外研版(2019)选择性必修第二册Unit 5 A delicate world 单元教学设计(表格式)
文档属性
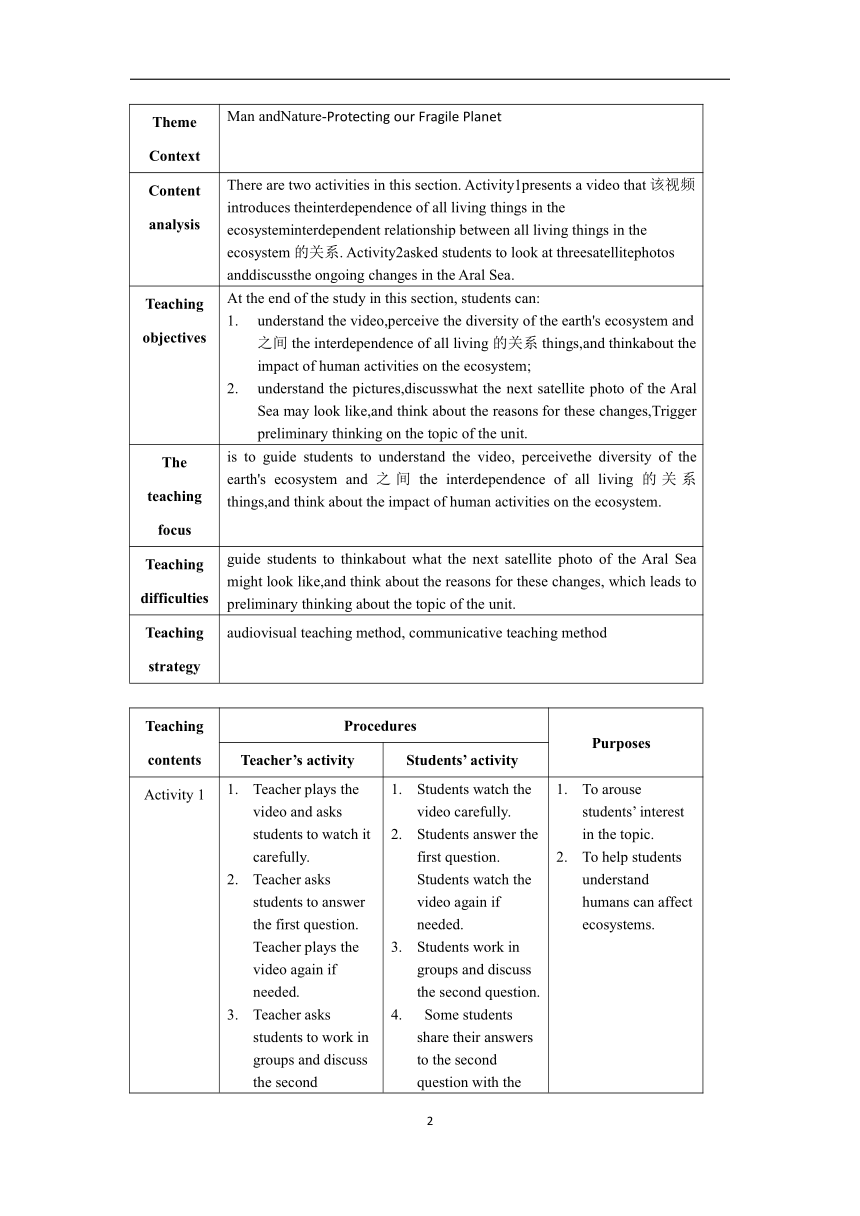
| 名称 | 外研版(2019)选择性必修第二册Unit 5 A delicate world 单元教学设计(表格式) |

|
|
| 格式 | docx | ||
| 文件大小 | 50.4KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-03-12 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览


文档简介
Book 5 Unit 5 A delicious world Teaching design
Unit theme The subject context of this unit is “Man and Nature”, and the subject context content involved is to protect our fragile planet. This module introduces the process of the ecosystem of Macquarie Island from being severely damaged to gradual recovery, the impact of the pet red-eared tortoise on the local ecosystem after being released, the restoration of the ecological environment of Saihamba National Forest Park, the relationship between the ecosystem and the survival of bees, Shennongjia and Fanjing Mountain ecosystemsGood protection guides students to realize that human survival must depend on a good natural ecosystem. Protecting ecology is to protect human beings and deepen students' understanding of the concept of harmonious coexistence between man and nature.
The target students of the unit can focus on the contextual content of the subject of this unit, based on the multi-modal discourse such as the phenomenon description and flow chart provided by the unit, comprehensively use various language skills to read different types of discourse content; be able to properly useit as a formal object to describe the problems and changes faced by different ecosystems, understand and grasp listeningThe core ideas and detailed information of the textbook, use the language learned to describe the disastrous impact that the disappearance of a single creature may have on mankind, deepen the understanding of the significance of the subject of the unit, raise the awareness of protecting the ecosystem and establishing a community of human destiny; at the same time, be able to use the knowledge learned in the unit to describe the current situation of the local ecosystem and think about adoptingWhat kind of protective measures to realize the expansion and migration of knowledge and thinking skills; through the use of various learning strategies, in the process of autonomous, cooperative and inquiry-based learning, combined with the reflective and evaluative issues provided by the unit, continuously monitor, evaluate, reflect on and adjust one's own learning content and process to improve oneselfThe ability to understand and express, and ultimately promote the comprehensive improvement of one's own language ability, cultural awareness, thinking quality and learning ability.
Starting outThe teaching design of the Starting out section (the recommended durationis 10-15minutes, and teachers can adjust it at their discretion according to the actual teaching. )
Course Type Listening + Viewing
Theme Context Man andNature-Protecting our Fragile Planet
Content analysis There are two activities in this section. Activity1presents a video that该视频introduces theinterdependence of all living things in the ecosysteminterdependent relationship between all living things in the ecosystem的关系. Activity2asked students to look at threesatellitephotos anddiscussthe ongoing changes in the Aral Sea.
Teaching objectives At the end of the study in this section, students can: understand the video,perceive the diversity of the earth's ecosystem and之间the interdependence of all living的关系things,and thinkabout the impact of human activities on the ecosystem; understand the pictures,discusswhat the next satellite photo of the Aral Sea may look like,and think about the reasons for these changes,Trigger preliminary thinking on the topic of the unit.
The teaching focus is to guide students to understand the video, perceivethe diversity of the earth's ecosystem and之间the interdependence of all living的关系things,and think about the impact of human activities on the ecosystem.
Teaching difficulties guide students to thinkabout what the next satellite photo of the Aral Sea might look like,and think about the reasons for these changes, which leads to preliminary thinking about the topic of the unit.
Teaching strategy audiovisual teaching method, communicative teaching method
Teaching contents Procedures Purposes
Teacher’s activity Students’ activity
Activity 1 Teacher plays the video and asks students to watch it carefully. Teacher asks students to answer the first question. Teacher plays the video again if needed. Teacher asks students to work in groups and discuss the second question. Teacher invites some students to share their answers to the second question. Students watch the video carefully. Students answer the first question. Students watch the video again if needed. Students work in groups and discuss the second question. Some students share their answers to the second question with the class. To arouse students’ interest in the topic. To help students understand humans can affect ecosystems.
