2024届高考英语二轮复习状语从句-寻梦环游记课件(共43张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2024届高考英语二轮复习状语从句-寻梦环游记课件(共43张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 109.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-02-16 19:39:29 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共43张PPT)
3.Which line impresses you most
1.If you want to tell something about the death to children, which film do you want to recommend
2.Have you ever watched the movie Coco
When there's no one left in the living world who remembers you, you disappear from this world.
当这个世上没有任何人记得你时,你将彻底消失。
Adverbial Clause
状语从句
The introduction of the movie
Coco, is a heartwarming story about love and dreams . A boy Mig from Mexico is lucky to have a big family.Although his family has the strict tradition forbidding learning music,he loves music .However,he enters the world of undead accidently.
With the help of his family's ancestors, Mig sets foot on a magical adventure to find his way home, realizing the meaning of family and affection more deeply.
accidently
With the help of
realizing
Although
to have
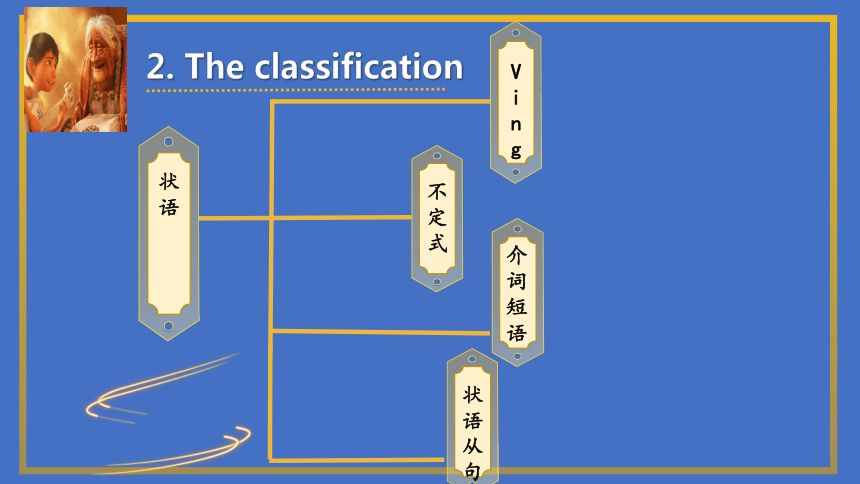
副词
动词不定式
V-ing形式
He stood there , playing the guitar.
介词短语
He is lucky to have a big family.
With the help of his family ancestors,he finds his way back home.
He enters the world of undead accidently.
状语一般由副词、介词短语、非谓语动词、从句等充当。
状语从句
Although Mig’family has the strict tradition of fobidding learning music, he loves music.
What is adverbial
1. Definition and types:
状语修饰_______、 ________、_____或___________。
动词
形容词
副词
整个句子
状语
介词短语
不定式
2. The classification
Ving
状语从句
十
大
词
类
实词
状语(adverbial)
1. How about meeting again at six
2. Last night she didn’t go to the dance party because of the rain.
3. I shall go there if it doesn’t rain.
4. Mr Smith lives on the third floor.
5. She put the eggs into the basket with great care.
6. She came in with a dictionary in her hand.
7. In order to catch up with the others, I must work harder.
8. He was so tired that he fell asleep immediately.
9. She works very hard though she is old.
10. I am taller than he is.
时间状语
原因状语
条件状语
地点状语
方式状语
伴随状语
结果状语
让步状语
比较状语
目的状语
状语从句
时间状语从句
原因状语从句
地点状语从句
结果状语从句
目的状语从句
方式状语从句
比较状语从句
条件状语从句
让步状语从句
Why did ancestor’s photos have to be put on the ofrenda on Día de Muertos or Day of the Dead
Because their ancestors’ spirits can cross over. If not, they can’t come back
Scene 1
原因状语从句
What is called the final death
When there's no one left in the living world who remembers you, you disappear from this world.
Scene 2
时间状语从句
What’s the worst part for Hector
Even if he never got to see Coco in the living world,he thought at least one day,he’d see her here. The moment she’s gone from the living world, he did disappear from this one.
Scene3
让步状语从句
时间状语从句
Spot all the adverbial clauses.
Task 1
1. If you forget him, he’ll be gone forever.
2. Remember me, though I have to say goodbye/travel far.
3. Remember me, even though I’m far away.
4. Remember me, each night we are part.
5. Remember me, each time you hear a sad guitar.
6. The only way that I can be until you’re in my arms again.
7. When I was a little girl , he and mama would sing such beautiful songs.
条件状语
让步状语
让步状语
时间状语
时间状语
时间状语
时间状语
The real death is that no one in the world remembers you.
