2025届高考英语第二轮复习语法专题和完形填空讲解(共57张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2025届高考英语第二轮复习语法专题和完形填空讲解(共57张ppt) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.7MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-07-10 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共57张PPT)
2025gaokao english second round review grammar and fill in the blanks
目录
CONTENTS
Overview of English Grammar Blank Filling in the College Entrance Examination
A detailed explanation of the usage of nouns and pronouns
A detailed explanation of the usage of adjectives and adverbs
目录
CONTENTS
A detailed explanation of verb tenses and voices
A detailed explanation of non finite verbs and modal verbs
On Subjunctive Mood and Emphasizing Sentence Patterns
Concise explanation of clauses and coordinate sentences
Introduction to Inverted and Omitted Sentences
目录
CONTENTS
Practical Practice of English Grammar Filling in the Blank for the College Entrance Examination
Course summary and exam preparation suggestions
01
Overview of English Grammar Blank Filling in the College Entrance Examination
Context-based
Grammar fill-in-the-blank questions often require students to understand the context of a sentence or passage to correctly fill in the blanks.
Characteristics of grammar fill in the blank question types
Grammar-focused
These questions test students' understanding of English grammar rules and their ability to apply them in a given context.
Vocabulary-dependent
A solid vocabulary is essential for identifying the correct words to fill in the blanks.
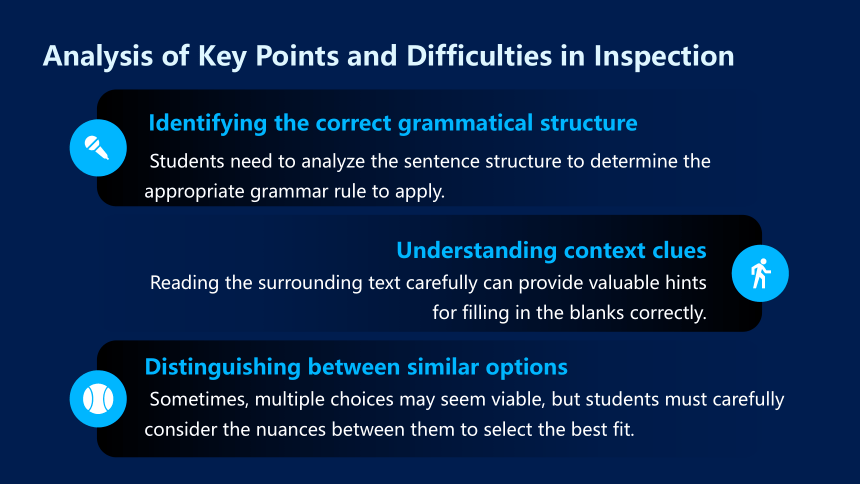
Analysis of Key Points and Difficulties in Inspection
Identifying the correct grammatical structure
Students need to analyze the sentence structure to determine the appropriate grammar rule to apply.
Understanding context clues
Reading the surrounding text carefully can provide valuable hints for filling in the blanks correctly.
Distinguishing between similar options
Sometimes, multiple choices may seem viable, but students must carefully consider the nuances between them to select the best fit.
Problem solving strategies and techniques
Analyze the sentence structure
01
Identify the subject, verb, and object of the sentence to determine the grammatical function of the missing word.
Use context clues
02
Look for keywords or phrases that provide hints about the missing word.
Eliminate incorrect options
03
Cross out choices that do not fit the context or grammatical structure of the sentence.
Practice makes perfect
04
Regular practice with grammar fill-in-the-blank questions can improve your ability to quickly identify the correct answers.
Common types of errors and prevention measures
Grammatical errors
01
Avoid common grammar mistakes, such as subject-verb disagreement or incorrect tense usage, by carefully reviewing your answers.
Vocabulary misuse
02
Ensure you understand the precise meaning of each word and how it fits into the context of the sentence.
Overlooking context clues
03
Pay attention to the surrounding text and use it to guide your choices.
Rushing through the questions
04
Take your time and carefully consider each option before making a selection.
02
A detailed explanation of the usage of nouns and pronouns
01
Nouns can be singular or plural, reflecting the quantity of the referred object.
The rules for the variation of noun numbers and gender
02
Gender in nouns is often linguistic, not biological, and varies across languages.
