人教版七年级英语下期末复习要点
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版七年级英语下期末复习要点 |  | |
| 格式 | docx | ||
| 文件大小 | 256.5KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教新目标(Go for it)版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-06-30 20:16:04 | ||
图片预览




文档简介
专题一:词性变化
名词变形
考点一:可数名词变复数
名词按其所表示的事物的性质可以分为可数名词与不可数名词。可数名词有单数和复数两种形式,复数构成形式的部分规则如下:
规则变化
情况 构成方法 例词
一般情况 加-s pen—pens, doctor—doctors, map—maps
以s, x, ch, sh 结尾 加-es bus—buses, box—boxes, watch—watches, brush—brushes
以辅音字母加y结尾 将y变为i再加-es story—stories, family—families
以元音字母加y结尾 只加-s boy—boys, day—days
以o结尾 有生命的加-es potato—potatoes, tomato—tomatoes
无生命的加-s photo—photos, radio—radios
2. 不规则变化
变单词内部元音字母 man—men, woman—women, tooth—teeth, , foot—feet, policeman—policemen
特殊变化 child—children, mouse—mice,sheep—sheep,fish—fish,
常用复数的词 shoes, glasses, trousers, jeans,clothes, pants, shorts, people
考点二、不可数名词
不可数名词的表达
不可数名词没有复数形式。★前面不能用不定冠词a(an) 修饰,但可用much, a lot of/lots of, plenty of, some, little, a little等修饰。作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式。
Eg:There is some tea in the cup. 杯子里有些茶
(2)常用“数词/不定冠词 + 名词 + of + 不可数名词”来表示不可数名词的量。
Eg:a piece of bread 一张纸,two cups of tea两杯茶, three bowls of rice。
★作主语时,谓语动词的数取决于of前面的名词的数。
Eg:There are three cups of orange juice on the table. 桌子上有三玻璃杯橙汁。
常考的不可数名词
fun乐趣,homework作业,housework家务,paper纸,work工作,news新闻(newspaper可数),weather天气, bread 面包, rice 米饭
有些名词既可数又不可数,意义不同
chicken, salad, ice-cream, cabbage, cake, orange,fruit,
exercise锻炼不可数,体操可数 morning exercises/eye exercises
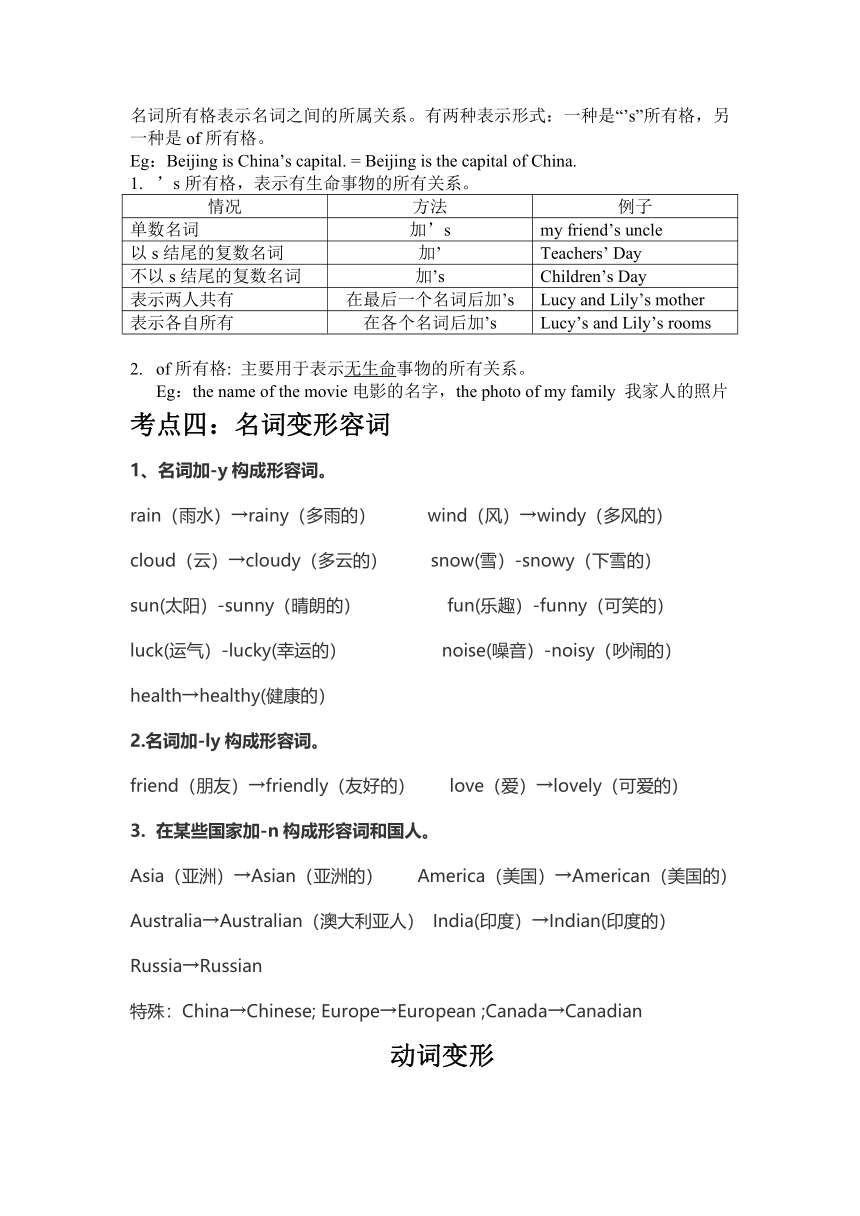
考点三:名词变所有格
名词所有格表示名词之间的所属关系。有两种表示形式:一种是“’s”所有格,另一种是of所有格。
Eg:Beijing is China’s capital. = Beijing is the capital of China.
