2024年中考人教版英语总复习课件 科学与技术语法专项复习 (共45张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2024年中考人教版英语总复习课件 科学与技术语法专项复习 (共45张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 228.8KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-03-08 22:59:28 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共45张PPT)
主题九 科学与技术
语法专项复习
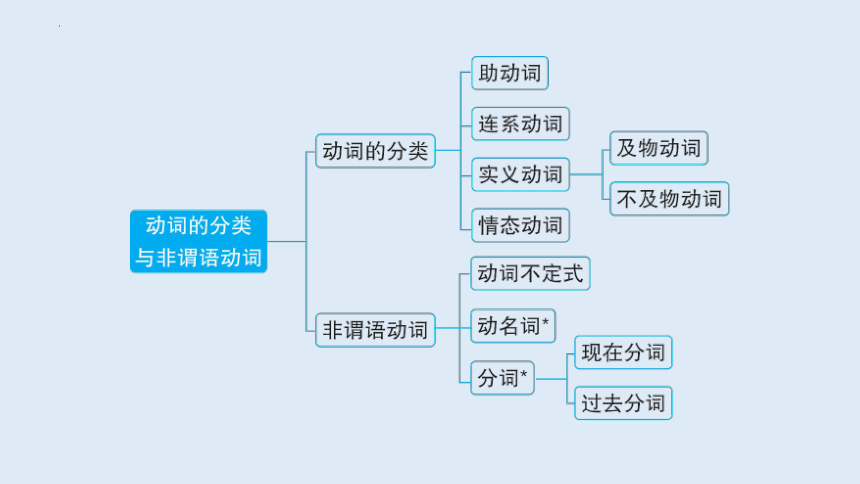
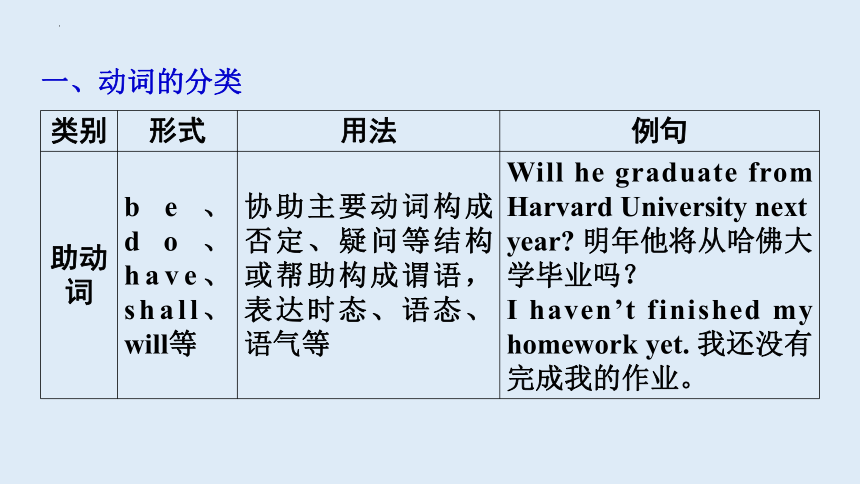
一、动词的分类
类别 形式 用法 例句
助动词 be、do、 have、shall、will等 协助主要动词构成否定、疑问等结构或帮助构成谓语,表达时态、语态、语气等 Will he graduate from Harvard University next year 明年他将从哈佛大学毕业吗?
