2024届高考英语语法专项复习:状语从句课件(共23张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2024届高考英语语法专项复习:状语从句课件(共23张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 38.6MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-05-14 19:22:36 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
(共23张PPT)
状语从句
状语从句概述与分类
状语从句的定义
状语从句是一种从句类型,它在句子中起修饰或限制主要动词的作用,说明动作发生的时间、地点、原因、条件、目的、结果、比较、方式等。状语从句由引导词引入,与主句之间存在逻辑关系。
状语从句的分类
状语从句可以按照其表达的意义进行分类,主要包括时间状语从句、条件状语从句、原因状语从句、目的状语从句、结果状语从句、让步状语从句、比较状语从句和方式状语从句。每种状语从句都有其特定的引导词和用法。
状语从句在句子中的作用
状语从句在复合句中扮演着重要角色,它丰富了句子的意义,提供了更多关于动作或状态的背景信息。通过状语从句,可以更准确地表达时间顺序、条件可能性、原因结果、目的意图等逻辑关系。
状语从句有九种,连词引导各不同;
时地原因条件状,目比结果方让步;
主句通常前面走,连词引导紧随后;
从句若在主前头,主从之间有个逗。
状语从句的分类
时间状语从句
1
2
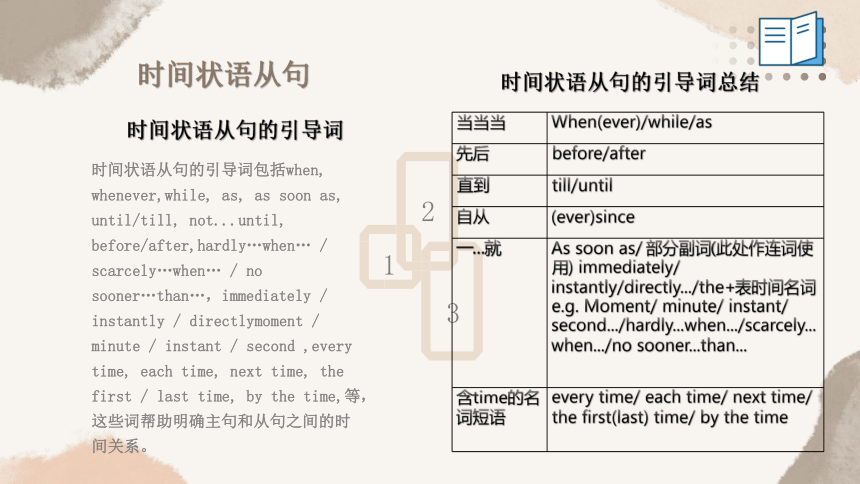
时间状语从句的引导词
时间状语从句的引导词包括when, whenever,while, as, as soon as, until/till, not...until, before/after,hardly…when… / scarcely…when… / no sooner…than…,immediately / instantly / directlymoment / minute / instant / second ,every time, each time, next time, the first / last time, by the time,等,这些词帮助明确主句和从句之间的时间关系。
时间状语从句的引导词总结
3
当当当 When(ever)/while/as
先后 before/after
直到 till/until
自从 (ever)since
一...就 As soon as/ 部分副词(此处作连词使用) immediately/ instantly/directly.../the+表时间名词e.g. Moment/ minute/ instant/ second.../hardly...when.../scarcely...when.../no sooner...than...
含time的名词短语 every time/ each time/ next time/ the first(last) time/ by the time
When I got home, my family were already having dinner.
Mary fell asleep while she was reading the newspaper.
As time goes on, Judy becomes stronger and stronger.
He almost knocked me down before he saw me.
The sun came out soon after the storm stopped.
It won’t be three days before I come back.
It wasn’t three days before I came back.
I didn’t go to bed until / till he came back.
She has been working in this factory since she left school.
I had hardly / scarcely got home when it began to rain.
I had no sooner got home than it began to rain.
Nick was in an ice cream shop the first time he met Judy.
Every time I see him, he looks miserable.
