北师大版(2019)选择性必修第一册Unit 3 Conservation 语法知识点课件(共20张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 北师大版(2019)选择性必修第一册Unit 3 Conservation 语法知识点课件(共20张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 2.4MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 北师大版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-04-14 10:29:31 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共20张PPT)
Unit 3 语法知识精讲
结构拓展
①It is+adj.+(for sb.) to do sth.
常用于此句型的形容词有important、necessary、wrong、possible、impossible、basic、dif-
ficult、vital、natural、common、strange、normal等。
It is vital to take short breaks after learning online for 30 minutes.在网上学习了30分钟
后,短暂休息一下是至关重要的。
It is impossible for them to have finished so much work in such a short time.= It is impossible
that they have finished so much work in such a short time.他们在这么短的时间内完成这么多
的工作是不可能的。
②It is+n.+that从句
It is a pity that you can’t go with us.很遗憾你不能和我们一起去。
It is a fact that every language changes.每种语言都在变,这是事实。
1 | It is+形容词(表语)+that从句(真正的主语)
Without forests, we would have no air to breathe...没有森林,我们就没有呼吸的空气……
(教材P53)
情景导学
Without air, man couldn’t exist on the earth.没有空气的话,人类就不能在地球上生存。
Without your help, I would have failed the exam last week.没有你的帮助的话,我上周考试就
不及格了。
Without his aid, my skills in English wouldn’t have been greatly improved.如果没有他的帮助,
我的英语技能就不会有很大的提高了。
2 | without用于含蓄虚拟语气
结构
用法归纳
(1)有时虚拟的条件并不是直接通过条件从句来表示,而是用一些词、短语或通过上下文暗
示来说明,这种句子使用的便是含蓄虚拟语气。
(2)当句子用介词without引出一个假设的条件时,句子的谓语动词就要用虚拟语气。
(3)without用于表示虚拟条件时,谓语动词有如下三种形式:
①与现在事实相反,谓语动词用“ ”形式;
②与过去事实相反,谓语动词用“ ”形式;
③与将来事实相反,谓语动词用“would/could/might do”形式。
特别提醒
并不是without所在的句子谓语动词一定要用虚拟语气。如果它表示一种真实的情况,就不
能用虚拟语气。
would/could/might do
would/could/might have done
How did you finish your work so fast without any help 没有任何协助,你是如何这么快完成
工作的
结构拓展
用于含蓄虚拟语气的词或短语还有otherwise、but for等。
But for the quick action, it would have hurt them.如果不是行动迅速,它就伤到他们了。
My parents gave me the money. Otherwise, I couldn’t have afforded the trip.我父母给了我
钱。否则,我可付不起这次旅费。
This morning, it took me 40 minutes to go downtown.今天早上,我去市中心花了40分钟。
(教材P58)
情景导学
It took us about 3 hours to go all the way around the Xi an City Wall.我们花了大约3个小时才一路绕过西安城墙。
It took a long time for her to change her attitude.她用了很长时间才改变了态度。
3 | It takes/took sb. some time to do sth.某人花费多长时间做某事
结构
用法归纳
It takes/took sb. some time to do sth.表示“某人花费多长时间做某事”。其中It为
,后面的不定式短语为 。此句型可与It takes/took some time for sb. to
do sth.互换。
形式主语
真正的主语
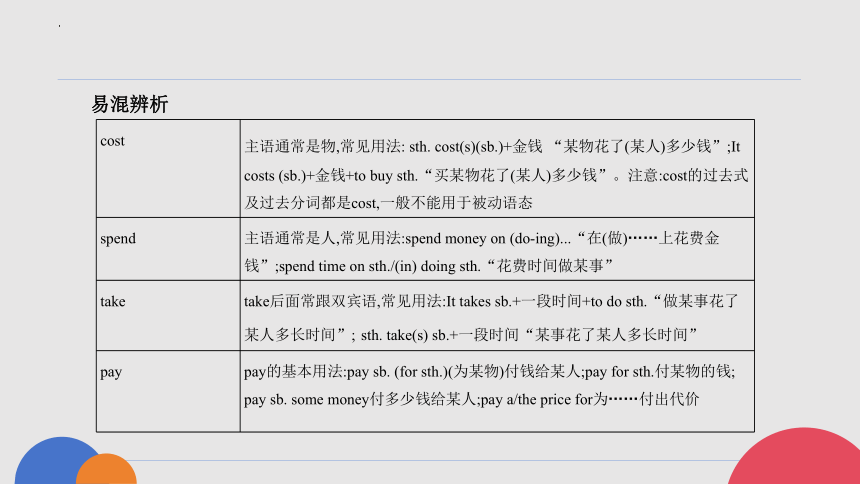
易混辨析
cost 主语通常是物,常见用法: sth. cost(s)(sb.)+金钱 “某物花了(某人)多少钱”;It