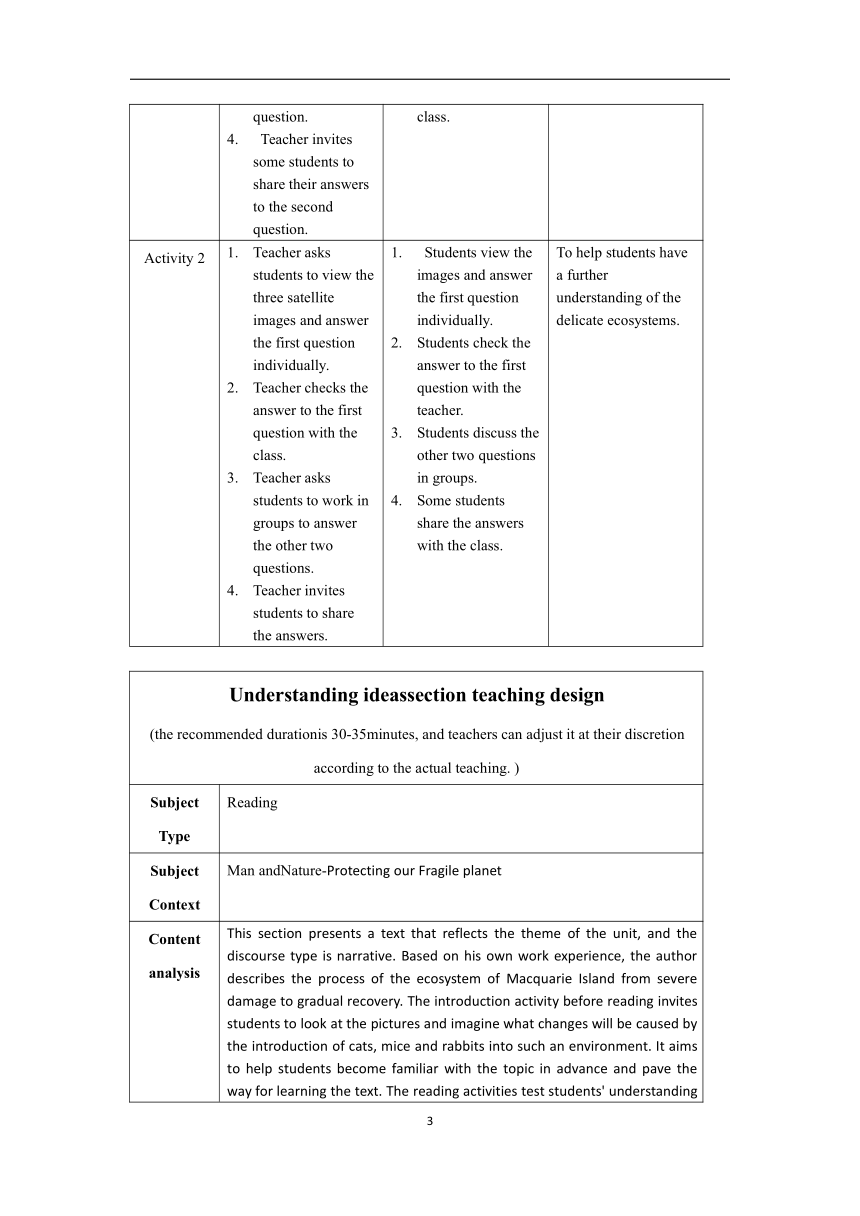
Activity 2 Teacher asks students to view the three satellite images and answer the first question individually. Teacher checks the answer to the first question with the class. Teacher asks students to work in groups to answer the other two questions. Teacher invites students to share the answers. Students view the images and answer the first question individually. Students check the answer to the first question with the teacher. Students discuss the other two questions in groups. Some students share the answers with the class. To help students have a further understanding of the delicate ecosystems.
Understanding ideassection teaching design (the recommended durationis 30-35minutes, and teachers can adjust it at their discretion according to the actual teaching. )
Subject Type Reading
Subject Context Man andNature-Protecting our Fragile planet
Content analysis This section presents a text that reflects the theme of the unit, and the discourse type is narrative. Based on his own work experience, the author describes the process of the ecosystem of Macquarie Island from severe damage to gradual recovery. The introduction activity before reading invites students to look at the pictures and imagine what changes will be caused by the introduction of cats, mice and rabbits into such an environment. It aims to help students become familiar with the topic in advance and pave the way for learning the text. The reading activities test students' understanding of the overall content of the text. Post-reading activities include activities such as analyzing the author's writing purpose, understanding the details of the text, and answering open questions, so as to inspire students to think deeply and actively explore the meaning of the topic.
Teaching objectives At the end of the study in this section, students can: quickly read the article tounderstand what happened on Macquarie Island; read the text, find out the author's writing purpose and say the reason; analyze the human intervention behavior, purpose and intention of Macquarie Island and the consequences caused, and use mind guidanceThe picture presents important information to improve learning efficiency; by thinking about open issues, the ability to speculate is improved.
The teaching focus is to guide students to read the text, findout the purpose of the author's writing, and understand the various behaviors that humans have done to save Macquarie Island.
Teaching difficulties guide students to analyze the humanintervention behavior, purpose and consequences of Macquarie Island, and deepen their understanding of the significance of the topic.
Teaching strategy P-W-Pmodel
Teaching contents Procedures Purposes
Teacher’s activity Students’ activity
Activity 1 Teacher asks students to look at the picture and think about the questions. Teacher divides the class into groups to have discussions about the questions. Teacher chooses one or two groups to share their results with the class. Students look at the picture and think about the questions individually. Students work in groups and discuss the questions. One or two groups present their results to the class. To let students understand invasive species can damage the local ecosystems. To arouse the students’ curiosity about the topic.
Activity 2 Teacher asks students to look at the title and predict what the passage mainly talks about. Teacher asks students to read the passage and find out what happened to Macquarie Island. Teacher asks some students to share the answers. Students look at the title and think about what the passage mainly talks about. Students read the passage and find out what happened to Macquarie Island . Some students share the answers with the class. To let students understand what happened to Macquarie Island.
Activity 3 Teacher asks students to choose the author’s purpose in writing this passage and give their reasons. Teacher invites some students to share their answers and others to make comments. Students read the passage again and choose the author’s purpose in writing this passage and give their reasons. Some students share their answers with the class. Others make comments. To help students figure out the author’s purpose in writing the passage.
