北师大版(2019)必修 第三册Unit 7 Art Lesson 1 Masterpieces语法名词性从句课件(共54张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 北师大版(2019)必修 第三册Unit 7 Art Lesson 1 Masterpieces语法名词性从句课件(共54张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 2.2MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 北师大版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-03-19 15:19:16 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共54张PPT)
第一讲 句子成分
1.主语(subject):
主语是一个句子的主题,是句子所陈述的主体,一般放于句首,可以是人,也可以是物,指动作的执行者。
例:那个学生问了老师一些问题.
The student asked the teacher some
questions.
主语
例:天气非常好.
The weather is very nice.
主语
2.谓语
谓语 (Predicate) 说明主语“做什么”、“是什么”或者“怎么样” , 有简单动词和动词短语构成。一般放在主语之后:
2.谓语
谓语 (Predicate) 说明主语“做什么”、“是什么”或者“怎么样” , 有简单动词和动词短语构成。:
1、简单谓语:由一个动词或动词短语构成。如:
He practices running every morning.
The plane took off at ten o’clock.
2、复合谓语:
(1)由情态动词或其他助动词加动词原形构成。如:
You may keep the book for two weeks.
He has caught a bad cold.
(2)由系动词加表语构成。如:
We are students.
注意:谓语与主语在人称与数方面要保持一致。
3.宾语表示动作、行为的对象,是动作的承受者,通常位于及物动词和介词后面。
She covered her face with her hands.
Do you mind opening the window
He wants to dream a nice dream.
We need know that he is a good boy.
名词 n
动名词
to do不定式
句子
4. 表语:
表语主要用于表述主语的特征,状态,身份等。它位于连系动词后,构成系表结构。
连系动词
I am a teacher.
This kind of fruit tastes very delicious.
1.be动词(am, is, are, was, were)
3.感官动词(look, smell, hear, feel…)
+表语
2.get/become/turn
The girl got worried.
5. 定语:修饰名词或代词的词、短语或从句称为定语。
定语可由以下等词性表示:
China is a developing country;
His rapid progress in English made us surprised.
Tom is a boy who likes music very much.
(分词)
(pron.代词)
(定语从句)
6. 状语:修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子,说明动作或状态特征的句子成分,叫做状语。通常由副词,介词短语和从句充当.状语表示地点、时间、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、伴随情况等。
I arrived late because of the traffic jam .
We'll send a car to fetch you.
原因状语
目的状语
7. 宾语补足语:英语有些及物动词,除了要有宾语之外,还要加上宾语补足语,对宾语进行适当地补充说明,才能使句子的意义完整。
We try to make our country strong.
We found everything in good order there.
I should advise you to get the chance.
I saw him going upstairs.
形容词
介词短语
to do 不定式
现在分词 doing
宾语和宾语补足语一起构成宾语的复合结构
8.同位语:对前面的名词或代词做进一步的解释,通常由名词、数词、代词或从句担任,如:
That boy, my classmate, is called Li Ming.
They each want to do something different.
There was no doubt that he had done wrong to her.
The news that our team got the first prize made everyone so excited.
_________
n.
代词
____
同位语从句
_______________________
同位语从句
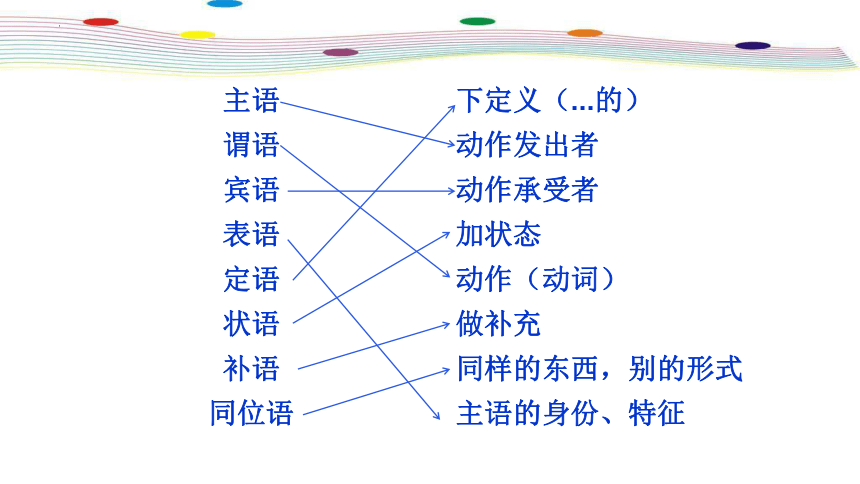
主语
谓语
宾语
表语
定语
状语
补语
同位语
下定义(...的)
动作发出者
动作承受者
加状态
动作(动词)
做补充
同样的东西,别的形式
主语的身份、特征
I met my best friend Tom at the station yesterday.
