2024年广东省中考英语二轮复习语法突破课件:动词的时态和语态课件(共46张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2024年广东省中考英语二轮复习语法突破课件:动词的时态和语态课件(共46张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 317.7KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-05-09 21:36:36 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共46张PPT)
动词的时态和语态
考点总览
考点精讲
时态是句子的谓语动词根据其所发生的时间和所处的状态而呈现出的不同形式。语态是动词的一种形式,用于说明主语和谓语动词之间的关系。如果主语是动作的执行者,使用主动语态;如果主语是动作的承受者,使用被动语态。
考点一 六种常用时态
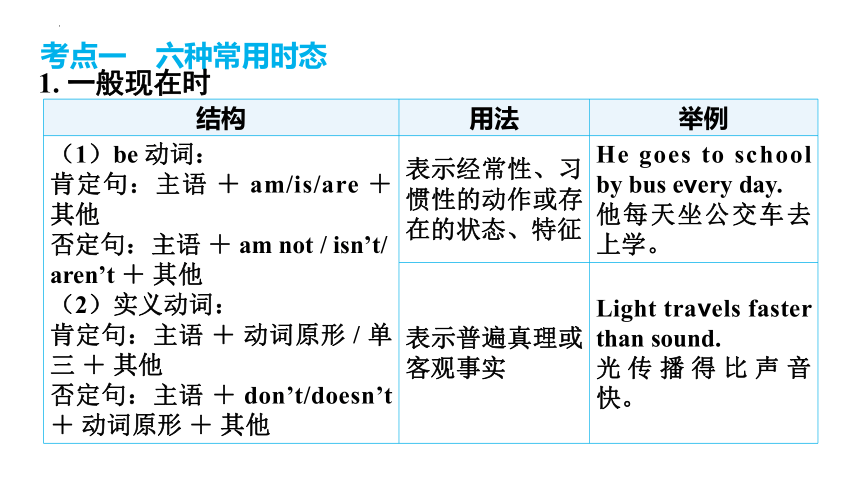
结构 用法 举例
(1)be 动词: 肯定句:主语 + am/is/are + 其他 否定句:主语 + am not / isn’t/ aren’t + 其他 (2)实义动词: 肯定句:主语 + 动词原形 / 单三 + 其他 否定句:主语 + don’t/doesn’t + 动词原形 + 其他 表示经常性、习惯性的动作或存在的状态、特征 He goes to school by bus every day.
他每天坐公交车去上学。
表示普遍真理或客观事实 Light travels faster than sound.
光传播得比声音快。
1. 一般现在时
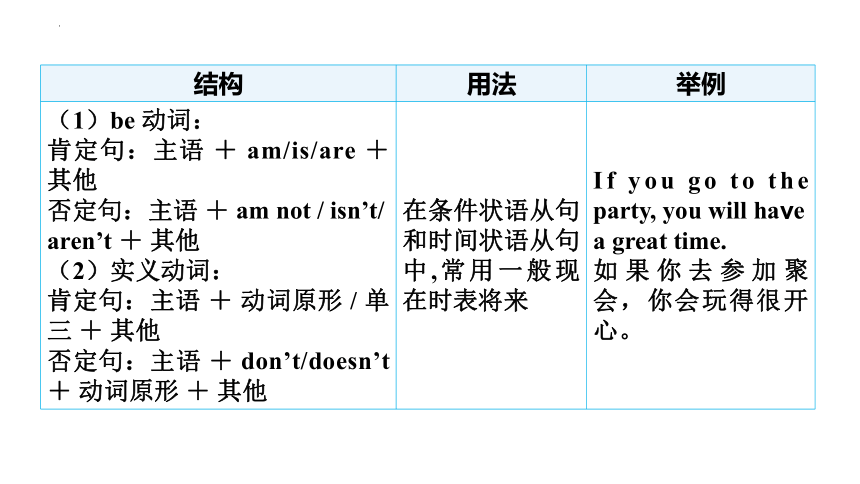
结构 用法 举例
(1)be 动词: 肯定句:主语 + am/is/are + 其他 否定句:主语 + am not / isn’t/ aren’t + 其他 (2)实义动词: 肯定句:主语 + 动词原形 / 单三 + 其他 否定句:主语 + don’t/doesn’t + 动词原形 + 其他 在条件状语从句和时间状语从句中,常用一般现在时表将来 If you go to the party, you will have a great time.