03
In English, most nouns do not have grammatical gender, but some, especially those borrowed from other languages, may retain it.
04
Number and gender variations can affect adjective and verb forms used with the noun.
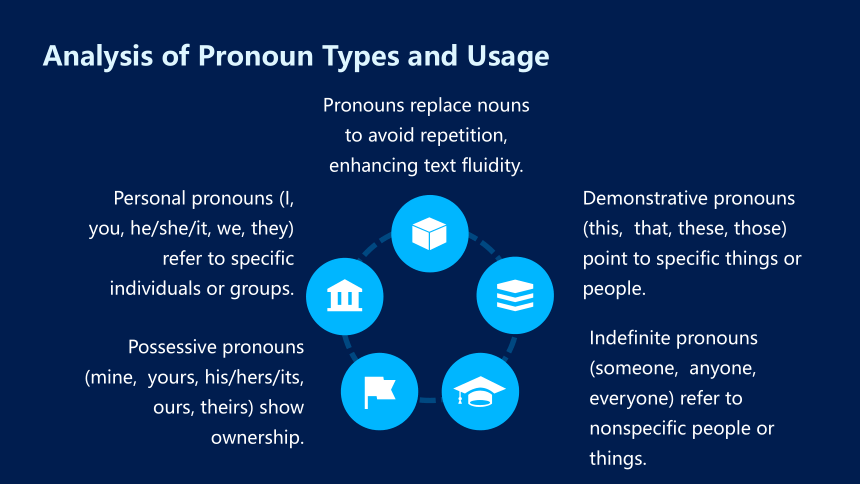
Demonstrative pronouns (this, that, these, those) point to specific things or people.
Pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition, enhancing text fluidity.
Indefinite pronouns (someone, anyone, everyone) refer to nonspecific people or things.
Personal pronouns (I, you, he/she/it, we, they) refer to specific individuals or groups.
Possessive pronouns (mine, yours, his/hers/its, ours, theirs) show ownership.
Analysis of Pronoun Types and Usage
Example 3
"_____ of the students passed the exam." Answer: All, illustrating the use of quantifiers.
Example 1
"Each student should bring _____ own book. " Answer: their, explaining the use of the possessive pronoun for a group.
Example 2
"The cat chased _____ mouse into _____ corner. " Answer: a, the, demonstrating the use of indefinite and definite articles.
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
"I saw _____ at the park." Answers could include: them, her, him, depending on the context and antecedent.
Practice Question 1
"The book belongs to _____. " Answers vary based on the owner: me, you, him/her, us, them.
Practice Question 2
It's crucial to identify the antecedent correctly and match the pronoun in number, gender, and case accordingly.
Answer Analysis
Practice questions and answer analysis
03
A detailed explanation of the usage of adjectives and adverbs
The comparative and superlative forms of adjectives and adverbs
used to compare two things, indicating one is better or worse than the other. For adjectives, add "-er" to the end (e.g., bigger, faster); for adverbs, use "more" before the adverb (e.g., more quickly, more efficiently).
Comparative form
used to compare three or more things, indicating one is the best or worst. For adjectives, add "-est" to the end (e.g., biggest, fastest); for adverbs, use "most" before the adverb (e.g., most quickly, most efficiently).
Superlative form
some adjectives and adverbs have irregular comparative and superlative forms, such as "good/better/best" and "bad/worse/worst. "
Irregular forms
01
02
03
typically placed before the noun they modify (e.g., "a beautiful garden"). They can also be used after the verb "be" (e.g., "The garden is beautiful").
Adjectives
usually placed after the verb or adjective they modify (e.g., "She sings beautifully" or "He is extremely tall"). Some adverbs, such as "always," "often," and "never," are placed before the verb.
Adverbs
The position of adjectives and adverbs in sentences
Example 1
Choose the correct form of the adjective to complete the sentence: "My brother is _______ (tall) than me." Answer: taller. Explanation: The sentence compares two people, so the comparative form of the adjective "tall" is used.
Example 2
Fill in the blank with the correct superlative form of the adverb: "She sings _______ (beautifully) in her class. " Answer: most beautifully. Explanation: The sentence compares the singing ability of multiple people, so the superlative form of the adverb "beautifully" is used.