I haven’t finished my homework yet. 我还没有完成我的作业。
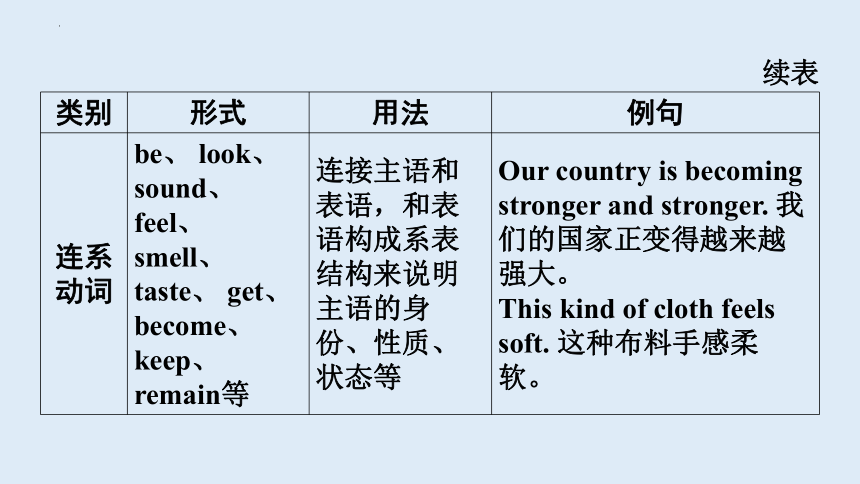
类别 形式 用法 例句
连系动词 be、 look、 sound、 feel、 smell、 taste、 get、 become、 keep、 remain等 连接主语和表语,和表语构成系表结构来说明主语的身份、性质、状态等 Our country is becoming stronger and stronger. 我们的国家正变得越来越强大。
This kind of cloth feels soft. 这种布料手感柔软。
续表
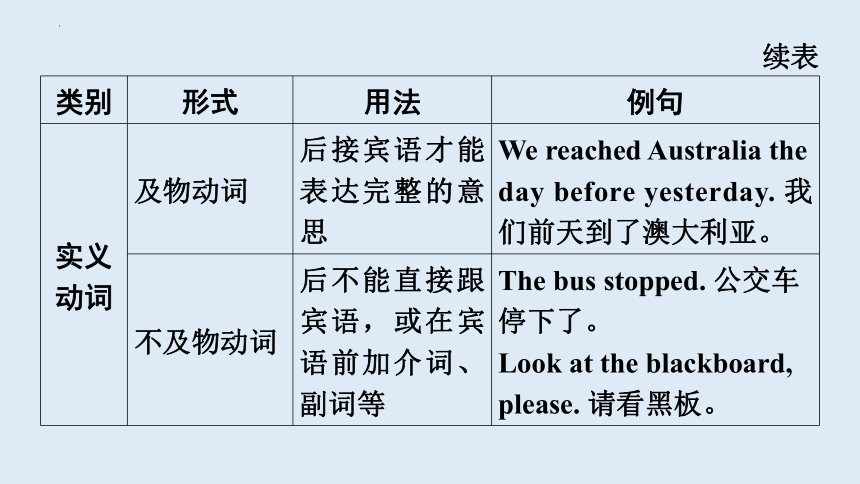
类别 形式 用法 例句
实义动词 及物动词 后接宾语才能表达完整的意思 We reached Australia the day before yesterday. 我们前天到了澳大利亚。
不及物动词 后不能直接跟宾语,或在宾语前加介词、副词等 The bus stopped. 公交车停下了。
Look at the blackboard, please. 请看黑板。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
情态动词 can/could、may/might、must、need、should、shall、will/would等 (情态动词详细用法见下文)
续表
情态动词
情态动词表示说话人对所说动作的观点,如需要、可能、意愿、怀疑等。在形式上,情态动词一般没有人称和数的变化,后接动词原形。
(1) can的用法
①表能力:can表能力时意味着凭体力、脑力或技术等能够去做某事。
例如:She is only five, but she can read. 她只有五岁,但她已经会阅读了。
②表可能性:多用于否定与疑问结构中,但也可用在肯定句中。
例如:This dictionary can be Linda’s. 这本字典可能是琳达的。
③表示征得他人许可(和may意思相近):常见于口语。
例如:Can/May I come in 我能进来吗?
(2) could的用法
①表可能性(过去或现在)。
例如:He said the news could be true. 他说消息可能是真的。(表示过去的可能性)
Someone is knocking at the door. Who could it be 有人在敲门,可能会是谁呢?(表示现在的可能性)
②表过去的能力。
例如:I could play the piano when I was only six. 我六岁时就能弹钢琴了。
③表允许。可表示委婉客气地提出问题或陈述看法,不是can的过去式。
例如:—Could I use your computer ——我可以用你的 电脑吗?