如果你去参加聚会,你会玩得很开心。
续表
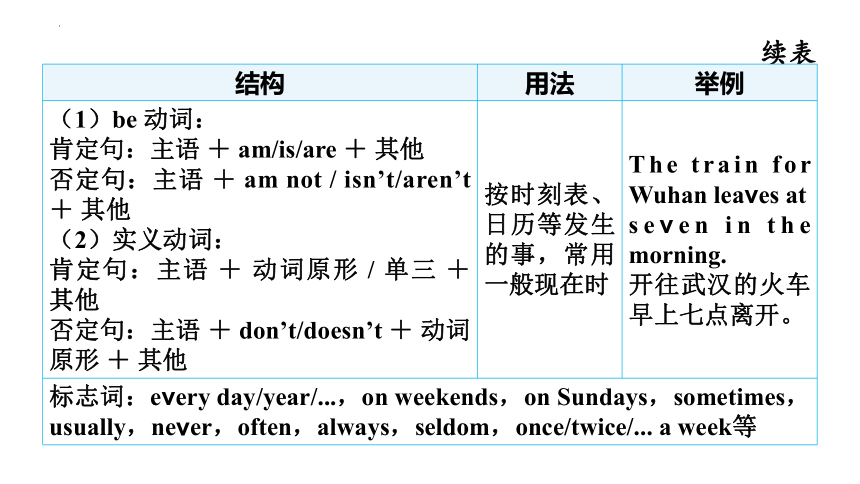
结构 用法 举例
(1)be 动词: 肯定句:主语 + am/is/are + 其他 否定句:主语 + am not / isn’t/aren’t + 其他 (2)实义动词: 肯定句:主语 + 动词原形 / 单三 + 其他 否定句:主语 + don’t/doesn’t + 动词原形 + 其他 按时刻表、日历等发生的事,常用一般现在时 The train for Wuhan leaves at seven in the morning.
开往武汉的火车早上七点离开。
标志词:every day/year/...,on weekends,on Sundays,sometimes,usually,never,often,always,seldom,once/twice/... a week等
2. 一般过去时
结构 用法 举例
(1)be 动词: 肯定句:主语 + was/were + 其他 否定句:主语 + wasn’t/weren’t + 其他 (2)实义动词: 肯定句:主语 + 动词过去式 + 其他 否定句:主语 + didn’t + 动词原形 + 其他 过去经常或反复发生的动作 When I was a child, I often played that game.
当我还是个孩子的时候,我经常玩那个游戏。
续表
结构 用法 举例
(1)be 动词: 肯定句:主语 + was/were + 其他 否定句:主语 + wasn’t/weren’t + 其他 (2)实义动词: 肯定句:主语 + 动词过去式 + 其他 否定句:主语 + didn’t + 动词原形 + 其他 表示过去时间发生的动作或存在的状态、特征 He went to school by bus last term.
他上学期坐公交车上学。
标志词:yesterday,last year/week/...,in 2009,three weeks/... ago,just now,in the past 等
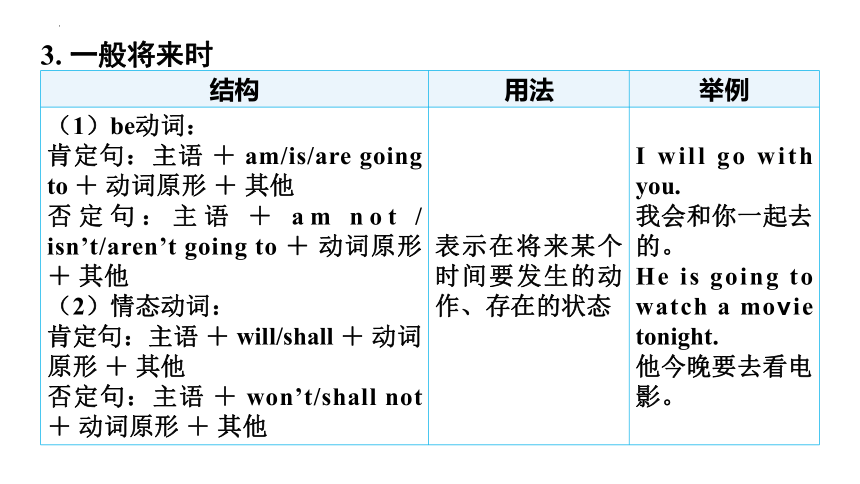
3. 一般将来时
结构 用法 举例
(1)be动词: 肯定句:主语 + am/is/are going to + 动词原形 + 其他 否定句:主语 + am not / isn’t/aren’t going to + 动词原形 + 其他 (2)情态动词: 肯定句:主语 + will/shall + 动词原形 + 其他 否定句:主语 + won’t/shall not + 动词原形 + 其他 表示在将来某个时间要发生的动作、存在的状态 I will go with you.
