2024年初中英语复习专题 英语语法学习纲要
文档属性
| 名称 | 2024年初中英语复习专题 英语语法学习纲要 |
|
|
| 格式 | doc | ||
| 文件大小 | 203.5KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-05-09 15:04:58 | ||
图片预览


文档简介
2024年初中英语复习专题 英语语法学习纲要
英语语法分为两个部分。一个部分是词法,即词的构成和词的使用规律。另一个部分是句法,即句子的组成和句子的使用方法。
英语语法的特点可以用三句话来表示:1, 每个词都有词性;2, 每句话都有动词(实意动词或系动词);3, 每句话都必须符合五个基本句型中的一个。
三句话用一句话来说,就是,标出句中每一个单词的词性,找出句中所有动词,并标出其种类和相应的句子成分。
理解,掌握,运用好这句话,按照一:词性;二:动词种类;三:动词相对应的句子成分;四:从句;五:非谓语动词的五步方法,就能透彻理解英语语法体系。
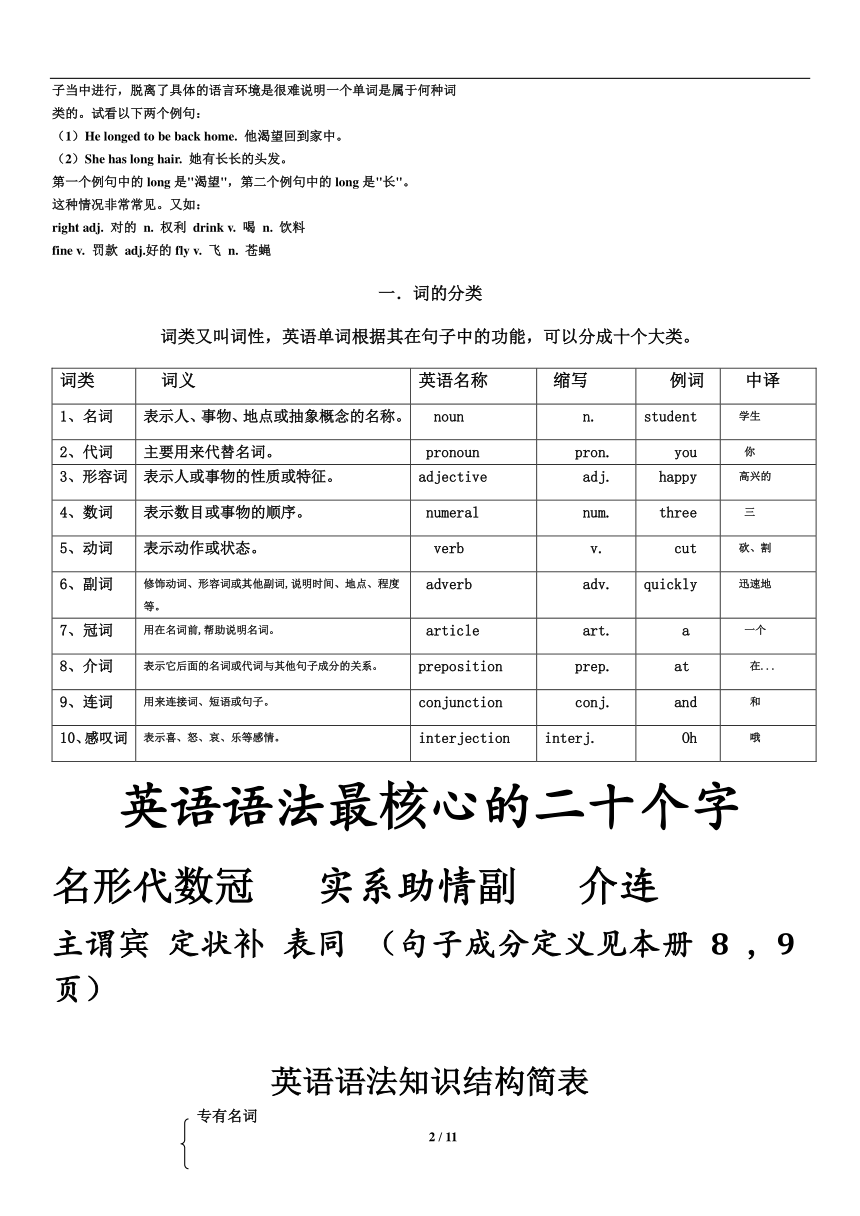
词性的分类
修饰 形容 数 冠 代词 名词 符号为()
(red) (one) (a/the) (my) wood
1.名词
代替 代词it 形容词 the red 数词one 符号为{}
及物动词 drink,eat 副词修饰实意动词。符号为[ ]
行为动词 实意动词
不及物动词 walk
①be 是 I am fat
2.动词 ㈡系动词 ②感官 smell,taste,feel,sound
③变化 get become turn
助动词 will,shall,be, do,have表否定,疑问,时态,语态,强调
(I am reading)
㈣情态动词 can,may,must
adj 修饰名
(形容) the man(at the table)
3.两靠两不靠 介词+名词
adv 修饰动
(副) stand [at the table]
并列连词 and,but,or
连词 从属连词 because,when,if (详细见本册10,11页)
注意:
词的兼类 有不少单词不仅仅属于一个词类,辨别一个单词属于何种词类只能在句
子当中进行,脱离了具体的语言环境是很难说明一个单词是属于何种词
类的。试看以下两个例句:
(1)He longed to be back home. 他渴望回到家中。
(2)She has long hair. 她有长长的头发。
第一个例句中的long是"渴望",第二个例句中的long是"长"。
这种情况非常常见。又如:
right adj. 对的 n. 权利 drink v. 喝 n. 饮料
fine v. 罚款 adj.好的fly v. 飞 n. 苍蝇
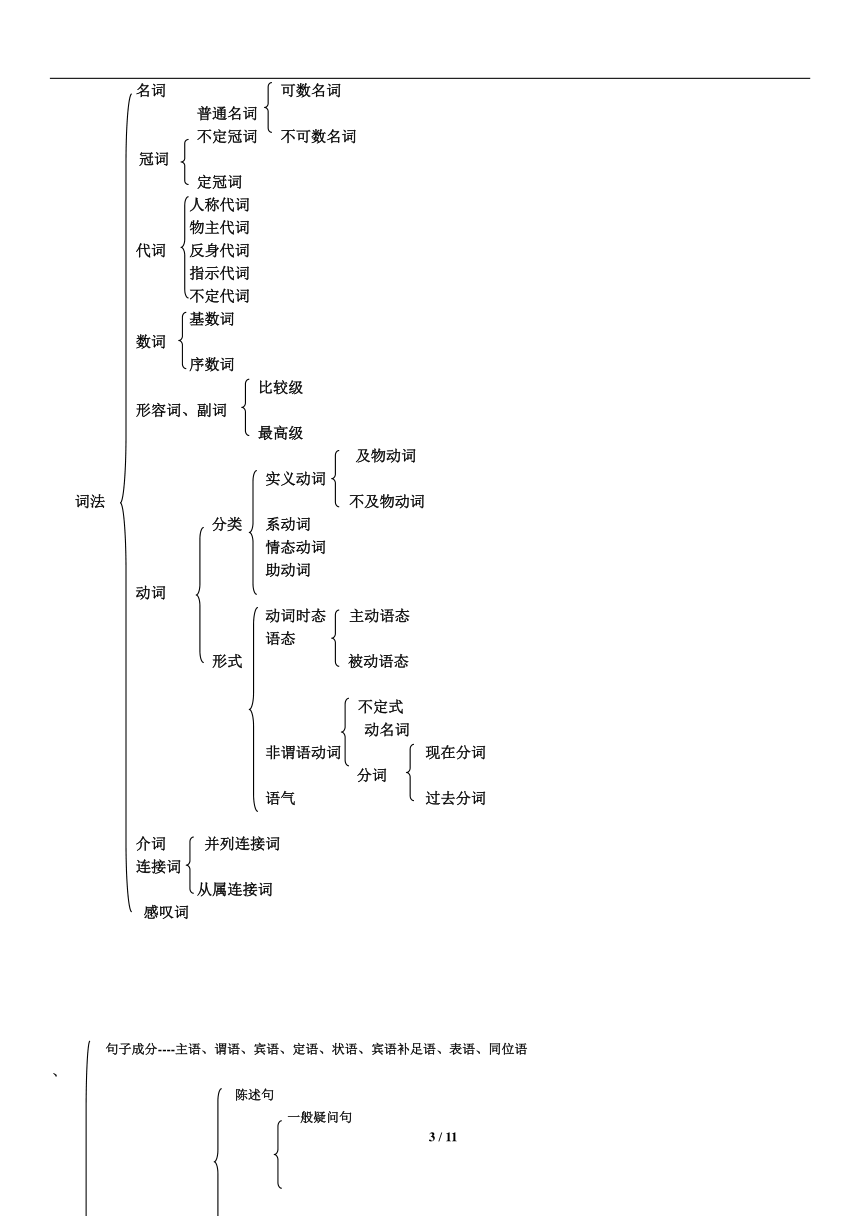
一.词的分类
词类又叫词性,英语单词根据其在句子中的功能,可以分成十个大类。
词类 词义 英语名称 缩写 例词 中译
1、名词 表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。 noun n. student 学生
2、代词 主要用来代替名词。 pronoun pron. you 你
3、形容词 表示人或事物的性质或特征。 adjective adj. happy 高兴的
4、数词 表示数目或事物的顺序。 numeral num. three 三
5、动词 表示动作或状态。 verb v. cut 砍、割
6、副词 修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、程度等。 adverb adv. quickly 迅速地
7、冠词 用在名词前,帮助说明名词。 article art. a 一个
8、介词 表示它后面的名词或代词与其他句子成分的关系。 preposition prep. at 在...
9、连词 用来连接词、短语或句子。 conjunction conj. and 和
