2024年中考 英语总复习 语法专题突破 简单句及句子种类(含答案)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2024年中考 英语总复习 语法专题突破 简单句及句子种类(含答案) |
|
|
| 格式 | doc | ||
| 文件大小 | 307.0KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-02-02 11:54:23 | ||
图片预览


文档简介
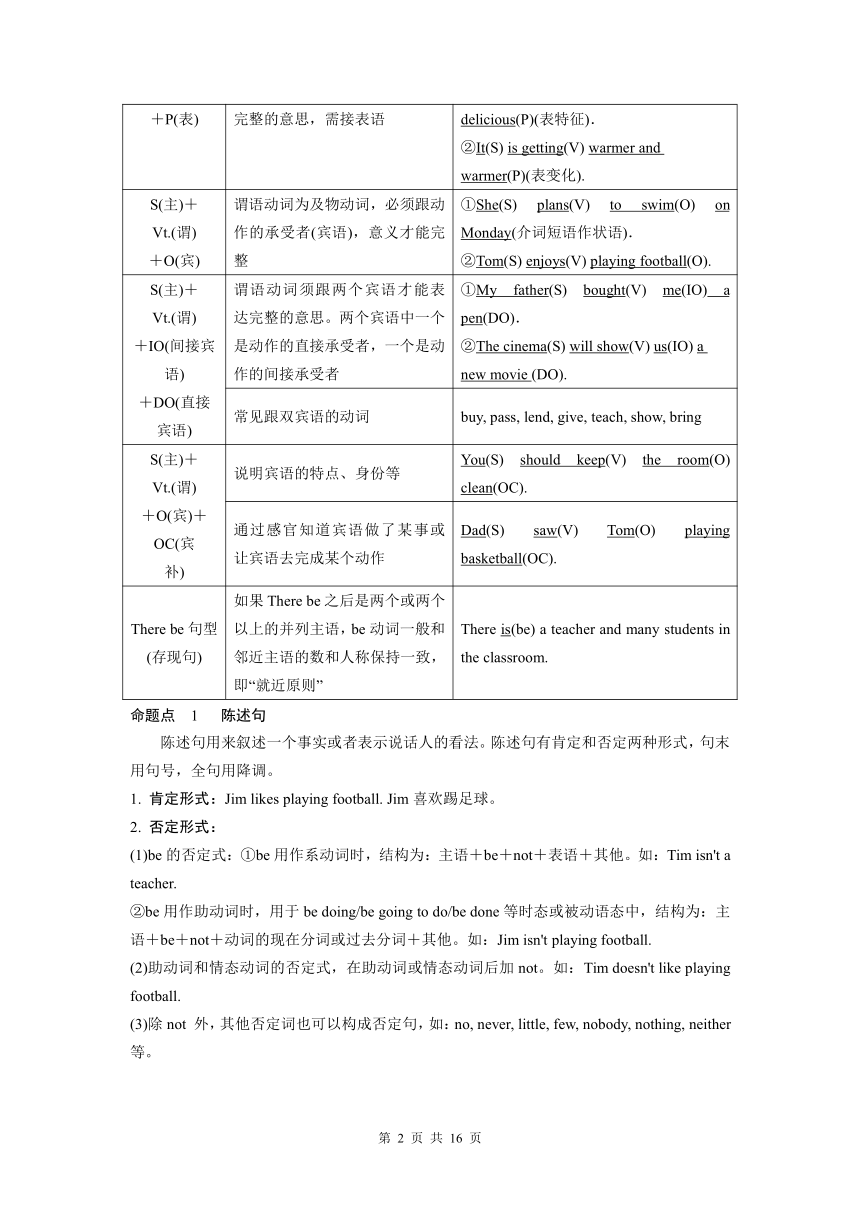
专题十一 简单句及句子种类
知识导图
考法精讲
英语中,只含有一个主谓结构并且句子各成分都只由单词或短语构成的独立句子或分句叫作简单句。在简单句中,主语和谓语是句子的主干和核心。除口语中的一些特殊句型外,英语的句子必须含有主语和谓语,否则不成句子,无法完整地表达相应的意思。除了主语和谓语外,简单句中还可以有宾语、表语、补语、状语、定语等。
简单句的五大基本句型
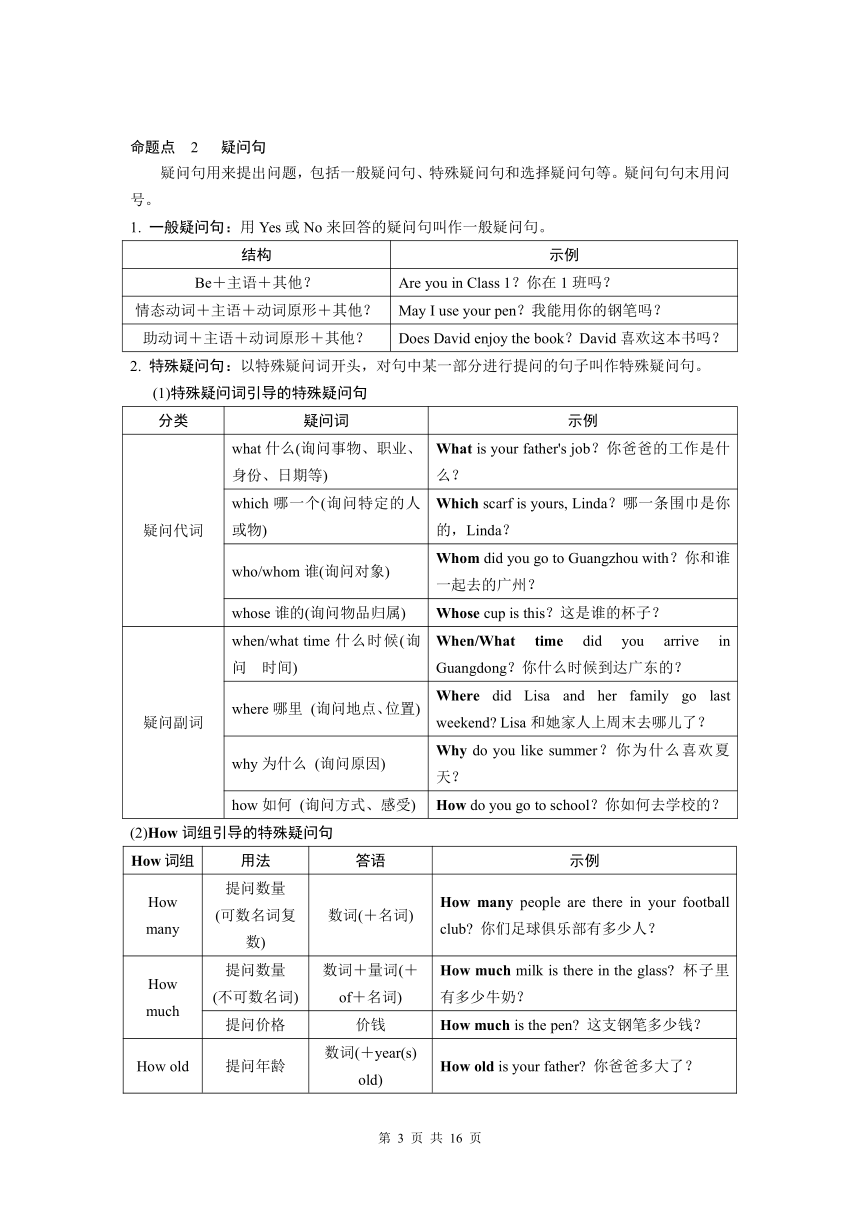
S(主)+Vi.(谓) 谓语动词为不及物动词,能表达完整的意思。不及物动词后可接状语进行修饰 ①They(S) talked(V) for half an hour(介词短语作状语).②The pen(S) writes(V) smoothly(副词作状语).