’s所有格,表示有生命事物的所有关系。
情况 方法 例子
单数名词 加’s my friend’s uncle
以s结尾的复数名词 加’ Teachers’ Day
不以s结尾的复数名词 加’s Children’s Day
表示两人共有 在最后一个名词后加’s Lucy and Lily’s mother
表示各自所有 在各个名词后加’s Lucy’s and Lily’s rooms
of所有格: 主要用于表示无生命事物的所有关系。
Eg:the name of the movie电影的名字,the photo of my family 我家人的照片
考点四:名词变形容词
1、名词加-y构成形容词。
rain(雨水)→rainy(多雨的) wind(风)→windy(多风的)
cloud(云)→cloudy(多云的) snow(雪)-snowy(下雪的)
sun(太阳)-sunny(晴朗的) fun(乐趣)-funny(可笑的)
luck(运气)-lucky(幸运的) noise(噪音)-noisy(吵闹的)
health→healthy(健康的)
2.名词加-ly构成形容词。
friend(朋友)→friendly(友好的) love(爱)→lovely(可爱的)
在某些国家加-n构成形容词和国人。
Asia(亚洲)→Asian(亚洲的) America(美国)→American(美国的)
Australia→Australian(澳大利亚人) India(印度)→Indian(印度的)
Russia→Russian
特殊:China→Chinese; Europe→European ;Canada→Canadian
动词变形
动词包括be动词、助动词、实义动词和情态动词。
动词类型 一般现在时 一般过去时 用法
be动词 am/is/are was/were 单用is,复用are;am和is的过去式为was.
助动词 do/does did
实义动词 原形/三单 动词过去式 主语为第三人称单数,谓语动词用三单形式
情态动词 原形 1.后用动词原形;2.无人称和数的变化
考点一:动词变-ing形式。
现在进行时:be+doing (标志词:listen, look, now, right now)
介词(for/at/with/in/on/about...)+doing
have fun +doing=have a good/great time +doing 愉快地做某事
enjoy +doing喜欢做某事 eg. enjoy reading
practice doing 练习做某事 practice playing the guitar
how about/what about +doing 提建议:做某事怎么样?
spend time/money (in)+doing花时间/钱做某事
thank you for doing sth 感谢某人做某事
forget/remember +doing 忘记/记得做过某事
finish +doing 做完某事
like+to do/doing 喜欢做某事
考点二、动词前加to(to do)
1. would like to do sth.=want do do sth.想要做某事
2. how+to do sth/what +to do
3. forget/remember to do sth 忘记/记得去做某事
4. have time to do sth. 有时间做某事
5. It takes sb some time to do sth. 花某人多少时间做某事
6. wish to do sth 希望做某事
7. plan to do sth 计划做某事
8 .it’s +adj( for) sb.to do sth. 做某事(对于某人)来说是怎样的
ask sb. to do sth. 叫某人做某事
10.tell sb (not)to do sth. 告诉某人做/不做某事
11.need to do sth. 需要做某事
12. help sb to do/do sth 帮助某人做某事
考点三:动词变名词
变为做动作的人+er/or/ist
work-worker,write-writer,teach-teacher,sing-singer,drive-driver,
farm-farmer,visit-visitor,act-actor,act-actress,art-artist,music-musician, piano-pianist, violin-violinist
形容词和副词变形
形容词常用来修饰名词或代词,多用作定语、表语。常以“的”结尾。
副词常用来修饰动词、形容词和副词本身。常以“地”结尾。
e.g. 1)He play the guitar well.
2) The tigers are really scary.
3) He runs quite fast.
考点一:形容词变副词
形变副的规则:
一般情况下,直接加-ly
quick-quickly; slow-slowly; quiet-quietly; different-differently;
以辅音字母加y结尾的形容词要变y为i,然后再加-ly。如:busy-busily; easy-easily;happy-happily; lucky-luckily;
考点二:ed 和ing形容词的区分
意义不同。-ed结尾的形容词常形容有某种感觉或产生某种感情,所以主语往往是人。如:interested感兴趣的; relaxed放松的; bored无聊的;scared惊慌的;excited激动的,兴奋的;
-ing 常形容让人/动物产生某种感情,译为“令人...”如:
Interesting令人感兴趣的;relaxing令人放松的; boring无聊的; exciting令人激动的
E.g. I am interested in the interesting movie.
专题二:人称代词和冠词
人称代词
1. 人称代词定义:表示“我,你,他,她,它,我们,你们,他们”的词叫做人称代词。人称代词分主格和宾格两类,有单、复数之分。 如:
We are the best. 我们是最棒的。
Please give us more time to finish it.请给我们更多的时间来完成它。
g. She is happy today. / It’s an interesting movie 2. 人称代词形式:
人称 代词 第一人称 第二人称 第三人称
单数 复数 单数 复数 单数 复数
主格 I we you you he she it they
宾格 me us you you him her it them
物主代词
1. 物主代词的定义:
表示所属关系的代词叫物主代词。物主代词有形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词。形容词性物主代词用在名词前(有名则形),不能单独使用。名词性物主代词相当于一个名词,使用时后面不能再加名词(无名则名)。
例句:This is my schoolbag. 这是我的书包。
That is his bike. = That is his. 这是他的自行车。
2. 物主代词的形式:
物主 代词 第一人称 第二人称 第三人称
单数 复数 单数 复数 单数 复数
形容词性 my our your your his her its their
名词性 mine ours yours yours his hers its theirs
3. 物主代词的用法:
1). 形容词性物主代词置于名词前,起修饰作用,表示“某人的”。如:
My name is Chris. 我的名字是克丽丝。
2). 名词性物主代词起名词的作用,表示“某人的……”,但是后面不能跟名词。
形容词性物主代词+名词=名词性物主代词。如:
This is her book. Where is yours 这是她的书。你的(书)呢?
