2024年中考英语语法复习讲义 句子成分,种类,结构
文档属性
| 名称 | 2024年中考英语语法复习讲义 句子成分,种类,结构 |
|
|
| 格式 | docx | ||
| 文件大小 | 51.2KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教新目标(Go for it)版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-06-26 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览


文档简介
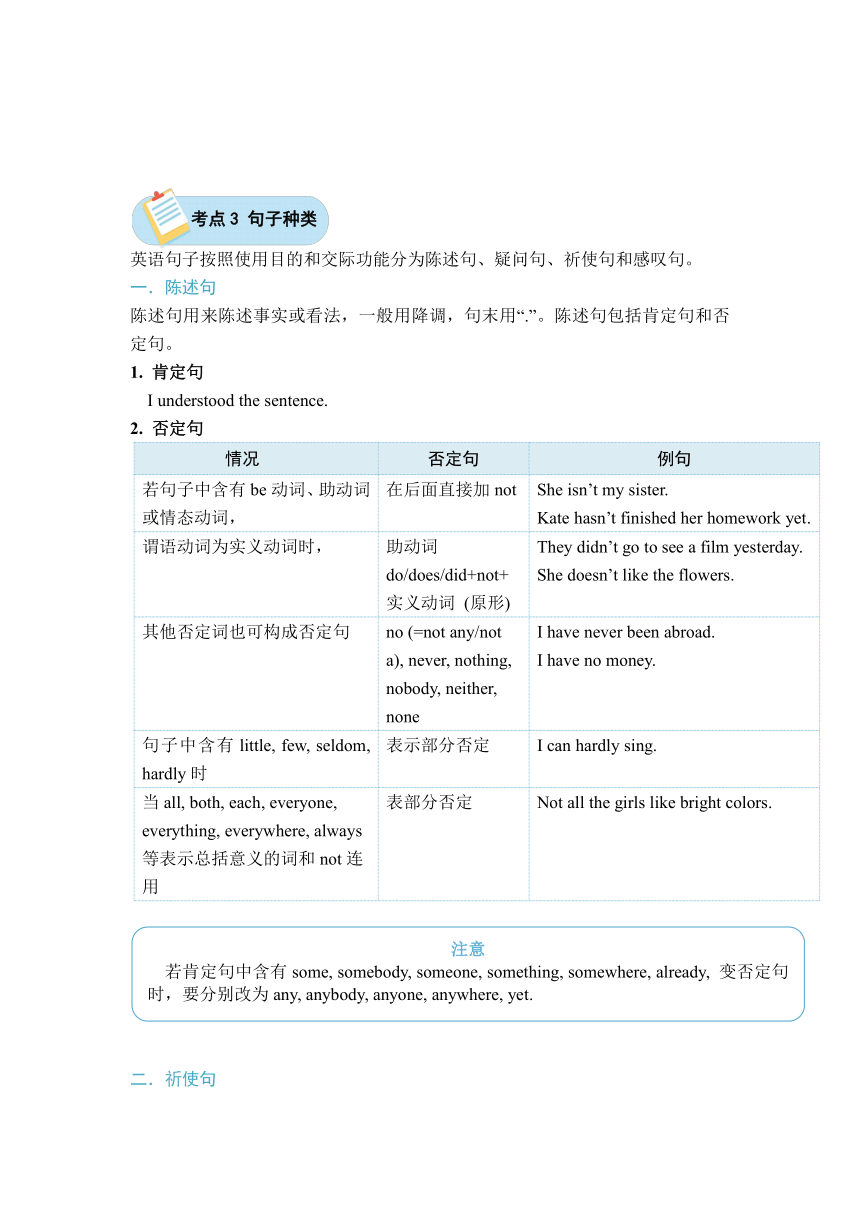
第12章 句子成分、结构和种类
组成句子的各个部分即句子成分。句子成分包括主语、谓语、表语、宾语、定语、状语、补足语、同位语等。
句子成分 说明 例句
主语 主语是句子中动作、行为的主体。主语由名词,代词,数词等担任。 A horse runs much faster than a cow. We should take care of our historic buildings. To drink a cup of cold juice is such hot weather is a great pleasure. *What we’ll do is leave a note for Mum to tell her we won’t be back till late.
谓语 谓语用来说明主语的行为,动作或所处的状态。谓语由动词充当。 She takes great care of her clothes. The little girl cried when he saw his toy gone.