我会和你一起去的。
He is going to watch a movie tonight.
他今晚要去看电影。
续表
结构 用法 举例
标志词:tomorrow,next week/month/...,soon,in five days 等
小贴士
will 还可以表示对将来的预测。am/is/are going to 还可以表示“决心;打算”。
例如:What will the weather be like tomorrow 明天的天气怎么样?
I am going to study hard this term. 这个学期我要努力学习。
4. 现在进行时
结构 用法 举例
肯定句:主语 + am/is/are + 现在分词 + 其他 否定形式:主语 + am not / isn’t/aren’t + 现在分词 + 其他 表示此刻正在进行的动作 Look! They are playing over there.
看!他们正在那边玩。
表示现阶段正在进行的动作或存在的状态 I am studying hard these days.
我最近在努力地学习。
续表
结构 用法 举例
肯定句:主语 + am/is/are + 现在分词 + 其他 否定形式:主语 + am not / isn’t/aren’t + 现在分词 + 其他 come,go,leave,arrive,start 等表示位置移动的动词,常用现在进行时表将来,表示动作很快要发生 My dad is leaving for Guangzhou.
我爸爸马上要去广州。
现在进行时与always 连用,表示赞扬、批评等感彩 He is always speaking in class.
他上课总是讲话。
标志词:now,listen,look,while,at the moment,these days 等
5. 过去进行时
结构 用法 举例
肯定句:主语+ was/were + 现在分词 + 其他 否定句:主语+ wasn’t/weren’t + 现在分词 + 其他 表示过去某个时刻正在进行的动作或存在的状态 They were playing basketball this time yesterday.
昨天这个时候他们正在打篮球。
What were you doing when the rainstorm came
暴风雨来的时候你在做什么?
表示过去某时间段内正在进行的动作或存在的状态 What was he doing in those days
那些日子他在做什么呢?
续表
结构 用法 举例
肯定句:主语+ was/were + 现在分词 + 其他 否定句:主语+ wasn’t/weren’t + 现在分词 + 其他 过去两个动作同时进行,用while 连接 He was doing his homework while his mom was cooking in the kitchen.
他(那时) 正在做功课,而他妈妈在厨房里做饭。
标志词:at this time yesterday,at that time,all night,at ten last night,when/while 引导的时间状语从句等
小贴士
1. 与一般过去时的使用区别:
I was writing a letter yesterday morning. (强调动作,信是否写完不知道) 昨天早上我在写一封信。
I wrote a letter yesterday morning. (强调结果,信写完了) 昨天早上我写了一封信。
2. while从句中的动词要用延续性动词,表示时间段;when从句中可用延续性动词或非延续性动词,可以表示时间段,也可以表示时间点,还可以表示突然性。
例如:I was walking in the park when it began to rain. 我正在公园里散步,天突然开始下雨。
While/When he was doing his homework, the door opened. 当他正在做作业时,门开了。
6. 现在完成时
结构 用法 举例
肯定句:主语 + have/has + 过去分词 + 其他 否定句:主语 + haven’t/hasn’t + 过去分词 + 其他 表示动作发生在过去并已结束,但对现在有影响(过去对现在) He has turned the light off. 他已把灯关了。(灯现在是关闭的状态。)
表示动作开始于过去,一直延续到现在甚至将来(过去到现在) He has lived here since 1978.
自从1978 年以来,他就住在这里。
标志词:already,yet,ever,never,just,before,so far,in the past/last few years,recently,over the years等
小贴士
● since & for
a. since + 时间点 例如:since 1989
since + 时间段 + ago 例如:since 2 years ago
since + 一般过去时的句子 例如:I have learned English since I was eight. 我从8岁起就开始学习英语。
b. for + 时间段 例如:He has been in Beijing for 3 days. 他在北京已经三天了。
● have/has gone to,have/has been to,have/has been in
a. have/has gone to ... 到……去了 (已去未回)
have/has been to ... 曾经去过…… (已去已回)
have/has been in ... 在某地待……多久 (与for ... / since ... 连用)
例如:Mary has gone to Beijing. 玛丽到北京去了。(在路上或者在北京)
Mary has been to Beijing three times. 玛丽去过北京三次。(现在不在北京)
Mary has been in Beijing for three years. 玛丽已经在北京待了三年了。
b. 后接副词时,需省略介词
例如:He has been abroad for five years. 他出国五年了。
Has she been there before 她以前去过那里吗?