Remember me before the memory of love disappers.
You can not be forgiven , but it should not be forgotten.
真正的死亡是世界上没人再认识你。
可以不需要原谅,但不应该被遗忘。
在爱的记忆消失前,请记得我。
Task 2
Enjoy some classical lines.
It resonates with adults, and leads children carefully through the more sad or scary moments, so they come out with a better understanding of life and death while also being thoroughly entertained.
“The grandmas, especially great-grandma Coco, reminded me of my grandmother. Although the movie brought back memories of the loss of my grandmother, I couldn’t help but smile through the tears (lots of tears) picturing my grandmother in such a beautiful place with her friends and family.”
Film review from(Forbes)《福布斯》
电影让成年人引起共鸣的同时,也小心翼翼地将孩子引入那些稍微悲伤和吓人的片段,这样他们走出影院的时候,不仅尽兴而归,还会对生死有更好的理解。
Kellie Alcozer:
Task 3
Do you think it’s necessary to worship our ancestors
He fell asleep ________________ he was reading.
She sang ________ she went. (她边走边唱)
It was raining hard ___________we arrived.
We were about to start _________ it began to rain.
用when, while或as填空
when /while/ as
as
when /as
when
2.11 时间状语从句(when while as)
It often rains in the south,_________ it seldom rains in the north.
be about to do sth when... be on the point of doing sth when...
be doing sth when... had done sth when...
Strike while the iron is hot. (用as或when不可,这里的while意思是“趁……”)
while
“when”也可以表示原因,意思是“既然;在…的情况下”
Why do you want a new job when you’ve got such a good one
It was foolish of you to take a taxi when you could easily walk there in 5 minutes.
2.11 时间状语从句(when while as)
引导词 相同点 不同点
表意 从句谓语动词 与主句谓语动词的先后关系 其他
when 都意为“当...时候” 可表时间点或时间段 延续性动词,或非延续性动词 谓语动作可在主句谓语动作之前或同时发生 有“突然”,‘正在这时“之意
while 表时间段 延续性动词 谓语动作必须是和主句谓语动作同时发生 常表对比
as 时间点或时间段 延续性动词,或非延续性动词 谓语动作必须是和主句谓语动作同时发生 表示“一边...一边...”;“随着…”
2.11 时间状语从句(when while as)
延续动词:能够延续的动作或状态,如live, work, study, learn, sleep等,
可以和表示一段时间的状语连用。
非延续动词:短暂性动词、瞬间动词,表示不能延续的动作,这类动词有: go, come, arrive, leave, begin, start, join, marry 等,它不能和一段时间连用。
e.g. The old man has died for ten years.
The old man has been dead for ten years.
The old man died ten years ago.
(× )
(√)
(√)
2.11 时间状语从句(when while as)
before引导时间状语从句表示“在…之前”, 从句中常用如下句型:
It will be long before...(得过好久才……)
It will not be long before...(不久就……)
It was long before...(过了好久才……)
It was not long before...(过了不久就……)
It will be half a year before I come back.
It won't be long before you regret for what you've done.
It wasn't be long before they came back.
It was long before they met again.
2.12 时间状语从句before
since+持续性动词过去式(从动作结束时算起)
since+瞬间动词过去式(从该动作发生时算起)
It is two years since he smoked.他戒烟已有两年了。
It is two years since he joined the army. 他参军两年了。
常用句式:
It is/has been+一段时间+since...(从句用一般过去时)
It has been three years since I began to learn English.
2.13 时间状语从句since
since一般用于“现在完成时”或“一般现在时”;since表示“自从”时,通常与现在完成时连用;主句表示“多长时间”时,动词可用一般现在时(也可用现在完成时)。
We shall wait until/till he comes back.
Until he comes back, nothing can be done.
I didn’t wake up until I heard the alarm clock.
= Not until I heard the alarm clock did I wake up.
= It was not until I heard the alarm clock that I woke up.
连词 位置 用法点津
until 可以放在句首 not...until (直到……才)
till 不可放在句首,常用于口语 一般不用于强调句型
2.14 时间状语从句until/till
Practice
I didn’t recognized her until she took off her dark glasses.
=Not until she took off her dark glasses did I recognize her.
=It was not until she took off her dark glasses that I recognized her.