S(主)+V.(系)+P(表) 谓语动词为连系动词,不能表达完整的意思,需接表语 ①This kind of food(S) tastes(V) delicious(P)(表特征).②It(S) is getting(V) warmer and warmer(P)(表变化).
S(主)+Vt.(谓)+O(宾) 谓语动词为及物动词,必须跟动作的承受者(宾语),意义才能完整 ①She(S) plans(V) to swim(O) on Monday(介词短语作状语).②Tom(S) enjoys(V) playing football(O).
S(主)+Vt.(谓)+IO(间接宾语)+DO(直接宾语) 谓语动词须跟两个宾语才能表达完整的意思。两个宾语中一个是动作的直接承受者,一个是动作的间接承受者 ①My father(S) bought(V) me(IO) a pen(DO).②The cinema(S) will show(V) us(IO) a new movie (DO).
常见跟双宾语的动词 buy, pass, lend, give, teach, show, bring
S(主)+Vt.(谓)+O(宾)+OC(宾补) 说明宾语的特点、身份等 You(S) should keep(V) the room(O) clean(OC).
通过感官知道宾语做了某事或让宾语去完成某个动作 Dad(S) saw(V) Tom(O) playing basketball(OC).
There be句型(存现句) 如果There be之后是两个或两个以上的并列主语,be动词一般和邻近主语的数和人称保持一致,即“就近原则” There is(be) a teacher and many students in the classroom.
命题点 1 陈述句
陈述句用来叙述一个事实或者表示说话人的看法。陈述句有肯定和否定两种形式,句末用句号,全句用降调。
1. 肯定形式:Jim likes playing football. Jim喜欢踢足球。
2. 否定形式:
(1)be的否定式:①be用作系动词时,结构为:主语+be+not+表语+其他。如:Tim isn't a teacher.
②be用作助动词时,用于be doing/be going to do/be done等时态或被动语态中,结构为:主语+be+not+动词的现在分词或过去分词+其他。如:Jim isn't playing football.
(2)助动词和情态动词的否定式,在助动词或情态动词后加not。如:Tim doesn't like playing football.
(3)除not 外,其他否定词也可以构成否定句,如:no, never, little, few, nobody, nothing, neither等。
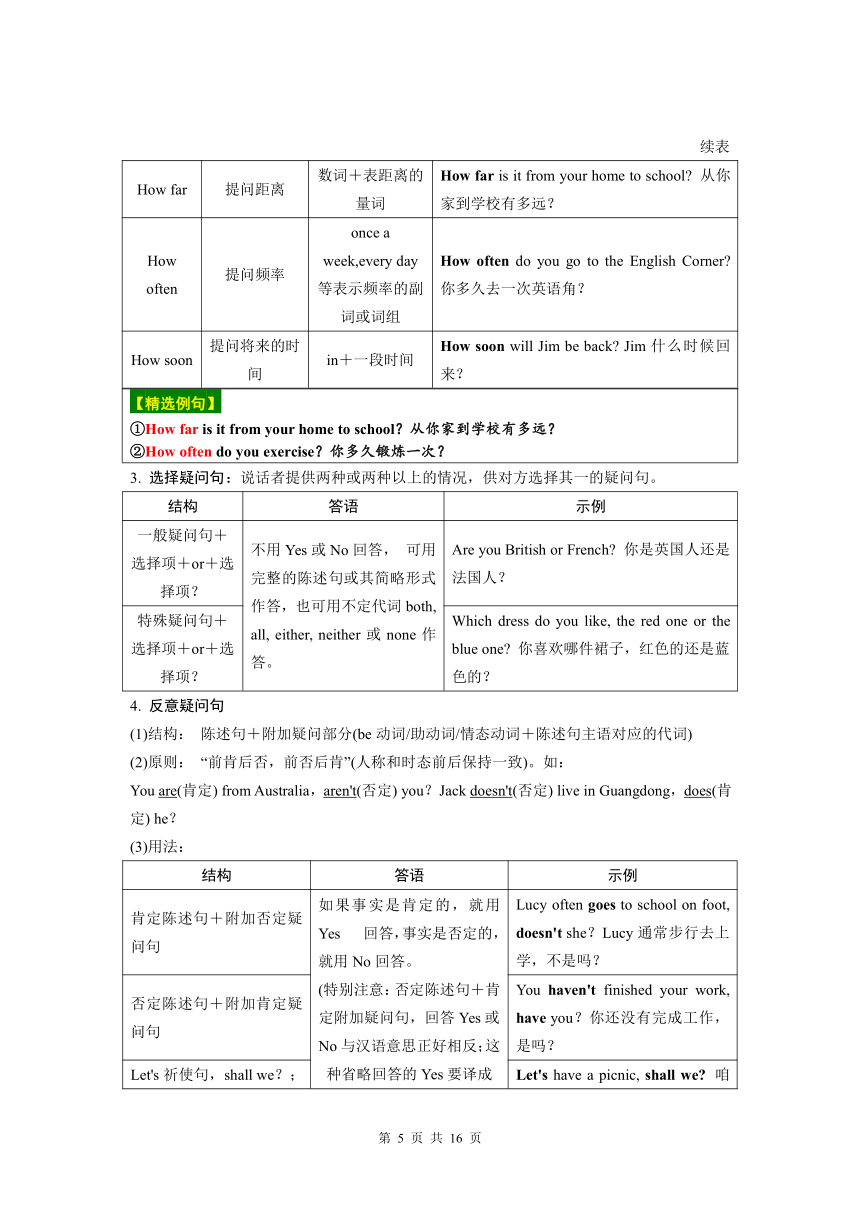
命题点 2 疑问句
疑问句用来提出问题,包括一般疑问句、特殊疑问句和选择疑问句等。疑问句句末用问号。
1. 一般疑问句:用Yes或No来回答的疑问句叫作一般疑问句。
结构 示例
Be+主语+其他? Are you in Class 1?你在1班吗?
