2025届高三英语二轮复习 语法核心考点(十大词类;句子成分;基本句型;句子类型;定语从句 宾语从句 状语从句)课件(共132张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2025届高三英语二轮复习 语法核心考点(十大词类;句子成分;基本句型;句子类型;定语从句 宾语从句 状语从句)课件(共132张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 9.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-07-14 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共132张PPT)
2025年高考英语核心语法
目录
十大词类
句子成分
简单句五种句型
句子类型
定语从句
状语从句
宾语从句
PART 01
十大词类
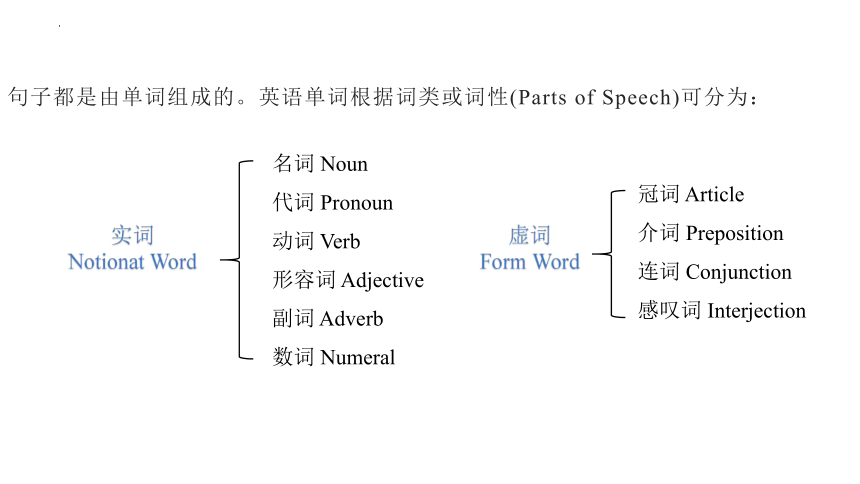
句子都是由单词组成的。英语单词根据词类或词性(Parts of Speech)可分为:
实词
Notionat Word
名词 Noun
代词 Pronoun
动词 Verb
形容词 Adjective
副词 Adverb
数词 Numeral
虚词
Form Word
冠词 Article
介词 Preposition
连词 Conjunction
感叹词 Interjection
PART 02
句子成分
必须有的句子成分:
主语(subject) 谓语(predicate)
选择性有的句子成分:
宾语(object) 定语(attribute)
状语(adverbial) 补语(complement)
表语(predicative) 同位语(appositive)
No. 1 主语
1. One-third of the students in this class are girls.( )
2. To swim in the river is a great pleasure.( )
3. The rich should help the poor.( )4. What benefits most to their study is reading English books.
( )
5. The arugula (芝麻菜)was to make a nice green salad, rounding out a roast chicken dinner. ( )6.Writing an essay is a difficult process for most people.
( )
7. It’s urgent for students themselves to improve their self-discipline( )
数词
不定式
名词化的形容词
主语从句
名词
动名词短语
it作形式主语,真正的主语为后面的不定式
round out 使变圆;使更完美;圆满结束
His face seemed to have rounded out.
His father insisted that he went to university to round out his education.
Chocolate cake rounded out the meal.
No. 2 谓语
简单谓语:由一个动词或动词短语构成。如:
This exhibition of some sixty masterpieces celebrating the life and work of Scotland's best loved painter, Sir Henry Raeburn, comes to London. ( )
复合谓语:(1)由情态动词或其他助动词加动词原形构成。如:By using the latest technologies, drones could also start providing higher-value services for railways, detecting faults in the rail or switches, before they can cause any safety problems.
( )(2)由系动词加表语构成。如:
Food became easier to chew at this point. ( )
实义动词
情态动词+实义动词
系动词
拓展:系动词(6大类别)
状态系动词:用来表示主语状态的只有be动词
感官系动词:主要有feel、smell、sound、taste......
表象系动词:表示外观的概念主要有seem、appear、look......
终止系动词:表示主语结束了动作,主要有prove、turn out...... 表示“证实”、“成为”的意思。
持续系动词:用来表示主语继续或维持某种情况或态度,主要有keep、remain、stay、lie、stand......
变化系动词:表示主语是怎样的,主要有become、grow、turn、fall、get、go、come、run......
1. Fitness Magazine recently ran an article titled “Five Reasons to ...”( )2. I’d appreciate it if you take my invitation into consideration.