2.14 时间状语从句until/till
以下引导词引导时间状语,表示“一……就……”
directly,immediately,instantly,as soon as
the moment,the minute,the instant,the second…
hardly/scarcely...when...,no sooner...than... (前半部分过去完成时,后半部分用一般过去时,位于句首时主句用部分倒装)
He left as soon as you came.
He made for the door directly he heard the knock.
The moment he saw his mother,he burst into tears.
Hardly had we went home when it began to rain.
= We had hardly went home when it began to rain
No sooner had he arrived than she started complaining.
2.15 表示“一……就”的引导词
each time,every time,any time, next time, the first/second time…等名词短语也可引导时间状语从句。
Each time he came to my city,he would call on me.
I fell in love with her the first time I saw her.
2.16 名词短语引导时间状语从句
by the time意为“到……时候”,表示动作在某一时间点前已完成。
(1)如果从句中的谓语动词是过去时,主句的谓语动词常用过去完成时。如果从句中的谓语动词为现在时或现在完成时,主句的谓语动词常用将来完成时。表示 "主句的动作到未来某个时候就已经完成了"。
By the time he was fourteen years old, Einstein had learned advanced mathematics all by himself.
We will have left by the time they arrive.
(2)如果主句动作不强调已经完成,只说明状况,则主句不用完成时态。
He was out of breath by the time he reached the top.
2.17 by the time 引导时间状语从句
常用引导词:where wherever anywhere everywhere
e.g. He lives where the climate is mild.
He thinks of us wherever he is.
where 引导的地点状语从句与定语从句的区别
where引导的地点状语从句,是用来说明主句谓语动作发生的地点。而where引导的定语从句是用来修饰一个名词,即先行词。该词应是一个表示地点的名词。
Bamboo grows best where it is warm and where it rains often.
Bamboo grows best in places where it is warm and where it rains often.
3.1 地点状语从句
连词 词义 从句位置 例句
where wherever ……的地方 指具体地点时,从句可用于主句之前或之后;表示抽象条件的含义时,从句需放在主句之前 You are free to go wherever you like.
Where there is a will, there is a way.
如果想说“我在操场上打篮球的时候把钥匙弄丢了。”,可以有两种表达方式:
① I lost my key on the playground. (初中知识)
② I lost my key where I played basketball. (高中知识)
我把钥匙丢在(我)打篮球的地方了。
从上面例句中我们可以看出where I played basketball的作用等同于on the playground,都是表示地点的状语,只是第二句说得更详细具体些。
1.表示不知道的原因时用because,因此because从句是全句最重要的部分。常用来回答why的问题。
I’m leaving because I’m fed up with the boss.
2.表示已经知道的原因时用as(由于,因为)或since(既然,因为),since要比as正式一些。
Seeing all of the children already seated,he said,“Since everyone is here,let’s start.”
3.下列情况下只能使用because:
(1)在回答why的问句时;
(2)在用于强调句型时。
4.1 原因状语从句
4.“when”也可以表示原因,意思是“既然;在…的情况下”
Why waste 50 when you could get it for free
Why use wood when you can use plastic
5.其他引导词:
now that(既然), in that(因为), given that(考虑到),considering that(考虑到)
Now that everybody has come, let’s begin our conference.
Given that she loves children, teaching is the right career for her.
常用引导词:so that,in order that,
in case(以免,以防), for fear that(以免,唯恐,)
You should take an umbrella for fear that it (should) rain.
注意:目的状语从句中的谓语动词常与情态动词连用,否则可能是结果状语从句,不可置于句首。
He got up early so that he could catch the early train.(目的状语从句)
He got up early so that he caught the early train.(结果状语从句)
He got up early so that he could catch the early train.
=He got up early so as to/ in order to catch the early train.(主从句主语一致时可以这样转换)
5.1 目的状语从句
1. He made a wrong decision so that he failed.
2. His progress was such that it surprised his teacher.
She is so good that we all like her.
It’s such a good chance that we must not miss it.
He is so good a boy that we all like him.
=He is such a good boy that we all like him.
so
形容词/副词
many/few+复数名词
much/little+不可数名词
形容词+a/an+可数名词单数形式
that 从句
such
a/an+可数名词单数形式
复数名词
不可数名词
that 从句
名词前有many,much,few,little 修饰时,用so…that来表示结果。但little意为“小的”时,仍用such…that.
常用引导词:such that,so that,so...that...,such...that...
1.although与though可以引导让步状语从句,不能与but连用,但可以与yet连用。
Although/Though they are poor,(yet) they are warmhearted.
2.even if或even though引导让步状语从句,表示“即使,纵然”。
I managed to get there even if/though it rained heavily.