情态动词+主语+动词原形+其他? May I use your pen?我能用你的钢笔吗?
助动词+主语+动词原形+其他? Does David enjoy the book?David喜欢这本书吗?
2. 特殊疑问句:以特殊疑问词开头,对句中某一部分进行提问的句子叫作特殊疑问句。
(1)特殊疑问词引导的特殊疑问句
分类 疑问词 示例
疑问代词 what什么(询问事物、职业、身份、日期等) What is your father's job?你爸爸的工作是什么?
which哪一个(询问特定的人或物) Which scarf is yours, Linda?哪一条围巾是你的,Linda?
who/whom谁(询问对象) Whom did you go to Guangzhou with?你和谁一起去的广州?
whose谁的(询问物品归属) Whose cup is this?这是谁的杯子?
疑问副词 when/what time什么时候(询问 时间) When/What time did you arrive in Guangdong?你什么时候到达广东的?
where哪里 (询问地点、位置) Where did Lisa and her family go last weekend Lisa和她家人上周末去哪儿了?
why为什么 (询问原因) Why do you like summer?你为什么喜欢夏天?
how如何 (询问方式、感受) How do you go to school?你如何去学校的?
(2)How词组引导的特殊疑问句
How词组 用法 答语 示例
How many 提问数量(可数名词复数) 数词(+名词) How many people are there in your football club 你们足球俱乐部有多少人?
How much 提问数量(不可数名词) 数词+量词(+of+名词) How much milk is there in the glass 杯子里有多少牛奶?
提问价格 价钱 How much is the pen 这支钢笔多少钱?
How old 提问年龄 数词(+year(s) old) How old is your father 你爸爸多大了?
How long 提问持续的时间 “for+一段时间”或“since+过去的时间点/从句” How long did you stay in Guangzhou?你在广州待了多久?
提问物体长度 物体长度 How long is the river 这条河有多长?
续表
How far 提问距离 数词+表距离的量词 How far is it from your home to school 从你家到学校有多远?
How often 提问频率 once a week,every day等表示频率的副词或词组 How often do you go to the English Corner 你多久去一次英语角?
How soon 提问将来的时间 in+一段时间 How soon will Jim be back Jim什么时候回来?
【精选例句】①How far is it from your home to school?从你家到学校有多远?②How often do you exercise?你多久锻炼一次?
3. 选择疑问句:说话者提供两种或两种以上的情况,供对方选择其一的疑问句。
结构 答语 示例
一般疑问句+选择项+or+选择项? 不用Yes或No回答, 可用完整的陈述句或其简略形式作答,也可用不定代词both, all, either, neither或none作答。 Are you British or French 你是英国人还是法国人?
特殊疑问句+选择项+or+选择项? Which dress do you like, the red one or the blue one 你喜欢哪件裙子,红色的还是蓝色的?
4. 反意疑问句
(1)结构: 陈述句+附加疑问部分(be动词/助动词/情态动词+陈述句主语对应的代词)
(2)原则: “前肯后否,前否后肯”(人称和时态前后保持一致)。如:
You are(肯定) from Australia,aren't(否定) you?Jack doesn't(否定) live in Guangdong,does(肯定) he?
(3)用法:
结构 答语 示例
肯定陈述句+附加否定疑问句 如果事实是肯定的,就用Yes 回答,事实是否定的,就用No回答。(特别注意:否定陈述句+肯定附加疑问句,回答Yes或No与汉语意思正好相反;这种省略回答的Yes要译成“不”,No要译成“是”) Lucy often goes to school on foot, doesn't she?Lucy通常步行去上学,不是吗?
否定陈述句+附加肯定疑问句 You haven't finished your work, have you?你还没有完成工作,是吗?
Let's祈使句,shall we?;Let us祈使句,will you? Let's have a picnic, shall we 咱们野餐吧,好吗?
肯定祈使句,will/won't you?;否定祈使句, will you? Be sure to come on time, will you?保证按时来,好吗?
即时训练
1. —Larry seldom has breakfast at home, ________?
—No. Because his home is too far from his workplace.
A. has he B. does he C. doesn't he
2. —Can you tell me ________ it took you to finish this painting
—For about two weeks.
A. how long B. how often C. how soon
3. —________ is the weather like today
—It's sunny!I think we can go out for a picnic.
A. What B. Why C. How
命题点 3 祈使句
祈使句表示请求、命令、建议或劝告等。主语通常被省略,谓语动词用原形,句末用感叹号或句号。主要有以下四种形式:
句式 肯定形式 否定形式
Do型:(Please+)动词原形+其他! (Please) Sit down! (Please)Don't draw here!
Be型:Be+表语! Be careful! Don't be late for class!
