人教版(2019)必修第一册Welcome Unit Discovering Useful Structures 句子基本结构课件(共68张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版(2019)必修第一册Welcome Unit Discovering Useful Structures 句子基本结构课件(共68张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 6.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-01-26 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共68张PPT)
词类、句子成分和基本句型
初高中衔接---语法奠基篇
十大词类
名词
动词
形容词
副词
数词
冠词
代词
介词
感叹词
连词
名词(n.)
Obama
thing
river
habit
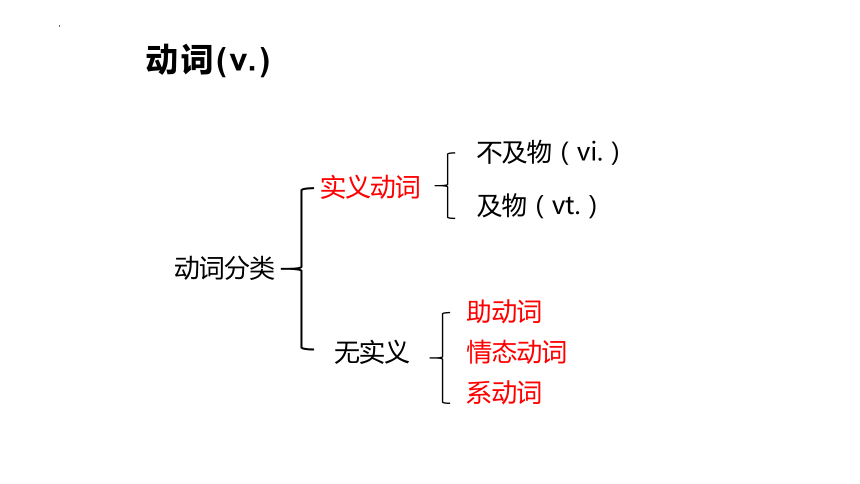
动词(v.)
动词分类
实义动词
无实义
不及物(vi.)
及物(vt.)
助动词
情态动词
系动词
及物动词(vt.) vs 不及物动词(vi.)
I see a bird.
I see.
The job will be finished.
助动词:帮助谓语动词表达精确含义。(时态、语态)
You should close the window.
情态动词:表示人对某种行为的情绪和态度。
(能 / 可能 / 应该 / 必须)
Lihua is a teacher.
系动词:把“事物”和“属性”联系起来
The leaves turn yellow.
You look tired.
形容词(adj.)
blue sky
修饰名词,表示特征。
beautiful girl
副词(adv.)
用来说明时间、地点、程度、方式等概念。
可以修饰动词、形容词、副词。
I sit still.
I am so cool.
I push the door very hard.
数词(num.)
one two three four 基数词
表示数量或顺序
first second third fourth 序数词
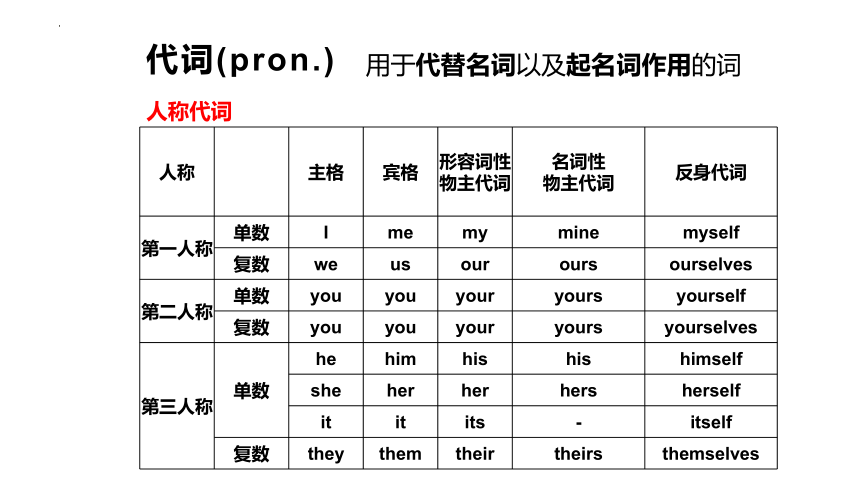
代词(pron.)
用于代替名词以及起名词作用的词
人称 主格 宾格 形容词性
物主代词 名词性
物主代词 反身代词
第一人称 单数 I me my mine myself
复数 we us our ours ourselves
第二人称 单数 you you your yours yourself
复数 you you your yours yourselves
第三人称 单数 he him his his himself
she her her hers herself
it it its - itself
复数 they them their theirs themselves
人称代词
代词
单数 复数
this(这个) these(这些)
that(那个) those(那些)
it (这)
指示代词
用来起指示作用,或用来代替前面已提到过的名词。
自我检测:
代词的分类和形式
冠词(art.)
a / an / the
I have an apple
位于名词前,帮助说明名词所指的人或事物
I have a pen
The apple is red.