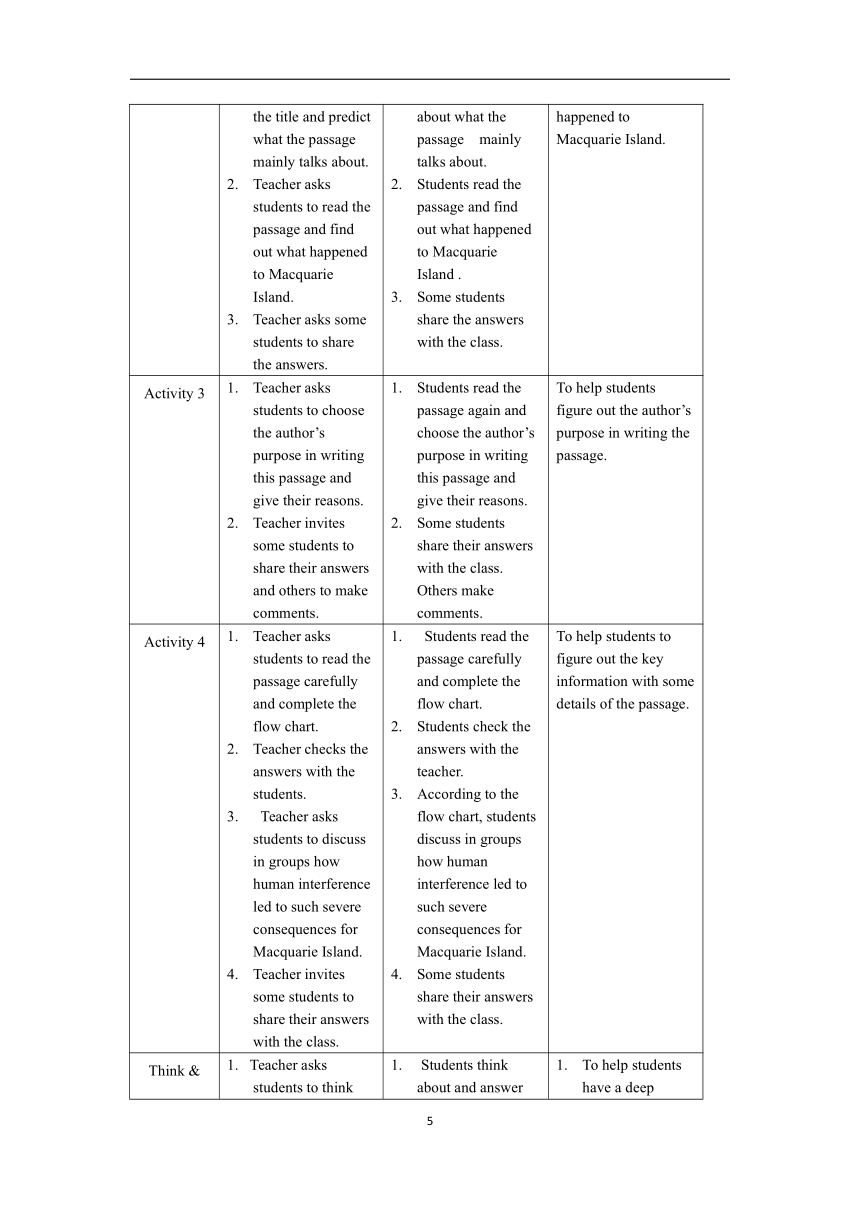
Activity 4 Teacher asks students to read the passage carefully and complete the flow chart. Teacher checks the answers with the students. Teacher asks students to discuss in groups how human interference led to such severe consequences for Macquarie Island. Teacher invites some students to share their answers with the class. Students read the passage carefully and complete the flow chart. Students check the answers with the teacher. According to the flow chart, students discuss in groups how human interference led to such severe consequences for Macquarie Island. Some students share their answers with the class. To help students to figure out the key information with some details of the passage.
Think & Share Teacher asks students to think about and answer the questions individually. Teacher asks students to discuss the questions in groups. Teacher invites some students to share the answers with the class. Students think about and answer the questions individually. Students discuss the questions in groups. Some students share the answers with the class. To help students have a deep understanding of the theme of the passage. To help students apply what they’ve learnt in life. To encourage students to apply cause and effect in their reading and writing.
Using languageTeaching design of the Using language section (the recommended durationis 80-90minutes, and teachers can adjust it at their discretion according to the actual teaching. )
Course type Reading + Listening + Speaking
Theme Context Man andNature-Protecting our Fragile Planet
Content analysis This section is a comprehensive activity that combines grammar, vocabulary, and listening and speaking under the topic of the unit. The main content of the grammar partis the usage of itas a formal object, including a small discourse and two comparative pictures. The short paragraph tells about the threat posed by the pet red-eared tortoises released in recent years to local species; the two pictures compare the present and past changes in Saihamba National Forest Park. The topic of the comprehensive language use part is “Ecosystem”. The vocabulary part presents the food chain in the ecosystem and its related expressions through a set of schematic diagrams and a small discourse; the next part is a dialogue about the potential impact of the decrease in the number of bees on the entire ecosystem. This section aims to help students deeply focus on the meaning and function of language, think and communicate in the real context, and enhance students' comprehensive language use ability in all directions.
Teaching objectives At the end of the study in this section, students can: master and useitas a formal object; masterrelevant expressionsofabout the food chain to understand the relationship between different speciesin the food chain; understandthe dialogue about bees on the verge of extinction对话tofurther understand the importance of ecological balance; useto express doubts and respond to doubtsto talk about somethingThe impact of species extinction on the ecosystem.
The teaching focus is to guide students to discover and understandthe usage of itas a formal object, and learn to use it in the real context; lead students to learn and use relevant expressions about the food chain to understand the relationship between different speciesin the food chain; guide students to complete listening activities to further understand the importance of ecological balance, while also being able toPay attention to pragmatic functions, learn to express doubts and respond to others' doubts.
Teaching difficulties guide students to useitas a formal object in the real context; guide studentsto realize that the extinction of a certain kind of creature will have a huge impact on the ecosystem, and encourage students to contribute to the protection of the ecological environment..
Teaching strategy task-based pedagogy, communicative pedagogy, listening and speaking pedagogy
Teaching contents Procedures Purposes
Teacher’s activity Students’ activity
Activity 1 Teacher asks students to read the sentences in each group in the box and pay special attention to the difference between them. Teacher asks students to work in groups and discuss the two questions. Teacher invites some students to share their answers. Teacher instructs students to look for more sentences with it as an empty object in the reading passage and summarise the use of it as an empty object in their own words. Teacher asks some students to share the answers. Students observe the sentences in each group in the box and pay attention to the difference between them. Students discuss the two questions in groups. Some students share their answers. Students look for more sentences with it as an empty object in the reading passage and summarise the use of it as an empty object in their own words. Some students share the answers with the class. To help students find out the structure and function of it as an empty object. To help students get familiar with the use of it as an empty object.
Activity 2 Teacher asks students to read the passage and get the main idea of the passage. Teacher asks students to rewrite the underlined parts using it as an empty object. Then asks students to make corrections in groups. Teacher checks the answers with the class. Students read the passage and get its main idea. Students rewrite the underlined parts using it as an empty object. Then make corrections in groups. Students check the answers with the teacher. To let students apply it as an empty object in a context.
Activity 3 Teacher asks students to look at the two pictures of the Saihanba National Forest Park and find its changes. Teacher asks students to work in groups and follow the model sentences to describe the changes in the Saihanba National Forest Park using it as an empty object where appropriate. Teacher invites one or two groups to share the answers with the class. Students look at the two pictures of the Saihanba National Forest Park and find its changes. Students work in groups and follow the model sentences to describe the changes in the Saihanba National Forest Park using it as an empty object where appropriate One or two groups share the answers with the class. To help students consolidate the application of it as an empty object in a real context.
Activity 4 Teacher asks students to think about a place they know has changed individually. Teacher asks students to work in groups and have a discussion, then describe how the place has changed using it as an empty object where appropriate. Teacher invites some students to share the answers with the class and others make comments. Students think about a place they know has changed individually. Students work in groups and have a discussion, then describe how the place has changed using it as an empty object where appropriate. Some students share the answers with the class. Others make comments. To help students to further understand a place that has changed and the use of it as an empty object.
Activity 5 Teacher asks students to look at the diagram and answer the first question. Teacher checks the answers with the class. Teacher asks students to pay attention to the expressions in bold and then answer the second question. Teacher invites some students to share the answers with the class. Students look at the diagram and answer the first question. Students check the answers with the teacher. Students pay attention to the expressions in bold and then answer the second question. Some students share the answers with the class. To let students learn some new expressions about the relationships between the living things.