( )3. ...,drones could also start providing higher-value services for railways, detecting faults in the rail or switches, before they can cause any safety problems. ( )4. The team showed that this change in bite was connected with the development of agriculture in the Neolithic period. ( )
5. How many dictionaries do you have I have five.( )6. They helped the old with their housework yesterday.( )7. He pretended not to see me.( )
No. 3 宾语
名词
代词it作形式宾语,if引导的条件状从为真正的宾语
动名词短语
宾语从句
数词
名词化的形容词
不定式短语
1. Helping the next generation to have a healthy and active childhood is of great importance. ( ) 2. Food became easier to chew at this point. ( )
3. I am down there in my wheelchair in the morning....( )
4. Needless to say, they were deeply moved.( )5. My dream is to become an English teacher.( )6. His hobby is playing football.( )7. The truth is that he has never been abroad.( )
No. 4 表语
介词短语
形容词
方位副词
过去分词
不定式
动名词
表语从句
No. 5 定语
1. Fruit juices, milk-based drinks and most alcoholic drinks are free of the tax.( )
2. Road accidents, which had fallen for years, are now rising sharply.( )
3. Throughout her career as a professional dancer, she toured in the UK.( )4. To perform these tasks, drones for rail don't need to be flying overhead. ( )
5. With their ability to see ahead, they could signal any problem, so that fast-moving trains would be able to react in time.
( )
名词,过去分词,形容词
定语从句
介词短语作后置定语
代词,介词
代词,不定式,代词,现在分词
动名词VS现在分词
虽然现在分词与动名词的格式完成相同,但它们在句子中的作用却是有明显的区别的。
1. 动名词相当于名词,所以在句子中可以充当的成分与名词类似,即主要充当主语、宾语、表语等成分。而现在分词的作用类似于副词和形容词,在句子主要充当状语、定语、补语、表语等。
Hearing the noise, they immediately stopped talking. 一听到有声音,他们立刻就停止谈话。(现在分词作状语)
He asked an embarrassing question. 他提了一个令人难堪的问题。(现在分词作定语)
Growing roses is her hobby. 种玫瑰是她的爱好。 (动名词作主语)
She like talking very much. 她很喜欢讲话。 (动名词作宾语)
1. Additionally from time to time I will assign group work to be completed ..( )
2. Although popular beliefs regarding emotional intelligence run far ahead of what research can reasonably support, the overall effects of the publicity have been more beneficial than harmful.( )
No. 6 状语
副词
让步状语从句
No. 7 补语
1. Cao believes this will make the hiking trip even more meaningful.( )
2. We sincerely wish you a quick recovery and an early return to China.( )
3. Beijing will make the Chinese culture better known to British students. ( )
形容词作宾补
名词短语作宾补
过去分词短语作宾补
No. 8 同位语
1.This exhibition of some sixty masterpieces celebrating the life and work of Scotland's best loved painter, Sir Henry Raeburn, comes to London. ( )
2. The news that Premier Li Keqiang passed away on Oct.27 made Chinese people deeply sad. ( )
名词
同位语从句
PART 03
简单句的五种基本句型
动作(动词)
1. 可以独立完成的动作
Michael sleeps.
主语+不及物动词
2. 有1个动作的承受者
Michael likes you.
主语+ 及物动词+宾语
3. 有2个动作的承受者
I teach you English.
主语+双及物动词+间宾+直宾
4. 有1个动作的承受者(但需补充)
单
I consider you smart.
主语+复杂及物动词+宾语+宾补
5. 非“动作”
Michael is in the room.
连系动词
Michael is tall.
主语+系动词+表语
SV
SVO
SVOO
SVOC
SVP
Michael looks tall.
Five basic patterns of sentences
Subject + Verb(SV)
Michael sleeps.
Subject + Verb + Predicative(SVP)
Michael likes you.
Subject + Verb + Object (SVO)
I teach you English.
Subject + Verb + Indirect object+ Direct object(SVOO)
I consider you smart.
Subject + Verb + Object + Object complement (SVOC)
Michael is tall.
PART 04
句子类型
按句子的结构可分三种:
1. 简单句(Simple Sentence)
2. 并列句(Compound Sentence)
3. 复合句(Complex Sentence)
简单句(Simple Sentence)
一个主语+一个谓语
He often reads English in the morning.
He is a school student in No. 1 Middle School.
Confidence in yourself is the first step on the road to success.
并列句(Compound Sentence)
≥2个简单句,由并列连词或分号连接
用分号:We fished all day; we didn’t catch a thing.
用并列连词:
(but, or, yet, so, for, and, nor [记忆口诀:boy’s fan ])Fields have eyes, and woods have ears. 隔墙有耳。
复合句(Complex Sentence)
主句+从句(≥1)
主句:独立存在&完整意思
从句:依附主句&充当一个句子成分的分句,由连词、
关系代词或关系副词引导
用作主语、宾语、表语、定语、状语、同位语等
Mary told me that she visited the Great Wall last year.
只有一个主谓结构
一个主句+
一个(以上)从句
两个或两个以上的简单句
英语语法作用:
造句
长句子
短句子
(简单句)
拆分
组合
简单句:
什么 + 怎么样
(主语)
(谓语)
人/物
动作/发生了什么事
动词
Verb
谓语动词
Sentence elements
按说话人说话的目的可分四种:
1.陈述句Decalarative Sentence(肯定、否定)
He is six years old. She didn’t hear of you before.
2.疑问句Interrogative Sentence(一般、特殊、选择、反意)
Do they like skating How old is he
Is he six or seven years old Mary can swim, can’t she
3.祈使句Imperative Sentence(用来表示建议、请求、命令等语气,由动词原形开头)
Don’t talk in class. Hurry up, or you will be late.
