人教版(2019)选择性必修第二册Unit 1 Science and Scientists Discover Useful Structures 表语从句课件(共41张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版(2019)选择性必修第二册Unit 1 Science and Scientists Discover Useful Structures 表语从句课件(共41张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 17.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-03-28 20:08:05 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
(共41张PPT)
Unit 1
Discover useful structures
Grammar
Predicative Clause
表语从句
练习:判断下列句子的句型
She is in good health.
Someone left you this note.
SVP
SVO
什么是谓语呢?谓语1由谁来充当呢?
英语其实很简单,它只有26进五四十八个音标,两个句子,只要
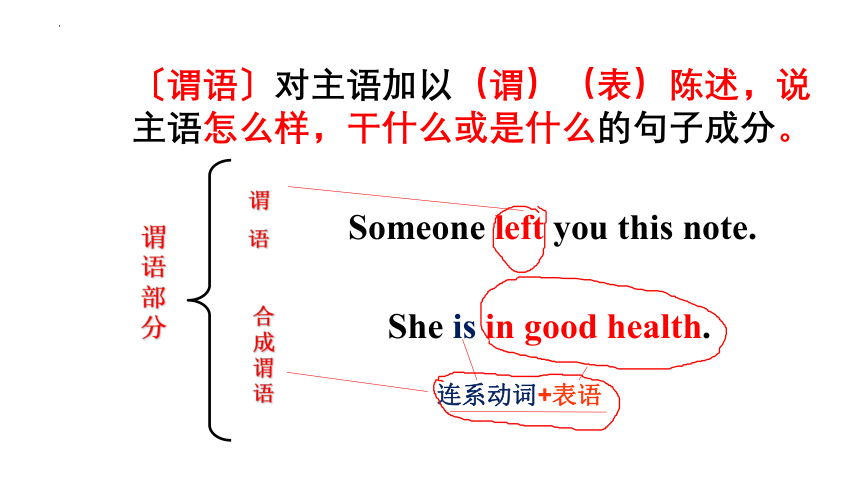
〔谓语〕对主语加以(谓)(表)陈述,说主语怎么样,干什么或是什么的句子成分。
Someone left you this note.
She is in good health.
谓 语部分
谓
语
合成谓 语
连系动词+表语
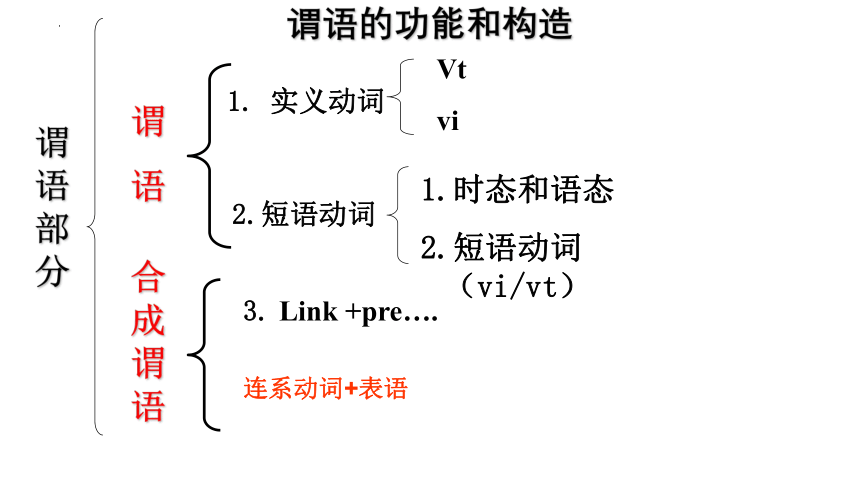
谓语的功能和构造
1. 实义动词
Vt
vi
2.短语动词
时态和语态
短语动词(vi/vt)
3. Link +pre….
谓
语
谓 语部分
合成谓 语
连系动词+表语
表语
表语的功能是表述主语的特征、状态、身份等。它也可以说是一个主语补足语。它位于连系动词之后,与之构成合成谓语;所谓的系表结构,在系表结构中,连系动词只是形式上的谓语动词起联系作用,而真正起谓语作用的则是表语。(谓语部分)
常见的系动词有:
1.状态系动词:be 动词;
2.感官系动词:look/ feel/ smell/ taste/ sound等;
3.变化系动词:get/ become/ turn/ grow/ fall/ grow等
4.持续系动词:remain/ stay/ keep(仍然)
5.表象系动词:seem/appear(似乎,好像)
6.终止系动词:prove/ turn out(结果是,证明是)
He is a boy.
