北师大版(2019)必修第三册Unit 7 Art Lesson 1 Masterpieces 名词性从句课件(共41张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 北师大版(2019)必修第三册Unit 7 Art Lesson 1 Masterpieces 名词性从句课件(共41张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 775.2KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 北师大版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-04-23 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共41张PPT)
名词性从句
English Grammar
名词性从句
名词性从句是由if, whether, that 和各种疑问词充当连接词所引导的从句,其功能同名词一样。
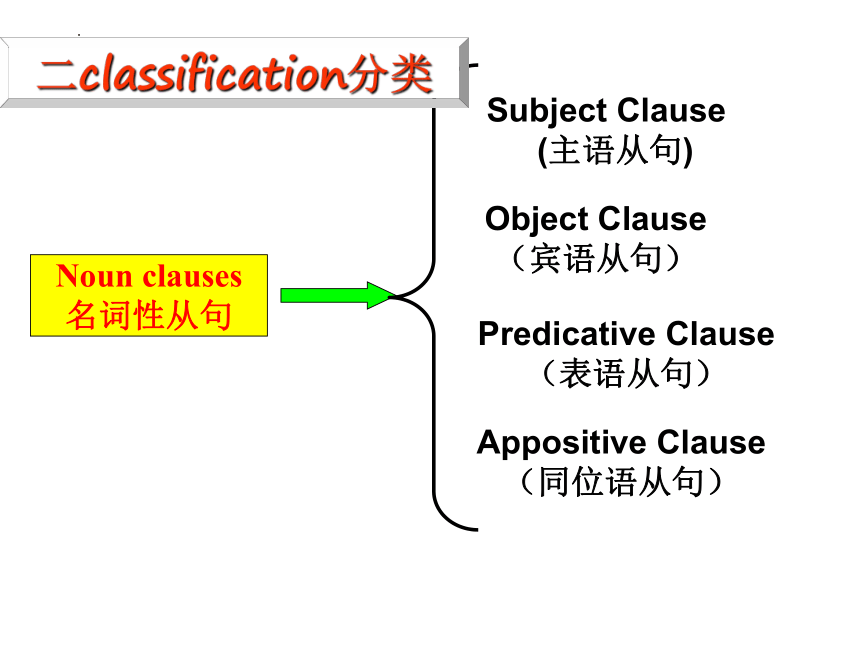
Subject Clause
(主语从句)
Object Clause
(宾语从句)
Predicative Clause
(表语从句)
Appositive Clause
(同位语从句)
Noun clauses
名词性从句
二classification分类
名词性从句分为:
主语从句—一个句子作主语
表语从句---一个句子作表语
宾语从句---一个句子作宾语
同位语从句---一个句子来解释或说明某一名词
引导名词性从句的连接词可分为三类:
连接词:that, whether, if
连接代词:what, whatever, who, whoever, whom, whose, which.
连接副词:when, where, how, why
1.that只起连接主句和从句的作用,在从句中不担任任何成分,本身也没有词义,除宾语从句中可省略外,其他都不能省略。
2.引导主语从句、表语从句和同位语从句,that不可省略。
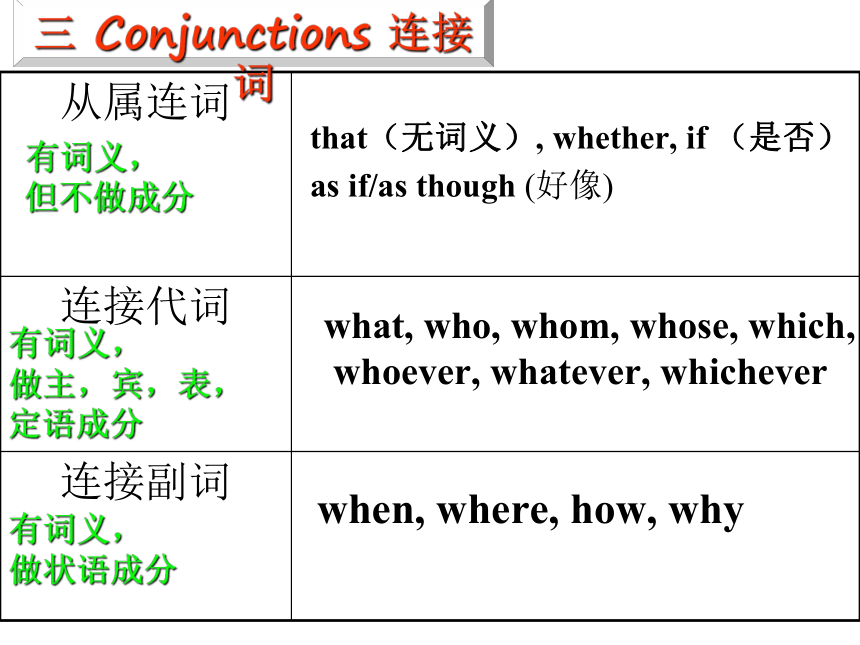
从属连词
连接代词
连接副词
that(无词义), whether, if (是否)
as if/as though (好像)
what, who, whom, whose, which,
whoever, whatever, whichever
when, where, how, why
三 Conjunctions 连接词
有词义,
但不做成分
有词义,
做主,宾,表,
定语成分
有词义,
做状语成分
1.What:作主、宾、表
意思是:….的(东西、地方、职业…)
2.whatever:…一切、凡是…的 无论什么
3.whoever/whomever:谁…谁. 任何 …的人 无论谁
4.whichever:任何一个,无论那一个。
5.when.什么时候,….的时间
6.Where在哪里,…的地方
7.Why为什么,…的原因
名词性从句注意事项
1.语序
2.时态
3.语态
4.主谓一致
5.语气
一.主语从句
主语从句是在复合句中充当主语的从句,通常放在主句谓语动词之前或由形式主语it代替,而本身放在句子末尾。
1. It 作形式主语和it引导强调句的比较
It 作形式主语代替主语从句,主要是为了平衡句子结构,主语从句的连接词没有变化,去掉句子还原。而it引导的强调句则是对句子某一部分进行强调,无论强调的是什么成分,都可用连词that。被强调部分指人是也可用who,去掉不成句子。例如:
