2024届高考英语 动词的时态和语态 课件(共58张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2024届高考英语 动词的时态和语态 课件(共58张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 6.4MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-05-19 11:19:36 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
(共58张PPT)
动词的时态和语态
目录
CONTENTS
动词的难点
动词的语态
动词的时态
动词的概述
PPT模板 http:///moban/
动词的概述
PART ONE
壹
1.什么是动词
表动作或状态的词。
谓语动词;非谓语动词。
动词
动词是用来描述主语的动作、行为或状态的词,用来说明主语是什么、处于什么状态或做什么,是句子不可缺少的部分。
2.动词的分类
按句法功能
Vi.不及物动词:
I come. I go. I fail. I win.
Vt.及物动词:
I take a book. I love him.
He give me a book. I send him a letter.
He made Mary angry. He found Tony crying.
本身意思完整的动词
本身意思不完整,需要添加宾语才能表达完整意思
主谓宾
主谓双宾
主谓宾宾补
实义动词:具有实际意义的动词
系动词+形容词/名词
be 类:am, is, are, was, were (是...) seem, appear(似乎是)
感官动词:sound, taste, feel, look,
表变化:become, go, turn, get
证明是: prove, turn out
表持续:stay, remain, keep
It tastes sweet. It sounds good. She looks tired.
She is an actress. The news finally proved (to be) true.
The leaves turn yellow when the autumn is coming.
He got angry when he heard the news.
助动词:帮助动词变形,变态
①be 类:am, is, are, was, were
②do类: do, does, did
③have 类:have, has, had
④will类: will, would
⑤情态动词:can, could, must, should
I am reading a book.
Do you like apples I don't like apples.
I have learned 3000 words.
I will go to Beijing next month.
I can play basketball.
+ doing/ done/to do
+动词原形
+done
+动词原形
+动词原形
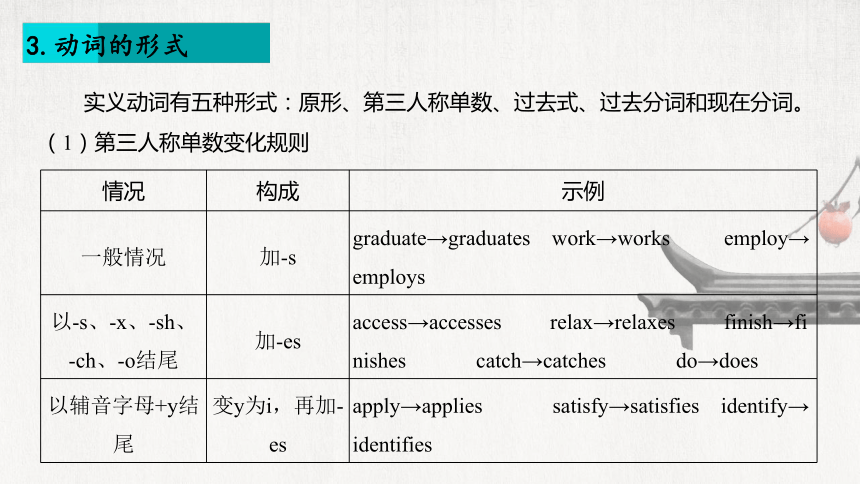
3.动词的形式
实义动词有五种形式:原形、第三人称单数、过去式、过去分词和现在分词。
(1)第三人称单数变化规则
情况 构成 示例
一般情况 加-s graduate→graduates work→works employ→employs
以-s、-x、-sh、 -ch、-o结尾 加-es access→accesses relax→relaxes finish→finishes catch→catches do→does
以辅音字母+y结尾 变y为i,再加-es apply→applies satisfy→satisfies identify→identifies
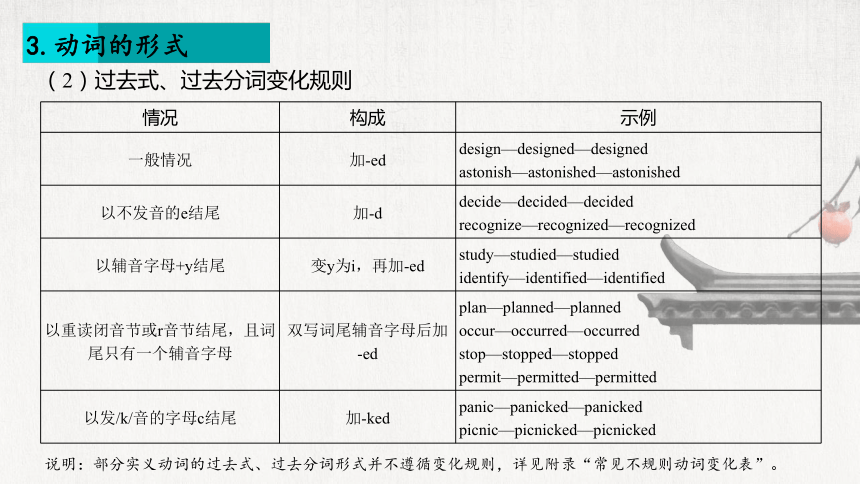
3.动词的形式
(2)过去式、过去分词变化规则
情况 构成 示例
一般情况 加-ed design—designed—designed
astonish—astonished—astonished
以不发音的e结尾 加-d decide—decided—decided
recognize—recognized—recognized
以辅音字母+y结尾 变y为i,再加-ed study—studied—studied
identify—identified—identified
以重读闭音节或r音节结尾,且词尾只有一个辅音字母 双写词尾辅音字母后加 -ed plan—planned—planned
occur—occurred—occurred
stop—stopped—stopped
permit—permitted—permitted
以发/k/音的字母c结尾 加-ked panic—panicked—panicked
picnic—picnicked—picnicked
说明:部分实义动词的过去式、过去分词形式并不遵循变化规则,详见附录“常见不规则动词变化表”。
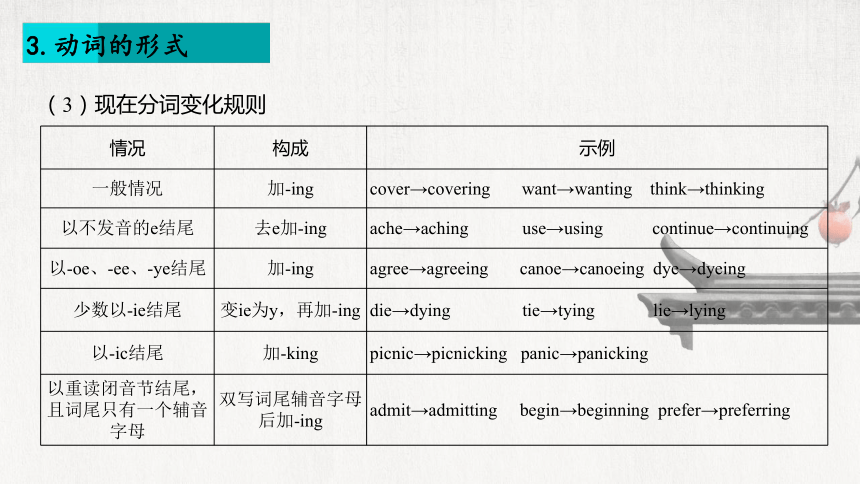
3.动词的形式
情况 构成 示例
一般情况 加-ing cover→covering want→wanting think→thinking
以不发音的e结尾 去e加-ing ache→aching use→using continue→continuing
以-oe、-ee、-ye结尾 加-ing agree→agreeing canoe→canoeing dye→dyeing
少数以-ie结尾 变ie为y,再加-ing die→dying tie→tying lie→lying
以-ic结尾 加-king picnic→picnicking panic→panicking
以重读闭音节结尾, 且词尾只有一个辅音字母 双写词尾辅音字母后加-ing admit→admitting begin→beginning prefer→preferring
(3)现在分词变化规则
动词的时态
PART TWO
贰
过去 一般过去时
过去进行时
过去完成时
过去将来时
现在 一般现在时
现在进行时
现在完成时
将来 一般将来时
将来进行时
将来完成时
现在完成进行时 have/has been doing
Ved did
was/were Ving was/were doing
had Ved had done
would V would do
V /Vs do/ does
am/is/are Ving am/is/are doing
have/has Ved have/ has done
will V will do