He is in the room
He is ill
He is to blame.
Predicative Clauses
( 表语从句)
在复合句中作表语的从句叫做表语从句。位于主句的系动词之后,对主语进行解释说明。一般结构是:“主语+系动词+表语从句”。表语从句必须用陈述语序。
5. The question is who broke the vase.
6. My suggestion is that we (should) start early tomorrow.
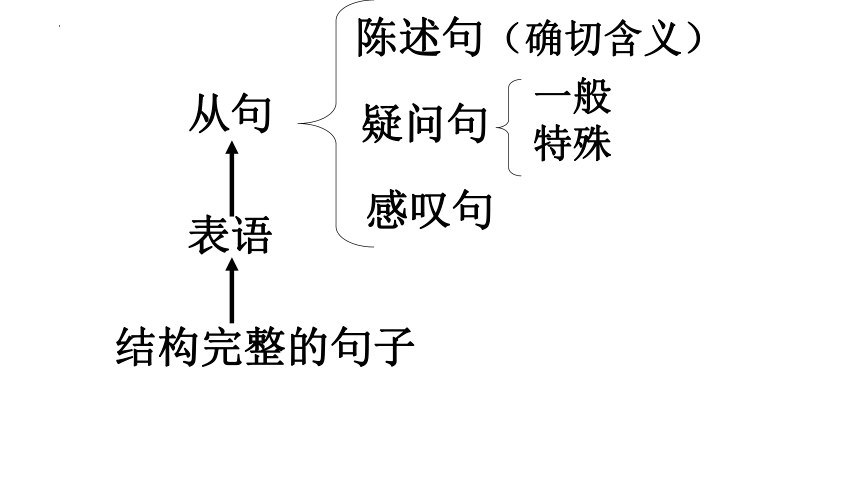
结构完整的句子
表语
从句
陈述句(确切含义)
疑问句
一般 特殊
感叹句
e.g. One advantage of playing the guitar is that it can give you a great deal of pleasure.
1. 表语从句一定要用陈述语序。
e.g. The trouble is that I have lost his address.
The reason for his absence is that he hasn't been informed.
2. that引导表语从句时,仅起连接作用 。
①无意义 ②不充当成分 ③不可省略
表语从句要点归纳
表语从句要点归纳
e.g. The question is whether your uncle will offer help to us.
3. whether引导表语从句时,起连接作用,
①有“是否”之意 ②不充当成分
注意: if 不能引导表语从句
(1)从属连词: that& whether
用法归纳:
a. that引导表语从句时,只起______作用,作/不作句子成分,有/没有意义。
b. whether引导表语从句时,只起______作用,作/不作句子成分,通常翻译为“______”。注意,引导表语从句时通常不用if。
连接
√
√
连接
√
是否
e.g. My hometown is no longer what it used to be.表语
The problem is who we can get to replace her宾语.
4. 连接代词who, whom, whose, what, which, whoever, whatever, whichever等除在句中起连接作用外,在从句中还充当主语、宾语、表语或定语,本身具有词义。
Task 2:Underline the predicative clauses in the following sentences and then work out the rules in groups.
2.连接代词who / whom / whose / which/what
连接代词在表语从句中根据句义可充当主语、宾语、表语或定语。依据“缺什么补什么”原则确定正确的连词。
所谓“缺什么补什么”是指从句与连词之间的关系。
如果句子中缺主语,指人用who ,如缺宾语,指人用whom。
指物用what。如缺定语用whose 或 which。
.g. The question is when they will start the project.时间状语从句
The question is how he did it.方式状语
5. 连接副词where, when, why, how等除在句中起连接作用,在从句中还充当地点、时间、原因、方式状语,本身具有词义。
Task 3:Underline the predicative clauses in the following sentences and then work out the rules in groups.
3.连接副词when / where / why / how
连接副词在表语从句中根据句义可充当状语,可表时间、地点、原因、方式等,因此不能省略。
依据“缺什么补什么”原则确定正确的连词。
所谓“缺什么补什么”是指从句与连词之间的关系。
如缺时间状语用when;地点状语用 where。
原因状语用why;方式状语用 how。
引导词/连接词 连词 在从句中不作成分 that, whether, as if, as though, because …
连接代词 在从句中作主语、宾语、表语、定语 what, who, whom, whose, which, 。, whoever, whichever …
连接副词 在从句中作状语 when, where, how, why …
既学既练:
1.The trouble is I have lost his address.