It is a pity that you didn’t go to see the film.
It doesn’t interest me whether you succeed or not.
It is in the morning that the murder took place.
It is John that broke the window.
1. 用it 作形式主语的结构
(1) It is + 名词 + 从句
It is a fact that … 事实是…
It is an honor that …非常荣幸
It is common knowledge that …是常识
(2) It is + 形容词 + 从句
It is natural that… 很自然…
It is strange that… 奇怪的是…
(3) It + 不及物动词 + 从句
It seems that… 似乎…
It happened that… 碰巧…
It appears that… 似乎…
(4) It + is+过去分词 + 从句
It is reported that… 据报道…
It has been proved that… 已证实…
It is said that… 据说…
1.___________________________ isn’t exactly known. (come) (地震是怎样发生的还不被人知道)
2.______________________ has been done. (ask)
(凡是她要求我们做的都已经做了)
3.____________________ won’t see it destroyed.(love)(任何爱这座城市的人都不愿意看到它被毁)
4.It happened____________________________(碰巧这个岗位空着).(vacant)
5._______________________ was that more than 90% of the students had been admitted to key universities. (proud)
(使学校骄傲的是90%的学生被重点大学录取)
6. It worried her a bit _____________________(使她担心的是她头发在变白).(grey)
7. _______________________is none of my business. (like)
(她不喜欢你不关我的事)
How the earthquake comes about
Whatever he asked us to
Whoever loves the city
that the position was vacant
What made the school proud
that her hair was turning grey
That she doesn’t like you
.
I know her.
2. I know what she likes .
主语
谓语
宾语
(简单句)
主语
谓语
宾 语 从 句
连词
从句主语
从句谓语
主 句
(复合句)
在复合句中,用来充当宾语的句子就叫宾语从句
宾语 是 动作 的承受者。
由名词,代词或相当于名词的词语或 从句 充当。
一. 宾语从句 句子成分分析
二.宾语从句
宾语从句就是在复合句中作宾语的名词性从句,通常放在主句谓语动词 (及物动词) 或介词之后。
1. 作动词的宾语
(1) 由that引导的宾语从句(that 通常可以省略), 例如:
I heard that he joined the army.