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
Practice question 1: Complete the sentence with the correct comparative form of the adjective: "This book is _______ (interesting) than that one. " Answer: more interesting.
Answer analysis: It's important to identify whether the sentence is comparing two or more things and choose the appropriate comparative or superlative form accordingly. Pay attention to irregular forms and the correct position of adjectives and adverbs in sentences.
Practice question 2: Fill in the blank with the correct superlative form of the adjective: "He is the _______ (smart) student in his class. " Answer: smartest.
Practice questions and answer analysis
04
A detailed explanation of verb tenses and voices
The usage and differences of commonly used tenses
Simple Present Tense: Used to express habits, general truths, and repeated actions.
Simple Past Tense: Describes actions or events that occurred in the past.
Simple Future Tense: Expresses actions or events that will happen in the future.
Present Perfect Tense: Describes actions that have been completed in the past but have relevance to the present.
Past Perfect Tense: Describes actions that had been completed before another past action or time.
01
02
03
04
05
The Composition and Usage of Passive Voice
Usage
Used when the focus is on the action rather than the performer of the action, or when the performer is unknown or unimportant.
Formation
The passive voice is formed by combining the appropriate tense of the verb "to be" with the past participle of the main verb.
1
2
3
Identifying the correct tense in a sentence.
Changing active sentences to passive and vice versa.
Correcting grammatical errors in sentences involving verb tenses and voices.
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
01
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate verb tense or voice.
Practice questions and answer analysis
02
03
04
Multiple choice questions testing understanding of verb tenses and voices.
Open-ended questions requiring students to construct sentences using specific tenses or voices.
Answer analysis provided for each practice question, explaining the reasoning behind the correct answer.
05
A detailed explanation of non finite verbs and modal verbs
The Types and Usage of Non finite Verbs
01
Express actions or states without specifying a specific time, used as subjects, objects, predicatives, or adverbials.
Used as the subject or object of a verb, expressing an action that is ongoing or habitual.
Used as adjectives or adverbials, describing the state or characteristic of the subject, or the manner, time, cause, and other circumstances of the action.
02
03
Infinitives
Gerunds
Participles
Can/Could
Expressing ability, possibility, or permission. "Could" is the past tense of "can" and is often used in conditional sentences or to express a more polite request.
May/Might
The Usage and Differences of Modal Verbs
Expressing possibility or permission. "Might" is the past tense of "may" and is often used in conditional sentences or to express a more uncertain possibility.
01
02
The Usage and Differences of Modal Verbs
Will/Would
Expressing future actions, willingness, or habits. "Would" is the past tense of "will" and is often used in conditional sentences or to express a more polite request or suggestion.
Shall/Should
Expressing obligation, suggestion, or inference. "Should" is often used to express a more polite or tentative suggestion.
Must
Expressing obligation, necessity, or strong inference.
Question types and strategies for approaching non-finite verb and modal verb questions.
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
Detailed explanations and answers to selected classic example questions, highlighting key points and common pitfalls.
Tips and tricks for identifying the correct answers quickly and accurately.
A set of practice questions designed to test understanding of non-finite verbs and modal verbs.
Answers and explanations for each practice question, identifying common mistakes and providing guidance for improvement.
Strategies for approaching similar questions in the future, with a focus on improving accuracy and speed.
Practice questions and answer analysis
06
On Subjunctive Mood and Emphasizing Sentence Patterns
Expressing wishes, suggestions, orders, or hypotheses
The Usage and Classification of Subjunctive Mood
01
Classified into present subjunctive and past subjunctive
02
Used in conditional sentences, wishes, and suggestions
03
Distinguishing between real and unreal conditions
04
01
03
02
04
Utilizing "It is/was ... that ..." structure
Functions to highlight specific information in a sentence
Emphasizing different sentence components such as subject, predicate, object, or adverbial
Enhancing clarity and impact of the statement
The Composition and Usage of Emphasizing Sentence Patterns
2014
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
Examining sentence structure and context
Identifying the correct subjunctive mood and emphasizing sentence patterns
Providing detailed explanations and answers to classic example questions
Enhancing understanding through in-depth analysis
04
01
02
03
Offering a range of practice questions for reinforcement
Providing answers and explanations for each practice question
Practice questions and answer analysis
01
02
03
04
Analyzing common mistakes and misunderstandings
Facilitating mastery of subjunctive mood and emphasizing sentence patterns through practice
07
Concise explanation of clauses and coordinate sentences
01
That-clause
functions as the subject, object, or complement in a sentence, expressing a fact, idea, or opinion.