costs (sb.)+金钱+to buy sth.“买某物花了(某人)多少钱”。注意:cost的过去式及过去分词都是cost,一般不能用于被动语态
spend 主语通常是人,常见用法:spend money on (do-ing)...“在(做)……上花费金
钱”;spend time on sth./(in) doing sth.“花费时间做某事”
take take后面常跟双宾语,常见用法:It takes sb.+一段时间+to do sth.“做某事花了某人多长时间”; sth. take(s) sb.+一段时间“某事花了某人多长时间”
pay pay的基本用法:pay sb. (for sth.)(为某物)付钱给某人;pay for sth.付某物的钱;
pay sb. some money付多少钱给某人;pay a/the price for为……付出代价
How often do we arrive at work or school, stressed out, tired and angry 有多少次我们抵达工
作地点或学校时感到焦虑、疲惫和愤怒呢
情景导学
He returned home, safe and sound.他回到了家,安然无恙。(表结果)
The survivors lay on the beach, frightened and exhausted.幸存者躺在海滩上,心有余悸,疲惫
不堪。(表伴随)
Hungry (=Because he was hungry), he hurried to the kitchen.因为太饿了,他匆忙跑到厨房。
(表原因)
Ripe (=When/If they are ripe), these apples are sweet.熟了的时候这些苹果很甜。(表条件)
Wet or fine(=Whether it was wet or fine), he got up at six and took a walk in the park.不管是下
雨天还是晴天,他都在六点钟起床到公园里散步。(表让步)
4 | 形容词(短语)作状语
结构
用法归纳
在句子中,形容词(短语)可充当状语,主要说明主语的 、特点等。当形容词(短语)作
状语时,通常用逗号与句子主干分开,位置可在句首、句中或句末。
特别提醒
(1)形容词(短语)作原因、条件、让步状语时,往往放在句首。
(2)形容词(短语)作伴随或结果状语时,通常放在句末。
结构拓展
副词作状语通常修饰动词、形容词或副词,有时修饰整个句子。
After the long journey, they went back home slowly and tiredly.经过长途旅行后,他们慢慢
地、疲惫地回家了。
状态
限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句
定语从句有两种:限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句。
一、作用不同
情景导学
People who take physical exercise regularly live longer.经常进行体育锻炼的人更长寿。
His daughter, who is in Shenzhen now, is coming home next week.他女儿现在在深圳,下星期
就要回家了。
This is the place where I visited last week.这是我上周参观的地方。
Yesterday Jimmy left for Canada, where he would stay for two years.昨天吉米出发去加拿大
了,他将在那里待两年。
Mr Liu wants to talk to the students whose homework hasn’t been handed in.刘老师要跟那些
没交作业的学生谈话。
Mr King, whose legs were badly hurt, was quickly taken to hospital.金先生的腿受了重伤,他很
快被送往医院。
用法归纳
限制性定语从句用来修饰和限制先行词,与先行词关系密切,使先行词的含义更具体、更明
确,若去掉,句子意义① 。非限制性定语从句是对先行词作附加或补充性的说明,即
使去掉,句子的意思仍然完整、清楚。
不完整
二、形式不同
情景导学
The book that/which you borrowed last week is really moving.上周你借的那本书真令人感动。
This is an important present, which I received yesterday.这是一件重要的礼物,我是昨天收到它的。
The person whom/who you are looking for is downstairs.你找的那个人正在楼下。
This note was left by Tom, who was here a moment ago.这个便条是汤姆留下的,刚才他还在
这里。
用法归纳
限制性定语从句与主句之间不用逗号隔开,常译成定语;非限制性定语从句与主句之间
用逗号隔开,常译成和主句并列的句子。
三、先行词不同
情景导学
This is the best novel that I have ever read.这是我看过的最好的小说。
He changed his mind, which made me very angry.他改变了主意,这使我很生气。
I can still remember the day when you were born.我仍然记得你出生的那天。