(2) 由what, whether (if) 引导的宾语从句,例如:
She did not know what had happened.
I wonder whether you can change this note for me.
(3) 动词+间接宾语+宾语从句。例如:
She told me that she would accept my invitation.
2. 作介词的宾语,例如:
Our success depends upon how well we can cooperate with one another.
3. 作形容词的宾语,例如:
I am afraid (that) I’ve made a mistake.
注意:that 引导的从句常跟在下列形容词后作宾语:
anxious, aware, certain, confident, convinced, determined, glad, proud, surprised, worried, sorry, thankful, ashamed, disappointed, annoyed, pleased, hurt, satisfied, content 等。也可以将此类词后的that 从句的看作原因状语从句。
4. it 可以作为形式宾语
it 不仅可以作为形式主语,还可以作为形式宾语而真正的宾语that 从句则放在句尾,特别是在带复合宾语的句子中。 例如:
Cellphones make it possible that people communicate to anyone in faraway places.
5. 否定的转移
若主句谓语动词为think, consider, suppose, believe, expect, fancy, guess, imagine等,其后的宾语从句若含有否定意义,一般要把否定词转移到主句谓语上,从句谓语用肯定式。例如:
I don’t think this dress fits you well. 我认为这件衣服不适合你穿。
1. He will give the dictionary to _________________(他会把字典给最需要的人).(need)
2. We’ll never remember__________________________ _(我们永远记得我们求助过的任何人)(turn)
3. I’ll read ___________________________(我会读你给我的任何书).(give)
4. Can you tell me _______________________(你能告诉我怎样能到达车站) (get)
5. Can you make sure _________________________(你能确保Alice把戒指放哪儿了) (put)
6. 26.You can‘t imagine ____________________(你不可能想象他们收到圣诞礼物时是多么兴奋) when they received these nice Christmas presents. (excited)
7.It was a matter of_______________________(问题是谁会占这个位置).(take)
whomever we turned to for help.
whichever book you give me.
how I can get to the station
where Alice has put the ring
how excited they were
whoever needs it most
who would take the position
8.We all thought ____________(很可惜)we had missed the lesson.(pity)
9.I heard ____________(据说)that he had great concern for his classmates.(say)
10.I wish I __________________________________(我去看电影)last night.(go)
11.It is said that the Stonehenge dates back to_________________________________(叫做石器时代的时间).(age)
had gone to the cinema
it a pity that
it said
What was called the Stone Ages
.
The fact is ture .
2. The fact is that she cried .
主语
系
表语
(简单句)
主语
系
表语从句
连词
从句主语
主 句
从句谓语
在复合句中,用来充当表语的句子就叫表语从句
二 . 句子成分分析
表语用来说明主语的 身份, 性质,特征 和 状态。
常由名词, 形容词或相当于名词或形容词的词语或 从句充当。
(复合句)
.
放在实意动词后做宾语的句子我们叫做宾语从句。
1. I know what she likes .
宾 语 从 句
实意动词
2. The fact is that she cried .
系
连词
表语 从 句
放在系动词后做表语的句子我们叫做表语从句。
连词
三. 宾语从句比较,表语从句比较
.
相同点:句子结构均是
主句 +连词(引导词)+ 从句
宾语从句 表语从句 比较:
不同点:
实意动词后---------宾语从句
系动词后-----------表语从句
三.表语从句
表语从句在复合句中作表语的名词性从句,放在系动词之后,一般结构是“主语+连系动词+表语从句”。可以接表语从句的连系动词有be, look, remain, seem等。引导表语从句的that常不可省略。另外,常用的还有the reason is that… 和It is because /as if等结构。例如:
1) The question is whether we can make good preparation in such a short time.
2) This is why we can’t get the support of the people.
3) But the fact remains that we are behind the other classes.
4) The reason he is late for school is that he missed the early bus.