● already & yet
a. already用于肯定句,常用于句中。
例如:I have already read this book. 我已经读过这本书了。
b. yet用于否定句和疑问句,常用于句末。
例如:The woman hasn’t found her watch yet. 那位女士还没有找到她的手表。
● in the past & in the past + 数词 + 时间单位
in the past用于一般过去时,in the past + 数词 + 时间单位(如:in the past three years, in the past few years),用于现在完成时。
例如:They lived a hard life in the past. 他们过去过着艰苦的生活。
Great changes have taken place in China in the past few years. 过去的几年里中国发生了巨大的变化。
● 特定句型:It is + 一段时间 + since ... / It has been + 一段时间 + since ...
例如:It is / has been 5 years since we last met. 自从上一次我们见面到现在已经五年了。
对点训练
一、请从方框内选择适当的词并用其正确形式填空
give watch play go eat
study sing rain fail read
1. (2023河北改编)I will go / am going to go ice skating this Sunday. Do you want to come
2. (2023河北改编)This book must be great. My sister has read it five times so far.
will go / am going to go
has
read
3. (2023甘肃白银改编)That was the best meal I have eaten in a long time.
4. (2023天津改编)While we were singing an English song, some visitors came to our class.
5. (2023山东滨州改编)Sorry, I can’t hear you clearly. I am watching a football match.
have
eaten
were singing
am watching
give watch play go eat
study sing rain fail read
6. (2023湖南怀化改编)Look! Our Chinese teacher is giving a talk in the meeting room.
7. (2023湖北武汉改编)Jessica studied every night before her Chinese test and got good results.
8. (2023四川成都改编)I’m sorry I didn’t answer your phone because I was playing the piano at that time.
is
giving
give watch play go eat
study sing rain fail read
studied
was playing
9. (2023湖北黄石改编)There is going to be a volleyball game next Saturday. If it rains , we’ll have to put it off.
10. (2023四川泸州改编)I will miss Mrs. Chen the most after graduation, because she encouraged me a lot when I failed the English exam.
rains
failed
give watch play go eat
study sing rain fail read
二、单句填空
1. He will help / is going to help his sister with her lessons tomorrow.
2. John has learnt/learned to speak Chinese for 3 years and he can speak it well now.
3. As a famous TV reporter, Jenny reports many big events in this city every day.
will help / is going to help
has learnt/learned
reports
4. When the teacher got into the classroom, Tom was reading a novel written by Lu Xun.
5. The students here have good manners. They shook hands politely when they met the students from other schools yesterday.
shook
was
reading
三、语篇练语法
原创
tell keep play is talk ask do
Jack is helpful. He is always ready to help other students in his class. This week, he will also do so, because March 5th 1. is the official “Lei Feng Day”.
He once got a prize for what he had done. And he has 2. kept doing such kind of things since then.
is
kept
When Jack entered the office, some teachers were 3. talking about him. They were very happy to see him and 4. told him that they had already decided to choose him again to get another prize. With the encouragement, Jack thinks that he will 5. do better because there are many people supporting him. He wants to keep improving himself.
talking
told
do
tell keep play is talk ask do
考点二 被动语态
如果主语是动作的执行者,使用主动语态;如果主语是动作的承受者,则使用被动语态。
例如:He wrote the book. 他写了这本书。(主语He是谓语动词wrote的执行者)
The book was written by him. 这本书是由他写的。(主语The book是谓语动词was written的承受者)
1. 课标要求掌握的三种时态的被动语态
时态 结构 举例
一般现在时 肯定式: am/is/are + done(过去分词) 否定式: am not / isn’t/aren’t + done(过去分词) The bridge is built by us.
这座桥是我们建造的。
续表
时态 结构 举例
一般过去时 肯定式: was/were + done(过去分词) 否定式: wasn’t/weren’t + done(过去分词) The bridge was built by us last year.
这座桥是我们去年建造的。
续表
时态 结构 举例
一般将来时 肯定式: will be + done(过去分词) am/is/are going to be + done(过去分词) 否定式: will not be / won’t be + done(过去分词) am not / isn’t/aren’t going to be + done(过去分词) The bridge will be built by us in two years.
这座桥将在两年后由我们建造。
2. 被动语态的注意事项
注意事项 举例
系动词如smell,look,sound,feel,seem,taste等,没有被动语态 The dress on you looks very beautiful.