4.感叹句Exclamatory Sentence
How clever the boy is!
PART 05
定语从句
一、几个重要概念
二、关系代词的用法
三、关系副词的用法
四、关系代词与关系副词的选择
目录
在复合句中,对名词、代词、名词性短语、句子进行修饰、限定的从句叫定语从句。
定语从句?
I like
先行词
(被修饰的成分)
关系词
(起引导作用)
that
I can dance to.
music
关系代词
(1)who指人,在定语从句中可充当主语或宾语。
Here comes the girl who wants to see you. 想见你的那个女孩过来了。
(2)whom指人,在定语从句中作宾语,在限制性定语从句中一般可以省略,也可用who代替。但如果指人的关系代词紧跟在介词之后,只能用whom, 不能用who。
The people (who/whom) you met in the campus yesterday are from England.
你昨天在校园里碰到的那些人是从英国来的。
The young man with whom I traveled could speak Spanish.
同我一起旅行的那个年轻人会说西班牙语。
单句改错
I live next door to a couple who children often make a lot of noise.
whose
Kate, whose sister I shared a room with when we were at college, has gone to work in Australia.凯特到澳大利亚去工作了,读大学的时候我和她的姐姐住一个寝室。
(3)Whose用于指人或物,在定语从句中作定语。whose= the+n.+of which/whom , 为了便于理解,可以把whose记成关系形容词。
(4) which一般指物,在定语从句中作主语、宾语或表语。作宾语时可省略,但作介词的宾语,且介词提前时,不可省略。
He cycles from home to office every day, which is pretty good for his health.他每天骑自行车从家去办公室,这对他的健康非常好。
这就是丘吉尔出生的房间。
This is the room (which) Churchill was born in. (which可省略)
This is the room in which Churchill was born. (which不可省略)
(5) that既可指人,也可指物,在定语从句中作主语宾语或表语,作宾语时可省略。作介词宾语时,介词不可提到that之前,如介词提前则需用which或whom来代替that。
The number of people that came to visit this city each year reaches one million.每年来参观这座城市的人数达一百万。
The chair (that) you broke yesterday is now being repaired. 你昨天弄坏的那把椅子正在被修。
(6) as用作关系代词,既可指人,也可指物,还可指整个句子,在句子中可作主语、宾语或表语。在限制性定语从句中,as常用在the same…as…, such/so…as… 等结构中,且不能省略。
Such teachers as know Tom think him smart. 那些认识汤姆的老师都认为他聪明。
I’ll buy the same dictionary as you have. 我要买和你一样的词典。
归纳拓展
as引导非限制性定语从句,代替整个主句的内容。从句可放在主句前、主句后或主句中间。常见的固定表达有:
as we all know 正如大家所知 as is well-known 众所周知
as often happens 这经常发生 as is often the case 情况总是如此
as (is) mentioned above 如上所述
as has been said before 如前所述
as I can remember 正如我所记得的
as may be imagined 正如可以想象出来的那样
as has been pointed out 正如已经指出的
as we expected/as is expected 正如我们预料的那样
1.宜用that不用which的情况
2. 宜用which不用that的情况
3.宜用who不用that的情况
定语从句中需注意的事项
当先行词是all, much, anything, something, everything, nothing, little, none等不定代词时
当先行词被all, no, few, any, little, the very, the only等词语修饰时
1.宜用that不用which的情况
She told me everything that she knew.
她把她知道的一切都告诉了我。
He is the only person that was presented at that time.
他是当时唯一在场的人。
1.宜用that不用which的情况
口诀:“程序问题最多”
“程”:程度
没有 no, none
不确定 any
一个 the one
只有一个 the only, the very
每一个 every, each
不到一半 a little, few
大约一半 some
一大部分 much
全部 all
everything
something
nothing
anything
There is no person ______ don’t make mistakes.
(没有人不犯错)
You can take any seat _____ is free.
(你可以去坐任何空着的位子)
This is the only thing ______ we can do now.
(这是我们现在唯一能做的事)
Much ______ I learned in this book is useful.
(我在这本书里学的很多东西都很有用)
that
that
that
that
Is there anything _____ I can do for you
(有什么我可以为你做的事情吗?)
that
Our teacher told us something ______ we should do.
(我们老师告诉了我们该做的事)
that
He knows everything ______ happened in that village.
(他知道那村里发生的所有事。)
that
“序”:序数词— the first, the second, …the last
The first place _____ they visited in Guilin was Elephant Trunk Hill. (在桂林他们参观的第一个地方是象鼻山。)
that
This is the 3rd film _____ has been shown.
(这是放映的第三部影片)
that
This is the last van _____ will go to Alabama.
(这是开往阿拉巴马最后一辆货车)
that
“问题”:当主句以who/which/what开头的特殊疑问句时
Which is the bike _____ you lost
(你丢的自行车是哪一辆?)
that
Who is the boy _____ won the gold medal
(那个赢得金牌的男孩是谁?)
that
“最”:当先行词被形容词最高级修饰时
This is the best film _____ I have ever seen.