一、连词(引导词)
1. 当表语从句是 陈述句 时(包括肯定句和否定
句),连词由that引导,因为that在从句中不作
任何成分,也没有任何具体意思,但是却不可省略
① The fact is that Jack is clever.
↑
(Jack is clever.)
② The problem is that Alex doesn’t eat carrots.
↑
(Alex doesn’t eat carrots.)
2.当表语从句是一般疑问句时,由连词whether
引导,它们在从句中不做任何成分,但因为whether翻译成:“是否”,具有一定的意义,也不能省略
注意 if不引导 表语从句
1) Is Linda on diet
My question is whether Linda is on diet
My question is if Linda is on diet.
My question is whether is Linda on diet.
3. 当表语从句是特殊疑问句时,由连接代词或者连接副词引导。
因为连接代词 或连接副词在从句中担任一定的句子成分,具 有一定的意义, 也不能省略.
★连接副词(when, where, how, why)whenever, however, however, 在从句中做 状语.
★连接代词(what, who, whom, which, whose), whatever, whoever, whichever.
在从句中常做 主语.宾语.表语.定语
.
例1. Why did the two brothers make a bet
That is why the two brothers made a bet. (原因状语)
That is why did the two brothers made a bet.
.
4.其他从属连词 because, as if/ though
(1)because引导表语从句通常只用于
固定句型“This/That/It is because…”结构中。
Zhilong Wang : Why did you bite me
Juwen Cui : It/ This/ That is because you lied to me yesterday.
(2)as if/though常置于感官系动词look, sound, feel;
be, become 等后面,
常用句型:It looks as if ………. ; It seems as if……..
e.g. It looks as if it is going to rain. 看起来要下雨
It seemed as if the world was at an end.
看起来似乎到了世界末日
.
1. 在引导表语从句时,不能用if。
2. 当主句的主语是表示 建议、命令、要求 等的名词
时,那么表语从句应该用虚拟语气,即谓语动词
用“should + 动词原形”,should可省略。常见的词有:advice, suggestion, order, proposal, plan例如:
例: His suggestion is that we (should) climb all the way to the top of the hill. 他的建议是我们一路爬到山顶。
表语从句中要注意的几个问题
.
3. 当the reason 做主语时,常用that 引导表语从句,构成固定句型:
The reason (why ………..) is that ………….
表语从句中要注意的几个问题
B
例: The reason (why he was so late )is that it was raining hard then.
题:
He failed in his exam. The reason is ________he was too careless.
A. because B. that C. for D. because of
二、时态
1. 如果主句是现在的时态 (包括一般现在时 ,
现在进行时,现在完成时),从句的时态可根
据实际情况而定,(包括一般现在时,一般过
去时,一般将来时,现在完成时等)
一句话:主将现从乱
2.如果主句是过去的时态(包括一般过去时,过去进行时),那么从句的时态一定要用相对应的过去的某种时态(包括一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时, 过去完成时)
一句话: 主过从过
3.当从句是客观真理,定义,公理,定理
时用一般现在时。
What the teacher said yesterday was that the earth travels around the sun .
.
1.The question is ________ we will have our sports meet next week.
A. that B. if C. when D. whether
D
3.当从句是客观真理,定义,公理,定理
时用一般现在时。
What the teacher said yesterday was that the earth travels around the sun .
.
2. The reason why he failed is ________he was too careless.
A. because B. that C. for D. because of
B
.
3.The problem is _________to take the place of John.
A. who can we get B. what we can get
C. who we can get D. that we can get
C
.
5. I’m afraid he’s more of a talker than
a doer, which is _____ he never
finishes anything.
A. that B. when
C. where D. why
D
1..Go and get your coat. It remains ________________(去拿你的大衣,它仍然在你原来放的地方).(leave)
2.I drove to Zhuhai for the air show last week.
