【期末备考】人教版七下英语期末基础语法知识梳理(标注重难点)
文档属性
| 名称 | 【期末备考】人教版七下英语期末基础语法知识梳理(标注重难点) |
|
|
| 格式 | docx | ||
| 文件大小 | 295.0KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教新目标(Go for it)版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-06-02 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览


文档简介
中小学教育资源及组卷应用平台
人教版七下英语期末基础语法知识梳理(标注重难点)
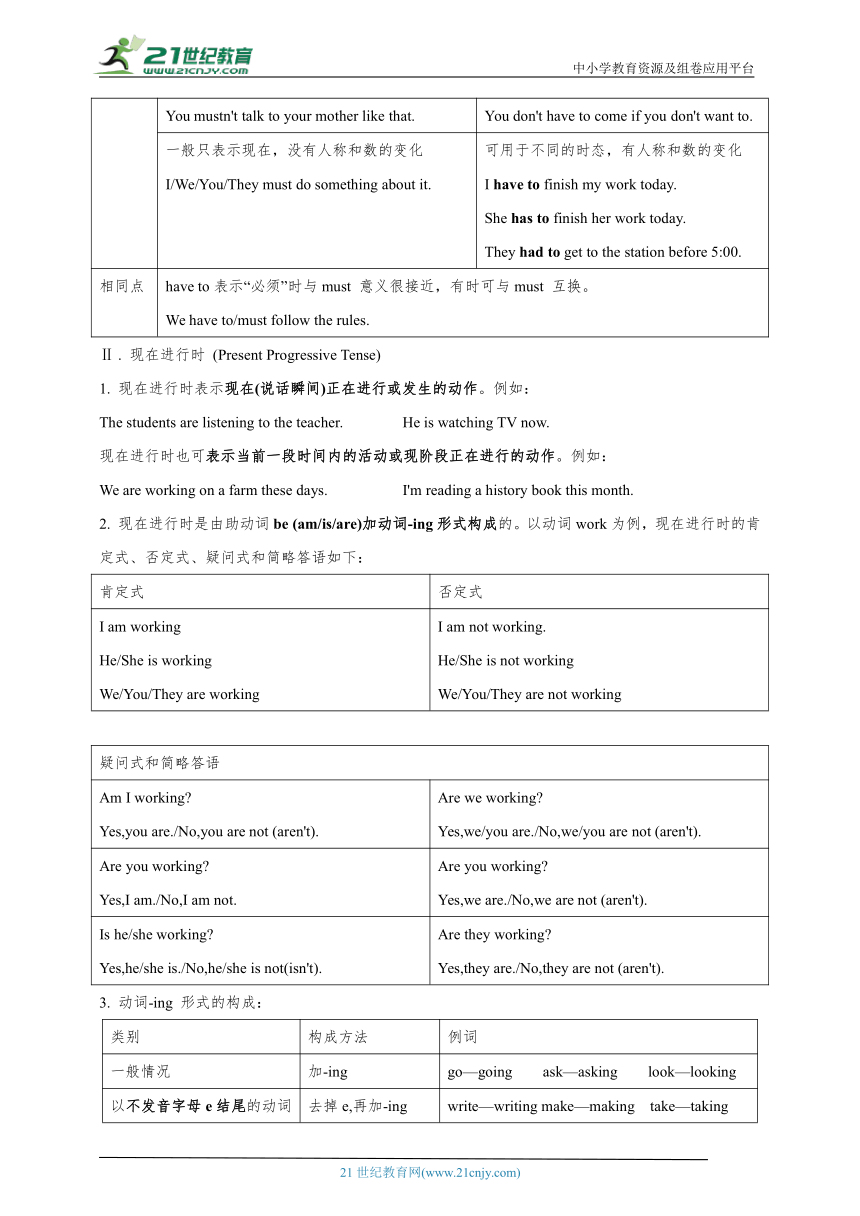
I.情态动词 (Modal Verbs)
情态动词①表示说话人对所说动作的观点,如需要、可能、意愿、怀疑等。②在形式上,情态动词一般没有人称和数的变化,有的情态动词没有时态的变化,如must。情态动词本身词义不完全,③不能单独作谓语动词,必须和不带to 的动词原形连用。④常见情态动词有can,may,must,have to,should, would等。情态动词一般有多个意义。⑤情态动词的否定式一般是在其后面加not 构成,一般疑问句通常将其提到句首。⑥情态动词的肯定式一般不重读。
1.can
表示能力 We can speak a little English. Her sister can play the violin. I can play badminton,but I can't play volleyball.
表示许可 You can play basketball on weekends. We can't run in the hallways.
表示请求 Can you help me with my Chinese
注:could也可表示请求,但比can的语气更委婉。如:Could you tell him to call me back
2.may
表示许可,意思是“可以” May I borrow your dictionary Class is over.You may go now.