will be Ving will be doing
will have Ved will have done
助动词
时间 状态 一般 进行 完成 完成进行
现在 一般现在时 do/does 现在进行时 am/is/are doing 现在完成时 have/has done 现在完成进行时
have/has been doing
过去 一般过去时 did 过去进行时 was/were doing 过去完成时 had done 过去完成进行时
had been doing
将来 一般将来时 will/shall do 将来进行时 will/shall be doing 将来完成时 will/shall have done 将来完成进行时
will/shall have been
doing
过去将来 过去将来时 would/should do 过去将来进行时 would/should be doing 过去将来完成时 would/should have
done 过去将来完成进行时
would/should have
been doing
……
……
1.一般现在时
2.一般过去时
3.一般将来时
4.现在进行时
5.过去进行时
6.将来进行时
8.过去完成时
9.将来完成时
11.过去完成进行时
12.过去将来时
①
②
③
④
⑤
⑥
⑦
⑧
⑨
⑩
现 在
将 来
过 去
7.现在完成时
10.现在完成进行时
时态名 构 成(以drive为例) 用 法
一般现在时 表示现在的状态或经常的习惯性的发生的动作。常跟often, usually, sometimes, every year等时间状语连用。
一般过去时 表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。常和表示过去的时间状语连用。如last week
一般将来时 表示将来某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。常和将来的时间状语连用。如;next week; tomorrow 等。
现在进行时 表示此时此刻或现阶段正在发生的动作。常用的时间状语有now, right now等。
过去进行时 表示过去某个时间正在发生的动作。常和at this time last night等状语连用。
drive
drives (单三人称)
drove
will / shall drive
am/is/are going to drive
am / is / are to drive
am / is / are driving
was / were driving
时态名 构 成(以drive为例) 用 法
现在完成时 表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。常跟ever, never just, yet等副词和 since, for 等引导时间状语(从句)连用。
过去完成时 表示过去某个时间或动作之前发生的动作或存在的状态。常有一个表示过去的时间状语或过去的动作作为参照。
过去将来时 从过去某个时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态。常常用在宾语从句中。
现在完成进行时 表示过去发生的动作一直持续到现在,有可能还要继须下去。常和these days, for over a month等时间状语连用。
have / has driven
had driven
would / should drive
was / were going to drive
was / were to drive
have/ has been driving
时态 例句
1.一般现在时:*** I do my homework every day
2.一般过去时:*** I did my homework yesterday.
3.一般将来时*** I will do my homework tomorrow.
4.过去将来时: I said I would do my homework the next day.
5.现在进行时:*** I am doing my homework now.
6.过去进行时:*** I was doing homework when you came.
7.将来进行时 : I will be doing my homework at this time tomorrow.
8.过去将来进行时 I said I would be doing my homework at that time the next day.
时态 例句
9.现在完成时:*** I have done my homework by now.
10过去完成时:*** I had done my homework before you came.
11将来完成时 I will have done my homework by next Friday.
12过去将来完成时: I said I would have done my homework by next Friday.
13现在完成进行时:*** I have been doing my homework for 3 hours.
14过去完成进行时: I had been doing my homework before my mom came.
15将来完成进行时 I will have been doing my homework for 3 days by the end of the week.
16过去将来完成进行时 I would have been doing my homework for 3 days by the end of the next week.
1. 一般现在时
构成:动词原形/动词的第三人称单数形式(do/does)或be动词(am/is/are) 形式:v. 原形 / 第三人称单数 (do / does)
1.表示经常性、习惯性发生的动作或存在的状态
A hard job usually needs great patience.
We are friends.
温馨提示 常与一般现在时连用的时间状语有:
①频度副词:never从不、seldom很少、sometimes有时、often经常、usually通常、always总是;
②其他时间状语:once in a while偶尔、once a week一周一次、twice a month每月两次、from time to time时不时、at weekends在周末、every day/week/month/year每天/周/月/年等。
1. 一般现在时
2.表示永恒(科学事实、客观真理、名言警句)
Knowledge comes from practice.