— Is that ____________________________(那就是你请假几天的原因) (take)
3.It depends on_________________________________(这要看天气是否适合我们做).(suitable)
4. The question is______________________________(问题是他是否出席会议).(present)
5.My idea is _____________________________(我的建议是派他去北京)(send)
6.Water is to fish_______________________(水对鱼就像空气对人的意义一样).(man)
7.It looked_________________________________(看起来好像他刚刚从童话故事中走出来).(come)
whether the weather is suitable for us to do it
Where you left it
Why you took a few days off
Whether he will be present at the meeting
that he should be sent to Beijing
What air is to man
as if he had just come out of a fairy story
四.同位语从句
1. 同位语从句的功能
同位语从句对于名词进一步解释,说明名词的具体内容,一般由that引导,例如:
1) The king’s decision that the prisoner would be set free surprised all the people.
2) The order that all the soldiers should stay still is given by the general.
同位语从句就是在复合句中作名词的同位语的名词性从句。
2. 同位语在句子中的位置
同位语从句有时可以不紧跟在它所说明的名词后面,而是被别的词隔开。例如:
He got the news from Mary that the sports meeting was put off.
3. 同位语从句与定语从句的区别
定语从句中的that既代替先行词,同时以在从句中作某个成分(主语或宾语),
而同位语从句中的that是连词,只起连接主句与从句的作用,不充当句中任何成分。同位语从句That不能省略,不能用其他词替换。If 不能引导同位语从句。
1) The news that he told me is that Tom would go abroad next year.(他告诉我的消息是汤姆明年将出国。)(第一个that引导的从句是定语从句,that在从句中作宾语)
2)The news that Tom would go abroad is told by him.(汤姆将出国的消息是他讲的。)(同位语从句,that在句中不作任何成分)
1. He had no idea________________________________________(他不知道我们能否克服目前的困难).(overcome)
2.Word came_______________________________(消息传来他要来看我们大家)(see)
3. They adopted my proposal_______________________________________(他们采纳了我的建议--要减少学生的课业量).(workload)
that he would come to see us all.
whether we could overcome the present difficulties
that the workload of the students should be reduced
名词性从句
English Grammar
名词性从句
名词性从句是由if, whether, that 和各种疑问词充当连接词所引导的从句,其功能同名词一样。
Subject Clause
(主语从句)
Object Clause
(宾语从句)
Predicative Clause
(表语从句)
Appositive Clause
(同位语从句)
Noun clauses
名词性从句
二classification分类
名词性从句分为:
主语从句—一个句子作主语
表语从句---一个句子作表语
宾语从句---一个句子作宾语
同位语从句---一个句子来解释或说明某一名词
引导名词性从句的连接词可分为三类:
连接词:that, whether, if
连接代词:what, whatever, who, whoever, whom, whose, which.
连接副词:when, where, how, why
1.that只起连接主句和从句的作用,在从句中不担任任何成分,本身也没有词义,除宾语从句中可省略外,其他都不能省略。
2.引导主语从句、表语从句和同位语从句,that不可省略。
从属连词
连接代词
连接副词
that(无词义), whether, if (是否)
as if/as though (好像)
what, who, whom, whose, which,
whoever, whatever, whichever
when, where, how, why
三 Conjunctions 连接词
有词义,
但不做成分
有词义,
做主,宾,表,
定语成分
有词义,
做状语成分
1.What:作主、宾、表
意思是:….的(东西、地方、职业…)
2.whatever:…一切、凡是…的 无论什么
3.whoever/whomever:谁…谁. 任何 …的人 无论谁
4.whichever:任何一个,无论那一个。
5.when.什么时候,….的时间
6.Where在哪里,…的地方
7.Why为什么,…的原因
名词性从句注意事项
1.语序
2.时态
3.语态
4.主谓一致
5.语气
一.主语从句
主语从句是在复合句中充当主语的从句,通常放在主句谓语动词之前或由形式主语it代替,而本身放在句子末尾。
1. It 作形式主语和it引导强调句的比较
It 作形式主语代替主语从句,主要是为了平衡句子结构,主语从句的连接词没有变化,去掉句子还原。而it引导的强调句则是对句子某一部分进行强调,无论强调的是什么成分,都可用连词that。被强调部分指人是也可用who,去掉不成句子。例如:
It is a pity that you didn’t go to see the film.
It doesn’t interest me whether you succeed or not.
It is in the morning that the murder took place.