Whether/if-clause
used to express conditions or doubts, often appearing in reported speech or indirect questions.
Wh-clause
introduced by wh-words (what, which, who, whose, when, where, why, how), functioning as the subject, object, or complement, asking for specific information.
The types and usage of noun clauses
02
03
Who, which, that
used to introduce relative clauses, modifying nouns or pronouns, providing additional information about the antecedent.
01.
The relative words and usage of relative clauses
Whose
used to show possession in a relative clause, referring to a person or thing that owns something.
02.
When, where
used to introduce relative clauses that describe time or place, respectively.
03.
introduced by words like when, while, as, after, before, etc., expressing the time relationship between the main clause and the adverbial clause.
Time clauses
The guide words and usage of adverbial clauses
introduced by words like because, since, as, so that, such that, etc., showing the reason or result of an action.
Cause and effect clauses
introduced by if, unless, provided that, etc., expressing a condition that must be met for the main clause to be true.
Condition clauses
01
And, but, or
used to connect two independent clauses, expressing addition, contrast, or choice, respectively.
Conjunctions and usage of coordinate sentences
02
So, for
used to show result or reason, connecting two independent clauses.
03
Yet, still
used to express contrast or opposition between two independent clauses.
This section will provide detailed explanations and answers to classic example questions related to clauses and coordinate sentences, helping students understand the application of grammatical rules in specific contexts.
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
“
Practice questions and answer analysis
This section will include practice questions designed to reinforce students' understanding of clauses and coordinate sentences. Answers and explanations will be provided for each question, allowing students to identify and correct any misunderstandings.
08
Introduction to Inverted and Omitted Sentences
Completely inverted: Place the entire predicate before the subject, such as "There goes the bell."
Inverted sentences are used to emphasize adverbials, express surprise, emphasis, and other moods
Pay attention to the issue of subject verb consistency in inverted sentences, as well as the position of negations in inverted sentences
Partial inversion: Place only a portion of the predicate (such as auxiliary verbs, modal verbs, etc.) before the subject, such as "Never have I seen such a beautiful sun."
The Types and Usage of Inverted Sentences
Omitting in simple sentences
In simple sentences, to avoid repetition, components that have already appeared or can be inferred from the context can be omitted, such as "I like coffee and (I like) tea."
Omitting in a coordinate sentence
In a coordinate sentence, the last clause can omit the same components as the previous clause to avoid repetition, such as "(I am) Writing is complicated, but (writing is) rewarding." "
The Common Forms and Usage of Ellipsis Sentences
The Common Forms and Usage of Ellipsis Sentences
Omitted sentences are widely used in spoken and written language, making language more concise and clear
Pay attention to the grammar and logical relationships in omitted sentences to ensure that the omitted sentence still maintains its complete meaning
Analyze the inverted and omitted sentences in classic examples, understand their grammatical structure and usage
Pay attention to traps in the question, such as subject verb inconsistency, tense errors, etc
Mastering problem-solving skills, such as inferring omitted components through context and identifying key information in inverted sentences
Improve sensitivity and accuracy towards inverted and omitted sentences through extensive practice
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
Provide a large number of practice questions, including multiple-choice questions, fill in the blank questions, etc., to help students consolidate their knowledge
Analyze the difficulties and common mistakes in the exercise questions, provide a detailed solution process and problem-solving ideas
Encourage students to think and summarize more, continuously improve their English proficiency and problem-solving abilities
Provide personalized tutoring and advice tailored to the different situations of students, helping them better master the usage and skills of inverted and omitted sentences
Practice questions and answer analysis
09
Practical Practice of English Grammar Filling in the Blank for the College Entrance Examination
Review and Analysis of Historical True Questions
Identification of common traps and pitfalls in blank filling questions
Strategies for approaching complex questions with multiple blanks
Discussion on how to avoid common mistakes made by students
Analysis of frequently tested grammar points in past exam papers
Practice with simulated questions designed to mimic real exam conditions
Examination of common errors and how to avoid them in future attempts
Step-by-step answer analysis to understand the reasoning behind correct answers
Discussion on effective time management during the exam
Simulated question training and answer analysis
Review of key grammar rules and their application in blank filling questions
Tips and tricks to identify the correct answers quickly and accurately
Strategies to improve accuracy and efficiency in solving blank filling questions
Discussion on maintaining focus and concentration during the exam
Summary and improvement of problem-solving skills
10
Course summary and exam preparation suggestions
Review and summary of key and difficult points
Key Grammar Points
Review of essential grammar rules, including tense, voice, modal verbs, and complex sentence structures.
