don’t like oranges.He/She doesn’t like oranges.We/ You/They don’t like oranges.
疑问式和简略答语
Do I like oranges Yes, you do. No, you do not.Do we like oranges Yes, we/ you do. No, we/you do not. Do you like oranges Yes,I do. No,I do not.Do you like oranges Yes, we do. No, we do not. Does he/ she like oranges Yes, he/she does. No,he/she does not.Do they like oranges Yes, they do. No, they do not.
在口语中,do not经常缩略为don't,does not经常缩略为doesn't。
当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词有下列几种变化形式:
类别 构成 方法 例词 读音
一般情况 加-s help→helps like→likescome→comes know→knowsplay→plays get→getsfind→finds 在清辅音后读/s/;在浊辅音和元音后读/z/;在/s/, /z/, / /, /t /, /d /等后读/ z/
以s,x,ch, sh等结尾的词 加-es guess→guesses fix→fixesteach→teaches finish→finishes
以辅音字母加y结尾的词 变y为i,再加-es study→studies
Ⅶ.介词(Prepositions)
介词一般用于名词或代词前,表示该词与句子其他成分的关系。介词后面的名词或代词称为介词宾语。介词和介词宾语一起构成介词短语。
在本册书中出现的含有介词的主要短语如下:
about: what about doing how about doing think about doing 考虑做...
after: after class after dinner
at: at school at three (o’clock) e-mail me at + 电子邮箱地址
call me at + 电话号码 sell ... at good prices 以...价格出售
For :Thank you for your help. thanks for for boys
ask the teacher for it for two hours (用特殊疑问词How long提问)
have...for breakfast/lunch/dinner 早饭/午饭/晚饭吃...
from:from 12:00 to 1:00
in: in the schoolbag in your grandparents' room in purple 穿着紫色的衣服
in the photo in July in my family
in China in the afternoon in English 用英语
of: a photo of my family the name of my dog
on: on the table on January fifth
on TV/radio/internet 在电视/收音机/互联网上
on your head on Saturday
under: under the desk under your bed
with: play with our friends
Ⅷ.句子种类(Sentence Types)
英语句子按照用途可分为以下四类:
种类 用途 例句
陈述句 用于说明事实或说话人的看法 My name is Jenny Green.I like him because he always plays games with us.Hamburgers are not healthy.I think history is interesting.
疑问句 用于提出问题 Are you Jenny Do you like ice-cream How much are those yellow socks When is your mother's birthday
祈使句 用于表示请求、命令、劝告、建议等 Spell it, e and buy your clothes at our great sale!Let's play basketball.Please come next week.
感叹句 用于表达强烈的感情 What a fine day it is!How clean the classroom is!Have a good day, Jane!
陈述句包括肯定结构和否定结构,在肯定结构中,谓语动词不含否定词,否定结构在be动词、助动词或情态动词后加not,常用缩略形式。陈述句句末用句号。
疑问句包括一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句、附加疑问句等。其中一般疑问句和特殊疑问句的解释见下页,其他疑问句将在后面的册次学习。疑问句句末用问号。
祈使句的结构与陈述句一样,但主语常常省略,谓语动词用原形。祈使句的否定结构用don't加动词原形形式,句末用句号或感叹号。
感叹句句末常用感叹号。将感叹词what或how及其所修饰的词置于句首,即可构成感叹句。what后接名词,how后接形容词或副词,其他部分用陈述句语序。陈述句句末加感叹号,朗读时加强语气亦可构成感叹句。
注:陈述语序:主语+谓语+其他 主语+连系动词+表语
疑问语序:be/情态动词/助动词+主语+谓语+其他 be动词+主语+表语
疑问句(Questions)
1.一般疑问句(Yes/No-Questions)
一般疑问句是在句子中用提问的方式提供一些信息,要求对方用Yes 或No 回答的疑问句。在答语中通常重复问句里的be动词、助动词或情态动词,完全否定时口语中通常使用缩略词,例如: aren't, doesn't。例句如下:
A: Is this your pencil B: Yes,it is./No, it isn't.
A: Do you have a soccer ball B: Yes, 1I do./No, I don't.
A: Does she like tomatoes B: Yes, she does./No, she doesn't.
当然,一般疑问句的回答有时可以省去Yes 或No,或者补充更多信息,例如:
A: Do you like salad B: Yes, I really like it.
A: Do you have a tennis ball Jane B: Sorry, 1 don't.
2.特殊疑问句(Wh-Questions) 【特殊疑问句 = 特殊疑问词 + 一般疑问句】
特殊疑问句是以特殊疑问词开始的以寻求信息为目的的疑问句。
常见的特殊疑问词包括:what(什么),who(谁),where(在哪里),when(何时),why(为什么),how(如何)等。例句如下:
A: What's your name B: My name's Alan.
A: What's your favorite subject B: My favorite subject is PE.
A: Who're they B: They're my grandparents,
A: Who's your PE. teacher B: Mr. Hu.
A: Where are my books B: They're on the sofa.
A: When is your birthday, Linda B: It's on May 2nd.
A:When is Sally's birthday party B:It's on October 5th
A: When s the class B: On Monday and Wednesday:
A: Why do you like PE B: Because it's fun.
A: How much is this T-shirt B:It's seven dollars.
(=What’s the price of ... )
A: How old are you B: I'm thirteen.
(=What’s your age )
在特殊疑问句中,疑问词与后面的be动词或助动词常用缩略形式,例如: what’s,where’s.特殊疑问句既可以使用完整答语,其中名词常用代词替代,也可以只回答提问部分。
例如:
A:What's your phone number B:It's 587-6275.
A: How much are they B: Thirty-nine dollars.
21世纪教育网 www.21cnjy.com 精品试卷·第 2 页 (共 2 页)
HYPERLINK "http://21世纪教育网(www.21cnjy.com)
" 21世纪教育网(www.21cnjy.com)
同课章节目录