你穿的这条裙子很好看。
绝大部分及物动词有被动语态 Many trees are planted on both sides of the road.
这条路的两边种了许多树。
续表
注意事项 举例
不及物动词(短语)如:rise,happen,take place,succeed,remain,lie等,没有被动语态 The sun rises as usual.
太阳照常升起。
不及物动词 + 介词构成的动词短语,可以有被动语态 The children are looked after well in the kindergarten.
孩子们在幼儿园被照顾得很好。
续表
注意事项 举例
write,sell 等词常用主动表被动 The new product sells well. 这款新产品卖得很好。
The pen writes smoothly. 这支笔写字很流畅。
续表
注意事项 举例
主语 + 动词(感官动词 / 使役动词)+ 宾语 +(宾补),变成被动语态时则要变成:主语 + be done + to do 主动语态:
The boss makes the workers work 12 hours a day.
老板让工人们每天工作12 小时。
被动语态:
The workers are made to work(by the boss)12 hours a day. 工人们被(老板)要求每天工作12 小时。
对点训练
一、请从方框内选择适当的词并用其正确形式填空
provide build learn show give
1. (2023天津改编)Some photos of the moon will be shown / are going to be shown in the Space Club next week.
2. (2023河北改编)Breakfast is provided every day for people aged over 60 for free in this village.
will be
shown / are going to be shown
is provided
3. (2023黑龙江改编)Many research labs will be built / are going to be built in the future to develop science and technology in China.
4. (2023江西改编)Hou Yi was given magic medicine for shooting down the 9 suns. However, Pang Meng tried to steal it.
5. (2023四川凉山改编)We’re so proud that China is getting stronger and stronger. And Chinese is learnt/learned by more and more foreigners nowadays.
will be built /
are going to be built
was given
is learnt/learned
provide build learn show give
二、单句填空
1. The book was translated into many other languages last year.
2. To make the environment much better, more trees will be planted / are going to be planted next year.
3. The old houses in the village were painted/colored white by all the villagers last week.
was translated
will be
planted / are going to be planted
were painted/colored
4. German is spoken/used by most people in Germany, and many can speak English, too.
5. Fishing isn’t allowed in order to protect the ecosystem(生态系统) of the rivers in our city.
isn’t allowed
is spoken/used
三、语篇练语法
原创
make buy call throw know eat invent
Do you know xun(埙) It is 1. called one of the oldest musical instruments in China. It has a history of at least 7,000 years. Let me tell you how it was 2. invented .
The idea of xun came from a hunting tool. In ancient times, people often tied a stone to the rope and threw it to hunt animals. Some of the stones were hollow(空心的).
called
invented
When they were 3. thrown , they could make a special sound. To have fun, people invented the musical instrument — xun. At first, people used stones or bones to make xun. Now, it is 4. made of clay(陶土) commonly. In the future, I hope xun will be 5. known by more people. I’d like to share more information about it with you.
thrown
made
known
make buy call throw know eat invent
动词的时态和语态
考点总览
考点精讲
时态是句子的谓语动词根据其所发生的时间和所处的状态而呈现出的不同形式。语态是动词的一种形式,用于说明主语和谓语动词之间的关系。如果主语是动作的执行者,使用主动语态;如果主语是动作的承受者,使用被动语态。
考点一 六种常用时态
结构 用法 举例
(1)be 动词: 肯定句:主语 + am/is/are + 其他 否定句:主语 + am not / isn’t/ aren’t + 其他 (2)实义动词: 肯定句:主语 + 动词原形 / 单三 + 其他 否定句:主语 + don’t/doesn’t + 动词原形 + 其他 表示经常性、习惯性的动作或存在的状态、特征 He goes to school by bus every day.
他每天坐公交车去上学。
表示普遍真理或客观事实 Light travels faster than sound.
光传播得比声音快。
1. 一般现在时
结构 用法 举例
(1)be 动词: 肯定句:主语 + am/is/are + 其他 否定句:主语 + am not / isn’t/ aren’t + 其他 (2)实义动词: 肯定句:主语 + 动词原形 / 单三 + 其他 否定句:主语 + don’t/doesn’t + 动词原形 + 其他 在条件状语从句和时间状语从句中,常用一般现在时表将来 If you go to the party, you will have a great time.
如果你去参加聚会,你会玩得很开心。
续表
结构 用法 举例
(1)be 动词: 肯定句:主语 + am/is/are + 其他 否定句:主语 + am not / isn’t/aren’t + 其他 (2)实义动词: 肯定句:主语 + 动词原形 / 单三 + 其他 否定句:主语 + don’t/doesn’t + 动词原形 + 其他 按时刻表、日历等发生的事,常用一般现在时 The train for Wuhan leaves at seven in the morning.