2.The question is they will go by plane or by train.
3.It sounds someone is knocking at the door.
4.This is the weather here is cold and wet.
5.That's Tony got angry with me.
6.He has become he wanted to be ten years ago.
7.The question is we can find the suitable man for the job.
that
whether
as if / though
because
why
what
how
高考链接
1.What puzzles Lily's friends is _______ she always has so many crazy ideas.(2021 天津卷改编)
2.Without his support, we wouldn’t be _________ we are now(2018·北京改编).
3.This is _________ my father has taught me—to always face difficulties and hope for the best(2018·北京改编).
请填入适当的引导词
why
where
what
表
语
从
句
定义:
位置:
系动词
分类
引导词
连词:
连接代词:
连接副词:
Draw a mind map to summarize the usage of predicative clause.
表
语
从
句
定义:在复合句中充当表语的从句叫做表语从句。
位置:表语从句放在连系动词之后。
系动词
分类
状态类:be 动词,seem,appear,keep
感官类: look, smell, taste, sound,
变化类:become, get, turn, grow, fall,
引导词
连词:that, whether, as if, as though...
连接代词:what, who, whom, whose, which, whatever, whoever, …
连接副词:when, where, how, why …
“证明”类:prove;
turn out
Review the words, expressions and sentences we have learned.
Review Grammar.
3. Finish the exercises in the workbook.
Thank you!
6. 表语从句的特殊句式:
the reason why ...is that...。。。的原因是。。(定从;表从)
That is because ... 那是因为。。。(表从,表原因或理由)
That is why ... 那就是。。的原因(表从,表结果)
e.g.
1)The reason why he didn’t come is that he didn’t recieve the invitation.
2)Bruce did not watch the game last night. That was because he had to help his little sister with her homework.
3)Bob had seen the film before. That was why he did not see it yesterday.
7. 表语从句中的虚拟语气
主语是表示“建议、劝告、命令、要求”的名词,如suggestion,advice, proposal,order, command,request, requirement, demand等时,表语从句应使用虚拟语气,即从句谓语动词用“should +动词原形”,should可省略。
e.g.
My suggestion is that we (should) start early tomorrow.
His order was that the handle of the water pump (should) be removed.
8. as if/though引导的表语从句的语气
as if/though引导的表语从句常位于连系动词look,seem,appear,sound,feel等后。
若表示客观事实或极有可能发生,就用陈述语气;
若表述与客观事实相反的假设,则用虚拟语气。
eg:
Dark clouds are gathering. It looks as if it is going to rain.
It looks as if he were drunk.
真实语气
虚拟语气
as if/though引导的表语从句的虚拟语气具体用法
描述的情况 表语从句的谓语动词
与现在事实不符 were/did (一般过去时)
与过去事实不符 had done (过去完成时)
与将来情况不符 would/could/might + do
1)You will feel as if you (be) at home while here.
2)Local people said after the storm it was as if there (be) a
nuclear explosion.
were
had been
高考链接
5.Taking a bus is the only way to get here, which is _______ we arrived (2018﹒江苏).
Lead-in Presentation Activity Exercise Use Summary
请在空格处填入适当的引导词
6. Our country is developing at an amazing speed,which is ______makes me feel so proud.
4. From space, the earth looks blue. This is _________about seventy-one percent of its surface is covered by water (2013﹒安徽).
because
how
what
About her
1.Where was she born
Lead-in Presentation Activity Exercise Use Summary
About her
Lead-in Presentation Activity Exercise Use Summary
3.Why do she chooses to be a teacher
About her
Lead-in Presentation Activity Exercise Use Summary
2.What do she like to do in my spare time
About her
Lead-in Presentation Activity Exercise Use Summary
4.How do she learns English
Task 1 introduction--Try to use predicative clauses to introduce yourself.
1)Zhanjiang is
where she was born.
where= (in Zhanjiang)状语
(2)Travelling and cooking are
what she like to do in my spare time.
(Travelling and cooking)=what宾语
(3) She likes children and this is
why she wants to be a teacher.
soShe likes children =why状语
(4) Watching English movies is
how she learn English well.
(by Watching English movies)=how状语
A. Absolutely. You may not believe it, but that was ________ happened at the initial stage of our group's research on developing a vaccine for malaria.