My favourite season is autumn, when we celebrate the Mid-Autumn Festival.我最喜欢的季节
是秋天,我们在那时候过中秋节。
用法归纳
限制性定语从句的先行词是② 或代词,表明所修饰的是哪个/些人或物。非限制性定
语从句的先行词既可为名词或代词,也可为整个主句或其中的一部分。
名词
四、关系词的使用情况不同
情景导学1
He passed the exam, which made his teacher relieved.他通过了考试,这使他的老师感到欣慰。
She has a small office which/that is used for a meeting.她有一个用来开会的小办公室。
This is the reason why she refused your invitation.这就是她拒绝你的邀请的原因。
I have told them the reason, for which I didn’t attend the party.我已经告诉他们我没参加聚会
的原因了。
This is the man (whom/who/that) we are talking about.这就是我们正在谈论的那个人。
The young man had a new girlfriend, whom he wanted to impress.那个年轻人新交了一个女朋
友,他想给她留下深刻的好印象。
用法归纳1
(1)在限制性定语从句中,先行词指人时,关系代词可用③ ,先行词指物时,关系代词可用④ ;但在非限制性定语从句中,先行词指人时,关系代词只能用who/whom,
先行词指物时,关系代词只能用which,即that不能引导非限制性定语从句。
(2)关系代词whom在限制性定语从句中作宾语时可用⑤ 代替,但在非限制性定
语从句中作宾语时不可用⑥ 代替。
(3)why不能引导非限制性定语从句,需用for which代替。
情景导学2
This is a good film (which/that) I saw a few days ago.这是我几天前看过的一部好电影。
The summer holiday, which we have been looking forward to, is drawing near.我们一直盼望着
的暑假就要来了。
that/who/whom
that/which
who/that
who/that
用法归纳2
关系代词在限制性定语从句中作宾语时⑦ 省略,而非限制性定语从句中的关系
代词均⑧ 省略。
五、使用非限制性定语从句的情况
情景导学1
Mr Smith, who was my English teacher, retired last year.史密斯先生去年退休了,他是我的英
语老师。
Hangzhou, which is a beautiful city, attracts many visitors during summer.杭州是一个美丽的
城市,夏季会吸引很多游客。
可以
不可以
用法归纳1
当先行词是世界上独一无二的事物或专有名词时,用非限制性定语从句。
情景导学2
My father, who is an architect, is very good at painting.我父亲是一名建筑师,他十分擅长绘画。
She has a younger brother, who is a doctor.她有一个弟弟,他是一名医生。(只有一个弟弟)
She has a younger brother who/that is a doctor.她有一个当医生的弟弟。(可能有几个弟弟,其
中一个是医生)
用法归纳2
当先行词指某人仅有的一个亲属时,用非限制性定语从句。
即时巩固
Ⅰ.单句语法填空
1.I didn’t believe the reason he referred to the other day at the press conference.
2.It’s our honor to meet the chairman on this occasion everybody is focusing on his
talk.
3.It is important to create an atmosphere wild ideas are honored rather than dis-
missed.
4.I’m grateful that the assistant responded in a way made me rethink the power of
my words.
that/which
when
where
that/which
5.Lisa is an outstanding graduate life story has greatly inspired her fellow school-mates.
6.We employed a foreigner as our coach, for life here in China was totally differ-ent.
7.The famous scientist made another wonderful discovery, is of great importance to
science.
8.That day, along with the barber there was an assistant, had recently joined.
9.I prefer to work in black and white, allows me to show different specific worlds
more clearly.