宾语 宾语表示动作,行为的对象,有名词,代词,动名词等担任。 I will go to see an exhibition this weekend. I try to avoid going shopping on Saturday. I will get the computer repaired tomorrow.
表语 表语用来说明主语的特征,属性,状态等。表语通常由名词,代词,形容词,副词等充当。 My new roommate is an American boy. My work is to clean the room every day. The machine is out of date.
定语 定语是用来描述名词或代词的修饰语。它常和名词一起构成名词短语。定语有前置定语和后置定语。 How often do you run your washing machine Jenny sat on the stone step in front of the house. The model plane flying in the sky is made by him The book on the desk is mine.
状语 状语常用来修饰动词,形容词,副词,或整个句子。状语常由副词,介词短语,不定式,分词短语,从句等担当。 I will meet her at the airport at 9 o’clock tomorrow morning. The old building are pulled down because a new road will be built.
补语 补足主语意义的句子成分是主语补足语,补足宾语意义的句子成分是宾语补足语。 The singer was seen to enter a cafe. We must keep the classroom clean. He was made to stay at home by his mother.
同位语 对句子中某一成分作进一步解释说明,与前面的名词在语法上处于同等地位的句子成分即同位语。 We Chinese are proud of our history. They two wanted to go with us, too.
英语句子按照结构可分为简单句,并列句和复合句。
一.简单句
只有一个主语 (或并列主语) 和一个谓语 (或并列谓语) 的句子叫作简单句。简单句有 5种基本句型。
基本句型一:S+V (主 + 谓)
They walked and laughed.
基本句型二:S+V+P (主 + 系 + 表)
That pie looks good.
He became a famous doctor.
基本句型三:S+V+O (主 + 谓 + 宾)
Her father studies history.
基本句型四:S+V+O+O (主 + 谓 + 间宾 + 直宾)
They offered me a very good job.
I will send a copy to you.
基本句型五:S+V+O+P (主 + 谓 + 宾 + 宾补)
He made his younger brother happy.
Mun asked me to lay the table for the dinner.
二.并列句
两个或两个以上的简单句用并列连词或分号连接而成的句子叫作并列句。
He has a lot of money but he doesn’t have many friend.
Tom knocked at the door and it opened.
复合句
由一个主句和一个或者多个从句构成的句子叫作复合句。
I worked for a foreign company when I was in Shanghai.
A doctor is a person who looks after people’s health.
Parents shouldn’t give their children whatever they want.
英语句子按照使用目的和交际功能分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
一.陈述句
陈述句用来陈述事实或看法,一般用降调,句末用“.”。陈述句包括肯定句和否定句。
肯定句
I understood the sentence.
否定句
情况 否定句 例句
若句子中含有be动词、助动词或情态动词, 在后面直接加not She isn’t my sister. Kate hasn’t finished her homework yet.
谓语动词为实义动词时, 助动词do/does/did+not+实义动词 (原形) They didn’t go to see a film yesterday. She doesn’t like the flowers.
其他否定词也可构成否定句 no (=not any/not a), never, nothing, nobody, neither, none I have never been abroad. I have no money.
句子中含有little, few, seldom, hardly时 表示部分否定 I can hardly sing.
当all, both, each, everyone, everything, everywhere, always等表示总括意义的词和not连用 表部分否定 Not all the girls like bright colors.
二.祈使句
祈使句通常表示命令,请求,建议或劝告等,主语省略。主语省略。
肯定祈使句 否定祈使句
动词原形+其他 Open the door, please. Don’t+动词原形+其他 Don’t play football on the road.
Let’s+动词原形+其他 Let’s go to the park this Sunday. Let sb. not+动词原形+其他 Let’s not make so much noise here.
\ Never+动词原形+其他 Never late for school.
No+名词或动名词 No photos.
三.感叹句
感叹句由what, how引导。表示赞美,惊叹,喜悦等感情。
情况 引导词 结构
对句子中的名词或名词词组表示感叹 what What+a/an+adj. +单数名词 (+主语+谓语) What an interesting book (it is)!
What+adj. +名词复数/不可数名词 (+主语+谓语) What beautiful flowers (they are)! What interesting books you’ve bought us!
对句子中的形容词、副词或动词表示感叹 how How+adj. /adv. + (主语+谓语) How hard the people are working!