开往武汉的火车早上七点离开。
标志词:every day/year/...,on weekends,on Sundays,sometimes,usually,never,often,always,seldom,once/twice/... a week等
2. 一般过去时
结构 用法 举例
(1)be 动词: 肯定句:主语 + was/were + 其他 否定句:主语 + wasn’t/weren’t + 其他 (2)实义动词: 肯定句:主语 + 动词过去式 + 其他 否定句:主语 + didn’t + 动词原形 + 其他 过去经常或反复发生的动作 When I was a child, I often played that game.
当我还是个孩子的时候,我经常玩那个游戏。
续表
结构 用法 举例
(1)be 动词: 肯定句:主语 + was/were + 其他 否定句:主语 + wasn’t/weren’t + 其他 (2)实义动词: 肯定句:主语 + 动词过去式 + 其他 否定句:主语 + didn’t + 动词原形 + 其他 表示过去时间发生的动作或存在的状态、特征 He went to school by bus last term.
他上学期坐公交车上学。
标志词:yesterday,last year/week/...,in 2009,three weeks/... ago,just now,in the past 等
3. 一般将来时
结构 用法 举例
(1)be动词: 肯定句:主语 + am/is/are going to + 动词原形 + 其他 否定句:主语 + am not / isn’t/aren’t going to + 动词原形 + 其他 (2)情态动词: 肯定句:主语 + will/shall + 动词原形 + 其他 否定句:主语 + won’t/shall not + 动词原形 + 其他 表示在将来某个时间要发生的动作、存在的状态 I will go with you.
我会和你一起去的。
He is going to watch a movie tonight.
他今晚要去看电影。
续表
结构 用法 举例
标志词:tomorrow,next week/month/...,soon,in five days 等
小贴士
will 还可以表示对将来的预测。am/is/are going to 还可以表示“决心;打算”。
例如:What will the weather be like tomorrow 明天的天气怎么样?
I am going to study hard this term. 这个学期我要努力学习。
4. 现在进行时
结构 用法 举例
肯定句:主语 + am/is/are + 现在分词 + 其他 否定形式:主语 + am not / isn’t/aren’t + 现在分词 + 其他 表示此刻正在进行的动作 Look! They are playing over there.
看!他们正在那边玩。
表示现阶段正在进行的动作或存在的状态 I am studying hard these days.
我最近在努力地学习。
续表
结构 用法 举例
肯定句:主语 + am/is/are + 现在分词 + 其他 否定形式:主语 + am not / isn’t/aren’t + 现在分词 + 其他 come,go,leave,arrive,start 等表示位置移动的动词,常用现在进行时表将来,表示动作很快要发生 My dad is leaving for Guangzhou.
我爸爸马上要去广州。
现在进行时与always 连用,表示赞扬、批评等感彩 He is always speaking in class.
他上课总是讲话。
标志词:now,listen,look,while,at the moment,these days 等
5. 过去进行时
结构 用法 举例
肯定句:主语+ was/were + 现在分词 + 其他 否定句:主语+ wasn’t/weren’t + 现在分词 + 其他 表示过去某个时刻正在进行的动作或存在的状态 They were playing basketball this time yesterday.
昨天这个时候他们正在打篮球。
What were you doing when the rainstorm came
暴风雨来的时候你在做什么?
表示过去某时间段内正在进行的动作或存在的状态 What was he doing in those days
那些日子他在做什么呢?
续表
结构 用法 举例
肯定句:主语+ was/were + 现在分词 + 其他 否定句:主语+ wasn’t/weren’t + 现在分词 + 其他 过去两个动作同时进行,用while 连接 He was doing his homework while his mom was cooking in the kitchen.
他(那时) 正在做功课,而他妈妈在厨房里做饭。
标志词:at this time yesterday,at that time,all night,at ten last night,when/while 引导的时间状语从句等
小贴士
1. 与一般过去时的使用区别:
I was writing a letter yesterday morning. (强调动作,信是否写完不知道) 昨天早上我在写一封信。
I wrote a letter yesterday morning. (强调结果,信写完了) 昨天早上我写了一封信。
2. while从句中的动词要用延续性动词,表示时间段;when从句中可用延续性动词或非延续性动词,可以表示时间段,也可以表示时间点,还可以表示突然性。
例如:I was walking in the park when it began to rain. 我正在公园里散步,天突然开始下雨。
While/When he was doing his homework, the door opened. 当他正在做作业时,门开了。
6. 现在完成时
结构 用法 举例
肯定句:主语 + have/has + 过去分词 + 其他 否定句:主语 + haven’t/hasn’t + 过去分词 + 其他 表示动作发生在过去并已结束,但对现在有影响(过去对现在) He has turned the light off. 他已把灯关了。(灯现在是关闭的状态。)
表示动作开始于过去,一直延续到现在甚至将来(过去到现在) He has lived here since 1978.
