2023-2024学年七年级英语下学期期末复习之 重点语法知识归纳(Units 1-11)(牛津上海版)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2023-2024学年七年级英语下学期期末复习之 重点语法知识归纳(Units 1-11)(牛津上海版) |  | |
| 格式 | docx | ||
| 文件大小 | 152.4KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津上海版(试用本) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-05-31 20:53:34 | ||
图片预览




文档简介
重点语法知识归纳(Units 1-11)
·模块一 Grammar 1:条件状语从句
1. 条件状语从句
(1)主句为一般将来时,从句用一般现在时表将来。如:
I'll visit the Great Wall if it isn't windy tomorrow. 如果明天不刮风,我将去长城。
(2) “祈使句十and/or引导的结果状语从句”中,祈使句在意义上相当于一个条件状语从句。如:
Use your head, and you'll find a way. =If you use your head, you'll find a way. 动动脑筋,你就会想出办法来。
2. 介词in和on
(1) 在表示方位时,in表示在某一地区之内的某方位(属于该范围);on表示与某地的毗邻关系。如:
Taiwan is in the south-east of China. 台湾位于中国的东南部。
in表示较大的地方。如:in China, in the world
on表示在一个平面上。如:on the farm
(2) 除表示方位外,in和on还可表时间,in表示一段时间,用于年、月、世纪、四季或泛指的一天的上午、下午、晚上前。如:in the twenty-first century在21世纪,in autumn在秋天,in the morning在早上,in还可用于表示“多久之后”如:in five years
on主要用在星期几,具体某一天或某一天的早、中、晚或节日前。如:on Mid-Autumn Day在中秋节
on June 1st在6月1日
·模块二 Grammar 2:口语表达
1. So do I. /Neither do I. 我也是。/我也不。
(1) So…I表示同意对方的话语,意为“我也是”。So和I间的助动词由上下文决定。如:
-I like playing computer games. 我喜欢玩电脑游戏。
-So do I. 我也是。
-I can paint well. 我擅长画画。
-So can I. 我也是。
-I went to the cinema last night. 我昨晚去看电影了。
-So did I. 昨晚我也去看了。
【友情提示】 这里的人称并不仅限于I。
-My brother is a doctor. 我哥哥是一名医生。
-So is Mary’s. 玛丽的哥哥也是(医生)。
(2) Neither…I也是用来附和对方的话语,意为“我也不……”。与So…I不同的是,So…I的上文为肯定句,而Neither…I的上文是否定句。Neither…I中的助动词也是由上下文决定。同样这里的人称并不仅限于I。
-I don't like films about love stories. 我不喜欢看爱情电影。
-Neither do I. 我也不喜欢(看爱情电影)。
-My brother can’t play the piano. 我哥哥不会弹钢琴。
-Neither can his. 他哥哥也不会。
-I have never been to Beijing. 我从未去过北京。
-Neither has Mary. 玛丽也没去过。
(3)这两种结构的不同点是:
① “so+助动词/be动词/情态动词十主语”依附于肯定句,表示前边的肯定情况也适合后边的人,意为“我也……”,相当于“I do, too”。
② “neither+助动词/be动词/情态动词+主语”依附于否定句,表示前边的否定情况也适合后边的人,意为“我也不……”,相当于“I don't, either"。如:
Peter watched TV last night, so did Ann. 彼得昨晚看电视了,安也看了。
Mary didn't watch TV last night, neither did Jill. 玛丽昨晚没有看电视,吉尔也没看。
2. Next, turn left into Tree Road and walk along Tree Road. 然后,左转进入树路,并且沿着它走。
turn left/right表示“左/右转”。这里的动词turn表示“转向…”
这是给别人指路时常用的表达方式。
walk along是“沿着……走”的意思。介词along是“沿着”的意思。
We went for a walk along the shore. 我们沿着海岸散步。
其他用于指路的句子还有:
Turn left, Walk along Rose Street. 左转,沿着玫瑰街走。
Turn right into Rose Street and walk along. 右转进入玫瑰街并沿着走。
Walk straight ahead. 向前直走。
Take the first turning on the right. 在第一个路口右转。
Take the second turning on the left. 在第二个路口左转。
Walk to the end of the road. 这条路走到底。
Walk down the street. 沿着这条街走。
Walk up Green Road. 沿着格林路往前走。
You'll see the post office in front of you. 你会看到邮局在你的前方。
You'll see the cinema on your right. 你会看到电影院在你的右边。
·模块三 Grammar 3:现在完成时和被动语态
★现在完成时
(1)表示过去发生的或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果。如:
-Have you had your lunch yet 你吃过午饭了吗?
-Yes, I have. I've just had it. 是的,我刚吃过。(说明现在饱了。)
I have lost my pen. 我把钢笔弄丢了。(过去某时丢的,现在还没有找到。)
I have already watched the TV play. 我已经看过这部电视剧了。
-Have you found your lost pen yet 一你找到丢失的钢笔了吗?
-No. I haven't found it yet. 一不,我还没有找到。
【友情提示】 already,yet常和现在完成时连用,already用于肯定句,可放在助动词之后、过去分词之前,也可放在句末。yet用在疑问句中意为“已经”,用在否定句中表示“还”,常放在句末。
(2)表示动作或状态在过去已经开始,持续到现在,也许还要持续下去,常和for,since连用,表示持续的动作或状态多为延续性动词。如:
We have lived here since 2000.
自从2000年以来我们一直住在这里。(说明一直住在这里也许还会住下去。)
(3)现在完成时中经常使用的几个副词:
1) just意为“刚刚”,表示动作刚刚结束,常放在助动词与过去分词之间。如:
He has just come back from Beijing. 他刚从北京回来。
2) ever意为“曾经”,用于疑问句或否定句中,放在助动词与过去分词之间。如:
Have you ever been to Shanghai 你去过上海吗?
3) never意为“从来没有”,常与before连用,多放在助动词与过去分词之间。如:
I have never travelled by plane before. 我以前从来没有乘飞机旅行过。
4) before意为“以前”,指过去不确定的某个时间,总是放在句末,不受句型的限制。如:
I haven’t heard of it before. 我以前从来没有听说过这件事。
5) since+时间点,for+时间段
I have been in Beijing for two years/since two years ago. 我在北京两年了。
(4)延续性动词与非延续性动词的用法
1) 现在完成时表示动作从过去某个时候开始一直持续到现在,与一段时间连用时应注意句中的谓语动词应是延续性动词,非延续性动词不可与一段时间连用。如:
我离开这所学校已八年了。
误:I've left this school for eight years.
正:I've been away from this school for eight years.
他借用我的词典已两天了。
误:He has borrowed my dictionary for two days.
正:He has kept my dictionary for two days.
不过,在否定句中非延续性动词可与一段时间连用。如:
I haven't gone to see him for several months. 我已经好几个月没去看他了。
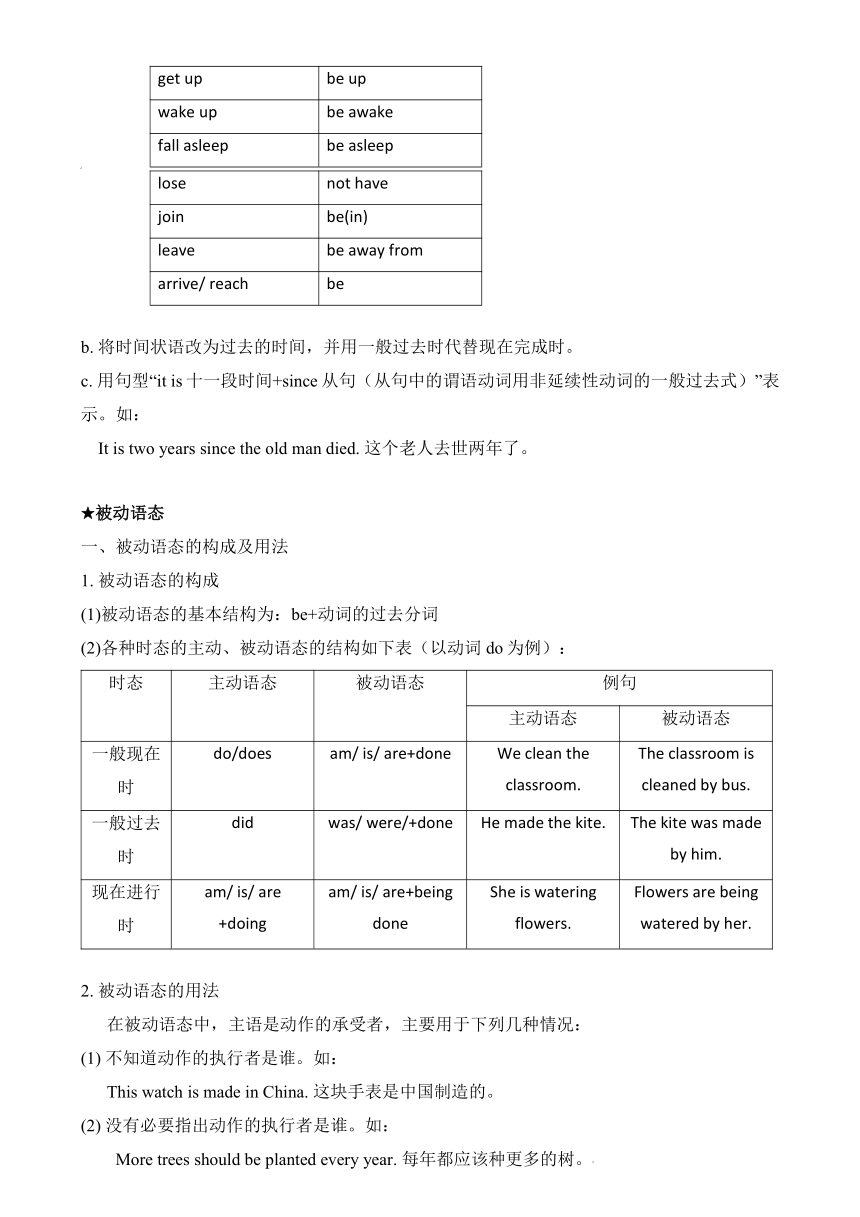
2) 非延续性动词与一段时间连用时可采用下述三种方法:
a. 将非延续性动词转化为延续性动词
非延续性动词 延续性动词
buy have
borrow keep
open be open
close be closed
begin/ start be on
come be here
go be away
finish be over
died be dead
catch a cold have a cold
put on wear
get up be up
wake up be awake
fall asleep be asleep
lose not have
join be(in)
leave be away from
arrive/ reach be
b. 将时间状语改为过去的时间,并用一般过去时代替现在完成时。
c. 用句型“it is十一段时间+since从句(从句中的谓语动词用非延续性动词的一般过去式)”表示。如:
It is two years since the old man died. 这个老人去世两年了。
★被动语态
一、被动语态的构成及用法
1. 被动语态的构成
(1)被动语态的基本结构为:be+动词的过去分词
(2)各种时态的主动、被动语态的结构如下表(以动词do为例):
时态 主动语态 被动语态 例句
主动语态 被动语态
一般现在时 do/does am/ is/ are+done We clean the classroom. The classroom is cleaned by bus.
一般过去时 did was/ were/+done He made the kite. The kite was made by him.
现在进行时 am/ is/ are +doing am/ is/ are+being done She is watering flowers. Flowers are being watered by her.
2. 被动语态的用法
在被动语态中,主语是动作的承受者,主要用于下列几种情况:
(1) 不知道动作的执行者是谁。如:
This watch is made in China. 这块手表是中国制造的。
(2) 没有必要指出动作的执行者是谁。如:
More trees should be planted every year. 每年都应该种更多的树。
(3) 需要强调或突出动作的承受者时。如:
Chinese is spoken by more and more people in the world. 世界上越来越多的人说汉语。(强调汉语的使用广泛)
(4) 句子的主语是动作的承受者。如:
Many houses were washed away by the flood. 许多房屋被洪水冲走了。
二、主动语态和被动语态的转换
1. 主动语态变为被动语态
(1)要将主动句里的宾语变为被动句中的主语,若主动句中的宾语是人称代词,要将宾格变成主格。
(2)把主动句中的主语变为被动句中的宾语,主格变成宾格,并由by引导。
(3)谓语动词变成相应的被动形式。
We asked him to sing an English song. (变为被动语态)→He was asked to sing an English song by us.
2. 带双宾语的谓语动词变为被动语态
谓语动词带双宾语时,既可以将间接宾语转化成主语,也可以将直接宾语转化成主语。若将间接宾语转化成主语,则保留直接宾语;若将直接宾语转化成主语,则保留间接宾语,且在被保留的间接宾语前加上介词to或for。如:
She gave me a book.(变为被动语态)
I was given a book by her.(间接宾语me变为了主语)
A book was given to me by her.(直接宾语a book变为了主语)
3. 动词短语变为被动语态
许多由不及物动词和介词、副词构成的动词短语相当于及物动词,可以有宾语,也可以有被动语态。但是动词短语是一个不可分割的整体,在变为被动语态时,不可丢掉构成动词短语的介词或副词。如:
We should speak to old men politely.(变为被动语态)
Old men should be spoken to politely.(to不可省略)
4. 带复合宾语的动词变为被动语态
宾语加上宾语补足语一起构成复合宾语。变为被动语态时,只把宾语变为被动句的主语,宾语补足语保留在原处,成为主语补足语。如:
I heard Jane playing the piano in her room.(变为被动语态)
Jane was heard playing the piano in her room.
5. 变被动语态后动词形式的选择
主动句中在感官动词see,hear,watch,feel,notice等,及使役动词let,make,have等后跟省略to的不定式,
变为被动语态时,应加上不定式符号to。如:
He makes the girl stay at home.(变为被动语态)→The girl is made to stay at home by him.
·模块四 Grammar4:动词need
1. 动词need
need可以作情态动词,这时need没有时态,人称和数的变化,多用于否定句和疑问句意为“必须”,后接动词原形。其否定形式为need not(缩略式为needn’t),意为“不必”,但need作情态动词时只能用于表达现在的时间含义。
Need I pay the whole amount now 我现在必须全部付清吗?
You needn't do it now. You can do it later.你不必现在做,稍后再做也可以。
need可以用作行为动词,意为“需要”
I'll call you if anything is needed. 要是需要什么,我就叫你。
【注意】 在need的后面接动词的-ing形式时,这个动词和句子的主语之间有逻辑上的被动关系,但这时应用主动形式表示被动,但如果在need的后面接不定式时,不定式应该使用被动形式。
He will need to be looked after. 必须让人去照料他。
Whose chair needs fixing 谁的椅子需要修理?
2. Alice, do you like the jeans with the yellow belt or the ones with the blue belt
the jeans with the yellow belt意为“配黄色腰带的牛仔裤”,with表示“带着;带有”。在此介绍一些服装的表达方法,如下:
the jeans with the blue/yellow belt配蓝色/黄色腰带的牛仔裤
the shirt with the blue/red spots带蓝点/红点的衬衫
the sweater with the short/long sleeves短袖/长袖毛衣
the T-shirt with the V-neck/round neck鸡心领/圆领T恤衫
the trousers with the checks/stripes格子/条纹长裤
·模块五 Grammar5:让步状语从句和不定代词
1. 让步状语从句
表示让步含义的从句结构,它主要有although,though等连词引导。让步状语在句中可前置,也可后置。
前置时,强调的是主句的内容;
后置时,强调的是从句的内容。
e.g. Although/though he is tired, he still finishes his work on time.
虽然他很累,但仍然按时完成了工作。
He knows what to do, although/though he is a child.
他知道该做什么,尽管他是一个孩子。
【注意】
让步状语从句中不可再使用but等并列连词,但可以用yet,still等连接副词来加强语气。
e.g. Although/Though he worked hard at Maths, yet he didn’t pass the exam.
虽然他很努力地学习数学,但仍然考试不及格。
Although/Though her father is very old, he is still working.
虽然她的父亲年迈,但他仍然坚持工作。
2. 不定代词
other; one…the other; some…others/the others…
1) other + 名词的复数形式;
e.g. Some students are playing football and other students are playing basketball.
一些学生在踢足球,另一些在打篮球。
2) one…the other…表示“一个…,另一个…”总数=2。
the other + 可数名词的复数,表示≧ 3 的人或物中剩余的全部。
the other + 数词
e.g. Some students are inside the classroom but the other students are outside the classroom.
一些学生在教室内,但另一些在教室外。
This girl is good at English. How about the other three
这个女孩擅长英语。其他三个怎么样?
3) some…others/the others… 都表示“一些…,另一些…”,前者没有固定范围,后者有一定范围内而言的。
Some people like playing badminton and others like playing volleyball.(剩余的部分)
一些人爱打羽毛球,而另一些人哎打排球。
Some students are playing badminton on the playground and the others are playing volleyball.(剩余的全部)
一些学生正在操场上打羽毛球,其他的正在打排球。
·模块六 Grammar6:含形容词的固定句型和使役动词make
1. It is+形容词+to…
It is+adj. +to do sth. 做某事…
例如:It’ s easy to learn swimming. 学游泳很简单。
It is+adj. +doing sth.