Activity 6 Teacher asks students to complete the passage with the correct form of the words and expressions in Activity 5. Teacher checks the answers with the class. Students complete the passage with the correct form of the words and expressions in Activity 5. Students check the answers with the teacher. To help students review the expressions about the relationships between the living things.
Activity 7 Teacher asks students to read the statements in Did You Know and learn about the facts about honey bees. Teacher asks students to read the statements and choose the true ones. Teacher plays the audio and asks students to choose the true statements. Teacher checks the answer with the class. Students read the statements in Did You Know and learn about the facts about honey bees. Students read the statements and choose the true ones. Students listen to the audio and choose the true statements. Students check the answer with the teacher. To train students’ skills in grasping the main idea of a conversation through listening.
Activity 8 Teacher asks students to look at the flow chart first. Then play the audio again and ask students to complete the flow chart. Teacher asks students to listen for a third time and check the answers by themselves. Teacher invites some students to share the answers with the class. Teacher asks students to talk about the importance of bees in their own words. Students look at the flow chart first. Then listen to the audio again and complete the flow chart. Students listen to the audio for a third time and check the answers by themselves. Some students share the answers with the class. Students talk about the importance of bees in their own words. To let students get the details of the listening material.
Activity 9 Teacher asks students to look at the two headers and tell what they know about the different functions. Teacher asks students to complete the boxes with the expressions from the conversation. Teacher checks the answers with the class. Students look at the two headers and tell what they know about the different functions. Students complete the boxes with the expressions from the conversation. Students check the answers with the teacher. To help students consolidate the expressions of expressing doubt and responding to doubt.
Activity 10 Teacher divides students into groups and asks them to talk about what would happen to the ecosystem if another species died out using the expressions in this section. Teacher invites several groups to present their ideas in front of the class. Teacher asks students to think about how their knowledge helped them contribute to the discussion. Students work in groups and talk about what would happen to the ecosystem if another species died out using the expressions in this section. Several groups present their ideas in front of the class. Students think about how their knowledge helped them contribute to the discussion. To encourage students to further practise describing the delicate ecosystem.
Developing ideasThe teaching design of the Developing ideas section (the recommended durationis 80-90minutes, and teachers can adjust it at their discretion according to the actual teaching. )
Course type Reading + Writing
Theme Context Man andNature-Protecting our Fragile Planet
Content analysis This section presents a text that reflects the theme of the unit from another perspective. The type of discourseis speech. The text introduces the reasons why Shennongjia hasbeen includedin the UNESCO World Heritage List, and shows that human beings can coexist in harmony with the ecological environment while developing. The second part introduces Fanjing Mountain, another model of ecosystem protection in our country, and asksstudents to draft a lecture on Fanjing Mountain. Through the study of this sector, students can think deeply about the relationship between human development and the protection of ecosystems, and finally realize that the two are not antagonistic. Humans can also protect ecosystems while pursuing development, thereby enhancing students' environmental awareness and further improving students' thinking quality.
Teaching objectives At the end of the study in this section, students can: grasp the meaning of the article andunderstand thereasons why Shennongjia was selected for the UNESCO World Intangible Cultural HeritageList; understand演讲the organizational structure characteristics of the speech and how to use data, examples and comparisons to support their own views; use the knowledge they have learned to write a lecture on Fanjing MountainTo further enhance the abilityto use languageand deepen the understanding of the meaning of the subject of the unit.
The focus of teaching is to lead students to grasp the meaning of the articleand understand the reasons why Shennongjia was selected for the UNESCO WorldIntangible Cultural HeritageList; guide studentsto writelecture drafts to further improve their language skills and deepen their understanding of the significance of the subject of the unit.
Teaching difficulties guide students to learn演讲the characteristics of the organizational structure of the speech and how to use data, examples and comparisons to support their own views;
teaching strategy P-W-Pmodel
Teaching contents Procedures Purposes
Teacher’s activity Students’ activity
Activity 1 Teacher asks students to watch the video and answer the questions. Teacher invites some students to give answers. Students watch the video and answer the questions. Some students give answers. To lead students into the topic of Shennongjia.
Activity 2 Teacher asks students to look at the title of the passage and think about what it means. Teacher asks students to work in groups and discuss the question. Then invite some students to share the answers. Teacher asks students to read the passage and check their answer. Students look at the title of the passage and think about what it means. Students work in groups and discus the question. Some students share the answers. Students read the passage and check their answers. To strengthen students’ ability to understand the topic.
Activity 3 Teacher asks students to read the sentences from the passage and decide if they serve to give data, examples or make comparisons. Teacher asks students to discuss in groups, and decide their answers. Teacher invites some students to give answers. Students read the sentences from the passage and decide if they serve to give data, examples or make comparisons. Students discuss in groups and decide their answers. Some students give answers. To help students learn giving data, examples and making comparisons.
Think & Share Teacher asks students to think about the questions and discuss them in groups. Teacher invites some students to give answers. Students think about the questions and discuss them in groups. Some students give answers. To enhance students’ understanding of the theme of the passage and encourage students to show their own opinions.
Activity 4 Teacher asks students to think about the similarities and differences between Macquarie Island and Shennongjia and make notes. Teacher asks students to discuss their answers in groups, decide the key points and prepare for a talk. Teacher invites several students to give their talk to the class and others to make comments. Teacher asks students to think about how effectively they used the language they have learnt to talk about the similarities and differences. Students think about the similarities and differences between Macquarie Island and Shennongjia and make notes. Students discuss their answers in groups, decide the key points and prepare for a talk. Some students give their talk to the class and others make comments. Students think about how effectively they used the language they have learnt to talk about the similarities and differences. To help students learn to compare and contrast. To improve students’ speaking skill and performance ability.
Activity 5 Teacher asks students to read the passage and think about the questions. Teacher divides the class into groups and asks them to discuss the two questions in groups. Teacher invites one or two groups to share their answers and others to make comments. Students read the passage and think about the questions. Students discuss the questions in groups. One or two groups share their answers and others make comments. To help students learn why Fanjing Mountain was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List.
Activity 6 Teacher asks students to complete the outline based on the information in Activity 5. Teacher asks students to draft their lectures about Fanjing Mountain. Students complete the outline based on the information in Activity 5. Students draft their lectures about Fanjing Mountain. To help students organise the lecture draft before making a lecture.
Activity 7 Teacher divides students into pairs and asks them to make improvements to each other’s lecture drafts. Teacher invites one or two pairs to share their answers to the class and others to make comments. Students work in pairs and make improvements to each other’s lecture drafts. One or two pairs share their answers to the class and others make comments. To encourage students to learn from their partners. To improve students’ writing and speaking skills.
Presentation ideas & Reflectionsection teaching design (the recommended durationis 40-45minutes, and teachers can adjust it at their discretion according to the actual teaching. )
Course type Speaking
Topic Context People and society-Protecting our fragile planet
Content analysis The Presenting ideassection requires students to first read总书记the famous sentences of General Secretary Xi Jinping and think about the meaning of ”green water and green mountains“ and ”Golden mountains and Silver mountains" and the message conveyed by these sentences. Then, in the form of speeches, students are promoted to comprehensively use the content they have learned, cooperate with each other, show their individuality, and fully express their understanding and understanding of the subject ideas of the unit. The Reflectionsection guides students to review the knowledge they have learned in this unit, evaluate and judge their learning behavior and effectiveness in a timely manner, reflect on themselves and make improvements.