The earth moves around the sun.
3. 一般现在时表将来
1. come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return等的一般现在时可表示将来,主要用于时间表上已安排好的事情。
The train (leave) at six tomorrow morning.
The bus starts in ten minutes.
leaves
1. 一般现在时
3. 一般现在时表将来
2. 主将从现(时间、条件状语从句)
I will discuss this with you when we meet next time.
If you leave next week, I will see you off at the airport.
从句
2. 一般过去时
(1)构成:动词的过去式(did)或be动词(was/were)
形式:v. 过去式 (did)
1. 表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态
I was a boy.
She had a boyfriend.
温馨提示 常与一般过去时连用的时间状语有:
①具体时间词:yesterday昨天、yesterday morning/afternoon/evening昨天早上/下午/晚上、once曾经等;
②其他时间状语:last night/year昨晚/去年、a few days ago几天前、the other day几天前、at that time当时、at that moment在那一刻、just now刚刚、in 2005在2005年、in the old days在过去的岁月里等。
2. 一般过去时
2. 其他结构:used to do/ would do
表示过去经常发生的动作
I used to smoke every night.
She would _____(go) to her mother’s grave during every summer.
go
侧重今昔对比
侧重回忆过去
3.一般将来时
表示将来某一时段的动作或状态,或将来某一段时间内经常的动作或状态。常用的时间状语:
1.next time/year/month/week
2.tomorrow
3.tomorrow evening
4.in the future
5.next year
6.in+一段时间(in two days)
7.when/as soon as/if引导的状语从句中的主句
8.in 2050
3. 一般将来时
一般将来时的多种表示形式
(1) will + do
He will be 17 next year.
(2)be going to + do
I am going to stay for a week.
(3)is/am/are+doing现在进行时表将来
We are leaving for Germany next week.
(4)be+ to do表将来
(5)be + about to do
3. 一般将来时
1. 表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态
标志性的时间状语:tomorrow 、in the future、next year、next time、in+时间段、after+时间点
e.g. 下周我要开始减肥
I will start to lose weight next week.
= I am going to lose weight next week.
3. 一般将来时
1、be about to do 表将来(眼下马上要发生的事情)
The film is about to start.
2、be to do sth 表将来
She is to be married next month.
Your plan is to be a failure.
2. 其他常用结构
4. 过去将来时
形式:would do
was / were going to do
表示从过去某个时间看将要发生的动作或状态
I told Laura that I home the following day. (go)
She said she another foreign language.(learn)
would go
would learn
was going to learn
常用于主句是过去时的宾语从句中
I knew you would agree.
↓
过去时
↓
过去将来时
4. 过去将来时
其他结构
1、was / were to do 表过去将来
He said he was to finish the work the next day.
2、was / were about to do sth when …
was / were on the point of doing sth when …
刚要做某事,这时突然…
I was about to go out when a friend dropped in.
We were on the point of leaving when it started to rain.
5. 现在进行时
形式:am / is /are doing
① 表示说话时正在进行的动作或存在的状态,
常与now、at this moment等连用
It’s raining outside.
She is to the teacher carefully now.
listening
①表示说话时正在进行的动作或存在的状态
②表示现阶段正在进行的动作或存在的状态,但说话时动作不一定在进行
5. 现在进行时
② 表示目前一段时间内在做某一件事,但说话时未必在做, 常与these days、this week等连用
I’m reading a work by Lu Xun this month.
He is teaching in a middle school.
进行时与always、constantly、continually、forever等副词连用时,往往表达说话者生气、赞扬、同情、不满、好奇等情感。
She is constantly disturbing me.
Maria is always thinking of others instead of herself.
6. 过去进行时
表示过去某个时刻正在进行的动作
时间状语:
1.at that time
2.at ten o'clock last night
3.this time yesterday
4 be doing sth when...
She was reading at this time yesterday.
When you phoned, I was watching a movie.
6. 过去进行时
形式:was / were doing
表示过去某一时刻或某段时间内正在进行的动作,
I was preparing the lessons this time yesterday.
He was reading a novel when I came in.
温馨提示 有些动词(短语)通常不用于进行时态。
①感官动词:see、hear、feel、smell、sound、taste、notice等;
②表示情感、想法的动词:love、like、hate、understand、believe、think(认为)、mind、agree等;
③表示状态的动词(短语):have、want、own、possess、seem、belong to等;
④非延续性动词:accept、allow、decide、give、receive、promise等。
7. 将来进行时
(1)构成:will/shall be doing
(2)用法:表示将来某一时间正在进行的动作或存在的状态,或按计划、安排将要发生
的事情。常用的时间状语有soon、then、in two days、this time tomorrow、tomorrow
morning、at 9:00 next Monday、from 10:00 to 11:00 tomorrow、the day after tomorrow
等。
I will be waiting for you at the school gate then.届时我将在学校大门口等你。
This time tomorrow we'll be sitting in the cinema and watching a film.
明天这个时候我们将坐在电影院里看电影。
8. 现在完成时
(1)构成:have/has+过去分词(done)
now
past
future
现在完成时:借古讽今
have/has done
It has been / is + 一段时间+ since+did 自从…以来已经过去多久
It has been 10 years since he was a doctor.
It is 10 years since he died.
It is two years since he lived in Hangzhou.
It is two years since he left Hanzhou.
8. 现在完成时
现在完成时常用时间状语:
1.just刚刚 2.already已经
3.ever曾经 4.recently最近
5.never从不 6.yet 还,仍然
7.twice两次 8.so far到目前为止
9.up to now到目前为止 10.since+时间点(自从...)
11.for+时间段(for a long time)一段时间
12.in/over the last/past5 years在过去的5年时间里
8. 现在完成时
① 表示过去发生的动作,对现在造成了影响
I saw the movie.
I have seen the movie.
I got married.
I have got married.
② 表示动作从过去延续到现在
I have learned English for ten years/since 10 years ago.
I have lived in Hangzhou for six years/since six years ago.