How+主语+谓语 How time flies! How she dances!
四.疑问句
用以提出问题的句子叫疑问句。
一般疑问句
能用yes或no回答的问句叫一般疑问句。一般疑问句主要有以下三种形式。
结构 例句
be+主语+其他 Is your sister a nurse
情态动词+主语+谓语+其他 Can you lend me your bike
助动词+主语+谓语+其他 Have you friends ever visited your home
2. 特殊疑问句
就句中某一部分进行提问的疑问句叫特殊疑问句。回答时要根据具体情况做出回答,不能用yes或no。
情况 常用的疑问代词/副词/词组 例句
疑问代词引导的特殊疑问句 who/what/which/whose/whom What is the girl doing
疑问副词引导的特殊疑问句 when/how/why/where Where are you from
疑问词组引导的特殊疑问句 what/which/whose+名词 What color is your new coat
how+adj. /adv. 构成的疑问短语:how many, how much, how old, how tall, how long, how often, how soon, how far How often do you do exercise How long have you been swimming
3. 选择疑问句
选择疑问句是提供两种或两种以上的情况,要求对方选择一种情况回答的问句,用or连接.
一般疑问句+or+被选择的部分+其他? —Do you like football or basketball —I like basketball.
特殊疑问句+A or B —Which do you like better, apples or pears —I like apples better.
4. 反义疑问句
反义疑问句是附加在陈述句之后,对陈述句所说的事实或观点提出疑问。陈述句是肯定句时,附加疑问句用否定形式,否定形式必须缩写;陈述句是否定句时,附加疑问句用肯定形式,即“前肯后否,前否后肯”。
John is kind, isn’t he
Jack doesn’t pass the exam, does he
反义疑问句的特殊用法
①. 当陈述部分为 there be 结构时,附加疑问句用“be的相应形式+there”。
There was a lot of traffic, wasn’t there
②. 当陈述部分是祈使句时,附加疑问句用will you。
Please pen the window, will you
Don’t make any noise, will you
③. 陈述部分是以Let us/me 开头的祈使句时,附加问句用will you;陈述部分是以let’s 开头的祈使句时,附加疑问句用shall we。
Let us wait for you in the reading room, will you
Let’s go out to play, shall we
④. 陈述部分的主语是指物的不定代词everything, anything, something, nothing等时,附加疑问句的主语用it。
Everything goes well with you, doesn’t it
Nothing is impossible, is it
⑤. 陈述部分的主语是指人的不定代词 no one, everyone, someone, everybody等,强调全体时,附加问句的主语用they;强调个体时附加疑问句的主语用he。
Everyone knows the answer, don’t they (强调全体)
Someone is expecting you, isn’t he (强调个体)
⑥.陈述部分含有little, few, never, no, nobody, hardly, seldom等否定词时,附加问句应用肯定形式。
They hardly speak English, do they
⑦.陈述部分是主从复合句时,附加问句的主语和动词通常与主句一致。
Tim thinks that Chinese is very hard, doesn’t he
⑧.陈述部分主句的主语为第一人称,谓语动词为think,believe等,后面接宾语从句时,附加问句的主语和动词应与宾语从句相一致;若陈述部分包含“I don’t think/believe/suppose. . . ”时,附加问句部分用肯定形式。
I think he is an excellent student, isn’t he
I don’t think he likes playing football, does he
⑨.回答反义疑问句时必须要基于事实来回答,即如果事实是肯定的,就用“Yes, 代词+肯定式”;如果事实是否定的,就用“No, 代词+否定式”。在“前否后肯”的句子中,答语中的 yes的含义为“不”,no的含义为“是”。
---Jack is a teacher, isn’t he
---Yes, he is. 是,他是教师。 (“杰克是教师”这一论述为事实)
---No, he isn’t. 不,他不是教师。 (“杰克是教师”这一论述不是事实)
---Jane didn’t go to the park yesterday, did she
---Yes, she did. 不,她去了 (此时Yes含义为“不”)
---No. she didn’t. 是的,他没去。 (此时No含义为“是”)
组成句子的各个部分即句子成分。句子成分包括主语、谓语、表语、宾语、定语、状语、补足语、同位语等。
句子成分 说明 例句
主语 主语是句子中动作、行为的主体。主语由名词,代词,数词等担任。 A horse runs much faster than a cow. We should take care of our historic buildings. To drink a cup of cold juice is such hot weather is a great pleasure. *What we’ll do is leave a note for Mum to tell her we won’t be back till late.