介词(prep.)
She looked at me.
表示名词与句中其它词的关系
感叹词(interj.)
表示说话时的情感。
Oh, hello, well, please
连词(conj.)
Ladies and gentlemen,…
I am ugly but I am gentle.
连接词与词、短语与短语或句与句
句子成分和基本句型
Learning objectives
1.Master the basic sentence components of English.
掌握句子成分。
2.Learn to analyze the structure of the sentences.
学会分析句子结构。
语
法
脉
图
定义 :
构成句子的各个部分叫做句子成分。句子成分有主要成分和次要成分。
主要成分:主语和谓语
次要成分:表语、宾语、定语、状语、补足语、同位语
S 表示 “主语(subject)”
V 表示 “谓语(verb)”
O 表示 “宾语(object)”
P 表示 “表语(predicative)”
A 表示 “状语(adverbial)”
IO 表示 “间接宾语(indirect object)”
DO 表示 “直接宾语(direct object)”
C 表示 “宾语补足语(object complement)”
The baby is sleeping.
He drives fast.
One is enough.
To see is to believe.
Smoking is bad for health.
What she has said is true.
(名词)
(代词)
(数词)
(不定式)
(动名词)
(句子)
主语是谓语讲述的对象,表示所说的“是什么”或“是谁”。主语是谓语动作或状态的执行者。
Observe: What can be “subject” in a sentence
Subject
主 语
主语一般由名词(短语)、代词、数词、动名词(短语)、动词不定式
(短语)和主语从句等充当。
注意:主语一般位于句首,但若不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)、名词性从句作主语,常用it作形式主语,则把真正的主语放在句后。
It drives me mad to teach her.
It’s a pity that you missed the exciting football match.
Find the subject in the sentence
Twenty years is a short time in history.
The poor are now living in the shelter.
Running is good for our health.
To study hard is your duty.
She likes dancing.
What I want is some apples .
Verb
谓 语
说明主语所做的动作或具有的特征和状态,有完整的时态和语态。一般在主语之后。
谓语中最重要的是谓语动词 (通常由实义动词充当),
它有时态,语态的变化,并受主语人称和数的影响。
实义动词 有实在意义并能独立作谓语 read eat look drink
助动词 本身没有意义,不单独作谓语,协助主要动词构成谓语 be have do will
情态动词 有一定词义,不能单独作谓语,后加动词原形 can must may need shall
系动词 有词义,但不能独立做谓语,必须和表语构成主系表结构 am is are keep stay sound feel become
动词的分类:
主谓(宾)
主系表
be动词 am, is , are , was, were
表变化类动词 become, get, turn, grow, go
感官动词 look, sound, smell, taste, feel
延续性动词 remain, stay, keep
英文中常见的系动词
4. We have finished reading this book.
5. They can speak English well.
助动词和情态动词须和
实义动词一起构成谓语
2. He looked after two boys.
找出句子中的谓语
6. My sister is crying over there.
1. A tiger eats meat.
3. He doesn’t like fruit.
注意:复合谓语的划分要把时态、被动语态、情态动词和否定词归入进去。
宾语表示动作的对象,是动作的承受者。
宾语一般位于及物动词和介词之后。
Object
宾 语
Observe: What can be “object” in a sentence
(句子)
Show your book, please.
She didn't know anything.
They want to know my idea.
I like staying with you.
Did you know what she want
(名词 )
( 代词)
(不定式)
(动名词短语)
宾语一般由名词、代词、不定式、动名词(短语)及宾语从句等充当
注意:不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)、名词性从句作宾语,常用it作形式宾语,则把真正的宾语放在句后。
Some students find it difficult to study English.
Most of us think it no use arguing with her.
Miss Tan teaches us English.
双宾语(IO + DO)
在动词后方所跟的双宾语中
表示物的叫做直接宾语direct object(简称“直宾”)
表示人的叫做间接宾语indirect object(简称“间宾”)
S
V
DO
IO
常见接双宾语的动词:teach, buy, bring, take, give, send, sell, show, tell, write, lend, make ...
He gave me a pen.
IO DO
We bought him a gift.
IO DO
He wrote me a letter.
IO DO
He gave a pen to me.
DO IO
We bought a gift for him.
DO IO
He wrote me a letter to me.