标志性时间状语:by +时间词, lately、recently、in the past / last few years、up to now、so far、since+某一时刻、for+时间段
8. 现在完成时
② 表示动作从过去延续到现在
到现在为止,他已经写了八本书
He has written 8 books so far.
在过去几年中,我的家乡发生了巨变
In the past few years, my hometown has changed a lot.
瞬间性动词的现在完成时不可与一段时间连用,若要连用需要变换成对应的延续性动词。
die→ be dead leave/go→ be away join→be in begin→be on
fall ill→ be ill finish→ be over come→be return→be back
borrow→keep buy→have marry→ be married make friends -be friends
9. 过去完成时
表示在过去某一时刻或动作之前已经完成的动作,即
“过去的过去”;通常以一般过去时作参照。
句中常含有:by/before+过去, by last year, by the end of 1998, by the time +过去
That/It was the first/second/third... time +that 从句(过去完成时)
is (现在完成时)
now
past
future
一般过去时
过去完成时
B
A
9. 过去完成时
now
past
future
表示过去/将来某一时刻前完成的动作,对过去/将来这一时刻产生影响
I have seen the movie.
现在完成时:借古讽今
从古至今
have/has done
过去完成时
had done
将来完成时
will have done
过完→
将完→
I had seen the movie.
I will have seen the movie.
×
×
I had seen the movie when she invited me.
I will have seen the movie when she arrives in Beijing.
10. 现在完成进行时
(1)构成:have/has been doing
(2)用法:表示从过去某时开始的动作一直持续到现在,这个动作可能刚刚结束,也可能
仍在继续,强调动作的持续过程。
It has been raining heavily all day.大雨下了一整天了。
You are out of breath. Have you been running 你气喘吁吁的,你刚刚一直在跑步吗
now
past
future
现在完成进行时
have/has been doing
过去完成进行时
had been doing
将来完成进行时
will have been doing
11. 过去完成进行时
构成:“had been+现在分词(doing)”
表示:从过去的过去开始,持续到过去的动作。
The old clock had been being taken apart of and fixed up again for several times by my 10-year- old son before I came back home
12. 将来完成进行时
构成:“will have been+现在分词(doing)”
表示:表示一个动作延续到将来某个时间,期间一直有规律在进行、不曾间断,并且有可能继续延续下去。
By the end of next month, they will have been working for 3 years.
动词的语态
PART THREE
叁
— 主动语态和被动语态
1. 主动语态用于主动句,表示主语是动作的执行者;
The mouse eats the cheese.
2. 被动语态用于被动句,表示主语是动作的承受者。
The cheese is eaten by the mouse.
被动语态基本结构:be + done (by)
语态
be 有______、____和______的的变化
数
人称
时态
1.被动语态的构成
时态 现在 过去 将来 过去将来
一般 is/am/ are done was/were done will/shall be done would/ should be done
进行 is/am/are being done was/were being done - -
完成 have/has been done had been done will/shall have been done would/ should have been done
一般现在时 过去式 现在分词 过去分词
be的形式
被动语态结构:be + done
am/is/are
being
been
一般现在时: done You are required to do this
一般过去时: done The story was told by her.
一般将来时: done The problem will be discussed tomorrow
现在进行时: done The road is being widened
过去进行时: done The new tool was being made
现在完成时: done The novel has been read
过去完成时: done He said that the work had been finished
过去将来时: done He said that the trees would be planted
am/is/are
was/were
will be
am/is/are being
was/were being
have/has been
had been
would be
三步走
was/were
各种时态的被动语态:
一些特殊的被动结构
1)带情态动词的被动结构:
含有情态动词: done
2)带不定式的被动结构:
Someone is going to paint the room.
The room is going to be painted (by someone).
We need to do the homework with care.
The homework needs to be done with care (by us).
情态动词 +be
这个问题必须尽快解决。
The problem must be solved soon.
带双宾语的句子的被动语态
常见的后接双宾语的动词有:
to: give...to, teach...to;
改为:______________,______________
for: make...for, buy...for
改为:_______________,_______________
带双宾语的句子变被动语态有两种变法:
①用“人”当主语时,_________照抄下来。
②用“物”当主语时,在保留的间接宾语(人)前必须加____或____.
加_____或_____由前面的动词决定。
直接宾语
to
for
to
for
be given to
be taught to
be made for
be bought for
含宾语补足语的被动语态
在一感____
二听________ 、 _____
三让___、 ______、 _____
四看____ 、_____、 ______、_____
这十大动词后跟不带to的不定式作宾语补足语,但改成被动语态时,必需带to,以便隔开两个动词。
feel
listen to
hear
let
make
have
see
watch
notice
look
含有短语的主动语态改为被动语态时
后面的介词不能丢。
They take good care of my child.
_______ ___________________.
I turned off the radio.
________ ______________ _______.
My child
The radio
was turned off
(by me)
is taken good care of
注意点:
表示“据说”“相信”的词组
It is said that... 据说
It is reported that... 据报道
It is believed that... 大家相信
It is hoped that... 大家希望
It is well known that... 众所周知
It is thought that... 大家认为
It is suggested that... 据建议
人们认为网购有许多优点。
众所周知,外卖有许多优点。
动词的难点
PART FOUR
肆
1.用主动形式表示被动意义
用法 例句
使用连系动词的结构:look,sound,feel,smell,taste,prove,appear+形容词或名词。 The steel feels cold.
某些表示“发生”的动词(短语),如 happen,take place,occur,break out等。 The war broke out in 1937.战争爆发于1937年。
某些由及物动词转化来的不及物动词;read,write, clean, wash, iron, burn, draw, cook, keep, cut, open, blow,peel,sell,act等,常和副词well,easily,smoothly等 连用,且通常用主动结构表示被动含义。 This pen writes smoothly.这笔写起来很流畅。
The cloth washes well.这种布料好洗。
2.take, spend, pay, cost的用法
spend的宾语通常是金钱或时间,句型: sb.+ spend+时间/金钱+ on sth/in doing sth.
take的主语通常是事情,句型: sth./it+take+sb.+时间+to do. (如果是动作则常用it作形式主语将动词不定式后移)
cost的宾语通常是时间、金钱,句型: sth.+cost+sb.+时间/金钱
pay的宾语通常是金钱,句型: sb.+pay+金钱+for+事物。如:
spend sb.+ spend+时间/金钱+ on sth sb.+ spend+时间/金钱 (in) doing sth She spent the whole night reading the novel.
take sth./it+take+(sb.)+时间+to do sth. This job will take me two days.