做某事很……(对话结束时使用)
例如:It was nice talking to you. 和你谈话很愉快。
It十is+adj. +for+sb. +to do sth. 对某人来说做某事真是太……了。
本句型中的形容词通常是表示客观情况的。如:easy, hard, difficult, important, necessary, impossible, interesting等。
例如:It was difficult for him to finish the work on time. 对他来说,按时完成这项工作真是太难了。
It is necessary for us to study English well.对我们来说学好英语是必要的。
2. 使役动词make
“make+宾语+宾语补足语”的这一结构用得很多,其中宾语补足语部分可以用形容词、介词短语、名词、不定式、分词等充当。
“make+宾语+形容词作宾语补足语”。例如:
We are working hard to make our country more beautiful. 我们正努力工作,使我们的国家更美丽。
“make+宾语+介词短语作宾语补足语”。例如:
Mother made her coat into my skirt. 母亲把她的外套改成裙子给我穿。
“make+宾语+名词作宾语补足语”。例如:
We made him our monitor. 我们都选他当班长。
“make十宾语十省略to的不定式作宾语补足语”,若将其改为被动语态,to须加上。例如:
The boy makes faces just to make others laugh. 这个男孩做鬼脸的目的是让其他人笑。
·模块七 Grammar7:一般将来时
一般将来时
(1)表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态,其构成:是will+动词原形,常与表示将来的时间状语连用,如tomorrow, next week, in a few days, next Sunday, in十一段时间,in 2020等。 如:
They will leave for Shanghai next week. 他们下周将去上海。
Will you be back in two days 你将在两天后回来吗?
当主语是I或we时,疑问句中一般使用shall,表示征求对方意见。如:
Where shall we meet tomorrow 明天我们在哪里会面?
(2) be going to+动词原形”表示计划、打算做某事,表示已决定的、很可能发生的事,或有某种迹象表明要发生的事。如:What are you going to do next Sunday 下周日你打算干什么?
Look at the clouds. There is going to be a storm. 看那些乌云,暴风雨就要来临了。(客观迹象)
注意:在下面几种情况下只可用shall( will)表示将来,而不可用be going to结构。
1)表示有礼貌地询问对方是否愿意或表示客气的邀请或命令时。如:
Will you please lend me your bike 请你把自行车借给我用一下好吗?
2)表示意愿时。如:
We will help him if he asks us. 如果他请我们,我们愿意帮助他。
3)表示单纯的将来,与人的主观愿望和判断无关时。如:
The sun will rise at 6:30 tomorrow morning. 明天早上太阳将在6:30升起。
(3) be doing表示将来
常用这种结构的动词有go,come,leave,stay,start,begin等,表示即将发生或安排好要做的事情。如:
We are leaving for London. 我们就要动身去伦敦了。
She is going there tomorrow. 她明天要去那里。
(4) "be about to+动词原形”和“be to+动词原形”结构表示即将发生的动作。如:
I was about to leave when the phone rang. 我刚要离开,这时电话响了。
(5)用一般现在时表示将来的情况
1)表示按规定或时间表预计将发生的动作。如:
We're going to Changchun. Our plane takes off at 8:10. 我们打算去长春。我们的飞机8:10起飞。
2)当主句为一般将来时态时,在if,as soon as,until,when等引导的状语从句中用一般现在时代替一般将来时。如:
If it doesn't rain this afternoon, we'll have a football match.
如果今天下午不下雨,我们将进行一场足球比赛。
·模块八 Grammar8:重点语法
1. would like something和would like to do something的结构。
(1) Would you like…?可用来给出提议。
A: Would you like some coffee 你想来点咖啡吗?
B: No, thank you. 不了,谢谢。
A: Would you like some rice 你想来些米饭吗?
B: Yes, please. 好的。
A: What would you like, tea or coffee 你想喝点什么,茶还是咖啡?
B: Tea, please. 茶,谢谢。
(2)Would you like to…?可用来向别人发出邀请。
A: Would you like to have dinner with us on Sunday 周日你想和我们一起吃饭吗?
B: Yes, I'd love to. 我很乐意。
(3)另外,I'd like…是I want…的礼貌说法。
I'm thirsty. I'd like a drink. 我渴了,想喝杯饮料。
I'd like to see the film on television this evening. 今晚我想看电视上播放的电影。
指点迷津:Would you like… 和 Do you like…
Would you like . . . /I'd like . . . Do you like ... / I like …
·Would you like some tea =Do you want some tea 你想来点茶吗 ·Do you like tea =Do you think tea is nice 你喜欢喝茶吗?
·A: Would you like to go to the cinema tonight (=Do you want to go to the cinema tonight ) 今晚你想去看电影吗? ·B:Yes, I'd love to. 我想去。 ·A: Do you like going to the cinema (泛指)你喜欢看电影吗? ·B: Yes, I go to the cinema a lot. 是的,我经常去看电影
·I'd like an orange, please.(=Can I have an orange ) 我想要一个橘子,可以吗 ·I like oranges.(泛指)我喜欢橘子。
·What would you like to do next weekend 下周末你想做什么? ·What do you like to do at weekends 你周末都喜欢做些什么?
2. It would be possible to have more books in our library. 丰富我们校图书馆里的藏书是可以做到的。
“It would be+形容词+动词不定式”的结构与“It is+形容词+动词不定式”的结构所表达的含义接近,但有所区别。试比较:
It is nice to eat ice cream in summer. 夏天吃冰淇淋很爽。①
It would be nice to have a swimming pool in our school. 要是我们学校有一个游泳池多好。②
第①句表达的含义:夏天吃冰淇淋很不错。这个句子表达的是经常性发生的动作,是广泛的爱好。
第②句表达的含义:学校目前没有游泳池,但倘若有,就是一件不错的事情。它所表达的内容与现状相反,有假设的成分。
3. 反身代词使用时应与主语相呼应。下表为反身代词与人称代词主格形式的对应关系:
主格 I you he she it
单数 myself yourself himself herself itself
复数 ourselves yourselves themselves
反身代词有如下作用:
(1) 作动词或介词的宾语,尤其常在enjoy,teach,hurt,buy,introduce,seat,dress,express,amuse,behave等动词和by,for,to,of等介词后作宾语。如:
He is teaching himself English. 他正在自学英语。
She was talking to herself. 那时她在自言自语。
He lives in the country by himself. 他独自住在乡下。
(2) 作主语的同位语,主要起加强语气的作用,意为“亲自;本身;本人”。
Did you make the cake yourself 这蛋糕是你亲自做的吗?(yourself作主语you的同位语)
The work itself is easy. 这工作本身很容易。(itself作主语the work的同位语)
(3) 作表语,常位于be,feel,look,seem等系动词后,表示身体或精神状态。
I’ m not myself today. 我今天不舒服。
I am feeling myself again. 我觉得身体舒服了。
(4) 用于一些简短的会话或固定用法中。
Help yourself! 请随便吃吧!/请自己去取吧! Make yourself at home!别客气!
Don't upset yourself! 别自寻烦恼! Make yourself heard/understood.使你自己被人听到/理解。
·模块九 Grammar9:形容词比较级和最高级、反身代词和物主代词
1. 形容词比较级的构成:
(1)通常是在形容词后面加上-er,形成比较级。
原级 比较级 原级 比较级
clean cleaner(比较干净的;更干净的) tall taller(比较高的;更高的)
(2)原形容词词尾已有字母-e时,则只在形容词词尾加-r。
原级 比较级 原级 比较级
nice nicer(比较好的;更好的) brave braver(比较勇敢的;更勇敢的)
(3)原形容词词尾为“辅音字母+y”时,则先去掉字母y,再加-ier。
原级 比较级 原级 比较级
happy happier(比较快乐的;更快乐的) friendly friendlier(比较友善的;更友善的)
(4)原形容词词尾有“辅元辅”现象(即后三个字母的排列是“辅音字母+元音字母+辅音字母”)时,则要双写词末的辅音字母,再加-er。
原级 比较级 原级 比较级
big bigger(比较大的;更大的) sad sadder(比较悲伤的;更悲伤的)
(5)部分双音节形容词及三音节以上的形容词,只需在其前加more便构成比较级。(注意:more后的形容词须用原级。)
原级 比较级 原级 比较级
beautiful more beautiful(比较美丽的,更美丽的) comfortable more comfortable,比较舒适的;更舒适的)
(6)不规则变化形式,须一一记忆。
原级 比较级 原级、 比较级
many/much more(比较多的;更多的) good/well better(比较好的;更好的)
bad worse(比较坏的,更坏的) little less(比较少的;更少的)
比较级句型:对象A+动词+比较级(有时加名词)+than+对象B(意为“A比B……”)。
John is taller than Mary. 约翰比玛丽高。
We are happier than they are/them. 我们比他们快乐。
He is shorter than I am/me. 他比我矮。
Mary is more beautiful than Ann. 玛丽比安漂亮。
【注意】(1)这种句型中的动词不一定是be,也可以是一般动词;
(2)比较级之后可视需要加名词。
John has more books than Mary. 约翰拥有的书比玛丽多。
2. 形容词最高级的构成:
(1)通常只在形容词的原级后加上-est即可。
原 级 比较级 最高级
cold colder coldest(最冷的)
young younger youngest(最年轻的)
fast faster fastest(最快的;最快地)
cheap cheaper cheapest(最便宜的)
(2)原形容词词尾是字母e时,则只在形容词词尾加-st。
原 级 比较级 最高级
large larger largest(最大的)
nice nicer nicest(最好的)
(3)原形容词词尾是“辅音字母+y”时,则先去掉字母y,再加-iest。
原 级 比较级 最高级
dry drier driest(最干的)
easy easier easiest(最容易的)
pretty prettier prettiest(最美丽的)
(4)原形容词词尾的三个字母是“辅元辅”结构时,则要双写词末辅音字母,再加-est。
原 级 比较级 最高级
big bigger biggest(最大的)
hot hotter hottest(最热的)
thin thinner thinnest(最瘦的)
wet wetter wettest(最潮湿的)
(5)部分双音节及三音节以上的形容词,在其前加most。
原 级 比较级 最高级
beautiful more beautiful most beautiful(最漂亮的)
comfortable more comfortable most comfortable(最舒适的)
difficult more difficult most difficult(最困难的)
expensive more expensive most expensive(最昂贵的)
(6)不规则变化形式,须一一记忆。
原 级 比较级 最高级
bad worse worst(最差的)
good/well better best(最佳的)
many/much more most(最多的)
【注意】 形容词最高级前须加the。
形容词最高级的常见句型是:主语十动词+the+形容词最高级(+in/on/at...+群体)。
Tom is the best student in class. 汤姆是班级里最优秀的学生。
They are the most expensive. 它们是价钱最贵的。
Which watch is the cheapest 哪块手表最便宜?
【注意】 形容词最高级的用法并不仅限于上述句型。
The largest one is the cheapest. 最大的那个是最便宜的。
The oldest student in her class is 73 years old. 她班上年纪最大的学生73岁。
Can you give me the prettiest dress 你能把最漂亮的连衣裙给我吗?
Jane has the longest hair. 简的头发最长。
3. 人称代词与物主代词列表如下:
主格 宾格 形容词性物主代词 名词性物主代词
第一人称单数形式 I me my mine
第二人称单数形式 you you your yours
第三人称单数形式 he she it him her it his her its his hers its
第一人称复数形式 we us our ours
第二人称复数形式 you you your yours
第三人称复数形式 they them their theirs
(1)名词性物主代词的句法功能
作主语:May I use your pen Yours works better. 我可以用一下你的钢笔吗?你的更好用。
作宾语:I love my motherland as much as you love yours. 我和你一样爱自己的祖国。
作介词宾语:You should interpret what I said in my sense of the word, not in yours. 你应当按我所用的词义去解释我说的话,而不能按你自己的意义去解释。
作主语补语:The red scarf is hers. 这个红色的围巾是她的。
(2)名词性物主代词=形容词性物主代词+名词
为避免重复使用名词,有时可用名词性物主代词来代替“形容词性物主代词+名词”的结构。
My bag is yellow, her bag is red, his bag is blue and your bag is pink. 我的包是黄色的,她的(包)是红色,他的(包)是蓝色,而你的(包)是粉红色。
为避免重复使用bag,上例可改写成My bag is yellow, hers is red, his is blue and yours is pink.
·模块十 Grammar10:When的用法
★When的用法
(一)作为副词,它有以下的用法:
1. 作为疑问副词,引导特殊疑问句,意为“什么时候;何时”,例如:
(1) When will they come back (2)What time will they come back
回答when引导的从句,不一定指出具体的时间点。如回答句(1)可用tomorrow, next month等。
2. 作连接副词,引导名词性从句或不定式,意为“什么时候”。从句使用陈述句语序,时态根据实际情况而定。
Have you decided when to go sightseeing 你们已经决定什么时候去郊游了吗?(when引导不定式结构)
(二)作为从属连词,引导状语从句,表示多种语法意义:
表示时间,意为“当……时,在……的时候”。
A. 在时间、条件等状语从句里,用一般现在时表示将来时,当需要表达将来完成的意义时,必须使用现在完成时来代替。如:
When you see him, please say hello to him. 见到他时,代我问他好。
B. 表示过去发生的事情,在when引导的时间状语从句的主从复合句中,动作发生在先的用过去完成时,在后的用过去时。如:
When I was in Japan, I bought some beautiful pearls. 我在日本时,买了一些漂亮的珍珠。
★No ball games. 禁止球类游戏。
除了使用祈使句及带有情态动词的句子表示不同的规则之外,我们也可以使用no来表示禁止某项活动的规则,no后一般可加名词或动词ing形式。本例中的句子也相当于Don't play ball games!或We mustn't play ball games here!。使用no的句子表达各类规则时显得更为简练。
No U-turn!禁止调头!
No parking here!此处禁止停车!
1.They took a trip to Paris and enjoyed ________ very much.
A.they B.their C.them D.themselves
2.— The girls can clean their room by ________.
— They are all good girls.
A.they B.their C.them D.themselves
3.—I’ll have a tennis game tomorrow. I’m a little bit nervous.
—Believe in ________. You’re the best in our club.
A.herself B.myself C.yourself D.himself
4.—Are these shirts Gina’s
—No, they aren’t. These are black, but ________ are blue.
A.his B.hers C.theirs D.mine
5.—Sally, there is a pencil on the floor. Is it yours
—Oh…yes. It’s ________. Thank you.
A.his B.hers C.yours D.mine
6.—Lily, is this your bicycle
—Yes, it’s ________.
A.my B.me C.mine D.hers
7.—Is this book ________
—No, it is ________ book.
A.her; mine B.her; me C.hers; my D.hers; mine
8.Cathy is one of ______ in her school.
A.most beautiful girls B.the most beautiful girls
C.most beautiful girl D.the most beautiful girl
9.Bella ________ Nanjing next week.
A.visit B.visited C.visits D.is going to visit
10.— Linda, do you want to watch a film with me this evening
— Yes. But I need to finish my homework first and then I ________ you at the cinema.
A.meet B.don’t meet C.will meet D.won’t meet
11.There __________ a new film in the local cinema this weekend. Why not __________ your friends to see it
A.is going to be; invite B.is going to have; invite
C.is going to be; to invite D.is going to have; to invite
12.It is important for us ________ English well.
A.learn B.learning C.learned D.to learn
13.It’s not easy for Mr. Black ________ his students English well.
A.teach B.teaches C.teaching D.to teach
14.—It usually takes Lisa two hours ________ the violin every day.
—she needs to practice more for it.
A.play B.plays C.playing D.to play
15.________ you can use your dictionary, you will learn English better.
A.If B.Unless C.Though D.Before
16.—What are you thinking about
—________. I’m just looking at the sky.
A.Everything B.Nothing C.Anything D.Something
17.I will help you, so you ________worry about it.
A.don’t need B.needn’t to C.not need D.needn’t
18.The new software can help us call a taxi immediately, so we ________wait too long.
A.needn’t to B.need C.don’t need to D.not need to
19.—Must I stay here with you
—No, you ________. Just do your own business.
A.mustn’t B.needn’t C.can’t D.may not
20.My parents and I ________ in that old house since I was born.
A.live B.lived C.have lived D.has lived
21.—I ________ up at 5 am this morning, so I am very sleepy now.
—Take good care of ________.
A.wake; you B.woke; yourself C.wake; yours D.woke; yourselves
22.When times are difficult, tell____________ that pain is part of growing.
A.herself B.myself C.yourself D.himself
23.—Excuse me. Does this teacher teach ________ English
—No, ________ is over there under the tree.
A.their; theirs B.their; their C.them; theirs D.them; their
24.— What do you think of the song in the film Titanic
— I think it is one of ________ movie songs I have seen.
A.the most beautiful B.most beautiful C.more beautiful D.much more
beautiful
25.Linda, one of ________ in our class, is never late for school.
A.best students B.the best students C.best student D.the best student
26.Shanghai is one of ________ in China.
A.the big cities B.the bigger city C.the bigger cities D.the biggest cities
27.You’re not good at ________. You should read ________ books.
A.writing; more B.write; much more C.write; much D.writing; much
28.What a good idea! In this way, we can use ________ time to finish ________ work.
A.less; less B.more; fewer C.less; more D.fewer; more
29.There will be ___________ cars in the future.
A.many B.much C.more D.most
30.________ is better worth my respect than Yuan Longping. He is a great scientist.
A.Somebody B.Anybody C.Nobody D.Everybody
31.I want to know _________ the book. Could you help me
A.many about B.more about C.much of D.lot of
32.Try to sing ______ English songs, and you will find it interesting to learn English.
A.more B.much C.little D.most
33.If she ________ to Beijing tomorrow, I ________ with her.
A.goes, go B.will go, goes C.goes, will go D.go, will go
34.—I hear there ________ a sports meeting in our school.
—Yes, you are right.
A.are going to be B.is going to be C.is D.is going to have
35.My sister is coming to my home today. She ________with me for a week.
A.stay B.stayed C.is staying D.will stay
36.—I don’t think robots ________ the place of teachers fifty years from now.
—A science professor ________ us a lecture on robots this afternoon. You may ask him the question after the lecture.