DO IO
双宾语易位
常借助介词to的常用动词
teach/tell sb. sth =
teach/tell sth. to sb.
take/bring/give sb. sth=
take/bring/give sth to sb.
send/write sb. sth.=
send/write sth. to sb.
show sb. sth.=
show sth. to sb.
常借助介词for的常用动词
buy sb. sth=
buy sth. for sb.
lend sb. sth.(借)=
lend sth. for sb.
make sb. sth=
make sth. for sb.
双宾语易位
VS
Complement
宾语补足语
英语中有些及物动词接宾语后,意义仍然不完整,还需要一个句子成分来补充说明宾语的意义,状态等,这就是宾语补足语。
1. They made her their monitor.
2. The fire left him homeless.
3. When he woke up, he found himself lying in the street.
4. When he came to himself, he found himself surrounded by his family and friends.
5. The farmer asked us to have dinner.
6. We saw him play soccer.
名词
形容词
过去分词
现在分词
(省略to不定式)
动词不定式短语
1. His father named him Dongming.
2. They painted their boat white.
3. You mustn’t force him to lend his money to you.
4. We saw her entering the room.
5. We found everything in the lab in good order.
6. I want your homework done on time.
Find the object complement in the sentence
My mom made me a cake.
My mom made a cake for me.
S
V
DO
IO
S
V
DO
IO
My mom made me happy.
S
V
O
OC 宾补
区分以下句子成分:宾补?双宾语?
My mom made me a fool.
S
V
O
OC 宾补
Attributive
定语
定语是用于对名词或代词起修饰、限定作用的词、短语或句子。
注意:单个词作定语时常放在被修饰词之前(前置定语),
而短语或从句作定语时,则放在被修饰词之后(后置定语)。
Observe: What can be “Attributive” in a sentence
常用作定语的有名词、代词、数词、形容词、副词、介词短语、动名词、动词不定式、现在分词、过去分词、定语从句等。
(1)形容词作定语 The black bike is mine.
(2)代词作定语 What's your name
(3)名词作定语 They made some paper flowers.
(4)介词短语作定语The boys in the room are in Class Three,Grade One.
(5)不定式作定语 I have no time to travel in spring.
(6)从句作定语 The tall boy who is standing there is Peter.
(7)过去分词作定语 There are fallen leaves on the ground.
1.The letter on the desk is for Mr Wu.
2.The woman with a baby in her arms is his mother.
3.She carried a basket full of eggs.
4.It’s a city far from the coast.
5.He has enough money to buy a car.
6.The man downstairs was trying to sleep.
7.There are lots of places of interest needing repairing in our city.
Find the attributive in the sentence
What is Adverbial
A (adverbial) 状语
1 He lives in Shenzhen.
A
2 You go to school by bus.
A
3 He was born in 1918.
A
状语(A):是用来说明动词、形容词、副词或整个句子的成分。
常由副词,介词+其他担任。
修饰动词时可以放在动词之前,也可以放在动词之后;修饰形容词或副词时放在它们之前。
地点状语
方式状语
时间状语
The students study hard.
I often write to him.
The bag is too heavy.
副词
You each have a chance to go to college.
We students should put our heart into the study.
I am Li Hua, a Chinese student studying in London.
The thought came to him that Mary had probably fallen ill.
Appositive
同位语
同位语用于对名词或代词的进一步解释说明,常位于名词或代词之后。
常用作同位语的有名词、名词短语、数词、代词、同位语从句等。
I met my best friend Tom at the station yesterday.
↓
主语
↓
谓
语
↓
定语
↓
宾
语
↓
同位语
↓
状
语
分析句子成分:
I.选出下列句子中画线部分的成分
1. We all study hard at English.
A.主语 B.谓语 C.宾语 D.表语
2. Betty likes her new bike very much.
A.主语 B.谓语 C.宾语 D.表语
3. My brother is a policeman.
A.主语 B.谓语 C.宾补 D.表语
4. Were you at home last night
A.定语 B.状语 C.宾补 D.表语
即时训练
5. Winter is the coldest season of the year.
A.定语 B.状语 C.宾补 D.表语
6. He often walks in the park.
A.定语 B.状语 C.宾语 D.表语
7. Mary asked me to help her yesterday.
A.定语 B.状语 C.宾补 D.表语
8. He bought me a nice present last week.
A.宾语 B.直接宾语 C.间接宾语 D.宾补
9. His parents are doctors.
A.宾语 B.表语 C.谓语 D.定语
10. I'll get you some tea now.
A.主语 B.直接宾语 C.间接宾语 D.宾补
11. My mother told us an interesting story last night.
A.表语 B.直接宾语 C.间接宾语 D.宾补
12. He has read the book twice.
A.主语 B.谓语 C.表语 D.宾语
13. They seemed unhappy when they heard the news.
A.表语 B.谓语 C.宾语 D.定语
14. Do you have something to eat
A.状语 B. 定语 C.宾语 D.宾补
15. We made him our monitor.
A.宾语 B.定语 C.状语 D.宾补
Welcome Unit
Discovering Useful Structures
P6
S (subject) 主语
V (verb) 动词
O (object) 宾语
P (predicative) 表语
A (adverbial) 状语
DO (direct object) 直接宾语
IO (indirect object) 间接宾语
OC (object complement) 宾语补足语
Sentence structure Sentence
SV All of us laughed!