注:may和can 都可以表示许可,但两者有区别,may的用法比can更正式,语气更委婉。
表示可能性,意思是“也许,可能” I may be late,so don't wait for me. That may be true=Maybe that’s true.
注:could也可表示请求,但比can的语气更委婉。如:Could you tell him to call me back
3.must 表示“必须”
Don't arrive late for class.We must be on time. You must read a book before you watch TV.
4.have to 表示“不得不;必须”
We have to be quiet in the library. She has to do her homework first when she gets home.
异同点 must have to
不同点 常表示的是说话人的主观看法,语气比较强烈 I must go now. 往往强调客观需要。 It's a little late and I have to go now.
mustn't 表示“不准;禁止” You mustn't talk to your mother like that. don't have to表示“不必” You don't have to come if you don't want to.
一般只表示现在,没有人称和数的变化 I/We/You/They must do something about it. 可用于不同的时态,有人称和数的变化 I have to finish my work today. She has to finish her work today. They had to get to the station before 5:00.
相同点 have to表示“必须”时与must 意义很接近,有时可与must 互换。 We have to/must follow the rules.
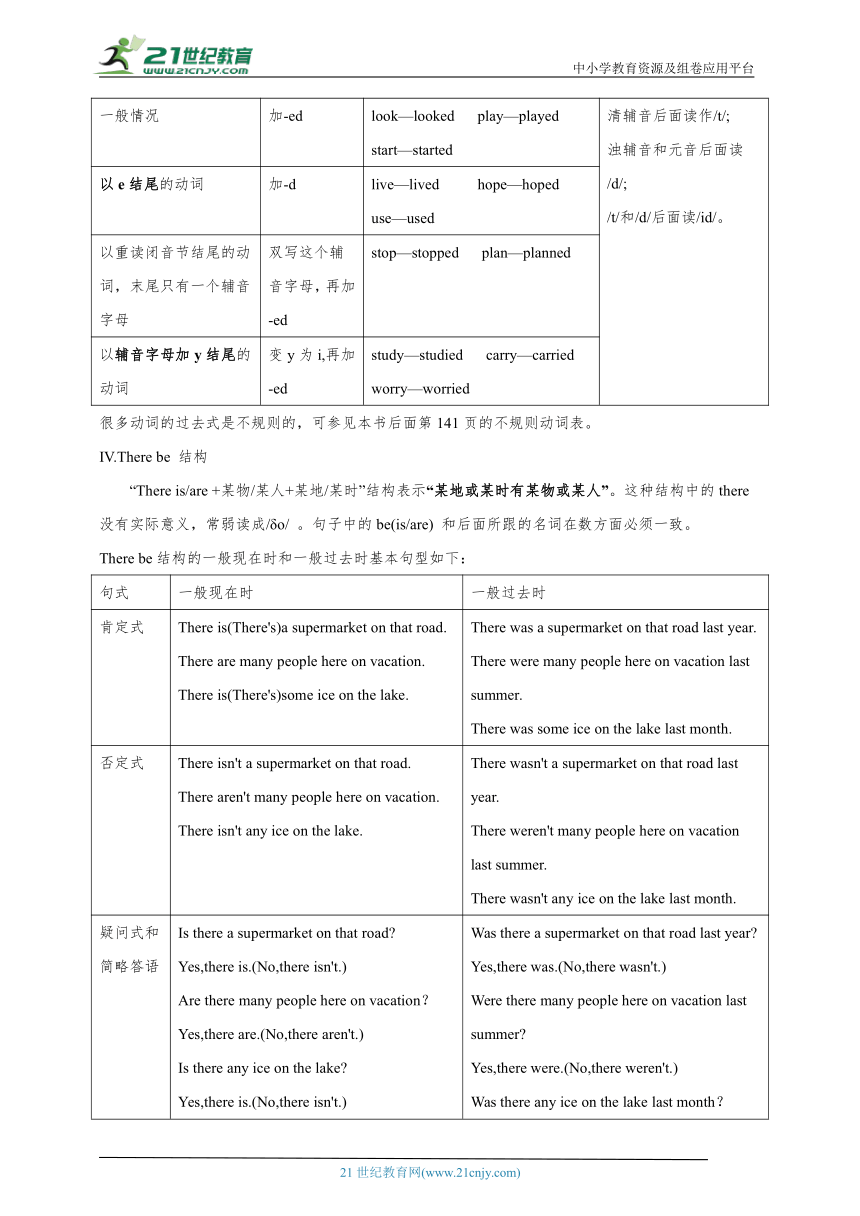
Ⅱ . 现在进行时 (Present Progressive Tense)
1. 现在进行时表示现在(说话瞬间)正在进行或发生的动作。例如:
The students are listening to the teacher. He is watching TV now.