—Sure. / No, you can’t. ——当然可以。/ 不,你不能。
(3) may与might的用法
①表示可能性较小的推测,意为“可能,也许”,常用于肯定句中。might表推测时,可能性低于may。
例如:It might rain the day after tomorrow. 后天可能下雨。
②表示许可或请求,意为“可以”。在疑问句中,might比may的语气更加委婉和客气。对may引导的一般疑问句,否定回答时要用mustn’t或can’t。
例如:—May I come in ——我可以进来吗?
—Yes, you can. ——是的,你可以。
—No, you can’t. ——不,你不可以。
—No, you mustn’t. ——不,绝不行。
小贴士
may be与maybe区分
①may是情态动词,be是动词原形,只能用于句子中。
例如:It’s eight o’clock now. Jack may be at home. 现在八点钟了,杰克可能在家。
②maybe是副词,相当于perhaps、probably或likely,常用于句首。
例如:It’s eight o’clock now. Maybe Jack is at home. 现在八点钟了,杰克也许在家。
(4) must的用法
①表示“必须、必要”。
例如:We must follow the school rules. 我们必须遵守学校的规则。
②表示“一定”,常用于must be + 表语的结构中,通常表示猜测(只用在肯定句中)。
例如:This must be Lucy’s room. 这一定是露西的房间。
③must的否定式有两个:当回答由must引起的问题时,否定回答要用needn’t或don’t have to,表示“无须”“用不着” “不一定”的意义。当表示“不应该”“不许可”“禁止” 时,就用must not。
例如:—Must I go tomorrow? ——明天我必须去吗?
—Yes, you must. ——是的,你必须去。
—No, you needn’t. ——不,你不用去。
注:must = have to,但有区别。must表示说话人的主观思想,have to意为“不得不,必须”,表示客观需要,客观条件只能如此。
例如:You must do it now. 你必须现在就做。(说话人认为必须现在做)
I have to go now. 我现在必须走。(受客观条件限制必须现在走)
(5) need 的用法
①need作情态动词,表“需要”,多用在否定句或疑问句中。
例如:—Need I hand in the report tomorrow ——我需要明天交报告吗?
—Yes, you must. / No, you needn’t. ——是的,你需要。/ 不,你没必要。
②need也作实义动词,用法是“need to do sth.”。
例如:As students, we need to finish our homework on time. 作为学生,我们需要按时完成作业。
③need主动表被动,用法是“sth. need(s) doing = sth. need(s) to be done”。
例如:The room needs cleaning. = The room needs to be cleaned. 这个房间需要清扫。
④need作名词。
例如:This bag meets Ann’s need. 这个包满足安的需要。
(6) should的用法
意思为“应该”,表示劝告、建议、命令,其同义词是ought to;在疑问句中,通常用should代替ought to。
例如:You should go to class right away. 你应该马上去上课。
Should I open the door 我应该开门吗?
(7) shall的用法
意思为“将要 / 应该”,多用于第一人称征求对方的意见。
例如:What shall I wear at my birthday party 在我的生日宴会上我穿什么好呢?
(8) will与would的用法
①表示意志、愿望和决心等,意为“要,愿”,可用于各种人称。would是will的过去式。
例如:I will never do it again and that’s the last time. 我再也不会这样做了,那是最后一次。
My brother said he would help me to solve the problem. 我哥哥说他将会帮助我解决这个问题。
②表示提出请求或征求对方的意见,多用于第二人称作主语的一般疑问句中。would比will的语气更加委婉。
例如:Would you please do me a favor 请你帮我一个忙,好吗?