SVO I miss my grandma.
SP The teacher was kind and friendly.
S V IO DO He told us a funny story.
S V OC I found most of my classmates and teachers friendly and helpful.
SVA He talked too much.
SVOA I had my first maths class at senior high school.
There be... There's a lot to explore at senior high school.
Study the sentence structures.
All of us laughed!
I miss my grandma.
The teacher was kind and friendly.
He told us a funny story.
I found most of my classmates and teachers friendly and helpful.
主语+谓语 (SV)
主语+谓语+宾语 (SVO)
主语+谓语+表语 (SVP)
主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语 (SV IO DO)
主语+谓语+宾语+宾补 (SVOC)
He talked too much.
I had my first maths class at senior high school.
There’s a lot to explore at senior high.
主语+谓语+状语 (SVA)
主语+谓语+宾语 +状语(SVOA)
There be句型
Basic Sentence Structures
英文中基本的句子结构有以下五种:
1. 主+谓(不及物动词) SV
2. 主+谓(及物动词)+宾语 SVO
3. 主+系动词+表语 SVP
4. 主+谓(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语
5. 主+谓(及物动词)+宾语+宾语补足语 SVOC
SV IO DO
6. There be 句型
SV 主语+谓语(不及物动词Vi.)
①
此句型中 “主语+不及物动词/词组”构成句子的主体部分,不及物动词后不能直接带宾语。
注意:有时为了表示发生的频率、原因、结果、目的、地点或时间等,可以有状语来修饰。
例1 Class begins.
例3 Her mother has gone abroad.
例2 The rain has stopped.
例4 The red sun rise in the east.
状语修饰动词
状语修饰动词
②
SVO 主语+谓语(及物动词Vt.)+宾语
此句型中谓语是及物动词,其后必须跟宾语才能使句意表达完整。
注意:一些不及物动词后面加介词相当于一个及物动词,之后可加宾语。Vi+prep.=Vt.
例1 You must listen to your teacher.
例2 My father arrived in London yesterday.
例3 He is laughing at the crippled woman.
例4 I’ll write about my football team in my
future books.
③
SVP 主语+系动词+表语
此类型的句子,谓语动词不能表达一个完整的意思,必须加上一个表明主语性质或状态的表语,才能表达完整的意思。
例1 She became a singer.
例2 My brother is out now.
例3 Breakfast smells good.
④
SV IO DO
主语+谓语(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语
例2 I bought Tom a birthday gift.
间接宾语
直接宾语
例1 I showed her my photos.
间接宾语
直接宾语
常见的可接双宾语的动词有:give, send, bring, owe, take, offer, pass, lend, tell, return, promise, show, write, throw, hand, award, grant(授予)等。
⑤
SVOC
主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语+宾语补足语
在某些及物动词的后面,需要用一个宾语再加一个宾补才能表达完整的意思。
常见的可做宾语补足语的有:名词,形容词,介词短语,动词不定式,不带to的动词不定式等
例1 I will make you captain.
例2 You should keep the room clean and tidy.
例3 The engineer made the robort clean
the room everyday.
6.1 There is an apple on the table.
V S A
6.2 There are seven days in a week.
V S A
6.3 There is milk and bread.
V S
在这种结构中,S和V是倒置的。V的数由S的第一个名词决定。
⑥
There be句型 某地存在什么东西
例句:我们学校有很多很漂亮的教学楼。
There are many beautiful teaching buildings in our school.
Group Work
Finish task 2 on P6.
Read the sentences and analyse the structures.
1 The 100-year-old school lies in the centre of
the city.
2 We must act.
3 The maths homework looks easy.
4 The teacher found the classroom empty.
S
V
A
S
V
S
P
S
V
O
C
Read the sentences and analyse the
structures.
5 My mum bought me a new dictionary.
6 Tom is looking forward to meeting the new
exchange student.
7 There is an English Corner at our school.
8 We had chemistry in the newly built lab.
S
V
IO
DO
S
V
O
There be ......