Teaching objectives At the end of the study in this section, students can: understand the importance of protecting the ecological environment conveyed by “green water and green mountains are golden mountains and silver mountains”保护生态环境的重要性; give examples to provethat “green water and green mountains are golden mountains and silver mountains”to further deepentheir understanding of this topic.
The teaching focus is to guide students保护生态环境to have a deeper understanding of the topic of protecting the ecological environment through the study of this unit; guide studentsto give examples to provethe theme of “green water and green mountains are golden mountains and silver mountains”.
Teaching difficulties guide students to deeply realize the importance and urgency of protecting the ecological environment, and exercise students' logical thinking skills.
Teaching strategy task-based pedagogy, communicative pedagogy
Teaching contents Procedures Purposes
Teacher’s activity Students’ activity
Presenting ideas
Activity 1 Teacher divides students in group and asks students to look at the picture and answer the questions. Teacher invites one or two groups to share their answers to the class and others to make comments. Students work in groups and look at the pictures and answer the questions. One or two groups to share their answers to the class and others make comments. To help students understand the message conveyed by the quote.
Activity 2 Teacher asks students to talk about their understanding of the quote in groups and find examples that can prove it. Teacher asks students to make notes according to their discussion. Teacher asks students to share the answers and others to make comments. Students talk about their understanding of the quote in groups and find examples that can prove it. Students make notes according to their discussion. Students share the answers and others make comments. To help students to think deeply about “Clear waters and lush mountains are as valuable as gold and silver”.
Activity 3 Teacher asks students to prepare a short presentation considering the structure and useful words, expressions and structures. Teacher asks each group to choose one student to give the presentation. Teacher and other students make comments, and teacher gives evaluation. Asks students to vote for the most creative and the most popular presentation. Students prepare a short presentation considering the structure and useful words, expressions and structures. Each group chooses one student to give the presentation. Other students make comments. Students vote for the most creative and the most popular presentation. To encourage students to express their opinions, and help them correctly understand the unit theme.
Reflection
Teacher asks students to rate their performance in this unit, summarise what they’ve learnt and think about what they need to improve. Teacher asks students to write a reflection. Students rate their performance in this unit, summarise what they’ve learnt and think about what they need to improve. Students write a reflection. To help students evaluate their performance, review the unit, and think about ways to improve.
Projectsection teaching design (this part of the teacher can handle it at his discretion according to the actual teaching.)
Course type Speaking
Theme Context People and Society-Protecting our Fragile Planet
Content analysis The practical activities of this unit require students toexplorethe ecosystems around them, understand the importance of these ecosystems and think about how to protect them. Students can use the Internet or the library to query information, conduct research, and analyze the current situation of the ecosystem around them. Through independent learning, cooperative learning, and inquiry-based learning, we comprehensively use what we have learned in this unit to effectively complete open tasks, further deepen our understanding of the subject context of the unit, and learn to protect the environment from me.
Teaching objectives At the end of the study in this section, students can: be familiar with research methods and techniques, and choose appropriate ways to conduct research; comprehensively use what they have learned in this unit to present the survey results of the local ecosystem in a graphic manner; improve communication and inquiry skills through group cooperation and reasonable division of labor; fully understand the surroundingsThe ecosystem truly raises awareness of environmental protection.
The teaching focus is to guide students to familiarize themselves with research methods and techniques, choose appropriate ways to conduct research,organizethe research results, make slideshows and进行display them.
Teaching difficulties guide students to carry out cooperative exploration and improve communication and collaboration skills; guide students to fully understand the ecosystem around them, and truly improve the awareness of environmental
protection teaching strategies and task-based teaching methods
Teaching contents Procedures Purposes
Teacher’s activity Students’ activity
Investigate (In the previous class,) Teacher divides the class into groups and asks students to think about the ecosystems around them. Then asks students to go online or a library to find out how they might investigate them. Teacher asks each group to choose one of the ecosystems and find out information on it online. Students think about the ecosystems around them and go online or to a library to find out how they might investigate them. Each group chooses one of the ecosystems and find out information on it online. To get students prepared for the activities, and develop their ability to learn and explore individually. To help students get to know the ecosystems in the local area.
Plan Teacher asks students to decide how they will further investigate each of these aspects when they visit the ecosystems. Teacher encourages students to decide how best to present their information. Students decide how they will further investigate each of these aspects when they visit the ecosystems. Students decide how best to present their information. To help students prepare for the investigation and emphasise the importance of cooperation with others.
Create Teacher asks students to carry out the investigation, making notes and taking photos. Teacher asks students to write the text for their presentations. Teacher asks students to look for suitable photos, maps, diagrams, charts and any other visuals. Teacher asks students to put all the contents together into their chosen presentation format. Students carry out the investigation, making notes and taking photos. Students write the text for their presentations. Students look for suitable photos, maps, diagrams, charts and any other visuals. Students put all the contents together into their chosen presentation format. To offer students a chance to investigate one of the local ecosystems and learn to create a presentation.
Present Teacher encourages students to present the ecosystem to the class. Teacher encourages students to discuss how to protect the local ecosystem and how to reduce the impact of human activity on it. Students present the ecosystem to the class. Students discuss how to protect the local ecosystem and how to reduce the impact of human activity on it. To help students improve skills in giving presentation. To raise students’ awareness of the importance of ecosystems.
1
Unit theme The subject context of this unit is “Man and Nature”, and the subject context content involved is to protect our fragile planet. This module introduces the process of the ecosystem of Macquarie Island from being severely damaged to gradual recovery, the impact of the pet red-eared tortoise on the local ecosystem after being released, the restoration of the ecological environment of Saihamba National Forest Park, the relationship between the ecosystem and the survival of bees, Shennongjia and Fanjing Mountain ecosystemsGood protection guides students to realize that human survival must depend on a good natural ecosystem. Protecting ecology is to protect human beings and deepen students' understanding of the concept of harmonious coexistence between man and nature.
The target students of the unit can focus on the contextual content of the subject of this unit, based on the multi-modal discourse such as the phenomenon description and flow chart provided by the unit, comprehensively use various language skills to read different types of discourse content; be able to properly useit as a formal object to describe the problems and changes faced by different ecosystems, understand and grasp listeningThe core ideas and detailed information of the textbook, use the language learned to describe the disastrous impact that the disappearance of a single creature may have on mankind, deepen the understanding of the significance of the subject of the unit, raise the awareness of protecting the ecosystem and establishing a community of human destiny; at the same time, be able to use the knowledge learned in the unit to describe the current situation of the local ecosystem and think about adoptingWhat kind of protective measures to realize the expansion and migration of knowledge and thinking skills; through the use of various learning strategies, in the process of autonomous, cooperative and inquiry-based learning, combined with the reflective and evaluative issues provided by the unit, continuously monitor, evaluate, reflect on and adjust one's own learning content and process to improve oneselfThe ability to understand and express, and ultimately promote the comprehensive improvement of one's own language ability, cultural awareness, thinking quality and learning ability.
Starting outThe teaching design of the Starting out section (the recommended durationis 10-15minutes, and teachers can adjust it at their discretion according to the actual teaching. )
Course Type Listening + Viewing
Theme Context Man andNature-Protecting our Fragile Planet
Content analysis There are two activities in this section. Activity1presents a video that该视频introduces theinterdependence of all living things in the ecosysteminterdependent relationship between all living things in the ecosystem的关系. Activity2asked students to look at threesatellitephotos anddiscussthe ongoing changes in the Aral Sea.