↓
主语
↓
谓
语
↓
定语
↓
宾
语
↓
同位语
↓
状
语
第二讲 句子结构
1)简单句(Simple Sentences):只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句。例如:
She enjoys collecting stamps. 她喜欢集邮。
Light travels faster than sound. 光比声传播速度快。
The film is rather boring. 这部电影很乏味。(说明看法)
3)复合句(Complex Sentences):包含一个主句和一个或几个从句的句子叫复合句,从句由从属连词引导。例如:
The film had begun when we got to the cinema.
我们到达电影院的时候,电影已经开演了。
Therefore,I firmly believe that our future is in our own hands.(宾语从句)
因此,我坚信未来掌控在我们自己的手中。
He was ready to help others,which won him a good reputation.
他总是帮助别人,这给他赢得了很好的名声。
2)并列句(Compound Sentences):包含两个或两个以上主谓结构的句子叫并列句,句与句之间通常用并列连词或分号来连接。
例如:
The food was good, but he had little appetite. 食物很精美,但他却没什么胃口。
Traveling can not only get us close to nature and relax us, but also broaden our horizons and enrich our knowledge.
第三讲 名词性从句
1.名词性从句的基本概念
2.名词性从句连接词的判断
名词性从句
1.名词性从句的基本概念
1.名词性从句的基本概念
(2)名词性从句的概念
定义:
名词从句就是把完整句子当作名词来使用,使之在另一个句子中充当某种成分。名词从句是从属性句子,一般在句中作主语,宾语,表语或同位语。
1.名词性从句的基本概念
(1)Review: 名词在句子中都可以作什么成分?
名词的功能
主语
宾语
表语
同位语:位于同一位置的名词结构
名词性从句
主语从句:在句中充当主语
宾语从句:在句中充当宾语
表语从句:在句中充当表语
同位语从句:在句中充当某一名词的同位语,一般位于该名词的后面,解释说明该名词的具体内容。
分类:
1(1) His job is important.
(2) What he does is important.
2(1) This is his job.
(2) This is what he does every day.
表语
主语
系动词
主语从句
系动词
表语
主语
系动词
表语
主语
表语从句
系动词
分析句子的成分
3(1) I don’t like his job.
(2) I don’t like what he does every day.
4(1) I don’t know the man, Mr. White.
(2) I don’t know the fact that he is a teacher.
主语
谓语
宾语
主语
谓语
宾语从句
同位语
主语
谓语
宾语
同位语从句
主语
谓语
宾语
主语从句一般有三种结构:
1. 主语从句+谓语
That she will win the match is certain.
2.It+be+形容词(名词词组、过去分词)+that从句
It is important that we teens should learn English.
It is said that our school will hold a sports meeting
3. It +seem (happen,appear等不及物动词)+that从句
It seems that Katy is not coming to this party.
Subject Clause (主语从句)
在复合句中,如作主语的是一个从句,该从句被称为主语从句。
宾语从句的结构
主句 + 连接词(引导词) + 宾语从句
I don't know why he is always late for school.
We all agree with what you said at the meeting.
Object Clause ( 宾语从句)
在复合句中,如作宾语的是一个从句,该从句被称为宾语从句。宾语从句放在及物动词或介词之后作宾语。
其基本结构为:主语 + 系动词 + that从句。
1. be, look, remain, 等系动词后均可跟表语从句:
My suggestion is that we should go shopping.
2. as if 也可引导表语从句。
It looks as if it’s going to rain.
3.the reason why … is that … 和It is because …等结构。
It was because I got up late.
Predicative Clause ( 表语从句)
在复合句中,如作表语的是一个从句,该从句被称为表语从句。
Beijing ,the capital of China, is my hometown.