S
V
O
A
1. That dream has come true!
2. Tim and his classmates are living on a ship!
3. They also learn about ships and the sea.
S
V
S
V
S
V
A
O
Read the passage and analyse the structures
of the underlined sentences.
4. Tim writes his parents an email every week and tells them what happened on the ship.
5. There’s always something exciting to do.
6. Studying and doing homework seem
much more fun.
S
V
IO
DO
V
IO
There be ......
S
P
DO
并列句
Answers
Thank you
【语境应用】判断句子结构类型。
1) Everybody smiled.
2) The car caught fire.
3) Did the milk turn sour
4) He bought his wife a dress.
5) Roy found his new job rather boring.
6) Your brother got up at 10 o’clock.
7) I haven’t seen Daniel for long.
SVOC
SVA
SVOA
SV
SVO
SP
SVIODO
翻译练习:
1. 他们走着,笑着。
2. 英语老师很友好。
3. 树上有一只可爱的小鸟。
4. 他给她妹妹买了一架钢琴。
5. 老师发现教室是空的。
They walked and laughed.
The English teacher is friendly.
There is a lovely bird in the tree.
He bought his sister a piano.
The teacher found the classroom empty.
翻译练习:
6. 我听到她正在唱歌。
7. 英语作业看上去很简单。
8. 我们笑得很开心。
9. 我们学校有许多学生。
10. 她是一个爱交际的女孩。
I heard her singing a song.
The English homework looks easy.
We laugh happily.
There are many students in our school.
She is an outgoing girl.
词类、句子成分和基本句型
初高中衔接---语法奠基篇
十大词类
名词
动词
形容词
副词
数词
冠词
代词
介词
感叹词
连词
名词(n.)
Obama
thing
river
habit
动词(v.)
动词分类
实义动词
无实义
不及物(vi.)
及物(vt.)
助动词
情态动词
系动词
及物动词(vt.) vs 不及物动词(vi.)
I see a bird.
I see.
The job will be finished.
助动词:帮助谓语动词表达精确含义。(时态、语态)
You should close the window.
情态动词:表示人对某种行为的情绪和态度。
(能 / 可能 / 应该 / 必须)
Lihua is a teacher.
系动词:把“事物”和“属性”联系起来
The leaves turn yellow.
You look tired.
形容词(adj.)
blue sky
修饰名词,表示特征。
beautiful girl
副词(adv.)
用来说明时间、地点、程度、方式等概念。
可以修饰动词、形容词、副词。
I sit still.
I am so cool.
I push the door very hard.
数词(num.)
one two three four 基数词
表示数量或顺序
first second third fourth 序数词
代词(pron.)
用于代替名词以及起名词作用的词
人称 主格 宾格 形容词性
物主代词 名词性
物主代词 反身代词
第一人称 单数 I me my mine myself
复数 we us our ours ourselves
第二人称 单数 you you your yours yourself
复数 you you your yours yourselves
第三人称 单数 he him his his himself
she her her hers herself
it it its - itself
复数 they them their theirs themselves
人称代词
代词
单数 复数
this(这个) these(这些)
that(那个) those(那些)
it (这)
指示代词
用来起指示作用,或用来代替前面已提到过的名词。
自我检测:
代词的分类和形式
冠词(art.)
a / an / the
I have an apple
位于名词前,帮助说明名词所指的人或事物
I have a pen
The apple is red.
介词(prep.)
She looked at me.
表示名词与句中其它词的关系
感叹词(interj.)
表示说话时的情感。
Oh, hello, well, please
连词(conj.)
Ladies and gentlemen,…
I am ugly but I am gentle.
连接词与词、短语与短语或句与句
句子成分和基本句型
Learning objectives
1.Master the basic sentence components of English.
掌握句子成分。
2.Learn to analyze the structure of the sentences.
学会分析句子结构。
语
法
脉
图
定义 :
构成句子的各个部分叫做句子成分。句子成分有主要成分和次要成分。
主要成分:主语和谓语
次要成分:表语、宾语、定语、状语、补足语、同位语
S 表示 “主语(subject)”
V 表示 “谓语(verb)”
O 表示 “宾语(object)”
P 表示 “表语(predicative)”
A 表示 “状语(adverbial)”
IO 表示 “间接宾语(indirect object)”
DO 表示 “直接宾语(direct object)”
C 表示 “宾语补足语(object complement)”
The baby is sleeping.
He drives fast.
One is enough.
To see is to believe.
Smoking is bad for health.
What she has said is true.