It will take me two days to do the job.
cost sth.+cost+sb.+时间/金钱 How much does a house like this cost
pay sb.+pay+金钱+for+sth. I paid him twenty dollars for the book.
3.made相关短语的区别
be made of 指从制成品中可以看得出原材料.
be made from 指从制成品中可以看不出原材料
be made into表示“被制成……”
be made of “物理变化” The desk is made of wood and metal.
be made from “化学变化” This kind of paper is made from bamboo.
be made into “+成品” This piece of cloth can be made into a curtain.
be made in “产地” Computers are made in these cities.
be made by “制造者” This kite was made by Uncle Wang.
be made for “制造目的” A big bag was made for me to hold my waste things.
be made in表达被制造的地点;
be made by表达制造的人;
be made for表达被制造的目的。
4.used相关短语的区别
be used for+名词/代词或动名词;
be used to+动词原形,表示两个短语意思相近,表示“用于……”
used to+动词原形,表示“过去常常”,定式可以是“didn' t use to”也可以是“ usedn't to”
get/be used to+动名词,表示“习惯于……”。如:
be used for+sth (名词/代词或动名词) 被用于…… A knife can be used for cutting things.
be used to+do (动词原形) 被用于…… A knife can be used to cut things.
get/be used to+doing (动名词) 习惯于…… He is used to getting up early in the morning.
used to+do (动词原形) 过去常常 He used to borrow novels from the library when he was at school.
5.解动词填空题“三步曲”
are planted
一看时间状语
1.Every year, many trees (plant) along the river.
2.Keep quiet, please! They (have) a lesson.
are having
3.---Hi,Lin Tao. I didn’t see you at the party.
---Oh, I (get) ready for the exam.
was getting
4.Tom (go) to bed early, but his brother doesn’t.
5. Listen! Jim’s radio (make) a loud noise. Would you please tell him to turn it down
goes
is making
二观上下文联系
三找隐含条件
动词的时态和语态
目录
CONTENTS
动词的难点
动词的语态
动词的时态
动词的概述
PPT模板 http:///moban/
动词的概述
PART ONE
壹
1.什么是动词
表动作或状态的词。
谓语动词;非谓语动词。
动词
动词是用来描述主语的动作、行为或状态的词,用来说明主语是什么、处于什么状态或做什么,是句子不可缺少的部分。
2.动词的分类
按句法功能
Vi.不及物动词:
I come. I go. I fail. I win.
Vt.及物动词:
I take a book. I love him.
He give me a book. I send him a letter.
He made Mary angry. He found Tony crying.
本身意思完整的动词
本身意思不完整,需要添加宾语才能表达完整意思
主谓宾
主谓双宾
主谓宾宾补
实义动词:具有实际意义的动词
系动词+形容词/名词
be 类:am, is, are, was, were (是...) seem, appear(似乎是)
感官动词:sound, taste, feel, look,
表变化:become, go, turn, get
证明是: prove, turn out
表持续:stay, remain, keep
It tastes sweet. It sounds good. She looks tired.
She is an actress. The news finally proved (to be) true.
The leaves turn yellow when the autumn is coming.
He got angry when he heard the news.
助动词:帮助动词变形,变态
①be 类:am, is, are, was, were
②do类: do, does, did
③have 类:have, has, had
④will类: will, would
⑤情态动词:can, could, must, should
I am reading a book.
Do you like apples I don't like apples.
I have learned 3000 words.
I will go to Beijing next month.
I can play basketball.
+ doing/ done/to do
+动词原形
+done
+动词原形
+动词原形
3.动词的形式
实义动词有五种形式:原形、第三人称单数、过去式、过去分词和现在分词。
(1)第三人称单数变化规则
情况 构成 示例
一般情况 加-s graduate→graduates work→works employ→employs
以-s、-x、-sh、 -ch、-o结尾 加-es access→accesses relax→relaxes finish→finishes catch→catches do→does
以辅音字母+y结尾 变y为i,再加-es apply→applies satisfy→satisfies identify→identifies
3.动词的形式
(2)过去式、过去分词变化规则
情况 构成 示例
一般情况 加-ed design—designed—designed
astonish—astonished—astonished
以不发音的e结尾 加-d decide—decided—decided
recognize—recognized—recognized
以辅音字母+y结尾 变y为i,再加-ed study—studied—studied
identify—identified—identified
以重读闭音节或r音节结尾,且词尾只有一个辅音字母 双写词尾辅音字母后加 -ed plan—planned—planned
occur—occurred—occurred
stop—stopped—stopped
permit—permitted—permitted
以发/k/音的字母c结尾 加-ked panic—panicked—panicked
picnic—picnicked—picnicked
说明:部分实义动词的过去式、过去分词形式并不遵循变化规则,详见附录“常见不规则动词变化表”。
3.动词的形式
情况 构成 示例
一般情况 加-ing cover→covering want→wanting think→thinking
以不发音的e结尾 去e加-ing ache→aching use→using continue→continuing
以-oe、-ee、-ye结尾 加-ing agree→agreeing canoe→canoeing dye→dyeing
少数以-ie结尾 变ie为y,再加-ing die→dying tie→tying lie→lying
以-ic结尾 加-king picnic→picnicking panic→panicking
以重读闭音节结尾, 且词尾只有一个辅音字母 双写词尾辅音字母后加-ing admit→admitting begin→beginning prefer→preferring
(3)现在分词变化规则
动词的时态
PART TWO
贰
过去 一般过去时
过去进行时
过去完成时
过去将来时
现在 一般现在时
现在进行时
现在完成时
将来 一般将来时
将来进行时
将来完成时
现在完成进行时 have/has been doing
Ved did
was/were Ving was/were doing
had Ved had done
would V would do
V /Vs do/ does
am/is/are Ving am/is/are doing
have/has Ved have/ has done
will V will do
will be Ving will be doing
will have Ved will have done
助动词
时间 状态 一般 进行 完成 完成进行
现在 一般现在时 do/does 现在进行时 am/is/are doing 现在完成时 have/has done 现在完成进行时
have/has been doing
过去 一般过去时 did 过去进行时 was/were doing 过去完成时 had done 过去完成进行时
had been doing