时间状语从句范例展示
条件状语从句-- 表示主句动作发生的前提或条件的状语从句
1
2
3
条件状语从句的引导词
条件状语从句的引导词包括if, unless, as/so long as, in case(如果),once(一旦), on condition that (条件是),provided that,supposing that (假设)等,它们用于表达条件与结果的关系。
真实条件句与非真实条件句
真实条件句用以描述现实生活中可能实现的条件,而非真实条件句则用于假设或幻想不可能实现的情况,通常使用过去时态或虚拟语气。
条件状语从句的特殊用法 即 主将从现
如果主句是一般将来时态、祈使句或者是含有将来的动作和意味时,由if引导的条件状语从句和 when, till / until, as soon as 引导的时间状语从句一般用现在时态来代替将来时。即主将从现。
If plastics are burned, they give off poisonous gases.
Unless you work hard, you will fail.
You can go out, as / so long as you promise to be back before eleven.
In case I forget, please remind me about that.
条件状语从句范例展示
Once you get down to doing your homework, you’ll find it easy.
I can help you out on condition that you promise not to make the same mistake again.
Supposing that they refuse us, who else can we turn to for help
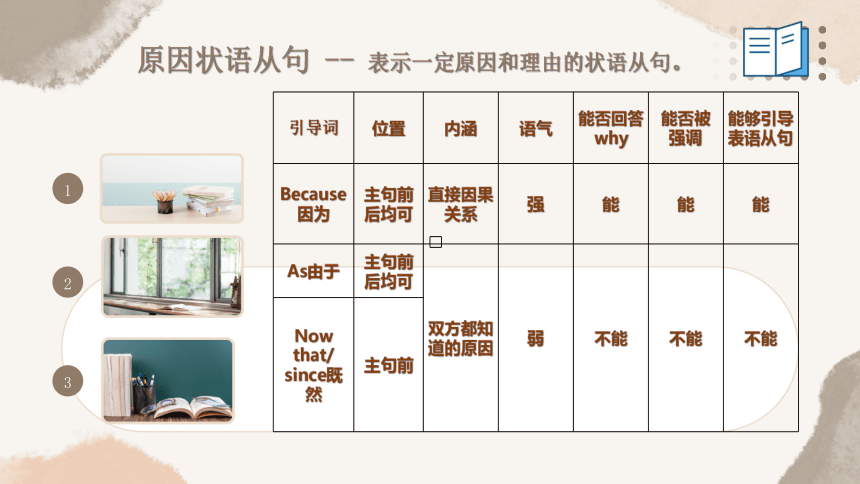
原因状语从句 -- 表示一定原因和理由的状语从句。
1
2
3
引导词 位置 内涵 语气 能否回答why 能否被 强调 能够引导表语从句
Because 因为 主句前后均可 直接因果关系 强 能 能 能
As由于 主句前后均可 双方都知道的原因 弱 不能 不能 不能
Now that/ since既然 主句前
原因状语从句范例展示
1. -- Why didn’t he come -- Because he was ill.2. He didn’t come because he was ill.3. Because he was ill, he didn’t come.4. It was because he was ill that he didn’t come.5. He deserves failure. It is all because he is too lazy.6. You needn’t go with me, as you are busy.7. As I was afraid, I hid myself.8. Since you are here, you must do it.9. Now that all the guests have arrived, let’s have our dinner.
原因状语从句使用的注意事项
because和so不能同用在一个句子里,即用了because不用so.
1
2
because和because of 的运用区别:
because 用于引导原因状语从句;而because of 用于连接词或词组或引
导名词性从句。
eg. 1. It was because Nick reached out his foot that Judy tripped and fell.
2. He was late for work because of getting up late.
目的状语从句 -- 表示行为目的的状语从句
目的状语从句的引导词
通常由so that, in order that, in case(以防、免得), for fear that(担心), lest(以免)等引导;
由lest, for fear that引导的目的状语从句要使用“should+动词原形“的虚拟语气。
We got up early so that we could catch the first train.
He studies hard so that he could work better in the future.
We used the computer in order that we might save time.