It is John that broke the window.
1. 用it 作形式主语的结构
(1) It is + 名词 + 从句
It is a fact that … 事实是…
It is an honor that …非常荣幸
It is common knowledge that …是常识
(2) It is + 形容词 + 从句
It is natural that… 很自然…
It is strange that… 奇怪的是…
(3) It + 不及物动词 + 从句
It seems that… 似乎…
It happened that… 碰巧…
It appears that… 似乎…
(4) It + is+过去分词 + 从句
It is reported that… 据报道…
It has been proved that… 已证实…
It is said that… 据说…
1.___________________________ isn’t exactly known. (come) (地震是怎样发生的还不被人知道)
2.______________________ has been done. (ask)
(凡是她要求我们做的都已经做了)
3.____________________ won’t see it destroyed.(love)(任何爱这座城市的人都不愿意看到它被毁)
4.It happened____________________________(碰巧这个岗位空着).(vacant)
5._______________________ was that more than 90% of the students had been admitted to key universities. (proud)
(使学校骄傲的是90%的学生被重点大学录取)
6. It worried her a bit _____________________(使她担心的是她头发在变白).(grey)
7. _______________________is none of my business. (like)
(她不喜欢你不关我的事)
How the earthquake comes about
Whatever he asked us to
Whoever loves the city
that the position was vacant
What made the school proud
that her hair was turning grey
That she doesn’t like you
.
I know her.
2. I know what she likes .
主语
谓语
宾语
(简单句)
主语
谓语
宾 语 从 句
连词
从句主语
从句谓语
主 句
(复合句)
在复合句中,用来充当宾语的句子就叫宾语从句
宾语 是 动作 的承受者。
由名词,代词或相当于名词的词语或 从句 充当。
一. 宾语从句 句子成分分析
二.宾语从句
宾语从句就是在复合句中作宾语的名词性从句,通常放在主句谓语动词 (及物动词) 或介词之后。
1. 作动词的宾语
(1) 由that引导的宾语从句(that 通常可以省略), 例如:
I heard that he joined the army.
(2) 由what, whether (if) 引导的宾语从句,例如:
She did not know what had happened.
I wonder whether you can change this note for me.
(3) 动词+间接宾语+宾语从句。例如:
She told me that she would accept my invitation.
2. 作介词的宾语,例如:
Our success depends upon how well we can cooperate with one another.
3. 作形容词的宾语,例如:
I am afraid (that) I’ve made a mistake.
注意:that 引导的从句常跟在下列形容词后作宾语:
anxious, aware, certain, confident, convinced, determined, glad, proud, surprised, worried, sorry, thankful, ashamed, disappointed, annoyed, pleased, hurt, satisfied, content 等。也可以将此类词后的that 从句的看作原因状语从句。
4. it 可以作为形式宾语
it 不仅可以作为形式主语,还可以作为形式宾语而真正的宾语that 从句则放在句尾,特别是在带复合宾语的句子中。 例如:
Cellphones make it possible that people communicate to anyone in faraway places.
5. 否定的转移
若主句谓语动词为think, consider, suppose, believe, expect, fancy, guess, imagine等,其后的宾语从句若含有否定意义,一般要把否定词转移到主句谓语上,从句谓语用肯定式。例如:
I don’t think this dress fits you well. 我认为这件衣服不适合你穿。
1. He will give the dictionary to _________________(他会把字典给最需要的人).(need)
2. We’ll never remember__________________________ _(我们永远记得我们求助过的任何人)(turn)
3. I’ll read ___________________________(我会读你给我的任何书).(give)
4. Can you tell me _______________________(你能告诉我怎样能到达车站) (get)
5. Can you make sure _________________________(你能确保Alice把戒指放哪儿了) (put)
6. 26.You can‘t imagine ____________________(你不可能想象他们收到圣诞礼物时是多么兴奋) when they received these nice Christmas presents. (excited)
7.It was a matter of_______________________(问题是谁会占这个位置).(take)
whomever we turned to for help.
whichever book you give me.
how I can get to the station
where Alice has put the ring
how excited they were
whoever needs it most
who would take the position
8.We all thought ____________(很可惜)we had missed the lesson.(pity)
9.I heard ____________(据说)that he had great concern for his classmates.(say)
10.I wish I __________________________________(我去看电影)last night.(go)
11.It is said that the Stonehenge dates back to_________________________________(叫做石器时代的时间).(age)
had gone to the cinema
it a pity that
it said
What was called the Stone Ages
.