二、非谓语动词
非谓语动词是指在句子中不是谓语的动词,主要包括动词不定式、动名词和分词(现在分词和过去分词)。非谓语动词除了不能独立作谓语外,可以承担句子的其他成分。
类别 形式 用法 例句
动词 不定式 to do; not to do 作宾语:可接不定式作宾语的动词有choose、 decide、 expect、 fail、 hope、 learn、 manage、 offer、 promise、 refuse、 want、 plan、 agree等 I plan to go to the movies this afternoon. 我打算今天下午去看电影。
He has decided to go to the countryside. 他已决心去乡下。
类别 形式 用法 例句
动词 不定式 to do; not to do 作状语:常表示目的、原因、结果等 He is strong enough to move the heavy box. 他足够强壮能搬动这个箱子。
They ran over to welcome the foreign guests. 他们跑过来欢迎外宾。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动词 不定式 to do; not to do 作宾语补足语:可接不定式作补语的动词有tell、 advise、 allow、 encourage、 remind、 warn、 require等 He asked the driver to stop the motorbike. 他请那位司机拦下那辆摩托车。
Our school allows students to wear their own clothes on Fridays. 我们学校允许学生在周五穿自己的衣服。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动词 不定式 to do; not to do 作主语:用it作形式主语 It is not easy for us to learn a foreign language. 学习外语对我们来说不容易。
It is careless of you to do that. 你这么做真粗心。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动词 不定式 to do; not to do 作表语 My dream is to be a scientist. 我的梦想是成为一名科学家。
作定语:置于所修饰的词之后 I have a chance to study abroad. 我有一个出国进修的机会。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动词不定式 省略to的不定式* 感官动词hear、 see、feel、 watch等以及使役动词let、 make、have 后的不定式省略to I heard him sing in the next room. 我听到他在隔壁房间唱歌了。
The boss made them work day and night. 老板让他们日夜工作。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动名词* v. + ing 常跟动名词作宾语的动词有enjoy、 finish、 miss、 suggest、consider、 mind、 practice、 keep等 Alice enjoys reading so much. 爱丽丝非常喜欢阅读。
Have you finished washing the dishes 你刷完碗了吗?
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动名词* v. + ing 常跟动名词作宾语的短语有have fun、have difficulty (in)、 feel like、 give up等 Tony has some difficulty (in) learning math. 托尼学习数学有困难。
His father gave up smoking two years ago. 他的爸爸两年前就戒烟了。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动名词* v. + ing need、 require作需要讲时,后加动名词等于加动词不定式的被动式 The window needs cleaning. = The window needs to be cleaned. 窗户需要擦一擦了。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
分词* 现在分词 v. + ing 感官动词see、 hear、feel、watch、notice等词之后接现在分词表示动作正在进行 I heard someone laughing. 我听到有人在笑。
Snakes can feel things moving. 蛇能感觉到物体在动。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
分词* 过去分词 v. + ed / 动词不规则形式 表示已经完成的动作或被动意义 the risen sun 已经升起的太阳
the tea contained in a box 装在盒子里的茶
续表
小贴士
①有些动词后面既可以接不定式,又可以接动词-ing形式,意义没有明显区别。
例如:begin to do / doing sth. 开始做某事
start to do / doing sth. 开始做某事
hate to do / doing sth. 讨厌做某事
love/like to do / doing sth. 热爱 / 喜欢做某事
有些动词后面既可以接不定式,又可以接动词-ing形式,意义区别较大。
例如:
remember to do sth. 记得做某事(还未做)
remember doing sth. 记得做过某事(做过了)
forget to do sth. 忘记做某事(还未做)
forget doing sth. 忘记做过某事(做过了)
regret to do sth. 对要做的事遗憾(还未做)
regret doing sth. 后悔做过某事(做过了)
try to do sth. 努力做某事
try doing sth. 尝试做某事
stop to do sth. 停下来去做某事
stop doing sth. 停止做某事
②help to do sth. = help do sth.有助于做某事
③在谓语动词 + 宾语 + 形容词 / 名词(宾补)中,如果宾语为不定式,可用it作形式宾语,真正的宾语放在后面,构成“主语 + 谓语 + it + 宾语补足语(形容词或名词) + to do sth. ”的结构。谓语动词常为 find、think、feel等。
例如:I found it difficult to learn English. 我发现学英语很难。
用方框中所给的情态动词完成下面句子
should can need will may
1. Some schools have vending machines(自动售货机). Students can put their study points into them as money to buy the snacks and drinks they want.