1.英语人称代词用法口诀:
人称代词主宾格, 作用不同莫用错。 主格动词前做主, 动词介词后宾格。
You和it主宾同, 其他主宾须分清。 人称代词并列现, 尊重他人礼当先。
单数人称二三一, 复数人称一二三。 若把错误责任担, 第一人称我靠前。
2.英语物主代词用法口诀:
物主代词分两种,形容词性名词性。形容词性能力差,自己不能来当家。
句子当中作定语,身后定把名词加。物主代词名词性,相当名词可单用。
句中充当主宾表,身后没有名词影。两种代词形不同,添个 s 形变名。
his, its不用变,my变mine要记清。
冠词专项
含义:冠词通常用在名词前,可以简单理解为是名词的帽子。其中冠词分为定冠词the,不定冠词a/an和零冠词。
用法。
1.定冠词:定冠词在名词前面是具有特指的功能,给了这个名词限定了范围,通常可翻译为“这个this 、那个that、这些these、那些those”。
下面情况都需用定冠词:①世界上独一无二的事物、②说话对方都知道的人或事、③用于海洋、山脉、江河、湖泊、群岛名之前、④the+姓的复数形式,表示一家人 the Smiths、⑤乐器 play the piano、⑦序数词前加定冠词 the first one、⑧上文已经提到的、⑨用在特指的人或物前 the boy is my brother.
常见搭配短语:in the end in the future the same at the moment The next day In the morning on the left......
2.不定冠词:a/an通常表示事物的数量,有一的含义。Eg: I have a book on my desk.也可表示一类事物。Eg: A dog can run.注意:a用在以辅音因素开头的单词前,而an用在以元音因素开头的单词前,(记住不是强调字母哦!)Eg: a ruler an eraser
常见用a的词:( useful usual unit uniform....)
常见用an的词:(umbrella uncle ugly.....)
常见搭配短语: have a good time
3.零冠词:
下面情况都需用零冠词:(不用冠词)。
①吃喝玩乐类(一日三餐、棋类)eg: play chess
②季节、月份、星期、节日。Eg: in summer.......
③人名、地名、国家名、城市名、街道名。Eg: People square.
④称呼、职位、头衔。Eg: Mike, come here please.
⑤名词前已经有代词及some、 any 等修饰时。Eg: Some people go to the cinema to watch movie.
⑥by+交通工具。Eg: by bus/ subway.....
⑦语言、学科前。Eg: I am not good at English.
常见搭配短语:play tennis play chess in July in August
by taxi by bus on Monday on Friday
have lunch have dinner on foot on time........
专题三:时态
(一般现在时、一般过去时、现在进行时)
一、一般现在时
时态 含义 时间状语
一般现在时 表示经常发生的动作或存在的状态。 always , usually, often, sometimes ,seldom, never, every day, every… ,three times a day 等
构成及变化 例句
be动词的句式结构:
肯定句:主语+be (am/is/ are)+其它。 I am a boy. 我是一个男孩。
否定句:主语+ be (am/is/ are) + not +其它。 He is not a worker. 他不是工人。
一般疑问句:Be (Am/Is/Are) +主语+其它 ---Are you a student ---Yes. I am. / No, I'm not.
特殊疑问句:疑问词Be动词开头的一般疑问句 Where is my bike
行为动词的句式结构:
1. 当主语为第一,二人称及复数时,助动词为do,
肯定句:主语+动词原形(+其它)。 We often play basketball after school.
否定句:主语+ don’t+动词原形(+其它)。 We don’t play basketball after school.
一般疑问句:Do +主语+动词原形+其它 ---Do you often play basketball after school ---Yes, we do. / No, we don't.
特殊疑问句:疑问词+以do开头的一般疑问句 What do you often do after school
2. 当主语为第三人称单数时 , 助动词为does
肯定句:主语+动词三单式(+其它)。 He swims well.
否定句:主语+ doesn’t+动词原形(+其它)。 He doesn’t swim well.
一般疑问句:Does +主语+动词原形+其它 ---Does he swim well ---Yes, he does. / No, he doesn't.
特殊疑问句:疑问词+以does开头的一般疑问句 How does your father go to work
【注意】第三人称单数的动词变化规则(只有在第三人称为主语的肯定句中,动词才用三单式) (1) 多数动词直接加s:runs, likes, takes, (2) 结尾是s, x, sh, ch, o,前为辅音字母, 结尾加es:watch-watches, go-goes, do-does, wash-washes, dress-dresses, (3) 动词辅音+y结尾:将y改为i加es:study-studies, fly-flies, 但在y前如果为元音则直接加s:buys, plays...... (4) 不规则变化have和be动词:have-has, be-am / is / are
【注意】第三人称单数的动词变化规则(只有在第三人称为主语的肯定句中,动词才用三单式) (1) 多数动词直接加s:runs, likes, takes, (2) 结尾是s, x, sh, ch, o,前为辅音字母, 结尾加es:watch-watches, go-goes, do-does, wash-washes, dress-dresses, (3) 动词辅音+y结尾:将y改为i加es:study-studies, fly-flies, 但在y前如果为元音则直接加s:buys, plays...... (4) 不规则变化have和be动词:have-has, be-am / is / are
一般过去时
时态 含义 时间状语
一般过去时 表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态,也可表示过去经常性的动作。 last night, last+时间, two days ago, 时间+ago, in +过去的年份, just now 刚才, yesterday, yesterday+时间 等
基本结构
构成及变化 例句
be动词的句式结构:
肯定句:主语+be (was/were)+其它。 I was a student. 我是一个学生。
否定句:主语+ be (was/were) + not +其它。 He was not a worker. 他不是工人。
一般疑问句:Be (Was/Were) +主语+其它 ---Are you a student ---Yes. I was. / No, I wasn’t.
特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句 Where was my bike
行为动词的句式结构:
肯定句:主语 + 动词的过去式+其它。 I watched a film last Sunday .
否定句:主语+ didn’t + 动词原形+其它。 I didn’t watch a film last Sunday .
一般疑问句:Did + 主语 + 动词原形+其它 ---Did you watch a film last Sunday ---Yes, I did . / No , I didn’t .