Ⅱ.完成句子
whose
whom
which
who
which
1.他有好几个表兄弟,最小的那个很聪明。
He has several cousins, .
2.整个夏天,他都在有需要的地方做志愿者。
Throughout the summer,he worked as a volunteer in the place
.
3.特别令人惊讶的是他的勤奋,这点给我们留下了深刻的印象。
Particularly surprising was his diligence,
.
4.明天我将去看望在旅游中给过我们很多帮助的那个人。
Tomorrow I’ll go to see the man
during the trip.
the youngest of whom is very clever
where he was
needed
which left a deep impression
on us
who gave us a lot of
help
Unit 3 语法知识精讲
结构拓展
①It is+adj.+(for sb.) to do sth.
常用于此句型的形容词有important、necessary、wrong、possible、impossible、basic、dif-
ficult、vital、natural、common、strange、normal等。
It is vital to take short breaks after learning online for 30 minutes.在网上学习了30分钟
后,短暂休息一下是至关重要的。
It is impossible for them to have finished so much work in such a short time.= It is impossible
that they have finished so much work in such a short time.他们在这么短的时间内完成这么多
的工作是不可能的。
②It is+n.+that从句
It is a pity that you can’t go with us.很遗憾你不能和我们一起去。
It is a fact that every language changes.每种语言都在变,这是事实。
1 | It is+形容词(表语)+that从句(真正的主语)
Without forests, we would have no air to breathe...没有森林,我们就没有呼吸的空气……
(教材P53)
情景导学
Without air, man couldn’t exist on the earth.没有空气的话,人类就不能在地球上生存。
Without your help, I would have failed the exam last week.没有你的帮助的话,我上周考试就
不及格了。
Without his aid, my skills in English wouldn’t have been greatly improved.如果没有他的帮助,
我的英语技能就不会有很大的提高了。
2 | without用于含蓄虚拟语气
结构
用法归纳
(1)有时虚拟的条件并不是直接通过条件从句来表示,而是用一些词、短语或通过上下文暗
示来说明,这种句子使用的便是含蓄虚拟语气。
(2)当句子用介词without引出一个假设的条件时,句子的谓语动词就要用虚拟语气。
(3)without用于表示虚拟条件时,谓语动词有如下三种形式:
①与现在事实相反,谓语动词用“ ”形式;
②与过去事实相反,谓语动词用“ ”形式;
③与将来事实相反,谓语动词用“would/could/might do”形式。
特别提醒
并不是without所在的句子谓语动词一定要用虚拟语气。如果它表示一种真实的情况,就不
能用虚拟语气。
would/could/might do
would/could/might have done
How did you finish your work so fast without any help 没有任何协助,你是如何这么快完成
工作的
结构拓展
用于含蓄虚拟语气的词或短语还有otherwise、but for等。
But for the quick action, it would have hurt them.如果不是行动迅速,它就伤到他们了。
My parents gave me the money. Otherwise, I couldn’t have afforded the trip.我父母给了我
钱。否则,我可付不起这次旅费。
This morning, it took me 40 minutes to go downtown.今天早上,我去市中心花了40分钟。
(教材P58)
情景导学
It took us about 3 hours to go all the way around the Xi an City Wall.我们花了大约3个小时才一路绕过西安城墙。
It took a long time for her to change her attitude.她用了很长时间才改变了态度。
3 | It takes/took sb. some time to do sth.某人花费多长时间做某事
结构
用法归纳
It takes/took sb. some time to do sth.表示“某人花费多长时间做某事”。其中It为
,后面的不定式短语为 。此句型可与It takes/took some time for sb. to
do sth.互换。
形式主语
真正的主语
易混辨析
cost 主语通常是物,常见用法: sth. cost(s)(sb.)+金钱 “某物花了(某人)多少钱”;It
costs (sb.)+金钱+to buy sth.“买某物花了(某人)多少钱”。注意:cost的过去式及过去分词都是cost,一般不能用于被动语态
spend 主语通常是人,常见用法:spend money on (do-ing)...“在(做)……上花费金
钱”;spend time on sth./(in) doing sth.“花费时间做某事”
take take后面常跟双宾语,常见用法:It takes sb.+一段时间+to do sth.“做某事花了某人多长时间”; sth. take(s) sb.+一段时间“某事花了某人多长时间”