B. Yes, it is. And it seemed _______ all the theories were useful, but the fact was _____ we couldn't persuade one another that one theory was better than another.
what
as if
that
as if, that, what, who, when,
how, why, whose, which, whether
C. Exactly. The problem was not about ________ all our theories were equally good, but in deciding _______ theory to depend upon.
D. We realised that what we cared about was not _______ aspect we needed to develop a theory in, but rather ______ we can reduce the cost of a vaccine without reducing its effect!
E. You're right. At last, we became focused on the key issue, which was ______ we had to carry out the research in the first place.
whose
which
how
as if, that, what, who, when,
how, why, whose, which, whether
why
whether
Maria: This mix of theory and data is one of the key characteristics of what we call science.
David:
Maria: With your theoretical framework
David:
Maria: Deciding on a theory is definitely of critical importance.
A. Absolutely. You may not believe it, but that was what happened at the initial stage of our group's research on developing a vaccine for malaria.
C. Exactly. The problem was not about whether all our theories were equally good, but in deciding whose theory to depend upon.
David:
Maria: This was when you should have calmed down and got down to doing some solid work.
David:
B. Yes, it is. And it seemed as if all the theories were useful, but the fact was that we couldn't persuade one another that one theory was better than another.
E. You're right. At last, we became focused on the key issue, which was why we had to carry out the research in the first place.
Maria: So what happened in the end
David:
D. We realised that what we cared about was not which aspect we needed to develop a theory in, but rather how we can reduce the cost of a vaccine without reducing its effect!
Homework
Science is simply _______ you can do. And doing science makes you a scientist! So, what do scientists do Actually, what matters is not only _______ they observe in the world around them and what questions they ask, but also _______ they use evidence or data to answer the questions. They identify useful data and take new measurements. Some of the key issues that scientists face are _______ calculations they do
Fill in each blank with a word or expression that introduces a predicative clause. (page 10)
Homework
Fill in each blank with a word or expression that introduces a predicative clause. (page 10)
and _______ they analyse their data to draw conclusions about the questions they ask. The final issue, which many believe to be the most important, is _______ they need to communicate their results. This is _______ they want everyone to benefit from their work! It seems _______ science is all around us. You see, by doing science, scientists get a better understanding of the world around them and share that understanding with the whole world.
Unit 1
Discover useful structures
Grammar
Predicative Clause
表语从句
练习:判断下列句子的句型
She is in good health.
Someone left you this note.
SVP
SVO
什么是谓语呢?谓语1由谁来充当呢?
英语其实很简单,它只有26进五四十八个音标,两个句子,只要
〔谓语〕对主语加以(谓)(表)陈述,说主语怎么样,干什么或是什么的句子成分。
Someone left you this note.
She is in good health.
谓 语部分
谓
语
合成谓 语
连系动词+表语
谓语的功能和构造
1. 实义动词
Vt
vi
2.短语动词
时态和语态
短语动词(vi/vt)
3. Link +pre….
谓
语
谓 语部分
合成谓 语
连系动词+表语
表语
表语的功能是表述主语的特征、状态、身份等。它也可以说是一个主语补足语。它位于连系动词之后,与之构成合成谓语;所谓的系表结构,在系表结构中,连系动词只是形式上的谓语动词起联系作用,而真正起谓语作用的则是表语。(谓语部分)
常见的系动词有:
1.状态系动词:be 动词;
2.感官系动词:look/ feel/ smell/ taste/ sound等;
3.变化系动词:get/ become/ turn/ grow/ fall/ grow等
4.持续系动词:remain/ stay/ keep(仍然)
5.表象系动词:seem/appear(似乎,好像)
6.终止系动词:prove/ turn out(结果是,证明是)
He is a boy.
He is in the room
He is ill
He is to blame.
Predicative Clauses
( 表语从句)
在复合句中作表语的从句叫做表语从句。位于主句的系动词之后,对主语进行解释说明。一般结构是:“主语+系动词+表语从句”。表语从句必须用陈述语序。
5. The question is who broke the vase.
6. My suggestion is that we (should) start early tomorrow.
结构完整的句子
表语
从句
陈述句(确切含义)
疑问句
一般 特殊
感叹句
e.g. One advantage of playing the guitar is that it can give you a great deal of pleasure.
1. 表语从句一定要用陈述语序。
e.g. The trouble is that I have lost his address.
The reason for his absence is that he hasn't been informed.
