外研版(2019) 必修第二册Unit 2 Let's celebrate Using language 情态动词 课件(共16张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版(2019) 必修第二册Unit 2 Let's celebrate Using language 情态动词 课件(共16张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 5.8MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-01-25 07:46:27 | ||
图片预览






文档简介
(共16张PPT)
Unit 2
Using language
Modals (2)
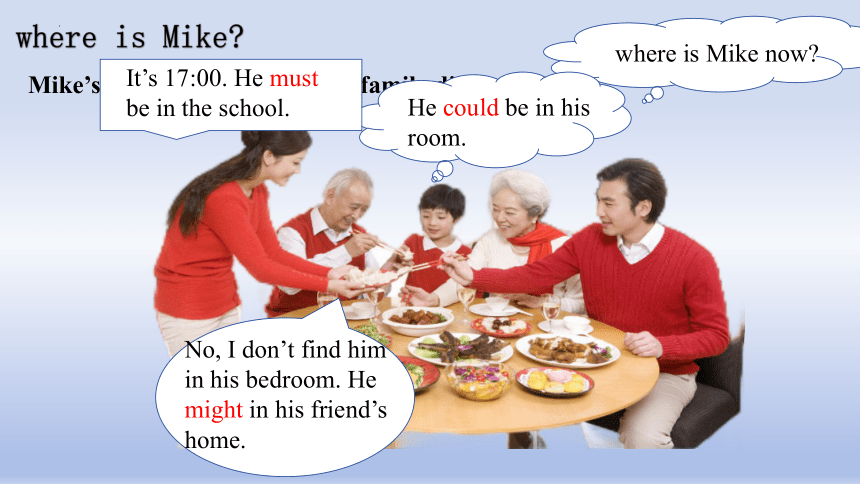
where is Mike
where is Mike now
No, I don’t find him in his bedroom. He might in his friend’s home.
Mike’s family is enjoying their family dinner.
He could be in his room.
It’s 17:00. He must be in the school.
Where is Mike most possibly
1
2
3
表示对现在的推测:must>can>could>may>might>can’t
Activity 2
Rewrite the underlined sentences in the conversation using can/could, may/might and must.
(At a fancy dress party.)
Chris: I spent ages putting up all the balloons and flowers last night.
Jean: I expect you are feeling tired now!
Chris: Yes, I am. Look, that guy is dressed as Batman. Is that Mike
Jean: It’s possibly him. Check out that girl over there. I’m sure that’s Lucy.
Chris: No, I don’t think that’s Lucy. Lucy isn’t that tall.
Jean: Look at those two guys dressed as chickens! Oh, they’re
waving at us! Maybe they’re from our school.
Chris: Let’s go and find out.
You must be tired now!
It may/might/could be him.
That must be Lucy.
that can’t be Lucy.
They may / might / could be from our school.
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: The ground is so wet today.
Judy: Yes. It must have rained last night.
must have done表示对过去事情的肯定推测,“一定做过某事”。
Translation:
今天地面好湿啊。
——昨天晚上肯定下雨了。
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: Where is Mike Has he already gone to Beijing
Judy: He can’t have gone to Beijing, for I saw him this morning.
Translation:
Mike人呢?他已经去北京了吗?
——他肯定没去北京,今早我还看见他了。
can’t have done表示对过去事情的否定推测,“不可能做过某事”, 用于否定句。
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: What has happened to Mike
Judy: I don’t know. He may have got lost.
Translation:
Mike怎么了?
——我不知道,他可能迷路了。
may have done表示对过去事情的推测,“可能已经”,用于肯定句,但可能性低于must have done。
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: I can't find Mike. Where can he have gone
Judy: I have no idea.
Translation:
我找不到Mike了,他能去哪儿呢?
——我不知道。
can have done表示对过去行为的怀疑,“可能做过”,用于疑问句。
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: Did you pass the exam
Judy: I could have pass the exam, but I was too careless.
Translation:
你通过考试了吗?
——我本来能通过考试了,但是我太粗心了。
could have done表示对过去事情的假设,“本来能够做某事(而没有做)”,用于虚拟语气。
假设:
实际:
我能通过考试。
我没有通过考试。
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: Mike didn’t pass the exam.
Judy: He might have passed the exam if he had studied harder.
Translation:
Mike考试没及格
——如果他学习更努力的话,他可能已经及格了。
might have done表示对过去事情的推测,意义与may相同,但可能性更小,多用于虚拟语气。
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: What is Mike like
Judy: I would have told you all about his story, but you didn’t ask me.
Translation:
Mike是个什么样的人?
——我本来会告诉你Mike的事情,但你之前没问我呀。
would have done表示对过去事情的假设,意义“本来会做(但没有做)”,用于虚拟语气。
假设:
实际:
我告诉你Mike的事情。
我没有告诉你Mike的事情。
情态动词+have done用法
Judy: I wouldn’t have told you all about Mike’s story.
Lucy: But you did.
Translation:
我本来不应该告诉你Mike的事情的
——但是你告诉我了呀。
wouldn’t have done是would have done 的否定形式。
情态动词+have done用法
Judy: Ah! I can’t finish my homework!
Lucy: You are too lazy. You ought to /should have finished it last week.
Translation:
啊!我作业写不完啦!