Let型:Let+宾语+动词原形+其他. Let's make a salad. Don't make noises.
No型:No+名词/动名词! / No smoking!
【拓展】
(1)祈使句的回答用一般将来时,如:—Please remember to take an umbrella. 请记得带一把伞。
—Yes, I will. 好,我会的。
(2)“祈使句,and/or+陈述句(表结果)”结构。此结构可以转换成if引导的条件状语从句,如:
Hurry up, or you'll be late for class. 快点儿,否则你上课将会迟到。
→If you don't hurry up, you'll be late for class. 如果你不快点儿,你上课就会迟到。
【巧学妙记】祈使句,无主语,动词原形作开始;否定式,加don't,放在动词的前面;表命令,提请求,please可前也可后。
命题点 4 感叹句
感叹句用来表示喜、怒、哀、乐等强烈感情,通常用What或How引导。
形式 结构 示例
What引导 What+ a/an+形容词+可数名词单数(+主语+谓语)! What an excellent girl (she is)!多么优秀的女孩啊!
What+形容词+可数名词复数(+主语+谓语)! What beautiful flowers (they are)!多么漂亮的花呀!
What+形容词+不可数名词(+主语+谓语)! What bad weather (it is)!天气真糟糕!
续表
How引导(6年3考) How+形容词/副词+主语+谓语! How useful the suggestions are! 这些建议多么有用呀!
How+主语+谓语! How time flies!时光飞逝!
【巧学妙记】感叹句,并不难;what, how放句前。how后跟形或副;what后面名词连。
即时训练
4. Andy taught himself how to play the guitar on the website. ________ clever boy he is!
A. How B. What C. What a
5. ________ kind Lucy is! She often takes food to the animals in the park.
A. How B. What C. What a
6. ________ interesting story! We couldn't help laughing.
A. What a B. What an C. What
7. These students get the key points of planting vegetables quickly. ________ fast they learn!
A. How B. What C. What a
8. —________ useful information our English teacher provided for us!
—So it was. Thanks to him, we were able to complete the task.
A. How B. What C. What a
命题点 5 There be 句型(存现句)
1. 基本结构与用法
(1)结构:“There be +主语(人或物)+地点状语”,表示“某处有某人(或某物)”。
(2)用法:遵循“就近原则”。be动词必须和主语在人称和数上保持一致。如果主语部分是两个或两个以上的并列主语时,be动词一般和邻近主语的数和人称保持一致,即“就近原则”。如:
①There on the desk.
②There in the bottle.
③There on the wall.
④ There is a desk and five chairs here.
(单数) (单数+复数)
There here.
2. There be句型的时态
There be句型时态的变化体现在be动词上, 而且可以和助动词或情态动词连用。具体用法:
(1)一般现在时There is/are...;
(2)一般过去时There was/were...;
(3)一般将来时There will be... /There is/are going to be...;
(4)现在完成时There has/have been...;
(5)含情态动词There can/may/should be...。
3. There be句型的不同句式
(1)否定句:be动词后加not, no或not any。如:There is no such thing as true failure. 没有真正的失败。[冀教九(全)Unit 10 P152]
(2)一般疑问句:be动词提到句首,some变any。如:There are some apples in the fridge. 冰箱里有一些苹果。→Are there any apples in the fridge?冰箱里有苹果吗?
4. There be 句型和have的区别
There be意为“某处有某人(或某物)”;have意为“某人(或某地)拥有某物”,表示“所有、拥有关系”。如:There is a girl in the room. 房间里有一个女孩。I have a new computer. 我有一台新电脑。
【精选例句】①When the earthquake is over, there is still plenty of danger.当地震结束时,仍然有很多危险。[冀教九(全)Unit 3 P42]②There are a lot of good restaurants in Sunville.在桑维尔有许多不错的餐馆。[人教九(全)Unit 3 P136]③Is there a good movie theater near here?这附近有好的电影院吗?[人教八(上)Unit 4 P98]
命题点 6 主谓一致
主谓一致,即谓语动词必须和主语在人称和数上保持一致,这种一致常由三种不同的原则所支配,即就近一致原则、语法一致原则和意义一致原则。
1. 就近一致原则:谓语动词的形式与它临近的名词或代词一致(与离它最近的主语保持一致)。
情况 示例
由either... or..., neither... nor..., not only... but also... 连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词和距离较近的主语在数上保持 一致。 Either Jane or Tom knows the answer. 要么是Jane要么就是Tom知道答案。Not only Mia but also I like singing. 不但Mia喜欢唱歌,而且我也喜欢唱歌。
There be... 句式中的be动词与最近的主语在数上保持一致。 There is an English book and three storybooks on the desk. 桌子上有一本英语书和三本故事书。
2. 语法一致原则:主语和谓语通常是在语法形式上取得一致,即单数主语谓语动词用单数,复数主语谓语动词用复数。
主语成分 谓语 示例
单数名词或代词 单数 She believes that it is important to have a healthy diet. 她认为有一个健康的饮食很重要。
动词不定式短语、动名词短语或从句单数 To get up early is a good habit. 早起是个好习惯。
续表
the number of+可数名词复数 单数 The number of candles is the person's age. 蜡烛的数量是过生日的人的年龄。[人教七(下)Unit 10 P59]
one of+可数名词复数 One of my favorite films is Cinderella. 我最喜欢的电影之一是《灰姑娘》。
either, neither, each, every或no +单数名词, 以及由some, any, no, every构成的复合不定代词 Everyone is born with the ability to learn. 每个人生来就有学习的能力。[人教九(全)Unit1 P6]
a number of+可数名词复数 复数 A number of workers are needed for the project. 这个项目需要一些工人。
both... and... 连接两个主语 Both Tom and Sam play the drums well. Tom和Sam都打鼓打得很好。
由and连接两个名词 两个名词指不同的人或物 复数 Joyce and Arthur are talking about the newspaper. Joyce和Arthur在谈论这份报纸。 [上海牛津八(下)Module 2 P58]
两个名词指同一人或物 单数 The writer and actor has come. 这个既是作家又是演员的人已经来了。
主语后面跟有with, together with, except, as well as, rather than, besides, including, but等词或结构 取决于主语的数 Everyone except Jim and Tim gets a new book. 除了Jim和Tim,所有人都得到了一本新书。
由“a lot of, lots of, plenty of, the rest of+ 名词”构成的短语 取决于短语后面的名词的数 There are a lot of interesting activities we can take part in. 有很多有趣的活动我们可以参加。
由“分数/百分数+名词”构成的短语 Two thirds of the work has been finished. 三分之二的工作已经完成了。
定语从句关系代词that, who, which 与先行词的数一致 A volunteer is someone who gives their time for free. 志愿者是指免费提供时间的人。
3. 意义一致原则:指概念一致,即谓语动词的形式要和主语所表达的概念一致。
主语 谓语 示例
集体名词(如:family/class/ team/group/public等) 取决于 主语意义 Jeff 's family is having a yard sale. Jeff家正在进行一场庭院拍卖。[人教八(下)Unit10 P73]It's 9:00 a.m. and Zhu Hui's family are at home. 现在是上午9点,朱辉的家人在家。[人教七(下)Unit6 P35]
不定代词all, most, more, some, any做主语 All the work has been finished. 所有的工作都已经完成了。All the students have gone. 所有的学生都走了。
续表
集合名词(如:people/police等) 复数 Finally, the police come and the men are taken away. 最后,警察来了,他们被带走了。[外研九(上)Module 4 P32]