1
2
注意事项
3
目的状语从句范例展示
1. In order that she could solve the case, Judy turned to Nick for help unwillingly.
2. Judy turned to Nick for help unwillingly so that she could solve the case.
3. Nick agreed to help Judy reluctantly in case his secret should be given away.
4. Nick agreed to help Judy reluctantly for fear that / lest his secret should be given away.
5. It’s a surprise they haven’t managed to grow square ones they can pack them easily.
A. to B. so that C. such that D. in order to
结果状语从句--表示事态结果的状语从句
S + be/v.+ so + adj./adv +that + Clause
+adj.+a/an+n
S + be/v.+ such + a/an + adj. + n. + Clause
+ adj. +[U]
+ adj. + pl.
1
2
结果状语从句的引导词
结果状语从句的引导词包括so that, so...that, such...that等,用于突出动作或状态的结果。
结果状语从句的常用表达
1. It was very cold, so that the river froze.
2. Flash works so fast that he runs a plate in a few minutes.
3. Flash is so skilled an officer that he can run a plate in a few minutes.
4. Flash is such a skilled officer that he can run a plate in a few minutes.
5. My pencil was on the floor, so that I didn’t see it.
6. He is so poor that he can’t buy a bike for his son.
7. She is such a good teacher that everybody likes her.
结果状语从句范例展示
1. Flash works so fast that he runs a plate in a few minutes.So fast does Flash work that…
2. Flash is so skilled an officer that he can run a plate in a few minutes.So skilled an officer is Flash that…
3. Flash is such a skilled officer that he can run a plate in a few minutes.Such a skilled officer is Flash that…
目的状语从句的倒装情况展示
让步状语从句-表示在某种相反的条件下,主句中的情况依然会出现的状语从句
让步状语从句的引导词
由though,although,as(尽管), even if,even though,疑问词+ever, no matter+疑问词,whether...or...引导, 引导让步状语从句时,no matter+疑问词=疑问词+ever。
让步状语从句引导词的注意事项
although 与though不能在同一个句子中与but连用,但可以与yet连用,即用了but不用though/although。
eg.
1. 误:Although / Though he is old, but he is active.
2. 正:Although / Though he is old, yet he is active.
辨析 although/ though/as
Although/Though he is young, he can write in several foreign languages. = Young as/though he is,...Although/Though we were surrounded by the enemy, we managed to escape. = Surrounded as/though we were by the enemy, …Although/Though he was a child, he had to support the family. = Child as/though he was,...
as引导让步状语从句时,从句部分语序要部分倒装。though 可倒可不倒,although一定不倒。表语名词提前常省去冠词。
1.例句
2.总结
比较状语从句--表示比较关系的状语从句
比较状语从句的引导词
比较状语从句的引导词包括as, than,以及同等程度的比较:as…as… / not so…as… / the same …as…。用于比较两种事物的性质或状态。
Chief Bogo is much taller than Judy.
No one can be fitter for his office than he is.
It snows more often in Shanxi than in Guangdong.
同级比较与不同级比较
同级比较通常使用形容词或副词的原级,而比较级用于不同级比较,如"He runs as fast as I do"(同级比较)和"He runs faster than I do"(不同级比较)。
He can’t run so fast as she.
She works in the same building as my sister.
比较状语从句的其它句型
1. the+形容词比较级…the+形容词比较级… “越……越……”
The harder you work, the luckier you will be.
越努力,越幸运。
The more you read, the better you understand.
你看的书越多,你懂得就越多。
The more difficult the questions are, the less likely I am to be able to answer them.
方式状语从句--描述动作方式的状语从句
01
02
03
方式状语从句的引导词
方式状语从句由连词as, just as(正如),as if/though引导,用以描述动作执行的方式。
方式状语从句的注意事项
as if / though引导的从句若可能符合事实,则用陈述语气;若与事实相反,则用虚拟语气退一格。
方式状语从句的实例
He heard a noise, as if / though someone was breathing.
I saw the man looking about him as if / though he wished to impress upon his mind everything.
He treats me as if / though I were his own son.
He behaved as if / though nothing had happened.