Teaching objectives At the end of the study in this section, students can: understand the video,perceive the diversity of the earth's ecosystem and之间the interdependence of all living的关系things,and thinkabout the impact of human activities on the ecosystem; understand the pictures,discusswhat the next satellite photo of the Aral Sea may look like,and think about the reasons for these changes,Trigger preliminary thinking on the topic of the unit.
The teaching focus is to guide students to understand the video, perceivethe diversity of the earth's ecosystem and之间the interdependence of all living的关系things,and think about the impact of human activities on the ecosystem.
Teaching difficulties guide students to thinkabout what the next satellite photo of the Aral Sea might look like,and think about the reasons for these changes, which leads to preliminary thinking about the topic of the unit.
Teaching strategy audiovisual teaching method, communicative teaching method
Teaching contents Procedures Purposes
Teacher’s activity Students’ activity
Activity 1 Teacher plays the video and asks students to watch it carefully. Teacher asks students to answer the first question. Teacher plays the video again if needed. Teacher asks students to work in groups and discuss the second question. Teacher invites some students to share their answers to the second question. Students watch the video carefully. Students answer the first question. Students watch the video again if needed. Students work in groups and discuss the second question. Some students share their answers to the second question with the class. To arouse students’ interest in the topic. To help students understand humans can affect ecosystems.
Activity 2 Teacher asks students to view the three satellite images and answer the first question individually. Teacher checks the answer to the first question with the class. Teacher asks students to work in groups to answer the other two questions. Teacher invites students to share the answers. Students view the images and answer the first question individually. Students check the answer to the first question with the teacher. Students discuss the other two questions in groups. Some students share the answers with the class. To help students have a further understanding of the delicate ecosystems.
Understanding ideassection teaching design (the recommended durationis 30-35minutes, and teachers can adjust it at their discretion according to the actual teaching. )
Subject Type Reading
Subject Context Man andNature-Protecting our Fragile planet
Content analysis This section presents a text that reflects the theme of the unit, and the discourse type is narrative. Based on his own work experience, the author describes the process of the ecosystem of Macquarie Island from severe damage to gradual recovery. The introduction activity before reading invites students to look at the pictures and imagine what changes will be caused by the introduction of cats, mice and rabbits into such an environment. It aims to help students become familiar with the topic in advance and pave the way for learning the text. The reading activities test students' understanding of the overall content of the text. Post-reading activities include activities such as analyzing the author's writing purpose, understanding the details of the text, and answering open questions, so as to inspire students to think deeply and actively explore the meaning of the topic.
Teaching objectives At the end of the study in this section, students can: quickly read the article tounderstand what happened on Macquarie Island; read the text, find out the author's writing purpose and say the reason; analyze the human intervention behavior, purpose and intention of Macquarie Island and the consequences caused, and use mind guidanceThe picture presents important information to improve learning efficiency; by thinking about open issues, the ability to speculate is improved.
The teaching focus is to guide students to read the text, findout the purpose of the author's writing, and understand the various behaviors that humans have done to save Macquarie Island.
Teaching difficulties guide students to analyze the humanintervention behavior, purpose and consequences of Macquarie Island, and deepen their understanding of the significance of the topic.
Teaching strategy P-W-Pmodel
Teaching contents Procedures Purposes
Teacher’s activity Students’ activity
Activity 1 Teacher asks students to look at the picture and think about the questions. Teacher divides the class into groups to have discussions about the questions. Teacher chooses one or two groups to share their results with the class. Students look at the picture and think about the questions individually. Students work in groups and discuss the questions. One or two groups present their results to the class. To let students understand invasive species can damage the local ecosystems. To arouse the students’ curiosity about the topic.
Activity 2 Teacher asks students to look at the title and predict what the passage mainly talks about. Teacher asks students to read the passage and find out what happened to Macquarie Island. Teacher asks some students to share the answers. Students look at the title and think about what the passage mainly talks about. Students read the passage and find out what happened to Macquarie Island . Some students share the answers with the class. To let students understand what happened to Macquarie Island.
Activity 3 Teacher asks students to choose the author’s purpose in writing this passage and give their reasons. Teacher invites some students to share their answers and others to make comments. Students read the passage again and choose the author’s purpose in writing this passage and give their reasons. Some students share their answers with the class. Others make comments. To help students figure out the author’s purpose in writing the passage.
Activity 4 Teacher asks students to read the passage carefully and complete the flow chart. Teacher checks the answers with the students. Teacher asks students to discuss in groups how human interference led to such severe consequences for Macquarie Island. Teacher invites some students to share their answers with the class. Students read the passage carefully and complete the flow chart. Students check the answers with the teacher. According to the flow chart, students discuss in groups how human interference led to such severe consequences for Macquarie Island. Some students share their answers with the class. To help students to figure out the key information with some details of the passage.
Think & Share Teacher asks students to think about and answer the questions individually. Teacher asks students to discuss the questions in groups. Teacher invites some students to share the answers with the class. Students think about and answer the questions individually. Students discuss the questions in groups. Some students share the answers with the class. To help students have a deep understanding of the theme of the passage. To help students apply what they’ve learnt in life. To encourage students to apply cause and effect in their reading and writing.
Using languageTeaching design of the Using language section (the recommended durationis 80-90minutes, and teachers can adjust it at their discretion according to the actual teaching. )
Course type Reading + Listening + Speaking
Theme Context Man andNature-Protecting our Fragile Planet
Content analysis This section is a comprehensive activity that combines grammar, vocabulary, and listening and speaking under the topic of the unit. The main content of the grammar partis the usage of itas a formal object, including a small discourse and two comparative pictures. The short paragraph tells about the threat posed by the pet red-eared tortoises released in recent years to local species; the two pictures compare the present and past changes in Saihamba National Forest Park. The topic of the comprehensive language use part is “Ecosystem”. The vocabulary part presents the food chain in the ecosystem and its related expressions through a set of schematic diagrams and a small discourse; the next part is a dialogue about the potential impact of the decrease in the number of bees on the entire ecosystem. This section aims to help students deeply focus on the meaning and function of language, think and communicate in the real context, and enhance students' comprehensive language use ability in all directions.
Teaching objectives At the end of the study in this section, students can: master and useitas a formal object; masterrelevant expressionsofabout the food chain to understand the relationship between different speciesin the food chain; understandthe dialogue about bees on the verge of extinction对话tofurther understand the importance of ecological balance; useto express doubts and respond to doubtsto talk about somethingThe impact of species extinction on the ecosystem.
The teaching focus is to guide students to discover and understandthe usage of itas a formal object, and learn to use it in the real context; lead students to learn and use relevant expressions about the food chain to understand the relationship between different speciesin the food chain; guide students to complete listening activities to further understand the importance of ecological balance, while also being able toPay attention to pragmatic functions, learn to express doubts and respond to others' doubts.
Teaching difficulties guide students to useitas a formal object in the real context; guide studentsto realize that the extinction of a certain kind of creature will have a huge impact on the ecosystem, and encourage students to contribute to the protection of the ecological environment..