(这是我看过的最好的电影)
that
This is the most interesting guy _____ I’ve ever met.
(这是我见过最有趣的人了)
that
“多”:先行词又有人又有物的时候,用that
They are talking about the teachers and schools _____ they have just visited.
(他们在讨论他们刚刚访问过的那些学校和老师们)
that
The writer and his novel _____ you have just talked about are really well known.
(你刚刚谈起的那位作家以及他的小说确实很著名。)
that
2.宜用which不用that的情况
口诀:“都借钱,不用that”
“都”:有逗号,不用that
Until now, we have raised 50,000 pounds for the poor children, _____ is quite unexpected.
(令人意外的是,到现在我们已经为贫困孩子募捐了50,000英镑了)
which
引导非限制性定语从句时,用which
“借”:有介词,不用that
当关系词在定语从句中作介词的宾语,且介词位于关系代词前。
This is the question about _____ they have had so much discussion in the past few weeks.
(这就是过去几周来他们反复讨论的那个问题。)
which
“钱”:前面有that,不用that
当先行词是that时
在限制性定语从句中,如果前一句的关系代词是that,那么后一句的关系代词就要用which
What’s that _____ he asked for 他要的那个是什么?
which
Let me show you the novel that I borrowed from the library _____ was newly open.
(我给你看这本从新开放的图书馆借来的小说。)
which
3.宜用who不用that的情况
口诀:是人,就用who
先行词是指人的不定代词时,如:one, anyone, no one, all, nobody, anybody, none等,或先行词为those且指人时。
先行词指人且关系代词引导非限制性定语从句时。
一个句子中带有两个定语从句,且先行词都为人时,其中一个定语从句的关系代词是that,另一个一般应用who。
口诀:是人,就用who
Chances favor only those _____ are ready.
(机会总是垂青有准备的人。)
who
The famous star, _____ tries to make a comeback, draws a lot of attention. (那个试图复出的著名影星引起了很多关注。)
who
The boy that you met last night is the group leader _____ studies very hard. (昨晚你遇到的那个男孩是学习非常努力的组长。)
who
Exercises
一、填空
1. A study shows the students who are engaged in after-school activities are happier than those ______ are not.
2. Tom came back, ______ made us very happy.
who
which
二、用定语从句连接两个句子(使用关系代词)
1. They live in a room. It’s window faces south.
______________________________________________________________
2. She wants to visit the village. She grew up in it.
______________________________________________________________
They live in a room whose window faces south.
She wants to visit the village which/that she grew up in.
限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句的区别
Ⅱ. 关系副词
Winter is the time of year when the days are short while nights are long. 冬天是一年中昼短夜长的时候。
(2)When可以换成“介词+which”。
When引导定语从句的用法
She is looking forward to the day when (=on which) her daughter wins the gold medal in the Olympics. 她盼望有一天她的女儿能在奥运会上赢得金牌。
(1)当先行词是表示时间的名词(如time, day, year, month, week等),且关系词在句中作时间状语时,定语从句用when引导。
Do you still remember the days ___________ we spent together on the farm
Do you still remember the days ___________ we chatted with each other all night
when
that/which
当先行词是表示时间的名词时,既可以用when引导定语从句,也可以用that或which引导定语从句,关键要看关系词在定语从句中作何种成分。若关系词在定语从句中充当状语,则用when引导;若关系词在定语从句中充当主语或宾语,则用that或which引导。
This is the hotel where (=in which) they stayed. 这就是他们待过的旅馆。
2. Where引导定语从句的用法
(1)当先行词是表示具体地点的名词(如place, room, mountain, airport等)或表示抽象地点的名词(如case, state, stage, condition, point, situation等),且关系词在从句中作地点状语时,定语从句用where引导。
We have reached a point where a change is needed. 我们已经到了需要做出改变的地步了。
He gets into a situation where it is hard to decide where is right or wrong. 他陷入一种难以判断对错的境地。
(2)Where可以换成“介词+which”。
His father works in a factory ___________ makes radio parts.
他的父亲在一家生产收音机零件的工厂里工作。
which/that
Their child is at the stage ________ she can say individual words but not full sentence.
A. That B. where C. which D. when
B
当先行词为地点名词时,如果指代先行词的关系词在定语从句中作主语或宾语,则用that或which引导状语从句。
3. Why引导定语从句的用法
This is the reason why (=for which) he left in a hurry.这就是他匆匆离去的原因。
(1)当先行词是表示原因的名词reason,且关系词在句中作原因状语时,定语从句用why引导。
There are several reasons why…
(2)Why可以用for which来代替。
The reason ___________ he told me yesterday is a lie.
that/which
Is this the reason __________ he gave at the meeting for his careless in his work
which/that
若代替先行词reason的关系词在定语从句中不作状语,而是充当主语或宾语,则用that或which引导定语从句。
用关系副词或“介词+关系代词”将下列每对句子合并成一个句子。
1. I didn’t come this morning. The reason was that it rained heavily.
________________________________________________________
2. Yesterday Mary bought a few clothes. All of them were beautiful.
___________________________________________________________
Exercises
The reason why/for which I didn’t come this morning was that it rained heavily.