A.will take; gives B.are going to take; gives C.will take; is giving D.are going to take; is giving
37.—Hi, Mike. Are you free tomorrow Mr. Zhang ________ a talk on the future cities.
—Sounds great! I think we can learn a lot from his talk. See you there.
A.give B.gives C.is giving D.will give
38.— ________ your brother _________ a magazine from the library
— Yes.
A.Are; going to borrow B.Is; going to borrow
C.Is; going to borrows D.Are; going to borrows
39.Tomorrow he __________ a kite in the open air first, and then ___________ boating in the park.
A.will fly; will go B.will fly; goes
C.is going to fly; will goes D.is going to fly; goes
40.Mike is cleaning his bike now. He ________ it to the park with his friends.
A.rides B.will ride C.riding D.ride
41.You’d better text her first. She ________ angry if you ________ by her house suddenly tomorrow.
A.may be; stop B.may be; will stop C.maybe; stop D.maybe; will stop
42.There a test tomorrow.
A.is B.will be C.will have D.have
43.Where __________ you __________ have a meeting tomorrow
A.do; go B.will; go C.are; go D.are; going to
44.Look at the black clouds. I think it ________ soon.
A.will rain B.is going to rain C.to rain D.is raining
45.A: Do you like your Chinese teacher
B: No, she always makes us ________ a lot of homework.
A.to do B.do C.does D.doing
46.Her moving words make me ________.
A.to cry B.crying
C.will cry D.cry
47.Books give us knowledge and make us ________ happy.
A.feeling B.feel C.to feel D.felt
48.Reading books ________ me ________ great.
A.make; feel B.makes; to feel C.makes; feel D.make; to feel
49.All the children like Mr. White very much because he often makes them________.
A.laughed B.laugh C.laughing D.to laugh
50.His boss made him ________ twelve hours a day in the past.
A.work B.worked C.working D.to work
51.The present makes me ________ my mother.
A.think over B.thinking over C.think of D.thinking of
52.I’m waiting for my friend. ________, I will go shopping alone (独自).
A.If she comes B.If she will come C.If she doesn’t come D.If she came
53.The teacher made the students ________ a lot of homework.
A.do B.did C.to do D.doing
54.It’s not difficult for some people ________ friends in a new school.
A.make B.making C.to make D.make
55.It’s difficult for me ________ the work in such a short time.
A.to finish B.finish C.finishing D.finishes
56.It’s very kind ________ you to help me.
A.for B.to C.of D.with
57.In the future, I think it won’t be difficult for us ________ all over the world.
A.to travel B.travels C.travel D.travelling
58.It only ________ him 20 minutes ________ to his office yesterday.
A.takes; to drive B.took; drive
C.takes; drive D.took; to drive
59.It’s important ________ us ________ to the teachers carefully in class.
A.of; to listen B.of; listening
C.for; to listen D.for; listening
60.During the break my friend Susan asked me ________.
A.what did I want to have for lunch B.what is wrong with my left leg
C.if the moon moved around the earth D.if the USA was founded in 1776
61.________ they are twins, they don’t look the same.
A.Though B.Because C.If D.As long as
62.________ English is difficult for Tom, he never gives up.
A.So B.Although C.And D.But
63.________ it was very hot inside, John didn’t turn on the air conditioner.
A.If B./ C.Although D.Because
64.________ the hut is old and small, it’s warm and comfortable.
A.Because B.But
C.So D.Although
65.Mr. Wang is always the first one to be in the office _______ he lives far from his company.
A.although B.because C.when D.as
66._______ it was hot outside, Tom didn’t turn on the air-conditioner.
A.Although B.If C.Because D.When
67.________ my grandpa is over 80 years old, he still looks strong and healthy.
A.Although B.Because C.Unless D.If
68.________ the fisherman lived a poor life, he was very happy every day.
A.Because B.So C.But D.Although
69.________ Jeff is busy with work, ________ he never gives up studying.
A.Although; / B.But; / C.Though; but D.But; although
70.________ of us tried to solve the maths problem, but ________ of us was able to do it.
A.Everyone; no one B.Everyone; none C.Each; no one D.Each; none
71.—Which shirt do you like better, the blue one or the white one
—I’ll take ____________. They are expensive and out of fashion.
A.neither B.either C.none D.both
72.Mike has two cats. One is black and ________ is white.
A.other B.the other C.others D.the others
73.—Must I wash my clothes today
—I’m afraid you ________. You should learn to do something by yourself.
A.need B.have to C.can D.could
74.—Mom, I want to play football.
—Sorry, Jack. Not now, but you ________ play it on weekends.
A.have to B.must C.need D.can
75.—Must I stay at home for dinner
—No, you ________. You can go out with your friends.
A.can’t B.needn’t C.shouldn’t D.may not
76.— Must I clean the classroom now
— No, you _______.
A.can’t B.may not C.mustn’t D.needn’t
77.Please bring your schoolbag to school if it ________ tomorrow.
A.won’t rain B.doesn’t rain C.isn’t raining D.didn’t rain
78.I will get everything ready for Bill’s birthday party. You ________ buy anything.
A.can’t B.mustn’t C.couldn’t D.needn’t
79.—Must I clean all the plates after dinner
—No, you ________. But you ________ clean them before seven thirty this evening.
A.mustn’t; must B.needn’t; must C.can’t; must D.don’t have to; may
80.You ________ buy anything else. We have got everything ready for your dinner.
A.don’t need to B.needn’t to C.don’t need D.need
81.—________ I swim here
—I’m sorry. Children ________ swim alone here. It’s very dangerous.
A.Must; can’t B.May; have not
C.Can; mustn’t D.Can; needn’t
82.Jack ________ any help. He can do it by himself.
A.needs not B.needn’t
C.doesn’t need D.needn’t to
83.Mr. Wang ________ in Hangzhou since he left the army.
A.lives B.lived C.has lived D.will live
84.If it ________ heavily tomorrow, we ________ at late.
A.will snow, will stay B.snows, will stay C.will snow, stay D.snows, stay
85.My father and I ________ to England before.
A.have been B.went C.have gone D.go
86.________ you ever ________ to Beijing
A.Do; go B.Did; go C.Have; gone D.Have; been
87.Look, the wind ________ now. Let’s go out to play.
A.is stopping B.has stopped C.will stop D.stopped
88.—Where is your sales manager, Jessica
—She’s not here. She _______ to Beijing to attend a meeting. She left this morning.
A.went B.goes C.has gone D.has been
89.My uncle went to Australia last year. We haven’t seen him ________.
A.since almost a year B.from almost a year on
C.after almost a year D.since almost a year ago
90.—How long can I ________ your CD player
—For two weeks.
A.lend B.borrow C.get D.keep
91.—Who teaches ________ English
—Nobody. I teach ________.
A.your; myself B.your; me C.you; myself D.you; me
92.—Shall we invite Mr. White to our birthday party
—That will be nice if you ________.
A.shall B.do C.will do D.are
93.If it ________ tomorrow, we’ll go to visit Sheshan State Resort.
A.won’t rain B.hasn’t rained C.doesn’t rain D.didn’t rain
94.If it ________ tomorrow, we’ll go roller-skating.
A.isn’t rain B.won’t rain C.doesn’t rain D.didn’t rain
95.________ my grandmother is 72, she is strong enough to grow and sell vegetables every day.
A.Since B.Because C.So D.Though
96.This picture isn’t beautiful. Could you show me _________ one
A.other B.the other C.another D.others
97.Susan’s sister ________ the MP3 for two years.
A.has had B.has bought C.has borrowed D.has lent
98.Angel isn’t here now. She ________ the library.
A.has been to B.went to C.has gone to D.goes to
99.Several new members have come into the club _______ 2017.
A.since B.for C.in D.at
100.My elder brother ________ a soldier for two years.
A.becomes B.has become C.became D.has been
参考答案:
1.D
【详解】句意:他们去巴黎旅行,玩得很开心。
考查人称代词。they他们,人称代词主格;their他们的,形容词性物主代词;them他们,人称代词宾格;themselves他们自己,反身代词。enjoy+反身代词“玩得开心”,动词短语,故选D。
2.D
【详解】句意:——女孩们可以自己打扫房间。——她们都是好女孩。
考查代词辨析。they她们,主格;their她们的,形容词性物主代词;them她们,宾格;themselves她们自己,反身代词。by oneself意为“单独地,靠自己地”,所以此处应用反身代词themselves,故选D。
3.C
【详解】句意:——我明天有一个网球比赛。我有点紧张。——相信自己。你是我们俱乐部最好的。
考查反身代词。herself她自己;myself我自己;yourself你自己;himself他自己。根据“Believe in ... You’re the best in our club.”可知,相信你自己,你是俱乐部最好的。故选C。
4.B
【详解】句意:——这些衬衫是吉娜的吗?——不,它们不是。它们是黑色的,但她的是蓝色的。
考查代词辨析。his他的;hers她的;theirs他们的;mine我的。根据“Are these shirts Gina’s ”和“These are black, but ... are blue.”可知,此处指吉娜的衬衫是蓝色的,用hers。故选B。
5.D
【详解】句意:——Sally,地板上有一支铅笔。它是你的吗?——哦……是的。它是我的。谢谢你。
考查代词辨析。his他的;hers她的;yours你的;mine我的。根据“Is it yours”以及“yes.”可知此处表示铅笔是“我的”。故选D。
6.C
【详解】句意:——莉莉,这是你的自行车吗?——是的,它是我的。
考查代词辨析。my我的,形容词性物主代词;me我,人称代词宾格;mine我的,名词性物主代词;hers她的,名词性物主代词。根据“Lily, is this your bicycle ”可知答句中要回答是“我的自行车”,用mine。故选
C。
7.C
【详解】句意:——这本书是她的吗?——不,它是我的书。
考查物主代词。her她的,形容词性物主代词;hers她的,名词性物主代词;my我的,形容词性物主代词;mine我的,名词性物主代词;me人称代词的宾格。根据句子结构可知,第一空后没有名词,则需要用名词性物主代词hers,指代“她的书”;第二空要用形容词性物主代词my,作定语,修饰名词book。故选C。
8.B
【详解】句意:凯茜是学校里最漂亮的女孩之一。
考查形容词最高级用法。根据“one of the+形容词最高级+可数名词复数”,可知“most beautiful”前面要有“the”,girl是可数名词,要使用其复数形式,故选B。
9.D
【详解】句意:Bella下周要去参观南京。
考查动词时态。根据“next week”可知,此处用一般将来时be going to do的结构,故选D。
10.C
【详解】句意:——Linda,今晚你想要和我看电影吗?——是的。但是我需要先完成作业,然后在电影院和你见面。
考查一般将来时。根据“Yes”可知Linda同意一起看电影,而由“I need to finish my homework first”和“then”可知此处应用一般将来时,其谓语结构为“will+do”,故选C。
11.A
【详解】句意:这个周末当地电影院将上映一部新电影。为什么不邀请你的朋友去看呢?
考查一般将来时和非谓语动词。there be与一般将来时连用时,结构为there is/are going to be/there will be,排除BD选项;再根据why not do sth.“为什么不做某事”可知,动词应用原形。故选A。
12.D
【详解】句意:学好英语对我们来说很重要。
考查非谓语动词。It is adj. for sb. to do sth.“做某事对某人来说是……的”,It作形式主语,动词不定式作真正主语。故选D。
13.D
【详解】句意:布莱克老师教他的学生们学好英语是不容易的。
考查非谓语动词。根据“It’s not easy for Mr. Black”可知,It’s+形容词+for sb to do sth“对某人来说做某事是怎么样的”,是固定句型。故选D。
14.D
【详解】句意:——丽莎每天通常要花两个小时拉小提琴。——她需要多练习。
考查固定搭配。It takes sb. some time to do sth. 是固定搭配,意为“某人花多长时间做某事”,空处用不定式形式,故选D。
15.A
【详解】句意:如果你能使用字典,你会学英语学得更好。
考查从属连词辨析。If如果;Unless除非;Though虽然;Before在……之前。根据“…you can use your dictionary, you will learn English better.”可知,此处空后为条件,且为肯定条件,使用if引导条件状语从句,故选A。
16.B
【详解】句意:——你正在想什么?——没什么。我只是正在看天空。
考查代词辨析。everything一切;nothing没什么;anything任何事;something某事。根据“I’m just looking at the sky.”可知应是没看什么,故选B。
17.D
【详解】句意:我会帮助你的,因此你不需要担心它。
考查情态动词。need可以作实意动词,常用于need to do sth.“需要做某事”,否定形式应用助动词do的形式构成;need也可以作情态动词,后跟动词原形,否定形式直接在need后加not。A选项缺少to;B选项多了to;C选项形式错误。故选D。
18.C
【详解】句意:这款新的软件能帮助我们立刻打到出租车,因此我们不需要等太长时间。
考查need的用法。need作情态动词,其否定形式为needn’t;而need作实意动词的时候,常用短语为need to do,否定形式为don’t need to。本题中只有选项C符合要求,故选 C。
19.B
【详解】句意:——我必须和你待在这里吗?——不,你不必。做你自己的事吧。
考查情态动词。mustn’t禁止;needn’t不必;can’t不能;may not可能不。根据“Must I...”可知其否定回答为No, I needn’t。故选B。
20.C
【详解】句意:自从我出生以来,我的父母和我一直住在那所老房子里。
考查动词的时态。根据“since I was born”可知,应该用现在完成时,主语“My parents and I”是复数,助动词用have。故选C。
21.B
【详解】句意:——我今天早晨5点起床的,所以我现在感觉很困。——照顾好自己。
考查时态和反身代词。根据this morning可知,描述发生过的事,用一般过去时,排除A和C;take care of oneself表示“照顾自己”,说话者是单数。故选B。
22.C
【详解】句意:遇到困难时,告诉你自己痛苦是成长的一部分。
考查反身代词。herself她自己;myself我自己;yourself你自己;himself他自己。根据“tell ... that pain is part of growing.”是祈使句,省略的是第二人称you,因此是告诉你自己。故选C。
23.C
【详解】句意:——打扰一下。这个老师教他们英语吗?——不,他们的在那边树下。
考查代词词义辨析。their他们的,形容词性物主代词;theirs他们的,名词性物主代词;them他们,宾格。第一空考查teach sb. sth.表示“教某人某事”,所以此处应用人称代词宾格;第二空应用名词性物主代词作主语。故选C。
24.A
【详解】句意:——您如何看待电影《泰坦尼克号》中的歌曲?——我认为这是我看过的最美的电影歌曲之一。
考查形容词最高级。短语one of the+最高级+可数名词复数表示“最……的……之一”,选项A符合该结构。故选A。
25.B
【详解】句意:琳达,我们班里最好的学生之一,上学从来不迟到。
考查形容词最高级。one of the+形容词最高级+名词复数+范围:表示“最……之一”,B选项是形容词最高级,且前面有定冠词the,后接可数名词复数,故选B。
26.D
【详解】句意:上海是中国最大的城市之一。
考查形容词最高级和名词复数。“one of+the+形容词最高级+可数名词复数”,表示“最……的……之一”,此空应是the biggest cities。故选D。
27.A
【详解】句意:你不擅长写作。你应该多读书。
考查非谓语动词和比较级。第一个空是:be good at doing sth.意为“擅长做某事”;much修饰不可数名词;more修饰不可数名词和可数名词复数,more books意为“更多的书”。故选A。
28.C
【详解】句意:非常好的想法!这样我们就可以用更少的时间完成更多的工作。
考查形容词比较级辨析。less更少,little的比较级,后面接不可数名词;more更多,much或many的比较级,后面接复数名词或不可数名词;fewer更少,few的比较级。time是不可数名词;work是不可数名词,根据“What a good idea”可知,应该是用更少的时间完成更多的工作是个好主意,故选C。
29.C
【详解】句意:将来会有更多的汽车。
考查比较级。many许多,修饰可数名词;much许多,修饰不可数名词;more更多;most最多。根据“There will be...cars in the future.”可知此处暗含比较,把将来和现在相比,应用比较级,故选C。
30.C
【详解】句意:没有人比袁隆平更值得我尊敬。他是一位伟大的科学家。
考查不定代词。Somebody某人;Anybody任何人;Nobody没有人;Everybody人人。根据“He is a great scientist.”可知,袁隆平是伟大的科学家,没有人比他更值得我尊敬,“否定+比较级”表最高级。故选C。
31.B
【详解】句意:我想了解更多关于这本书的信息。你能帮我吗?