2. If the noise monitor(监测器) finds that your voice is too loud, then it will send voice tips reminding you to lower your voice.
can
will
3. There’s no car in the ETC channel(通道). It may be broken.
4. In my view, students should not learn geography through rote learning(死记硬背). A kind of VR glasses can bring them to the Himalayas and the Pacific.
5. — Need I take a map when I visit a new city
— Of course not. You just have to download an App.
may
should
Need
should can need will may
用所给词的适当形式填空
1. Maybe in the future we can hear robot students talk (talk) about their homework.
2. Art works painted by robot dogs will be shown (show) in an exhibition at the art museum.
3. Paul wants to invent a bed-desk. With it, we can have (have) better sleep and a healthier body.
4. Not everyone is good at computer. However, many jobs require us to use (use) computer skills.
talk
be shown
have
to use
5. Polish artist Pilat usually teaches (teach) robot dogs how to paint through AI technology.
6. Not listening to Mom as much as you used to There may be (be) a scientific reason for it.
7. Disabled people have difficulty typing (type) words on a computer, but now they can do it by moving their eyes.
8. Magic Mirror is a software for people to check (check) their health. You can have a try.
teaches
be
typing
to check
9. China has (have) done a good job exploring space — the Tiangong space station is a good example.
10. Connected (connect) to 5G, all kinds of environment information can be known by users.
has
Connected
用所给词的适当形式填空
Developed by US company OpenAI, ChatGPT(人工智能聊天机器人程序) has taken the Internet by storm, winning lots of users since it 1. came (come) out in November, 2022. People can ask the robot to write stories and emails, create instructions for 2. cooking (cook) a certain food, translate languages, and answer all kinds of questions. In its own words, it is “a language model trained in a large amount of Internet text 3. to help (help) users get human-like text”.
came
cooking
to help
4. Compared (compare) with Siri or other chatbots, ChatGPT uses a much bigger information center for training. It also 5. uses (use) stronger software and hardware to learn things by itself. For example, if it provides a wrong answer to your question, you can tell it the right one and it 6. will correct (correct) itself. “It’s a totally different chatbot,” a computer scientist from Nankai University told Tianjin Daily. “The knowledge level ChatGPT shows 7. is (be) the same as a university student. That’s why it surprised the world.”
Compared
uses
will correct
is
But one big problem with ChatGPT is that it makes mistakes or even 8. gives (give) false information. When Rezza, a 28-year-old man, used the robot 9. to write (write) an essay(论文). “It gave out many examples which other writers actually hadn’t mentioned at all,” he told The Guardian. Since the robot 10. was trained (train) by using words from the Internet, it has picked up biases(偏见) about certain groups. These are all things that need to be dealt with.
gives
to write
was trained
主题九 科学与技术
语法专项复习
一、动词的分类
类别 形式 用法 例句
助动词 be、do、 have、shall、will等 协助主要动词构成否定、疑问等结构或帮助构成谓语,表达时态、语态、语气等 Will he graduate from Harvard University next year 明年他将从哈佛大学毕业吗?
I haven’t finished my homework yet. 我还没有完成我的作业。
类别 形式 用法 例句
连系动词 be、 look、 sound、 feel、 smell、 taste、 get、 become、 keep、 remain等 连接主语和表语,和表语构成系表结构来说明主语的身份、性质、状态等 Our country is becoming stronger and stronger. 我们的国家正变得越来越强大。
This kind of cloth feels soft. 这种布料手感柔软。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
实义动词 及物动词 后接宾语才能表达完整的意思 We reached Australia the day before yesterday. 我们前天到了澳大利亚。
不及物动词 后不能直接跟宾语,或在宾语前加介词、副词等 The bus stopped. 公交车停下了。
Look at the blackboard, please. 请看黑板。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
情态动词 can/could、may/might、must、need、should、shall、will/would等 (情态动词详细用法见下文)
续表
情态动词
情态动词表示说话人对所说动作的观点,如需要、可能、意愿、怀疑等。在形式上,情态动词一般没有人称和数的变化,后接动词原形。
(1) can的用法
①表能力:can表能力时意味着凭体力、脑力或技术等能够去做某事。
例如:She is only five, but she can read. 她只有五岁,但她已经会阅读了。
②表可能性:多用于否定与疑问结构中,但也可用在肯定句中。
例如:This dictionary can be Linda’s. 这本字典可能是琳达的。
③表示征得他人许可(和may意思相近):常见于口语。
例如:Can/May I come in 我能进来吗?