10、感叹词 表示喜、怒、哀、乐等感情。 interjection interj. Oh 哦
英语语法最核心的二十个字
名形代数冠 实系助情副 介连
主谓宾 定状补 表同 (句子成分定义见本册8,9页)
英语语法知识结构简表
专有名词
名词 可数名词
普通名词
不定冠词 不可数名词
冠词
定冠词
人称代词
物主代词
代词 反身代词
指示代词
不定代词
基数词
数词
序数词
比较级
形容词、副词
最高级
及物动词
实义动词
词法 不及物动词
分类 系动词
情态动词
助动词
动词
动词时态 主动语态
语态
形式 被动语态
不定式
动名词
非谓语动词 现在分词
分词
语气 过去分词
介词 并列连接词
连接词
从属连接词
感叹词
句子成分----主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、宾语补足语、表语、同位语
、
陈述句
一般疑问句
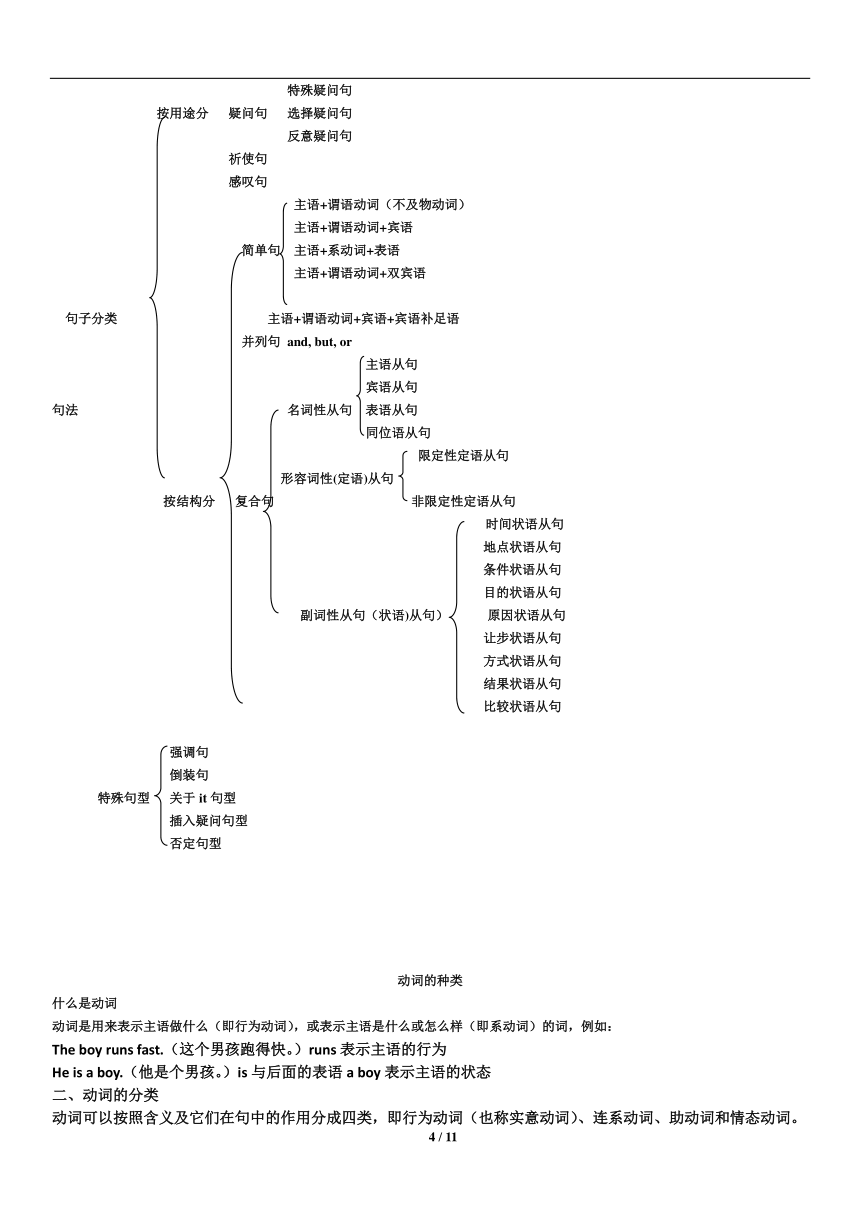
特殊疑问句
按用途分 疑问句 选择疑问句
反意疑问句
祈使句
感叹句
主语+谓语动词(不及物动词)
主语+谓语动词+宾语
简单句 主语+系动词+表语
主语+谓语动词+双宾语
句子分类 主语+谓语动词+宾语+宾语补足语
并列句 and, but, or
主语从句
宾语从句
句法 名词性从句 表语从句
同位语从句
限定性定语从句
形容词性(定语)从句
按结构分 复合句 非限定性定语从句
时间状语从句
地点状语从句
条件状语从句
目的状语从句
副词性从句(状语)从句) 原因状语从句
让步状语从句
方式状语从句
结果状语从句
比较状语从句
强调句
倒装句
特殊句型 关于it句型
插入疑问句型
否定句型
动词的种类
什么是动词
动词是用来表示主语做什么(即行为动词),或表示主语是什么或怎么样(即系动词)的词,例如:
The boy runs fast.(这个男孩跑得快。)runs表示主语的行为
He is a boy.(他是个男孩。)is与后面的表语a boy表示主语的状态
二、动词的分类
动词可以按照含义及它们在句中的作用分成四类,即行为动词(也称实意动词)、连系动词、助动词和情态动词。
(一)行为动词
行为动词(实意动词)是表示行为、动作或状态的词。它的词义完整,可以单独作谓语。例如:
I live in Beijing with my mother.(我和我妈妈住在北京。)live,住
It has a round face.(它有一张圆脸。)has,有
(二)连系动词
连系动词是表示主语“是什么”或“怎么样”的词,它虽有词义,但不完整,所以不能单独作谓语,必须跟表语一起构成合成谓语,例如:
We are in Grade Two this year.(今年我们在两年级。)are,是
are 这个词的词义“是”在句子中常常不译出。
连系动词可具体分为三类:
1、表示“是”的动词be。这个词在不同的主语后面和不同的时态中有不同的形式,is,am,are,was,were,have/has been等要特别予以注意。例如:
He is a teacher.(他是个教师。)
He was a soldier two years ago.(两年前他是个士兵。)
We are Chinese.(我们是中国人。)
2、表示“感觉”的词,如look(看起来),feel(觉得,摸起来),smell(闻起来),sound(听起来),taste(尝起来)等,例如:
She looked tired.(她看一去很疲劳。)
I feel ill.(我觉得不舒服。)
Cotton feels soft.(棉花摸起来很软。)
The story sounds interesting.(这个故事听起来很有趣。)
The flowers smell sweet.(这些花闻起来很香。)
The mixture tasted horrible.(这药水太难喝了。)
3、表示“变”、“变成”的意思的词,如become, get, grow, turn, 都解释为“变”、“变得”,例如:
She became a college student.(她成了一名大学生。)
He feels sick. His face turns white.(他感到不舒服,他的脸色变苍白了。)
The weather gets warmer and the days get longer when spring comes.(春天来了,天气变得暖和些了,白天也变得较长些了。)
He grew old.(他老了。)
[难点解释]
注意区别以下一些动词的用法,它们既可以作为行为动词,又可以作为连系动词。
1、look看;看起来
He is looking at the picture.(他正在看这图片。)行为动词
It looks beautiful.(它看上去很美丽。)连系动词
2、feel摸;感觉
1)I felt someone touch my arm.(我感到有人碰我的手臂。)行为动词
Are you feeling better today than before (你今天比以前感到好些了吗?)连系动词
3、smell嗅;闻起来
My little brother likes to smell the apple before he eats it.(我的小弟弟喜欢在吃苹果前闻一闻。)行为动词
Great! The flowers smell nice.(这些花闻起来多香啊!)连系动词
4、sound弄响,发音;听起来
The letter “h” in hour is not sounded.(在hour这个词中字母h是不发音的。)行为动词
The gun sounded much closer.(枪声听起来更近了。)连系动词
5、taste辨味;尝起来
Please taste the soup.(请尝一口汤。)行为动词
The soup tastes terrible.(这汤尝起来味道太差了。)连系动词
6、get得到,获得;变
There are some bananas on the table. Each of you can get one.桌上有些香蕉,你们每个人可以拿一个。行为动词
7、grow生长,种植;变
Do you grow rice in your country (你们的国家种水稻吗?)行为动词
It’s too late. It’s growing dark.(太迟了,天渐渐变暗了。)连系动词
8、turn转动,翻动,使变得;变
The earth turns around the sun.(地球绕着太阳转。)行为动词
When spring comes, the trees turn green and the flowers come out.(春天来了,树叶变经绿了,花儿开了。)连系动词
上述句子中的动词如grow、get、turn等,既可以作连系动词,又可以作行为动词。如何来辨别它们呢?有一个最简便的方法,即用连系动词be替换句子中的这些动词,句子仍然成立就是连系动词;反之,不能替换的,就是行为动词。例如:
The trees turn/are green when spring comes.(春天来临,树叶变绿。)
The earth turns around the sun.(地球绕着太阳转。)
这第二句句子中的turn是行为动词,意为“转动”。无法以is替换。
(三)助动词
这类词本身无词义,不能单独作谓语,只能与主要动词一起构成谓语,表示不同的时态、语态、表示句子的否定和疑问,例如:
He does not speak English well.(他英语讲得不好。)
句中的does是助动词,既表示一般现在时,又与not一起构成否定形式。
A dog is running after a cat.(一条狗正在追逐一只猫。)
句中的is 是助动词,和run的现在分词一起构成现在进行时。
Did he have any milk and bread for his breakfast (他早餐喝牛奶、吃面包吗?)