考查比较级的用法。many很多;more更多;much很多;lot of错误形式。根据“I want to know...the book. Could you help me”可知是想了解更多信息,不能用many修饰,排除A;此处表示“关于这本书”,用介词about,排除C。故选B。
32.A
【详解】句意:尝试唱更多的英文歌,你就会发现学习英语是有趣的。
考查形容词比较级。more更多的;much许多,后接不可数名词;little几乎没有;most最多的。根据“Try to sing... English songs, and you will find it interesting to learn English.”可知,空后是名词复数,排除B、C选项;发现英语有趣,应是唱更多的英文歌,将发现英语有趣前后的行为进行对比,空处应用比较级more。故选A。
33.C
【详解】句意:如果她明天去北京,我将会和她一起去。
考查条件状语从句。if引导的条件状语从句,主将从现;she是第三人称,谓语动词用三单,故选C。
34.B
【详解】句意:——我听说我们学校将举行运动会。——是的,你是对的。
考查there be句型的一般将来时。there are going to be将有,一般将来时;there is going to be将有,一般将
来时;there is有,一般现在时;there is going to have无此用法。根据“hear”可知,此处用一般将来时;“a sports meeting”单数做主语,要用there is going to be。故选B。
35.D
【详解】句意:我妹妹今天要来我家。她将和我待一个星期。
考查一般将来时。根据“My sister is coming to my home today.”可知,此处是指今天妹妹要来“我”家,将陪伴“我”一个星期,时态应用一般将来时,其结构为will+动词原形。故选D。
36.C
【详解】句意:——我认为五十年后机器人不会取代教师。——今天下午一位科学教授给我们做了一次关于机器人的讲座。你可以在讲座结束后问他这个问题。
考查动词。“will”通常用于表达说话人的意图、决定或信念,强调的是主观意愿或未来的确定性,因此第一空用will;第二空时间状语是this afternoon,还未发生,因此可以用be+doing的形式表将来,故选C。
37.D
【详解】句意:——嗨,迈克。你明天有空吗?张老师将做一个关于未来城市的演讲。——听上去太棒了!我认为我们可以从他的演讲中学到很多东西。到时见。
考查一般将来时。根据“tomorrow”可知,时态是一般将来时:will+动词原形。故选D。
38.B
【详解】句意:——你哥哥打算从图书馆借本杂志吗?——是的。
考查时态。be going to do sth.“打算做某事”;主语“your brother”单数,用be动词单数is。故选B。
39.A
【详解】句意:明天他将先在户外放风筝,然后去公园划船。
考查一般将来时态。will fly/is going to fly一般将来时;will go一般将来时;goes一般现在时三单形式。根据Tomorrow可知,时态为一般将来时,and连接前后语法时态保持一致。故选A。
40.B
【详解】句意:迈克正在清洗他的自行车。他将和他的朋友们骑着它去公园。
考查时态。根据“Mike is cleaning his bike now.”可知现在正在洗自行车,由此推出骑自行车去公园是将来发生的事情,用一般将来时will ride。故选B。
41.A
【详解】句意:你最好先给她发个短信。如果你明天突然去她家,她可能会生气的。
考查情态动词和动词时态。may be可能,是“情态动词+be”的结构,可以作谓语;maybe可能,是副词,不能作谓语。第一空需要谓语动词,排除CD;if引导的条件状语从句,遵循主将从现原则,从句用一般
现在时,故选A。
42.B
【详解】句意:明天将进行测试。
考查there be句型。there is有,一般现在时;there will be将会有,一般将来时;there will have无此用法;there have无此用法。根据句中的“tomorrow”,可知时态是一般将来时,故选B.
43.D
【详解】句意:你明天打算在哪里开会?
考查时态。根据“have a meeting tomorrow”可知,此处为“一般将来时”,结构为be going to do,动词“have”前要有to,故选D。
44.B
【详解】句意:看那些乌云。我认为很快就要下雨了。
考查一般将来时。根据“soon”可知该句时态是一般将来时。再结合“Look at the black clouds”可知此处是表示一种迹象,表明即将发生的事情,一般用be going to+动词原形结构。故选B。
45.B
【详解】句意:A:你喜欢你的中文老师吗?B:不,她总是让我们做很多功课。
考查非谓语动词。短语make sb do sth表示“让某人做某事”。故选B。
46.D
【详解】句意:她感人的话使我哭了。
考查动词短语。to cry哭,cry的不定式形式;crying哭,cry的现在分词形式;will cry哭,cry的将来时;cry哭,动词原形。make sb do sth“使某人做某事”,用省略to的不定式作宾补,故填cry。故选D。
47.B
【详解】句意:书籍给我们知识,使我们感到快乐。
考查非谓语动词。make sb do sth“使某人做某事”,省略to的动词不定式作宾补,故选B。
48.C
【详解】句意:读书使我感觉很好。
本题考查使役动词make的用法。短语make sb feel...意为“使某人感到……”。本句为现在分词“Reading books”做主语,所以空格处的谓语动词要用其单数形式,即makes。第二空要用动词原形形式,即feel。故选C。
49.B
【详解】句意:所有的孩子都非常喜欢怀特先生,因为他常常让他们笑。
考查固定句型。make sb do sth“让某人做某事”。所以此处应用动词原形laugh。故选B。
50.A
【详解】句意:他的老板过去让他每天工作12个小时。
考查非谓语动词。make sb do sth“使某人做某事”,省略to的动词不定式作宾补,故选A。
51.C
【详解】句意:这份礼物使我想起了我的母亲。
考查动词短语和非谓语。think over仔细考虑;think of想起。根据“The present makes me...my mother.”可知,此处表达想起了我的母亲,空处应填think of,make sb do sth“使某人做某事”,用省略to的不定式。故选C。
52.C
【详解】句意:我正在等我的朋友。如果她不来,我将独自去购物。
考查if引导的条件状语从句。if引导的条件状语从句遵循主将从现原则,排除BD;if从句表示肯定的条件,将独自去购物的肯定条件是“如果她不来”,排除A。故选C。
53.A
【详解】句意:老师给学生布置了很多家庭作业。
考查动词形式。do做,原形;did过去式;to do不定式;doing动名词。make sb. do sth.“让某人做某事”,故选A。
54.C
【详解】句意:对一些人来说,在新学校交朋友并不困难。
考查不定式用法。It is adj for sb to do sth表示“做某事对某人来讲是……”,it作形式主语,不定式作真正的主语。故选C。
55.A
【详解】句意:在这么短的时间内完成这项工作对我来说是困难的。
考查非谓语动词。根据“It’s difficult for me ... the work in such a short time.”可知,it is+形容词+for sb.+to do sth.表示“做某事对某人而言是……的”,不定式作真正的主语。故选A。
56.C
【详解】句意:你/你们帮助我真是太好了。
考查it的特殊句型和介词辨析。for为了;to到;of……的;with和。根据语境可知,形容词kind“友好的”用来表示不定式行为者的性格品德,故用it特殊句型“It’s+adj+of sb to do sth.”表示“某人做某事真是……”,空处需填介词,介词of“……的”符合语境。故选C。
57.A
【详解】句意:在将来,我认为对我们来说去环游世界那将不是困难。
考查it的固定句型。由“it won’t be difficult for us…”可知,考的是it的固定句型:it+be+adj.+for sb.+to do sth.“对某人来说做某事怎么样”,应用动词不定式。故选A。
58.D
【详解】句意:昨天他开车去办公室只花了20分钟。
考查时态以及非谓语动词。it takes/took sb. time to do sth.“做某事花费某人多长时间”,排除BC;根据“yesterday”可知句子用一般过去时,动词用took。故选D。
59.C
【详解】句意:在课堂上认真听老师讲课对我们来说很重要。
考查it的固定句型。“It is+形容词+for sb.+to do sth.”意为“对某人来说做某事怎么样”,这种结构中的形容词常与事物的特征有关;“It is+形容词+of sb.+to do sth.”表示“某人做某事怎样”,这种结构中的形容词常与人的性格特点有关。important是形容“课上认真听老师讲课”这件事,所以第一空用for。在这个两个句型中,it是形式主语,动词不定式是真正主语,所以第二空用to listen。故选C。
60.D
【详解】句意:课间休息时,我的朋友苏珊问我美国是否成立于1776年。
考查宾语从句。句子是宾语从句,用陈述语序,排除A;根据“asked”可知主句是过去时,从句应用过去的某个时态,排除B;选项C描述的是客观事实,故从句应用现在时,排除C。故选D。
61.A
【详解】句意:虽然他们是双胞胎,但长得不一样。
考查连词辨析。Though虽然;Because因为;If如果;As long as只要。根据“they are twins, they don’t look the same.”可知,前后两句是让步关系,因此用连词“Though”。故选A。
62.B
【详解】句意:尽管英语对Tom来说很难,但他从不放弃。
考查连词辨析。so所以;although尽管;and和;but但是。根据语境可知,尽管英语对Tom来说很难,但他从未放弃,此处应用although引导让步状语从句。故选B。
63.C
【详解】句意:虽然里面很热,约翰却没有开空调。
考查从属连词。If 如果;Although虽然,尽管;Because因为。由句意可知,“it was very hot inside”和“didn’t turn on the air conditioner”有让步关系,所以用although引导让步状语从句。故选C。
64.D
【详解】句意:虽然这个小屋又旧又小,但是它温暖舒适。
考查连词辨析。Because因为;But但是;So所以;Although虽然。根据“the hut is old and small, it’s warm and comfortable.”可知,句子前后是让步关系,因此用although引导状语从句。故选D。
65.A
【详解】句意:王先生虽然住得离公司很远,但他总是第一个到办公室。
考查连词辨析。although尽管,虽然;because因为;when当……时候;as因为。根据“Mr. Wang is always the first one to be in the office ... he lives far from his company.”可知,句子前后是让步关系,用although引导让步状语从句。故选A。
66.A
【详解】句意:虽然外面很热,但汤姆没有打开空调。
考查从属连词辨析。Although虽然,尽管;If如果;Because因为;When当……时候。“it was very hot outside”和“Tom didn’t turn on the air-conditioner”之间有让步关系,所以用although引导让步状语从句。故选A。
67.A
【详解】句意:虽然我爷爷已经80多岁了,但他看起来仍然很强壮很健康。
考查连词辨析。Although尽管;Because因为;Unless除非;If如果。根据“…he still looks strong and healthy.”可知,虽然爷爷年纪大了,但身体仍然强健,用although引导让步状语从句。故选A。
68.D
【详解】句意:尽管渔夫过着贫穷的生活,但他每天都很快乐。
考查连词。Because因为;So所以;But但是;Although尽管。根据“...the fisherman lived a poor life, he was very happy every day.”渔夫尽管很穷,但是很快乐。用although引导让步状语从句,故选D。
69.A
【详解】句意:虽然杰夫工作很忙,但他从不放弃学习。
考查连词辨析。Although/Though虽然、尽管,用来引导让步状语从句,不能与but连用,所以排查C、D选项;but表示转折关系,应放在“he never gives up studying.”前面,排除B选项。故选A。
70.D
【详解】句意:我们每个人都试图解决这道数学题,但没有一个人能做出来。
考查代词辨析。everyone每人;each每个;none没有;no one没有人。everyone、no one不与of搭配,第一空填each,第二空none符合句意,故选D。
71.A
【详解】句意:——你更喜欢哪件衬衫,蓝色的还是白色的? ——我两个都不要。它们又贵又过时。
考查代词辨析。neither两者都不;either两者中的任何一个;none一个也没有;both两者都。根据“They are expensive and out of fashion”可知,两个都不要,应用neither。 故选A。
72.B
【详解】句意:迈克有两只猫。一只是黑色的,另一只是白色的。
考查不定代词的辨析。other作形容词,意为“其他的、另外的”,用在名词前做定语;the other(两者中的)另一个人或事物;others另外的人或物,一般指三者或以上,表泛指;the others等于“the other +复数名词”,指某一范围内的“其他的(人或物)”。根据上文“Mike has two cats”可知,此处指的是两只猫中的“另一只”,故选B。
73.B
【详解】句意:——我今天必须洗衣服吗?——恐怕你不得不洗。你应该学会自己做一些事情。
考查情态动词辨析。need需要;have to必须、不得不;can能、会;could能、会,是can的过去式。根据空后句“You should learn to do something by yourself.”可知,空处应用have to“不得不”。故选B。
74.D
【详解】句意:——妈妈,我想要踢足球。——抱歉杰克。不是现在,但是你周末的时候可以去踢足球。
考查情态动词辨析。have to不得不;must必须;need需要;can能够,可以。现在玩不了,但是周末可以玩,这里用can表示允许。故选D。
75.B
【详解】句意:——我必须在家吃晚餐吗?——不用,你不需要。你可以和朋友出去。
考查情态动词need的用法。can’t不能;needn’t不需要;shouldn’t不应该;may not不可以。根据“You can go out with your friends.”可知,可以和朋友出去,说明不需要在家吃晚餐。故选B。
76.D
【详解】句意:—— 我现在必须打扫教室吗?—— 不,你不需要。
考查情态动词。can’t不能;may not不可以;mustn’t禁止;needn’t没有必要。“Must I do … ”的否定回答是“No, you needn’t.”或者 “No , you don’t have to.”,此句是must 开头的一般疑问句否定回答,故选D。
77.B
【详解】句意:如果明天不下雨,请把你书包带到学校来。
考查动词时态。含有if引导的条件状语从句的主从复合句中,主句用祈使句,从句用一般现在时。根据“bring your schoolbag to school if it.”可知空处应用一般现在时态。故选B。
78.D
【详解】句意:我将为比尔的生日聚会准备一切。你不需要买任何东西。
考查情态动词。can’t不能;mustn’t禁止;couldn’t不能;needn’t不需要。根据“I will get everything ready for Bill’s birthday party”可知,因为一切都会准备好,所以对方不需要买任何东西。故选D。
79.B
【详解】句意:——晚饭后我必须把所有的盘子都洗干净吗?——不,你不需要。但是你必须在今晚七点半之前把它们洗干净。
考查情态动词。mustn’t不得;must必须;needn’t不必;can’t不能;don’t have to不必;may可以。根据“Must I clean all the plates after dinner ”及“No,”可知,含情态动词must的一般疑问句,否定回答用needn’t或don’t have to,排除AC选项;再根据“But you ... clean them before seven thirty this evening.”可知,第二空表示必须在七点半之前把它们清洗干净,用must。故选B。
80.A
【详解】句意:你不需要买其他东西,我们已经为您的晚餐准备好了一切。
考查动词的用法。need作为行为动词,need to do sth“需要做某事”,否定式don’t/doesn’t/didn’t need to do sth“不需要做某事”;need作为情态动词,一般用于否定句或疑问句,needn’t do sth“不需要做某事”。空格后buy是动词,所以“不需要买”表达成don’t need to buy或needn’t buy。故选A。
81.C
【详解】句意:——我能在这里游泳吗? ——非常抱歉。孩子们禁止独自在这里游泳。这非常危险。
考查情态动词。Must必须;can’t不能;May可以,表请求;have not没有;Can可以,表请求;mustn’t禁止;needn’t不必。根据后句“I’m sorry.”可知,第一空应是表示请求的提问;再根据“It’s very dangerous.”可知,这里很危险,故推测第二空是禁止孩子们独自在这里游泳,应用mustn’t表示“禁止,不准”。故选C。
82.C
【详解】句意:杰克不需要任何帮助。他可以自己做这件事。
考查动词。need有两种词性,一种是情态动词,没有时态和三单变化,表示“需要”,其后接动词原形构成谓语;另一种是实义动词,本身充当谓语,有时态和三单变化,表示“需要”,其后接sth或to do作宾语。情态动词的否定直接在其后加not,实义动词的否定要借助助动词;根据设空处后的名词“any help”,可知此处need为实义动词,其否定要借助助动词,故选C。
83.C
【详解】句意:王先生自离开部队以来就在杭州生活。
考查现在完成时。根据“since he left the army”可知该句应用现在完成时,其结构为:have/has+过去分词。故选C。
84.B
【详解】句意:如果明天下大雪,我们将待在家里。
考查动词时态。此句中“If”意为“如果”,所以该句为if引导的条件状语从句,主句用一般将来时态,从句用一般现在时态,B选项符合,故选B。
85.A
【详解】句意:我和爸爸之前去过英国。
考查现在完成时。根据“before”可知该句谈论之前“去过某地”,应用现在完成时,谓语动词用have been to。故选A。
86.D
【详解】句意:你曾经去过北京吗?
考查现在完成时。根据“ever”可知此处询问是否曾经去过北京,句子应用现在完成时。结合语境,可知此处询问的是“去过”,人已经回来了,因此应用have been to。故选D。
87.B
【详解】句意:看,风已经停了。我们出去玩吧。
考查动词时态。根据“Lets go out to play.”判断风已经停了。这里描述过去发生的动作对现在造成了影响,时态用现在完成时,结构为:have/has+动词的过去分词。故选B。
88.C
【详解】句意:——杰西卡,你的销售经理在哪里?——她不在这里。她去北京参加会议了。她今天早上离开了。
考查现在完成时。根据“She’s not here.”可知,她不在这里,说明是“已经去了某地”,还没有回来,句子应用现在完成时,应用have gone to表示“已经去了某地”。故选C。
89.D
【详解】句意:去年我的叔叔去了澳大利亚。自从一年前我们没有见到他。
考查since现在完成时。根据横线前的句子时态为现在完成时,可知此处应是since接时间点;或since+时间段+ago。故选D。
90.D
【详解】句意:——你的CD机我可以借多久?——两周。
考查动词辨析。lend借出;borrow借进;get得到;keep保留。根据“For two weeks”可知,回答是时间段,
空处填的动词应是延续性动词,只有选项D是延续性动词。故选D。
91.C
【详解】句意:——谁教你英语?——没有人。我自学的。
考查代词辨析。your你的/你们的,形容词性物主代词;you你/你们,主格代词/宾格代词;myself我自己,反身代词;me我,宾格代词。teach sb sth“教某人……”,空一位于动词之后,需用宾格代词;teach oneself意为“自学”,主语是I,需用myself。故选C。
92.B
【详解】句意:——我们邀请怀特先生参加我们的生日聚会好吗?——如果你这样做,那就太好了。
考查动词及时态。句子是if引导的条件状语从句,应用“主将从现”的原则,从句用一般现在时,排除A/C选项,结合语境可知,此处指的是“做”,应用动词do,故选B。
93.C
【详解】句意:如果明天不下雨,我们就去佘山国家旅游度假区。
考查动词时态。根据“If it...tomorrow, we’ll go to...”可知此处是if引导的条件状语从句,需遵循主将从现的原则,因此if从句需使用一般现在时表示将来。故选C。
94.C
【详解】句意:如果明天不下雨,我们将去轮滑。
考查时态。该句为if引导的条件状语从句,句子时态遵循“主将从现”的原则,主句时态为一般将来时,从句为一般现在时,主语为it,否定句用助动词doesn’t,故选C。
95.D
【详解】句意:虽然我的祖母已经72岁了,但她仍然很强壮,可以每天种菜、卖菜。
考查连词辨析。Since自……以来;Because因为;So所以;Though尽管。“my grandmother is 72”和“she is strong enough to grow and sell vegetables every day.”之间在句意上存在让步关系,所以应用though引导让步状语从句。故选D。
96.C
【详解】句意:这幅画不漂亮。你能展示给我另一幅吗?