地点状语从句--表示空间关系的状语从句。
通常由连词where和wherever引导;
where 在地点状语从句中,除指地点外,还可指处境;
地点状语从句的引导词
1. Go back where you came from.
2. Judy believes that where there is a will, there is a way.
3. Wherever you go, you must write to your parents.
4. He said he was happy where he was.
5. It’s your fault that she is where she is.
地点状语从句的范例
练习:
Located D the Belt meets the Road, Jiangsu will contribute more to the Belt and Road construction.A. why B. when C. which D. where
状语从句与其他从句的区别
01
02
状语从句与定语从句的区别
状语从句与定语从句的主要区别在于其在句中的作用和位置。状语从句通常放在主句前后修饰动词,而定语从句紧随先行词之后,起修饰或说明先行词的作用。
状语从句与名词性从句的区别
名词性从句能承担主句中的主语、宾语、表语等名词角色,而状语从句则不行。状语从句主要用来修饰谓语,提供关于时间、地点、原因、条件等的额外信息。
My classmate Tom studied very hard 1.__________ he went to senior school. Every day he worked 2.__________ everyone else in my class left the classroom. He said he wouldn't stop trying 3.__________ he got satisfying scores in his studies. Hard 4.__________ he tried, he made little progress. But he didn't lose heart at all 5.______________ he believed as long as he persisted he would succeed one day. 6.__________ time went by, he made improvements in his studies and he was admitted to a university in Beijing at last. We had a get-together party 7.__________ we started our new life in university. Everyone had got offers from universities, 8.__________ we had a very good time. When we stood 9.__________ we used to play and study, we couldn't help thinking of our happy old days. We believed we would never forget each other,10._____________ we would go or whatever we would do.
after
until
unless
though
because
As
before
so
where
wherever
语篇填空
Thanks for listening!
状语从句
状语从句概述与分类
状语从句的定义
状语从句是一种从句类型,它在句子中起修饰或限制主要动词的作用,说明动作发生的时间、地点、原因、条件、目的、结果、比较、方式等。状语从句由引导词引入,与主句之间存在逻辑关系。
状语从句的分类
状语从句可以按照其表达的意义进行分类,主要包括时间状语从句、条件状语从句、原因状语从句、目的状语从句、结果状语从句、让步状语从句、比较状语从句和方式状语从句。每种状语从句都有其特定的引导词和用法。
状语从句在句子中的作用
状语从句在复合句中扮演着重要角色,它丰富了句子的意义,提供了更多关于动作或状态的背景信息。通过状语从句,可以更准确地表达时间顺序、条件可能性、原因结果、目的意图等逻辑关系。
状语从句有九种,连词引导各不同;
时地原因条件状,目比结果方让步;
主句通常前面走,连词引导紧随后;
从句若在主前头,主从之间有个逗。
状语从句的分类
时间状语从句
1
2
时间状语从句的引导词
时间状语从句的引导词包括when, whenever,while, as, as soon as, until/till, not...until, before/after,hardly…when… / scarcely…when… / no sooner…than…,immediately / instantly / directlymoment / minute / instant / second ,every time, each time, next time, the first / last time, by the time,等,这些词帮助明确主句和从句之间的时间关系。
时间状语从句的引导词总结
3
当当当 When(ever)/while/as
先后 before/after
直到 till/until
自从 (ever)since
一...就 As soon as/ 部分副词(此处作连词使用) immediately/ instantly/directly.../the+表时间名词e.g. Moment/ minute/ instant/ second.../hardly...when.../scarcely...when.../no sooner...than...
含time的名词短语 every time/ each time/ next time/ the first(last) time/ by the time
When I got home, my family were already having dinner.
Mary fell asleep while she was reading the newspaper.
As time goes on, Judy becomes stronger and stronger.
He almost knocked me down before he saw me.
The sun came out soon after the storm stopped.
It won’t be three days before I come back.
It wasn’t three days before I came back.
I didn’t go to bed until / till he came back.
She has been working in this factory since she left school.
I had hardly / scarcely got home when it began to rain.
I had no sooner got home than it began to rain.
Nick was in an ice cream shop the first time he met Judy.
Every time I see him, he looks miserable.