特殊疑问句:疑问词+ 以did 开头的一般疑问句 What did you do last Sunday
【注意】动词过去式变化规则: 1. 规则动词的过去式 (1) 一般在动词原形末尾加–ed:help- helped, look- looked , play-played (2) 结尾是辅音字母+不发音-e,加–d:live-lived,like-liked,taste-tasted (3) 重读闭音节结尾,双写末尾的字母,再加-ed:stop-stopped,shop-shopped (4) 结尾是辅音字母+y , 先变“y”为“i”,再加-ed:study---studied, worry ---worried 2.不规则变化详见课本不规则动词表
时态 含义 时间状语
现在进行时 表示现在或现阶段正在进行的动作或发生的事。 now , Look! Listen! at this time Where is … Don’t talk! It’s 8:00am. at the moment,等
现在进行时
基本结构
构成及变化 例句
肯定句:主语+be(am/is/are)+Ving+其他。 They are playing basketball in the park.
否定句:主语+be(am/is/are)+not+Ving+其他。 He isn’t studying at classroom now.
一般疑问句:Be(Am/Is/Are)+主语+Ving+其他 Is Lisa talking on the phone
特殊疑问句:疑问词+ 以be+ ving的一般疑问句 What are they doing
现在分词的构成: ①直接加-ing. look -looking study- studying play-playing ②重读闭音节结尾,双写末尾的字母,再加-ing. run-running swim-swimming get-getting shop-shopping stop-stopping ③以不发音的e 结尾去e加-ing .make-making dance-dancing have-having
数词与介词用法
核心语法:数词
基数词的构成
(1)0—12单独记。如: zero, one, two, three等。
(2)13—19的词尾都是teen。但13—thirteen,15—fifteen,18—eighteen需要特殊记。
(3)20以上的整十的基数词均以ty结尾。如:20—twenty,30—thirty,40—forty,等。
(4)"几十几"要加连字符号"-"。如:48—forty-eight, 97—ninety-seven等。
(5)"几百几十"或者"几百几十几"在"百"后加and。
156—one hundred and fifty-six, 509—five hundred and nine。
二、序数词的构成
(1)"第一"、"第二"、"第三"分别是first, second, third。
(2)"第四"到"第十九"除了fifth, eighth, ninth, twelfth是特殊的拼写外,其余的都在相应基数词后面加"th"构成。如:fourth。
(3)20以上的整十的序数词由相应的基数词变y为i,再加"-eth"。如:thirty→thirtieth; fifty→fiftieth。
(4)20以上的非整十的基数词变序数词时,只变化个位数。如:twenty-one→twenty-first; one hundred and one→one hundred and first。
(5)口诀:一二三、特殊记,末尾加上th, 8去t, 9去e, f 来把ve替,ty 变作tie, 若是要变几十几,只变个位就可以。
三、时间表达法
用法速记口诀:顺读方法最常见,先读小时再分钟;逆读方法分两类,过半用to不到past.
时刻读法:“整点数+分钟”;(分钟数小于或等于30分钟)“分钟数+past+整点数”;
(分钟数大于30分钟)“所差分钟数+to+下一整点数”
Eg: 6:30读作six thirty 或 half past six;8:45 读作 a quarter to nine
注意:15分钟常用a quarter,半小时常用half。
对时间提问:when(大小时间都可以) 和what time(对时刻提问)
年 year:时间(年月日)的表达:月日,年(月份+序数词, 年份)。例:January 1st, 2024 。
月 month:January (Jan.) 一月、February (Feb.) 二月、March(Mar.) 三月、April (Apr.) 四月、May 五月、June (Jun. ) 六月、July (Jul.) 七月、August (Aug.) 八月、September (Sep.)九月、October (Oct. )十月、November (Nov.) 十一月、December (Dec.) 十二月
周 week: weekday(工作日)、weekend(周末)
日 day:星期一Monday、星期二Tuesday、星期三Wednesday、星期四 Thursday、星期五Friday、星期六Saturday、星期日Sunday
季节season: spring(春)、summer(夏)、autumn(秋)、winter(冬)
核心语法:介词 (介词一般用于名词、代词或动名词之前,在句中不单独作句子成分,只表示其后的名词或相当于名词的短语与其他句子成分的关系。注:介词后面的动词要加ing。本学期学过的介词有in, about, for, at, on, under,with, after, from, of等。)
基础时间介词
at
用在黎明、中午、夜晚和午夜前 at dawn、at noon、at night 、at midnight
用在具体时刻前 at 6:45、at 8 p.m.
on
用在具体的某一天前 on Monday on Sunday on June 1st on July 1st,1997on Children's Day on Mother's Day
用在某一天的早、中、晚前 on a sunny morning on Sunday night on the evening of October 20th
【口诀】具体某一天,被修饰的早午晚
用在普通的早、午、晚前 in the morning、in the afternoon、in the evening
用在年份、月份、季节前 in 2019、in August、in December、in summer、in winter
【口诀】早午晚,年月季
in:
普通的早、中、晚。
before 表示“在...之前” e.g. You should wash your hands before meals.
after 表示“在...之后” e.g. Spring comes after winter.
from 表示“从...(开始)” e.g. My sister began to learn dance from the age of five. 【常见搭配】from...to... 从...到...
for for+一段时间,表示“长达...”. e.g. I do my homework for an hour every day.我每天做作业的时间长达一小时。
三、方式介词
by by+交通工具 I go to school by bus/ car.
with 与......在一起,附有 They have a butterfly house with over 200 kinds of butterflies. I’d like some mapo tofu with rice.