the+姓氏名词复数,表示“……一家”或“……夫妇” The Smiths like travelling. Smith一家喜欢旅行。
the+形容词 表示一类人 The rich are not always happy. 富人并不总是快乐的。
表示重量、度量、时间、长度、价格、数学运算等的词或短语 单数 1,000 yuan has been raised. 已经筹集了1000元。
即时训练
9. I eat vegetables every day, because eating vegetables ________ good for my body.
A. was B. is C. are
10. There ________ different kinds of fruits and some milk in the fridge. Let's make a salad.
A. is B. are C. was
11. Neither Lucy nor Amy ________ fried food. They think it's unhealthy for them.
A. like B. likes C. liked
12. The Greens often ________ family trips during the holidays. They think it's a good way to relax.
A. had B. has C. have
【好词佳句积累】 be good for...对……有好处 different kinds of不同种类的 in the fridge在冰箱里 make a salad制作沙拉 during the holidays在假期期间 it's a good way to do sth.它是一个做某事的好方式
13. The number of the teachers in the school ________ about 300 and one fifth of them are women.
A. is B. are C. was
综合提升
语法选择
A. 小题夯基
1. Everything was magical. ________ excited David was!
A. How B. What C. What an
2.“Wow!” she cried proudly. “________ high my butterfly flies!”
A. What B. What a C. What an D. How
3. ________ smart the driverless car is! I really want to have one.
A. What B. What a C. What an D. How
4. ________ interesting movie it is! I want to see it again.
A. What B. What an C. How
5. —________ do you learn these words by heart
—By using them in different ways.
A. When B. How C. Why
6. Look! There ________ some information about animals in this book.
A. is B. are C. was
7. The young ________ not allowed to start eating at first before the elders pick up the chopsticks in China.
A. is B. were C. are
【好词佳句积累】 the number of……的数量 sb. be (not) allowed to do sth.某人(不)被允许做某事 at first首先 pick up捡起;拾起
B.微语篇提能
中华优秀传统文化·银花丝工艺 The Silver Flower Silk(银花丝) is a traditional hand made work of art. There __1__ two styles in the Silver Flower Silk Craft(工艺).
Born in 1962, Dao An became interested in drawing from childhood, and she worked in the Silver Flower Silk Craft Company in 1982. People found __2__ beautiful her paintings were, so she was made to create Silver Flower Silk works, but she __3__ not satisfied with that. She worked so hard to make better works. She has become one of the very few masters of the craft in China.
About twenty years has passed since she took up the job. Many Silver Flower Silk factories were shut down because of the market. Dao An didn't want the skill to go away. “__4__ important traditional hand made work of art it is. And the Silver Flower Silk __5__ worth being known by more people. We should stick to spreading this craft and have good creativity to develop it better,” she said.
1. A. is B. are C. was
2. A. what B. what a C. how
3. A. is B. was C. are
4. A. What B. What an C. How
5. A. is B. are C. was
【语篇研读】What:讲述了道安对非遗手工艺品——银花丝工艺传承的故事。Why:旨在鼓励学生了解中华传统技艺的发展现状,感受非遗技艺的魅力,激发学生对优秀传统文化的兴趣,引导学生积极传承中华优秀传统文化。How:①文体特征:记叙文。②语言特点:本文使用“became interested in”, “worked so hard to make better works”, “has become one of the very few masters of the craft in china”讲述了传承人道安传承银花丝工艺的历程以及成就。
专题十一 简单句及句子种类
【即时训练】
1. B 2. A 3. A 4. C 5. A 6. B 7. A 8. B 9. B 10. B 11. B 12. C 13. A
【综合提升】
A. 1. A 2. D 3. D 4. B 5. B 6. A 7. C
B. 【主旨大意】本文是一篇记叙文。主要讲述了银花丝工艺的传承人道安40多年来努力传承银花丝工艺的故事。
1. B 2. C 3. B 4. B 5. A
知识导图
考法精讲
英语中,只含有一个主谓结构并且句子各成分都只由单词或短语构成的独立句子或分句叫作简单句。在简单句中,主语和谓语是句子的主干和核心。除口语中的一些特殊句型外,英语的句子必须含有主语和谓语,否则不成句子,无法完整地表达相应的意思。除了主语和谓语外,简单句中还可以有宾语、表语、补语、状语、定语等。
简单句的五大基本句型
S(主)+Vi.(谓) 谓语动词为不及物动词,能表达完整的意思。不及物动词后可接状语进行修饰 ①They(S) talked(V) for half an hour(介词短语作状语).②The pen(S) writes(V) smoothly(副词作状语).
S(主)+V.(系)+P(表) 谓语动词为连系动词,不能表达完整的意思,需接表语 ①This kind of food(S) tastes(V) delicious(P)(表特征).②It(S) is getting(V) warmer and warmer(P)(表变化).