3.no matter后接who,what,where,how等疑问词引导让步状语从句,也可以在这类疑问词后面加上-ever构成whoever,whatever,wherever,however等。但在引导名词性从句时只能用“疑问词+-ever”类词。
Don’t trust him,no matter what/whatever he says.
I will eat whatever you give me.
No matter how hard the work is,you’d better try to do it well.
7.1 让步状语从句
4.as也可以引导让步状语从句,引起倒装,需要倒装前置的内容有表语名词去冠词;表语形容词;动词后副词;情态动词后动原。though引导的从句可以倒装也可以不倒装,但although引导的从句不可以倒装。
Child as (though) he is,he knows a lot.
Much as I like it,I won’t buy.
Try as he might,he couldn’t lift the heavy box.
Young as she is, she has traveled to many countries.
5.while也可以引导让步状语从句,表示“尽管”,比though/although语气弱。while引导的让步状语从句一般要位于句首。
7.2 让步状语从句
比较状语从句:than;as...as...; not as(so)... as...; the same as;
the+比较级,the+比较级
从句中有时使用省略形式,只保留被比较的对象。
He works as hard as others.
We treat boys exactly the same as girls.
The sun is much bigger than the earth.
The more you eat,the fatter you will be.
8.1 比较状语从句
连词 词义 例句
if 如果 If you water a plant, it grows.
Unless(if…not…) 除非,如果不 We are going to have a picnic unless it rains.
so/as long as 只要 As long as you keep on trying, you will succeed.
in case 万一,如果 In case I forget, please remind me of my promise.
on condition that 条件是 We’ll let you use the room on condition that you keep it clean.
suppose/supposing (that) 假设,如果 Supposing that you fail, don’t lose heart, but try again.
provided/providing that 如果 We’ll visit Europe next year provided we have enough money.
what if 如果……将会怎样 What if we couldn’t get the preparation done in time
9.1 条件状语从句
I shall not go to the movie unless I finish my homework.
=I shall not go to the movie if I don’t finish my homework.
Only if you finish the work can you play computer games.
方式状语从句描述主句中动作或状态发生的方式或方法,主要由下列引导词引导:as,just as, (in) the way,as if,as though等。
You should do the experiment as the teacher tells you to.
你应该按照老师的要求做实验。
Do as the Romans do.
入乡随俗。
The old man runs very fast as though he were a young man.
那位老人跑得很快,就像年轻人似的。
It looks as if it will rain.
看来好像要下雨。
10.1 方式状语从句
as if/as though意为“好像,仿佛”,从句所述的是非真实的情况,用虚拟语气;若所述的是事实或是极可能发生的情况,用陈述语气。可以引导方式状语从句,也可以跟在系动词seem,appear,look,taste,sound,feel,smell等之后引导表语从句。
as if/as though引导从句
表语从句:He looked as if he was going to cry.
He looks as if he were from the Mars.
状语从句:Do as you are told, or you’ll be fired.
The lady treats the boy as if he were her own son. (虚拟语气)
He closed his eyes as if he was tired. (陈述语气)
1. 当状语从句的主语和主句的主语一致时,可以省略从句中的主语和系动词be.
While ( I was ) walking along the street, I heard my name called.
Don’t speak until(you are)spoken to .
Tom raised his hand as if (he was ) to say something.
when(he was)asked why he was late,he kept silent.
Unless(you are ) invited to speak, you should remain silent at the conference.
Correct mistakes, if any.
2. 当从句的主语是it, 谓语动词中又含有系动词be时,可以把it 和系动词be一起省略。
Unless ( it is ) necessary, you’d better not refer to the dictionary.
状语从句的省略
如果我是你,我就会努力学习.
如果我知道他的电话号码,我就给他打电话了.
如果明天下雨的话,我们会取消比赛.
If I were you, I would work harder at my lessons.
If I had known his telephone number, I would have called him.
If it should \were to rain, we would call off the match.
虚拟语气 从句谓语动词 主句谓语动词
与现在事实相反 did/ were would/ should/ could/ might + do
与过去事实相反 had done would/ should/ could/ might + have done
与将来事实相反 did/were to do/should do would/ should/ could/ might + do
虚拟语气在状语从句的运用
(1)在条件句中,可省略 if,把were ,had, should 提到句首,变为倒装句式.
If I were at school again, I would study harder.
Were I at school again, I would study harder.
If you had come earlier, you would have met him.
Had you come earlier, you would have met him.
If it should rain tomorrow, we would not go climbing.