地点介词
on 表示”在...上面“,通常指跟事物相接触,例如:on the sofa在沙发上;又如:The apples are on the tree.树上结着苹果;特别注意:鸟儿再树上,用介词in,例如:There are some birds in the tree.树上有一些鸟儿。
in表示”在...里面“,例如:in my book case在我的书柜里面;又如:in my room在in表示”在...里面“,例如:in my book case在我的书柜里面;又如:in my room在我的房间里面。
under表示”在...下面“,例如:My shoes are under my bed.我的鞋子在我的床底下。
by表示”在...旁边“;例如:camp by the lake
in front of 在··前面 Jack is sitting in front of John.
in the front of 在··前部 There are some chairs in the front of the room.(某物内部的前面)
in the middle of 在··中间 My home is in the middle of the city.
behind 在··的后面 The hotel is behind the library.
near 靠近;在··附近 There is a big supermarket near your house.
next to 在···旁边;附近 The pay phone is next to the post office.
beside 在··旁边 Look! There's a dog beside Lily.
inside 在··的里面 I never went inside the building.
outside 在··外边 We can eat outside the classroom but we can't eat inside.
between…and…在···之间 The library is between the restaurant and the supermarket.
across from 在··对面 Our house is across from the supermarket.
along沿着 You pass a bank on your right and then go along Long Street.
at the back of在……的后面 At the back of the school is a playground.
at表示一个点(或小地点);in表示一个范围(或大地方)。
六、其他一些常用介词的主要用法及示例
1.about表示“有关;关于” Let's think about the food. / It's a book about birds.
2.for(1) 表示目的、目标、用途。如:I need a jacket for school. / For girls, we have fruit salad.
(2) 表示交换。如:We have blue pens for only ten dollars.
(3) 表示原因。如:Thank you for your help.
(4) 表示“为了,作为”。如:What do you have for lunch
3.from(1) 表示时间的起点(从…;自…). 如:Lunch is from 12:00 to 1:00.
(2) 表示来源、出处(从…;由…).如:-Where are you from -I'm from Shanghai.
I received a letter from my mother.
4.of表示“关于”或所属关系“…的”。如:Here are two nice photos of my family.
5.to表示方向(到…去;向…;往…).如:I go to school at 7:00.
6.with (1) 表示同伴、同道(和…一起;偕同)Come with me. / I go swimming with Lisa after school.
(2) with+工具”,表“用”. 如:We can make a paper plane with some paper.
7. as 表示担任;当……时。如:As a boy, he often went skating in winter.
8. like 表示像;怎么样。如:What does he look like / What’s the weather like
名词变形
考点一:可数名词变复数
名词按其所表示的事物的性质可以分为可数名词与不可数名词。可数名词有单数和复数两种形式,复数构成形式的部分规则如下:
规则变化
情况 构成方法 例词
一般情况 加-s pen—pens, doctor—doctors, map—maps
以s, x, ch, sh 结尾 加-es bus—buses, box—boxes, watch—watches, brush—brushes
以辅音字母加y结尾 将y变为i再加-es story—stories, family—families
以元音字母加y结尾 只加-s boy—boys, day—days
以o结尾 有生命的加-es potato—potatoes, tomato—tomatoes
无生命的加-s photo—photos, radio—radios
2. 不规则变化
变单词内部元音字母 man—men, woman—women, tooth—teeth, , foot—feet, policeman—policemen
特殊变化 child—children, mouse—mice,sheep—sheep,fish—fish,
常用复数的词 shoes, glasses, trousers, jeans,clothes, pants, shorts, people
考点二、不可数名词
不可数名词的表达
不可数名词没有复数形式。★前面不能用不定冠词a(an) 修饰,但可用much, a lot of/lots of, plenty of, some, little, a little等修饰。作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式。
Eg:There is some tea in the cup. 杯子里有些茶
(2)常用“数词/不定冠词 + 名词 + of + 不可数名词”来表示不可数名词的量。
Eg:a piece of bread 一张纸,two cups of tea两杯茶, three bowls of rice。
★作主语时,谓语动词的数取决于of前面的名词的数。
Eg:There are three cups of orange juice on the table. 桌子上有三玻璃杯橙汁。
常考的不可数名词
fun乐趣,homework作业,housework家务,paper纸,work工作,news新闻(newspaper可数),weather天气, bread 面包, rice 米饭
有些名词既可数又不可数,意义不同
chicken, salad, ice-cream, cabbage, cake, orange,fruit,
exercise锻炼不可数,体操可数 morning exercises/eye exercises
考点三:名词变所有格
名词所有格表示名词之间的所属关系。有两种表示形式:一种是“’s”所有格,另一种是of所有格。
Eg:Beijing is China’s capital. = Beijing is the capital of China.
’s所有格,表示有生命事物的所有关系。
情况 方法 例子
单数名词 加’s my friend’s uncle
以s结尾的复数名词 加’ Teachers’ Day
不以s结尾的复数名词 加’s Children’s Day
表示两人共有 在最后一个名词后加’s Lucy and Lily’s mother
表示各自所有 在各个名词后加’s Lucy’s and Lily’s rooms
of所有格: 主要用于表示无生命事物的所有关系。
Eg:the name of the movie电影的名字,the photo of my family 我家人的照片
考点四:名词变形容词
1、名词加-y构成形容词。
rain(雨水)→rainy(多雨的) wind(风)→windy(多风的)
cloud(云)→cloudy(多云的) snow(雪)-snowy(下雪的)
sun(太阳)-sunny(晴朗的) fun(乐趣)-funny(可笑的)
luck(运气)-lucky(幸运的) noise(噪音)-noisy(吵闹的)
health→healthy(健康的)
2.名词加-ly构成形容词。
friend(朋友)→friendly(友好的) love(爱)→lovely(可爱的)
在某些国家加-n构成形容词和国人。
Asia(亚洲)→Asian(亚洲的) America(美国)→American(美国的)
Australia→Australian(澳大利亚人) India(印度)→Indian(印度的)
Russia→Russian
特殊:China→Chinese; Europe→European ;Canada→Canadian
动词变形
动词包括be动词、助动词、实义动词和情态动词。
动词类型 一般现在时 一般过去时 用法
be动词 am/is/are was/were 单用is,复用are;am和is的过去式为was.