We heard the news that our team had won.
We were happy to hear the news that was announced
by our boss.
定语从句
同位语从句
同位语短语
Appositive Clause ( 同位语从句)
在复合句中,从句作某一名词的同位语,对该名词作进一步解释说明,该从句被称为同位语从句。可跟同位语从句的名词主要有:fact, news, promise, reason, idea, hope, word, belief, advice,conclusion,doubt,question, suggestion,thought,truth,wish等
定义:
同位语从句:解释(啥是啥)
定语从句:定义(怎样的啥)
Appositive Clause(同从) V.S. Attributive Clause(定从)
1. I was shocked at the fact that he died.
2. I was shocked at the fact that he told me.
Differences
that作用:
同位语从句:在从句中不做成分
定语从句:在从句中做成分
(1)The story that the book told you is true.
(2)The story that Man has been to the moon is true.
(3)Mom made a promise that she would take us to Disneyland.
(4)Mom made a promise that pleased us.
(5)She heard the terrible news, which brought her heart into her mouth.
(6)She heard the terrible news that he died.
I. What kinds of noun clauses is
P11, EX8
1. Van Gogh painted what he saw from his window.
2. What makes it sticking is that it shows a thin figure with an expression of fear.
3. What is strange is that above the house and the tree, we see a daytime sky full of brightness and soft white clouds.
4. Some feel that the painting look dark and troubling.
宾从
主从+表从
主从+表从
表从
I hope that people will spend more money on education.
Whether he’ll take the job is still unknown.
His suggestion is that we should hire more experienced people.
That’s why he was late for school.
The report that he was going to resign was false.
宾从
主从
表从
表从
同位从
He asked if I could show him how to operate the air conditioner.
Where they’ll move their office is not clear.
That was when my mum was in hospital.
The fact is that he won’t come back.
It’s obvious that he enjoys his family life very much.
That is a fact that men are usually stronger than women.
宾从
主从
表从
表从
同位从
主从
连接词
连词:that, whether, if···
连接代词: who(ever), whom(ever), whose(ever),which(ever), what(ever)...
连接副词:when(ever),where(ever), why, how(ever)···
(2)连接词的分类:
(2)连词:
分类 词形 词义 从句是否担当成分 主语从句 宾语从句 表语从句 同位语从句 功能区别
连词 that × × √ √ √ √ 只起连接作用,在从句中不担任成分
whether 是否 × √ √ √ √ if 是否 × × √ × × (2)连词:
Marvel’s movies are popular is an undoubted fact.
That
1.判断句子类型:名词性从句中的主语从句,
2.主语从句中结构、句子含义完整,不缺任何成分,从that whether if中选择。根据句意,句中没有是否的含义,因此选择没有实际语义的that.
这里的that 不充当任何成分,单纯起连接作用。
(1)划分主句和从句(分析并确定从句类型)
(2)分析从句是否缺成分
名词性从句
从句缺成分
从句不缺成分
指人:who / whom
指物:what / which
(连接代词)
(连接副词+连词)
陈述句语序
that
疑问句语序
when / where / why / how / whether / if
(3)翻译句子,看是否通顺
判断方法:
从属:whose
(2)连词:
I wonder he will have a girl friend.
he will have a girl friend is still uncertain.
1.判断句子类型:第一句宾语从句;第二句主语从句。
2.从句:结构完整,缺“是否”含义。
3.whether\if 不充当成分,起连接作用。if 只能用于宾从,whether可以用于所有名词性从句。
whether\if
Whether
(3)连词的判断规则:
确定从句位置,是否是名词性从句
分析从句成分,是否缺主干成分,若不缺
首先考虑是否直接用连词连接使语义通顺
(4)连接代词:
分类 词形 词义 在从句中担当的成分 主语从句 宾语从句 表语从句 同位语从句 功能区别
连接代词 who 谁 主宾表 √ √ √ √ 既起连接作用,本身又可作从句主语,宾语,表语或定语
whom 谁(宾格) 宾语 √ √ √ √ whose 谁的 主宾表定 √ √ √ √ which 哪一个 主宾表定 √ √ √ √ what 什么、···的东西 主宾表定 √ √ √ √ (4)连接代词:
China is not it used to be.
what 中国已经不是它过去的样子了。
1.判断句子类型:名词性从句中的表语从句,
2.表语从句中结构、句子含义不完整,缺成分,从连接代词中选择。
3.表语从句中缺表语,根据句意选择词义为“什么,什么东西,什么样子”的what.