Difficult Vocabulary
Highlight challenging words and phrases commonly found in the exam, with examples and practice exercises.
Common Mistakes
Discuss common errors students make in grammar and usage, and how to avoid them.
Understanding the Exam Format
Familiarize students with the exam structure, question types, and scoring criteria.
Time Management
Strategies for effectively managing time during the exam to ensure all sections are completed.
Practice Tests
Utilize simulated exams to identify areas of weakness and focus revision efforts.
Sharing of exam preparation strategies and suggestions
Encourage students to actively prepare for exams and achieve good grades
Setting Goals
Assist students in setting achievable goals for their exam performance.
Regular Revision
Positive Mindset
Emphasize the importance of consistent and focused revision.
Encourage students to maintain a positive attitude towards the exam and believe in their ability to succeed.
THANKS
感谢观看
2025gaokao english second round review grammar and fill in the blanks
目录
CONTENTS
Overview of English Grammar Blank Filling in the College Entrance Examination
A detailed explanation of the usage of nouns and pronouns
A detailed explanation of the usage of adjectives and adverbs
目录
CONTENTS
A detailed explanation of verb tenses and voices
A detailed explanation of non finite verbs and modal verbs
On Subjunctive Mood and Emphasizing Sentence Patterns
Concise explanation of clauses and coordinate sentences
Introduction to Inverted and Omitted Sentences
目录
CONTENTS
Practical Practice of English Grammar Filling in the Blank for the College Entrance Examination
Course summary and exam preparation suggestions
01
Overview of English Grammar Blank Filling in the College Entrance Examination
Context-based
Grammar fill-in-the-blank questions often require students to understand the context of a sentence or passage to correctly fill in the blanks.
Characteristics of grammar fill in the blank question types
Grammar-focused
These questions test students' understanding of English grammar rules and their ability to apply them in a given context.
Vocabulary-dependent
A solid vocabulary is essential for identifying the correct words to fill in the blanks.
Analysis of Key Points and Difficulties in Inspection
Identifying the correct grammatical structure
Students need to analyze the sentence structure to determine the appropriate grammar rule to apply.
Understanding context clues
Reading the surrounding text carefully can provide valuable hints for filling in the blanks correctly.
Distinguishing between similar options
Sometimes, multiple choices may seem viable, but students must carefully consider the nuances between them to select the best fit.
Problem solving strategies and techniques
Analyze the sentence structure
01
Identify the subject, verb, and object of the sentence to determine the grammatical function of the missing word.
Use context clues
02
Look for keywords or phrases that provide hints about the missing word.
Eliminate incorrect options
03
Cross out choices that do not fit the context or grammatical structure of the sentence.
Practice makes perfect
04
Regular practice with grammar fill-in-the-blank questions can improve your ability to quickly identify the correct answers.
Common types of errors and prevention measures
Grammatical errors
01
Avoid common grammar mistakes, such as subject-verb disagreement or incorrect tense usage, by carefully reviewing your answers.
Vocabulary misuse
02
Ensure you understand the precise meaning of each word and how it fits into the context of the sentence.
Overlooking context clues
03
Pay attention to the surrounding text and use it to guide your choices.
Rushing through the questions
04
Take your time and carefully consider each option before making a selection.
02
A detailed explanation of the usage of nouns and pronouns
01
Nouns can be singular or plural, reflecting the quantity of the referred object.
The rules for the variation of noun numbers and gender
02
Gender in nouns is often linguistic, not biological, and varies across languages.
03
In English, most nouns do not have grammatical gender, but some, especially those borrowed from other languages, may retain it.