S(主)+Vt.(谓)+O(宾) 谓语动词为及物动词,必须跟动作的承受者(宾语),意义才能完整 ①She(S) plans(V) to swim(O) on Monday(介词短语作状语).②Tom(S) enjoys(V) playing football(O).
S(主)+Vt.(谓)+IO(间接宾语)+DO(直接宾语) 谓语动词须跟两个宾语才能表达完整的意思。两个宾语中一个是动作的直接承受者,一个是动作的间接承受者 ①My father(S) bought(V) me(IO) a pen(DO).②The cinema(S) will show(V) us(IO) a new movie (DO).
常见跟双宾语的动词 buy, pass, lend, give, teach, show, bring
S(主)+Vt.(谓)+O(宾)+OC(宾补) 说明宾语的特点、身份等 You(S) should keep(V) the room(O) clean(OC).
通过感官知道宾语做了某事或让宾语去完成某个动作 Dad(S) saw(V) Tom(O) playing basketball(OC).
There be句型(存现句) 如果There be之后是两个或两个以上的并列主语,be动词一般和邻近主语的数和人称保持一致,即“就近原则” There is(be) a teacher and many students in the classroom.
命题点 1 陈述句
陈述句用来叙述一个事实或者表示说话人的看法。陈述句有肯定和否定两种形式,句末用句号,全句用降调。
1. 肯定形式:Jim likes playing football. Jim喜欢踢足球。
2. 否定形式:
(1)be的否定式:①be用作系动词时,结构为:主语+be+not+表语+其他。如:Tim isn't a teacher.
②be用作助动词时,用于be doing/be going to do/be done等时态或被动语态中,结构为:主语+be+not+动词的现在分词或过去分词+其他。如:Jim isn't playing football.
(2)助动词和情态动词的否定式,在助动词或情态动词后加not。如:Tim doesn't like playing football.
(3)除not 外,其他否定词也可以构成否定句,如:no, never, little, few, nobody, nothing, neither等。
命题点 2 疑问句
疑问句用来提出问题,包括一般疑问句、特殊疑问句和选择疑问句等。疑问句句末用问号。
1. 一般疑问句:用Yes或No来回答的疑问句叫作一般疑问句。
结构 示例
Be+主语+其他? Are you in Class 1?你在1班吗?
情态动词+主语+动词原形+其他? May I use your pen?我能用你的钢笔吗?
助动词+主语+动词原形+其他? Does David enjoy the book?David喜欢这本书吗?
2. 特殊疑问句:以特殊疑问词开头,对句中某一部分进行提问的句子叫作特殊疑问句。
(1)特殊疑问词引导的特殊疑问句
分类 疑问词 示例
疑问代词 what什么(询问事物、职业、身份、日期等) What is your father's job?你爸爸的工作是什么?
which哪一个(询问特定的人或物) Which scarf is yours, Linda?哪一条围巾是你的,Linda?
who/whom谁(询问对象) Whom did you go to Guangzhou with?你和谁一起去的广州?
whose谁的(询问物品归属) Whose cup is this?这是谁的杯子?
疑问副词 when/what time什么时候(询问 时间) When/What time did you arrive in Guangdong?你什么时候到达广东的?
where哪里 (询问地点、位置) Where did Lisa and her family go last weekend Lisa和她家人上周末去哪儿了?
why为什么 (询问原因) Why do you like summer?你为什么喜欢夏天?
how如何 (询问方式、感受) How do you go to school?你如何去学校的?
(2)How词组引导的特殊疑问句
How词组 用法 答语 示例
How many 提问数量(可数名词复数) 数词(+名词) How many people are there in your football club 你们足球俱乐部有多少人?
How much 提问数量(不可数名词) 数词+量词(+of+名词) How much milk is there in the glass 杯子里有多少牛奶?
提问价格 价钱 How much is the pen 这支钢笔多少钱?
How old 提问年龄 数词(+year(s) old) How old is your father 你爸爸多大了?
How long 提问持续的时间 “for+一段时间”或“since+过去的时间点/从句” How long did you stay in Guangzhou?你在广州待了多久?
提问物体长度 物体长度 How long is the river 这条河有多长?
续表
How far 提问距离 数词+表距离的量词 How far is it from your home to school 从你家到学校有多远?
How often 提问频率 once a week,every day等表示频率的副词或词组 How often do you go to the English Corner 你多久去一次英语角?
How soon 提问将来的时间 in+一段时间 How soon will Jim be back Jim什么时候回来?
【精选例句】①How far is it from your home to school?从你家到学校有多远?②How often do you exercise?你多久锻炼一次?
3. 选择疑问句:说话者提供两种或两种以上的情况,供对方选择其一的疑问句。
结构 答语 示例
一般疑问句+选择项+or+选择项? 不用Yes或No回答, 可用完整的陈述句或其简略形式作答,也可用不定代词both, all, either, neither或none作答。 Are you British or French 你是英国人还是法国人?
特殊疑问句+选择项+or+选择项? Which dress do you like, the red one or the blue one 你喜欢哪件裙子,红色的还是蓝色的?
4. 反意疑问句
(1)结构: 陈述句+附加疑问部分(be动词/助动词/情态动词+陈述句主语对应的代词)
(2)原则: “前肯后否,前否后肯”(人称和时态前后保持一致)。如:
You are(肯定) from Australia,aren't(否定) you?Jack doesn't(否定) live in Guangdong,does(肯定) he?
(3)用法:
结构 答语 示例
肯定陈述句+附加否定疑问句 如果事实是肯定的,就用Yes 回答,事实是否定的,就用No回答。(特别注意:否定陈述句+肯定附加疑问句,回答Yes或No与汉语意思正好相反;这种省略回答的Yes要译成“不”,No要译成“是”) Lucy often goes to school on foot, doesn't she?Lucy通常步行去上学,不是吗?
否定陈述句+附加肯定疑问句 You haven't finished your work, have you?你还没有完成工作,是吗?
Let's祈使句,shall we?;Let us祈使句,will you? Let's have a picnic, shall we 咱们野餐吧,好吗?