(名词)
(代词)
(数词)
(不定式)
(动名词)
(句子)
主语是谓语讲述的对象,表示所说的“是什么”或“是谁”。主语是谓语动作或状态的执行者。
Observe: What can be “subject” in a sentence
Subject
主 语
主语一般由名词(短语)、代词、数词、动名词(短语)、动词不定式
(短语)和主语从句等充当。
注意:主语一般位于句首,但若不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)、名词性从句作主语,常用it作形式主语,则把真正的主语放在句后。
It drives me mad to teach her.
It’s a pity that you missed the exciting football match.
Find the subject in the sentence
Twenty years is a short time in history.
The poor are now living in the shelter.
Running is good for our health.
To study hard is your duty.
She likes dancing.
What I want is some apples .
Verb
谓 语
说明主语所做的动作或具有的特征和状态,有完整的时态和语态。一般在主语之后。
谓语中最重要的是谓语动词 (通常由实义动词充当),
它有时态,语态的变化,并受主语人称和数的影响。
实义动词 有实在意义并能独立作谓语 read eat look drink
助动词 本身没有意义,不单独作谓语,协助主要动词构成谓语 be have do will
情态动词 有一定词义,不能单独作谓语,后加动词原形 can must may need shall
系动词 有词义,但不能独立做谓语,必须和表语构成主系表结构 am is are keep stay sound feel become
动词的分类:
主谓(宾)
主系表
be动词 am, is , are , was, were
表变化类动词 become, get, turn, grow, go
感官动词 look, sound, smell, taste, feel
延续性动词 remain, stay, keep
英文中常见的系动词
4. We have finished reading this book.
5. They can speak English well.
助动词和情态动词须和
实义动词一起构成谓语
2. He looked after two boys.
找出句子中的谓语
6. My sister is crying over there.
1. A tiger eats meat.
3. He doesn’t like fruit.
注意:复合谓语的划分要把时态、被动语态、情态动词和否定词归入进去。
宾语表示动作的对象,是动作的承受者。
宾语一般位于及物动词和介词之后。
Object
宾 语
Observe: What can be “object” in a sentence
(句子)
Show your book, please.
She didn't know anything.
They want to know my idea.
I like staying with you.
Did you know what she want
(名词 )
( 代词)
(不定式)
(动名词短语)
宾语一般由名词、代词、不定式、动名词(短语)及宾语从句等充当
注意:不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)、名词性从句作宾语,常用it作形式宾语,则把真正的宾语放在句后。
Some students find it difficult to study English.
Most of us think it no use arguing with her.
Miss Tan teaches us English.
双宾语(IO + DO)
在动词后方所跟的双宾语中
表示物的叫做直接宾语direct object(简称“直宾”)
表示人的叫做间接宾语indirect object(简称“间宾”)
S
V
DO
IO
常见接双宾语的动词:teach, buy, bring, take, give, send, sell, show, tell, write, lend, make ...
He gave me a pen.
IO DO
We bought him a gift.
IO DO
He wrote me a letter.
IO DO
He gave a pen to me.
DO IO
We bought a gift for him.
DO IO
He wrote me a letter to me.
DO IO
双宾语易位
常借助介词to的常用动词
teach/tell sb. sth =
teach/tell sth. to sb.
take/bring/give sb. sth=
take/bring/give sth to sb.
send/write sb. sth.=
send/write sth. to sb.
show sb. sth.=
show sth. to sb.
常借助介词for的常用动词
buy sb. sth=
buy sth. for sb.
lend sb. sth.(借)=
lend sth. for sb.
make sb. sth=
make sth. for sb.
双宾语易位
VS
Complement
宾语补足语
英语中有些及物动词接宾语后,意义仍然不完整,还需要一个句子成分来补充说明宾语的意义,状态等,这就是宾语补足语。
1. They made her their monitor.
2. The fire left him homeless.
3. When he woke up, he found himself lying in the street.
4. When he came to himself, he found himself surrounded by his family and friends.
5. The farmer asked us to have dinner.
6. We saw him play soccer.
名词
形容词
过去分词
现在分词
(省略to不定式)
动词不定式短语
1. His father named him Dongming.
2. They painted their boat white.
3. You mustn’t force him to lend his money to you.
4. We saw her entering the room.
5. We found everything in the lab in good order.
6. I want your homework done on time.
Find the object complement in the sentence
My mom made me a cake.
My mom made a cake for me.
S
V
DO
IO
S
V
DO
IO
My mom made me happy.
S
V
O
OC 宾补
区分以下句子成分:宾补?双宾语?
My mom made me a fool.