句中的did是助动词,既表示一般过去时,又和动词have一起构成疑问。
(四)情态动词
这类词本身虽有意义,但不完整。它们表示说话人的能力、说话人的语气或情态,如“可能”、“应当”等。这类动词有can, may, must, need, dare, could, might等。它们不能单独作谓语,必须与行为动词(原形)一起作谓语,表示完整的意思,例如:
I can dance.(我会跳舞。)can, 能, 会
He can’t walk because he is a baby.(因为他是个婴儿,不会走路。)can’t, 不会
May I come in?(我可以进来吗?)may, 可以
第二节 及物动词与不及物动词
行为动词(即实义动词)按其是否需要宾语,可以分为及物动词和不及物动词。
一、及物动词
后面必须跟宾语,意思才完整,例如:Give me some ink, please.(请给我一些墨水。)
If you have any questions, you can raise your hands.(如果你们有问题,你们可以举手。)
二、不及物动词
后面不能跟宾语,意思已完整。不及物动词有时可以加上副词或介词,构成短语动词,相当于一个及物动词。例如:He works hard.(他工作努力。)
Jack runs faster than Mike.(杰克跑步比迈克要快些。)
Please look at the blackboard and listen to me.(请看黑板,听我说。)
He got an “A” this time because he went over his lessons carefully.(这次他得了个“A”,因为他仔细地复习了功课。)
[难点解释]
1、许多动词可用作及物动词,也可用作不及物动词,他阅读中必须仔细体会和区别,例如:
Who is going to speak at the meeting (谁打算在会上发言?)speak, 不及物动词
Few people outside China speak Chinese.(在中国外很少人讲汉语。)speak,及物动词
2、要特别注意有些动词英汉之间的差异。某些词在英语中是不及物的,而在汉语中却是及物的。有时则相反。例如:He is waiting for you.(他在等你。)英语wait为不及物动词,汉语“等”为及物动词。
Serve the people.(为人民服务。)英语serve为及物动词,汉语“服务”为不及物动词。
简单句的五种基本句型
主语+谓语动词 S+V 此句型的特点是:谓语动词是不及物动词,本身能表达完整的意思,后面不需跟宾语,但有时可跟副词、介词短语等作状语。如: He laughed. John has read widely. He lives in London.
2. 主语+谓语动词+宾语 S+V+O 此句型的特点是:谓语动词是及物动词,不能表达完整的意思,必须跟有一个宾语。如: Our team beat all the others.
3. 主语+系动词+表语 S+V+P 此句型的特点是:谓语动词是连系动词,不能表达完整的意思,必须加上一个表明主语特征、身份、状态的表语。常见的系动词 有:be(是),become(成为),get(变得),turn(变得),grow(变得),look(看起来),feel(感到),smell(闻起 来),taste(尝起来),sound(听起来),seem(似乎),keep(保持),stay(保持)等。如: The rose smells sweet.
4.主语+谓语动词+间接宾语+直接宾语 S+V+INO+DO 此句型的特点是:谓语动词跟有两个宾语,这两个宾语都是动作的对象或承受者,其中指人的是间接宾语,指物的是直接宾语。当间接宾语放在直接宾语之后时,通常需要加介词for或to。可跟双宾语answer,bring,buy,find,get,give,lend,make,pass,pay,send,show,sing,take,teach,tell,write等。如: Mr. Li told us an interesting story. Would you please give this dictionary to Li Hua
My father makes me an apple pie. Hobo built Eddie a tent.
5. 主语+谓语动词+宾语+宾语补足语 S+V+O+OC此句型的特点是:谓语动词虽然跟有一个宾语,但意思还不完整,必须加上另外一个成分(宾语补足语)对宾语进行补充说明。可以用作宾语补足语的有:名词、形容词、不定式、动名词、分词、介词短语等。如:
He thinks himself somebody but we think him nobody. We must keep our school clean. They made him their monitor.
【注】S=Subject(主语); V=Verb(谓语动词); P=Predicative(表语); O=Object(宾语); INO=Indirect Object(间接宾语); DO=Direct Object(直接宾语); OC=Object Complement(宾语补足语)
词性与句子成分关系图:
句子成分 词类或短语 主语* 谓语 宾语* 表语* 定语* 状语* 宾语 补足语 同位语
名词 √√√ × √√√ √√ √ × √ √√√
代词 √√√ × √√√ √√ √√ × × √
形容词 × × × √√√ √√√ × √√ ×
数词 √ × √ √ √√√ × √ √
动词 时态语态形式 × √√√ × × × × × ×
动词不定式 √√ × √√ √ √ √√ √√√ √
动名词 √√ × √√√ √ √ × × √
动词现在分词 × × × √ √ √√ √√√ ×
动词过去分词 × × × √ √ √√ √√ ×
副词 × × × √ √ √√√ √ ×
介词短语 × × × √√ √ √√ √ ×
1, 主语(subject): 句子说明的人或事物。
The sun rises in the east. (名词) He likes dancing. (代词)
Twenty years is a short time in history. (数词) Seeing is believing. (动名词)
To see is to believe. (不定式) What he needs is a book. (主语从句)
It is very clear that the elephant is round and tall like a tree.
(It形式主语,主语从句是真正主语)
2, 谓语动词(predicate): 说明主语的动作。
We study English. He is sleeping.
3, 宾语:1)动作的承受者-----动宾
I like China. (名词) He hates you. (代词)
How many do you need We need two. (数词)
We should help the old and the poor. (形容词) I enjoy working with you. (动名词)
I hope to see you again. (不定式) Did you write down what he said (宾语从句)
2) 介词后的名词、代词和动名词-----介宾
Are you afraid of the snake Under the snow, there are many rocks.
3) 双宾语-----间宾(指人)和直宾(指物)
He gave me(间宾) a book (直宾)yesterday.
Give the poor man(间宾) some money(直宾).
4, 定语:修饰或限制名词或代词的词、词组或句子。
Miss Yang is a chemistry teacher.(名词) He is our friend. (代词)
We belong to the third world. (数词) He was advised to teach the lazy boy a lesson.(形容词)
The man over there is my old friend.(副词)
The woman with a baby in her arms is my sister. (介词)
The boys playing football are in Class 2. (现在分词)
The trees planted last year are growing well now. (过去分词)
I have an idea to do it well. (不定式)
You should do everything that I do. (定语从句)
5, 状语:用来修饰v., adj., adv., or 句子。 表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、程度、条件、方式、让步和伴随。
(以下例句按上述顺序排列)
I will go there tomorrow. The meeting will be held in the meeting room.
The meat went bad because of the hot weather. He studies hard to learn English well.
He didn’t study hard so that he failed in the exam. I like some of you very much.
If you study hard, you will pass the exam. He goes to school by bike.
Though he is young, he can do it well. The teacher came in, with a book in his hand.
6, 宾补:对宾语的补充,全称为宾语补足语。宾语与宾补的关系=主语与表语的关系
We elected him monitor. He is(名词)monitor.
We all think it a pity that she didn’t come here.(名) It is a pity that she didn’t come here.
We will make them happy.(形容词) We found nobody in. ( 副词 )
Please make yourself at home. You are 介词短语 Don’t let him do that. (省to不定式)逻辑上主谓关系
His father advised him to teach the lazy boy a lesson. (带to不定式)
Don’t keep the lights burning. (现在分词) I’ll have my bike repaired. (过去分词)逻辑上的动宾关系
He was elected monitor.逻辑上主谓关系 She was found singing in the next room.