自从1978 年以来,他就住在这里。
标志词:already,yet,ever,never,just,before,so far,in the past/last few years,recently,over the years等
小贴士
● since & for
a. since + 时间点 例如:since 1989
since + 时间段 + ago 例如:since 2 years ago
since + 一般过去时的句子 例如:I have learned English since I was eight. 我从8岁起就开始学习英语。
b. for + 时间段 例如:He has been in Beijing for 3 days. 他在北京已经三天了。
● have/has gone to,have/has been to,have/has been in
a. have/has gone to ... 到……去了 (已去未回)
have/has been to ... 曾经去过…… (已去已回)
have/has been in ... 在某地待……多久 (与for ... / since ... 连用)
例如:Mary has gone to Beijing. 玛丽到北京去了。(在路上或者在北京)
Mary has been to Beijing three times. 玛丽去过北京三次。(现在不在北京)
Mary has been in Beijing for three years. 玛丽已经在北京待了三年了。
b. 后接副词时,需省略介词
例如:He has been abroad for five years. 他出国五年了。
Has she been there before 她以前去过那里吗?
● already & yet
a. already用于肯定句,常用于句中。
例如:I have already read this book. 我已经读过这本书了。
b. yet用于否定句和疑问句,常用于句末。
例如:The woman hasn’t found her watch yet. 那位女士还没有找到她的手表。
● in the past & in the past + 数词 + 时间单位
in the past用于一般过去时,in the past + 数词 + 时间单位(如:in the past three years, in the past few years),用于现在完成时。
例如:They lived a hard life in the past. 他们过去过着艰苦的生活。
Great changes have taken place in China in the past few years. 过去的几年里中国发生了巨大的变化。
● 特定句型:It is + 一段时间 + since ... / It has been + 一段时间 + since ...
例如:It is / has been 5 years since we last met. 自从上一次我们见面到现在已经五年了。
对点训练
一、请从方框内选择适当的词并用其正确形式填空
give watch play go eat
study sing rain fail read
1. (2023河北改编)I will go / am going to go ice skating this Sunday. Do you want to come
2. (2023河北改编)This book must be great. My sister has read it five times so far.
will go / am going to go
has
read
3. (2023甘肃白银改编)That was the best meal I have eaten in a long time.
4. (2023天津改编)While we were singing an English song, some visitors came to our class.
5. (2023山东滨州改编)Sorry, I can’t hear you clearly. I am watching a football match.
have
eaten
were singing
am watching
give watch play go eat
study sing rain fail read
6. (2023湖南怀化改编)Look! Our Chinese teacher is giving a talk in the meeting room.
7. (2023湖北武汉改编)Jessica studied every night before her Chinese test and got good results.
8. (2023四川成都改编)I’m sorry I didn’t answer your phone because I was playing the piano at that time.
is
giving
give watch play go eat
study sing rain fail read
studied
was playing
9. (2023湖北黄石改编)There is going to be a volleyball game next Saturday. If it rains , we’ll have to put it off.
10. (2023四川泸州改编)I will miss Mrs. Chen the most after graduation, because she encouraged me a lot when I failed the English exam.
rains
failed
give watch play go eat
study sing rain fail read
二、单句填空
1. He will help / is going to help his sister with her lessons tomorrow.
2. John has learnt/learned to speak Chinese for 3 years and he can speak it well now.
3. As a famous TV reporter, Jenny reports many big events in this city every day.
will help / is going to help
has learnt/learned
reports
4. When the teacher got into the classroom, Tom was reading a novel written by Lu Xun.
5. The students here have good manners. They shook hands politely when they met the students from other schools yesterday.
shook
was
reading
三、语篇练语法
原创
tell keep play is talk ask do
Jack is helpful. He is always ready to help other students in his class. This week, he will also do so, because March 5th 1. is the official “Lei Feng Day”.