助动词 do/does did
实义动词 原形/三单 动词过去式 主语为第三人称单数,谓语动词用三单形式
情态动词 原形 1.后用动词原形;2.无人称和数的变化
考点一:动词变-ing形式。
现在进行时:be+doing (标志词:listen, look, now, right now)
介词(for/at/with/in/on/about...)+doing
have fun +doing=have a good/great time +doing 愉快地做某事
enjoy +doing喜欢做某事 eg. enjoy reading
practice doing 练习做某事 practice playing the guitar
how about/what about +doing 提建议:做某事怎么样?
spend time/money (in)+doing花时间/钱做某事
thank you for doing sth 感谢某人做某事
forget/remember +doing 忘记/记得做过某事
finish +doing 做完某事
like+to do/doing 喜欢做某事
考点二、动词前加to(to do)
1. would like to do sth.=want do do sth.想要做某事
2. how+to do sth/what +to do
3. forget/remember to do sth 忘记/记得去做某事
4. have time to do sth. 有时间做某事
5. It takes sb some time to do sth. 花某人多少时间做某事
6. wish to do sth 希望做某事
7. plan to do sth 计划做某事
8 .it’s +adj( for) sb.to do sth. 做某事(对于某人)来说是怎样的
ask sb. to do sth. 叫某人做某事
10.tell sb (not)to do sth. 告诉某人做/不做某事
11.need to do sth. 需要做某事
12. help sb to do/do sth 帮助某人做某事
考点三:动词变名词
变为做动作的人+er/or/ist
work-worker,write-writer,teach-teacher,sing-singer,drive-driver,
farm-farmer,visit-visitor,act-actor,act-actress,art-artist,music-musician, piano-pianist, violin-violinist
形容词和副词变形
形容词常用来修饰名词或代词,多用作定语、表语。常以“的”结尾。
副词常用来修饰动词、形容词和副词本身。常以“地”结尾。
e.g. 1)He play the guitar well.
2) The tigers are really scary.
3) He runs quite fast.
考点一:形容词变副词
形变副的规则:
一般情况下,直接加-ly
quick-quickly; slow-slowly; quiet-quietly; different-differently;
以辅音字母加y结尾的形容词要变y为i,然后再加-ly。如:busy-busily; easy-easily;happy-happily; lucky-luckily;
考点二:ed 和ing形容词的区分
意义不同。-ed结尾的形容词常形容有某种感觉或产生某种感情,所以主语往往是人。如:interested感兴趣的; relaxed放松的; bored无聊的;scared惊慌的;excited激动的,兴奋的;
-ing 常形容让人/动物产生某种感情,译为“令人...”如:
Interesting令人感兴趣的;relaxing令人放松的; boring无聊的; exciting令人激动的
E.g. I am interested in the interesting movie.
专题二:人称代词和冠词
人称代词
1. 人称代词定义:表示“我,你,他,她,它,我们,你们,他们”的词叫做人称代词。人称代词分主格和宾格两类,有单、复数之分。 如:
We are the best. 我们是最棒的。
Please give us more time to finish it.请给我们更多的时间来完成它。
g. She is happy today. / It’s an interesting movie 2. 人称代词形式:
人称 代词 第一人称 第二人称 第三人称
单数 复数 单数 复数 单数 复数
主格 I we you you he she it they
宾格 me us you you him her it them
物主代词
1. 物主代词的定义:
表示所属关系的代词叫物主代词。物主代词有形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词。形容词性物主代词用在名词前(有名则形),不能单独使用。名词性物主代词相当于一个名词,使用时后面不能再加名词(无名则名)。
例句:This is my schoolbag. 这是我的书包。
That is his bike. = That is his. 这是他的自行车。
2. 物主代词的形式:
物主 代词 第一人称 第二人称 第三人称
单数 复数 单数 复数 单数 复数
形容词性 my our your your his her its their
名词性 mine ours yours yours his hers its theirs
3. 物主代词的用法:
1). 形容词性物主代词置于名词前,起修饰作用,表示“某人的”。如:
My name is Chris. 我的名字是克丽丝。
2). 名词性物主代词起名词的作用,表示“某人的……”,但是后面不能跟名词。
形容词性物主代词+名词=名词性物主代词。如:
This is her book. Where is yours 这是她的书。你的(书)呢?
1.英语人称代词用法口诀:
人称代词主宾格, 作用不同莫用错。 主格动词前做主, 动词介词后宾格。
You和it主宾同, 其他主宾须分清。 人称代词并列现, 尊重他人礼当先。
单数人称二三一, 复数人称一二三。 若把错误责任担, 第一人称我靠前。
2.英语物主代词用法口诀:
物主代词分两种,形容词性名词性。形容词性能力差,自己不能来当家。
句子当中作定语,身后定把名词加。物主代词名词性,相当名词可单用。
句中充当主宾表,身后没有名词影。两种代词形不同,添个 s 形变名。
his, its不用变,my变mine要记清。
冠词专项
含义:冠词通常用在名词前,可以简单理解为是名词的帽子。其中冠词分为定冠词the,不定冠词a/an和零冠词。
用法。
1.定冠词:定冠词在名词前面是具有特指的功能,给了这个名词限定了范围,通常可翻译为“这个this 、那个that、这些these、那些those”。
下面情况都需用定冠词:①世界上独一无二的事物、②说话对方都知道的人或事、③用于海洋、山脉、江河、湖泊、群岛名之前、④the+姓的复数形式,表示一家人 the Smiths、⑤乐器 play the piano、⑦序数词前加定冠词 the first one、⑧上文已经提到的、⑨用在特指的人或物前 the boy is my brother.
常见搭配短语:in the end in the future the same at the moment The next day In the morning on the left......
2.不定冠词:a/an通常表示事物的数量,有一的含义。Eg: I have a book on my desk.也可表示一类事物。Eg: A dog can run.注意:a用在以辅音因素开头的单词前,而an用在以元音因素开头的单词前,(记住不是强调字母哦!)Eg: a ruler an eraser
常见用a的词:( useful usual unit uniform....)
常见用an的词:(umbrella uncle ugly.....)
常见搭配短语: have a good time
3.零冠词:
下面情况都需用零冠词:(不用冠词)。
①吃喝玩乐类(一日三餐、棋类)eg: play chess
②季节、月份、星期、节日。Eg: in summer.......
③人名、地名、国家名、城市名、街道名。Eg: People square.
④称呼、职位、头衔。Eg: Mike, come here please.