pay pay的基本用法:pay sb. (for sth.)(为某物)付钱给某人;pay for sth.付某物的钱;
pay sb. some money付多少钱给某人;pay a/the price for为……付出代价
How often do we arrive at work or school, stressed out, tired and angry 有多少次我们抵达工
作地点或学校时感到焦虑、疲惫和愤怒呢
情景导学
He returned home, safe and sound.他回到了家,安然无恙。(表结果)
The survivors lay on the beach, frightened and exhausted.幸存者躺在海滩上,心有余悸,疲惫
不堪。(表伴随)
Hungry (=Because he was hungry), he hurried to the kitchen.因为太饿了,他匆忙跑到厨房。
(表原因)
Ripe (=When/If they are ripe), these apples are sweet.熟了的时候这些苹果很甜。(表条件)
Wet or fine(=Whether it was wet or fine), he got up at six and took a walk in the park.不管是下
雨天还是晴天,他都在六点钟起床到公园里散步。(表让步)
4 | 形容词(短语)作状语
结构
用法归纳
在句子中,形容词(短语)可充当状语,主要说明主语的 、特点等。当形容词(短语)作
状语时,通常用逗号与句子主干分开,位置可在句首、句中或句末。
特别提醒
(1)形容词(短语)作原因、条件、让步状语时,往往放在句首。
(2)形容词(短语)作伴随或结果状语时,通常放在句末。
结构拓展
副词作状语通常修饰动词、形容词或副词,有时修饰整个句子。
After the long journey, they went back home slowly and tiredly.经过长途旅行后,他们慢慢
地、疲惫地回家了。
状态
限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句
定语从句有两种:限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句。
一、作用不同
情景导学
People who take physical exercise regularly live longer.经常进行体育锻炼的人更长寿。
His daughter, who is in Shenzhen now, is coming home next week.他女儿现在在深圳,下星期
就要回家了。
This is the place where I visited last week.这是我上周参观的地方。
Yesterday Jimmy left for Canada, where he would stay for two years.昨天吉米出发去加拿大
了,他将在那里待两年。
Mr Liu wants to talk to the students whose homework hasn’t been handed in.刘老师要跟那些
没交作业的学生谈话。
Mr King, whose legs were badly hurt, was quickly taken to hospital.金先生的腿受了重伤,他很
快被送往医院。
用法归纳
限制性定语从句用来修饰和限制先行词,与先行词关系密切,使先行词的含义更具体、更明
确,若去掉,句子意义① 。非限制性定语从句是对先行词作附加或补充性的说明,即
使去掉,句子的意思仍然完整、清楚。
不完整
二、形式不同
情景导学
The book that/which you borrowed last week is really moving.上周你借的那本书真令人感动。
This is an important present, which I received yesterday.这是一件重要的礼物,我是昨天收到它的。
The person whom/who you are looking for is downstairs.你找的那个人正在楼下。
This note was left by Tom, who was here a moment ago.这个便条是汤姆留下的,刚才他还在
这里。
用法归纳
限制性定语从句与主句之间不用逗号隔开,常译成定语;非限制性定语从句与主句之间
用逗号隔开,常译成和主句并列的句子。
三、先行词不同
情景导学
This is the best novel that I have ever read.这是我看过的最好的小说。
He changed his mind, which made me very angry.他改变了主意,这使我很生气。
I can still remember the day when you were born.我仍然记得你出生的那天。
My favourite season is autumn, when we celebrate the Mid-Autumn Festival.我最喜欢的季节
是秋天,我们在那时候过中秋节。
用法归纳
限制性定语从句的先行词是② 或代词,表明所修饰的是哪个/些人或物。非限制性定
语从句的先行词既可为名词或代词,也可为整个主句或其中的一部分。
名词
四、关系词的使用情况不同
情景导学1
He passed the exam, which made his teacher relieved.他通过了考试,这使他的老师感到欣慰。
She has a small office which/that is used for a meeting.她有一个用来开会的小办公室。
This is the reason why she refused your invitation.这就是她拒绝你的邀请的原因。
I have told them the reason, for which I didn’t attend the party.我已经告诉他们我没参加聚会
的原因了。
This is the man (whom/who/that) we are talking about.这就是我们正在谈论的那个人。