Teaching strategy task-based pedagogy, communicative pedagogy, listening and speaking pedagogy
Teaching contents Procedures Purposes
Teacher’s activity Students’ activity
Activity 1 Teacher asks students to read the sentences in each group in the box and pay special attention to the difference between them. Teacher asks students to work in groups and discuss the two questions. Teacher invites some students to share their answers. Teacher instructs students to look for more sentences with it as an empty object in the reading passage and summarise the use of it as an empty object in their own words. Teacher asks some students to share the answers. Students observe the sentences in each group in the box and pay attention to the difference between them. Students discuss the two questions in groups. Some students share their answers. Students look for more sentences with it as an empty object in the reading passage and summarise the use of it as an empty object in their own words. Some students share the answers with the class. To help students find out the structure and function of it as an empty object. To help students get familiar with the use of it as an empty object.
Activity 2 Teacher asks students to read the passage and get the main idea of the passage. Teacher asks students to rewrite the underlined parts using it as an empty object. Then asks students to make corrections in groups. Teacher checks the answers with the class. Students read the passage and get its main idea. Students rewrite the underlined parts using it as an empty object. Then make corrections in groups. Students check the answers with the teacher. To let students apply it as an empty object in a context.
Activity 3 Teacher asks students to look at the two pictures of the Saihanba National Forest Park and find its changes. Teacher asks students to work in groups and follow the model sentences to describe the changes in the Saihanba National Forest Park using it as an empty object where appropriate. Teacher invites one or two groups to share the answers with the class. Students look at the two pictures of the Saihanba National Forest Park and find its changes. Students work in groups and follow the model sentences to describe the changes in the Saihanba National Forest Park using it as an empty object where appropriate One or two groups share the answers with the class. To help students consolidate the application of it as an empty object in a real context.
Activity 4 Teacher asks students to think about a place they know has changed individually. Teacher asks students to work in groups and have a discussion, then describe how the place has changed using it as an empty object where appropriate. Teacher invites some students to share the answers with the class and others make comments. Students think about a place they know has changed individually. Students work in groups and have a discussion, then describe how the place has changed using it as an empty object where appropriate. Some students share the answers with the class. Others make comments. To help students to further understand a place that has changed and the use of it as an empty object.
Activity 5 Teacher asks students to look at the diagram and answer the first question. Teacher checks the answers with the class. Teacher asks students to pay attention to the expressions in bold and then answer the second question. Teacher invites some students to share the answers with the class. Students look at the diagram and answer the first question. Students check the answers with the teacher. Students pay attention to the expressions in bold and then answer the second question. Some students share the answers with the class. To let students learn some new expressions about the relationships between the living things.
Activity 6 Teacher asks students to complete the passage with the correct form of the words and expressions in Activity 5. Teacher checks the answers with the class. Students complete the passage with the correct form of the words and expressions in Activity 5. Students check the answers with the teacher. To help students review the expressions about the relationships between the living things.
Activity 7 Teacher asks students to read the statements in Did You Know and learn about the facts about honey bees. Teacher asks students to read the statements and choose the true ones. Teacher plays the audio and asks students to choose the true statements. Teacher checks the answer with the class. Students read the statements in Did You Know and learn about the facts about honey bees. Students read the statements and choose the true ones. Students listen to the audio and choose the true statements. Students check the answer with the teacher. To train students’ skills in grasping the main idea of a conversation through listening.
Activity 8 Teacher asks students to look at the flow chart first. Then play the audio again and ask students to complete the flow chart. Teacher asks students to listen for a third time and check the answers by themselves. Teacher invites some students to share the answers with the class. Teacher asks students to talk about the importance of bees in their own words. Students look at the flow chart first. Then listen to the audio again and complete the flow chart. Students listen to the audio for a third time and check the answers by themselves. Some students share the answers with the class. Students talk about the importance of bees in their own words. To let students get the details of the listening material.
Activity 9 Teacher asks students to look at the two headers and tell what they know about the different functions. Teacher asks students to complete the boxes with the expressions from the conversation. Teacher checks the answers with the class. Students look at the two headers and tell what they know about the different functions. Students complete the boxes with the expressions from the conversation. Students check the answers with the teacher. To help students consolidate the expressions of expressing doubt and responding to doubt.
Activity 10 Teacher divides students into groups and asks them to talk about what would happen to the ecosystem if another species died out using the expressions in this section. Teacher invites several groups to present their ideas in front of the class. Teacher asks students to think about how their knowledge helped them contribute to the discussion. Students work in groups and talk about what would happen to the ecosystem if another species died out using the expressions in this section. Several groups present their ideas in front of the class. Students think about how their knowledge helped them contribute to the discussion. To encourage students to further practise describing the delicate ecosystem.
Developing ideasThe teaching design of the Developing ideas section (the recommended durationis 80-90minutes, and teachers can adjust it at their discretion according to the actual teaching. )
Course type Reading + Writing
Theme Context Man andNature-Protecting our Fragile Planet
Content analysis This section presents a text that reflects the theme of the unit from another perspective. The type of discourseis speech. The text introduces the reasons why Shennongjia hasbeen includedin the UNESCO World Heritage List, and shows that human beings can coexist in harmony with the ecological environment while developing. The second part introduces Fanjing Mountain, another model of ecosystem protection in our country, and asksstudents to draft a lecture on Fanjing Mountain. Through the study of this sector, students can think deeply about the relationship between human development and the protection of ecosystems, and finally realize that the two are not antagonistic. Humans can also protect ecosystems while pursuing development, thereby enhancing students' environmental awareness and further improving students' thinking quality.
Teaching objectives At the end of the study in this section, students can: grasp the meaning of the article andunderstand thereasons why Shennongjia was selected for the UNESCO World Intangible Cultural HeritageList; understand演讲the organizational structure characteristics of the speech and how to use data, examples and comparisons to support their own views; use the knowledge they have learned to write a lecture on Fanjing MountainTo further enhance the abilityto use languageand deepen the understanding of the meaning of the subject of the unit.
The focus of teaching is to lead students to grasp the meaning of the articleand understand the reasons why Shennongjia was selected for the UNESCO WorldIntangible Cultural HeritageList; guide studentsto writelecture drafts to further improve their language skills and deepen their understanding of the significance of the subject of the unit.
Teaching difficulties guide students to learn演讲the characteristics of the organizational structure of the speech and how to use data, examples and comparisons to support their own views;
teaching strategy P-W-Pmodel
Teaching contents Procedures Purposes
Teacher’s activity Students’ activity
Activity 1 Teacher asks students to watch the video and answer the questions. Teacher invites some students to give answers. Students watch the video and answer the questions. Some students give answers. To lead students into the topic of Shennongjia.
Activity 2 Teacher asks students to look at the title of the passage and think about what it means. Teacher asks students to work in groups and discuss the question. Then invite some students to share the answers. Teacher asks students to read the passage and check their answer. Students look at the title of the passage and think about what it means. Students work in groups and discus the question. Some students share the answers. Students read the passage and check their answers. To strengthen students’ ability to understand the topic.
Activity 3 Teacher asks students to read the sentences from the passage and decide if they serve to give data, examples or make comparisons. Teacher asks students to discuss in groups, and decide their answers. Teacher invites some students to give answers. Students read the sentences from the passage and decide if they serve to give data, examples or make comparisons. Students discuss in groups and decide their answers. Some students give answers. To help students learn giving data, examples and making comparisons.
Think & Share Teacher asks students to think about the questions and discuss them in groups. Teacher invites some students to give answers. Students think about the questions and discuss them in groups. Some students give answers. To enhance students’ understanding of the theme of the passage and encourage students to show their own opinions.