考查单词辨析。other其它的,形容词,后面通常接复数名词;the other另一个,通常作代词;another另一个,可作形容词,后接单数名词;others其它的,代词。根据“one”可知此处应填形容词,且one代替“picture”,为单数,故选C。
97.A
【详解】句意:苏珊的姐姐有这台MP3两年了。
考查现在完成时。buy买;borrow借入;lend借出。本句是现在完成时,当谓语动词和一段时间连用,必须是延续性动词,BCD都是短暂性动词,只有A选项符合。故选A。
98.C
【详解】句意:Angel现在不在这里。她去了图书馆。
考查动词的时态。根据“Angel isn’t here now”可知,Angel不在这里,说明她去了图书馆,应用现在完成时。has been to表示“去过(已回)”;has gone to“去了(未回)”。Angel不在说话现场,应用has gone to。故选C。
99.A
【详解】句意:自2017年以来,又有几名新成员加入了该俱乐部。
考查时间介词。since“自……以来”,后接具体的年、月、日等;for与一段时间连用;in用在年、月、季节等较长一段时间前;at用在时刻前。根据“Several new members have come into the club”可知,时态为现在完成时,现在完成时通常与“since+时间点”连用。故选A。
100.D
【详解】句意:我的哥哥已经参军两年了。
考查现在完成时和延续性动词。根据“for two years”可知时态为现在完成时,其谓语结构为“have/has+done”,而two years为时间段,所以谓语动词应用延续性动词,故选D。
·模块一 Grammar 1:条件状语从句
1. 条件状语从句
(1)主句为一般将来时,从句用一般现在时表将来。如:
I'll visit the Great Wall if it isn't windy tomorrow. 如果明天不刮风,我将去长城。
(2) “祈使句十and/or引导的结果状语从句”中,祈使句在意义上相当于一个条件状语从句。如:
Use your head, and you'll find a way. =If you use your head, you'll find a way. 动动脑筋,你就会想出办法来。
2. 介词in和on
(1) 在表示方位时,in表示在某一地区之内的某方位(属于该范围);on表示与某地的毗邻关系。如:
Taiwan is in the south-east of China. 台湾位于中国的东南部。
in表示较大的地方。如:in China, in the world
on表示在一个平面上。如:on the farm
(2) 除表示方位外,in和on还可表时间,in表示一段时间,用于年、月、世纪、四季或泛指的一天的上午、下午、晚上前。如:in the twenty-first century在21世纪,in autumn在秋天,in the morning在早上,in还可用于表示“多久之后”如:in five years
on主要用在星期几,具体某一天或某一天的早、中、晚或节日前。如:on Mid-Autumn Day在中秋节
on June 1st在6月1日
·模块二 Grammar 2:口语表达
1. So do I. /Neither do I. 我也是。/我也不。
(1) So…I表示同意对方的话语,意为“我也是”。So和I间的助动词由上下文决定。如:
-I like playing computer games. 我喜欢玩电脑游戏。
-So do I. 我也是。
-I can paint well. 我擅长画画。
-So can I. 我也是。
-I went to the cinema last night. 我昨晚去看电影了。
-So did I. 昨晚我也去看了。
【友情提示】 这里的人称并不仅限于I。
-My brother is a doctor. 我哥哥是一名医生。
-So is Mary’s. 玛丽的哥哥也是(医生)。
(2) Neither…I也是用来附和对方的话语,意为“我也不……”。与So…I不同的是,So…I的上文为肯定句,而Neither…I的上文是否定句。Neither…I中的助动词也是由上下文决定。同样这里的人称并不仅限于I。
-I don't like films about love stories. 我不喜欢看爱情电影。
-Neither do I. 我也不喜欢(看爱情电影)。
-My brother can’t play the piano. 我哥哥不会弹钢琴。
-Neither can his. 他哥哥也不会。
-I have never been to Beijing. 我从未去过北京。
-Neither has Mary. 玛丽也没去过。
(3)这两种结构的不同点是:
① “so+助动词/be动词/情态动词十主语”依附于肯定句,表示前边的肯定情况也适合后边的人,意为“我也……”,相当于“I do, too”。
② “neither+助动词/be动词/情态动词+主语”依附于否定句,表示前边的否定情况也适合后边的人,意为“我也不……”,相当于“I don't, either"。如:
Peter watched TV last night, so did Ann. 彼得昨晚看电视了,安也看了。
Mary didn't watch TV last night, neither did Jill. 玛丽昨晚没有看电视,吉尔也没看。
2. Next, turn left into Tree Road and walk along Tree Road. 然后,左转进入树路,并且沿着它走。
turn left/right表示“左/右转”。这里的动词turn表示“转向…”
这是给别人指路时常用的表达方式。
walk along是“沿着……走”的意思。介词along是“沿着”的意思。
We went for a walk along the shore. 我们沿着海岸散步。
其他用于指路的句子还有:
Turn left, Walk along Rose Street. 左转,沿着玫瑰街走。
Turn right into Rose Street and walk along. 右转进入玫瑰街并沿着走。
Walk straight ahead. 向前直走。
Take the first turning on the right. 在第一个路口右转。
Take the second turning on the left. 在第二个路口左转。
Walk to the end of the road. 这条路走到底。
Walk down the street. 沿着这条街走。
Walk up Green Road. 沿着格林路往前走。
You'll see the post office in front of you. 你会看到邮局在你的前方。
You'll see the cinema on your right. 你会看到电影院在你的右边。
·模块三 Grammar 3:现在完成时和被动语态
★现在完成时
(1)表示过去发生的或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果。如:
-Have you had your lunch yet 你吃过午饭了吗?
-Yes, I have. I've just had it. 是的,我刚吃过。(说明现在饱了。)
I have lost my pen. 我把钢笔弄丢了。(过去某时丢的,现在还没有找到。)
I have already watched the TV play. 我已经看过这部电视剧了。
-Have you found your lost pen yet 一你找到丢失的钢笔了吗?
-No. I haven't found it yet. 一不,我还没有找到。
【友情提示】 already,yet常和现在完成时连用,already用于肯定句,可放在助动词之后、过去分词之前,也可放在句末。yet用在疑问句中意为“已经”,用在否定句中表示“还”,常放在句末。
(2)表示动作或状态在过去已经开始,持续到现在,也许还要持续下去,常和for,since连用,表示持续的动作或状态多为延续性动词。如:
We have lived here since 2000.
自从2000年以来我们一直住在这里。(说明一直住在这里也许还会住下去。)
(3)现在完成时中经常使用的几个副词:
1) just意为“刚刚”,表示动作刚刚结束,常放在助动词与过去分词之间。如:
He has just come back from Beijing. 他刚从北京回来。
2) ever意为“曾经”,用于疑问句或否定句中,放在助动词与过去分词之间。如:
Have you ever been to Shanghai 你去过上海吗?
3) never意为“从来没有”,常与before连用,多放在助动词与过去分词之间。如:
I have never travelled by plane before. 我以前从来没有乘飞机旅行过。
4) before意为“以前”,指过去不确定的某个时间,总是放在句末,不受句型的限制。如:
I haven’t heard of it before. 我以前从来没有听说过这件事。
5) since+时间点,for+时间段
I have been in Beijing for two years/since two years ago. 我在北京两年了。
(4)延续性动词与非延续性动词的用法
1) 现在完成时表示动作从过去某个时候开始一直持续到现在,与一段时间连用时应注意句中的谓语动词应是延续性动词,非延续性动词不可与一段时间连用。如:
我离开这所学校已八年了。
误:I've left this school for eight years.
正:I've been away from this school for eight years.
他借用我的词典已两天了。
误:He has borrowed my dictionary for two days.
正:He has kept my dictionary for two days.
不过,在否定句中非延续性动词可与一段时间连用。如:
I haven't gone to see him for several months. 我已经好几个月没去看他了。
2) 非延续性动词与一段时间连用时可采用下述三种方法:
a. 将非延续性动词转化为延续性动词
非延续性动词 延续性动词
buy have
borrow keep
open be open
close be closed
begin/ start be on
come be here
go be away
finish be over
died be dead
catch a cold have a cold
put on wear
get up be up
wake up be awake
fall asleep be asleep
lose not have
join be(in)
leave be away from
arrive/ reach be
b. 将时间状语改为过去的时间,并用一般过去时代替现在完成时。
c. 用句型“it is十一段时间+since从句(从句中的谓语动词用非延续性动词的一般过去式)”表示。如:
It is two years since the old man died. 这个老人去世两年了。
★被动语态
一、被动语态的构成及用法
1. 被动语态的构成
(1)被动语态的基本结构为:be+动词的过去分词
(2)各种时态的主动、被动语态的结构如下表(以动词do为例):
时态 主动语态 被动语态 例句
主动语态 被动语态
一般现在时 do/does am/ is/ are+done We clean the classroom. The classroom is cleaned by bus.
一般过去时 did was/ were/+done He made the kite. The kite was made by him.
现在进行时 am/ is/ are +doing am/ is/ are+being done She is watering flowers. Flowers are being watered by her.
2. 被动语态的用法
在被动语态中,主语是动作的承受者,主要用于下列几种情况:
(1) 不知道动作的执行者是谁。如:
This watch is made in China. 这块手表是中国制造的。
(2) 没有必要指出动作的执行者是谁。如:
More trees should be planted every year. 每年都应该种更多的树。
(3) 需要强调或突出动作的承受者时。如:
Chinese is spoken by more and more people in the world. 世界上越来越多的人说汉语。(强调汉语的使用广泛)
(4) 句子的主语是动作的承受者。如:
Many houses were washed away by the flood. 许多房屋被洪水冲走了。
二、主动语态和被动语态的转换
1. 主动语态变为被动语态
(1)要将主动句里的宾语变为被动句中的主语,若主动句中的宾语是人称代词,要将宾格变成主格。
(2)把主动句中的主语变为被动句中的宾语,主格变成宾格,并由by引导。
(3)谓语动词变成相应的被动形式。
We asked him to sing an English song. (变为被动语态)→He was asked to sing an English song by us.
2. 带双宾语的谓语动词变为被动语态
谓语动词带双宾语时,既可以将间接宾语转化成主语,也可以将直接宾语转化成主语。若将间接宾语转化成主语,则保留直接宾语;若将直接宾语转化成主语,则保留间接宾语,且在被保留的间接宾语前加上介词to或for。如:
She gave me a book.(变为被动语态)
I was given a book by her.(间接宾语me变为了主语)
A book was given to me by her.(直接宾语a book变为了主语)
3. 动词短语变为被动语态
许多由不及物动词和介词、副词构成的动词短语相当于及物动词,可以有宾语,也可以有被动语态。但是动词短语是一个不可分割的整体,在变为被动语态时,不可丢掉构成动词短语的介词或副词。如:
We should speak to old men politely.(变为被动语态)
Old men should be spoken to politely.(to不可省略)
4. 带复合宾语的动词变为被动语态
宾语加上宾语补足语一起构成复合宾语。变为被动语态时,只把宾语变为被动句的主语,宾语补足语保留在原处,成为主语补足语。如:
I heard Jane playing the piano in her room.(变为被动语态)
Jane was heard playing the piano in her room.
5. 变被动语态后动词形式的选择
主动句中在感官动词see,hear,watch,feel,notice等,及使役动词let,make,have等后跟省略to的不定式,
变为被动语态时,应加上不定式符号to。如:
He makes the girl stay at home.(变为被动语态)→The girl is made to stay at home by him.
·模块四 Grammar4:动词need
1. 动词need
need可以作情态动词,这时need没有时态,人称和数的变化,多用于否定句和疑问句意为“必须”,后接动词原形。其否定形式为need not(缩略式为needn’t),意为“不必”,但need作情态动词时只能用于表达现在的时间含义。
Need I pay the whole amount now 我现在必须全部付清吗?
You needn't do it now. You can do it later.你不必现在做,稍后再做也可以。
need可以用作行为动词,意为“需要”
I'll call you if anything is needed. 要是需要什么,我就叫你。
【注意】 在need的后面接动词的-ing形式时,这个动词和句子的主语之间有逻辑上的被动关系,但这时应用主动形式表示被动,但如果在need的后面接不定式时,不定式应该使用被动形式。
He will need to be looked after. 必须让人去照料他。
Whose chair needs fixing 谁的椅子需要修理?
2. Alice, do you like the jeans with the yellow belt or the ones with the blue belt
the jeans with the yellow belt意为“配黄色腰带的牛仔裤”,with表示“带着;带有”。在此介绍一些服装的表达方法,如下:
the jeans with the blue/yellow belt配蓝色/黄色腰带的牛仔裤
the shirt with the blue/red spots带蓝点/红点的衬衫
the sweater with the short/long sleeves短袖/长袖毛衣
the T-shirt with the V-neck/round neck鸡心领/圆领T恤衫
the trousers with the checks/stripes格子/条纹长裤
·模块五 Grammar5:让步状语从句和不定代词
1. 让步状语从句
表示让步含义的从句结构,它主要有although,though等连词引导。让步状语在句中可前置,也可后置。
前置时,强调的是主句的内容;
后置时,强调的是从句的内容。
e.g. Although/though he is tired, he still finishes his work on time.
虽然他很累,但仍然按时完成了工作。
He knows what to do, although/though he is a child.
他知道该做什么,尽管他是一个孩子。
【注意】
让步状语从句中不可再使用but等并列连词,但可以用yet,still等连接副词来加强语气。
e.g. Although/Though he worked hard at Maths, yet he didn’t pass the exam.
虽然他很努力地学习数学,但仍然考试不及格。
Although/Though her father is very old, he is still working.
虽然她的父亲年迈,但他仍然坚持工作。
2. 不定代词
other; one…the other; some…others/the others…
1) other + 名词的复数形式;
e.g. Some students are playing football and other students are playing basketball.
一些学生在踢足球,另一些在打篮球。
2) one…the other…表示“一个…,另一个…”总数=2。
the other + 可数名词的复数,表示≧ 3 的人或物中剩余的全部。
the other + 数词
e.g. Some students are inside the classroom but the other students are outside the classroom.
一些学生在教室内,但另一些在教室外。
This girl is good at English. How about the other three
这个女孩擅长英语。其他三个怎么样?
3) some…others/the others… 都表示“一些…,另一些…”,前者没有固定范围,后者有一定范围内而言的。
Some people like playing badminton and others like playing volleyball.(剩余的部分)
一些人爱打羽毛球,而另一些人哎打排球。
Some students are playing badminton on the playground and the others are playing volleyball.(剩余的全部)
一些学生正在操场上打羽毛球,其他的正在打排球。
·模块六 Grammar6:含形容词的固定句型和使役动词make
1. It is+形容词+to…
It is+adj. +to do sth. 做某事…
例如:It’ s easy to learn swimming. 学游泳很简单。
It is+adj. +doing sth.
做某事很……(对话结束时使用)
例如:It was nice talking to you. 和你谈话很愉快。
It十is+adj. +for+sb. +to do sth. 对某人来说做某事真是太……了。
本句型中的形容词通常是表示客观情况的。如:easy, hard, difficult, important, necessary, impossible, interesting等。
例如:It was difficult for him to finish the work on time. 对他来说,按时完成这项工作真是太难了。
It is necessary for us to study English well.对我们来说学好英语是必要的。
2. 使役动词make
“make+宾语+宾语补足语”的这一结构用得很多,其中宾语补足语部分可以用形容词、介词短语、名词、不定式、分词等充当。
“make+宾语+形容词作宾语补足语”。例如:
We are working hard to make our country more beautiful. 我们正努力工作,使我们的国家更美丽。
“make+宾语+介词短语作宾语补足语”。例如:
Mother made her coat into my skirt. 母亲把她的外套改成裙子给我穿。
“make+宾语+名词作宾语补足语”。例如:
We made him our monitor. 我们都选他当班长。
“make十宾语十省略to的不定式作宾语补足语”,若将其改为被动语态,to须加上。例如:
The boy makes faces just to make others laugh. 这个男孩做鬼脸的目的是让其他人笑。
·模块七 Grammar7:一般将来时
一般将来时
(1)表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态,其构成:是will+动词原形,常与表示将来的时间状语连用,如tomorrow, next week, in a few days, next Sunday, in十一段时间,in 2020等。 如:
They will leave for Shanghai next week. 他们下周将去上海。
Will you be back in two days 你将在两天后回来吗?
当主语是I或we时,疑问句中一般使用shall,表示征求对方意见。如:
Where shall we meet tomorrow 明天我们在哪里会面?
(2) be going to+动词原形”表示计划、打算做某事,表示已决定的、很可能发生的事,或有某种迹象表明要发生的事。如:What are you going to do next Sunday 下周日你打算干什么?
Look at the clouds. There is going to be a storm. 看那些乌云,暴风雨就要来临了。(客观迹象)
注意:在下面几种情况下只可用shall( will)表示将来,而不可用be going to结构。
1)表示有礼貌地询问对方是否愿意或表示客气的邀请或命令时。如:
Will you please lend me your bike 请你把自行车借给我用一下好吗?
