牛津译林版(2019)必修 第二册Unit 4 Exploring literature Grammar and usage 导学案
文档属性
| 名称 | 牛津译林版(2019)必修 第二册Unit 4 Exploring literature Grammar and usage 导学案 |
|
|
| 格式 | docx | ||
| 文件大小 | 162.3KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津译林版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-04-18 08:40:48 | ||
图片预览


文档简介
B2U4 Grammar and Usage Modal verbs
Learning aims:
By the end of this class, students will be able to:
identify and categorize the usage of modal verbs;
summarize general rules of modal verbs;
distinguish and use the right modal verbs to finish tasks of offering suggestions and making rules;
Step 1 Lead-in
What shall I read
Step 2 Reading
Task 1 Find the key phrases in part A on page 48
1.不止一次 2.首先
3.特别;尤其 4.值得做某事
5.浏览 6.有可能做...
7.偶然发现 8.慢慢地
9.物色到;挑选出 10.更加
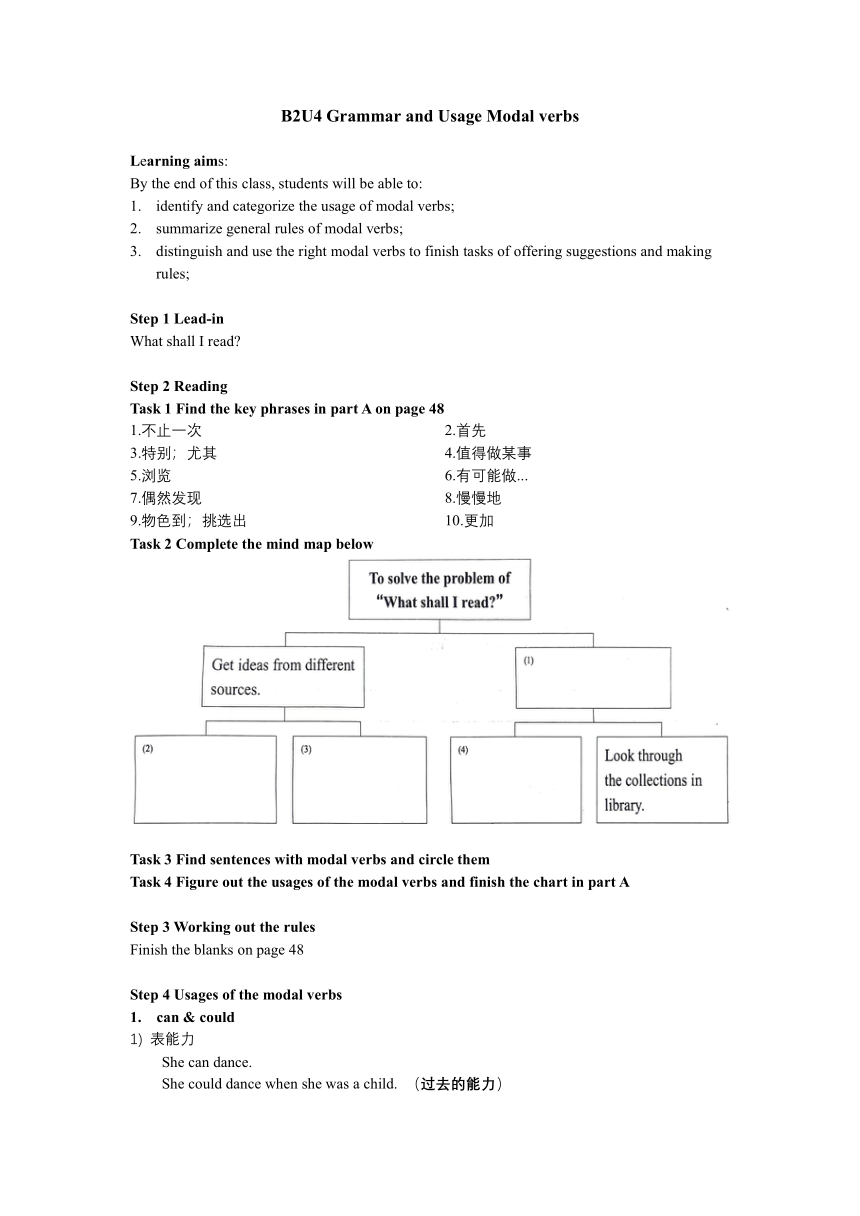
Task 2 Complete the mind map below
Task 3 Find sentences with modal verbs and circle them
Task 4 Figure out the usages of the modal verbs and finish the chart in part A
Step 3 Working out the rules
Finish the blanks on page 48
Step 4 Usages of the modal verbs
1. can & could
1) 表能力
She can dance.