S
V
O
OC 宾补
Attributive
定语
定语是用于对名词或代词起修饰、限定作用的词、短语或句子。
注意:单个词作定语时常放在被修饰词之前(前置定语),
而短语或从句作定语时,则放在被修饰词之后(后置定语)。
Observe: What can be “Attributive” in a sentence
常用作定语的有名词、代词、数词、形容词、副词、介词短语、动名词、动词不定式、现在分词、过去分词、定语从句等。
(1)形容词作定语 The black bike is mine.
(2)代词作定语 What's your name
(3)名词作定语 They made some paper flowers.
(4)介词短语作定语The boys in the room are in Class Three,Grade One.
(5)不定式作定语 I have no time to travel in spring.
(6)从句作定语 The tall boy who is standing there is Peter.
(7)过去分词作定语 There are fallen leaves on the ground.
1.The letter on the desk is for Mr Wu.
2.The woman with a baby in her arms is his mother.
3.She carried a basket full of eggs.
4.It’s a city far from the coast.
5.He has enough money to buy a car.
6.The man downstairs was trying to sleep.
7.There are lots of places of interest needing repairing in our city.
Find the attributive in the sentence
What is Adverbial
A (adverbial) 状语
1 He lives in Shenzhen.
A
2 You go to school by bus.
A
3 He was born in 1918.
A
状语(A):是用来说明动词、形容词、副词或整个句子的成分。
常由副词,介词+其他担任。
修饰动词时可以放在动词之前,也可以放在动词之后;修饰形容词或副词时放在它们之前。
地点状语
方式状语
时间状语
The students study hard.
I often write to him.
The bag is too heavy.
副词
You each have a chance to go to college.
We students should put our heart into the study.
I am Li Hua, a Chinese student studying in London.
The thought came to him that Mary had probably fallen ill.
Appositive
同位语
同位语用于对名词或代词的进一步解释说明,常位于名词或代词之后。
常用作同位语的有名词、名词短语、数词、代词、同位语从句等。
I met my best friend Tom at the station yesterday.
↓
主语
↓
谓
语
↓
定语
↓
宾
语
↓
同位语
↓
状
语
分析句子成分:
I.选出下列句子中画线部分的成分
1. We all study hard at English.
A.主语 B.谓语 C.宾语 D.表语
2. Betty likes her new bike very much.
A.主语 B.谓语 C.宾语 D.表语
3. My brother is a policeman.
A.主语 B.谓语 C.宾补 D.表语
4. Were you at home last night
A.定语 B.状语 C.宾补 D.表语
即时训练
5. Winter is the coldest season of the year.
A.定语 B.状语 C.宾补 D.表语
6. He often walks in the park.
A.定语 B.状语 C.宾语 D.表语
7. Mary asked me to help her yesterday.
A.定语 B.状语 C.宾补 D.表语
8. He bought me a nice present last week.
A.宾语 B.直接宾语 C.间接宾语 D.宾补
9. His parents are doctors.
A.宾语 B.表语 C.谓语 D.定语
10. I'll get you some tea now.
A.主语 B.直接宾语 C.间接宾语 D.宾补
11. My mother told us an interesting story last night.
A.表语 B.直接宾语 C.间接宾语 D.宾补
12. He has read the book twice.
A.主语 B.谓语 C.表语 D.宾语
13. They seemed unhappy when they heard the news.
A.表语 B.谓语 C.宾语 D.定语
14. Do you have something to eat
A.状语 B. 定语 C.宾语 D.宾补
15. We made him our monitor.
A.宾语 B.定语 C.状语 D.宾补
Welcome Unit
Discovering Useful Structures
P6
S (subject) 主语
V (verb) 动词
O (object) 宾语
P (predicative) 表语
A (adverbial) 状语
DO (direct object) 直接宾语
IO (indirect object) 间接宾语
OC (object complement) 宾语补足语
Sentence structure Sentence
SV All of us laughed!
SVO I miss my grandma.
SP The teacher was kind and friendly.
S V IO DO He told us a funny story.
S V OC I found most of my classmates and teachers friendly and helpful.
SVA He talked too much.
SVOA I had my first maths class at senior high school.
There be... There's a lot to explore at senior high school.
Study the sentence structures.
All of us laughed!
I miss my grandma.
The teacher was kind and friendly.
He told us a funny story.
I found most of my classmates and teachers friendly and helpful.
主语+谓语 (SV)
主语+谓语+宾语 (SVO)
主语+谓语+表语 (SVP)
主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语 (SV IO DO)
主语+谓语+宾语+宾补 (SVOC)
He talked too much.
I had my first maths class at senior high school.
There’s a lot to explore at senior high.