将来 一般将来时 will/shall do 将来进行时 will/shall be doing 将来完成时 will/shall have done 将来完成进行时
will/shall have been
doing
过去将来 过去将来时 would/should do 过去将来进行时 would/should be doing 过去将来完成时 would/should have
done 过去将来完成进行时
would/should have
been doing
……
……
1.一般现在时
2.一般过去时
3.一般将来时
4.现在进行时
5.过去进行时
6.将来进行时
8.过去完成时
9.将来完成时
11.过去完成进行时
12.过去将来时
①
②
③
④
⑤
⑥
⑦
⑧
⑨
⑩
现 在
将 来
过 去
7.现在完成时
10.现在完成进行时
时态名 构 成(以drive为例) 用 法
一般现在时 表示现在的状态或经常的习惯性的发生的动作。常跟often, usually, sometimes, every year等时间状语连用。
一般过去时 表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。常和表示过去的时间状语连用。如last week
一般将来时 表示将来某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。常和将来的时间状语连用。如;next week; tomorrow 等。
现在进行时 表示此时此刻或现阶段正在发生的动作。常用的时间状语有now, right now等。
过去进行时 表示过去某个时间正在发生的动作。常和at this time last night等状语连用。
drive
drives (单三人称)
drove
will / shall drive
am/is/are going to drive
am / is / are to drive
am / is / are driving
was / were driving
时态名 构 成(以drive为例) 用 法
现在完成时 表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。常跟ever, never just, yet等副词和 since, for 等引导时间状语(从句)连用。
过去完成时 表示过去某个时间或动作之前发生的动作或存在的状态。常有一个表示过去的时间状语或过去的动作作为参照。
过去将来时 从过去某个时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态。常常用在宾语从句中。
现在完成进行时 表示过去发生的动作一直持续到现在,有可能还要继须下去。常和these days, for over a month等时间状语连用。
have / has driven
had driven
would / should drive
was / were going to drive
was / were to drive
have/ has been driving
时态 例句
1.一般现在时:*** I do my homework every day
2.一般过去时:*** I did my homework yesterday.
3.一般将来时*** I will do my homework tomorrow.
4.过去将来时: I said I would do my homework the next day.
5.现在进行时:*** I am doing my homework now.
6.过去进行时:*** I was doing homework when you came.
7.将来进行时 : I will be doing my homework at this time tomorrow.
8.过去将来进行时 I said I would be doing my homework at that time the next day.
时态 例句
9.现在完成时:*** I have done my homework by now.
10过去完成时:*** I had done my homework before you came.
11将来完成时 I will have done my homework by next Friday.
12过去将来完成时: I said I would have done my homework by next Friday.
13现在完成进行时:*** I have been doing my homework for 3 hours.
14过去完成进行时: I had been doing my homework before my mom came.
15将来完成进行时 I will have been doing my homework for 3 days by the end of the week.
16过去将来完成进行时 I would have been doing my homework for 3 days by the end of the next week.
1. 一般现在时
构成:动词原形/动词的第三人称单数形式(do/does)或be动词(am/is/are) 形式:v. 原形 / 第三人称单数 (do / does)
1.表示经常性、习惯性发生的动作或存在的状态
A hard job usually needs great patience.
We are friends.
温馨提示 常与一般现在时连用的时间状语有:
①频度副词:never从不、seldom很少、sometimes有时、often经常、usually通常、always总是;
②其他时间状语:once in a while偶尔、once a week一周一次、twice a month每月两次、from time to time时不时、at weekends在周末、every day/week/month/year每天/周/月/年等。
1. 一般现在时
2.表示永恒(科学事实、客观真理、名言警句)
Knowledge comes from practice.
The earth moves around the sun.
3. 一般现在时表将来
1. come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return等的一般现在时可表示将来,主要用于时间表上已安排好的事情。
The train (leave) at six tomorrow morning.
The bus starts in ten minutes.
leaves
1. 一般现在时
3. 一般现在时表将来
2. 主将从现(时间、条件状语从句)
I will discuss this with you when we meet next time.
If you leave next week, I will see you off at the airport.
从句
2. 一般过去时
(1)构成:动词的过去式(did)或be动词(was/were)
形式:v. 过去式 (did)
1. 表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态
I was a boy.
She had a boyfriend.
温馨提示 常与一般过去时连用的时间状语有:
①具体时间词:yesterday昨天、yesterday morning/afternoon/evening昨天早上/下午/晚上、once曾经等;
②其他时间状语:last night/year昨晚/去年、a few days ago几天前、the other day几天前、at that time当时、at that moment在那一刻、just now刚刚、in 2005在2005年、in the old days在过去的岁月里等。
2. 一般过去时
2. 其他结构:used to do/ would do
表示过去经常发生的动作
I used to smoke every night.
She would _____(go) to her mother’s grave during every summer.
go
侧重今昔对比
侧重回忆过去
3.一般将来时
表示将来某一时段的动作或状态,或将来某一段时间内经常的动作或状态。常用的时间状语:
1.next time/year/month/week
2.tomorrow
3.tomorrow evening
4.in the future
5.next year
6.in+一段时间(in two days)
7.when/as soon as/if引导的状语从句中的主句
8.in 2050
3. 一般将来时
一般将来时的多种表示形式
(1) will + do
He will be 17 next year.
(2)be going to + do
I am going to stay for a week.
(3)is/am/are+doing现在进行时表将来
We are leaving for Germany next week.
(4)be+ to do表将来
(5)be + about to do
3. 一般将来时
1. 表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态
标志性的时间状语:tomorrow 、in the future、next year、next time、in+时间段、after+时间点
e.g. 下周我要开始减肥
I will start to lose weight next week.
= I am going to lose weight next week.
3. 一般将来时
1、be about to do 表将来(眼下马上要发生的事情)
The film is about to start.