Yesterday Mary bought a few clothes, all of which were beautiful.
关系代词or关系副词?
用法 依据
根据从句的谓语动词 是及物动词,后面若无宾语,用关系代词;是不及物动词则用关系副词。
根据先行词在从句中所作的成分 把先行词放入定语从句中,若作主语或宾语用关系代词;作状语则用关系副词。
This is the house _____ he lived last year.
This is the house _____ he visited last year.
He told her the reason _____ he is unhappy, but she doesn’t believe the reason _____ he gives her.
why
that
where
which
Examples
PART 06
状语从句
状语:修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子,常见时间、地点、原因等。
1. We work in Beijing.我们在北京工作。(“in Beijing” 作地点状语修饰谓语“work”.)
2. We are learning English now.我们正在学英语。(“now” 作时间状语修饰谓语“are learning”)
3. She reads English loudly.她大声地朗读英语。(副词“loudly”作方式状语修饰谓语“reads”)
4. Helmets are made to protect our brain. 头盔是用来保护我们的大脑的。(不定式“to prevent”作目的状语修饰谓语“are made”)
5. He works very hard. 他工作非常努力。(副词“very”作程度状语修饰“副词”“hard” )
It is a very beautiful picture.它是一幅非常美丽的图画。(“very” 修饰形容词beautiful)
6. Unluckily, he didn‘t pass the exam. 很不幸,他没通过考试。(副词“unluckily”作状语,用来修饰“整个句子”)
状语从句在复合句中一般修饰主句或主句中的谓语动词。
状语从句有时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、方式、比较、让步等种类。
位于句首时,常用逗号与主句分开,位于句末时,前面一般不用逗号。如,
I feel very happy when you come to see me.
When you are crossing the street, you must be careful.
一、时间状语从句
引导时间状语从句的连接词有: when, as, while, after, before, since, ever since, as soon as, once, till, until, whenever, no sooner…than, hardly/scarcely...when, the moment/minute/instant/second, every time, each time, any time, the first time, next time, last time, all the time, by the time, directly, immediately, instantly 等。
1、表示“一···就···”的句型
1) as soon as/once
As soon as he arrives, I'll call you. 他一到,我就给你打电话。
(as soon as 侧重时间或动作先后衔接紧,而 once 侧重条件,表示“一旦...”)
2)the moment, the instant, the minute, the second
The moment I saw him, I recognized him.
我一看见他,就认出了他。
We'll leave the minute you are ready.
你一准备好,我们就出发。
4)有些副词如:instantly, immediately, directly 可用作连词,后接从句。
I left immediately the clock struck 5.
2.、when, while, as 引导时间状语从句
1) when 的用法
①when 既指时间点,也指时间段(即:从句动词可以是短暂的也可是延续的);主从句动作可同时也可先后发生。
I was thin when I was a child. 当我是个孩子的时候,我很瘦。
It was raining when I arrived. 我到达时,天正在下雨。
②when 在下列结构中, 译成“这时”,它引导的是并列句
be about to do ... when, be doing ... when, had done ···when,
be on one's way ... when, be on the point of doing ... when
2)while 用法
while 只能指一段时间,从句中的动词必须是延续性动词。强调某一段时间内发生主句动作,相当于 during the time that....
My mother was cooking while I was doing my homework.
当我在做作业时,妈妈在做饭。
I am safe while I am here.我在这儿的时候,我很安全。
注:while 除引导时间状语从句外,还引导对比句,作“然而”讲;并可在句首引出让步状语从句作“虽然···但”讲。
I like watching TV, while he likes reading. 我喜欢看电视,而他喜欢读书。
3.、until 和 till
1)“延续性动词肯定式+until”表示“动作延续到…为止,”译为“直到…为止”,如:
I waited for him until he came back. 我一直等到他回来。
2)“终止性动词的否定式+ until”表示“直到···才”。
He didn't go to bed until he had finished his work. 直到完成工作他才睡觉。
3)用于强调句式“It is not until ...that ...”
It was not until the professor came that we began the experiment.
在教授到来之后,我们才开始实验。
4) not until 放在句首时,主句倒装。
Not until he graduated did he succeed in obtaining this compound.
直到他毕业他才成功获得这种化合物。
二、地点状语从句
1、地点状语从句主要由 where, wherever anywhere, everywhere 引导。
We must camp where we can get water.
我们必须在能找到水的地方露营。
I will follow you wherever you go.
无论你到何处我都要跟随你。
注:地点状语从句与定语从句的区别:
where 引导定语从句,从句前应有一个表示地点的名词作先行词。
Go back where you came from.(where 引导地点状语从句)
Go back to the village where you came from. (where 引导定语从句,village 为先行词)
三、原因状语从句
原因状语从句由 because, as , since, now (that)(既然), in that(因为,多于口语中),seeing
(that)(鉴于,由于),considering that(考虑到)等引导。
1、 because 用来回答 why 提出的问题,表直接的因果关系,用于告知对方不知道的原因,语气最强,可用于强调句。
He didn't attend the meeting because he was ill.