Activity 4 Teacher asks students to think about the similarities and differences between Macquarie Island and Shennongjia and make notes. Teacher asks students to discuss their answers in groups, decide the key points and prepare for a talk. Teacher invites several students to give their talk to the class and others to make comments. Teacher asks students to think about how effectively they used the language they have learnt to talk about the similarities and differences. Students think about the similarities and differences between Macquarie Island and Shennongjia and make notes. Students discuss their answers in groups, decide the key points and prepare for a talk. Some students give their talk to the class and others make comments. Students think about how effectively they used the language they have learnt to talk about the similarities and differences. To help students learn to compare and contrast. To improve students’ speaking skill and performance ability.
Activity 5 Teacher asks students to read the passage and think about the questions. Teacher divides the class into groups and asks them to discuss the two questions in groups. Teacher invites one or two groups to share their answers and others to make comments. Students read the passage and think about the questions. Students discuss the questions in groups. One or two groups share their answers and others make comments. To help students learn why Fanjing Mountain was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List.
Activity 6 Teacher asks students to complete the outline based on the information in Activity 5. Teacher asks students to draft their lectures about Fanjing Mountain. Students complete the outline based on the information in Activity 5. Students draft their lectures about Fanjing Mountain. To help students organise the lecture draft before making a lecture.
Activity 7 Teacher divides students into pairs and asks them to make improvements to each other’s lecture drafts. Teacher invites one or two pairs to share their answers to the class and others to make comments. Students work in pairs and make improvements to each other’s lecture drafts. One or two pairs share their answers to the class and others make comments. To encourage students to learn from their partners. To improve students’ writing and speaking skills.
Presentation ideas & Reflectionsection teaching design (the recommended durationis 40-45minutes, and teachers can adjust it at their discretion according to the actual teaching. )
Course type Speaking
Topic Context People and society-Protecting our fragile planet
Content analysis The Presenting ideassection requires students to first read总书记the famous sentences of General Secretary Xi Jinping and think about the meaning of ”green water and green mountains“ and ”Golden mountains and Silver mountains" and the message conveyed by these sentences. Then, in the form of speeches, students are promoted to comprehensively use the content they have learned, cooperate with each other, show their individuality, and fully express their understanding and understanding of the subject ideas of the unit. The Reflectionsection guides students to review the knowledge they have learned in this unit, evaluate and judge their learning behavior and effectiveness in a timely manner, reflect on themselves and make improvements.
Teaching objectives At the end of the study in this section, students can: understand the importance of protecting the ecological environment conveyed by “green water and green mountains are golden mountains and silver mountains”保护生态环境的重要性; give examples to provethat “green water and green mountains are golden mountains and silver mountains”to further deepentheir understanding of this topic.
The teaching focus is to guide students保护生态环境to have a deeper understanding of the topic of protecting the ecological environment through the study of this unit; guide studentsto give examples to provethe theme of “green water and green mountains are golden mountains and silver mountains”.
Teaching difficulties guide students to deeply realize the importance and urgency of protecting the ecological environment, and exercise students' logical thinking skills.
Teaching strategy task-based pedagogy, communicative pedagogy
Teaching contents Procedures Purposes
Teacher’s activity Students’ activity
Presenting ideas
Activity 1 Teacher divides students in group and asks students to look at the picture and answer the questions. Teacher invites one or two groups to share their answers to the class and others to make comments. Students work in groups and look at the pictures and answer the questions. One or two groups to share their answers to the class and others make comments. To help students understand the message conveyed by the quote.
Activity 2 Teacher asks students to talk about their understanding of the quote in groups and find examples that can prove it. Teacher asks students to make notes according to their discussion. Teacher asks students to share the answers and others to make comments. Students talk about their understanding of the quote in groups and find examples that can prove it. Students make notes according to their discussion. Students share the answers and others make comments. To help students to think deeply about “Clear waters and lush mountains are as valuable as gold and silver”.
Activity 3 Teacher asks students to prepare a short presentation considering the structure and useful words, expressions and structures. Teacher asks each group to choose one student to give the presentation. Teacher and other students make comments, and teacher gives evaluation. Asks students to vote for the most creative and the most popular presentation. Students prepare a short presentation considering the structure and useful words, expressions and structures. Each group chooses one student to give the presentation. Other students make comments. Students vote for the most creative and the most popular presentation. To encourage students to express their opinions, and help them correctly understand the unit theme.
Reflection
Teacher asks students to rate their performance in this unit, summarise what they’ve learnt and think about what they need to improve. Teacher asks students to write a reflection. Students rate their performance in this unit, summarise what they’ve learnt and think about what they need to improve. Students write a reflection. To help students evaluate their performance, review the unit, and think about ways to improve.
Projectsection teaching design (this part of the teacher can handle it at his discretion according to the actual teaching.)
Course type Speaking
Theme Context People and Society-Protecting our Fragile Planet
Content analysis The practical activities of this unit require students toexplorethe ecosystems around them, understand the importance of these ecosystems and think about how to protect them. Students can use the Internet or the library to query information, conduct research, and analyze the current situation of the ecosystem around them. Through independent learning, cooperative learning, and inquiry-based learning, we comprehensively use what we have learned in this unit to effectively complete open tasks, further deepen our understanding of the subject context of the unit, and learn to protect the environment from me.
Teaching objectives At the end of the study in this section, students can: be familiar with research methods and techniques, and choose appropriate ways to conduct research; comprehensively use what they have learned in this unit to present the survey results of the local ecosystem in a graphic manner; improve communication and inquiry skills through group cooperation and reasonable division of labor; fully understand the surroundingsThe ecosystem truly raises awareness of environmental protection.
The teaching focus is to guide students to familiarize themselves with research methods and techniques, choose appropriate ways to conduct research,organizethe research results, make slideshows and进行display them.
Teaching difficulties guide students to carry out cooperative exploration and improve communication and collaboration skills; guide students to fully understand the ecosystem around them, and truly improve the awareness of environmental
protection teaching strategies and task-based teaching methods
Teaching contents Procedures Purposes
Teacher’s activity Students’ activity
Investigate (In the previous class,) Teacher divides the class into groups and asks students to think about the ecosystems around them. Then asks students to go online or a library to find out how they might investigate them. Teacher asks each group to choose one of the ecosystems and find out information on it online. Students think about the ecosystems around them and go online or to a library to find out how they might investigate them. Each group chooses one of the ecosystems and find out information on it online. To get students prepared for the activities, and develop their ability to learn and explore individually. To help students get to know the ecosystems in the local area.
Plan Teacher asks students to decide how they will further investigate each of these aspects when they visit the ecosystems. Teacher encourages students to decide how best to present their information. Students decide how they will further investigate each of these aspects when they visit the ecosystems. Students decide how best to present their information. To help students prepare for the investigation and emphasise the importance of cooperation with others.
Create Teacher asks students to carry out the investigation, making notes and taking photos. Teacher asks students to write the text for their presentations. Teacher asks students to look for suitable photos, maps, diagrams, charts and any other visuals. Teacher asks students to put all the contents together into their chosen presentation format. Students carry out the investigation, making notes and taking photos. Students write the text for their presentations. Students look for suitable photos, maps, diagrams, charts and any other visuals. Students put all the contents together into their chosen presentation format. To offer students a chance to investigate one of the local ecosystems and learn to create a presentation.
Present Teacher encourages students to present the ecosystem to the class. Teacher encourages students to discuss how to protect the local ecosystem and how to reduce the impact of human activity on it. Students present the ecosystem to the class. Students discuss how to protect the local ecosystem and how to reduce the impact of human activity on it. To help students improve skills in giving presentation. To raise students’ awareness of the importance of ecosystems.
1