现在进行时也可表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作。例如:
We are working on a farm these days. I'm reading a history book this month.
现在进行时是由助动词be (am/is/are)加动词-ing形式构成的。以动词work为例,现在进行时的肯定式、否定式、疑问式和简略答语如下:
肯定式 否定式
I am working He/She is working We/You/They are working I am not working. He/She is not working We/You/They are not working
疑问式和简略答语
Am I working Yes,you are./No,you are not (aren't). Are we working Yes,we/you are./No,we/you are not (aren't).
Are you working Yes,I am./No,I am not. Are you working Yes,we are./No,we are not (aren't).
Is he/she working Yes,he/she is./No,he/she is not(isn't). Are they working Yes,they are./No,they are not (aren't).
3. 动词-ing 形式的构成:
类别 构成方法 例词
一般情况 加-ing go—going ask—asking look—looking
以不发音字母e结尾的动词 去掉e,再加-ing write—writing make—making take—taking
以重读闭音节结尾的动词,末尾只有一个辅音字母 双写这个辅音字母,再加-ing get—getting sit—sitting put—putting run—running begin—beginning
Ⅲ.一般过去时 (Simple Past Tense)
1. 一般过去时表示过去某个时间或某一段时间内发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用,如yesterday,last night,in 1990,two days ago 等。例如:
He got up at 6:30 yesterday. I visited my grandparents last week.
一般过去时也表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,常和often,always等表示频度的时间状语连用。例如:
He always went to work by bus last year.
2.以动词be 和work 为例,一般过去时的肯定式、否定式、疑问式和简略答语构成如下:
动词 肯定式 否定式
be I/He/She was at home yesterday We/You/They were at home yesterday. I/He/She was not(wasn't)at home yesterday. We/You/They were not(weren't)at home yesterday.
work I/You/He/She/We/They worked in a hospital last year. I/You/He/She/We/They did not(didn't) work in a hospital last year.
动词 疑问式和简略答语
be Was I late yesterday? Yes,you were. No,you were not (weren't). Were you late yesterday Yes,I was. No,I was not (wasn't). Was he/she late yesterday Yes,he/she was. No,he/she was not (wasn't).
Were we early yesterday Yes,we/you were. No,we/you were not (weren't) Were you early yesterday Yes,we were. No,we were not (weren't). Were they early yesterday Yes,they were. No,they were not (weren't).