(2) could的用法
①表可能性(过去或现在)。
例如:He said the news could be true. 他说消息可能是真的。(表示过去的可能性)
Someone is knocking at the door. Who could it be 有人在敲门,可能会是谁呢?(表示现在的可能性)
②表过去的能力。
例如:I could play the piano when I was only six. 我六岁时就能弹钢琴了。
③表允许。可表示委婉客气地提出问题或陈述看法,不是can的过去式。
例如:—Could I use your computer ——我可以用你的 电脑吗?
—Sure. / No, you can’t. ——当然可以。/ 不,你不能。
(3) may与might的用法
①表示可能性较小的推测,意为“可能,也许”,常用于肯定句中。might表推测时,可能性低于may。
例如:It might rain the day after tomorrow. 后天可能下雨。
②表示许可或请求,意为“可以”。在疑问句中,might比may的语气更加委婉和客气。对may引导的一般疑问句,否定回答时要用mustn’t或can’t。
例如:—May I come in ——我可以进来吗?
—Yes, you can. ——是的,你可以。
—No, you can’t. ——不,你不可以。
—No, you mustn’t. ——不,绝不行。
小贴士
may be与maybe区分
①may是情态动词,be是动词原形,只能用于句子中。
例如:It’s eight o’clock now. Jack may be at home. 现在八点钟了,杰克可能在家。
②maybe是副词,相当于perhaps、probably或likely,常用于句首。
例如:It’s eight o’clock now. Maybe Jack is at home. 现在八点钟了,杰克也许在家。
(4) must的用法
①表示“必须、必要”。
例如:We must follow the school rules. 我们必须遵守学校的规则。
②表示“一定”,常用于must be + 表语的结构中,通常表示猜测(只用在肯定句中)。
例如:This must be Lucy’s room. 这一定是露西的房间。
③must的否定式有两个:当回答由must引起的问题时,否定回答要用needn’t或don’t have to,表示“无须”“用不着” “不一定”的意义。当表示“不应该”“不许可”“禁止” 时,就用must not。
例如:—Must I go tomorrow? ——明天我必须去吗?
—Yes, you must. ——是的,你必须去。
—No, you needn’t. ——不,你不用去。
注:must = have to,但有区别。must表示说话人的主观思想,have to意为“不得不,必须”,表示客观需要,客观条件只能如此。
例如:You must do it now. 你必须现在就做。(说话人认为必须现在做)
I have to go now. 我现在必须走。(受客观条件限制必须现在走)
(5) need 的用法
①need作情态动词,表“需要”,多用在否定句或疑问句中。
例如:—Need I hand in the report tomorrow ——我需要明天交报告吗?
—Yes, you must. / No, you needn’t. ——是的,你需要。/ 不,你没必要。
②need也作实义动词,用法是“need to do sth.”。
例如:As students, we need to finish our homework on time. 作为学生,我们需要按时完成作业。
③need主动表被动,用法是“sth. need(s) doing = sth. need(s) to be done”。
例如:The room needs cleaning. = The room needs to be cleaned. 这个房间需要清扫。
④need作名词。
例如:This bag meets Ann’s need. 这个包满足安的需要。
(6) should的用法
意思为“应该”,表示劝告、建议、命令,其同义词是ought to;在疑问句中,通常用should代替ought to。
例如:You should go to class right away. 你应该马上去上课。
Should I open the door 我应该开门吗?