Should it rain tomorrow, we would not go climbing.
(2)当从句表示的行为和主句表示的行为所发生的时间不一致时,被称为:错综时间条件句. 动词的形式要根据它所表
示的时间作出相应的调整.
If you had followed my advice , you would be better now.
If you had studied hard before, you would be a college student now.
(3) 含蓄虚拟条件句,通常借助这些词without, but for ( 要不是 ), or/ otherwise等来表达条件。
I couldn’t have succeeded without your generous help.
We got lost, otherwise we would have visited more places of interest yesterday.
(4)虚拟语气用于if only 引导的条件句或感叹句
If only I had known the news earlier! 要是我早知道这个消息就好了!
(5)虚拟语气在方式状语从句的运用
The lady treats the boy as if he were her own son.
虚拟语气在状语从句的运用
3.Which line impresses you most
1.If you want to tell something about the death to children, which film do you want to recommend
2.Have you ever watched the movie Coco
When there's no one left in the living world who remembers you, you disappear from this world.
当这个世上没有任何人记得你时,你将彻底消失。
Adverbial Clause
状语从句
The introduction of the movie
Coco, is a heartwarming story about love and dreams . A boy Mig from Mexico is lucky to have a big family.Although his family has the strict tradition forbidding learning music,he loves music .However,he enters the world of undead accidently.
With the help of his family's ancestors, Mig sets foot on a magical adventure to find his way home, realizing the meaning of family and affection more deeply.
accidently
With the help of
realizing
Although
to have
副词
动词不定式
V-ing形式
He stood there , playing the guitar.
介词短语
He is lucky to have a big family.
With the help of his family ancestors,he finds his way back home.
He enters the world of undead accidently.
状语一般由副词、介词短语、非谓语动词、从句等充当。
状语从句
Although Mig’family has the strict tradition of fobidding learning music, he loves music.
What is adverbial
1. Definition and types:
状语修饰_______、 ________、_____或___________。
动词
形容词
副词
整个句子
状语
介词短语
不定式
2. The classification
Ving
状语从句
十
大
词
类
实词
状语(adverbial)
1. How about meeting again at six
2. Last night she didn’t go to the dance party because of the rain.
3. I shall go there if it doesn’t rain.
4. Mr Smith lives on the third floor.
5. She put the eggs into the basket with great care.
6. She came in with a dictionary in her hand.
7. In order to catch up with the others, I must work harder.
8. He was so tired that he fell asleep immediately.
9. She works very hard though she is old.
10. I am taller than he is.
时间状语
原因状语
条件状语
地点状语
方式状语
伴随状语
结果状语
让步状语
比较状语
目的状语
状语从句
时间状语从句
原因状语从句
地点状语从句
结果状语从句
目的状语从句
方式状语从句
比较状语从句
条件状语从句
让步状语从句
Why did ancestor’s photos have to be put on the ofrenda on Día de Muertos or Day of the Dead
Because their ancestors’ spirits can cross over. If not, they can’t come back
Scene 1
原因状语从句
What is called the final death
When there's no one left in the living world who remembers you, you disappear from this world.
Scene 2
时间状语从句
What’s the worst part for Hector
Even if he never got to see Coco in the living world,he thought at least one day,he’d see her here. The moment she’s gone from the living world, he did disappear from this one.
Scene3
让步状语从句
时间状语从句
Spot all the adverbial clauses.
Task 1
1. If you forget him, he’ll be gone forever.
2. Remember me, though I have to say goodbye/travel far.
3. Remember me, even though I’m far away.
4. Remember me, each night we are part.
5. Remember me, each time you hear a sad guitar.
6. The only way that I can be until you’re in my arms again.
7. When I was a little girl , he and mama would sing such beautiful songs.
条件状语
让步状语
让步状语
时间状语
时间状语
时间状语
时间状语
The real death is that no one in the world remembers you.
Remember me before the memory of love disappers.
You can not be forgiven , but it should not be forgotten.
真正的死亡是世界上没人再认识你。
可以不需要原谅,但不应该被遗忘。
在爱的记忆消失前,请记得我。
Task 2
Enjoy some classical lines.
It resonates with adults, and leads children carefully through the more sad or scary moments, so they come out with a better understanding of life and death while also being thoroughly entertained.
“The grandmas, especially great-grandma Coco, reminded me of my grandmother. Although the movie brought back memories of the loss of my grandmother, I couldn’t help but smile through the tears (lots of tears) picturing my grandmother in such a beautiful place with her friends and family.”