宾 谓 宾补 宾 谓 宾补
He was advised to teach the lazy boy a lesson.
宾 谓 宾补
7, 表语(predicative): 系动词之后的成分,表示主语的性质、状态和特征。
He is a teacher. (名词) Seventy-four! You don’t look it. (代词)
Five and five is ten. (数词) He is asleep. (形容词)
His father is in. (副词) The picture is on the wall. ( 介词短语)
My watch is gone / missing / lost. (形容词化的分词)
To wear a flower is to say I’m poor, I can’t buy a ring. (不定式)
The question is whether they will come. (表语从句)
(常见的连系动词有: be, sound(听起来), look(看起来), feel(摸起来,smell(闻起来),
taste(尝、吃起来), remain(保持,仍是), feel(感觉) ...等等)
It sounds a good idea. The sound sounds strange.
Her voice sounds sweet. Tom looks thin.
The food smells delicious. The food tastes good.
The door remains open. Now I feel tired.
8, 同位语(1)定义:某一名词或代词后的等同解释部分。
(2)同位语的表示:同位语可由名词、名词词组、从句等充当。
We love our country, China. (名词)I live in Shijiazhuang, a city not far from Beijing. (名词词组)
注:作同位语的名词或名词词组与被解释部分指同一人或同一物。
I happened to hear the news that we would have a three-day off. (从句)
注:作同位语的从句内容即为被解释部分所要表达的内容。
1、实义→行为
主谓宾 2、行为发出者→主语 1、 主谓 不及物
3、行为的对象→宾语 2、 主谓宾
3、 主谓宾 宾补
4、主谓间宾直宾→间人直物
1、名
2、代
1、 系动词无实义 1、 名词 ←→ 主〓表 3、数
↓ 4、to do
主系表 2、连系主语和表语 5、动词—ing 动名词
↓ 6、名词性从句
3、表语对主语起说明的作用
1、形
2、介词短语
2、形容词(主表) 3、动词—ing 形容词性 (现在分词)
4、副
(一) 【状语从句】
种类 连接词(即从属连词) 注意点
时间状语 when, whenever, while, as, before, after, until, till, by the time, as soon as, hardly…when, no sooner…than, the moment, the minute, immediately, directly, instantly 主句表示将来意义时,从句须用一般现在时;while引导的从句中动词一般是延续性的;until用在肯定句中主句动词是延续性的,而否定句中主句动词为短暂性的。I was doing my homework [when he came in].
地点状语 where, wherever [Wherever you go], you must be kind to others.
原因状语 because, as, since, now that because语气最强,since较弱,表示大家都明了的原因,as次之。I like English [because it's very useful].[Since everyone is here],let's begin our class.
条件状语 if, unless, once, in case, as long as, on condition that 从句中动词时态不可用将来时,常用一般时代替,即所谓主将从现I'll go to the park[ if it is fine tomorrow] .[Unless bad weather stops me],I go for a walk every day.
目的状语 so that, in order that, for fear that so that和in order that后常接may, should, could, would等情态动词She came back to my home [so that she could borrow my bike yesterday].
结果状语 so…that, such…that It's so cold outside that nobody wants to go out.
比较状语 than, as…as, not so/as…as, the more…the more He doesn't run as fast[ as Bill]. John is taller [than his brother].
方式状语 as if, as though, as as if 和as though引导的从句一般用虚拟语气。 He spoke [ as if he knew everything].
让步状语 though, although, even if, even though, as, no matter what, whatever, no matter who, whoever, no matter which, whichever, no matter how, however, no matter when, whenever as在让步状语从句中常用倒装形式;although和though用正常语序,可和yet连用,但不可和but连用[Though they are poor], they are very happy.[Poor as they are] , they are very happy.I won't mind [even if he doesn't come here].
(二)﹛宾语从句﹜
引导词(即从属连词) 引导词的作用 举例
that 本身无意义,只起连接作用,口语中可省略 He said {that the fastest way to travel was by plane}.
If/whether 意为“是否”,不做句子成分,但不能省略 Do you know {if /whether we can find out some information about that city}.
What,which, who, whose,whom等连接代词 在从句中做一定的成分,如主语、宾语、定语等 Please tell me {whom we have to see}.The teacher told us { whose writing was the best in our class}.
When (指时间),where(指地点),why(表原因),how(表方式)等连接副词 在从句中做状语 Do you know {where we can stay on the island} He asked me {when I was going to write a letter to Jim}.
(三)(定语从句)
关系词(即从属连词) 作用 先行词 例句
That,who,whom(只做宾语) 主语 宾语 表语 人 Do you know the girl (who/that is wearing a red coat) I don't know the girl( that /whom you are waiting for).
That,which 主语 宾语 表语 物 时间 地点 原因 She can't find the pen( that /which I lent to her).The school( that /which we visited) is very beautiful.Do you remember the days( that/which we spent together)
whose 定语 人 The boy (whose mother is a teacher) studies very hard.
whose 定语 物 The house (whose window is open) is mine.
when 状语 时间 I still remember the day (when you come here).
where 状语 地点 This is the factory (where my father works).
why 状语 原因 Do you know the reason (why he was late)
1
4 / 14
英语语法分为两个部分。一个部分是词法,即词的构成和词的使用规律。另一个部分是句法,即句子的组成和句子的使用方法。
英语语法的特点可以用三句话来表示:1, 每个词都有词性;2, 每句话都有动词(实意动词或系动词);3, 每句话都必须符合五个基本句型中的一个。
三句话用一句话来说,就是,标出句中每一个单词的词性,找出句中所有动词,并标出其种类和相应的句子成分。
理解,掌握,运用好这句话,按照一:词性;二:动词种类;三:动词相对应的句子成分;四:从句;五:非谓语动词的五步方法,就能透彻理解英语语法体系。
词性的分类
修饰 形容 数 冠 代词 名词 符号为()
(red) (one) (a/the) (my) wood
1.名词
代替 代词it 形容词 the red 数词one 符号为{}
及物动词 drink,eat 副词修饰实意动词。符号为[ ]
行为动词 实意动词
不及物动词 walk
①be 是 I am fat
2.动词 ㈡系动词 ②感官 smell,taste,feel,sound
③变化 get become turn
助动词 will,shall,be, do,have表否定,疑问,时态,语态,强调
(I am reading)
㈣情态动词 can,may,must
adj 修饰名
(形容) the man(at the table)
3.两靠两不靠 介词+名词
adv 修饰动
(副) stand [at the table]
并列连词 and,but,or
连词 从属连词 because,when,if (详细见本册10,11页)
注意:
词的兼类 有不少单词不仅仅属于一个词类,辨别一个单词属于何种词类只能在句
子当中进行,脱离了具体的语言环境是很难说明一个单词是属于何种词
类的。试看以下两个例句:
(1)He longed to be back home. 他渴望回到家中。
(2)She has long hair. 她有长长的头发。
第一个例句中的long是"渴望",第二个例句中的long是"长"。
这种情况非常常见。又如:
right adj. 对的 n. 权利 drink v. 喝 n. 饮料
fine v. 罚款 adj.好的fly v. 飞 n. 苍蝇
一.词的分类
词类又叫词性,英语单词根据其在句子中的功能,可以分成十个大类。
词类 词义 英语名称 缩写 例词 中译
1、名词 表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。 noun n. student 学生
2、代词 主要用来代替名词。 pronoun pron. you 你
3、形容词 表示人或事物的性质或特征。 adjective adj. happy 高兴的
4、数词 表示数目或事物的顺序。 numeral num. three 三
5、动词 表示动作或状态。 verb v. cut 砍、割
6、副词 修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、程度等。 adverb adv. quickly 迅速地
7、冠词 用在名词前,帮助说明名词。 article art. a 一个
8、介词 表示它后面的名词或代词与其他句子成分的关系。 preposition prep. at 在...