work Did I work last week Yes,you did. No,you did not (didn't). Did you work last week Yes,I did. No,I did not (didn't). Did he/she work last week Yes,he/she did. No,he/she did not (didn't).
Did we work last week Yes,we/you did. No,we/you did not (didn't). Did you work last week: Yes,we did. No,we did not (didn't). Did they work last week Yes,they did. No,they did not (didn't).
英语中动词过去式的构成分为规则与不规则两类。规则动词过去式的构成如下:
类别 构成方法 例词 读音规则
一般情况 加-ed look—looked play—played start—started 清辅音后面读作/t/; 浊辅音和元音后面读/d/; /t/和/d/后面读/id/。
以e结尾的动词 加-d live—lived hope—hoped use—used
以重读闭音节结尾的动词,末尾只有一个辅音字母 双写这个辅音字母,再加-ed stop—stopped plan—planned
以辅音字母加y结尾的动词 变y为i,再加-ed study—studied carry—carried worry—worried
很多动词的过去式是不规则的,可参见本书后面第141页的不规则动词表。
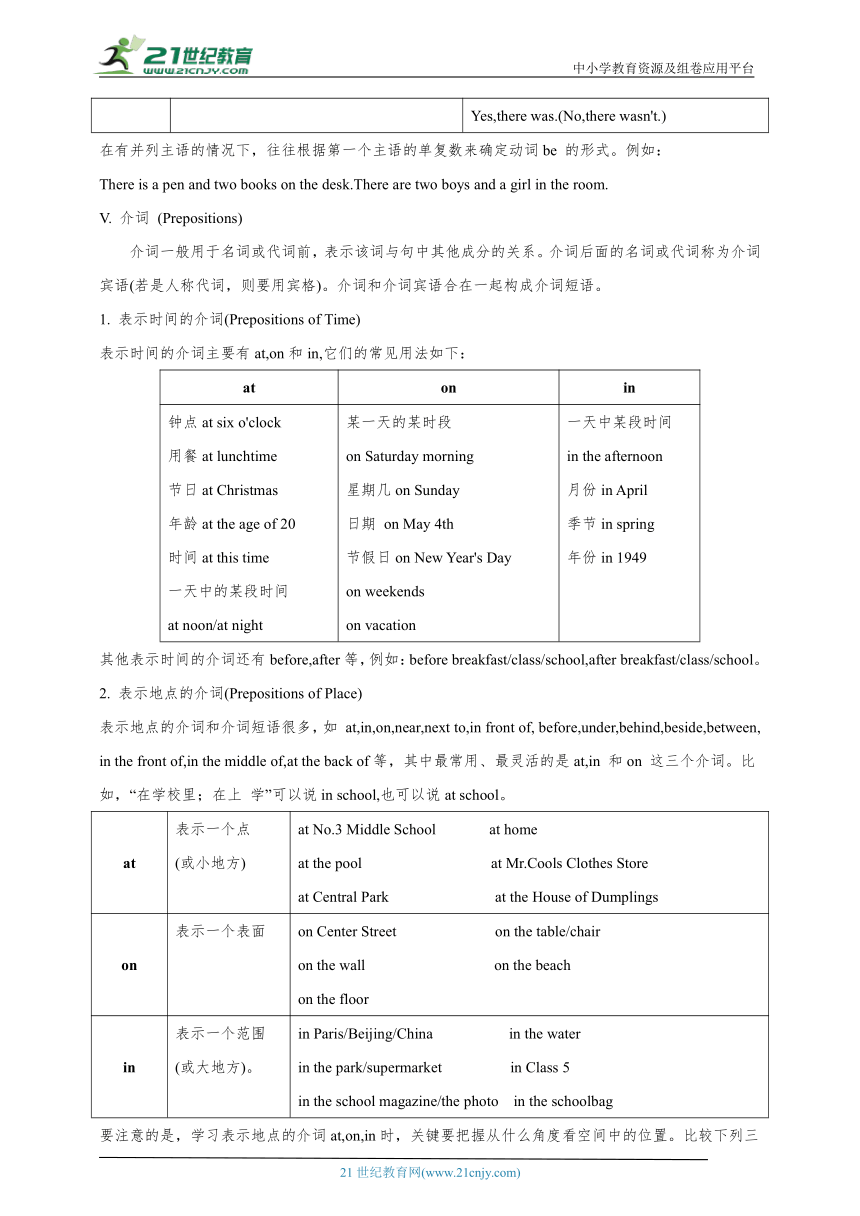
IV.There be 结构
“There is/are +某物/某人+某地/某时”结构表示“某地或某时有某物或某人”。这种结构中的there 没有实际意义,常弱读成/δo/ 。句子中的be(is/are) 和后面所跟的名词在数方面必须一致。
There be结构的一般现在时和一般过去时基本句型如下:
句式 一般现在时 一般过去时
肯定式 There is(There's)a supermarket on that road. There are many people here on vacation. There is(There's)some ice on the lake. There was a supermarket on that road last year. There were many people here on vacation last summer. There was some ice on the lake last month.
否定式 There isn't a supermarket on that road. There aren't many people here on vacation. There isn't any ice on the lake. There wasn't a supermarket on that road last year. There weren't many people here on vacation last summer. There wasn't any ice on the lake last month.
疑问式和简略答语 Is there a supermarket on that road Yes,there is.(No,there isn't.) Are there many people here on vacation? Yes,there are.(No,there aren't.) Is there any ice on the lake Yes,there is.(No,there isn't.) Was there a supermarket on that road last year Yes,there was.(No,there wasn't.) Were there many people here on vacation last summer Yes,there were.(No,there weren't.) Was there any ice on the lake last month? Yes,there was.(No,there wasn't.)
在有并列主语的情况下,往往根据第一个主语的单复数来确定动词be 的形式。例如:
There is a pen and two books on the desk.There are two boys and a girl in the room.