2、be to do sth 表将来
She is to be married next month.
Your plan is to be a failure.
2. 其他常用结构
4. 过去将来时
形式:would do
was / were going to do
表示从过去某个时间看将要发生的动作或状态
I told Laura that I home the following day. (go)
She said she another foreign language.(learn)
would go
would learn
was going to learn
常用于主句是过去时的宾语从句中
I knew you would agree.
↓
过去时
↓
过去将来时
4. 过去将来时
其他结构
1、was / were to do 表过去将来
He said he was to finish the work the next day.
2、was / were about to do sth when …
was / were on the point of doing sth when …
刚要做某事,这时突然…
I was about to go out when a friend dropped in.
We were on the point of leaving when it started to rain.
5. 现在进行时
形式:am / is /are doing
① 表示说话时正在进行的动作或存在的状态,
常与now、at this moment等连用
It’s raining outside.
She is to the teacher carefully now.
listening
①表示说话时正在进行的动作或存在的状态
②表示现阶段正在进行的动作或存在的状态,但说话时动作不一定在进行
5. 现在进行时
② 表示目前一段时间内在做某一件事,但说话时未必在做, 常与these days、this week等连用
I’m reading a work by Lu Xun this month.
He is teaching in a middle school.
进行时与always、constantly、continually、forever等副词连用时,往往表达说话者生气、赞扬、同情、不满、好奇等情感。
She is constantly disturbing me.
Maria is always thinking of others instead of herself.
6. 过去进行时
表示过去某个时刻正在进行的动作
时间状语:
1.at that time
2.at ten o'clock last night
3.this time yesterday
4 be doing sth when...
She was reading at this time yesterday.
When you phoned, I was watching a movie.
6. 过去进行时
形式:was / were doing
表示过去某一时刻或某段时间内正在进行的动作,
I was preparing the lessons this time yesterday.
He was reading a novel when I came in.
温馨提示 有些动词(短语)通常不用于进行时态。
①感官动词:see、hear、feel、smell、sound、taste、notice等;
②表示情感、想法的动词:love、like、hate、understand、believe、think(认为)、mind、agree等;
③表示状态的动词(短语):have、want、own、possess、seem、belong to等;
④非延续性动词:accept、allow、decide、give、receive、promise等。
7. 将来进行时
(1)构成:will/shall be doing
(2)用法:表示将来某一时间正在进行的动作或存在的状态,或按计划、安排将要发生
的事情。常用的时间状语有soon、then、in two days、this time tomorrow、tomorrow
morning、at 9:00 next Monday、from 10:00 to 11:00 tomorrow、the day after tomorrow
等。
I will be waiting for you at the school gate then.届时我将在学校大门口等你。
This time tomorrow we'll be sitting in the cinema and watching a film.
明天这个时候我们将坐在电影院里看电影。
8. 现在完成时
(1)构成:have/has+过去分词(done)
now
past
future
现在完成时:借古讽今
have/has done
It has been / is + 一段时间+ since+did 自从…以来已经过去多久
It has been 10 years since he was a doctor.
It is 10 years since he died.
It is two years since he lived in Hangzhou.
It is two years since he left Hanzhou.
8. 现在完成时
现在完成时常用时间状语:
1.just刚刚 2.already已经
3.ever曾经 4.recently最近
5.never从不 6.yet 还,仍然
7.twice两次 8.so far到目前为止
9.up to now到目前为止 10.since+时间点(自从...)
11.for+时间段(for a long time)一段时间
12.in/over the last/past5 years在过去的5年时间里
8. 现在完成时
① 表示过去发生的动作,对现在造成了影响
I saw the movie.
I have seen the movie.
I got married.
I have got married.
② 表示动作从过去延续到现在
I have learned English for ten years/since 10 years ago.
I have lived in Hangzhou for six years/since six years ago.
标志性时间状语:by +时间词, lately、recently、in the past / last few years、up to now、so far、since+某一时刻、for+时间段
8. 现在完成时
② 表示动作从过去延续到现在
到现在为止,他已经写了八本书
He has written 8 books so far.
在过去几年中,我的家乡发生了巨变
In the past few years, my hometown has changed a lot.
瞬间性动词的现在完成时不可与一段时间连用,若要连用需要变换成对应的延续性动词。
die→ be dead leave/go→ be away join→be in begin→be on
fall ill→ be ill finish→ be over come→be return→be back
borrow→keep buy→have marry→ be married make friends -be friends
9. 过去完成时
表示在过去某一时刻或动作之前已经完成的动作,即
“过去的过去”;通常以一般过去时作参照。
句中常含有:by/before+过去, by last year, by the end of 1998, by the time +过去
That/It was the first/second/third... time +that 从句(过去完成时)
is (现在完成时)
now
past
future
一般过去时
过去完成时
B
A
9. 过去完成时
now
past
future
表示过去/将来某一时刻前完成的动作,对过去/将来这一时刻产生影响
I have seen the movie.
现在完成时:借古讽今
从古至今
have/has done
过去完成时
had done
将来完成时
will have done
过完→
将完→
I had seen the movie.
I will have seen the movie.
×
×
I had seen the movie when she invited me.
I will have seen the movie when she arrives in Beijing.
10. 现在完成进行时
(1)构成:have/has been doing
(2)用法:表示从过去某时开始的动作一直持续到现在,这个动作可能刚刚结束,也可能
仍在继续,强调动作的持续过程。
It has been raining heavily all day.大雨下了一整天了。
You are out of breath. Have you been running 你气喘吁吁的,你刚刚一直在跑步吗
now
past
future
现在完成进行时
have/has been doing
过去完成进行时
had been doing
将来完成进行时
will have been doing
11. 过去完成进行时
构成:“had been+现在分词(doing)”
表示:从过去的过去开始,持续到过去的动作。
The old clock had been being taken apart of and fixed up again for several times by my 10-year- old son before I came back home
12. 将来完成进行时
构成:“will have been+现在分词(doing)”
表示:表示一个动作延续到将来某个时间,期间一直有规律在进行、不曾间断,并且有可能继续延续下去。
By the end of next month, they will have been working for 3 years.