04
Number and gender variations can affect adjective and verb forms used with the noun.
Demonstrative pronouns (this, that, these, those) point to specific things or people.
Pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition, enhancing text fluidity.
Indefinite pronouns (someone, anyone, everyone) refer to nonspecific people or things.
Personal pronouns (I, you, he/she/it, we, they) refer to specific individuals or groups.
Possessive pronouns (mine, yours, his/hers/its, ours, theirs) show ownership.
Analysis of Pronoun Types and Usage
Example 3
"_____ of the students passed the exam." Answer: All, illustrating the use of quantifiers.
Example 1
"Each student should bring _____ own book. " Answer: their, explaining the use of the possessive pronoun for a group.
Example 2
"The cat chased _____ mouse into _____ corner. " Answer: a, the, demonstrating the use of indefinite and definite articles.
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
"I saw _____ at the park." Answers could include: them, her, him, depending on the context and antecedent.
Practice Question 1
"The book belongs to _____. " Answers vary based on the owner: me, you, him/her, us, them.
Practice Question 2
It's crucial to identify the antecedent correctly and match the pronoun in number, gender, and case accordingly.
Answer Analysis
Practice questions and answer analysis
03
A detailed explanation of the usage of adjectives and adverbs
The comparative and superlative forms of adjectives and adverbs
used to compare two things, indicating one is better or worse than the other. For adjectives, add "-er" to the end (e.g., bigger, faster); for adverbs, use "more" before the adverb (e.g., more quickly, more efficiently).
Comparative form
used to compare three or more things, indicating one is the best or worst. For adjectives, add "-est" to the end (e.g., biggest, fastest); for adverbs, use "most" before the adverb (e.g., most quickly, most efficiently).
Superlative form
some adjectives and adverbs have irregular comparative and superlative forms, such as "good/better/best" and "bad/worse/worst. "
Irregular forms
01
02
03
typically placed before the noun they modify (e.g., "a beautiful garden"). They can also be used after the verb "be" (e.g., "The garden is beautiful").
Adjectives
usually placed after the verb or adjective they modify (e.g., "She sings beautifully" or "He is extremely tall"). Some adverbs, such as "always," "often," and "never," are placed before the verb.
Adverbs
The position of adjectives and adverbs in sentences
Example 1
Choose the correct form of the adjective to complete the sentence: "My brother is _______ (tall) than me." Answer: taller. Explanation: The sentence compares two people, so the comparative form of the adjective "tall" is used.
Example 2
Fill in the blank with the correct superlative form of the adverb: "She sings _______ (beautifully) in her class. " Answer: most beautifully. Explanation: The sentence compares the singing ability of multiple people, so the superlative form of the adverb "beautifully" is used.
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
Practice question 1: Complete the sentence with the correct comparative form of the adjective: "This book is _______ (interesting) than that one. " Answer: more interesting.
Answer analysis: It's important to identify whether the sentence is comparing two or more things and choose the appropriate comparative or superlative form accordingly. Pay attention to irregular forms and the correct position of adjectives and adverbs in sentences.
Practice question 2: Fill in the blank with the correct superlative form of the adjective: "He is the _______ (smart) student in his class. " Answer: smartest.
Practice questions and answer analysis
04
A detailed explanation of verb tenses and voices
The usage and differences of commonly used tenses
Simple Present Tense: Used to express habits, general truths, and repeated actions.
Simple Past Tense: Describes actions or events that occurred in the past.
Simple Future Tense: Expresses actions or events that will happen in the future.
Present Perfect Tense: Describes actions that have been completed in the past but have relevance to the present.
Past Perfect Tense: Describes actions that had been completed before another past action or time.
01
02
03
04
05
The Composition and Usage of Passive Voice
Usage
Used when the focus is on the action rather than the performer of the action, or when the performer is unknown or unimportant.
Formation
The passive voice is formed by combining the appropriate tense of the verb "to be" with the past participle of the main verb.
1
2
3
Identifying the correct tense in a sentence.
Changing active sentences to passive and vice versa.
Correcting grammatical errors in sentences involving verb tenses and voices.
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
01
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate verb tense or voice.
Practice questions and answer analysis
02
03
04
Multiple choice questions testing understanding of verb tenses and voices.