⑤名词前已经有代词及some、 any 等修饰时。Eg: Some people go to the cinema to watch movie.
⑥by+交通工具。Eg: by bus/ subway.....
⑦语言、学科前。Eg: I am not good at English.
常见搭配短语:play tennis play chess in July in August
by taxi by bus on Monday on Friday
have lunch have dinner on foot on time........
专题三:时态
(一般现在时、一般过去时、现在进行时)
一、一般现在时
时态 含义 时间状语
一般现在时 表示经常发生的动作或存在的状态。 always , usually, often, sometimes ,seldom, never, every day, every… ,three times a day 等
构成及变化 例句
be动词的句式结构:
肯定句:主语+be (am/is/ are)+其它。 I am a boy. 我是一个男孩。
否定句:主语+ be (am/is/ are) + not +其它。 He is not a worker. 他不是工人。
一般疑问句:Be (Am/Is/Are) +主语+其它 ---Are you a student ---Yes. I am. / No, I'm not.
特殊疑问句:疑问词Be动词开头的一般疑问句 Where is my bike
行为动词的句式结构:
1. 当主语为第一,二人称及复数时,助动词为do,
肯定句:主语+动词原形(+其它)。 We often play basketball after school.
否定句:主语+ don’t+动词原形(+其它)。 We don’t play basketball after school.
一般疑问句:Do +主语+动词原形+其它 ---Do you often play basketball after school ---Yes, we do. / No, we don't.
特殊疑问句:疑问词+以do开头的一般疑问句 What do you often do after school
2. 当主语为第三人称单数时 , 助动词为does
肯定句:主语+动词三单式(+其它)。 He swims well.
否定句:主语+ doesn’t+动词原形(+其它)。 He doesn’t swim well.
一般疑问句:Does +主语+动词原形+其它 ---Does he swim well ---Yes, he does. / No, he doesn't.
特殊疑问句:疑问词+以does开头的一般疑问句 How does your father go to work
【注意】第三人称单数的动词变化规则(只有在第三人称为主语的肯定句中,动词才用三单式) (1) 多数动词直接加s:runs, likes, takes, (2) 结尾是s, x, sh, ch, o,前为辅音字母, 结尾加es:watch-watches, go-goes, do-does, wash-washes, dress-dresses, (3) 动词辅音+y结尾:将y改为i加es:study-studies, fly-flies, 但在y前如果为元音则直接加s:buys, plays...... (4) 不规则变化have和be动词:have-has, be-am / is / are
【注意】第三人称单数的动词变化规则(只有在第三人称为主语的肯定句中,动词才用三单式) (1) 多数动词直接加s:runs, likes, takes, (2) 结尾是s, x, sh, ch, o,前为辅音字母, 结尾加es:watch-watches, go-goes, do-does, wash-washes, dress-dresses, (3) 动词辅音+y结尾:将y改为i加es:study-studies, fly-flies, 但在y前如果为元音则直接加s:buys, plays...... (4) 不规则变化have和be动词:have-has, be-am / is / are
一般过去时
时态 含义 时间状语
一般过去时 表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态,也可表示过去经常性的动作。 last night, last+时间, two days ago, 时间+ago, in +过去的年份, just now 刚才, yesterday, yesterday+时间 等
基本结构
构成及变化 例句
be动词的句式结构:
肯定句:主语+be (was/were)+其它。 I was a student. 我是一个学生。
否定句:主语+ be (was/were) + not +其它。 He was not a worker. 他不是工人。
一般疑问句:Be (Was/Were) +主语+其它 ---Are you a student ---Yes. I was. / No, I wasn’t.
特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句 Where was my bike
行为动词的句式结构:
肯定句:主语 + 动词的过去式+其它。 I watched a film last Sunday .
否定句:主语+ didn’t + 动词原形+其它。 I didn’t watch a film last Sunday .
一般疑问句:Did + 主语 + 动词原形+其它 ---Did you watch a film last Sunday ---Yes, I did . / No , I didn’t .
特殊疑问句:疑问词+ 以did 开头的一般疑问句 What did you do last Sunday
【注意】动词过去式变化规则: 1. 规则动词的过去式 (1) 一般在动词原形末尾加–ed:help- helped, look- looked , play-played (2) 结尾是辅音字母+不发音-e,加–d:live-lived,like-liked,taste-tasted (3) 重读闭音节结尾,双写末尾的字母,再加-ed:stop-stopped,shop-shopped (4) 结尾是辅音字母+y , 先变“y”为“i”,再加-ed:study---studied, worry ---worried 2.不规则变化详见课本不规则动词表
时态 含义 时间状语
现在进行时 表示现在或现阶段正在进行的动作或发生的事。 now , Look! Listen! at this time Where is … Don’t talk! It’s 8:00am. at the moment,等
现在进行时
基本结构
构成及变化 例句
肯定句:主语+be(am/is/are)+Ving+其他。 They are playing basketball in the park.
否定句:主语+be(am/is/are)+not+Ving+其他。 He isn’t studying at classroom now.
一般疑问句:Be(Am/Is/Are)+主语+Ving+其他 Is Lisa talking on the phone
特殊疑问句:疑问词+ 以be+ ving的一般疑问句 What are they doing
现在分词的构成: ①直接加-ing. look -looking study- studying play-playing ②重读闭音节结尾,双写末尾的字母,再加-ing. run-running swim-swimming get-getting shop-shopping stop-stopping ③以不发音的e 结尾去e加-ing .make-making dance-dancing have-having
数词与介词用法
核心语法:数词
基数词的构成
(1)0—12单独记。如: zero, one, two, three等。
(2)13—19的词尾都是teen。但13—thirteen,15—fifteen,18—eighteen需要特殊记。
(3)20以上的整十的基数词均以ty结尾。如:20—twenty,30—thirty,40—forty,等。
(4)"几十几"要加连字符号"-"。如:48—forty-eight, 97—ninety-seven等。
(5)"几百几十"或者"几百几十几"在"百"后加and。
156—one hundred and fifty-six, 509—five hundred and nine。
二、序数词的构成
(1)"第一"、"第二"、"第三"分别是first, second, third。
(2)"第四"到"第十九"除了fifth, eighth, ninth, twelfth是特殊的拼写外,其余的都在相应基数词后面加"th"构成。如:fourth。
(3)20以上的整十的序数词由相应的基数词变y为i,再加"-eth"。如:thirty→thirtieth; fifty→fiftieth。
(4)20以上的非整十的基数词变序数词时,只变化个位数。如:twenty-one→twenty-first; one hundred and one→one hundred and first。
(5)口诀:一二三、特殊记,末尾加上th, 8去t, 9去e, f 来把ve替,ty 变作tie, 若是要变几十几,只变个位就可以。
三、时间表达法
用法速记口诀:顺读方法最常见,先读小时再分钟;逆读方法分两类,过半用to不到past.