She could dance when she was a child. (过去的能力)
2) 表征求意见
Can/Could you stop chasing me
3) 表猜测,can表猜测多用于否定和疑问
--Oh my god! Can it be true --It can’t be true.
2. may/might
1) 表示许可,请求,作"可以"解释
May I take photos here
2) 表示猜测,作“可能,也许”解释
They may/might be relatives. (might可能性更小)
3) 表示愿望,祝愿
May you smile all the time.
4) 常用词组积累may/might as well do sth. 不妨做某事
You may/might as well do the experiment again
3. must
1) 表示必须,应该
I must take care of my hairstyle.
2) mustn’t表示禁止,不允许
You mustn’t bully your brother.
3) 表示“一定是”,用于肯定猜测,
must do/ be doing肯定做某事/正在做某事
must have done肯定做过某事(完成)
He must have seen the answer.
4. will & would
1) 表示习惯性动作(habit),will 表示现在的习惯,would 表示过去的习惯。如:
Mary will listen to music for hours in her room.
I would take a walk after supper when I was young.
2) 表示意愿(willingness)。如:
The baby won’t go to sleep.
3) 表示请求(request),would 比 will 更委婉些
Would you give me some advice
5. should
1). 表责任或义务,应该,应当
You should complete your test in time.
2). 表较大可能实现的猜测,推断,意为“可能,应该”
The street should be crowed at weekends.
3). 表万一
Should I be free tomorrow, I will come
4). 表意外,“竟然,居然”
A gentleman like him should be rude to a lady.
6. ought to
表义务,意为“应该”(因责任、义务等该做),语气比should稍重。
You are his father. You ought to take care of him.
You oughtn’t to smoke so much.
7. shall
1)用于第一、第三人称的疑问句中,表征询意见或请求允许,多与I或we连用。
What shall we do this weekend
When shall my brother be able to leave hospital
2)用于第二、第三人称,表示说话人的命令、警告、允诺或威胁。
He shall be punished. (威胁)
You shall go with me. (命令)
You shall have a new dress for your birthday. (允诺)
3)常用于主语是第三人称的条约、法律法规、规章制度等文件中表“义务”或“规定”。
Every student shall wear school uniform at school.
8. need & dare
1)need 和dare可以作实义动词或情态动词。作情态动词时,后跟动词原形,表示“需要,有必要”,无人称和数的变化,多用于否定句、疑问句或条件句中。
I dare not walk through the woods at night.
You needn’t go there now.
Need I hand in the paper now
2)作实义动词时,同其他实义动词一样,可用于各种句式,有时态、人称和数的变化,构成否定句和疑问句时要借助于助动词。在否定句和疑问句中不定式符号to也可以省略。
You don’t need to be so worried. You need to be more careful.
They don’t dare (to) make a sound while their parents are sleeping.
Step 5 modal verbs + have done
1. must have done 表示对过去行为的推测, 意为 “一定, 想必做过” , 语气十分肯定
It must have rained last night, as the ground is wet.
2. could have done在肯定句中是虚拟语气表示“本来能做但却没做”
couldn’t have done 多用于语气强烈的否定, 意为“过去不可能做过”
Don’t worry. They could have just forgotten to call.
I saw Mr. Li just now. He couldn’t have gone to Beijing.
3. may/might have done 表示对过去行为的推测, 意为“可能做过”,might 所表示可能性较弱
Smith might have gone to see the movie yesterday.
4. should/ought to have done 本该做某事而实际上未做,shouldn’t/oughtn’t to have done 不该做某事反而做了
You should have made full preparations.
You shouldn't have bullied your brother
5. needn’t have done表示对过去的虚拟意为 “本来不必做某事而实际上却做了”
I actually needn’t have bought so much food—only three people came.
6. had better have done 用于事后的建议,含轻微责备的口吻,意为“当时最好做了某事”。
I had better have started earlier.
Step 6 Summary
用法 请求/许可 可能/推测 义务/职责 意图/打算 意愿/愿意 意志/决心 才能/能力
can/could
may/might
shall/should
will/would
must
ought to
Step 7 Applying the rules
Finish part B on page 49
Learning aims:
By the end of this class, students will be able to:
identify and categorize the usage of modal verbs;
summarize general rules of modal verbs;
distinguish and use the right modal verbs to finish tasks of offering suggestions and making rules;
Step 1 Lead-in
What shall I read
Step 2 Reading
Task 1 Find the key phrases in part A on page 48
1.不止一次 2.首先
3.特别;尤其 4.值得做某事
5.浏览 6.有可能做...