2)表示意愿时。如:
We will help him if he asks us. 如果他请我们,我们愿意帮助他。
3)表示单纯的将来,与人的主观愿望和判断无关时。如:
The sun will rise at 6:30 tomorrow morning. 明天早上太阳将在6:30升起。
(3) be doing表示将来
常用这种结构的动词有go,come,leave,stay,start,begin等,表示即将发生或安排好要做的事情。如:
We are leaving for London. 我们就要动身去伦敦了。
She is going there tomorrow. 她明天要去那里。
(4) "be about to+动词原形”和“be to+动词原形”结构表示即将发生的动作。如:
I was about to leave when the phone rang. 我刚要离开,这时电话响了。
(5)用一般现在时表示将来的情况
1)表示按规定或时间表预计将发生的动作。如:
We're going to Changchun. Our plane takes off at 8:10. 我们打算去长春。我们的飞机8:10起飞。
2)当主句为一般将来时态时,在if,as soon as,until,when等引导的状语从句中用一般现在时代替一般将来时。如:
If it doesn't rain this afternoon, we'll have a football match.
如果今天下午不下雨,我们将进行一场足球比赛。
·模块八 Grammar8:重点语法
1. would like something和would like to do something的结构。
(1) Would you like…?可用来给出提议。
A: Would you like some coffee 你想来点咖啡吗?
B: No, thank you. 不了,谢谢。
A: Would you like some rice 你想来些米饭吗?
B: Yes, please. 好的。
A: What would you like, tea or coffee 你想喝点什么,茶还是咖啡?
B: Tea, please. 茶,谢谢。
(2)Would you like to…?可用来向别人发出邀请。
A: Would you like to have dinner with us on Sunday 周日你想和我们一起吃饭吗?
B: Yes, I'd love to. 我很乐意。
(3)另外,I'd like…是I want…的礼貌说法。
I'm thirsty. I'd like a drink. 我渴了,想喝杯饮料。
I'd like to see the film on television this evening. 今晚我想看电视上播放的电影。
指点迷津:Would you like… 和 Do you like…
Would you like . . . /I'd like . . . Do you like ... / I like …
·Would you like some tea =Do you want some tea 你想来点茶吗 ·Do you like tea =Do you think tea is nice 你喜欢喝茶吗?
·A: Would you like to go to the cinema tonight (=Do you want to go to the cinema tonight ) 今晚你想去看电影吗? ·B:Yes, I'd love to. 我想去。 ·A: Do you like going to the cinema (泛指)你喜欢看电影吗? ·B: Yes, I go to the cinema a lot. 是的,我经常去看电影
·I'd like an orange, please.(=Can I have an orange ) 我想要一个橘子,可以吗 ·I like oranges.(泛指)我喜欢橘子。
·What would you like to do next weekend 下周末你想做什么? ·What do you like to do at weekends 你周末都喜欢做些什么?
2. It would be possible to have more books in our library. 丰富我们校图书馆里的藏书是可以做到的。
“It would be+形容词+动词不定式”的结构与“It is+形容词+动词不定式”的结构所表达的含义接近,但有所区别。试比较:
It is nice to eat ice cream in summer. 夏天吃冰淇淋很爽。①
It would be nice to have a swimming pool in our school. 要是我们学校有一个游泳池多好。②
第①句表达的含义:夏天吃冰淇淋很不错。这个句子表达的是经常性发生的动作,是广泛的爱好。
第②句表达的含义:学校目前没有游泳池,但倘若有,就是一件不错的事情。它所表达的内容与现状相反,有假设的成分。
3. 反身代词使用时应与主语相呼应。下表为反身代词与人称代词主格形式的对应关系:
主格 I you he she it
单数 myself yourself himself herself itself
复数 ourselves yourselves themselves
反身代词有如下作用:
(1) 作动词或介词的宾语,尤其常在enjoy,teach,hurt,buy,introduce,seat,dress,express,amuse,behave等动词和by,for,to,of等介词后作宾语。如:
He is teaching himself English. 他正在自学英语。
She was talking to herself. 那时她在自言自语。
He lives in the country by himself. 他独自住在乡下。
(2) 作主语的同位语,主要起加强语气的作用,意为“亲自;本身;本人”。
Did you make the cake yourself 这蛋糕是你亲自做的吗?(yourself作主语you的同位语)
The work itself is easy. 这工作本身很容易。(itself作主语the work的同位语)
(3) 作表语,常位于be,feel,look,seem等系动词后,表示身体或精神状态。
I’ m not myself today. 我今天不舒服。
I am feeling myself again. 我觉得身体舒服了。
(4) 用于一些简短的会话或固定用法中。
Help yourself! 请随便吃吧!/请自己去取吧! Make yourself at home!别客气!
Don't upset yourself! 别自寻烦恼! Make yourself heard/understood.使你自己被人听到/理解。
·模块九 Grammar9:形容词比较级和最高级、反身代词和物主代词
1. 形容词比较级的构成:
(1)通常是在形容词后面加上-er,形成比较级。
原级 比较级 原级 比较级
clean cleaner(比较干净的;更干净的) tall taller(比较高的;更高的)
(2)原形容词词尾已有字母-e时,则只在形容词词尾加-r。
原级 比较级 原级 比较级
nice nicer(比较好的;更好的) brave braver(比较勇敢的;更勇敢的)
(3)原形容词词尾为“辅音字母+y”时,则先去掉字母y,再加-ier。
原级 比较级 原级 比较级
happy happier(比较快乐的;更快乐的) friendly friendlier(比较友善的;更友善的)
(4)原形容词词尾有“辅元辅”现象(即后三个字母的排列是“辅音字母+元音字母+辅音字母”)时,则要双写词末的辅音字母,再加-er。
原级 比较级 原级 比较级
big bigger(比较大的;更大的) sad sadder(比较悲伤的;更悲伤的)
(5)部分双音节形容词及三音节以上的形容词,只需在其前加more便构成比较级。(注意:more后的形容词须用原级。)
原级 比较级 原级 比较级
beautiful more beautiful(比较美丽的,更美丽的) comfortable more comfortable,比较舒适的;更舒适的)
(6)不规则变化形式,须一一记忆。
原级 比较级 原级、 比较级
many/much more(比较多的;更多的) good/well better(比较好的;更好的)
bad worse(比较坏的,更坏的) little less(比较少的;更少的)
比较级句型:对象A+动词+比较级(有时加名词)+than+对象B(意为“A比B……”)。
John is taller than Mary. 约翰比玛丽高。
We are happier than they are/them. 我们比他们快乐。
He is shorter than I am/me. 他比我矮。
Mary is more beautiful than Ann. 玛丽比安漂亮。
【注意】(1)这种句型中的动词不一定是be,也可以是一般动词;
(2)比较级之后可视需要加名词。
John has more books than Mary. 约翰拥有的书比玛丽多。
2. 形容词最高级的构成:
(1)通常只在形容词的原级后加上-est即可。
原 级 比较级 最高级
cold colder coldest(最冷的)
young younger youngest(最年轻的)
fast faster fastest(最快的;最快地)
cheap cheaper cheapest(最便宜的)
(2)原形容词词尾是字母e时,则只在形容词词尾加-st。
原 级 比较级 最高级
large larger largest(最大的)
nice nicer nicest(最好的)
(3)原形容词词尾是“辅音字母+y”时,则先去掉字母y,再加-iest。
原 级 比较级 最高级
dry drier driest(最干的)
easy easier easiest(最容易的)
pretty prettier prettiest(最美丽的)
(4)原形容词词尾的三个字母是“辅元辅”结构时,则要双写词末辅音字母,再加-est。
原 级 比较级 最高级
big bigger biggest(最大的)
hot hotter hottest(最热的)
thin thinner thinnest(最瘦的)
wet wetter wettest(最潮湿的)
(5)部分双音节及三音节以上的形容词,在其前加most。
原 级 比较级 最高级
beautiful more beautiful most beautiful(最漂亮的)
comfortable more comfortable most comfortable(最舒适的)
difficult more difficult most difficult(最困难的)
expensive more expensive most expensive(最昂贵的)
(6)不规则变化形式,须一一记忆。
原 级 比较级 最高级
bad worse worst(最差的)
good/well better best(最佳的)
many/much more most(最多的)
【注意】 形容词最高级前须加the。
形容词最高级的常见句型是:主语十动词+the+形容词最高级(+in/on/at...+群体)。
Tom is the best student in class. 汤姆是班级里最优秀的学生。
They are the most expensive. 它们是价钱最贵的。
Which watch is the cheapest 哪块手表最便宜?
【注意】 形容词最高级的用法并不仅限于上述句型。
The largest one is the cheapest. 最大的那个是最便宜的。
The oldest student in her class is 73 years old. 她班上年纪最大的学生73岁。
Can you give me the prettiest dress 你能把最漂亮的连衣裙给我吗?
Jane has the longest hair. 简的头发最长。
3. 人称代词与物主代词列表如下:
主格 宾格 形容词性物主代词 名词性物主代词
第一人称单数形式 I me my mine
第二人称单数形式 you you your yours
第三人称单数形式 he she it him her it his her its his hers its
第一人称复数形式 we us our ours
第二人称复数形式 you you your yours
第三人称复数形式 they them their theirs
(1)名词性物主代词的句法功能
作主语:May I use your pen Yours works better. 我可以用一下你的钢笔吗?你的更好用。
作宾语:I love my motherland as much as you love yours. 我和你一样爱自己的祖国。
作介词宾语:You should interpret what I said in my sense of the word, not in yours. 你应当按我所用的词义去解释我说的话,而不能按你自己的意义去解释。
作主语补语:The red scarf is hers. 这个红色的围巾是她的。
(2)名词性物主代词=形容词性物主代词+名词
为避免重复使用名词,有时可用名词性物主代词来代替“形容词性物主代词+名词”的结构。
My bag is yellow, her bag is red, his bag is blue and your bag is pink. 我的包是黄色的,她的(包)是红色,他的(包)是蓝色,而你的(包)是粉红色。
为避免重复使用bag,上例可改写成My bag is yellow, hers is red, his is blue and yours is pink.
·模块十 Grammar10:When的用法
★When的用法
(一)作为副词,它有以下的用法:
1. 作为疑问副词,引导特殊疑问句,意为“什么时候;何时”,例如:
(1) When will they come back (2)What time will they come back
回答when引导的从句,不一定指出具体的时间点。如回答句(1)可用tomorrow, next month等。
2. 作连接副词,引导名词性从句或不定式,意为“什么时候”。从句使用陈述句语序,时态根据实际情况而定。
Have you decided when to go sightseeing 你们已经决定什么时候去郊游了吗?(when引导不定式结构)
(二)作为从属连词,引导状语从句,表示多种语法意义:
表示时间,意为“当……时,在……的时候”。
A. 在时间、条件等状语从句里,用一般现在时表示将来时,当需要表达将来完成的意义时,必须使用现在完成时来代替。如:
When you see him, please say hello to him. 见到他时,代我问他好。
B. 表示过去发生的事情,在when引导的时间状语从句的主从复合句中,动作发生在先的用过去完成时,在后的用过去时。如:
When I was in Japan, I bought some beautiful pearls. 我在日本时,买了一些漂亮的珍珠。
★No ball games. 禁止球类游戏。
除了使用祈使句及带有情态动词的句子表示不同的规则之外,我们也可以使用no来表示禁止某项活动的规则,no后一般可加名词或动词ing形式。本例中的句子也相当于Don't play ball games!或We mustn't play ball games here!。使用no的句子表达各类规则时显得更为简练。
No U-turn!禁止调头!
No parking here!此处禁止停车!
1.They took a trip to Paris and enjoyed ________ very much.
A.they B.their C.them D.themselves
2.— The girls can clean their room by ________.
— They are all good girls.
A.they B.their C.them D.themselves
3.—I’ll have a tennis game tomorrow. I’m a little bit nervous.
—Believe in ________. You’re the best in our club.
A.herself B.myself C.yourself D.himself
4.—Are these shirts Gina’s
—No, they aren’t. These are black, but ________ are blue.
A.his B.hers C.theirs D.mine
5.—Sally, there is a pencil on the floor. Is it yours
—Oh…yes. It’s ________. Thank you.
A.his B.hers C.yours D.mine
6.—Lily, is this your bicycle
—Yes, it’s ________.
A.my B.me C.mine D.hers
7.—Is this book ________
—No, it is ________ book.
A.her; mine B.her; me C.hers; my D.hers; mine
8.Cathy is one of ______ in her school.
A.most beautiful girls B.the most beautiful girls
C.most beautiful girl D.the most beautiful girl
9.Bella ________ Nanjing next week.
A.visit B.visited C.visits D.is going to visit
10.— Linda, do you want to watch a film with me this evening
— Yes. But I need to finish my homework first and then I ________ you at the cinema.
A.meet B.don’t meet C.will meet D.won’t meet
11.There __________ a new film in the local cinema this weekend. Why not __________ your friends to see it
A.is going to be; invite B.is going to have; invite
C.is going to be; to invite D.is going to have; to invite
12.It is important for us ________ English well.
A.learn B.learning C.learned D.to learn
13.It’s not easy for Mr. Black ________ his students English well.
A.teach B.teaches C.teaching D.to teach
14.—It usually takes Lisa two hours ________ the violin every day.
—she needs to practice more for it.
A.play B.plays C.playing D.to play
15.________ you can use your dictionary, you will learn English better.
A.If B.Unless C.Though D.Before
16.—What are you thinking about
—________. I’m just looking at the sky.
A.Everything B.Nothing C.Anything D.Something
17.I will help you, so you ________worry about it.
A.don’t need B.needn’t to C.not need D.needn’t
18.The new software can help us call a taxi immediately, so we ________wait too long.
A.needn’t to B.need C.don’t need to D.not need to
19.—Must I stay here with you
—No, you ________. Just do your own business.
A.mustn’t B.needn’t C.can’t D.may not
20.My parents and I ________ in that old house since I was born.
A.live B.lived C.have lived D.has lived
21.—I ________ up at 5 am this morning, so I am very sleepy now.
—Take good care of ________.
A.wake; you B.woke; yourself C.wake; yours D.woke; yourselves
22.When times are difficult, tell____________ that pain is part of growing.
A.herself B.myself C.yourself D.himself
23.—Excuse me. Does this teacher teach ________ English
—No, ________ is over there under the tree.
A.their; theirs B.their; their C.them; theirs D.them; their
24.— What do you think of the song in the film Titanic
— I think it is one of ________ movie songs I have seen.
A.the most beautiful B.most beautiful C.more beautiful D.much more
beautiful
25.Linda, one of ________ in our class, is never late for school.
A.best students B.the best students C.best student D.the best student
26.Shanghai is one of ________ in China.
A.the big cities B.the bigger city C.the bigger cities D.the biggest cities
27.You’re not good at ________. You should read ________ books.
A.writing; more B.write; much more C.write; much D.writing; much
28.What a good idea! In this way, we can use ________ time to finish ________ work.
A.less; less B.more; fewer C.less; more D.fewer; more
29.There will be ___________ cars in the future.
A.many B.much C.more D.most
30.________ is better worth my respect than Yuan Longping. He is a great scientist.
A.Somebody B.Anybody C.Nobody D.Everybody
31.I want to know _________ the book. Could you help me
A.many about B.more about C.much of D.lot of
32.Try to sing ______ English songs, and you will find it interesting to learn English.
A.more B.much C.little D.most
33.If she ________ to Beijing tomorrow, I ________ with her.
A.goes, go B.will go, goes C.goes, will go D.go, will go
34.—I hear there ________ a sports meeting in our school.
—Yes, you are right.
A.are going to be B.is going to be C.is D.is going to have
35.My sister is coming to my home today. She ________with me for a week.
A.stay B.stayed C.is staying D.will stay
36.—I don’t think robots ________ the place of teachers fifty years from now.
—A science professor ________ us a lecture on robots this afternoon. You may ask him the question after the lecture.
A.will take; gives B.are going to take; gives C.will take; is giving D.are going to take; is giving
37.—Hi, Mike. Are you free tomorrow Mr. Zhang ________ a talk on the future cities.
—Sounds great! I think we can learn a lot from his talk. See you there.
A.give B.gives C.is giving D.will give
38.— ________ your brother _________ a magazine from the library
— Yes.
A.Are; going to borrow B.Is; going to borrow
C.Is; going to borrows D.Are; going to borrows
39.Tomorrow he __________ a kite in the open air first, and then ___________ boating in the park.
A.will fly; will go B.will fly; goes
C.is going to fly; will goes D.is going to fly; goes
40.Mike is cleaning his bike now. He ________ it to the park with his friends.
A.rides B.will ride C.riding D.ride
41.You’d better text her first. She ________ angry if you ________ by her house suddenly tomorrow.
A.may be; stop B.may be; will stop C.maybe; stop D.maybe; will stop
42.There a test tomorrow.
A.is B.will be C.will have D.have
43.Where __________ you __________ have a meeting tomorrow
A.do; go B.will; go C.are; go D.are; going to
44.Look at the black clouds. I think it ________ soon.
A.will rain B.is going to rain C.to rain D.is raining
45.A: Do you like your Chinese teacher
B: No, she always makes us ________ a lot of homework.
A.to do B.do C.does D.doing
46.Her moving words make me ________.
A.to cry B.crying
C.will cry D.cry
47.Books give us knowledge and make us ________ happy.
A.feeling B.feel C.to feel D.felt
48.Reading books ________ me ________ great.
A.make; feel B.makes; to feel C.makes; feel D.make; to feel
49.All the children like Mr. White very much because he often makes them________.
A.laughed B.laugh C.laughing D.to laugh
50.His boss made him ________ twelve hours a day in the past.
A.work B.worked C.working D.to work
51.The present makes me ________ my mother.
A.think over B.thinking over C.think of D.thinking of
52.I’m waiting for my friend. ________, I will go shopping alone (独自).