他没参加会议,因为他病了。
It was because he was ill that he didn't go with us.
因为他有病,他没有和我们一起去。
注:because 和 because of 的区别:because 是连词,引导从句,because of 是短语介词,后接名词性词语,如:
The football match was put off because it rained.
The football match was put off because of the rain.
因为下雨,足球赛延期了。
since, as, now that 也可引导原因状语从句。
2、for 也可以表示原因,属并列连词,不是说明直接原因,而是对某种情况加以推断,表示补充说明理由。而推断的理由会因人而异。语气很弱,它引出的分句必须放在另一分句后。
He must be ill, for he is absent today.
四、条件状语从句
1.由 if, unless(if...not), so/as long as, supposing(that)(假设), in case(万一…, 以防…),
so/as far as(就...而言), on condition that(条件是...), provided/providing (that)(假若)引导。
Tell me about it if you have time.
I won't go unless I'm invited.
Take an umbrella with you in case it rains.
You may use the room as/so long as you clean it up afterwards.
e.g . Should he be here tomorrow, I would give him a hand.
五、目的状语从句
由 so that(以便), in order that(为了),for fear that(= in case)(以免),lest(以防)引导,
谓语常含 may, might, can, could, will, would 等情态动词。
They set out early so that they might arrive at the station in good time.
I'll speak slowly so that/in order that you can understand.
He wrote the name down for fear that(lest)he would forget.
注:当从句与主句主语一致时,可用 to do, so as to do, in order to do 结构换。
He worked day and night in order that he could succeed.
He worked day and night in order to succeed.
六、结果状语从句
1.常用的连词有 so that,so ... that, such...that, that。(结果状语从句中一般无情态动词)
He had overslept so that he was late for work. 他起晚了,所以上班迟到了。
My pen fell under my desk that I couldn't see it. 我的笔掉到桌子底下,所以我看不到。
2. so/such ...that 所用句式
①so + adj(adv) + that 从句
The box is so heavy that I can't carry it. 这个箱子很重,以至于我拿不动它。
②so+adj +a/an+单名+ that 从句=such a/an+adj.+单名+that 从句
She is so beautiful a girl that all the boys of our class like her.
=She is such a beautiful girl that all the boys of our class like her.
③so many/few +复名+ that 从句
so much/little+不可数名词+ that 从句
There are so many apples on the desk that we each have one.
There is so little water that you can't drink.
④such +a/an + adj + 单名+ that 从句
She is such a good girl that she can help you.
⑤such + adj +复名/不可数名+ that 从句
It was such bad weather that we all stayed home.
He has such interesting books that he keeps reading all day.
知识拓展:
little 表“小,可爱”时,用 such 不用 so 修饰。
He is such a little boy that his patents often teach him something.
七、方式状语从句
由 as, as if (as though)引导。
Do as you like.
He spoke as if he had been there before.
注意 as if, as though 从句与事实相反时用虚拟语气,与事实相符,不用虚拟语气。
八、比较状语从句
①常用连词 than, as ...as..., not as/so... as
He ran as far as he could.
I'm not as/so tall as he/him.
She studies harder than I(study).
②the more ... the more...引导
The harder you try, the better you will understand.
九、让步状语从句
由 though, although, as, even if/though , no matter wh-, wh-ever 词,whether...or(不管...都),when, while 等引导。
1. though, although 这两个连词用法基本一样,只是前者口语化,后者较正式,常位于句首,都不与 but 连用,但可以和 yet,still,nevertheless 连用。though 还可作副词单独放在句尾,表示“然而”的意思。
Although the TV set is very dear, I still want to buy it.
Though /Although he was worn out, he kept on working.
2. as 引导让步状语时,从句部分用倒装语序,句型为:
①形容词/副词/名词+ as +主 +谓
②动词+ as +主 +情态动词
Child as he is, he knows a lot.
Proud as these nobles are, they are afraid to see me.
3. even if(尽管;即使), even though(尽管)
这两个复合连词意义基本相同,常用以强调让步概念,有退一步想的意思(有时用于虚拟)。
表“即使”时有假设含义,一般用 even if。
We'll make trip even if(though) the weather is bad.
Even if I were in your place, I wouldn't take the job.(虚拟)
4.“whether... or...”可引导让步状语从句
Whether you believe it or not, it is true.
5.“no matter + wh-”引导让步状语从句
引导让步状语从句时“疑问句-ever”相当于“no matter +疑问词”,此时:
no matter who = whoever
no matter what = whatever
no matter which = whichever
no matter where = wherever
no matter how = however
No matter what happened, he would not mind.
It's a nice room no matter whom (whoever) it belongs to.