V. 介词 (Prepositions)
介词一般用于名词或代词前,表示该词与句中其他成分的关系。介词后面的名词或代词称为介词宾语(若是人称代词,则要用宾格)。介词和介词宾语合在一起构成介词短语。
1. 表示时间的介词(Prepositions of Time)
表示时间的介词主要有at,on和in,它们的常见用法如下:
at on in
钟点at six o'clock 用餐at lunchtime 节日at Christmas 年龄at the age of 20 时间at this time 一天中的某段时间 at noon/at night 某一天的某时段 on Saturday morning 星期几on Sunday 日期 on May 4th 节假日on New Year's Day on weekends on vacation 一天中某段时间 in the afternoon 月份in April 季节in spring 年份in 1949
其他表示时间的介词还有before,after等,例如:before breakfast/class/school,after breakfast/class/school。
2. 表示地点的介词(Prepositions of Place)
表示地点的介词和介词短语很多,如 at,in,on,near,next to,in front of, before,under,behind,beside,between, in the front of,in the middle of,at the back of等,其中最常用、最灵活的是at,in 和on 这三个介词。比如,“在学校里;在上 学”可以说in school,也可以说at school。
at 表示一个点 (或小地方) at No.3 Middle School at home at the pool at Mr.Cools Clothes Store at Central Park at the House of Dumplings
on 表示一个表面 on Center Street on the table/chair on the wall on the beach on the floor
in 表示一个范围(或大地方)。 in Paris/Beijing/China in the water in the park/supermarket in Class 5 in the school magazine/the photo in the schoolbag
要注意的是,学习表示地点的介词at,on,in时,关键要把握从什么角度看空间中的位置。比较下列三个句子:
They stood at the door and waited.他们站在门口等着。(站在门口那个点上)
He's putting up a picture on the door.他正在把一幅画贴到门上。(贴在门那个面上)
There's a hole in the door.门上有一个洞。(从立体的角度看门上的洞)
其他地点介词:
under 在…的下面 before 在…前面 in front of 在…前面 in the front of 在…前部 in the middle of 在…中间 behind 在…的后面 near 靠近;在…附近 next to 在…旁边;附近 beside 在…旁边 inside 在…的里面 outside 在…外边 between 在…之间 across from 在…对面 along 沿着 at the back of 在…的后面 The watch is under the bed. David is standing before the mirror. Jack is sitting in front of John. There are some chairs in the front of the room.(某物内部的前面) My home is in the middle of the city. The hotel is behind the library. There is a big supermarket near your house. The pay phone is next to the post office. Look!There's a dog beside Lily. I never went inside the building. We can eat outside the classroom but we can't eat inside. The library is between the restaurant and the supermarket. Our house is across from the supermarket. You pass a bank on your right and then go along Long Street. At the back of the school is a playground.
3. 其他介词
about 关于;对于 from 从…;自从 with 与…一起;附有 of …的;属于…的 to 向;到;对 as 担任;当…时 like 像;怎么样 at 在;对着;以 for 对于;为了 以…为代价; (时间持续)…之久 The American girl wants to learn about Chinese history. Could you tell me about your life He has a friend from England. What did you buy from the store Next to the hotel is a small house with an interesting garden She often goes to watch soccer matches with her father. Can you help the kids with their swimming Here is a photo of my family. What kind of movies do you like Let me tell you the way to my house. My English class is from 8:00 to 9:00. We have a job for you as a waiter. As a boy,he often went skating in winter. What does he look like What's the weather like Call Alan at 495-3539. We have sweaters at a very good price —only 25 dollars. For breakfast,he likes eggs,bananas and apples. For boys,we have socks for only five dollars each. After class,I play volleyball for two hours.
4. 固定搭配
1)常用介词和名词的连用
介词与其所带的宾语合在一起称作介词短语。以下是由at,on和in构成的一些常见介词短语:
at on in
at first起初;开始时 at last最后 at school在上学 at the moment此刻 at home在家 at present现在 at work上班;在工作 at the same time同时 on duty值日 on holiday度假 on time准时 on the left/right在左边/右边 on the radio在广播中 on foot步行 on sale出售;降价出售 on TV在电视上播放 on the phone在电话中 on the way在路上 in all总体 in class在课堂上 in English用英语 in the end最后 in bed躺在床上 in danger在危险中 in time及时地 in a minute立刻;马上
2)动词和介词的连用
arrive at/in到达 get off下车 learn from向…学习 look after照顾 look for寻找 think of想到 worry about担心 ask for请求 help sb.with sth.帮助某人做某事 listen to听 look at看;注视 talk about谈论 shout at对…大声叫喊 thank sb.for为…而感谢某人
3)形容词和介词的连用
be afraid of害怕 be careful with/about小心 be interested in对…感兴趣 be good at擅长 be good with善于应对 be strict with/about对…要求严格 be late for 迟到 be good for 对…有利
4)其他
by+ 交通工具 lots of /a lot of许多;大量 at least至少 by bus/train/plane/air/ship/bike at most 至多 at once 立即;马上
VI. 句子种类 (Sentence Types)
1.祈使句 (Imperative Sentences)
祈使句一般用来表示请求、命令、劝说、号召、警告等。在祈使句中,通常省略第二
人称主语you。肯定式以动词原形开头,否定式在动词原形前加don't 。例如:
Just go along New Street and turn left. Practice the guitar every day.
Don't arrive late for class. Don't fight.
为表示礼貌,祈使句中经常在句前或者句末加please 。句末用please 时,前面通常加逗号。例如:
Please write and tell me about yourself. Please call Karen at 555-e in,please.
以let开头的句子也是祈使句的一种结构,常用于第一、三人称,表示建议、邀请和劝说等。例如:
Let me tell you the way to my house Let's see the lions Let him come in.