主语+谓语+状语 (SVA)
主语+谓语+宾语 +状语(SVOA)
There be句型
Basic Sentence Structures
英文中基本的句子结构有以下五种:
1. 主+谓(不及物动词) SV
2. 主+谓(及物动词)+宾语 SVO
3. 主+系动词+表语 SVP
4. 主+谓(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语
5. 主+谓(及物动词)+宾语+宾语补足语 SVOC
SV IO DO
6. There be 句型
SV 主语+谓语(不及物动词Vi.)
①
此句型中 “主语+不及物动词/词组”构成句子的主体部分,不及物动词后不能直接带宾语。
注意:有时为了表示发生的频率、原因、结果、目的、地点或时间等,可以有状语来修饰。
例1 Class begins.
例3 Her mother has gone abroad.
例2 The rain has stopped.
例4 The red sun rise in the east.
状语修饰动词
状语修饰动词
②
SVO 主语+谓语(及物动词Vt.)+宾语
此句型中谓语是及物动词,其后必须跟宾语才能使句意表达完整。
注意:一些不及物动词后面加介词相当于一个及物动词,之后可加宾语。Vi+prep.=Vt.
例1 You must listen to your teacher.
例2 My father arrived in London yesterday.
例3 He is laughing at the crippled woman.
例4 I’ll write about my football team in my
future books.
③
SVP 主语+系动词+表语
此类型的句子,谓语动词不能表达一个完整的意思,必须加上一个表明主语性质或状态的表语,才能表达完整的意思。
例1 She became a singer.
例2 My brother is out now.
例3 Breakfast smells good.
④
SV IO DO
主语+谓语(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语
例2 I bought Tom a birthday gift.
间接宾语
直接宾语
例1 I showed her my photos.
间接宾语
直接宾语
常见的可接双宾语的动词有:give, send, bring, owe, take, offer, pass, lend, tell, return, promise, show, write, throw, hand, award, grant(授予)等。
⑤
SVOC
主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语+宾语补足语
在某些及物动词的后面,需要用一个宾语再加一个宾补才能表达完整的意思。
常见的可做宾语补足语的有:名词,形容词,介词短语,动词不定式,不带to的动词不定式等
例1 I will make you captain.
例2 You should keep the room clean and tidy.
例3 The engineer made the robort clean
the room everyday.
6.1 There is an apple on the table.
V S A
6.2 There are seven days in a week.
V S A
6.3 There is milk and bread.
V S
在这种结构中,S和V是倒置的。V的数由S的第一个名词决定。
⑥
There be句型 某地存在什么东西
例句:我们学校有很多很漂亮的教学楼。
There are many beautiful teaching buildings in our school.
Group Work
Finish task 2 on P6.
Read the sentences and analyse the structures.
1 The 100-year-old school lies in the centre of
the city.
2 We must act.
3 The maths homework looks easy.
4 The teacher found the classroom empty.
S
V
A
S
V
S
P
S
V
O
C
Read the sentences and analyse the
structures.
5 My mum bought me a new dictionary.
6 Tom is looking forward to meeting the new
exchange student.
7 There is an English Corner at our school.
8 We had chemistry in the newly built lab.
S
V
IO
DO
S
V
O
There be ......
S
V
O
A
1. That dream has come true!
2. Tim and his classmates are living on a ship!
3. They also learn about ships and the sea.
S
V
S
V
S
V
A
O
Read the passage and analyse the structures
of the underlined sentences.
4. Tim writes his parents an email every week and tells them what happened on the ship.
5. There’s always something exciting to do.
6. Studying and doing homework seem
much more fun.
S
V
IO
DO
V
IO
There be ......
S
P
DO
并列句
Answers
Thank you
【语境应用】判断句子结构类型。
1) Everybody smiled.
2) The car caught fire.
3) Did the milk turn sour
4) He bought his wife a dress.
5) Roy found his new job rather boring.
6) Your brother got up at 10 o’clock.
7) I haven’t seen Daniel for long.
SVOC
SVA
SVOA
SV
SVO
SP
SVIODO
翻译练习:
1. 他们走着,笑着。
2. 英语老师很友好。
3. 树上有一只可爱的小鸟。
4. 他给她妹妹买了一架钢琴。
5. 老师发现教室是空的。
They walked and laughed.
The English teacher is friendly.
There is a lovely bird in the tree.
He bought his sister a piano.
The teacher found the classroom empty.
翻译练习:
6. 我听到她正在唱歌。
7. 英语作业看上去很简单。
8. 我们笑得很开心。
9. 我们学校有许多学生。
10. 她是一个爱交际的女孩。
I heard her singing a song.
The English homework looks easy.
We laugh happily.
There are many students in our school.
She is an outgoing girl.