Film review from(Forbes)《福布斯》
电影让成年人引起共鸣的同时,也小心翼翼地将孩子引入那些稍微悲伤和吓人的片段,这样他们走出影院的时候,不仅尽兴而归,还会对生死有更好的理解。
Kellie Alcozer:
Task 3
Do you think it’s necessary to worship our ancestors
He fell asleep ________________ he was reading.
She sang ________ she went. (她边走边唱)
It was raining hard ___________we arrived.
We were about to start _________ it began to rain.
用when, while或as填空
when /while/ as
as
when /as
when
2.11 时间状语从句(when while as)
It often rains in the south,_________ it seldom rains in the north.
be about to do sth when... be on the point of doing sth when...
be doing sth when... had done sth when...
Strike while the iron is hot. (用as或when不可,这里的while意思是“趁……”)
while
“when”也可以表示原因,意思是“既然;在…的情况下”
Why do you want a new job when you’ve got such a good one
It was foolish of you to take a taxi when you could easily walk there in 5 minutes.
2.11 时间状语从句(when while as)
引导词 相同点 不同点
表意 从句谓语动词 与主句谓语动词的先后关系 其他
when 都意为“当...时候” 可表时间点或时间段 延续性动词,或非延续性动词 谓语动作可在主句谓语动作之前或同时发生 有“突然”,‘正在这时“之意
while 表时间段 延续性动词 谓语动作必须是和主句谓语动作同时发生 常表对比
as 时间点或时间段 延续性动词,或非延续性动词 谓语动作必须是和主句谓语动作同时发生 表示“一边...一边...”;“随着…”
2.11 时间状语从句(when while as)
延续动词:能够延续的动作或状态,如live, work, study, learn, sleep等,
可以和表示一段时间的状语连用。
非延续动词:短暂性动词、瞬间动词,表示不能延续的动作,这类动词有: go, come, arrive, leave, begin, start, join, marry 等,它不能和一段时间连用。
e.g. The old man has died for ten years.
The old man has been dead for ten years.
The old man died ten years ago.
(× )
(√)
(√)
2.11 时间状语从句(when while as)
before引导时间状语从句表示“在…之前”, 从句中常用如下句型:
It will be long before...(得过好久才……)
It will not be long before...(不久就……)
It was long before...(过了好久才……)
It was not long before...(过了不久就……)
It will be half a year before I come back.
It won't be long before you regret for what you've done.
It wasn't be long before they came back.
It was long before they met again.
2.12 时间状语从句before
since+持续性动词过去式(从动作结束时算起)
since+瞬间动词过去式(从该动作发生时算起)
It is two years since he smoked.他戒烟已有两年了。
It is two years since he joined the army. 他参军两年了。
常用句式:
It is/has been+一段时间+since...(从句用一般过去时)
It has been three years since I began to learn English.
2.13 时间状语从句since
since一般用于“现在完成时”或“一般现在时”;since表示“自从”时,通常与现在完成时连用;主句表示“多长时间”时,动词可用一般现在时(也可用现在完成时)。
We shall wait until/till he comes back.
Until he comes back, nothing can be done.
I didn’t wake up until I heard the alarm clock.
= Not until I heard the alarm clock did I wake up.
= It was not until I heard the alarm clock that I woke up.
连词 位置 用法点津
until 可以放在句首 not...until (直到……才)
till 不可放在句首,常用于口语 一般不用于强调句型
2.14 时间状语从句until/till
Practice
I didn’t recognized her until she took off her dark glasses.
=Not until she took off her dark glasses did I recognize her.
=It was not until she took off her dark glasses that I recognized her.
2.14 时间状语从句until/till
以下引导词引导时间状语,表示“一……就……”
directly,immediately,instantly,as soon as
the moment,the minute,the instant,the second…
hardly/scarcely...when...,no sooner...than... (前半部分过去完成时,后半部分用一般过去时,位于句首时主句用部分倒装)
He left as soon as you came.
He made for the door directly he heard the knock.
The moment he saw his mother,he burst into tears.
Hardly had we went home when it began to rain.
= We had hardly went home when it began to rain
No sooner had he arrived than she started complaining.
2.15 表示“一……就”的引导词
each time,every time,any time, next time, the first/second time…等名词短语也可引导时间状语从句。
Each time he came to my city,he would call on me.
I fell in love with her the first time I saw her.