The fact is ture .
2. The fact is that she cried .
主语
系
表语
(简单句)
主语
系
表语从句
连词
从句主语
主 句
从句谓语
在复合句中,用来充当表语的句子就叫表语从句
二 . 句子成分分析
表语用来说明主语的 身份, 性质,特征 和 状态。
常由名词, 形容词或相当于名词或形容词的词语或 从句充当。
(复合句)
.
放在实意动词后做宾语的句子我们叫做宾语从句。
1. I know what she likes .
宾 语 从 句
实意动词
2. The fact is that she cried .
系
连词
表语 从 句
放在系动词后做表语的句子我们叫做表语从句。
连词
三. 宾语从句比较,表语从句比较
.
相同点:句子结构均是
主句 +连词(引导词)+ 从句
宾语从句 表语从句 比较:
不同点:
实意动词后---------宾语从句
系动词后-----------表语从句
三.表语从句
表语从句在复合句中作表语的名词性从句,放在系动词之后,一般结构是“主语+连系动词+表语从句”。可以接表语从句的连系动词有be, look, remain, seem等。引导表语从句的that常不可省略。另外,常用的还有the reason is that… 和It is because /as if等结构。例如:
1) The question is whether we can make good preparation in such a short time.
2) This is why we can’t get the support of the people.
3) But the fact remains that we are behind the other classes.
4) The reason he is late for school is that he missed the early bus.
一、连词(引导词)
1. 当表语从句是 陈述句 时(包括肯定句和否定
句),连词由that引导,因为that在从句中不作
任何成分,也没有任何具体意思,但是却不可省略
① The fact is that Jack is clever.
↑
(Jack is clever.)
② The problem is that Alex doesn’t eat carrots.
↑
(Alex doesn’t eat carrots.)
2.当表语从句是一般疑问句时,由连词whether
引导,它们在从句中不做任何成分,但因为whether翻译成:“是否”,具有一定的意义,也不能省略
注意 if不引导 表语从句
1) Is Linda on diet
My question is whether Linda is on diet
My question is if Linda is on diet.
My question is whether is Linda on diet.
3. 当表语从句是特殊疑问句时,由连接代词或者连接副词引导。
因为连接代词 或连接副词在从句中担任一定的句子成分,具 有一定的意义, 也不能省略.
★连接副词(when, where, how, why)whenever, however, however, 在从句中做 状语.
★连接代词(what, who, whom, which, whose), whatever, whoever, whichever.
在从句中常做 主语.宾语.表语.定语
.
例1. Why did the two brothers make a bet
That is why the two brothers made a bet. (原因状语)
That is why did the two brothers made a bet.
.
4.其他从属连词 because, as if/ though
(1)because引导表语从句通常只用于
固定句型“This/That/It is because…”结构中。
Zhilong Wang : Why did you bite me
Juwen Cui : It/ This/ That is because you lied to me yesterday.
(2)as if/though常置于感官系动词look, sound, feel;
be, become 等后面,
常用句型:It looks as if ………. ; It seems as if……..
e.g. It looks as if it is going to rain. 看起来要下雨
It seemed as if the world was at an end.
看起来似乎到了世界末日
.
1. 在引导表语从句时,不能用if。
2. 当主句的主语是表示 建议、命令、要求 等的名词
时,那么表语从句应该用虚拟语气,即谓语动词
用“should + 动词原形”,should可省略。常见的词有:advice, suggestion, order, proposal, plan例如:
例: His suggestion is that we (should) climb all the way to the top of the hill. 他的建议是我们一路爬到山顶。
表语从句中要注意的几个问题
.
3. 当the reason 做主语时,常用that 引导表语从句,构成固定句型:
The reason (why ………..) is that ………….