(7) shall的用法
意思为“将要 / 应该”,多用于第一人称征求对方的意见。
例如:What shall I wear at my birthday party 在我的生日宴会上我穿什么好呢?
(8) will与would的用法
①表示意志、愿望和决心等,意为“要,愿”,可用于各种人称。would是will的过去式。
例如:I will never do it again and that’s the last time. 我再也不会这样做了,那是最后一次。
My brother said he would help me to solve the problem. 我哥哥说他将会帮助我解决这个问题。
②表示提出请求或征求对方的意见,多用于第二人称作主语的一般疑问句中。would比will的语气更加委婉。
例如:Would you please do me a favor 请你帮我一个忙,好吗?
二、非谓语动词
非谓语动词是指在句子中不是谓语的动词,主要包括动词不定式、动名词和分词(现在分词和过去分词)。非谓语动词除了不能独立作谓语外,可以承担句子的其他成分。
类别 形式 用法 例句
动词 不定式 to do; not to do 作宾语:可接不定式作宾语的动词有choose、 decide、 expect、 fail、 hope、 learn、 manage、 offer、 promise、 refuse、 want、 plan、 agree等 I plan to go to the movies this afternoon. 我打算今天下午去看电影。
He has decided to go to the countryside. 他已决心去乡下。
类别 形式 用法 例句
动词 不定式 to do; not to do 作状语:常表示目的、原因、结果等 He is strong enough to move the heavy box. 他足够强壮能搬动这个箱子。
They ran over to welcome the foreign guests. 他们跑过来欢迎外宾。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动词 不定式 to do; not to do 作宾语补足语:可接不定式作补语的动词有tell、 advise、 allow、 encourage、 remind、 warn、 require等 He asked the driver to stop the motorbike. 他请那位司机拦下那辆摩托车。
Our school allows students to wear their own clothes on Fridays. 我们学校允许学生在周五穿自己的衣服。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动词 不定式 to do; not to do 作主语:用it作形式主语 It is not easy for us to learn a foreign language. 学习外语对我们来说不容易。
It is careless of you to do that. 你这么做真粗心。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动词 不定式 to do; not to do 作表语 My dream is to be a scientist. 我的梦想是成为一名科学家。
作定语:置于所修饰的词之后 I have a chance to study abroad. 我有一个出国进修的机会。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动词不定式 省略to的不定式* 感官动词hear、 see、feel、 watch等以及使役动词let、 make、have 后的不定式省略to I heard him sing in the next room. 我听到他在隔壁房间唱歌了。
The boss made them work day and night. 老板让他们日夜工作。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动名词* v. + ing 常跟动名词作宾语的动词有enjoy、 finish、 miss、 suggest、consider、 mind、 practice、 keep等 Alice enjoys reading so much. 爱丽丝非常喜欢阅读。
Have you finished washing the dishes 你刷完碗了吗?