(4)连接代词:
She doesn’t know he is.
who 她不知道他是谁。
1.判断句子类型:名词性从句中的宾语从句,
2.宾语从句中结构、句子含义不完整,缺成分,从连接代词中选择。
3.宾语从句中缺表语,根据句意选择词义为“谁”的who.
(5)连接代词的判断规则:
确定从句位置,是否是名词性从句
分析从句成分,是否缺主干成分。
若缺乏主干,结合句意选择合适的连接代词。
若不缺乏主干,但是句子含义中需要填入一个表示“哪一个,谁的,什么”作为定语,应根据句意选择which whose what
(6)连接副词:
分类 词形 词义 在从句中担当的成分 主语从句 宾语从句 表语从句 同位语从句 功能区别
连接副词 when 什么时间 状语 √ √ √ √ 既起连接作用,本身又是从句的状语
where 什么地方 状语 √ √ √ √ why 为什么 状语 √ √ √ √ how 怎样,如何 状语 √ √ √ √ (6)连接副词:
We must find out Karl is coming, so we can book a room for him.
when 我们必须知道卡尔什么时间到,所以我们才可以给他预定房间。
1.判断句子类型:名词性从句中的宾语从句,
2.宾语从句中句子含义不完整。
3.根据句意选择词义为“什么时间”的when.
(6)连接副词:
Scientists study human brains work to make computers.
how 科学家们为制造计算机而去研究人类的大脑是如何工作的。
(7)连接副词的判断规则:
确定从句位置,是否是名词性从句
分析从句成分,是否缺主干成分
若不缺,且结合句意需要填入状语修饰,则考虑when,where,why, how
补充:定语从句与同位语从句区别
I received the news that we won the game yesterday.
The news that we received yesterday was from my teacher.
同位语从句
定语从句
that的成分 that 是否可省略 作用 中心词
定语从句 作主干成分(主语,宾语,表语)指人或物 作宾语可省略 修饰限定先行词 没有限制
同位语从句 不做成分,没有含义 不可省略 中心词=从句内容 一般为抽象意义名词,如fact,truth,thought等
(1)划分主句和从句(分析并确定从句类型)
(2)分析从句是否缺成分
名词性从句
从句缺成分
从句不缺成分
指人:who / whom
指物:what / which
(连接代词)
(连接副词+连词)
陈述句语序
that
疑问句语序
when / where / why / how / whether / if
(3)翻译句子,看是否通顺
小结:
从属:whose
II.单句填空
1.Before the sales start,I make a list of my kids will need for the coming season.
2. struck me most in the movie was the father’s deep love for his son.
3.Scientists study human brains work to make computers.
4.Modern science has given clear evidence smoking can lead to many diseases.
5.Generally speaking,being hard-working is just it takes to be successful in your career.
what
What
how
that
what
6.The shocking news made me realize terrible problems we would face.
7.I’m afraid he’s more of a talker than a doer,which is he never finishes anything.
8.We’ve offered her the job,but I don’t know she’ll accept it.
9.It never occurred to me you could succeed in persuading him to change his mind.
10.The notice came around two o’clock in the afternoon the meeting would be put off.
what
why
whether/if
that
that
III.单句改错
1.All what is hard is to do good all one’s life and never do anything bad.
2.It’s uncertain that the experiment is worth doing.
3.This is a fact that English is widely used as an international language.
4.When we’ll finish translating the book depend on the time.
5.The reason why he failed in the exam was because he was too careless.
what→that
that→whether
This→It
depend→depends
because→that
6.At the meeting he raised a question if the project would be cancelled.
7.He ordered that the injured were taken good care of.
8.The fact which she had not said anything surprised all of us.
9.When and where we shall have the lecture are not decided.
10.The news they had won the game surprised us.
if→whether
were→be
which→that
are→is
在news后加that
IV.使用合适的连词/连接代词/连接副词填空。
who
I am going to tell you an unbelievable thing that happened in my restaurant today.