时刻读法:“整点数+分钟”;(分钟数小于或等于30分钟)“分钟数+past+整点数”;
(分钟数大于30分钟)“所差分钟数+to+下一整点数”
Eg: 6:30读作six thirty 或 half past six;8:45 读作 a quarter to nine
注意:15分钟常用a quarter,半小时常用half。
对时间提问:when(大小时间都可以) 和what time(对时刻提问)
年 year:时间(年月日)的表达:月日,年(月份+序数词, 年份)。例:January 1st, 2024 。
月 month:January (Jan.) 一月、February (Feb.) 二月、March(Mar.) 三月、April (Apr.) 四月、May 五月、June (Jun. ) 六月、July (Jul.) 七月、August (Aug.) 八月、September (Sep.)九月、October (Oct. )十月、November (Nov.) 十一月、December (Dec.) 十二月
周 week: weekday(工作日)、weekend(周末)
日 day:星期一Monday、星期二Tuesday、星期三Wednesday、星期四 Thursday、星期五Friday、星期六Saturday、星期日Sunday
季节season: spring(春)、summer(夏)、autumn(秋)、winter(冬)
核心语法:介词 (介词一般用于名词、代词或动名词之前,在句中不单独作句子成分,只表示其后的名词或相当于名词的短语与其他句子成分的关系。注:介词后面的动词要加ing。本学期学过的介词有in, about, for, at, on, under,with, after, from, of等。)
基础时间介词
at
用在黎明、中午、夜晚和午夜前 at dawn、at noon、at night 、at midnight
用在具体时刻前 at 6:45、at 8 p.m.
on
用在具体的某一天前 on Monday on Sunday on June 1st on July 1st,1997on Children's Day on Mother's Day
用在某一天的早、中、晚前 on a sunny morning on Sunday night on the evening of October 20th
【口诀】具体某一天,被修饰的早午晚
用在普通的早、午、晚前 in the morning、in the afternoon、in the evening
用在年份、月份、季节前 in 2019、in August、in December、in summer、in winter
【口诀】早午晚,年月季
in:
普通的早、中、晚。
before 表示“在...之前” e.g. You should wash your hands before meals.
after 表示“在...之后” e.g. Spring comes after winter.
from 表示“从...(开始)” e.g. My sister began to learn dance from the age of five. 【常见搭配】from...to... 从...到...
for for+一段时间,表示“长达...”. e.g. I do my homework for an hour every day.我每天做作业的时间长达一小时。
三、方式介词
by by+交通工具 I go to school by bus/ car.
with 与......在一起,附有 They have a butterfly house with over 200 kinds of butterflies. I’d like some mapo tofu with rice.
地点介词
on 表示”在...上面“,通常指跟事物相接触,例如:on the sofa在沙发上;又如:The apples are on the tree.树上结着苹果;特别注意:鸟儿再树上,用介词in,例如:There are some birds in the tree.树上有一些鸟儿。
in表示”在...里面“,例如:in my book case在我的书柜里面;又如:in my room在in表示”在...里面“,例如:in my book case在我的书柜里面;又如:in my room在我的房间里面。
under表示”在...下面“,例如:My shoes are under my bed.我的鞋子在我的床底下。
by表示”在...旁边“;例如:camp by the lake
in front of 在··前面 Jack is sitting in front of John.
in the front of 在··前部 There are some chairs in the front of the room.(某物内部的前面)
in the middle of 在··中间 My home is in the middle of the city.
behind 在··的后面 The hotel is behind the library.
near 靠近;在··附近 There is a big supermarket near your house.
next to 在···旁边;附近 The pay phone is next to the post office.
beside 在··旁边 Look! There's a dog beside Lily.
inside 在··的里面 I never went inside the building.
outside 在··外边 We can eat outside the classroom but we can't eat inside.
between…and…在···之间 The library is between the restaurant and the supermarket.
across from 在··对面 Our house is across from the supermarket.
along沿着 You pass a bank on your right and then go along Long Street.
at the back of在……的后面 At the back of the school is a playground.
at表示一个点(或小地点);in表示一个范围(或大地方)。
六、其他一些常用介词的主要用法及示例
1.about表示“有关;关于” Let's think about the food. / It's a book about birds.
2.for(1) 表示目的、目标、用途。如:I need a jacket for school. / For girls, we have fruit salad.
(2) 表示交换。如:We have blue pens for only ten dollars.
(3) 表示原因。如:Thank you for your help.
(4) 表示“为了,作为”。如:What do you have for lunch
3.from(1) 表示时间的起点(从…;自…). 如:Lunch is from 12:00 to 1:00.
(2) 表示来源、出处(从…;由…).如:-Where are you from -I'm from Shanghai.
I received a letter from my mother.
4.of表示“关于”或所属关系“…的”。如:Here are two nice photos of my family.
5.to表示方向(到…去;向…;往…).如:I go to school at 7:00.
6.with (1) 表示同伴、同道(和…一起;偕同)Come with me. / I go swimming with Lisa after school.
(2) with+工具”,表“用”. 如:We can make a paper plane with some paper.
7. as 表示担任;当……时。如:As a boy, he often went skating in winter.
8. like 表示像;怎么样。如:What does he look like / What’s the weather like
同课章节目录