——你太懒了,你上周就应该写完了。
ought to/should have done表示对过去事情的假设,意义“本来应该做某事(但实际没做)”,用于虚拟语气。
假设:
实际:
你上周就写完作业了。
你没有写完作业。
情态动词+have done用法
Judy: Mike is crying. You oughtn’t to/shouldn’t been so rude to him.
Lucy: I’m sorry.
Translation:
Mike 哭了,你本来不应该对他如此粗鲁的。
——对不起。
oughtn’t to/shouldn’t have done表示对过去事情的假设,意义“本来不应该做某事(但实际做了)”,用于虚拟语气。
假设:
实际:
你对Mike不粗鲁。
你对Mike粗鲁。
情态动词+have done用法
Judy: I bought 10 bottles of wine.
Lucy: You needn’t have bought so much wine, for only 5 people were here.
needn’t have done意义“本来不必做某事(但实际做了)”。
Translation:
我买了10瓶酒。
——你不必买那么多酒的,这里只有5个人。
Thank you
Unit 2
Using language
Modals (2)
where is Mike
where is Mike now
No, I don’t find him in his bedroom. He might in his friend’s home.
Mike’s family is enjoying their family dinner.
He could be in his room.
It’s 17:00. He must be in the school.
Where is Mike most possibly
1
2
3
表示对现在的推测:must>can>could>may>might>can’t
Activity 2
Rewrite the underlined sentences in the conversation using can/could, may/might and must.
(At a fancy dress party.)
Chris: I spent ages putting up all the balloons and flowers last night.
Jean: I expect you are feeling tired now!
Chris: Yes, I am. Look, that guy is dressed as Batman. Is that Mike
Jean: It’s possibly him. Check out that girl over there. I’m sure that’s Lucy.
Chris: No, I don’t think that’s Lucy. Lucy isn’t that tall.
Jean: Look at those two guys dressed as chickens! Oh, they’re
waving at us! Maybe they’re from our school.
Chris: Let’s go and find out.
You must be tired now!
It may/might/could be him.
That must be Lucy.
that can’t be Lucy.
They may / might / could be from our school.
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: The ground is so wet today.
Judy: Yes. It must have rained last night.
must have done表示对过去事情的肯定推测,“一定做过某事”。
Translation:
今天地面好湿啊。
——昨天晚上肯定下雨了。
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: Where is Mike Has he already gone to Beijing
Judy: He can’t have gone to Beijing, for I saw him this morning.
Translation:
Mike人呢?他已经去北京了吗?
——他肯定没去北京,今早我还看见他了。
can’t have done表示对过去事情的否定推测,“不可能做过某事”, 用于否定句。
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: What has happened to Mike
Judy: I don’t know. He may have got lost.
Translation:
Mike怎么了?
——我不知道,他可能迷路了。
may have done表示对过去事情的推测,“可能已经”,用于肯定句,但可能性低于must have done。
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: I can't find Mike. Where can he have gone
Judy: I have no idea.
Translation:
我找不到Mike了,他能去哪儿呢?
——我不知道。
can have done表示对过去行为的怀疑,“可能做过”,用于疑问句。
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: Did you pass the exam
Judy: I could have pass the exam, but I was too careless.
Translation:
你通过考试了吗?
——我本来能通过考试了,但是我太粗心了。
could have done表示对过去事情的假设,“本来能够做某事(而没有做)”,用于虚拟语气。
假设:
实际:
我能通过考试。
我没有通过考试。
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: Mike didn’t pass the exam.
Judy: He might have passed the exam if he had studied harder.
Translation:
Mike考试没及格
——如果他学习更努力的话,他可能已经及格了。
might have done表示对过去事情的推测,意义与may相同,但可能性更小,多用于虚拟语气。
情态动词+have done用法
Lucy: What is Mike like
Judy: I would have told you all about his story, but you didn’t ask me.
Translation:
Mike是个什么样的人?
——我本来会告诉你Mike的事情,但你之前没问我呀。
would have done表示对过去事情的假设,意义“本来会做(但没有做)”,用于虚拟语气。
假设:
实际:
我告诉你Mike的事情。
我没有告诉你Mike的事情。
情态动词+have done用法
Judy: I wouldn’t have told you all about Mike’s story.
Lucy: But you did.
Translation:
我本来不应该告诉你Mike的事情的
——但是你告诉我了呀。
wouldn’t have done是would have done 的否定形式。
情态动词+have done用法
Judy: Ah! I can’t finish my homework!
Lucy: You are too lazy. You ought to /should have finished it last week.
Translation:
啊!我作业写不完啦!
——你太懒了,你上周就应该写完了。
ought to/should have done表示对过去事情的假设,意义“本来应该做某事(但实际没做)”,用于虚拟语气。
假设:
实际:
你上周就写完作业了。
你没有写完作业。
情态动词+have done用法
Judy: Mike is crying. You oughtn’t to/shouldn’t been so rude to him.
Lucy: I’m sorry.
Translation:
Mike 哭了,你本来不应该对他如此粗鲁的。
——对不起。
oughtn’t to/shouldn’t have done表示对过去事情的假设,意义“本来不应该做某事(但实际做了)”,用于虚拟语气。
假设:
实际:
你对Mike不粗鲁。
你对Mike粗鲁。
情态动词+have done用法
Judy: I bought 10 bottles of wine.
Lucy: You needn’t have bought so much wine, for only 5 people were here.
needn’t have done意义“本来不必做某事(但实际做了)”。
Translation:
我买了10瓶酒。
——你不必买那么多酒的,这里只有5个人。
Thank you