6.“no matter + wh-”结构只能引导让步状语从句,而“wh-ever”形式除引导让步状语从句外,还可以引导名词性从句。
引导名词性从句时:
whoever = anyone who 任何…的人…
whatever = anything that 任何…的事(物)
whenever = anyplace where 任何…的地方
I will give the book to whoever needs it.
I like whatever you like.
7.when 引导让步状语从句时置于主句后
①虽然·却·,尽管·但·
He walks when he might take a taxi.
②本(应...,可以...)却...。
when 从句用虚拟式为:could/should ... have done
She stopped trying when she might succeed next time.
8.while 引导让步状语从句时置于主句前,与 though 同,但 though 从句可到装,while 从句不可倒装。
9.让步状语从句中用一般现在时表将来。
No matter what he is, he will be punished.
十、状语从句的省略现象
当状语从句的主语与主句的主语相同或为 it, 同时从句谓语含 be 动词,就可省去从句的主语和 be 动词。
①时间状语从句中:
Don’t speak until (you are) spoken to.
While (I was) in Beijing, I lived with my uncle.
I want to go swimming when (it is) possible.
②条件状语从句中:
Come tomorrow if (it is) possible.
If (it is) so, you would be punished.
③方式状语从句中:
She stood at the gate as if (she was) waiting for someone.
④其他状语从句中:
Though (it was) cold, he still wore a shirt.
Fill in the blanks with proper words where (it is) necessary
小测:
1.He pretended that he was ill_______ he could stay at home .
A.so that B. even if C. though D. unless
2.Some people waste a lot of food,_______others haven‘t enough to eat. 题目出错。
A. since B. when C.as D. while
3.Read it loud ______ the whole class can hear you .
A.so that B. if C. when D. although
4.Busy_________ he was,he tried his best to help you .|
A. as B. when C. since D. for
5. Leave your key with a neighbor ______you may lock yourself out one day.
A. ever since B. even if C. soon after D.in case
6.Pop music is such an important part of society_____ it has even influenced our language .
A.as B. that C. which D. where
7 ._________ you are old enough to judge things , you should start your own career .
A. Even if B. Although C. As D. Now that
8. ______much of the town is fairly new,they are older,untouched comers where locals get on quietly with their lives.
A. Since B. While C. When D. Unless
9.He hurried out of the room ______the meeting was over.
A. the moment B. a moment ago C. after a minute D. a minute later
10.We had scarcely left our school_____ the rain began短暂性动词.
A. before B. than C. while D. when
11.I agree to his suggestion _____that he drops all charges.
A. if B.as long C. on condition D.in case
12.______ we have enough evidence,we can't win the case.
A. Once B.As long as C. Unless D. Since
13.Men differ from animals_____ they can think and speak.
A. for which B. for that C.in that D.in which
14.Mark needs to learn Chinese ______his company is opening a branch in Beijing.
A. unless B. until C. although D. since
15.John thinks it won't be long _____he is ready for his new job.
A. when B. after C. before D. since
it won‘t be long before …不久就
16.You can see the product to be advertised ______you go.
A. whatever B. whoever C. wherever D. whichever
17.If you happen to get lost in the wild, you'd better stay _you are and wait for help.
A. why B. where C. who D. what
18.Jack wasn't saying anything,but the teacher smiled at him______ he had done something very
clever .
A. as if B.in case C. while D. though
19. ______happens, we shall never lose hope.
A. No matter how B. Whoever C. However D. Whatever
20. You should have put the book____ you found it.
A. which B. that C. what D. where
21.It's much easier to achieve success ______you can get help from your family.
A. unless B. when C. even though D. so that
22.I will not go to Beijing_______ the company pays for the trip.
A.as B. unless C. where D. while
23.Air pollution is getting more and more serious, so we must take action_____ it is too late.
A. before B. after C. until D. when
24. Provide your doctor with a detailed medical history_____ he can give you accurate treatment.
A. even if B.in case C.so that D.as though
25. The pupils were playing games in the classroom______ a gunman entered and began shooting wildly at them.
A. while B. when C. though D. before
26. _____hard you try, it is difficult to lose weight without cutting down the amount you eat.
A. However B. Whatever C. Whichever D. Whenever
27. Actually, the London Olympic Park is built_____ there used to be a poor area called East London .
What B. when C. where D. why
28.I don't mind how you do it _you finish the painting on time.
A.as well as B. as far as C.as long as D.as fast as
As soon as 一…就,as well as既……又,不仅……而且
As far as 就…而言 as long as 只要
29.One can always manage to do more things, no matter____ full one’s schedule is in life.
A. how B. what C. when D. where
30.Greal changes have taken place in our school _____you left.
A. since B. until C. before D. when
PART 07
宾语从句
语法—名词性从句
之宾语从句
英语句子的种类
简单句 (simple sentence)
并列句 (compound sentence)
复合句 (complex sentence)
英语句子概论
简单句的五种基本句型
The weather is very cold.
主语+谓语(连系动词)+表语
He laughed.
主语+谓语(vi.)
I like Chinese food.
主语+谓语(vt.)+宾语
She taught them physics.