2. 疑问句 (Questions)
选择疑问句 (Alternative Questions)
选择疑问句是指说话人提出两种或两种以上情况,问对方选择哪一种,两个选择项用 or 连接。选择疑问句不能用Yes或No 来回答。朗读时or 前面部分用升调,后面部分用降调。例如:
Is she tall or short She's tall.
Do they have straight hair or curly hair They have curly hair.
Do you usually eat a birthday cake or noodles I usually eat noodles
What would you like,tea or coffee I'd like some tea,please.
21世纪教育网 www.21cnjy.com 精品试卷·第 2 页 (共 2 页)
21世纪教育网(www.21cnjy.com)
人教版七下英语期末基础语法知识梳理(标注重难点)
I.情态动词 (Modal Verbs)
情态动词①表示说话人对所说动作的观点,如需要、可能、意愿、怀疑等。②在形式上,情态动词一般没有人称和数的变化,有的情态动词没有时态的变化,如must。情态动词本身词义不完全,③不能单独作谓语动词,必须和不带to 的动词原形连用。④常见情态动词有can,may,must,have to,should, would等。情态动词一般有多个意义。⑤情态动词的否定式一般是在其后面加not 构成,一般疑问句通常将其提到句首。⑥情态动词的肯定式一般不重读。
1.can
表示能力 We can speak a little English. Her sister can play the violin. I can play badminton,but I can't play volleyball.
表示许可 You can play basketball on weekends. We can't run in the hallways.
表示请求 Can you help me with my Chinese
注:could也可表示请求,但比can的语气更委婉。如:Could you tell him to call me back
2.may
表示许可,意思是“可以” May I borrow your dictionary Class is over.You may go now.
注:may和can 都可以表示许可,但两者有区别,may的用法比can更正式,语气更委婉。
表示可能性,意思是“也许,可能” I may be late,so don't wait for me. That may be true=Maybe that’s true.
注:could也可表示请求,但比can的语气更委婉。如:Could you tell him to call me back
3.must 表示“必须”
Don't arrive late for class.We must be on time. You must read a book before you watch TV.
4.have to 表示“不得不;必须”
We have to be quiet in the library. She has to do her homework first when she gets home.
异同点 must have to
不同点 常表示的是说话人的主观看法,语气比较强烈 I must go now. 往往强调客观需要。 It's a little late and I have to go now.
mustn't 表示“不准;禁止” You mustn't talk to your mother like that. don't have to表示“不必” You don't have to come if you don't want to.
一般只表示现在,没有人称和数的变化 I/We/You/They must do something about it. 可用于不同的时态,有人称和数的变化 I have to finish my work today. She has to finish her work today. They had to get to the station before 5:00.
相同点 have to表示“必须”时与must 意义很接近,有时可与must 互换。 We have to/must follow the rules.
Ⅱ . 现在进行时 (Present Progressive Tense)
1. 现在进行时表示现在(说话瞬间)正在进行或发生的动作。例如:
The students are listening to the teacher. He is watching TV now.
现在进行时也可表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作。例如:
We are working on a farm these days. I'm reading a history book this month.
现在进行时是由助动词be (am/is/are)加动词-ing形式构成的。以动词work为例,现在进行时的肯定式、否定式、疑问式和简略答语如下:
肯定式 否定式
I am working He/She is working We/You/They are working I am not working. He/She is not working We/You/They are not working
疑问式和简略答语
Am I working Yes,you are./No,you are not (aren't). Are we working Yes,we/you are./No,we/you are not (aren't).
Are you working Yes,I am./No,I am not. Are you working Yes,we are./No,we are not (aren't).
Is he/she working Yes,he/she is./No,he/she is not(isn't). Are they working Yes,they are./No,they are not (aren't).
3. 动词-ing 形式的构成:
类别 构成方法 例词
一般情况 加-ing go—going ask—asking look—looking
以不发音字母e结尾的动词 去掉e,再加-ing write—writing make—making take—taking
以重读闭音节结尾的动词,末尾只有一个辅音字母 双写这个辅音字母,再加-ing get—getting sit—sitting put—putting run—running begin—beginning
Ⅲ.一般过去时 (Simple Past Tense)
1. 一般过去时表示过去某个时间或某一段时间内发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用,如yesterday,last night,in 1990,two days ago 等。例如:
He got up at 6:30 yesterday. I visited my grandparents last week.
一般过去时也表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,常和often,always等表示频度的时间状语连用。例如:
He always went to work by bus last year.
2.以动词be 和work 为例,一般过去时的肯定式、否定式、疑问式和简略答语构成如下:
动词 肯定式 否定式
be I/He/She was at home yesterday We/You/They were at home yesterday. I/He/She was not(wasn't)at home yesterday. We/You/They were not(weren't)at home yesterday.
work I/You/He/She/We/They worked in a hospital last year. I/You/He/She/We/They did not(didn't) work in a hospital last year.