The young man had a new girlfriend, whom he wanted to impress.那个年轻人新交了一个女朋
友,他想给她留下深刻的好印象。
用法归纳1
(1)在限制性定语从句中,先行词指人时,关系代词可用③ ,先行词指物时,关系代词可用④ ;但在非限制性定语从句中,先行词指人时,关系代词只能用who/whom,
先行词指物时,关系代词只能用which,即that不能引导非限制性定语从句。
(2)关系代词whom在限制性定语从句中作宾语时可用⑤ 代替,但在非限制性定
语从句中作宾语时不可用⑥ 代替。
(3)why不能引导非限制性定语从句,需用for which代替。
情景导学2
This is a good film (which/that) I saw a few days ago.这是我几天前看过的一部好电影。
The summer holiday, which we have been looking forward to, is drawing near.我们一直盼望着
的暑假就要来了。
that/who/whom
that/which
who/that
who/that
用法归纳2
关系代词在限制性定语从句中作宾语时⑦ 省略,而非限制性定语从句中的关系
代词均⑧ 省略。
五、使用非限制性定语从句的情况
情景导学1
Mr Smith, who was my English teacher, retired last year.史密斯先生去年退休了,他是我的英
语老师。
Hangzhou, which is a beautiful city, attracts many visitors during summer.杭州是一个美丽的
城市,夏季会吸引很多游客。
可以
不可以
用法归纳1
当先行词是世界上独一无二的事物或专有名词时,用非限制性定语从句。
情景导学2
My father, who is an architect, is very good at painting.我父亲是一名建筑师,他十分擅长绘画。
She has a younger brother, who is a doctor.她有一个弟弟,他是一名医生。(只有一个弟弟)
She has a younger brother who/that is a doctor.她有一个当医生的弟弟。(可能有几个弟弟,其
中一个是医生)
用法归纳2
当先行词指某人仅有的一个亲属时,用非限制性定语从句。
即时巩固
Ⅰ.单句语法填空
1.I didn’t believe the reason he referred to the other day at the press conference.
2.It’s our honor to meet the chairman on this occasion everybody is focusing on his
talk.
3.It is important to create an atmosphere wild ideas are honored rather than dis-
missed.
4.I’m grateful that the assistant responded in a way made me rethink the power of
my words.
that/which
when
where
that/which
5.Lisa is an outstanding graduate life story has greatly inspired her fellow school-mates.
6.We employed a foreigner as our coach, for life here in China was totally differ-ent.
7.The famous scientist made another wonderful discovery, is of great importance to
science.
8.That day, along with the barber there was an assistant, had recently joined.
9.I prefer to work in black and white, allows me to show different specific worlds
more clearly.
Ⅱ.完成句子
whose
whom
which
who
which
1.他有好几个表兄弟,最小的那个很聪明。
He has several cousins, .
2.整个夏天,他都在有需要的地方做志愿者。
Throughout the summer,he worked as a volunteer in the place
.
3.特别令人惊讶的是他的勤奋,这点给我们留下了深刻的印象。
Particularly surprising was his diligence,
.
4.明天我将去看望在旅游中给过我们很多帮助的那个人。
Tomorrow I’ll go to see the man
during the trip.
the youngest of whom is very clever
where he was
needed
which left a deep impression
on us
who gave us a lot of
help
同课章节目录
- Unit 1 Relationshis
- Lesson 1 Teachers
- Lesson 2 How Do We Like Teachers’ Feedback?
- Lesson 3 So Close,Yet So Fa
- Unit 2 Success
- Lesson 1 Money vs Success
- Lesson 2 Top Five Secrets of Success
- Lesson 3 Getting to the Top
- Unit 3 Conservation
- Lesson 1 The Sixth Extinction
- Lesson 2 War on Plastic Packets
- Lesson 3 The Road to Destruction