A.If she comes B.If she will come C.If she doesn’t come D.If she came
53.The teacher made the students ________ a lot of homework.
A.do B.did C.to do D.doing
54.It’s not difficult for some people ________ friends in a new school.
A.make B.making C.to make D.make
55.It’s difficult for me ________ the work in such a short time.
A.to finish B.finish C.finishing D.finishes
56.It’s very kind ________ you to help me.
A.for B.to C.of D.with
57.In the future, I think it won’t be difficult for us ________ all over the world.
A.to travel B.travels C.travel D.travelling
58.It only ________ him 20 minutes ________ to his office yesterday.
A.takes; to drive B.took; drive
C.takes; drive D.took; to drive
59.It’s important ________ us ________ to the teachers carefully in class.
A.of; to listen B.of; listening
C.for; to listen D.for; listening
60.During the break my friend Susan asked me ________.
A.what did I want to have for lunch B.what is wrong with my left leg
C.if the moon moved around the earth D.if the USA was founded in 1776
61.________ they are twins, they don’t look the same.
A.Though B.Because C.If D.As long as
62.________ English is difficult for Tom, he never gives up.
A.So B.Although C.And D.But
63.________ it was very hot inside, John didn’t turn on the air conditioner.
A.If B./ C.Although D.Because
64.________ the hut is old and small, it’s warm and comfortable.
A.Because B.But
C.So D.Although
65.Mr. Wang is always the first one to be in the office _______ he lives far from his company.
A.although B.because C.when D.as
66._______ it was hot outside, Tom didn’t turn on the air-conditioner.
A.Although B.If C.Because D.When
67.________ my grandpa is over 80 years old, he still looks strong and healthy.
A.Although B.Because C.Unless D.If
68.________ the fisherman lived a poor life, he was very happy every day.
A.Because B.So C.But D.Although
69.________ Jeff is busy with work, ________ he never gives up studying.
A.Although; / B.But; / C.Though; but D.But; although
70.________ of us tried to solve the maths problem, but ________ of us was able to do it.
A.Everyone; no one B.Everyone; none C.Each; no one D.Each; none
71.—Which shirt do you like better, the blue one or the white one
—I’ll take ____________. They are expensive and out of fashion.
A.neither B.either C.none D.both
72.Mike has two cats. One is black and ________ is white.
A.other B.the other C.others D.the others
73.—Must I wash my clothes today
—I’m afraid you ________. You should learn to do something by yourself.
A.need B.have to C.can D.could
74.—Mom, I want to play football.
—Sorry, Jack. Not now, but you ________ play it on weekends.
A.have to B.must C.need D.can
75.—Must I stay at home for dinner
—No, you ________. You can go out with your friends.
A.can’t B.needn’t C.shouldn’t D.may not
76.— Must I clean the classroom now
— No, you _______.
A.can’t B.may not C.mustn’t D.needn’t
77.Please bring your schoolbag to school if it ________ tomorrow.
A.won’t rain B.doesn’t rain C.isn’t raining D.didn’t rain
78.I will get everything ready for Bill’s birthday party. You ________ buy anything.
A.can’t B.mustn’t C.couldn’t D.needn’t
79.—Must I clean all the plates after dinner
—No, you ________. But you ________ clean them before seven thirty this evening.
A.mustn’t; must B.needn’t; must C.can’t; must D.don’t have to; may
80.You ________ buy anything else. We have got everything ready for your dinner.
A.don’t need to B.needn’t to C.don’t need D.need
81.—________ I swim here
—I’m sorry. Children ________ swim alone here. It’s very dangerous.
A.Must; can’t B.May; have not
C.Can; mustn’t D.Can; needn’t
82.Jack ________ any help. He can do it by himself.
A.needs not B.needn’t
C.doesn’t need D.needn’t to
83.Mr. Wang ________ in Hangzhou since he left the army.
A.lives B.lived C.has lived D.will live
84.If it ________ heavily tomorrow, we ________ at late.
A.will snow, will stay B.snows, will stay C.will snow, stay D.snows, stay
85.My father and I ________ to England before.
A.have been B.went C.have gone D.go
86.________ you ever ________ to Beijing
A.Do; go B.Did; go C.Have; gone D.Have; been
87.Look, the wind ________ now. Let’s go out to play.
A.is stopping B.has stopped C.will stop D.stopped
88.—Where is your sales manager, Jessica
—She’s not here. She _______ to Beijing to attend a meeting. She left this morning.
A.went B.goes C.has gone D.has been
89.My uncle went to Australia last year. We haven’t seen him ________.
A.since almost a year B.from almost a year on
C.after almost a year D.since almost a year ago
90.—How long can I ________ your CD player
—For two weeks.
A.lend B.borrow C.get D.keep
91.—Who teaches ________ English
—Nobody. I teach ________.
A.your; myself B.your; me C.you; myself D.you; me
92.—Shall we invite Mr. White to our birthday party
—That will be nice if you ________.
A.shall B.do C.will do D.are
93.If it ________ tomorrow, we’ll go to visit Sheshan State Resort.
A.won’t rain B.hasn’t rained C.doesn’t rain D.didn’t rain
94.If it ________ tomorrow, we’ll go roller-skating.
A.isn’t rain B.won’t rain C.doesn’t rain D.didn’t rain
95.________ my grandmother is 72, she is strong enough to grow and sell vegetables every day.
A.Since B.Because C.So D.Though
96.This picture isn’t beautiful. Could you show me _________ one
A.other B.the other C.another D.others
97.Susan’s sister ________ the MP3 for two years.
A.has had B.has bought C.has borrowed D.has lent
98.Angel isn’t here now. She ________ the library.
A.has been to B.went to C.has gone to D.goes to
99.Several new members have come into the club _______ 2017.
A.since B.for C.in D.at
100.My elder brother ________ a soldier for two years.
A.becomes B.has become C.became D.has been
参考答案:
1.D
【详解】句意:他们去巴黎旅行,玩得很开心。
考查人称代词。they他们,人称代词主格;their他们的,形容词性物主代词;them他们,人称代词宾格;themselves他们自己,反身代词。enjoy+反身代词“玩得开心”,动词短语,故选D。
2.D
【详解】句意:——女孩们可以自己打扫房间。——她们都是好女孩。
考查代词辨析。they她们,主格;their她们的,形容词性物主代词;them她们,宾格;themselves她们自己,反身代词。by oneself意为“单独地,靠自己地”,所以此处应用反身代词themselves,故选D。
3.C
【详解】句意:——我明天有一个网球比赛。我有点紧张。——相信自己。你是我们俱乐部最好的。
考查反身代词。herself她自己;myself我自己;yourself你自己;himself他自己。根据“Believe in ... You’re the best in our club.”可知,相信你自己,你是俱乐部最好的。故选C。
4.B
【详解】句意:——这些衬衫是吉娜的吗?——不,它们不是。它们是黑色的,但她的是蓝色的。
考查代词辨析。his他的;hers她的;theirs他们的;mine我的。根据“Are these shirts Gina’s ”和“These are black, but ... are blue.”可知,此处指吉娜的衬衫是蓝色的,用hers。故选B。
5.D
【详解】句意:——Sally,地板上有一支铅笔。它是你的吗?——哦……是的。它是我的。谢谢你。
考查代词辨析。his他的;hers她的;yours你的;mine我的。根据“Is it yours”以及“yes.”可知此处表示铅笔是“我的”。故选D。
6.C
【详解】句意:——莉莉,这是你的自行车吗?——是的,它是我的。
考查代词辨析。my我的,形容词性物主代词;me我,人称代词宾格;mine我的,名词性物主代词;hers她的,名词性物主代词。根据“Lily, is this your bicycle ”可知答句中要回答是“我的自行车”,用mine。故选
C。
7.C
【详解】句意:——这本书是她的吗?——不,它是我的书。
考查物主代词。her她的,形容词性物主代词;hers她的,名词性物主代词;my我的,形容词性物主代词;mine我的,名词性物主代词;me人称代词的宾格。根据句子结构可知,第一空后没有名词,则需要用名词性物主代词hers,指代“她的书”;第二空要用形容词性物主代词my,作定语,修饰名词book。故选C。
8.B
【详解】句意:凯茜是学校里最漂亮的女孩之一。
考查形容词最高级用法。根据“one of the+形容词最高级+可数名词复数”,可知“most beautiful”前面要有“the”,girl是可数名词,要使用其复数形式,故选B。
9.D
【详解】句意:Bella下周要去参观南京。
考查动词时态。根据“next week”可知,此处用一般将来时be going to do的结构,故选D。
10.C
【详解】句意:——Linda,今晚你想要和我看电影吗?——是的。但是我需要先完成作业,然后在电影院和你见面。
考查一般将来时。根据“Yes”可知Linda同意一起看电影,而由“I need to finish my homework first”和“then”可知此处应用一般将来时,其谓语结构为“will+do”,故选C。
11.A
【详解】句意:这个周末当地电影院将上映一部新电影。为什么不邀请你的朋友去看呢?
考查一般将来时和非谓语动词。there be与一般将来时连用时,结构为there is/are going to be/there will be,排除BD选项;再根据why not do sth.“为什么不做某事”可知,动词应用原形。故选A。
12.D
【详解】句意:学好英语对我们来说很重要。
考查非谓语动词。It is adj. for sb. to do sth.“做某事对某人来说是……的”,It作形式主语,动词不定式作真正主语。故选D。
13.D
【详解】句意:布莱克老师教他的学生们学好英语是不容易的。
考查非谓语动词。根据“It’s not easy for Mr. Black”可知,It’s+形容词+for sb to do sth“对某人来说做某事是怎么样的”,是固定句型。故选D。
14.D
【详解】句意:——丽莎每天通常要花两个小时拉小提琴。——她需要多练习。
考查固定搭配。It takes sb. some time to do sth. 是固定搭配,意为“某人花多长时间做某事”,空处用不定式形式,故选D。
15.A
【详解】句意:如果你能使用字典,你会学英语学得更好。
考查从属连词辨析。If如果;Unless除非;Though虽然;Before在……之前。根据“…you can use your dictionary, you will learn English better.”可知,此处空后为条件,且为肯定条件,使用if引导条件状语从句,故选A。
16.B
【详解】句意:——你正在想什么?——没什么。我只是正在看天空。
考查代词辨析。everything一切;nothing没什么;anything任何事;something某事。根据“I’m just looking at the sky.”可知应是没看什么,故选B。
17.D
【详解】句意:我会帮助你的,因此你不需要担心它。
考查情态动词。need可以作实意动词,常用于need to do sth.“需要做某事”,否定形式应用助动词do的形式构成;need也可以作情态动词,后跟动词原形,否定形式直接在need后加not。A选项缺少to;B选项多了to;C选项形式错误。故选D。
18.C
【详解】句意:这款新的软件能帮助我们立刻打到出租车,因此我们不需要等太长时间。
考查need的用法。need作情态动词,其否定形式为needn’t;而need作实意动词的时候,常用短语为need to do,否定形式为don’t need to。本题中只有选项C符合要求,故选 C。
19.B
【详解】句意:——我必须和你待在这里吗?——不,你不必。做你自己的事吧。
考查情态动词。mustn’t禁止;needn’t不必;can’t不能;may not可能不。根据“Must I...”可知其否定回答为No, I needn’t。故选B。
20.C
【详解】句意:自从我出生以来,我的父母和我一直住在那所老房子里。
考查动词的时态。根据“since I was born”可知,应该用现在完成时,主语“My parents and I”是复数,助动词用have。故选C。
21.B
【详解】句意:——我今天早晨5点起床的,所以我现在感觉很困。——照顾好自己。
考查时态和反身代词。根据this morning可知,描述发生过的事,用一般过去时,排除A和C;take care of oneself表示“照顾自己”,说话者是单数。故选B。
22.C
【详解】句意:遇到困难时,告诉你自己痛苦是成长的一部分。
考查反身代词。herself她自己;myself我自己;yourself你自己;himself他自己。根据“tell ... that pain is part of growing.”是祈使句,省略的是第二人称you,因此是告诉你自己。故选C。
23.C
【详解】句意:——打扰一下。这个老师教他们英语吗?——不,他们的在那边树下。
考查代词词义辨析。their他们的,形容词性物主代词;theirs他们的,名词性物主代词;them他们,宾格。第一空考查teach sb. sth.表示“教某人某事”,所以此处应用人称代词宾格;第二空应用名词性物主代词作主语。故选C。
24.A
【详解】句意:——您如何看待电影《泰坦尼克号》中的歌曲?——我认为这是我看过的最美的电影歌曲之一。
考查形容词最高级。短语one of the+最高级+可数名词复数表示“最……的……之一”,选项A符合该结构。故选A。
25.B
【详解】句意:琳达,我们班里最好的学生之一,上学从来不迟到。
考查形容词最高级。one of the+形容词最高级+名词复数+范围:表示“最……之一”,B选项是形容词最高级,且前面有定冠词the,后接可数名词复数,故选B。
26.D
【详解】句意:上海是中国最大的城市之一。
考查形容词最高级和名词复数。“one of+the+形容词最高级+可数名词复数”,表示“最……的……之一”,此空应是the biggest cities。故选D。
27.A
【详解】句意:你不擅长写作。你应该多读书。
考查非谓语动词和比较级。第一个空是:be good at doing sth.意为“擅长做某事”;much修饰不可数名词;more修饰不可数名词和可数名词复数,more books意为“更多的书”。故选A。
28.C
【详解】句意:非常好的想法!这样我们就可以用更少的时间完成更多的工作。
考查形容词比较级辨析。less更少,little的比较级,后面接不可数名词;more更多,much或many的比较级,后面接复数名词或不可数名词;fewer更少,few的比较级。time是不可数名词;work是不可数名词,根据“What a good idea”可知,应该是用更少的时间完成更多的工作是个好主意,故选C。
29.C
【详解】句意:将来会有更多的汽车。
考查比较级。many许多,修饰可数名词;much许多,修饰不可数名词;more更多;most最多。根据“There will be...cars in the future.”可知此处暗含比较,把将来和现在相比,应用比较级,故选C。
30.C
【详解】句意:没有人比袁隆平更值得我尊敬。他是一位伟大的科学家。
考查不定代词。Somebody某人;Anybody任何人;Nobody没有人;Everybody人人。根据“He is a great scientist.”可知,袁隆平是伟大的科学家,没有人比他更值得我尊敬,“否定+比较级”表最高级。故选C。
31.B
【详解】句意:我想了解更多关于这本书的信息。你能帮我吗?
考查比较级的用法。many很多;more更多;much很多;lot of错误形式。根据“I want to know...the book. Could you help me”可知是想了解更多信息,不能用many修饰,排除A;此处表示“关于这本书”,用介词about,排除C。故选B。
32.A
【详解】句意:尝试唱更多的英文歌,你就会发现学习英语是有趣的。
考查形容词比较级。more更多的;much许多,后接不可数名词;little几乎没有;most最多的。根据“Try to sing... English songs, and you will find it interesting to learn English.”可知,空后是名词复数,排除B、C选项;发现英语有趣,应是唱更多的英文歌,将发现英语有趣前后的行为进行对比,空处应用比较级more。故选A。
33.C
【详解】句意:如果她明天去北京,我将会和她一起去。
考查条件状语从句。if引导的条件状语从句,主将从现;she是第三人称,谓语动词用三单,故选C。
34.B
【详解】句意:——我听说我们学校将举行运动会。——是的,你是对的。
考查there be句型的一般将来时。there are going to be将有,一般将来时;there is going to be将有,一般将
来时;there is有,一般现在时;there is going to have无此用法。根据“hear”可知,此处用一般将来时;“a sports meeting”单数做主语,要用there is going to be。故选B。
35.D
【详解】句意:我妹妹今天要来我家。她将和我待一个星期。
考查一般将来时。根据“My sister is coming to my home today.”可知,此处是指今天妹妹要来“我”家,将陪伴“我”一个星期,时态应用一般将来时,其结构为will+动词原形。故选D。
36.C
【详解】句意:——我认为五十年后机器人不会取代教师。——今天下午一位科学教授给我们做了一次关于机器人的讲座。你可以在讲座结束后问他这个问题。
考查动词。“will”通常用于表达说话人的意图、决定或信念,强调的是主观意愿或未来的确定性,因此第一空用will;第二空时间状语是this afternoon,还未发生,因此可以用be+doing的形式表将来,故选C。
37.D
【详解】句意:——嗨,迈克。你明天有空吗?张老师将做一个关于未来城市的演讲。——听上去太棒了!我认为我们可以从他的演讲中学到很多东西。到时见。
考查一般将来时。根据“tomorrow”可知,时态是一般将来时:will+动词原形。故选D。
38.B
【详解】句意:——你哥哥打算从图书馆借本杂志吗?——是的。
考查时态。be going to do sth.“打算做某事”;主语“your brother”单数,用be动词单数is。故选B。
39.A
【详解】句意:明天他将先在户外放风筝,然后去公园划船。
考查一般将来时态。will fly/is going to fly一般将来时;will go一般将来时;goes一般现在时三单形式。根据Tomorrow可知,时态为一般将来时,and连接前后语法时态保持一致。故选A。
40.B
【详解】句意:迈克正在清洗他的自行车。他将和他的朋友们骑着它去公园。
考查时态。根据“Mike is cleaning his bike now.”可知现在正在洗自行车,由此推出骑自行车去公园是将来发生的事情,用一般将来时will ride。故选B。
41.A
【详解】句意:你最好先给她发个短信。如果你明天突然去她家,她可能会生气的。
考查情态动词和动词时态。may be可能,是“情态动词+be”的结构,可以作谓语;maybe可能,是副词,不能作谓语。第一空需要谓语动词,排除CD;if引导的条件状语从句,遵循主将从现原则,从句用一般
现在时,故选A。
42.B
【详解】句意:明天将进行测试。
考查there be句型。there is有,一般现在时;there will be将会有,一般将来时;there will have无此用法;there have无此用法。根据句中的“tomorrow”,可知时态是一般将来时,故选B.