动词 疑问式和简略答语
be Was I late yesterday? Yes,you were. No,you were not (weren't). Were you late yesterday Yes,I was. No,I was not (wasn't). Was he/she late yesterday Yes,he/she was. No,he/she was not (wasn't).
Were we early yesterday Yes,we/you were. No,we/you were not (weren't) Were you early yesterday Yes,we were. No,we were not (weren't). Were they early yesterday Yes,they were. No,they were not (weren't).
work Did I work last week Yes,you did. No,you did not (didn't). Did you work last week Yes,I did. No,I did not (didn't). Did he/she work last week Yes,he/she did. No,he/she did not (didn't).
Did we work last week Yes,we/you did. No,we/you did not (didn't). Did you work last week: Yes,we did. No,we did not (didn't). Did they work last week Yes,they did. No,they did not (didn't).
英语中动词过去式的构成分为规则与不规则两类。规则动词过去式的构成如下:
类别 构成方法 例词 读音规则
一般情况 加-ed look—looked play—played start—started 清辅音后面读作/t/; 浊辅音和元音后面读/d/; /t/和/d/后面读/id/。
以e结尾的动词 加-d live—lived hope—hoped use—used
以重读闭音节结尾的动词,末尾只有一个辅音字母 双写这个辅音字母,再加-ed stop—stopped plan—planned
以辅音字母加y结尾的动词 变y为i,再加-ed study—studied carry—carried worry—worried
很多动词的过去式是不规则的,可参见本书后面第141页的不规则动词表。
IV.There be 结构
“There is/are +某物/某人+某地/某时”结构表示“某地或某时有某物或某人”。这种结构中的there 没有实际意义,常弱读成/δo/ 。句子中的be(is/are) 和后面所跟的名词在数方面必须一致。
There be结构的一般现在时和一般过去时基本句型如下:
句式 一般现在时 一般过去时
肯定式 There is(There's)a supermarket on that road. There are many people here on vacation. There is(There's)some ice on the lake. There was a supermarket on that road last year. There were many people here on vacation last summer. There was some ice on the lake last month.
否定式 There isn't a supermarket on that road. There aren't many people here on vacation. There isn't any ice on the lake. There wasn't a supermarket on that road last year. There weren't many people here on vacation last summer. There wasn't any ice on the lake last month.
疑问式和简略答语 Is there a supermarket on that road Yes,there is.(No,there isn't.) Are there many people here on vacation? Yes,there are.(No,there aren't.) Is there any ice on the lake Yes,there is.(No,there isn't.) Was there a supermarket on that road last year Yes,there was.(No,there wasn't.) Were there many people here on vacation last summer Yes,there were.(No,there weren't.) Was there any ice on the lake last month? Yes,there was.(No,there wasn't.)
在有并列主语的情况下,往往根据第一个主语的单复数来确定动词be 的形式。例如:
There is a pen and two books on the desk.There are two boys and a girl in the room.
V. 介词 (Prepositions)
介词一般用于名词或代词前,表示该词与句中其他成分的关系。介词后面的名词或代词称为介词宾语(若是人称代词,则要用宾格)。介词和介词宾语合在一起构成介词短语。
1. 表示时间的介词(Prepositions of Time)
表示时间的介词主要有at,on和in,它们的常见用法如下:
at on in
钟点at six o'clock 用餐at lunchtime 节日at Christmas 年龄at the age of 20 时间at this time 一天中的某段时间 at noon/at night 某一天的某时段 on Saturday morning 星期几on Sunday 日期 on May 4th 节假日on New Year's Day on weekends on vacation 一天中某段时间 in the afternoon 月份in April 季节in spring 年份in 1949
其他表示时间的介词还有before,after等,例如:before breakfast/class/school,after breakfast/class/school。
2. 表示地点的介词(Prepositions of Place)
表示地点的介词和介词短语很多,如 at,in,on,near,next to,in front of, before,under,behind,beside,between, in the front of,in the middle of,at the back of等,其中最常用、最灵活的是at,in 和on 这三个介词。比如,“在学校里;在上 学”可以说in school,也可以说at school。
at 表示一个点 (或小地方) at No.3 Middle School at home at the pool at Mr.Cools Clothes Store at Central Park at the House of Dumplings
on 表示一个表面 on Center Street on the table/chair on the wall on the beach on the floor
in 表示一个范围(或大地方)。 in Paris/Beijing/China in the water in the park/supermarket in Class 5 in the school magazine/the photo in the schoolbag
要注意的是,学习表示地点的介词at,on,in时,关键要把握从什么角度看空间中的位置。比较下列三个句子:
They stood at the door and waited.他们站在门口等着。(站在门口那个点上)
He's putting up a picture on the door.他正在把一幅画贴到门上。(贴在门那个面上)
There's a hole in the door.门上有一个洞。(从立体的角度看门上的洞)
其他地点介词:
under 在…的下面 before 在…前面 in front of 在…前面 in the front of 在…前部 in the middle of 在…中间 behind 在…的后面 near 靠近;在…附近 next to 在…旁边;附近 beside 在…旁边 inside 在…的里面 outside 在…外边 between 在…之间 across from 在…对面 along 沿着 at the back of 在…的后面 The watch is under the bed. David is standing before the mirror. Jack is sitting in front of John. There are some chairs in the front of the room.(某物内部的前面) My home is in the middle of the city. The hotel is behind the library. There is a big supermarket near your house. The pay phone is next to the post office. Look!There's a dog beside Lily. I never went inside the building. We can eat outside the classroom but we can't eat inside. The library is between the restaurant and the supermarket. Our house is across from the supermarket. You pass a bank on your right and then go along Long Street. At the back of the school is a playground.