时间状语从句范例展示
条件状语从句-- 表示主句动作发生的前提或条件的状语从句
1
2
3
条件状语从句的引导词
条件状语从句的引导词包括if, unless, as/so long as, in case(如果),once(一旦), on condition that (条件是),provided that,supposing that (假设)等,它们用于表达条件与结果的关系。
真实条件句与非真实条件句
真实条件句用以描述现实生活中可能实现的条件,而非真实条件句则用于假设或幻想不可能实现的情况,通常使用过去时态或虚拟语气。
条件状语从句的特殊用法 即 主将从现
如果主句是一般将来时态、祈使句或者是含有将来的动作和意味时,由if引导的条件状语从句和 when, till / until, as soon as 引导的时间状语从句一般用现在时态来代替将来时。即主将从现。
If plastics are burned, they give off poisonous gases.
Unless you work hard, you will fail.
You can go out, as / so long as you promise to be back before eleven.
In case I forget, please remind me about that.
条件状语从句范例展示
Once you get down to doing your homework, you’ll find it easy.
I can help you out on condition that you promise not to make the same mistake again.
Supposing that they refuse us, who else can we turn to for help
原因状语从句 -- 表示一定原因和理由的状语从句。
1
2
3
引导词 位置 内涵 语气 能否回答why 能否被 强调 能够引导表语从句
Because 因为 主句前后均可 直接因果关系 强 能 能 能
As由于 主句前后均可 双方都知道的原因 弱 不能 不能 不能
Now that/ since既然 主句前
原因状语从句范例展示
1. -- Why didn’t he come -- Because he was ill.2. He didn’t come because he was ill.3. Because he was ill, he didn’t come.4. It was because he was ill that he didn’t come.5. He deserves failure. It is all because he is too lazy.6. You needn’t go with me, as you are busy.7. As I was afraid, I hid myself.8. Since you are here, you must do it.9. Now that all the guests have arrived, let’s have our dinner.
原因状语从句使用的注意事项
because和so不能同用在一个句子里,即用了because不用so.
1
2
because和because of 的运用区别:
because 用于引导原因状语从句;而because of 用于连接词或词组或引
导名词性从句。
eg. 1. It was because Nick reached out his foot that Judy tripped and fell.
2. He was late for work because of getting up late.
目的状语从句 -- 表示行为目的的状语从句
目的状语从句的引导词
通常由so that, in order that, in case(以防、免得), for fear that(担心), lest(以免)等引导;
由lest, for fear that引导的目的状语从句要使用“should+动词原形“的虚拟语气。
We got up early so that we could catch the first train.
He studies hard so that he could work better in the future.
We used the computer in order that we might save time.
1
2
注意事项
3
目的状语从句范例展示
1. In order that she could solve the case, Judy turned to Nick for help unwillingly.
2. Judy turned to Nick for help unwillingly so that she could solve the case.
3. Nick agreed to help Judy reluctantly in case his secret should be given away.
4. Nick agreed to help Judy reluctantly for fear that / lest his secret should be given away.
5. It’s a surprise they haven’t managed to grow square ones they can pack them easily.
A. to B. so that C. such that D. in order to
结果状语从句--表示事态结果的状语从句
S + be/v.+ so + adj./adv +that + Clause
+adj.+a/an+n
S + be/v.+ such + a/an + adj. + n. + Clause
+ adj. +[U]
+ adj. + pl.
1
2
结果状语从句的引导词
结果状语从句的引导词包括so that, so...that, such...that等,用于突出动作或状态的结果。
结果状语从句的常用表达
1. It was very cold, so that the river froze.
2. Flash works so fast that he runs a plate in a few minutes.
3. Flash is so skilled an officer that he can run a plate in a few minutes.
4. Flash is such a skilled officer that he can run a plate in a few minutes.
5. My pencil was on the floor, so that I didn’t see it.
6. He is so poor that he can’t buy a bike for his son.
7. She is such a good teacher that everybody likes her.
结果状语从句范例展示
1. Flash works so fast that he runs a plate in a few minutes.So fast does Flash work that…
2. Flash is so skilled an officer that he can run a plate in a few minutes.So skilled an officer is Flash that…
3. Flash is such a skilled officer that he can run a plate in a few minutes.Such a skilled officer is Flash that…
目的状语从句的倒装情况展示
让步状语从句-表示在某种相反的条件下,主句中的情况依然会出现的状语从句
让步状语从句的引导词
由though,although,as(尽管), even if,even though,疑问词+ever, no matter+疑问词,whether...or...引导, 引导让步状语从句时,no matter+疑问词=疑问词+ever。
让步状语从句引导词的注意事项
although 与though不能在同一个句子中与but连用,但可以与yet连用,即用了but不用though/although。
eg.