动词的语态
PART THREE
叁
— 主动语态和被动语态
1. 主动语态用于主动句,表示主语是动作的执行者;
The mouse eats the cheese.
2. 被动语态用于被动句,表示主语是动作的承受者。
The cheese is eaten by the mouse.
被动语态基本结构:be + done (by)
语态
be 有______、____和______的的变化
数
人称
时态
1.被动语态的构成
时态 现在 过去 将来 过去将来
一般 is/am/ are done was/were done will/shall be done would/ should be done
进行 is/am/are being done was/were being done - -
完成 have/has been done had been done will/shall have been done would/ should have been done
一般现在时 过去式 现在分词 过去分词
be的形式
被动语态结构:be + done
am/is/are
being
been
一般现在时: done You are required to do this
一般过去时: done The story was told by her.
一般将来时: done The problem will be discussed tomorrow
现在进行时: done The road is being widened
过去进行时: done The new tool was being made
现在完成时: done The novel has been read
过去完成时: done He said that the work had been finished
过去将来时: done He said that the trees would be planted
am/is/are
was/were
will be
am/is/are being
was/were being
have/has been
had been
would be
三步走
was/were
各种时态的被动语态:
一些特殊的被动结构
1)带情态动词的被动结构:
含有情态动词: done
2)带不定式的被动结构:
Someone is going to paint the room.
The room is going to be painted (by someone).
We need to do the homework with care.
The homework needs to be done with care (by us).
情态动词 +be
这个问题必须尽快解决。
The problem must be solved soon.
带双宾语的句子的被动语态
常见的后接双宾语的动词有:
to: give...to, teach...to;
改为:______________,______________
for: make...for, buy...for
改为:_______________,_______________
带双宾语的句子变被动语态有两种变法:
①用“人”当主语时,_________照抄下来。
②用“物”当主语时,在保留的间接宾语(人)前必须加____或____.
加_____或_____由前面的动词决定。
直接宾语
to
for
to
for
be given to
be taught to
be made for
be bought for
含宾语补足语的被动语态
在一感____
二听________ 、 _____
三让___、 ______、 _____
四看____ 、_____、 ______、_____
这十大动词后跟不带to的不定式作宾语补足语,但改成被动语态时,必需带to,以便隔开两个动词。
feel
listen to
hear
let
make
have
see
watch
notice
look
含有短语的主动语态改为被动语态时
后面的介词不能丢。
They take good care of my child.
_______ ___________________.
I turned off the radio.
________ ______________ _______.
My child
The radio
was turned off
(by me)
is taken good care of
注意点:
表示“据说”“相信”的词组
It is said that... 据说
It is reported that... 据报道
It is believed that... 大家相信
It is hoped that... 大家希望
It is well known that... 众所周知
It is thought that... 大家认为
It is suggested that... 据建议
人们认为网购有许多优点。
众所周知,外卖有许多优点。
动词的难点
PART FOUR
肆
1.用主动形式表示被动意义
用法 例句
使用连系动词的结构:look,sound,feel,smell,taste,prove,appear+形容词或名词。 The steel feels cold.
某些表示“发生”的动词(短语),如 happen,take place,occur,break out等。 The war broke out in 1937.战争爆发于1937年。
某些由及物动词转化来的不及物动词;read,write, clean, wash, iron, burn, draw, cook, keep, cut, open, blow,peel,sell,act等,常和副词well,easily,smoothly等 连用,且通常用主动结构表示被动含义。 This pen writes smoothly.这笔写起来很流畅。
The cloth washes well.这种布料好洗。
2.take, spend, pay, cost的用法
spend的宾语通常是金钱或时间,句型: sb.+ spend+时间/金钱+ on sth/in doing sth.
take的主语通常是事情,句型: sth./it+take+sb.+时间+to do. (如果是动作则常用it作形式主语将动词不定式后移)
cost的宾语通常是时间、金钱,句型: sth.+cost+sb.+时间/金钱
pay的宾语通常是金钱,句型: sb.+pay+金钱+for+事物。如:
spend sb.+ spend+时间/金钱+ on sth sb.+ spend+时间/金钱 (in) doing sth She spent the whole night reading the novel.
take sth./it+take+(sb.)+时间+to do sth. This job will take me two days.
It will take me two days to do the job.
cost sth.+cost+sb.+时间/金钱 How much does a house like this cost
pay sb.+pay+金钱+for+sth. I paid him twenty dollars for the book.
3.made相关短语的区别
be made of 指从制成品中可以看得出原材料.
be made from 指从制成品中可以看不出原材料
be made into表示“被制成……”
be made of “物理变化” The desk is made of wood and metal.
be made from “化学变化” This kind of paper is made from bamboo.
be made into “+成品” This piece of cloth can be made into a curtain.
be made in “产地” Computers are made in these cities.
be made by “制造者” This kite was made by Uncle Wang.
be made for “制造目的” A big bag was made for me to hold my waste things.
be made in表达被制造的地点;
be made by表达制造的人;
be made for表达被制造的目的。
4.used相关短语的区别
be used for+名词/代词或动名词;
be used to+动词原形,表示两个短语意思相近,表示“用于……”
used to+动词原形,表示“过去常常”,定式可以是“didn' t use to”也可以是“ usedn't to”
get/be used to+动名词,表示“习惯于……”。如:
be used for+sth (名词/代词或动名词) 被用于…… A knife can be used for cutting things.
be used to+do (动词原形) 被用于…… A knife can be used to cut things.
get/be used to+doing (动名词) 习惯于…… He is used to getting up early in the morning.
used to+do (动词原形) 过去常常 He used to borrow novels from the library when he was at school.
5.解动词填空题“三步曲”
are planted
一看时间状语
1.Every year, many trees (plant) along the river.
2.Keep quiet, please! They (have) a lesson.
are having
3.---Hi,Lin Tao. I didn’t see you at the party.
---Oh, I (get) ready for the exam.
was getting
4.Tom (go) to bed early, but his brother doesn’t.
5. Listen! Jim’s radio (make) a loud noise. Would you please tell him to turn it down
goes
is making
二观上下文联系
三找隐含条件