Open-ended questions requiring students to construct sentences using specific tenses or voices.
Answer analysis provided for each practice question, explaining the reasoning behind the correct answer.
05
A detailed explanation of non finite verbs and modal verbs
The Types and Usage of Non finite Verbs
01
Express actions or states without specifying a specific time, used as subjects, objects, predicatives, or adverbials.
Used as the subject or object of a verb, expressing an action that is ongoing or habitual.
Used as adjectives or adverbials, describing the state or characteristic of the subject, or the manner, time, cause, and other circumstances of the action.
02
03
Infinitives
Gerunds
Participles
Can/Could
Expressing ability, possibility, or permission. "Could" is the past tense of "can" and is often used in conditional sentences or to express a more polite request.
May/Might
The Usage and Differences of Modal Verbs
Expressing possibility or permission. "Might" is the past tense of "may" and is often used in conditional sentences or to express a more uncertain possibility.
01
02
The Usage and Differences of Modal Verbs
Will/Would
Expressing future actions, willingness, or habits. "Would" is the past tense of "will" and is often used in conditional sentences or to express a more polite request or suggestion.
Shall/Should
Expressing obligation, suggestion, or inference. "Should" is often used to express a more polite or tentative suggestion.
Must
Expressing obligation, necessity, or strong inference.
Question types and strategies for approaching non-finite verb and modal verb questions.
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
Detailed explanations and answers to selected classic example questions, highlighting key points and common pitfalls.
Tips and tricks for identifying the correct answers quickly and accurately.
A set of practice questions designed to test understanding of non-finite verbs and modal verbs.
Answers and explanations for each practice question, identifying common mistakes and providing guidance for improvement.
Strategies for approaching similar questions in the future, with a focus on improving accuracy and speed.
Practice questions and answer analysis
06
On Subjunctive Mood and Emphasizing Sentence Patterns
Expressing wishes, suggestions, orders, or hypotheses
The Usage and Classification of Subjunctive Mood
01
Classified into present subjunctive and past subjunctive
02
Used in conditional sentences, wishes, and suggestions
03
Distinguishing between real and unreal conditions
04
01
03
02
04
Utilizing "It is/was ... that ..." structure
Functions to highlight specific information in a sentence
Emphasizing different sentence components such as subject, predicate, object, or adverbial
Enhancing clarity and impact of the statement
The Composition and Usage of Emphasizing Sentence Patterns
2014
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
Examining sentence structure and context
Identifying the correct subjunctive mood and emphasizing sentence patterns
Providing detailed explanations and answers to classic example questions
Enhancing understanding through in-depth analysis
04
01
02
03
Offering a range of practice questions for reinforcement
Providing answers and explanations for each practice question
Practice questions and answer analysis
01
02
03
04
Analyzing common mistakes and misunderstandings
Facilitating mastery of subjunctive mood and emphasizing sentence patterns through practice
07
Concise explanation of clauses and coordinate sentences
01
That-clause
functions as the subject, object, or complement in a sentence, expressing a fact, idea, or opinion.
Whether/if-clause
used to express conditions or doubts, often appearing in reported speech or indirect questions.
Wh-clause
introduced by wh-words (what, which, who, whose, when, where, why, how), functioning as the subject, object, or complement, asking for specific information.
The types and usage of noun clauses
02
03
Who, which, that
used to introduce relative clauses, modifying nouns or pronouns, providing additional information about the antecedent.
01.
The relative words and usage of relative clauses
Whose
used to show possession in a relative clause, referring to a person or thing that owns something.
02.
When, where
used to introduce relative clauses that describe time or place, respectively.
03.
introduced by words like when, while, as, after, before, etc., expressing the time relationship between the main clause and the adverbial clause.
Time clauses
The guide words and usage of adverbial clauses
introduced by words like because, since, as, so that, such that, etc., showing the reason or result of an action.
Cause and effect clauses
introduced by if, unless, provided that, etc., expressing a condition that must be met for the main clause to be true.
Condition clauses
01
And, but, or
used to connect two independent clauses, expressing addition, contrast, or choice, respectively.
Conjunctions and usage of coordinate sentences
02
So, for
used to show result or reason, connecting two independent clauses.
03
Yet, still
used to express contrast or opposition between two independent clauses.