1. 误:Although / Though he is old, but he is active.
2. 正:Although / Though he is old, yet he is active.
辨析 although/ though/as
Although/Though he is young, he can write in several foreign languages. = Young as/though he is,...Although/Though we were surrounded by the enemy, we managed to escape. = Surrounded as/though we were by the enemy, …Although/Though he was a child, he had to support the family. = Child as/though he was,...
as引导让步状语从句时,从句部分语序要部分倒装。though 可倒可不倒,although一定不倒。表语名词提前常省去冠词。
1.例句
2.总结
比较状语从句--表示比较关系的状语从句
比较状语从句的引导词
比较状语从句的引导词包括as, than,以及同等程度的比较:as…as… / not so…as… / the same …as…。用于比较两种事物的性质或状态。
Chief Bogo is much taller than Judy.
No one can be fitter for his office than he is.
It snows more often in Shanxi than in Guangdong.
同级比较与不同级比较
同级比较通常使用形容词或副词的原级,而比较级用于不同级比较,如"He runs as fast as I do"(同级比较)和"He runs faster than I do"(不同级比较)。
He can’t run so fast as she.
She works in the same building as my sister.
比较状语从句的其它句型
1. the+形容词比较级…the+形容词比较级… “越……越……”
The harder you work, the luckier you will be.
越努力,越幸运。
The more you read, the better you understand.
你看的书越多,你懂得就越多。
The more difficult the questions are, the less likely I am to be able to answer them.
方式状语从句--描述动作方式的状语从句
01
02
03
方式状语从句的引导词
方式状语从句由连词as, just as(正如),as if/though引导,用以描述动作执行的方式。
方式状语从句的注意事项
as if / though引导的从句若可能符合事实,则用陈述语气;若与事实相反,则用虚拟语气退一格。
方式状语从句的实例
He heard a noise, as if / though someone was breathing.
I saw the man looking about him as if / though he wished to impress upon his mind everything.
He treats me as if / though I were his own son.
He behaved as if / though nothing had happened.
地点状语从句--表示空间关系的状语从句。
通常由连词where和wherever引导;
where 在地点状语从句中,除指地点外,还可指处境;
地点状语从句的引导词
1. Go back where you came from.
2. Judy believes that where there is a will, there is a way.
3. Wherever you go, you must write to your parents.
4. He said he was happy where he was.
5. It’s your fault that she is where she is.
地点状语从句的范例
练习:
Located D the Belt meets the Road, Jiangsu will contribute more to the Belt and Road construction.A. why B. when C. which D. where
状语从句与其他从句的区别
01
02
状语从句与定语从句的区别
状语从句与定语从句的主要区别在于其在句中的作用和位置。状语从句通常放在主句前后修饰动词,而定语从句紧随先行词之后,起修饰或说明先行词的作用。
状语从句与名词性从句的区别
名词性从句能承担主句中的主语、宾语、表语等名词角色,而状语从句则不行。状语从句主要用来修饰谓语,提供关于时间、地点、原因、条件等的额外信息。
My classmate Tom studied very hard 1.__________ he went to senior school. Every day he worked 2.__________ everyone else in my class left the classroom. He said he wouldn't stop trying 3.__________ he got satisfying scores in his studies. Hard 4.__________ he tried, he made little progress. But he didn't lose heart at all 5.______________ he believed as long as he persisted he would succeed one day. 6.__________ time went by, he made improvements in his studies and he was admitted to a university in Beijing at last. We had a get-together party 7.__________ we started our new life in university. Everyone had got offers from universities, 8.__________ we had a very good time. When we stood 9.__________ we used to play and study, we couldn't help thinking of our happy old days. We believed we would never forget each other,10._____________ we would go or whatever we would do.
after
until
unless
though
because
As
before
so
where
wherever
语篇填空
Thanks for listening!