表语从句中要注意的几个问题
B
例: The reason (why he was so late )is that it was raining hard then.
题:
He failed in his exam. The reason is ________he was too careless.
A. because B. that C. for D. because of
二、时态
1. 如果主句是现在的时态 (包括一般现在时 ,
现在进行时,现在完成时),从句的时态可根
据实际情况而定,(包括一般现在时,一般过
去时,一般将来时,现在完成时等)
一句话:主将现从乱
2.如果主句是过去的时态(包括一般过去时,过去进行时),那么从句的时态一定要用相对应的过去的某种时态(包括一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时, 过去完成时)
一句话: 主过从过
3.当从句是客观真理,定义,公理,定理
时用一般现在时。
What the teacher said yesterday was that the earth travels around the sun .
.
1.The question is ________ we will have our sports meet next week.
A. that B. if C. when D. whether
D
3.当从句是客观真理,定义,公理,定理
时用一般现在时。
What the teacher said yesterday was that the earth travels around the sun .
.
2. The reason why he failed is ________he was too careless.
A. because B. that C. for D. because of
B
.
3.The problem is _________to take the place of John.
A. who can we get B. what we can get
C. who we can get D. that we can get
C
.
5. I’m afraid he’s more of a talker than
a doer, which is _____ he never
finishes anything.
A. that B. when
C. where D. why
D
1..Go and get your coat. It remains ________________(去拿你的大衣,它仍然在你原来放的地方).(leave)
2.I drove to Zhuhai for the air show last week.
— Is that ____________________________(那就是你请假几天的原因) (take)
3.It depends on_________________________________(这要看天气是否适合我们做).(suitable)
4. The question is______________________________(问题是他是否出席会议).(present)
5.My idea is _____________________________(我的建议是派他去北京)(send)
6.Water is to fish_______________________(水对鱼就像空气对人的意义一样).(man)
7.It looked_________________________________(看起来好像他刚刚从童话故事中走出来).(come)
whether the weather is suitable for us to do it
Where you left it
Why you took a few days off
Whether he will be present at the meeting
that he should be sent to Beijing
What air is to man
as if he had just come out of a fairy story
四.同位语从句
1. 同位语从句的功能
同位语从句对于名词进一步解释,说明名词的具体内容,一般由that引导,例如:
1) The king’s decision that the prisoner would be set free surprised all the people.
2) The order that all the soldiers should stay still is given by the general.
同位语从句就是在复合句中作名词的同位语的名词性从句。
2. 同位语在句子中的位置
同位语从句有时可以不紧跟在它所说明的名词后面,而是被别的词隔开。例如:
He got the news from Mary that the sports meeting was put off.
3. 同位语从句与定语从句的区别
定语从句中的that既代替先行词,同时以在从句中作某个成分(主语或宾语),
而同位语从句中的that是连词,只起连接主句与从句的作用,不充当句中任何成分。同位语从句That不能省略,不能用其他词替换。If 不能引导同位语从句。
1) The news that he told me is that Tom would go abroad next year.(他告诉我的消息是汤姆明年将出国。)(第一个that引导的从句是定语从句,that在从句中作宾语)
2)The news that Tom would go abroad is told by him.(汤姆将出国的消息是他讲的。)(同位语从句,that在句中不作任何成分)
1. He had no idea________________________________________(他不知道我们能否克服目前的困难).(overcome)
2.Word came_______________________________(消息传来他要来看我们大家)(see)
3. They adopted my proposal_______________________________________(他们采纳了我的建议--要减少学生的课业量).(workload)
that he would come to see us all.
whether we could overcome the present difficulties
that the workload of the students should be reduced
同课章节目录
- Unit 7 Art
- Lesson 1 Masterpieces
- Lesson 2 Beijing Opera
- Lesson 3 A Musical Genius
- Unit 8 Green living
- Lesson 1 Roots and Shoots
- Lesson 2 Greening the Desert
- Lesson 3 "White Bikes" on the Road
- Unit 9 Learning
- Lesson 1 Active Learning
- Lesson 2 Language Learning Tips
- Lesson 3 The Secrets of Your Memory