43.D
【详解】句意:你明天打算在哪里开会?
考查时态。根据“have a meeting tomorrow”可知,此处为“一般将来时”,结构为be going to do,动词“have”前要有to,故选D。
44.B
【详解】句意:看那些乌云。我认为很快就要下雨了。
考查一般将来时。根据“soon”可知该句时态是一般将来时。再结合“Look at the black clouds”可知此处是表示一种迹象,表明即将发生的事情,一般用be going to+动词原形结构。故选B。
45.B
【详解】句意:A:你喜欢你的中文老师吗?B:不,她总是让我们做很多功课。
考查非谓语动词。短语make sb do sth表示“让某人做某事”。故选B。
46.D
【详解】句意:她感人的话使我哭了。
考查动词短语。to cry哭,cry的不定式形式;crying哭,cry的现在分词形式;will cry哭,cry的将来时;cry哭,动词原形。make sb do sth“使某人做某事”,用省略to的不定式作宾补,故填cry。故选D。
47.B
【详解】句意:书籍给我们知识,使我们感到快乐。
考查非谓语动词。make sb do sth“使某人做某事”,省略to的动词不定式作宾补,故选B。
48.C
【详解】句意:读书使我感觉很好。
本题考查使役动词make的用法。短语make sb feel...意为“使某人感到……”。本句为现在分词“Reading books”做主语,所以空格处的谓语动词要用其单数形式,即makes。第二空要用动词原形形式,即feel。故选C。
49.B
【详解】句意:所有的孩子都非常喜欢怀特先生,因为他常常让他们笑。
考查固定句型。make sb do sth“让某人做某事”。所以此处应用动词原形laugh。故选B。
50.A
【详解】句意:他的老板过去让他每天工作12个小时。
考查非谓语动词。make sb do sth“使某人做某事”,省略to的动词不定式作宾补,故选A。
51.C
【详解】句意:这份礼物使我想起了我的母亲。
考查动词短语和非谓语。think over仔细考虑;think of想起。根据“The present makes me...my mother.”可知,此处表达想起了我的母亲,空处应填think of,make sb do sth“使某人做某事”,用省略to的不定式。故选C。
52.C
【详解】句意:我正在等我的朋友。如果她不来,我将独自去购物。
考查if引导的条件状语从句。if引导的条件状语从句遵循主将从现原则,排除BD;if从句表示肯定的条件,将独自去购物的肯定条件是“如果她不来”,排除A。故选C。
53.A
【详解】句意:老师给学生布置了很多家庭作业。
考查动词形式。do做,原形;did过去式;to do不定式;doing动名词。make sb. do sth.“让某人做某事”,故选A。
54.C
【详解】句意:对一些人来说,在新学校交朋友并不困难。
考查不定式用法。It is adj for sb to do sth表示“做某事对某人来讲是……”,it作形式主语,不定式作真正的主语。故选C。
55.A
【详解】句意:在这么短的时间内完成这项工作对我来说是困难的。
考查非谓语动词。根据“It’s difficult for me ... the work in such a short time.”可知,it is+形容词+for sb.+to do sth.表示“做某事对某人而言是……的”,不定式作真正的主语。故选A。
56.C
【详解】句意:你/你们帮助我真是太好了。
考查it的特殊句型和介词辨析。for为了;to到;of……的;with和。根据语境可知,形容词kind“友好的”用来表示不定式行为者的性格品德,故用it特殊句型“It’s+adj+of sb to do sth.”表示“某人做某事真是……”,空处需填介词,介词of“……的”符合语境。故选C。
57.A
【详解】句意:在将来,我认为对我们来说去环游世界那将不是困难。
考查it的固定句型。由“it won’t be difficult for us…”可知,考的是it的固定句型:it+be+adj.+for sb.+to do sth.“对某人来说做某事怎么样”,应用动词不定式。故选A。
58.D
【详解】句意:昨天他开车去办公室只花了20分钟。
考查时态以及非谓语动词。it takes/took sb. time to do sth.“做某事花费某人多长时间”,排除BC;根据“yesterday”可知句子用一般过去时,动词用took。故选D。
59.C
【详解】句意:在课堂上认真听老师讲课对我们来说很重要。
考查it的固定句型。“It is+形容词+for sb.+to do sth.”意为“对某人来说做某事怎么样”,这种结构中的形容词常与事物的特征有关;“It is+形容词+of sb.+to do sth.”表示“某人做某事怎样”,这种结构中的形容词常与人的性格特点有关。important是形容“课上认真听老师讲课”这件事,所以第一空用for。在这个两个句型中,it是形式主语,动词不定式是真正主语,所以第二空用to listen。故选C。
60.D
【详解】句意:课间休息时,我的朋友苏珊问我美国是否成立于1776年。
考查宾语从句。句子是宾语从句,用陈述语序,排除A;根据“asked”可知主句是过去时,从句应用过去的某个时态,排除B;选项C描述的是客观事实,故从句应用现在时,排除C。故选D。
61.A
【详解】句意:虽然他们是双胞胎,但长得不一样。
考查连词辨析。Though虽然;Because因为;If如果;As long as只要。根据“they are twins, they don’t look the same.”可知,前后两句是让步关系,因此用连词“Though”。故选A。
62.B
【详解】句意:尽管英语对Tom来说很难,但他从不放弃。
考查连词辨析。so所以;although尽管;and和;but但是。根据语境可知,尽管英语对Tom来说很难,但他从未放弃,此处应用although引导让步状语从句。故选B。
63.C
【详解】句意:虽然里面很热,约翰却没有开空调。
考查从属连词。If 如果;Although虽然,尽管;Because因为。由句意可知,“it was very hot inside”和“didn’t turn on the air conditioner”有让步关系,所以用although引导让步状语从句。故选C。
64.D
【详解】句意:虽然这个小屋又旧又小,但是它温暖舒适。
考查连词辨析。Because因为;But但是;So所以;Although虽然。根据“the hut is old and small, it’s warm and comfortable.”可知,句子前后是让步关系,因此用although引导状语从句。故选D。
65.A
【详解】句意:王先生虽然住得离公司很远,但他总是第一个到办公室。
考查连词辨析。although尽管,虽然;because因为;when当……时候;as因为。根据“Mr. Wang is always the first one to be in the office ... he lives far from his company.”可知,句子前后是让步关系,用although引导让步状语从句。故选A。
66.A
【详解】句意:虽然外面很热,但汤姆没有打开空调。
考查从属连词辨析。Although虽然,尽管;If如果;Because因为;When当……时候。“it was very hot outside”和“Tom didn’t turn on the air-conditioner”之间有让步关系,所以用although引导让步状语从句。故选A。
67.A
【详解】句意:虽然我爷爷已经80多岁了,但他看起来仍然很强壮很健康。
考查连词辨析。Although尽管;Because因为;Unless除非;If如果。根据“…he still looks strong and healthy.”可知,虽然爷爷年纪大了,但身体仍然强健,用although引导让步状语从句。故选A。
68.D
【详解】句意:尽管渔夫过着贫穷的生活,但他每天都很快乐。
考查连词。Because因为;So所以;But但是;Although尽管。根据“...the fisherman lived a poor life, he was very happy every day.”渔夫尽管很穷,但是很快乐。用although引导让步状语从句,故选D。
69.A
【详解】句意:虽然杰夫工作很忙,但他从不放弃学习。
考查连词辨析。Although/Though虽然、尽管,用来引导让步状语从句,不能与but连用,所以排查C、D选项;but表示转折关系,应放在“he never gives up studying.”前面,排除B选项。故选A。
70.D
【详解】句意:我们每个人都试图解决这道数学题,但没有一个人能做出来。
考查代词辨析。everyone每人;each每个;none没有;no one没有人。everyone、no one不与of搭配,第一空填each,第二空none符合句意,故选D。
71.A
【详解】句意:——你更喜欢哪件衬衫,蓝色的还是白色的? ——我两个都不要。它们又贵又过时。
考查代词辨析。neither两者都不;either两者中的任何一个;none一个也没有;both两者都。根据“They are expensive and out of fashion”可知,两个都不要,应用neither。 故选A。
72.B
【详解】句意:迈克有两只猫。一只是黑色的,另一只是白色的。
考查不定代词的辨析。other作形容词,意为“其他的、另外的”,用在名词前做定语;the other(两者中的)另一个人或事物;others另外的人或物,一般指三者或以上,表泛指;the others等于“the other +复数名词”,指某一范围内的“其他的(人或物)”。根据上文“Mike has two cats”可知,此处指的是两只猫中的“另一只”,故选B。
73.B
【详解】句意:——我今天必须洗衣服吗?——恐怕你不得不洗。你应该学会自己做一些事情。
考查情态动词辨析。need需要;have to必须、不得不;can能、会;could能、会,是can的过去式。根据空后句“You should learn to do something by yourself.”可知,空处应用have to“不得不”。故选B。
74.D
【详解】句意:——妈妈,我想要踢足球。——抱歉杰克。不是现在,但是你周末的时候可以去踢足球。
考查情态动词辨析。have to不得不;must必须;need需要;can能够,可以。现在玩不了,但是周末可以玩,这里用can表示允许。故选D。
75.B
【详解】句意:——我必须在家吃晚餐吗?——不用,你不需要。你可以和朋友出去。
考查情态动词need的用法。can’t不能;needn’t不需要;shouldn’t不应该;may not不可以。根据“You can go out with your friends.”可知,可以和朋友出去,说明不需要在家吃晚餐。故选B。
76.D
【详解】句意:—— 我现在必须打扫教室吗?—— 不,你不需要。
考查情态动词。can’t不能;may not不可以;mustn’t禁止;needn’t没有必要。“Must I do … ”的否定回答是“No, you needn’t.”或者 “No , you don’t have to.”,此句是must 开头的一般疑问句否定回答,故选D。
77.B
【详解】句意:如果明天不下雨,请把你书包带到学校来。
考查动词时态。含有if引导的条件状语从句的主从复合句中,主句用祈使句,从句用一般现在时。根据“bring your schoolbag to school if it.”可知空处应用一般现在时态。故选B。
78.D
【详解】句意:我将为比尔的生日聚会准备一切。你不需要买任何东西。
考查情态动词。can’t不能;mustn’t禁止;couldn’t不能;needn’t不需要。根据“I will get everything ready for Bill’s birthday party”可知,因为一切都会准备好,所以对方不需要买任何东西。故选D。
79.B
【详解】句意:——晚饭后我必须把所有的盘子都洗干净吗?——不,你不需要。但是你必须在今晚七点半之前把它们洗干净。
考查情态动词。mustn’t不得;must必须;needn’t不必;can’t不能;don’t have to不必;may可以。根据“Must I clean all the plates after dinner ”及“No,”可知,含情态动词must的一般疑问句,否定回答用needn’t或don’t have to,排除AC选项;再根据“But you ... clean them before seven thirty this evening.”可知,第二空表示必须在七点半之前把它们清洗干净,用must。故选B。
80.A
【详解】句意:你不需要买其他东西,我们已经为您的晚餐准备好了一切。
考查动词的用法。need作为行为动词,need to do sth“需要做某事”,否定式don’t/doesn’t/didn’t need to do sth“不需要做某事”;need作为情态动词,一般用于否定句或疑问句,needn’t do sth“不需要做某事”。空格后buy是动词,所以“不需要买”表达成don’t need to buy或needn’t buy。故选A。
81.C
【详解】句意:——我能在这里游泳吗? ——非常抱歉。孩子们禁止独自在这里游泳。这非常危险。
考查情态动词。Must必须;can’t不能;May可以,表请求;have not没有;Can可以,表请求;mustn’t禁止;needn’t不必。根据后句“I’m sorry.”可知,第一空应是表示请求的提问;再根据“It’s very dangerous.”可知,这里很危险,故推测第二空是禁止孩子们独自在这里游泳,应用mustn’t表示“禁止,不准”。故选C。
82.C
【详解】句意:杰克不需要任何帮助。他可以自己做这件事。
考查动词。need有两种词性,一种是情态动词,没有时态和三单变化,表示“需要”,其后接动词原形构成谓语;另一种是实义动词,本身充当谓语,有时态和三单变化,表示“需要”,其后接sth或to do作宾语。情态动词的否定直接在其后加not,实义动词的否定要借助助动词;根据设空处后的名词“any help”,可知此处need为实义动词,其否定要借助助动词,故选C。
83.C
【详解】句意:王先生自离开部队以来就在杭州生活。
考查现在完成时。根据“since he left the army”可知该句应用现在完成时,其结构为:have/has+过去分词。故选C。
84.B
【详解】句意:如果明天下大雪,我们将待在家里。
考查动词时态。此句中“If”意为“如果”,所以该句为if引导的条件状语从句,主句用一般将来时态,从句用一般现在时态,B选项符合,故选B。
85.A
【详解】句意:我和爸爸之前去过英国。
考查现在完成时。根据“before”可知该句谈论之前“去过某地”,应用现在完成时,谓语动词用have been to。故选A。
86.D
【详解】句意:你曾经去过北京吗?
考查现在完成时。根据“ever”可知此处询问是否曾经去过北京,句子应用现在完成时。结合语境,可知此处询问的是“去过”,人已经回来了,因此应用have been to。故选D。
87.B
【详解】句意:看,风已经停了。我们出去玩吧。
考查动词时态。根据“Lets go out to play.”判断风已经停了。这里描述过去发生的动作对现在造成了影响,时态用现在完成时,结构为:have/has+动词的过去分词。故选B。
88.C
【详解】句意:——杰西卡,你的销售经理在哪里?——她不在这里。她去北京参加会议了。她今天早上离开了。
考查现在完成时。根据“She’s not here.”可知,她不在这里,说明是“已经去了某地”,还没有回来,句子应用现在完成时,应用have gone to表示“已经去了某地”。故选C。
89.D
【详解】句意:去年我的叔叔去了澳大利亚。自从一年前我们没有见到他。
考查since现在完成时。根据横线前的句子时态为现在完成时,可知此处应是since接时间点;或since+时间段+ago。故选D。
90.D
【详解】句意:——你的CD机我可以借多久?——两周。
考查动词辨析。lend借出;borrow借进;get得到;keep保留。根据“For two weeks”可知,回答是时间段,
空处填的动词应是延续性动词,只有选项D是延续性动词。故选D。
91.C
【详解】句意:——谁教你英语?——没有人。我自学的。
考查代词辨析。your你的/你们的,形容词性物主代词;you你/你们,主格代词/宾格代词;myself我自己,反身代词;me我,宾格代词。teach sb sth“教某人……”,空一位于动词之后,需用宾格代词;teach oneself意为“自学”,主语是I,需用myself。故选C。
92.B
【详解】句意:——我们邀请怀特先生参加我们的生日聚会好吗?——如果你这样做,那就太好了。
考查动词及时态。句子是if引导的条件状语从句,应用“主将从现”的原则,从句用一般现在时,排除A/C选项,结合语境可知,此处指的是“做”,应用动词do,故选B。
93.C
【详解】句意:如果明天不下雨,我们就去佘山国家旅游度假区。
考查动词时态。根据“If it...tomorrow, we’ll go to...”可知此处是if引导的条件状语从句,需遵循主将从现的原则,因此if从句需使用一般现在时表示将来。故选C。
94.C
【详解】句意:如果明天不下雨,我们将去轮滑。
考查时态。该句为if引导的条件状语从句,句子时态遵循“主将从现”的原则,主句时态为一般将来时,从句为一般现在时,主语为it,否定句用助动词doesn’t,故选C。
95.D
【详解】句意:虽然我的祖母已经72岁了,但她仍然很强壮,可以每天种菜、卖菜。
考查连词辨析。Since自……以来;Because因为;So所以;Though尽管。“my grandmother is 72”和“she is strong enough to grow and sell vegetables every day.”之间在句意上存在让步关系,所以应用though引导让步状语从句。故选D。
96.C
【详解】句意:这幅画不漂亮。你能展示给我另一幅吗?
考查单词辨析。other其它的,形容词,后面通常接复数名词;the other另一个,通常作代词;another另一个,可作形容词,后接单数名词;others其它的,代词。根据“one”可知此处应填形容词,且one代替“picture”,为单数,故选C。
97.A
【详解】句意:苏珊的姐姐有这台MP3两年了。
考查现在完成时。buy买;borrow借入;lend借出。本句是现在完成时,当谓语动词和一段时间连用,必须是延续性动词,BCD都是短暂性动词,只有A选项符合。故选A。
98.C
【详解】句意:Angel现在不在这里。她去了图书馆。
考查动词的时态。根据“Angel isn’t here now”可知,Angel不在这里,说明她去了图书馆,应用现在完成时。has been to表示“去过(已回)”;has gone to“去了(未回)”。Angel不在说话现场,应用has gone to。故选C。
99.A
【详解】句意:自2017年以来,又有几名新成员加入了该俱乐部。
考查时间介词。since“自……以来”,后接具体的年、月、日等;for与一段时间连用;in用在年、月、季节等较长一段时间前;at用在时刻前。根据“Several new members have come into the club”可知,时态为现在完成时,现在完成时通常与“since+时间点”连用。故选A。
100.D
【详解】句意:我的哥哥已经参军两年了。
考查现在完成时和延续性动词。根据“for two years”可知时态为现在完成时,其谓语结构为“have/has+done”,而two years为时间段,所以谓语动词应用延续性动词,故选D。
同课章节目录