2.16 名词短语引导时间状语从句
by the time意为“到……时候”,表示动作在某一时间点前已完成。
(1)如果从句中的谓语动词是过去时,主句的谓语动词常用过去完成时。如果从句中的谓语动词为现在时或现在完成时,主句的谓语动词常用将来完成时。表示 "主句的动作到未来某个时候就已经完成了"。
By the time he was fourteen years old, Einstein had learned advanced mathematics all by himself.
We will have left by the time they arrive.
(2)如果主句动作不强调已经完成,只说明状况,则主句不用完成时态。
He was out of breath by the time he reached the top.
2.17 by the time 引导时间状语从句
常用引导词:where wherever anywhere everywhere
e.g. He lives where the climate is mild.
He thinks of us wherever he is.
where 引导的地点状语从句与定语从句的区别
where引导的地点状语从句,是用来说明主句谓语动作发生的地点。而where引导的定语从句是用来修饰一个名词,即先行词。该词应是一个表示地点的名词。
Bamboo grows best where it is warm and where it rains often.
Bamboo grows best in places where it is warm and where it rains often.
3.1 地点状语从句
连词 词义 从句位置 例句
where wherever ……的地方 指具体地点时,从句可用于主句之前或之后;表示抽象条件的含义时,从句需放在主句之前 You are free to go wherever you like.
Where there is a will, there is a way.
如果想说“我在操场上打篮球的时候把钥匙弄丢了。”,可以有两种表达方式:
① I lost my key on the playground. (初中知识)
② I lost my key where I played basketball. (高中知识)
我把钥匙丢在(我)打篮球的地方了。
从上面例句中我们可以看出where I played basketball的作用等同于on the playground,都是表示地点的状语,只是第二句说得更详细具体些。
1.表示不知道的原因时用because,因此because从句是全句最重要的部分。常用来回答why的问题。
I’m leaving because I’m fed up with the boss.
2.表示已经知道的原因时用as(由于,因为)或since(既然,因为),since要比as正式一些。
Seeing all of the children already seated,he said,“Since everyone is here,let’s start.”
3.下列情况下只能使用because:
(1)在回答why的问句时;
(2)在用于强调句型时。
4.1 原因状语从句
4.“when”也可以表示原因,意思是“既然;在…的情况下”
Why waste 50 when you could get it for free
Why use wood when you can use plastic
5.其他引导词:
now that(既然), in that(因为), given that(考虑到),considering that(考虑到)
Now that everybody has come, let’s begin our conference.
Given that she loves children, teaching is the right career for her.
常用引导词:so that,in order that,
in case(以免,以防), for fear that(以免,唯恐,)
You should take an umbrella for fear that it (should) rain.
注意:目的状语从句中的谓语动词常与情态动词连用,否则可能是结果状语从句,不可置于句首。
He got up early so that he could catch the early train.(目的状语从句)
He got up early so that he caught the early train.(结果状语从句)
He got up early so that he could catch the early train.
=He got up early so as to/ in order to catch the early train.(主从句主语一致时可以这样转换)
5.1 目的状语从句
1. He made a wrong decision so that he failed.
2. His progress was such that it surprised his teacher.
She is so good that we all like her.
It’s such a good chance that we must not miss it.
He is so good a boy that we all like him.
=He is such a good boy that we all like him.
so
形容词/副词
many/few+复数名词
much/little+不可数名词
形容词+a/an+可数名词单数形式
that 从句
such
a/an+可数名词单数形式
复数名词
不可数名词
that 从句
名词前有many,much,few,little 修饰时,用so…that来表示结果。但little意为“小的”时,仍用such…that.
常用引导词:such that,so that,so...that...,such...that...
1.although与though可以引导让步状语从句,不能与but连用,但可以与yet连用。
Although/Though they are poor,(yet) they are warmhearted.
2.even if或even though引导让步状语从句,表示“即使,纵然”。
I managed to get there even if/though it rained heavily.
3.no matter后接who,what,where,how等疑问词引导让步状语从句,也可以在这类疑问词后面加上-ever构成whoever,whatever,wherever,however等。但在引导名词性从句时只能用“疑问词+-ever”类词。
Don’t trust him,no matter what/whatever he says.
I will eat whatever you give me.
No matter how hard the work is,you’d better try to do it well.
7.1 让步状语从句
4.as也可以引导让步状语从句,引起倒装,需要倒装前置的内容有表语名词去冠词;表语形容词;动词后副词;情态动词后动原。though引导的从句可以倒装也可以不倒装,但although引导的从句不可以倒装。
Child as (though) he is,he knows a lot.
Much as I like it,I won’t buy.
Try as he might,he couldn’t lift the heavy box.
Young as she is, she has traveled to many countries.