2. that引导表语从句时,仅起连接作用 。
①无意义 ②不充当成分 ③不可省略
表语从句要点归纳
表语从句要点归纳
e.g. The question is whether your uncle will offer help to us.
3. whether引导表语从句时,起连接作用,
①有“是否”之意 ②不充当成分
注意: if 不能引导表语从句
(1)从属连词: that& whether
用法归纳:
a. that引导表语从句时,只起______作用,作/不作句子成分,有/没有意义。
b. whether引导表语从句时,只起______作用,作/不作句子成分,通常翻译为“______”。注意,引导表语从句时通常不用if。
连接
√
√
连接
√
是否
e.g. My hometown is no longer what it used to be.表语
The problem is who we can get to replace her宾语.
4. 连接代词who, whom, whose, what, which, whoever, whatever, whichever等除在句中起连接作用外,在从句中还充当主语、宾语、表语或定语,本身具有词义。
Task 2:Underline the predicative clauses in the following sentences and then work out the rules in groups.
2.连接代词who / whom / whose / which/what
连接代词在表语从句中根据句义可充当主语、宾语、表语或定语。依据“缺什么补什么”原则确定正确的连词。
所谓“缺什么补什么”是指从句与连词之间的关系。
如果句子中缺主语,指人用who ,如缺宾语,指人用whom。
指物用what。如缺定语用whose 或 which。
.g. The question is when they will start the project.时间状语从句
The question is how he did it.方式状语
5. 连接副词where, when, why, how等除在句中起连接作用,在从句中还充当地点、时间、原因、方式状语,本身具有词义。
Task 3:Underline the predicative clauses in the following sentences and then work out the rules in groups.
3.连接副词when / where / why / how
连接副词在表语从句中根据句义可充当状语,可表时间、地点、原因、方式等,因此不能省略。
依据“缺什么补什么”原则确定正确的连词。
所谓“缺什么补什么”是指从句与连词之间的关系。
如缺时间状语用when;地点状语用 where。
原因状语用why;方式状语用 how。
引导词/连接词 连词 在从句中不作成分 that, whether, as if, as though, because …
连接代词 在从句中作主语、宾语、表语、定语 what, who, whom, whose, which, 。, whoever, whichever …
连接副词 在从句中作状语 when, where, how, why …
既学既练:
1.The trouble is I have lost his address.
2.The question is they will go by plane or by train.
3.It sounds someone is knocking at the door.
4.This is the weather here is cold and wet.
5.That's Tony got angry with me.
6.He has become he wanted to be ten years ago.
7.The question is we can find the suitable man for the job.
that
whether
as if / though
because
why
what
how
高考链接
1.What puzzles Lily's friends is _______ she always has so many crazy ideas.(2021 天津卷改编)
2.Without his support, we wouldn’t be _________ we are now(2018·北京改编).
3.This is _________ my father has taught me—to always face difficulties and hope for the best(2018·北京改编).
请填入适当的引导词
why
where
what
表
语
从
句
定义:
位置:
系动词
分类
引导词
连词:
连接代词:
连接副词:
Draw a mind map to summarize the usage of predicative clause.
表
语
从
句
定义:在复合句中充当表语的从句叫做表语从句。
位置:表语从句放在连系动词之后。
系动词
分类
状态类:be 动词,seem,appear,keep
感官类: look, smell, taste, sound,
变化类:become, get, turn, grow, fall,
引导词
连词:that, whether, as if, as though...
连接代词:what, who, whom, whose, which, whatever, whoever, …
连接副词:when, where, how, why …
“证明”类:prove;
turn out
Review the words, expressions and sentences we have learned.
Review Grammar.
3. Finish the exercises in the workbook.
Thank you!
6. 表语从句的特殊句式:
the reason why ...is that...。。。的原因是。。(定从;表从)
That is because ... 那是因为。。。(表从,表原因或理由)
That is why ... 那就是。。的原因(表从,表结果)
e.g.
1)The reason why he didn’t come is that he didn’t recieve the invitation.
2)Bruce did not watch the game last night. That was because he had to help his little sister with her homework.
3)Bob had seen the film before. That was why he did not see it yesterday.
7. 表语从句中的虚拟语气
主语是表示“建议、劝告、命令、要求”的名词,如suggestion,advice, proposal,order, command,request, requirement, demand等时,表语从句应使用虚拟语气,即从句谓语动词用“should +动词原形”,should可省略。
e.g.