谓语 谓语用来说明主语的行为,动作或所处的状态。谓语由动词充当。 She takes great care of her clothes. The little girl cried when he saw his toy gone.
宾语 宾语表示动作,行为的对象,有名词,代词,动名词等担任。 I will go to see an exhibition this weekend. I try to avoid going shopping on Saturday. I will get the computer repaired tomorrow.
表语 表语用来说明主语的特征,属性,状态等。表语通常由名词,代词,形容词,副词等充当。 My new roommate is an American boy. My work is to clean the room every day. The machine is out of date.
定语 定语是用来描述名词或代词的修饰语。它常和名词一起构成名词短语。定语有前置定语和后置定语。 How often do you run your washing machine Jenny sat on the stone step in front of the house. The model plane flying in the sky is made by him The book on the desk is mine.
状语 状语常用来修饰动词,形容词,副词,或整个句子。状语常由副词,介词短语,不定式,分词短语,从句等担当。 I will meet her at the airport at 9 o’clock tomorrow morning. The old building are pulled down because a new road will be built.
补语 补足主语意义的句子成分是主语补足语,补足宾语意义的句子成分是宾语补足语。 The singer was seen to enter a cafe. We must keep the classroom clean. He was made to stay at home by his mother.
同位语 对句子中某一成分作进一步解释说明,与前面的名词在语法上处于同等地位的句子成分即同位语。 We Chinese are proud of our history. They two wanted to go with us, too.
英语句子按照结构可分为简单句,并列句和复合句。
一.简单句
只有一个主语 (或并列主语) 和一个谓语 (或并列谓语) 的句子叫作简单句。简单句有 5种基本句型。
基本句型一:S+V (主 + 谓)
They walked and laughed.
基本句型二:S+V+P (主 + 系 + 表)
That pie looks good.
He became a famous doctor.
基本句型三:S+V+O (主 + 谓 + 宾)
Her father studies history.
基本句型四:S+V+O+O (主 + 谓 + 间宾 + 直宾)
They offered me a very good job.
I will send a copy to you.
基本句型五:S+V+O+P (主 + 谓 + 宾 + 宾补)
He made his younger brother happy.
Mun asked me to lay the table for the dinner.
二.并列句
两个或两个以上的简单句用并列连词或分号连接而成的句子叫作并列句。
He has a lot of money but he doesn’t have many friend.
Tom knocked at the door and it opened.
复合句
由一个主句和一个或者多个从句构成的句子叫作复合句。
I worked for a foreign company when I was in Shanghai.
A doctor is a person who looks after people’s health.
Parents shouldn’t give their children whatever they want.
英语句子按照使用目的和交际功能分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
一.陈述句
陈述句用来陈述事实或看法,一般用降调,句末用“.”。陈述句包括肯定句和否定句。
肯定句
I understood the sentence.
否定句
情况 否定句 例句
若句子中含有be动词、助动词或情态动词, 在后面直接加not She isn’t my sister. Kate hasn’t finished her homework yet.
谓语动词为实义动词时, 助动词do/does/did+not+实义动词 (原形) They didn’t go to see a film yesterday. She doesn’t like the flowers.
其他否定词也可构成否定句 no (=not any/not a), never, nothing, nobody, neither, none I have never been abroad. I have no money.
句子中含有little, few, seldom, hardly时 表示部分否定 I can hardly sing.
当all, both, each, everyone, everything, everywhere, always等表示总括意义的词和not连用 表部分否定 Not all the girls like bright colors.
二.祈使句
祈使句通常表示命令,请求,建议或劝告等,主语省略。主语省略。
肯定祈使句 否定祈使句
动词原形+其他 Open the door, please. Don’t+动词原形+其他 Don’t play football on the road.
Let’s+动词原形+其他 Let’s go to the park this Sunday. Let sb. not+动词原形+其他 Let’s not make so much noise here.
\ Never+动词原形+其他 Never late for school.
No+名词或动名词 No photos.
三.感叹句
感叹句由what, how引导。表示赞美,惊叹,喜悦等感情。
情况 引导词 结构
对句子中的名词或名词词组表示感叹 what What+a/an+adj. +单数名词 (+主语+谓语) What an interesting book (it is)!