This afternoon a poorly dressed gentleman came into my restaurant.Nobody knew ______he was.We wondered ________he was so hungry.We were surprised _____he finished two orders of food in a very limited time.We doubted ______ the man was able to pay the bill.The gentleman asked __________we would mind waiting for just a few minutes.Then we were shocked to see _______he took out of a letter and a million pound bank note.
I asked Mr.Clements __________ it was genuine.Mr.Clements said it was true because two of this amount had been issued by the Bank of England this year.He thought __________the gentleman showed them couldn't be a fake.
________a gentleman with a million pound bank note was in rags and ate in our small restaurant was a big puzzle to all the people there.I really couldn't describe __________excited I was.
why
that
whether/if
whether/if
that
whether/if
what
Why
how
第一讲 句子成分
1.主语(subject):
主语是一个句子的主题,是句子所陈述的主体,一般放于句首,可以是人,也可以是物,指动作的执行者。
例:那个学生问了老师一些问题.
The student asked the teacher some
questions.
主语
例:天气非常好.
The weather is very nice.
主语
2.谓语
谓语 (Predicate) 说明主语“做什么”、“是什么”或者“怎么样” , 有简单动词和动词短语构成。一般放在主语之后:
2.谓语
谓语 (Predicate) 说明主语“做什么”、“是什么”或者“怎么样” , 有简单动词和动词短语构成。:
1、简单谓语:由一个动词或动词短语构成。如:
He practices running every morning.
The plane took off at ten o’clock.
2、复合谓语:
(1)由情态动词或其他助动词加动词原形构成。如:
You may keep the book for two weeks.
He has caught a bad cold.
(2)由系动词加表语构成。如:
We are students.
注意:谓语与主语在人称与数方面要保持一致。
3.宾语表示动作、行为的对象,是动作的承受者,通常位于及物动词和介词后面。
She covered her face with her hands.
Do you mind opening the window
He wants to dream a nice dream.
We need know that he is a good boy.
名词 n
动名词
to do不定式
句子
4. 表语:
表语主要用于表述主语的特征,状态,身份等。它位于连系动词后,构成系表结构。
连系动词
I am a teacher.
This kind of fruit tastes very delicious.
1.be动词(am, is, are, was, were)
3.感官动词(look, smell, hear, feel…)
+表语
2.get/become/turn
The girl got worried.
5. 定语:修饰名词或代词的词、短语或从句称为定语。
定语可由以下等词性表示:
China is a developing country;
His rapid progress in English made us surprised.
Tom is a boy who likes music very much.
(分词)
(pron.代词)
(定语从句)
6. 状语:修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子,说明动作或状态特征的句子成分,叫做状语。通常由副词,介词短语和从句充当.状语表示地点、时间、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、伴随情况等。
I arrived late because of the traffic jam .
We'll send a car to fetch you.
原因状语
目的状语
7. 宾语补足语:英语有些及物动词,除了要有宾语之外,还要加上宾语补足语,对宾语进行适当地补充说明,才能使句子的意义完整。
We try to make our country strong.
We found everything in good order there.
I should advise you to get the chance.
I saw him going upstairs.
形容词
介词短语
to do 不定式
现在分词 doing
宾语和宾语补足语一起构成宾语的复合结构
8.同位语:对前面的名词或代词做进一步的解释,通常由名词、数词、代词或从句担任,如:
That boy, my classmate, is called Li Ming.
They each want to do something different.
There was no doubt that he had done wrong to her.
The news that our team got the first prize made everyone so excited.
_________
n.
代词
____
同位语从句
_______________________
同位语从句
主语
谓语
宾语
表语
定语
状语
补语
同位语
下定义(...的)
动作发出者
动作承受者
加状态
动作(动词)
做补充
同样的东西,别的形式
主语的身份、特征
I met my best friend Tom at the station yesterday.
↓
主语
↓
谓
语
↓
定语
↓
宾
语
↓
同位语
↓
状
语
第二讲 句子结构
1)简单句(Simple Sentences):只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句。例如:
She enjoys collecting stamps. 她喜欢集邮。
Light travels faster than sound. 光比声传播速度快。
The film is rather boring. 这部电影很乏味。(说明看法)
3)复合句(Complex Sentences):包含一个主句和一个或几个从句的句子叫复合句,从句由从属连词引导。例如:
The film had begun when we got to the cinema.