肯定祈使句,will/won't you?;否定祈使句, will you? Be sure to come on time, will you?保证按时来,好吗?
即时训练
1. —Larry seldom has breakfast at home, ________?
—No. Because his home is too far from his workplace.
A. has he B. does he C. doesn't he
2. —Can you tell me ________ it took you to finish this painting
—For about two weeks.
A. how long B. how often C. how soon
3. —________ is the weather like today
—It's sunny!I think we can go out for a picnic.
A. What B. Why C. How
命题点 3 祈使句
祈使句表示请求、命令、建议或劝告等。主语通常被省略,谓语动词用原形,句末用感叹号或句号。主要有以下四种形式:
句式 肯定形式 否定形式
Do型:(Please+)动词原形+其他! (Please) Sit down! (Please)Don't draw here!
Be型:Be+表语! Be careful! Don't be late for class!
Let型:Let+宾语+动词原形+其他. Let's make a salad. Don't make noises.
No型:No+名词/动名词! / No smoking!
【拓展】
(1)祈使句的回答用一般将来时,如:—Please remember to take an umbrella. 请记得带一把伞。
—Yes, I will. 好,我会的。
(2)“祈使句,and/or+陈述句(表结果)”结构。此结构可以转换成if引导的条件状语从句,如:
Hurry up, or you'll be late for class. 快点儿,否则你上课将会迟到。
→If you don't hurry up, you'll be late for class. 如果你不快点儿,你上课就会迟到。
【巧学妙记】祈使句,无主语,动词原形作开始;否定式,加don't,放在动词的前面;表命令,提请求,please可前也可后。
命题点 4 感叹句
感叹句用来表示喜、怒、哀、乐等强烈感情,通常用What或How引导。
形式 结构 示例
What引导 What+ a/an+形容词+可数名词单数(+主语+谓语)! What an excellent girl (she is)!多么优秀的女孩啊!
What+形容词+可数名词复数(+主语+谓语)! What beautiful flowers (they are)!多么漂亮的花呀!
What+形容词+不可数名词(+主语+谓语)! What bad weather (it is)!天气真糟糕!
续表
How引导(6年3考) How+形容词/副词+主语+谓语! How useful the suggestions are! 这些建议多么有用呀!
How+主语+谓语! How time flies!时光飞逝!
【巧学妙记】感叹句,并不难;what, how放句前。how后跟形或副;what后面名词连。
即时训练
4. Andy taught himself how to play the guitar on the website. ________ clever boy he is!
A. How B. What C. What a
5. ________ kind Lucy is! She often takes food to the animals in the park.
A. How B. What C. What a
6. ________ interesting story! We couldn't help laughing.
A. What a B. What an C. What
7. These students get the key points of planting vegetables quickly. ________ fast they learn!
A. How B. What C. What a
8. —________ useful information our English teacher provided for us!
—So it was. Thanks to him, we were able to complete the task.
A. How B. What C. What a
命题点 5 There be 句型(存现句)
1. 基本结构与用法
(1)结构:“There be +主语(人或物)+地点状语”,表示“某处有某人(或某物)”。
(2)用法:遵循“就近原则”。be动词必须和主语在人称和数上保持一致。如果主语部分是两个或两个以上的并列主语时,be动词一般和邻近主语的数和人称保持一致,即“就近原则”。如:
①There on the desk.
②There in the bottle.
③There on the wall.
④ There is a desk and five chairs here.
(单数) (单数+复数)
There here.
2. There be句型的时态
There be句型时态的变化体现在be动词上, 而且可以和助动词或情态动词连用。具体用法:
(1)一般现在时There is/are...;
(2)一般过去时There was/were...;
(3)一般将来时There will be... /There is/are going to be...;
(4)现在完成时There has/have been...;
(5)含情态动词There can/may/should be...。
3. There be句型的不同句式
(1)否定句:be动词后加not, no或not any。如:There is no such thing as true failure. 没有真正的失败。[冀教九(全)Unit 10 P152]
(2)一般疑问句:be动词提到句首,some变any。如:There are some apples in the fridge. 冰箱里有一些苹果。→Are there any apples in the fridge?冰箱里有苹果吗?
4. There be 句型和have的区别
There be意为“某处有某人(或某物)”;have意为“某人(或某地)拥有某物”,表示“所有、拥有关系”。如:There is a girl in the room. 房间里有一个女孩。I have a new computer. 我有一台新电脑。
【精选例句】①When the earthquake is over, there is still plenty of danger.当地震结束时,仍然有很多危险。[冀教九(全)Unit 3 P42]②There are a lot of good restaurants in Sunville.在桑维尔有许多不错的餐馆。[人教九(全)Unit 3 P136]③Is there a good movie theater near here?这附近有好的电影院吗?[人教八(上)Unit 4 P98]
命题点 6 主谓一致
主谓一致,即谓语动词必须和主语在人称和数上保持一致,这种一致常由三种不同的原则所支配,即就近一致原则、语法一致原则和意义一致原则。
1. 就近一致原则:谓语动词的形式与它临近的名词或代词一致(与离它最近的主语保持一致)。
情况 示例
由either... or..., neither... nor..., not only... but also... 连接两个并列主语时,谓语动词和距离较近的主语在数上保持 一致。 Either Jane or Tom knows the answer. 要么是Jane要么就是Tom知道答案。Not only Mia but also I like singing. 不但Mia喜欢唱歌,而且我也喜欢唱歌。
There be... 句式中的be动词与最近的主语在数上保持一致。 There is an English book and three storybooks on the desk. 桌子上有一本英语书和三本故事书。
2. 语法一致原则:主语和谓语通常是在语法形式上取得一致,即单数主语谓语动词用单数,复数主语谓语动词用复数。
主语成分 谓语 示例
单数名词或代词 单数 She believes that it is important to have a healthy diet. 她认为有一个健康的饮食很重要。
动词不定式短语、动名词短语或从句单数 To get up early is a good habit. 早起是个好习惯。
续表
the number of+可数名词复数 单数 The number of candles is the person's age. 蜡烛的数量是过生日的人的年龄。[人教七(下)Unit 10 P59]
one of+可数名词复数 One of my favorite films is Cinderella. 我最喜欢的电影之一是《灰姑娘》。
either, neither, each, every或no +单数名词, 以及由some, any, no, every构成的复合不定代词 Everyone is born with the ability to learn. 每个人生来就有学习的能力。[人教九(全)Unit1 P6]
a number of+可数名词复数 复数 A number of workers are needed for the project. 这个项目需要一些工人。
both... and... 连接两个主语 Both Tom and Sam play the drums well. Tom和Sam都打鼓打得很好。