7.偶然发现 8.慢慢地
9.物色到;挑选出 10.更加
Task 2 Complete the mind map below
Task 3 Find sentences with modal verbs and circle them
Task 4 Figure out the usages of the modal verbs and finish the chart in part A
Step 3 Working out the rules
Finish the blanks on page 48
Step 4 Usages of the modal verbs
1. can & could
1) 表能力
She can dance.
She could dance when she was a child. (过去的能力)
2) 表征求意见
Can/Could you stop chasing me
3) 表猜测,can表猜测多用于否定和疑问
--Oh my god! Can it be true --It can’t be true.
2. may/might
1) 表示许可,请求,作"可以"解释
May I take photos here
2) 表示猜测,作“可能,也许”解释
They may/might be relatives. (might可能性更小)
3) 表示愿望,祝愿
May you smile all the time.
4) 常用词组积累may/might as well do sth. 不妨做某事
You may/might as well do the experiment again
3. must
1) 表示必须,应该
I must take care of my hairstyle.
2) mustn’t表示禁止,不允许
You mustn’t bully your brother.
3) 表示“一定是”,用于肯定猜测,
must do/ be doing肯定做某事/正在做某事
must have done肯定做过某事(完成)
He must have seen the answer.
4. will & would
1) 表示习惯性动作(habit),will 表示现在的习惯,would 表示过去的习惯。如:
Mary will listen to music for hours in her room.
I would take a walk after supper when I was young.
2) 表示意愿(willingness)。如:
The baby won’t go to sleep.
3) 表示请求(request),would 比 will 更委婉些
Would you give me some advice
5. should
1). 表责任或义务,应该,应当
You should complete your test in time.
2). 表较大可能实现的猜测,推断,意为“可能,应该”
The street should be crowed at weekends.
3). 表万一
Should I be free tomorrow, I will come
4). 表意外,“竟然,居然”
A gentleman like him should be rude to a lady.
6. ought to
表义务,意为“应该”(因责任、义务等该做),语气比should稍重。
You are his father. You ought to take care of him.
You oughtn’t to smoke so much.
7. shall
1)用于第一、第三人称的疑问句中,表征询意见或请求允许,多与I或we连用。
What shall we do this weekend
When shall my brother be able to leave hospital
2)用于第二、第三人称,表示说话人的命令、警告、允诺或威胁。
He shall be punished. (威胁)
You shall go with me. (命令)
You shall have a new dress for your birthday. (允诺)
3)常用于主语是第三人称的条约、法律法规、规章制度等文件中表“义务”或“规定”。
Every student shall wear school uniform at school.
8. need & dare
1)need 和dare可以作实义动词或情态动词。作情态动词时,后跟动词原形,表示“需要,有必要”,无人称和数的变化,多用于否定句、疑问句或条件句中。
I dare not walk through the woods at night.
You needn’t go there now.
Need I hand in the paper now
2)作实义动词时,同其他实义动词一样,可用于各种句式,有时态、人称和数的变化,构成否定句和疑问句时要借助于助动词。在否定句和疑问句中不定式符号to也可以省略。
You don’t need to be so worried. You need to be more careful.
They don’t dare (to) make a sound while their parents are sleeping.
Step 5 modal verbs + have done
1. must have done 表示对过去行为的推测, 意为 “一定, 想必做过” , 语气十分肯定
It must have rained last night, as the ground is wet.
2. could have done在肯定句中是虚拟语气表示“本来能做但却没做”
couldn’t have done 多用于语气强烈的否定, 意为“过去不可能做过”
Don’t worry. They could have just forgotten to call.
I saw Mr. Li just now. He couldn’t have gone to Beijing.
3. may/might have done 表示对过去行为的推测, 意为“可能做过”,might 所表示可能性较弱
Smith might have gone to see the movie yesterday.
4. should/ought to have done 本该做某事而实际上未做,shouldn’t/oughtn’t to have done 不该做某事反而做了
You should have made full preparations.
You shouldn't have bullied your brother
5. needn’t have done表示对过去的虚拟意为 “本来不必做某事而实际上却做了”
I actually needn’t have bought so much food—only three people came.
6. had better have done 用于事后的建议,含轻微责备的口吻,意为“当时最好做了某事”。
I had better have started earlier.
Step 6 Summary
用法 请求/许可 可能/推测 义务/职责 意图/打算 意愿/愿意 意志/决心 才能/能力
can/could
may/might
shall/should
will/would
must
ought to
Step 7 Applying the rules
Finish part B on page 49