5.while也可以引导让步状语从句,表示“尽管”,比though/although语气弱。while引导的让步状语从句一般要位于句首。
7.2 让步状语从句
比较状语从句:than;as...as...; not as(so)... as...; the same as;
the+比较级,the+比较级
从句中有时使用省略形式,只保留被比较的对象。
He works as hard as others.
We treat boys exactly the same as girls.
The sun is much bigger than the earth.
The more you eat,the fatter you will be.
8.1 比较状语从句
连词 词义 例句
if 如果 If you water a plant, it grows.
Unless(if…not…) 除非,如果不 We are going to have a picnic unless it rains.
so/as long as 只要 As long as you keep on trying, you will succeed.
in case 万一,如果 In case I forget, please remind me of my promise.
on condition that 条件是 We’ll let you use the room on condition that you keep it clean.
suppose/supposing (that) 假设,如果 Supposing that you fail, don’t lose heart, but try again.
provided/providing that 如果 We’ll visit Europe next year provided we have enough money.
what if 如果……将会怎样 What if we couldn’t get the preparation done in time
9.1 条件状语从句
I shall not go to the movie unless I finish my homework.
=I shall not go to the movie if I don’t finish my homework.
Only if you finish the work can you play computer games.
方式状语从句描述主句中动作或状态发生的方式或方法,主要由下列引导词引导:as,just as, (in) the way,as if,as though等。
You should do the experiment as the teacher tells you to.
你应该按照老师的要求做实验。
Do as the Romans do.
入乡随俗。
The old man runs very fast as though he were a young man.
那位老人跑得很快,就像年轻人似的。
It looks as if it will rain.
看来好像要下雨。
10.1 方式状语从句
as if/as though意为“好像,仿佛”,从句所述的是非真实的情况,用虚拟语气;若所述的是事实或是极可能发生的情况,用陈述语气。可以引导方式状语从句,也可以跟在系动词seem,appear,look,taste,sound,feel,smell等之后引导表语从句。
as if/as though引导从句
表语从句:He looked as if he was going to cry.
He looks as if he were from the Mars.
状语从句:Do as you are told, or you’ll be fired.
The lady treats the boy as if he were her own son. (虚拟语气)
He closed his eyes as if he was tired. (陈述语气)
1. 当状语从句的主语和主句的主语一致时,可以省略从句中的主语和系动词be.
While ( I was ) walking along the street, I heard my name called.
Don’t speak until(you are)spoken to .
Tom raised his hand as if (he was ) to say something.
when(he was)asked why he was late,he kept silent.
Unless(you are ) invited to speak, you should remain silent at the conference.
Correct mistakes, if any.
2. 当从句的主语是it, 谓语动词中又含有系动词be时,可以把it 和系动词be一起省略。
Unless ( it is ) necessary, you’d better not refer to the dictionary.
状语从句的省略
如果我是你,我就会努力学习.
如果我知道他的电话号码,我就给他打电话了.
如果明天下雨的话,我们会取消比赛.
If I were you, I would work harder at my lessons.
If I had known his telephone number, I would have called him.
If it should \were to rain, we would call off the match.
虚拟语气 从句谓语动词 主句谓语动词
与现在事实相反 did/ were would/ should/ could/ might + do
与过去事实相反 had done would/ should/ could/ might + have done
与将来事实相反 did/were to do/should do would/ should/ could/ might + do
虚拟语气在状语从句的运用
(1)在条件句中,可省略 if,把were ,had, should 提到句首,变为倒装句式.
If I were at school again, I would study harder.
Were I at school again, I would study harder.
If you had come earlier, you would have met him.
Had you come earlier, you would have met him.
If it should rain tomorrow, we would not go climbing.
Should it rain tomorrow, we would not go climbing.
(2)当从句表示的行为和主句表示的行为所发生的时间不一致时,被称为:错综时间条件句. 动词的形式要根据它所表
示的时间作出相应的调整.
If you had followed my advice , you would be better now.
If you had studied hard before, you would be a college student now.
(3) 含蓄虚拟条件句,通常借助这些词without, but for ( 要不是 ), or/ otherwise等来表达条件。
I couldn’t have succeeded without your generous help.
We got lost, otherwise we would have visited more places of interest yesterday.
(4)虚拟语气用于if only 引导的条件句或感叹句
If only I had known the news earlier! 要是我早知道这个消息就好了!
(5)虚拟语气在方式状语从句的运用
The lady treats the boy as if he were her own son.
虚拟语气在状语从句的运用