由and连接两个名词 两个名词指不同的人或物 复数 Joyce and Arthur are talking about the newspaper. Joyce和Arthur在谈论这份报纸。 [上海牛津八(下)Module 2 P58]
两个名词指同一人或物 单数 The writer and actor has come. 这个既是作家又是演员的人已经来了。
主语后面跟有with, together with, except, as well as, rather than, besides, including, but等词或结构 取决于主语的数 Everyone except Jim and Tim gets a new book. 除了Jim和Tim,所有人都得到了一本新书。
由“a lot of, lots of, plenty of, the rest of+ 名词”构成的短语 取决于短语后面的名词的数 There are a lot of interesting activities we can take part in. 有很多有趣的活动我们可以参加。
由“分数/百分数+名词”构成的短语 Two thirds of the work has been finished. 三分之二的工作已经完成了。
定语从句关系代词that, who, which 与先行词的数一致 A volunteer is someone who gives their time for free. 志愿者是指免费提供时间的人。
3. 意义一致原则:指概念一致,即谓语动词的形式要和主语所表达的概念一致。
主语 谓语 示例
集体名词(如:family/class/ team/group/public等) 取决于 主语意义 Jeff 's family is having a yard sale. Jeff家正在进行一场庭院拍卖。[人教八(下)Unit10 P73]It's 9:00 a.m. and Zhu Hui's family are at home. 现在是上午9点,朱辉的家人在家。[人教七(下)Unit6 P35]
不定代词all, most, more, some, any做主语 All the work has been finished. 所有的工作都已经完成了。All the students have gone. 所有的学生都走了。
续表
集合名词(如:people/police等) 复数 Finally, the police come and the men are taken away. 最后,警察来了,他们被带走了。[外研九(上)Module 4 P32]
the+姓氏名词复数,表示“……一家”或“……夫妇” The Smiths like travelling. Smith一家喜欢旅行。
the+形容词 表示一类人 The rich are not always happy. 富人并不总是快乐的。
表示重量、度量、时间、长度、价格、数学运算等的词或短语 单数 1,000 yuan has been raised. 已经筹集了1000元。
即时训练
9. I eat vegetables every day, because eating vegetables ________ good for my body.
A. was B. is C. are
10. There ________ different kinds of fruits and some milk in the fridge. Let's make a salad.
A. is B. are C. was
11. Neither Lucy nor Amy ________ fried food. They think it's unhealthy for them.
A. like B. likes C. liked
12. The Greens often ________ family trips during the holidays. They think it's a good way to relax.
A. had B. has C. have
【好词佳句积累】 be good for...对……有好处 different kinds of不同种类的 in the fridge在冰箱里 make a salad制作沙拉 during the holidays在假期期间 it's a good way to do sth.它是一个做某事的好方式
13. The number of the teachers in the school ________ about 300 and one fifth of them are women.
A. is B. are C. was
综合提升
语法选择
A. 小题夯基
1. Everything was magical. ________ excited David was!
A. How B. What C. What an
2.“Wow!” she cried proudly. “________ high my butterfly flies!”
A. What B. What a C. What an D. How
3. ________ smart the driverless car is! I really want to have one.
A. What B. What a C. What an D. How
4. ________ interesting movie it is! I want to see it again.
A. What B. What an C. How
5. —________ do you learn these words by heart
—By using them in different ways.
A. When B. How C. Why
6. Look! There ________ some information about animals in this book.
A. is B. are C. was
7. The young ________ not allowed to start eating at first before the elders pick up the chopsticks in China.
A. is B. were C. are
【好词佳句积累】 the number of……的数量 sb. be (not) allowed to do sth.某人(不)被允许做某事 at first首先 pick up捡起;拾起
B.微语篇提能
中华优秀传统文化·银花丝工艺 The Silver Flower Silk(银花丝) is a traditional hand made work of art. There __1__ two styles in the Silver Flower Silk Craft(工艺).
Born in 1962, Dao An became interested in drawing from childhood, and she worked in the Silver Flower Silk Craft Company in 1982. People found __2__ beautiful her paintings were, so she was made to create Silver Flower Silk works, but she __3__ not satisfied with that. She worked so hard to make better works. She has become one of the very few masters of the craft in China.
About twenty years has passed since she took up the job. Many Silver Flower Silk factories were shut down because of the market. Dao An didn't want the skill to go away. “__4__ important traditional hand made work of art it is. And the Silver Flower Silk __5__ worth being known by more people. We should stick to spreading this craft and have good creativity to develop it better,” she said.
1. A. is B. are C. was
2. A. what B. what a C. how
3. A. is B. was C. are
4. A. What B. What an C. How
5. A. is B. are C. was
【语篇研读】What:讲述了道安对非遗手工艺品——银花丝工艺传承的故事。Why:旨在鼓励学生了解中华传统技艺的发展现状,感受非遗技艺的魅力,激发学生对优秀传统文化的兴趣,引导学生积极传承中华优秀传统文化。How:①文体特征:记叙文。②语言特点:本文使用“became interested in”, “worked so hard to make better works”, “has become one of the very few masters of the craft in china”讲述了传承人道安传承银花丝工艺的历程以及成就。
专题十一 简单句及句子种类
【即时训练】
1. B 2. A 3. A 4. C 5. A 6. B 7. A 8. B 9. B 10. B 11. B 12. C 13. A
【综合提升】
A. 1. A 2. D 3. D 4. B 5. B 6. A 7. C
B. 【主旨大意】本文是一篇记叙文。主要讲述了银花丝工艺的传承人道安40多年来努力传承银花丝工艺的故事。
1. B 2. C 3. B 4. B 5. A
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