My suggestion is that we (should) start early tomorrow.
His order was that the handle of the water pump (should) be removed.
8. as if/though引导的表语从句的语气
as if/though引导的表语从句常位于连系动词look,seem,appear,sound,feel等后。
若表示客观事实或极有可能发生,就用陈述语气;
若表述与客观事实相反的假设,则用虚拟语气。
eg:
Dark clouds are gathering. It looks as if it is going to rain.
It looks as if he were drunk.
真实语气
虚拟语气
as if/though引导的表语从句的虚拟语气具体用法
描述的情况 表语从句的谓语动词
与现在事实不符 were/did (一般过去时)
与过去事实不符 had done (过去完成时)
与将来情况不符 would/could/might + do
1)You will feel as if you (be) at home while here.
2)Local people said after the storm it was as if there (be) a
nuclear explosion.
were
had been
高考链接
5.Taking a bus is the only way to get here, which is _______ we arrived (2018﹒江苏).
Lead-in Presentation Activity Exercise Use Summary
请在空格处填入适当的引导词
6. Our country is developing at an amazing speed,which is ______makes me feel so proud.
4. From space, the earth looks blue. This is _________about seventy-one percent of its surface is covered by water (2013﹒安徽).
because
how
what
About her
1.Where was she born
Lead-in Presentation Activity Exercise Use Summary
About her
Lead-in Presentation Activity Exercise Use Summary
3.Why do she chooses to be a teacher
About her
Lead-in Presentation Activity Exercise Use Summary
2.What do she like to do in my spare time
About her
Lead-in Presentation Activity Exercise Use Summary
4.How do she learns English
Task 1 introduction--Try to use predicative clauses to introduce yourself.
1)Zhanjiang is
where she was born.
where= (in Zhanjiang)状语
(2)Travelling and cooking are
what she like to do in my spare time.
(Travelling and cooking)=what宾语
(3) She likes children and this is
why she wants to be a teacher.
soShe likes children =why状语
(4) Watching English movies is
how she learn English well.
(by Watching English movies)=how状语
A. Absolutely. You may not believe it, but that was ________ happened at the initial stage of our group's research on developing a vaccine for malaria.
B. Yes, it is. And it seemed _______ all the theories were useful, but the fact was _____ we couldn't persuade one another that one theory was better than another.
what
as if
that
as if, that, what, who, when,
how, why, whose, which, whether
C. Exactly. The problem was not about ________ all our theories were equally good, but in deciding _______ theory to depend upon.
D. We realised that what we cared about was not _______ aspect we needed to develop a theory in, but rather ______ we can reduce the cost of a vaccine without reducing its effect!
E. You're right. At last, we became focused on the key issue, which was ______ we had to carry out the research in the first place.
whose
which
how
as if, that, what, who, when,
how, why, whose, which, whether
why
whether
Maria: This mix of theory and data is one of the key characteristics of what we call science.
David:
Maria: With your theoretical framework
David:
Maria: Deciding on a theory is definitely of critical importance.
A. Absolutely. You may not believe it, but that was what happened at the initial stage of our group's research on developing a vaccine for malaria.
C. Exactly. The problem was not about whether all our theories were equally good, but in deciding whose theory to depend upon.
David:
Maria: This was when you should have calmed down and got down to doing some solid work.
David:
B. Yes, it is. And it seemed as if all the theories were useful, but the fact was that we couldn't persuade one another that one theory was better than another.
E. You're right. At last, we became focused on the key issue, which was why we had to carry out the research in the first place.
Maria: So what happened in the end
David:
D. We realised that what we cared about was not which aspect we needed to develop a theory in, but rather how we can reduce the cost of a vaccine without reducing its effect!
Homework
Science is simply _______ you can do. And doing science makes you a scientist! So, what do scientists do Actually, what matters is not only _______ they observe in the world around them and what questions they ask, but also _______ they use evidence or data to answer the questions. They identify useful data and take new measurements. Some of the key issues that scientists face are _______ calculations they do
Fill in each blank with a word or expression that introduces a predicative clause. (page 10)
Homework
Fill in each blank with a word or expression that introduces a predicative clause. (page 10)
and _______ they analyse their data to draw conclusions about the questions they ask. The final issue, which many believe to be the most important, is _______ they need to communicate their results. This is _______ they want everyone to benefit from their work! It seems _______ science is all around us. You see, by doing science, scientists get a better understanding of the world around them and share that understanding with the whole world.