9、连词 用来连接词、短语或句子。 conjunction conj. and 和
10、感叹词 表示喜、怒、哀、乐等感情。 interjection interj. Oh 哦
英语语法最核心的二十个字
名形代数冠 实系助情副 介连
主谓宾 定状补 表同 (句子成分定义见本册8,9页)
英语语法知识结构简表
专有名词
名词 可数名词
普通名词
不定冠词 不可数名词
冠词
定冠词
人称代词
物主代词
代词 反身代词
指示代词
不定代词
基数词
数词
序数词
比较级
形容词、副词
最高级
及物动词
实义动词
词法 不及物动词
分类 系动词
情态动词
助动词
动词
动词时态 主动语态
语态
形式 被动语态
不定式
动名词
非谓语动词 现在分词
分词
语气 过去分词
介词 并列连接词
连接词
从属连接词
感叹词
句子成分----主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、宾语补足语、表语、同位语
、
陈述句
一般疑问句
特殊疑问句
按用途分 疑问句 选择疑问句
反意疑问句
祈使句
感叹句
主语+谓语动词(不及物动词)
主语+谓语动词+宾语
简单句 主语+系动词+表语
主语+谓语动词+双宾语
句子分类 主语+谓语动词+宾语+宾语补足语
并列句 and, but, or
主语从句
宾语从句
句法 名词性从句 表语从句
同位语从句
限定性定语从句
形容词性(定语)从句
按结构分 复合句 非限定性定语从句
时间状语从句
地点状语从句
条件状语从句
目的状语从句
副词性从句(状语)从句) 原因状语从句
让步状语从句
方式状语从句
结果状语从句
比较状语从句
强调句
倒装句
特殊句型 关于it句型
插入疑问句型
否定句型
动词的种类
什么是动词
动词是用来表示主语做什么(即行为动词),或表示主语是什么或怎么样(即系动词)的词,例如:
The boy runs fast.(这个男孩跑得快。)runs表示主语的行为
He is a boy.(他是个男孩。)is与后面的表语a boy表示主语的状态
二、动词的分类
动词可以按照含义及它们在句中的作用分成四类,即行为动词(也称实意动词)、连系动词、助动词和情态动词。
(一)行为动词
行为动词(实意动词)是表示行为、动作或状态的词。它的词义完整,可以单独作谓语。例如:
I live in Beijing with my mother.(我和我妈妈住在北京。)live,住
It has a round face.(它有一张圆脸。)has,有
(二)连系动词
连系动词是表示主语“是什么”或“怎么样”的词,它虽有词义,但不完整,所以不能单独作谓语,必须跟表语一起构成合成谓语,例如:
We are in Grade Two this year.(今年我们在两年级。)are,是
are 这个词的词义“是”在句子中常常不译出。
连系动词可具体分为三类:
1、表示“是”的动词be。这个词在不同的主语后面和不同的时态中有不同的形式,is,am,are,was,were,have/has been等要特别予以注意。例如:
He is a teacher.(他是个教师。)
He was a soldier two years ago.(两年前他是个士兵。)
We are Chinese.(我们是中国人。)
2、表示“感觉”的词,如look(看起来),feel(觉得,摸起来),smell(闻起来),sound(听起来),taste(尝起来)等,例如:
She looked tired.(她看一去很疲劳。)
I feel ill.(我觉得不舒服。)
Cotton feels soft.(棉花摸起来很软。)
The story sounds interesting.(这个故事听起来很有趣。)
The flowers smell sweet.(这些花闻起来很香。)
The mixture tasted horrible.(这药水太难喝了。)
3、表示“变”、“变成”的意思的词,如become, get, grow, turn, 都解释为“变”、“变得”,例如:
She became a college student.(她成了一名大学生。)
He feels sick. His face turns white.(他感到不舒服,他的脸色变苍白了。)
The weather gets warmer and the days get longer when spring comes.(春天来了,天气变得暖和些了,白天也变得较长些了。)
He grew old.(他老了。)
[难点解释]
注意区别以下一些动词的用法,它们既可以作为行为动词,又可以作为连系动词。
1、look看;看起来
He is looking at the picture.(他正在看这图片。)行为动词
It looks beautiful.(它看上去很美丽。)连系动词
2、feel摸;感觉
1)I felt someone touch my arm.(我感到有人碰我的手臂。)行为动词
Are you feeling better today than before (你今天比以前感到好些了吗?)连系动词
3、smell嗅;闻起来
My little brother likes to smell the apple before he eats it.(我的小弟弟喜欢在吃苹果前闻一闻。)行为动词
Great! The flowers smell nice.(这些花闻起来多香啊!)连系动词
4、sound弄响,发音;听起来
The letter “h” in hour is not sounded.(在hour这个词中字母h是不发音的。)行为动词
The gun sounded much closer.(枪声听起来更近了。)连系动词
5、taste辨味;尝起来
Please taste the soup.(请尝一口汤。)行为动词
The soup tastes terrible.(这汤尝起来味道太差了。)连系动词
6、get得到,获得;变
There are some bananas on the table. Each of you can get one.桌上有些香蕉,你们每个人可以拿一个。行为动词
7、grow生长,种植;变
Do you grow rice in your country (你们的国家种水稻吗?)行为动词
It’s too late. It’s growing dark.(太迟了,天渐渐变暗了。)连系动词
8、turn转动,翻动,使变得;变
The earth turns around the sun.(地球绕着太阳转。)行为动词
When spring comes, the trees turn green and the flowers come out.(春天来了,树叶变经绿了,花儿开了。)连系动词
上述句子中的动词如grow、get、turn等,既可以作连系动词,又可以作行为动词。如何来辨别它们呢?有一个最简便的方法,即用连系动词be替换句子中的这些动词,句子仍然成立就是连系动词;反之,不能替换的,就是行为动词。例如:
The trees turn/are green when spring comes.(春天来临,树叶变绿。)
The earth turns around the sun.(地球绕着太阳转。)
这第二句句子中的turn是行为动词,意为“转动”。无法以is替换。
(三)助动词
这类词本身无词义,不能单独作谓语,只能与主要动词一起构成谓语,表示不同的时态、语态、表示句子的否定和疑问,例如:
He does not speak English well.(他英语讲得不好。)
句中的does是助动词,既表示一般现在时,又与not一起构成否定形式。
A dog is running after a cat.(一条狗正在追逐一只猫。)
句中的is 是助动词,和run的现在分词一起构成现在进行时。
Did he have any milk and bread for his breakfast (他早餐喝牛奶、吃面包吗?)