我们到达电影院的时候,电影已经开演了。
Therefore,I firmly believe that our future is in our own hands.(宾语从句)
因此,我坚信未来掌控在我们自己的手中。
He was ready to help others,which won him a good reputation.
他总是帮助别人,这给他赢得了很好的名声。
2)并列句(Compound Sentences):包含两个或两个以上主谓结构的句子叫并列句,句与句之间通常用并列连词或分号来连接。
例如:
The food was good, but he had little appetite. 食物很精美,但他却没什么胃口。
Traveling can not only get us close to nature and relax us, but also broaden our horizons and enrich our knowledge.
第三讲 名词性从句
1.名词性从句的基本概念
2.名词性从句连接词的判断
名词性从句
1.名词性从句的基本概念
1.名词性从句的基本概念
(2)名词性从句的概念
定义:
名词从句就是把完整句子当作名词来使用,使之在另一个句子中充当某种成分。名词从句是从属性句子,一般在句中作主语,宾语,表语或同位语。
1.名词性从句的基本概念
(1)Review: 名词在句子中都可以作什么成分?
名词的功能
主语
宾语
表语
同位语:位于同一位置的名词结构
名词性从句
主语从句:在句中充当主语
宾语从句:在句中充当宾语
表语从句:在句中充当表语
同位语从句:在句中充当某一名词的同位语,一般位于该名词的后面,解释说明该名词的具体内容。
分类:
1(1) His job is important.
(2) What he does is important.
2(1) This is his job.
(2) This is what he does every day.
表语
主语
系动词
主语从句
系动词
表语
主语
系动词
表语
主语
表语从句
系动词
分析句子的成分
3(1) I don’t like his job.
(2) I don’t like what he does every day.
4(1) I don’t know the man, Mr. White.
(2) I don’t know the fact that he is a teacher.
主语
谓语
宾语
主语
谓语
宾语从句
同位语
主语
谓语
宾语
同位语从句
主语
谓语
宾语
主语从句一般有三种结构:
1. 主语从句+谓语
That she will win the match is certain.
2.It+be+形容词(名词词组、过去分词)+that从句
It is important that we teens should learn English.
It is said that our school will hold a sports meeting
3. It +seem (happen,appear等不及物动词)+that从句
It seems that Katy is not coming to this party.
Subject Clause (主语从句)
在复合句中,如作主语的是一个从句,该从句被称为主语从句。
宾语从句的结构
主句 + 连接词(引导词) + 宾语从句
I don't know why he is always late for school.
We all agree with what you said at the meeting.
Object Clause ( 宾语从句)
在复合句中,如作宾语的是一个从句,该从句被称为宾语从句。宾语从句放在及物动词或介词之后作宾语。
其基本结构为:主语 + 系动词 + that从句。
1. be, look, remain, 等系动词后均可跟表语从句:
My suggestion is that we should go shopping.
2. as if 也可引导表语从句。
It looks as if it’s going to rain.
3.the reason why … is that … 和It is because …等结构。
It was because I got up late.
Predicative Clause ( 表语从句)
在复合句中,如作表语的是一个从句,该从句被称为表语从句。
Beijing ,the capital of China, is my hometown.
We heard the news that our team had won.
We were happy to hear the news that was announced
by our boss.
定语从句
同位语从句
同位语短语
Appositive Clause ( 同位语从句)
在复合句中,从句作某一名词的同位语,对该名词作进一步解释说明,该从句被称为同位语从句。可跟同位语从句的名词主要有:fact, news, promise, reason, idea, hope, word, belief, advice,conclusion,doubt,question, suggestion,thought,truth,wish等
定义:
同位语从句:解释(啥是啥)
定语从句:定义(怎样的啥)
Appositive Clause(同从) V.S. Attributive Clause(定从)
1. I was shocked at the fact that he died.
2. I was shocked at the fact that he told me.
Differences
that作用:
同位语从句:在从句中不做成分
定语从句:在从句中做成分
(1)The story that the book told you is true.
(2)The story that Man has been to the moon is true.
(3)Mom made a promise that she would take us to Disneyland.
(4)Mom made a promise that pleased us.
(5)She heard the terrible news, which brought her heart into her mouth.
(6)She heard the terrible news that he died.