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动名词* v. + ing 常跟动名词作宾语的短语有have fun、have difficulty (in)、 feel like、 give up等 Tony has some difficulty (in) learning math. 托尼学习数学有困难。
His father gave up smoking two years ago. 他的爸爸两年前就戒烟了。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
动名词* v. + ing need、 require作需要讲时,后加动名词等于加动词不定式的被动式 The window needs cleaning. = The window needs to be cleaned. 窗户需要擦一擦了。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
分词* 现在分词 v. + ing 感官动词see、 hear、feel、watch、notice等词之后接现在分词表示动作正在进行 I heard someone laughing. 我听到有人在笑。
Snakes can feel things moving. 蛇能感觉到物体在动。
续表
类别 形式 用法 例句
分词* 过去分词 v. + ed / 动词不规则形式 表示已经完成的动作或被动意义 the risen sun 已经升起的太阳
the tea contained in a box 装在盒子里的茶
续表
小贴士
①有些动词后面既可以接不定式,又可以接动词-ing形式,意义没有明显区别。
例如:begin to do / doing sth. 开始做某事
start to do / doing sth. 开始做某事
hate to do / doing sth. 讨厌做某事
love/like to do / doing sth. 热爱 / 喜欢做某事
有些动词后面既可以接不定式,又可以接动词-ing形式,意义区别较大。
例如:
remember to do sth. 记得做某事(还未做)
remember doing sth. 记得做过某事(做过了)
forget to do sth. 忘记做某事(还未做)
forget doing sth. 忘记做过某事(做过了)
regret to do sth. 对要做的事遗憾(还未做)
regret doing sth. 后悔做过某事(做过了)
try to do sth. 努力做某事
try doing sth. 尝试做某事
stop to do sth. 停下来去做某事
stop doing sth. 停止做某事
②help to do sth. = help do sth.有助于做某事
③在谓语动词 + 宾语 + 形容词 / 名词(宾补)中,如果宾语为不定式,可用it作形式宾语,真正的宾语放在后面,构成“主语 + 谓语 + it + 宾语补足语(形容词或名词) + to do sth. ”的结构。谓语动词常为 find、think、feel等。
例如:I found it difficult to learn English. 我发现学英语很难。
用方框中所给的情态动词完成下面句子
should can need will may
1. Some schools have vending machines(自动售货机). Students can put their study points into them as money to buy the snacks and drinks they want.
2. If the noise monitor(监测器) finds that your voice is too loud, then it will send voice tips reminding you to lower your voice.
can
will
3. There’s no car in the ETC channel(通道). It may be broken.
4. In my view, students should not learn geography through rote learning(死记硬背). A kind of VR glasses can bring them to the Himalayas and the Pacific.
5. — Need I take a map when I visit a new city
— Of course not. You just have to download an App.
may
should
Need
should can need will may
用所给词的适当形式填空
1. Maybe in the future we can hear robot students talk (talk) about their homework.
2. Art works painted by robot dogs will be shown (show) in an exhibition at the art museum.
3. Paul wants to invent a bed-desk. With it, we can have (have) better sleep and a healthier body.
4. Not everyone is good at computer. However, many jobs require us to use (use) computer skills.
talk
be shown
have
to use
5. Polish artist Pilat usually teaches (teach) robot dogs how to paint through AI technology.
6. Not listening to Mom as much as you used to There may be (be) a scientific reason for it.
7. Disabled people have difficulty typing (type) words on a computer, but now they can do it by moving their eyes.
8. Magic Mirror is a software for people to check (check) their health. You can have a try.
teaches
be
typing
to check
9. China has (have) done a good job exploring space — the Tiangong space station is a good example.
10. Connected (connect) to 5G, all kinds of environment information can be known by users.
has
Connected
用所给词的适当形式填空
Developed by US company OpenAI, ChatGPT(人工智能聊天机器人程序) has taken the Internet by storm, winning lots of users since it 1. came (come) out in November, 2022. People can ask the robot to write stories and emails, create instructions for 2. cooking (cook) a certain food, translate languages, and answer all kinds of questions. In its own words, it is “a language model trained in a large amount of Internet text 3. to help (help) users get human-like text”.
came
cooking
to help
4. Compared (compare) with Siri or other chatbots, ChatGPT uses a much bigger information center for training. It also 5. uses (use) stronger software and hardware to learn things by itself. For example, if it provides a wrong answer to your question, you can tell it the right one and it 6. will correct (correct) itself. “It’s a totally different chatbot,” a computer scientist from Nankai University told Tianjin Daily. “The knowledge level ChatGPT shows 7. is (be) the same as a university student. That’s why it surprised the world.”
Compared
uses
will correct
is
But one big problem with ChatGPT is that it makes mistakes or even 8. gives (give) false information. When Rezza, a 28-year-old man, used the robot 9. to write (write) an essay(论文). “It gave out many examples which other writers actually hadn’t mentioned at all,” he told The Guardian. Since the robot 10. was trained (train) by using words from the Internet, it has picked up biases(偏见) about certain groups. These are all things that need to be dealt with.
gives
to write
was trained
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