句中的did是助动词,既表示一般过去时,又和动词have一起构成疑问。
(四)情态动词
这类词本身虽有意义,但不完整。它们表示说话人的能力、说话人的语气或情态,如“可能”、“应当”等。这类动词有can, may, must, need, dare, could, might等。它们不能单独作谓语,必须与行为动词(原形)一起作谓语,表示完整的意思,例如:
I can dance.(我会跳舞。)can, 能, 会
He can’t walk because he is a baby.(因为他是个婴儿,不会走路。)can’t, 不会
May I come in?(我可以进来吗?)may, 可以
第二节 及物动词与不及物动词
行为动词(即实义动词)按其是否需要宾语,可以分为及物动词和不及物动词。
一、及物动词
后面必须跟宾语,意思才完整,例如:Give me some ink, please.(请给我一些墨水。)
If you have any questions, you can raise your hands.(如果你们有问题,你们可以举手。)
二、不及物动词
后面不能跟宾语,意思已完整。不及物动词有时可以加上副词或介词,构成短语动词,相当于一个及物动词。例如:He works hard.(他工作努力。)
Jack runs faster than Mike.(杰克跑步比迈克要快些。)
Please look at the blackboard and listen to me.(请看黑板,听我说。)
He got an “A” this time because he went over his lessons carefully.(这次他得了个“A”,因为他仔细地复习了功课。)
[难点解释]
1、许多动词可用作及物动词,也可用作不及物动词,他阅读中必须仔细体会和区别,例如:
Who is going to speak at the meeting (谁打算在会上发言?)speak, 不及物动词
Few people outside China speak Chinese.(在中国外很少人讲汉语。)speak,及物动词
2、要特别注意有些动词英汉之间的差异。某些词在英语中是不及物的,而在汉语中却是及物的。有时则相反。例如:He is waiting for you.(他在等你。)英语wait为不及物动词,汉语“等”为及物动词。
Serve the people.(为人民服务。)英语serve为及物动词,汉语“服务”为不及物动词。
简单句的五种基本句型
主语+谓语动词 S+V 此句型的特点是:谓语动词是不及物动词,本身能表达完整的意思,后面不需跟宾语,但有时可跟副词、介词短语等作状语。如: He laughed. John has read widely. He lives in London.
2. 主语+谓语动词+宾语 S+V+O 此句型的特点是:谓语动词是及物动词,不能表达完整的意思,必须跟有一个宾语。如: Our team beat all the others.
3. 主语+系动词+表语 S+V+P 此句型的特点是:谓语动词是连系动词,不能表达完整的意思,必须加上一个表明主语特征、身份、状态的表语。常见的系动词 有:be(是),become(成为),get(变得),turn(变得),grow(变得),look(看起来),feel(感到),smell(闻起 来),taste(尝起来),sound(听起来),seem(似乎),keep(保持),stay(保持)等。如: The rose smells sweet.
4.主语+谓语动词+间接宾语+直接宾语 S+V+INO+DO 此句型的特点是:谓语动词跟有两个宾语,这两个宾语都是动作的对象或承受者,其中指人的是间接宾语,指物的是直接宾语。当间接宾语放在直接宾语之后时,通常需要加介词for或to。可跟双宾语answer,bring,buy,find,get,give,lend,make,pass,pay,send,show,sing,take,teach,tell,write等。如: Mr. Li told us an interesting story. Would you please give this dictionary to Li Hua
My father makes me an apple pie. Hobo built Eddie a tent.
5. 主语+谓语动词+宾语+宾语补足语 S+V+O+OC此句型的特点是:谓语动词虽然跟有一个宾语,但意思还不完整,必须加上另外一个成分(宾语补足语)对宾语进行补充说明。可以用作宾语补足语的有:名词、形容词、不定式、动名词、分词、介词短语等。如:
He thinks himself somebody but we think him nobody. We must keep our school clean. They made him their monitor.
【注】S=Subject(主语); V=Verb(谓语动词); P=Predicative(表语); O=Object(宾语); INO=Indirect Object(间接宾语); DO=Direct Object(直接宾语); OC=Object Complement(宾语补足语)
词性与句子成分关系图:
句子成分 词类或短语 主语* 谓语 宾语* 表语* 定语* 状语* 宾语 补足语 同位语
名词 √√√ × √√√ √√ √ × √ √√√
代词 √√√ × √√√ √√ √√ × × √
形容词 × × × √√√ √√√ × √√ ×
数词 √ × √ √ √√√ × √ √
动词 时态语态形式 × √√√ × × × × × ×
动词不定式 √√ × √√ √ √ √√ √√√ √
动名词 √√ × √√√ √ √ × × √
动词现在分词 × × × √ √ √√ √√√ ×
动词过去分词 × × × √ √ √√ √√ ×
副词 × × × √ √ √√√ √ ×
介词短语 × × × √√ √ √√ √ ×
1, 主语(subject): 句子说明的人或事物。
The sun rises in the east. (名词) He likes dancing. (代词)
Twenty years is a short time in history. (数词) Seeing is believing. (动名词)
To see is to believe. (不定式) What he needs is a book. (主语从句)
It is very clear that the elephant is round and tall like a tree.
(It形式主语,主语从句是真正主语)
2, 谓语动词(predicate): 说明主语的动作。
We study English. He is sleeping.
3, 宾语:1)动作的承受者-----动宾
I like China. (名词) He hates you. (代词)
How many do you need We need two. (数词)
We should help the old and the poor. (形容词) I enjoy working with you. (动名词)
I hope to see you again. (不定式) Did you write down what he said (宾语从句)
2) 介词后的名词、代词和动名词-----介宾
Are you afraid of the snake Under the snow, there are many rocks.
3) 双宾语-----间宾(指人)和直宾(指物)
He gave me(间宾) a book (直宾)yesterday.
Give the poor man(间宾) some money(直宾).