I. What kinds of noun clauses is
P11, EX8
1. Van Gogh painted what he saw from his window.
2. What makes it sticking is that it shows a thin figure with an expression of fear.
3. What is strange is that above the house and the tree, we see a daytime sky full of brightness and soft white clouds.
4. Some feel that the painting look dark and troubling.
宾从
主从+表从
主从+表从
表从
I hope that people will spend more money on education.
Whether he’ll take the job is still unknown.
His suggestion is that we should hire more experienced people.
That’s why he was late for school.
The report that he was going to resign was false.
宾从
主从
表从
表从
同位从
He asked if I could show him how to operate the air conditioner.
Where they’ll move their office is not clear.
That was when my mum was in hospital.
The fact is that he won’t come back.
It’s obvious that he enjoys his family life very much.
That is a fact that men are usually stronger than women.
宾从
主从
表从
表从
同位从
主从
连接词
连词:that, whether, if···
连接代词: who(ever), whom(ever), whose(ever),which(ever), what(ever)...
连接副词:when(ever),where(ever), why, how(ever)···
(2)连接词的分类:
(2)连词:
分类 词形 词义 从句是否担当成分 主语从句 宾语从句 表语从句 同位语从句 功能区别
连词 that × × √ √ √ √ 只起连接作用,在从句中不担任成分
whether 是否 × √ √ √ √ if 是否 × × √ × × (2)连词:
Marvel’s movies are popular is an undoubted fact.
That
1.判断句子类型:名词性从句中的主语从句,
2.主语从句中结构、句子含义完整,不缺任何成分,从that whether if中选择。根据句意,句中没有是否的含义,因此选择没有实际语义的that.
这里的that 不充当任何成分,单纯起连接作用。
(1)划分主句和从句(分析并确定从句类型)
(2)分析从句是否缺成分
名词性从句
从句缺成分
从句不缺成分
指人:who / whom
指物:what / which
(连接代词)
(连接副词+连词)
陈述句语序
that
疑问句语序
when / where / why / how / whether / if
(3)翻译句子,看是否通顺
判断方法:
从属:whose
(2)连词:
I wonder he will have a girl friend.
he will have a girl friend is still uncertain.
1.判断句子类型:第一句宾语从句;第二句主语从句。
2.从句:结构完整,缺“是否”含义。
3.whether\if 不充当成分,起连接作用。if 只能用于宾从,whether可以用于所有名词性从句。
whether\if
Whether
(3)连词的判断规则:
确定从句位置,是否是名词性从句
分析从句成分,是否缺主干成分,若不缺
首先考虑是否直接用连词连接使语义通顺
(4)连接代词:
分类 词形 词义 在从句中担当的成分 主语从句 宾语从句 表语从句 同位语从句 功能区别
连接代词 who 谁 主宾表 √ √ √ √ 既起连接作用,本身又可作从句主语,宾语,表语或定语
whom 谁(宾格) 宾语 √ √ √ √ whose 谁的 主宾表定 √ √ √ √ which 哪一个 主宾表定 √ √ √ √ what 什么、···的东西 主宾表定 √ √ √ √ (4)连接代词:
China is not it used to be.
what 中国已经不是它过去的样子了。
1.判断句子类型:名词性从句中的表语从句,
2.表语从句中结构、句子含义不完整,缺成分,从连接代词中选择。
3.表语从句中缺表语,根据句意选择词义为“什么,什么东西,什么样子”的what.
(4)连接代词:
She doesn’t know he is.
who 她不知道他是谁。
1.判断句子类型:名词性从句中的宾语从句,
2.宾语从句中结构、句子含义不完整,缺成分,从连接代词中选择。
3.宾语从句中缺表语,根据句意选择词义为“谁”的who.
(5)连接代词的判断规则:
确定从句位置,是否是名词性从句
分析从句成分,是否缺主干成分。
若缺乏主干,结合句意选择合适的连接代词。
若不缺乏主干,但是句子含义中需要填入一个表示“哪一个,谁的,什么”作为定语,应根据句意选择which whose what
(6)连接副词:
分类 词形 词义 在从句中担当的成分 主语从句 宾语从句 表语从句 同位语从句 功能区别
连接副词 when 什么时间 状语 √ √ √ √ 既起连接作用,本身又是从句的状语
where 什么地方 状语 √ √ √ √ why 为什么 状语 √ √ √ √ how 怎样,如何 状语 √ √ √ √ (6)连接副词:
We must find out Karl is coming, so we can book a room for him.
when 我们必须知道卡尔什么时间到,所以我们才可以给他预定房间。
1.判断句子类型:名词性从句中的宾语从句,
2.宾语从句中句子含义不完整。
3.根据句意选择词义为“什么时间”的when.