3. 其他介词
about 关于;对于 from 从…;自从 with 与…一起;附有 of …的;属于…的 to 向;到;对 as 担任;当…时 like 像;怎么样 at 在;对着;以 for 对于;为了 以…为代价; (时间持续)…之久 The American girl wants to learn about Chinese history. Could you tell me about your life He has a friend from England. What did you buy from the store Next to the hotel is a small house with an interesting garden She often goes to watch soccer matches with her father. Can you help the kids with their swimming Here is a photo of my family. What kind of movies do you like Let me tell you the way to my house. My English class is from 8:00 to 9:00. We have a job for you as a waiter. As a boy,he often went skating in winter. What does he look like What's the weather like Call Alan at 495-3539. We have sweaters at a very good price —only 25 dollars. For breakfast,he likes eggs,bananas and apples. For boys,we have socks for only five dollars each. After class,I play volleyball for two hours.
4. 固定搭配
1)常用介词和名词的连用
介词与其所带的宾语合在一起称作介词短语。以下是由at,on和in构成的一些常见介词短语:
at on in
at first起初;开始时 at last最后 at school在上学 at the moment此刻 at home在家 at present现在 at work上班;在工作 at the same time同时 on duty值日 on holiday度假 on time准时 on the left/right在左边/右边 on the radio在广播中 on foot步行 on sale出售;降价出售 on TV在电视上播放 on the phone在电话中 on the way在路上 in all总体 in class在课堂上 in English用英语 in the end最后 in bed躺在床上 in danger在危险中 in time及时地 in a minute立刻;马上
2)动词和介词的连用
arrive at/in到达 get off下车 learn from向…学习 look after照顾 look for寻找 think of想到 worry about担心 ask for请求 help sb.with sth.帮助某人做某事 listen to听 look at看;注视 talk about谈论 shout at对…大声叫喊 thank sb.for为…而感谢某人
3)形容词和介词的连用
be afraid of害怕 be careful with/about小心 be interested in对…感兴趣 be good at擅长 be good with善于应对 be strict with/about对…要求严格 be late for 迟到 be good for 对…有利
4)其他
by+ 交通工具 lots of /a lot of许多;大量 at least至少 by bus/train/plane/air/ship/bike at most 至多 at once 立即;马上
VI. 句子种类 (Sentence Types)
1.祈使句 (Imperative Sentences)
祈使句一般用来表示请求、命令、劝说、号召、警告等。在祈使句中,通常省略第二
人称主语you。肯定式以动词原形开头,否定式在动词原形前加don't 。例如:
Just go along New Street and turn left. Practice the guitar every day.
Don't arrive late for class. Don't fight.
为表示礼貌,祈使句中经常在句前或者句末加please 。句末用please 时,前面通常加逗号。例如:
Please write and tell me about yourself. Please call Karen at 555-e in,please.
以let开头的句子也是祈使句的一种结构,常用于第一、三人称,表示建议、邀请和劝说等。例如:
Let me tell you the way to my house Let's see the lions Let him come in.
2. 疑问句 (Questions)
选择疑问句 (Alternative Questions)
选择疑问句是指说话人提出两种或两种以上情况,问对方选择哪一种,两个选择项用 or 连接。选择疑问句不能用Yes或No 来回答。朗读时or 前面部分用升调,后面部分用降调。例如:
Is she tall or short She's tall.
Do they have straight hair or curly hair They have curly hair.
Do you usually eat a birthday cake or noodles I usually eat noodles
What would you like,tea or coffee I'd like some tea,please.
21世纪教育网 www.21cnjy.com 精品试卷·第 2 页 (共 2 页)
21世纪教育网(www.21cnjy.com)
同课章节目录