4, 定语:修饰或限制名词或代词的词、词组或句子。
Miss Yang is a chemistry teacher.(名词) He is our friend. (代词)
We belong to the third world. (数词) He was advised to teach the lazy boy a lesson.(形容词)
The man over there is my old friend.(副词)
The woman with a baby in her arms is my sister. (介词)
The boys playing football are in Class 2. (现在分词)
The trees planted last year are growing well now. (过去分词)
I have an idea to do it well. (不定式)
You should do everything that I do. (定语从句)
5, 状语:用来修饰v., adj., adv., or 句子。 表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、程度、条件、方式、让步和伴随。
(以下例句按上述顺序排列)
I will go there tomorrow. The meeting will be held in the meeting room.
The meat went bad because of the hot weather. He studies hard to learn English well.
He didn’t study hard so that he failed in the exam. I like some of you very much.
If you study hard, you will pass the exam. He goes to school by bike.
Though he is young, he can do it well. The teacher came in, with a book in his hand.
6, 宾补:对宾语的补充,全称为宾语补足语。宾语与宾补的关系=主语与表语的关系
We elected him monitor. He is(名词)monitor.
We all think it a pity that she didn’t come here.(名) It is a pity that she didn’t come here.
We will make them happy.(形容词) We found nobody in. ( 副词 )
Please make yourself at home. You are 介词短语 Don’t let him do that. (省to不定式)逻辑上主谓关系
His father advised him to teach the lazy boy a lesson. (带to不定式)
Don’t keep the lights burning. (现在分词) I’ll have my bike repaired. (过去分词)逻辑上的动宾关系
He was elected monitor.逻辑上主谓关系 She was found singing in the next room.
宾 谓 宾补 宾 谓 宾补
He was advised to teach the lazy boy a lesson.
宾 谓 宾补
7, 表语(predicative): 系动词之后的成分,表示主语的性质、状态和特征。
He is a teacher. (名词) Seventy-four! You don’t look it. (代词)
Five and five is ten. (数词) He is asleep. (形容词)
His father is in. (副词) The picture is on the wall. ( 介词短语)
My watch is gone / missing / lost. (形容词化的分词)
To wear a flower is to say I’m poor, I can’t buy a ring. (不定式)
The question is whether they will come. (表语从句)
(常见的连系动词有: be, sound(听起来), look(看起来), feel(摸起来,smell(闻起来),
taste(尝、吃起来), remain(保持,仍是), feel(感觉) ...等等)
It sounds a good idea. The sound sounds strange.
Her voice sounds sweet. Tom looks thin.
The food smells delicious. The food tastes good.
The door remains open. Now I feel tired.
8, 同位语(1)定义:某一名词或代词后的等同解释部分。
(2)同位语的表示:同位语可由名词、名词词组、从句等充当。
We love our country, China. (名词)I live in Shijiazhuang, a city not far from Beijing. (名词词组)
注:作同位语的名词或名词词组与被解释部分指同一人或同一物。
I happened to hear the news that we would have a three-day off. (从句)
注:作同位语的从句内容即为被解释部分所要表达的内容。
1、实义→行为
主谓宾 2、行为发出者→主语 1、 主谓 不及物
3、行为的对象→宾语 2、 主谓宾
3、 主谓宾 宾补
4、主谓间宾直宾→间人直物
1、名
2、代
1、 系动词无实义 1、 名词 ←→ 主〓表 3、数
↓ 4、to do
主系表 2、连系主语和表语 5、动词—ing 动名词
↓ 6、名词性从句
3、表语对主语起说明的作用
1、形
2、介词短语
2、形容词(主表) 3、动词—ing 形容词性 (现在分词)
4、副
(一) 【状语从句】
种类 连接词(即从属连词) 注意点
时间状语 when, whenever, while, as, before, after, until, till, by the time, as soon as, hardly…when, no sooner…than, the moment, the minute, immediately, directly, instantly 主句表示将来意义时,从句须用一般现在时;while引导的从句中动词一般是延续性的;until用在肯定句中主句动词是延续性的,而否定句中主句动词为短暂性的。I was doing my homework [when he came in].
地点状语 where, wherever [Wherever you go], you must be kind to others.
原因状语 because, as, since, now that because语气最强,since较弱,表示大家都明了的原因,as次之。I like English [because it's very useful].[Since everyone is here],let's begin our class.
条件状语 if, unless, once, in case, as long as, on condition that 从句中动词时态不可用将来时,常用一般时代替,即所谓主将从现I'll go to the park[ if it is fine tomorrow] .[Unless bad weather stops me],I go for a walk every day.
目的状语 so that, in order that, for fear that so that和in order that后常接may, should, could, would等情态动词She came back to my home [so that she could borrow my bike yesterday].
结果状语 so…that, such…that It's so cold outside that nobody wants to go out.
比较状语 than, as…as, not so/as…as, the more…the more He doesn't run as fast[ as Bill]. John is taller [than his brother].
方式状语 as if, as though, as as if 和as though引导的从句一般用虚拟语气。 He spoke [ as if he knew everything].
让步状语 though, although, even if, even though, as, no matter what, whatever, no matter who, whoever, no matter which, whichever, no matter how, however, no matter when, whenever as在让步状语从句中常用倒装形式;although和though用正常语序,可和yet连用,但不可和but连用[Though they are poor], they are very happy.[Poor as they are] , they are very happy.I won't mind [even if he doesn't come here].
(二)﹛宾语从句﹜
引导词(即从属连词) 引导词的作用 举例
that 本身无意义,只起连接作用,口语中可省略 He said {that the fastest way to travel was by plane}.
If/whether 意为“是否”,不做句子成分,但不能省略 Do you know {if /whether we can find out some information about that city}.
What,which, who, whose,whom等连接代词 在从句中做一定的成分,如主语、宾语、定语等 Please tell me {whom we have to see}.The teacher told us { whose writing was the best in our class}.
When (指时间),where(指地点),why(表原因),how(表方式)等连接副词 在从句中做状语 Do you know {where we can stay on the island} He asked me {when I was going to write a letter to Jim}.
(三)(定语从句)
关系词(即从属连词) 作用 先行词 例句
That,who,whom(只做宾语) 主语 宾语 表语 人 Do you know the girl (who/that is wearing a red coat) I don't know the girl( that /whom you are waiting for).
That,which 主语 宾语 表语 物 时间 地点 原因 She can't find the pen( that /which I lent to her).The school( that /which we visited) is very beautiful.Do you remember the days( that/which we spent together)
whose 定语 人 The boy (whose mother is a teacher) studies very hard.
whose 定语 物 The house (whose window is open) is mine.
when 状语 时间 I still remember the day (when you come here).
where 状语 地点 This is the factory (where my father works).
why 状语 原因 Do you know the reason (why he was late)
1
4 / 14
同课章节目录