He once got a prize for what he had done. And he has 2. kept doing such kind of things since then.
is
kept
When Jack entered the office, some teachers were 3. talking about him. They were very happy to see him and 4. told him that they had already decided to choose him again to get another prize. With the encouragement, Jack thinks that he will 5. do better because there are many people supporting him. He wants to keep improving himself.
talking
told
do
tell keep play is talk ask do
考点二 被动语态
如果主语是动作的执行者,使用主动语态;如果主语是动作的承受者,则使用被动语态。
例如:He wrote the book. 他写了这本书。(主语He是谓语动词wrote的执行者)
The book was written by him. 这本书是由他写的。(主语The book是谓语动词was written的承受者)
1. 课标要求掌握的三种时态的被动语态
时态 结构 举例
一般现在时 肯定式: am/is/are + done(过去分词) 否定式: am not / isn’t/aren’t + done(过去分词) The bridge is built by us.
这座桥是我们建造的。
续表
时态 结构 举例
一般过去时 肯定式: was/were + done(过去分词) 否定式: wasn’t/weren’t + done(过去分词) The bridge was built by us last year.
这座桥是我们去年建造的。
续表
时态 结构 举例
一般将来时 肯定式: will be + done(过去分词) am/is/are going to be + done(过去分词) 否定式: will not be / won’t be + done(过去分词) am not / isn’t/aren’t going to be + done(过去分词) The bridge will be built by us in two years.
这座桥将在两年后由我们建造。
2. 被动语态的注意事项
注意事项 举例
系动词如smell,look,sound,feel,seem,taste等,没有被动语态 The dress on you looks very beautiful.
你穿的这条裙子很好看。
绝大部分及物动词有被动语态 Many trees are planted on both sides of the road.
这条路的两边种了许多树。
续表
注意事项 举例
不及物动词(短语)如:rise,happen,take place,succeed,remain,lie等,没有被动语态 The sun rises as usual.
太阳照常升起。
不及物动词 + 介词构成的动词短语,可以有被动语态 The children are looked after well in the kindergarten.
孩子们在幼儿园被照顾得很好。
续表
注意事项 举例
write,sell 等词常用主动表被动 The new product sells well. 这款新产品卖得很好。
The pen writes smoothly. 这支笔写字很流畅。
续表
注意事项 举例
主语 + 动词(感官动词 / 使役动词)+ 宾语 +(宾补),变成被动语态时则要变成:主语 + be done + to do 主动语态:
The boss makes the workers work 12 hours a day.
老板让工人们每天工作12 小时。
被动语态:
The workers are made to work(by the boss)12 hours a day. 工人们被(老板)要求每天工作12 小时。
对点训练
一、请从方框内选择适当的词并用其正确形式填空
provide build learn show give
1. (2023天津改编)Some photos of the moon will be shown / are going to be shown in the Space Club next week.
2. (2023河北改编)Breakfast is provided every day for people aged over 60 for free in this village.
will be
shown / are going to be shown
is provided
3. (2023黑龙江改编)Many research labs will be built / are going to be built in the future to develop science and technology in China.
4. (2023江西改编)Hou Yi was given magic medicine for shooting down the 9 suns. However, Pang Meng tried to steal it.
5. (2023四川凉山改编)We’re so proud that China is getting stronger and stronger. And Chinese is learnt/learned by more and more foreigners nowadays.
will be built /
are going to be built
was given
is learnt/learned
provide build learn show give
二、单句填空
1. The book was translated into many other languages last year.
2. To make the environment much better, more trees will be planted / are going to be planted next year.
3. The old houses in the village were painted/colored white by all the villagers last week.
was translated
will be
planted / are going to be planted
were painted/colored
4. German is spoken/used by most people in Germany, and many can speak English, too.
5. Fishing isn’t allowed in order to protect the ecosystem(生态系统) of the rivers in our city.
isn’t allowed
is spoken/used
三、语篇练语法
原创
make buy call throw know eat invent
Do you know xun(埙) It is 1. called one of the oldest musical instruments in China. It has a history of at least 7,000 years. Let me tell you how it was 2. invented .
The idea of xun came from a hunting tool. In ancient times, people often tied a stone to the rope and threw it to hunt animals. Some of the stones were hollow(空心的).
called
invented
When they were 3. thrown , they could make a special sound. To have fun, people invented the musical instrument — xun. At first, people used stones or bones to make xun. Now, it is 4. made of clay(陶土) commonly. In the future, I hope xun will be 5. known by more people. I’d like to share more information about it with you.
thrown
made
known
make buy call throw know eat invent
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