(6)连接副词:
Scientists study human brains work to make computers.
how 科学家们为制造计算机而去研究人类的大脑是如何工作的。
(7)连接副词的判断规则:
确定从句位置,是否是名词性从句
分析从句成分,是否缺主干成分
若不缺,且结合句意需要填入状语修饰,则考虑when,where,why, how
补充:定语从句与同位语从句区别
I received the news that we won the game yesterday.
The news that we received yesterday was from my teacher.
同位语从句
定语从句
that的成分 that 是否可省略 作用 中心词
定语从句 作主干成分(主语,宾语,表语)指人或物 作宾语可省略 修饰限定先行词 没有限制
同位语从句 不做成分,没有含义 不可省略 中心词=从句内容 一般为抽象意义名词,如fact,truth,thought等
(1)划分主句和从句(分析并确定从句类型)
(2)分析从句是否缺成分
名词性从句
从句缺成分
从句不缺成分
指人:who / whom
指物:what / which
(连接代词)
(连接副词+连词)
陈述句语序
that
疑问句语序
when / where / why / how / whether / if
(3)翻译句子,看是否通顺
小结:
从属:whose
II.单句填空
1.Before the sales start,I make a list of my kids will need for the coming season.
2. struck me most in the movie was the father’s deep love for his son.
3.Scientists study human brains work to make computers.
4.Modern science has given clear evidence smoking can lead to many diseases.
5.Generally speaking,being hard-working is just it takes to be successful in your career.
what
What
how
that
what
6.The shocking news made me realize terrible problems we would face.
7.I’m afraid he’s more of a talker than a doer,which is he never finishes anything.
8.We’ve offered her the job,but I don’t know she’ll accept it.
9.It never occurred to me you could succeed in persuading him to change his mind.
10.The notice came around two o’clock in the afternoon the meeting would be put off.
what
why
whether/if
that
that
III.单句改错
1.All what is hard is to do good all one’s life and never do anything bad.
2.It’s uncertain that the experiment is worth doing.
3.This is a fact that English is widely used as an international language.
4.When we’ll finish translating the book depend on the time.
5.The reason why he failed in the exam was because he was too careless.
what→that
that→whether
This→It
depend→depends
because→that
6.At the meeting he raised a question if the project would be cancelled.
7.He ordered that the injured were taken good care of.
8.The fact which she had not said anything surprised all of us.
9.When and where we shall have the lecture are not decided.
10.The news they had won the game surprised us.
if→whether
were→be
which→that
are→is
在news后加that
IV.使用合适的连词/连接代词/连接副词填空。
who
I am going to tell you an unbelievable thing that happened in my restaurant today.
This afternoon a poorly dressed gentleman came into my restaurant.Nobody knew ______he was.We wondered ________he was so hungry.We were surprised _____he finished two orders of food in a very limited time.We doubted ______ the man was able to pay the bill.The gentleman asked __________we would mind waiting for just a few minutes.Then we were shocked to see _______he took out of a letter and a million pound bank note.
I asked Mr.Clements __________ it was genuine.Mr.Clements said it was true because two of this amount had been issued by the Bank of England this year.He thought __________the gentleman showed them couldn't be a fake.
________a gentleman with a million pound bank note was in rags and ate in our small restaurant was a big puzzle to all the people there.I really couldn't describe __________excited I was.
why
that
whether/if
whether/if
that
whether/if
what
Why
how
同课章节目录
- Unit 7 Art
- Lesson 1 Masterpieces
- Lesson 2 Beijing Opera
- Lesson 3 A Musical Genius
- Unit 8 Green living
- Lesson 1 Roots and Shoots
- Lesson 2 Greening the Desert
- Lesson 3 "White Bikes" on the Road
- Unit 9 Learning
- Lesson 1 Active Learning
- Lesson 2 Language Learning Tips
- Lesson 3 The Secrets of Your Memory