This section will provide detailed explanations and answers to classic example questions related to clauses and coordinate sentences, helping students understand the application of grammatical rules in specific contexts.
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
“
Practice questions and answer analysis
This section will include practice questions designed to reinforce students' understanding of clauses and coordinate sentences. Answers and explanations will be provided for each question, allowing students to identify and correct any misunderstandings.
08
Introduction to Inverted and Omitted Sentences
Completely inverted: Place the entire predicate before the subject, such as "There goes the bell."
Inverted sentences are used to emphasize adverbials, express surprise, emphasis, and other moods
Pay attention to the issue of subject verb consistency in inverted sentences, as well as the position of negations in inverted sentences
Partial inversion: Place only a portion of the predicate (such as auxiliary verbs, modal verbs, etc.) before the subject, such as "Never have I seen such a beautiful sun."
The Types and Usage of Inverted Sentences
Omitting in simple sentences
In simple sentences, to avoid repetition, components that have already appeared or can be inferred from the context can be omitted, such as "I like coffee and (I like) tea."
Omitting in a coordinate sentence
In a coordinate sentence, the last clause can omit the same components as the previous clause to avoid repetition, such as "(I am) Writing is complicated, but (writing is) rewarding." "
The Common Forms and Usage of Ellipsis Sentences
The Common Forms and Usage of Ellipsis Sentences
Omitted sentences are widely used in spoken and written language, making language more concise and clear
Pay attention to the grammar and logical relationships in omitted sentences to ensure that the omitted sentence still maintains its complete meaning
Analyze the inverted and omitted sentences in classic examples, understand their grammatical structure and usage
Pay attention to traps in the question, such as subject verb inconsistency, tense errors, etc
Mastering problem-solving skills, such as inferring omitted components through context and identifying key information in inverted sentences
Improve sensitivity and accuracy towards inverted and omitted sentences through extensive practice
Analysis and Answers to Classic Example Questions
Provide a large number of practice questions, including multiple-choice questions, fill in the blank questions, etc., to help students consolidate their knowledge
Analyze the difficulties and common mistakes in the exercise questions, provide a detailed solution process and problem-solving ideas
Encourage students to think and summarize more, continuously improve their English proficiency and problem-solving abilities
Provide personalized tutoring and advice tailored to the different situations of students, helping them better master the usage and skills of inverted and omitted sentences
Practice questions and answer analysis
09
Practical Practice of English Grammar Filling in the Blank for the College Entrance Examination
Review and Analysis of Historical True Questions
Identification of common traps and pitfalls in blank filling questions
Strategies for approaching complex questions with multiple blanks
Discussion on how to avoid common mistakes made by students
Analysis of frequently tested grammar points in past exam papers
Practice with simulated questions designed to mimic real exam conditions
Examination of common errors and how to avoid them in future attempts
Step-by-step answer analysis to understand the reasoning behind correct answers
Discussion on effective time management during the exam
Simulated question training and answer analysis
Review of key grammar rules and their application in blank filling questions
Tips and tricks to identify the correct answers quickly and accurately
Strategies to improve accuracy and efficiency in solving blank filling questions
Discussion on maintaining focus and concentration during the exam
Summary and improvement of problem-solving skills
10
Course summary and exam preparation suggestions
Review and summary of key and difficult points
Key Grammar Points
Review of essential grammar rules, including tense, voice, modal verbs, and complex sentence structures.
Difficult Vocabulary
Highlight challenging words and phrases commonly found in the exam, with examples and practice exercises.
Common Mistakes
Discuss common errors students make in grammar and usage, and how to avoid them.
Understanding the Exam Format
Familiarize students with the exam structure, question types, and scoring criteria.
Time Management
Strategies for effectively managing time during the exam to ensure all sections are completed.
Practice Tests
Utilize simulated exams to identify areas of weakness and focus revision efforts.
Sharing of exam preparation strategies and suggestions
Encourage students to actively prepare for exams and achieve good grades
Setting Goals
Assist students in setting achievable goals for their exam performance.
Regular Revision
Positive Mindset
Emphasize the importance of consistent and focused revision.
Encourage students to maintain a positive attitude towards the exam and believe in their ability to succeed.
THANKS
感谢观看