What+adj. +名词复数/不可数名词 (+主语+谓语) What beautiful flowers (they are)! What interesting books you’ve bought us!
对句子中的形容词、副词或动词表示感叹 how How+adj. /adv. + (主语+谓语) How hard the people are working!
How+主语+谓语 How time flies! How she dances!
四.疑问句
用以提出问题的句子叫疑问句。
一般疑问句
能用yes或no回答的问句叫一般疑问句。一般疑问句主要有以下三种形式。
结构 例句
be+主语+其他 Is your sister a nurse
情态动词+主语+谓语+其他 Can you lend me your bike
助动词+主语+谓语+其他 Have you friends ever visited your home
2. 特殊疑问句
就句中某一部分进行提问的疑问句叫特殊疑问句。回答时要根据具体情况做出回答,不能用yes或no。
情况 常用的疑问代词/副词/词组 例句
疑问代词引导的特殊疑问句 who/what/which/whose/whom What is the girl doing
疑问副词引导的特殊疑问句 when/how/why/where Where are you from
疑问词组引导的特殊疑问句 what/which/whose+名词 What color is your new coat
how+adj. /adv. 构成的疑问短语:how many, how much, how old, how tall, how long, how often, how soon, how far How often do you do exercise How long have you been swimming
3. 选择疑问句
选择疑问句是提供两种或两种以上的情况,要求对方选择一种情况回答的问句,用or连接.
一般疑问句+or+被选择的部分+其他? —Do you like football or basketball —I like basketball.
特殊疑问句+A or B —Which do you like better, apples or pears —I like apples better.
4. 反义疑问句
反义疑问句是附加在陈述句之后,对陈述句所说的事实或观点提出疑问。陈述句是肯定句时,附加疑问句用否定形式,否定形式必须缩写;陈述句是否定句时,附加疑问句用肯定形式,即“前肯后否,前否后肯”。
John is kind, isn’t he
Jack doesn’t pass the exam, does he
反义疑问句的特殊用法
①. 当陈述部分为 there be 结构时,附加疑问句用“be的相应形式+there”。
There was a lot of traffic, wasn’t there
②. 当陈述部分是祈使句时,附加疑问句用will you。
Please pen the window, will you
Don’t make any noise, will you
③. 陈述部分是以Let us/me 开头的祈使句时,附加问句用will you;陈述部分是以let’s 开头的祈使句时,附加疑问句用shall we。
Let us wait for you in the reading room, will you
Let’s go out to play, shall we
④. 陈述部分的主语是指物的不定代词everything, anything, something, nothing等时,附加疑问句的主语用it。
Everything goes well with you, doesn’t it
Nothing is impossible, is it
⑤. 陈述部分的主语是指人的不定代词 no one, everyone, someone, everybody等,强调全体时,附加问句的主语用they;强调个体时附加疑问句的主语用he。
Everyone knows the answer, don’t they (强调全体)
Someone is expecting you, isn’t he (强调个体)
⑥.陈述部分含有little, few, never, no, nobody, hardly, seldom等否定词时,附加问句应用肯定形式。
They hardly speak English, do they
⑦.陈述部分是主从复合句时,附加问句的主语和动词通常与主句一致。
Tim thinks that Chinese is very hard, doesn’t he
⑧.陈述部分主句的主语为第一人称,谓语动词为think,believe等,后面接宾语从句时,附加问句的主语和动词应与宾语从句相一致;若陈述部分包含“I don’t think/believe/suppose. . . ”时,附加问句部分用肯定形式。
I think he is an excellent student, isn’t he
I don’t think he likes playing football, does he
⑨.回答反义疑问句时必须要基于事实来回答,即如果事实是肯定的,就用“Yes, 代词+肯定式”;如果事实是否定的,就用“No, 代词+否定式”。在“前否后肯”的句子中,答语中的 yes的含义为“不”,no的含义为“是”。
---Jack is a teacher, isn’t he
---Yes, he is. 是,他是教师。 (“杰克是教师”这一论述为事实)
---No, he isn’t. 不,他不是教师。 (“杰克是教师”这一论述不是事实)
---Jane didn’t go to the park yesterday, did she
---Yes, she did. 不,她去了 (此时Yes含义为“不”)
---No. she didn’t. 是的,他没去。 (此时No含义为“是”)
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