主语+谓语(vt.)+间接宾语+直接宾语
We must keep the room warm.
主语+谓语(vt.) +宾语+宾语补足语
并列句
把两个或几个简单句用并列连词连接起来。
I turned on the TV. My sister and I watched it.
I turned on the TV and my sister and I watched it.
I bought my sister a present. She didn’t like it.
I bought my sister a present,but she didn’t like it.
并列句
并列句
常用并列连词:
平行并列连词:
转折并列连词:
因果并列连词:
选择并列连词:
and, both…and, not only… but also, neither…nor
but, however, while, yet,
or,either…or
for, so
复合句:主句+从句
名词性从句
定语从句
状语从句
1.The boy who is standing over there is Tom
2.Because it is raining ,we have to stay at home
定语从句
状语从句
3.I know (that)he is from America
(宾语从句)
名词性从句---
Noun Clauses
(名词性从句)
Subject Clause
(主语从句)
Appositive Clause
(同位语从句)
Object Clause
(宾语从句)
Predicative Clause
(表语从句)
名词性从句在功能上相当于名词, 在复合句
中能担任主语、宾语、表语、同位语等。
主语
{
His job is important.
What he does is important.
表语
This is his job.
This is what he does every day.
{
宾语
I don’t like his job.
I don’t like what he does every day.
同位语
I don’t know about the man, Mr. White.
I don’t know about the fact that he is a teacher.
Who will win the match is still unknown.
I want to know what he has told you.
The fact is that we have lost the game.
The news that we won the game is exciting.
主语从句
宾语从句
表语从句
名词性从句的作用相当于名词,因此主语从句、表语从句 、宾语从句和同位语从句分别作主句的主语、表语、宾语和同位语。
同位语从句
宾语从句的定义
置于动词、介词等词性后面起宾语作用的从句叫宾语从句。
宾语从句的语序必须是陈述语序。谓语动词、介词、动词不定式,v.-ing形式后面都能带宾语从句。
有些形容词(afraid,sure,glad等)之后也可以带宾语从句。
宾语从句中引导词的用法
在复合句中作主句的宾语,引导词有:
从属连词:that (that 常可省略),whether, if
连接代词:who, whose, what ,which,whom,whatever,whoever等
连接副词:when ,where, how, why 等。
I know him .
2. I know who he is .
主语
谓语
宾语
(简单句)
主语
谓语
宾 语 从 句
连词
从句主语
从句谓语
主 句
(复合句)
宾语从句的概念:
宾语从句在复合句中作主句的宾语。
句子结构:
主句 +连词(引导词)+ 宾语从句
1)主句的谓语动词可以是及物动词:
2)如果主句的谓语动词是一个带有介词的词组,那么后接的从句做介词宾语从句。
3)有些形容词后也可以带有宾语从句。
I’m afraid (that) he won’t pass the exam .
He wondered if he could pass the exam .
They are talking about whether they can pass the exam .
注意:动词+副词形成的谓语动词词组后也可以带宾语从句。
一、从属连词
1. 当宾语从句是陈述句时(包括肯定句和否定
句),连词由that引导,因为that在从句中不作
任何成分,也没有任何具体意思,因此在口语
或非正式文体中常省略
Lin Tao knows (that) his own team is even better. (肯)
She says (that) she won’t take part in the sports meeting
next Sunday.(否)
Jim thought (that) the train was like a big moving party.
He said (that) he would like to see the headmaster.
引导词种类
2. 当宾语从句是一般疑问句时,由连词whether或if引导(口语中常用if),因为if/whether翻译成:“是否”,具有一定的意义,所以不能省略
Lily wanted to know if /whether her grandma liked the handbag .
Let’s see if /whether we can find out some information about that city .
It all depends on whether she likes the boss or not.
引导词种类
二、连接代词
which, what, whose, who, whom, whatever, whoever, whomever, whichever;连接代词在从句中作主语、宾语、表语、定语。
I wonder who will teach us.
Mr. Wang asked whose book that was.
You can take whatever you like.
引导词种类
三、连接副词
where, when, why, how等连接副词在句中作状语。
He didn’t tell me when we should meet again.
Could you please tell me how you use the new panel
None of us knows where these new parts can be bought.
引导词种类
带how的词组也都可以引导宾语从句
Could you tell us how often you go abroad for a holiday
Could you tell us how long the meeting will last
I don’t know how far it is to the cinema .
Please tell us how many students there are in your school
Can you tell us how old his brother is
Please tell us how soon you will be ready .
Could you tell us how much it costs to fly to Hainan
二、时态
1. 如果主句是现在的时态 (包括一般现在时 ,
现在进行时,现在完成时),从句的时态可根
据实际情况而定,(包括一般现在时,一般过
去时,一般将来时,现在完成时等)
I know he lives here .
I know he lived here ten years ago .
I have heard that he will come tomorrow .
2.如果主句是过去的时态(包括一般过去时,过去进行时),那么从句的时态一定要用相对应的过去的某种时态(包括一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时, 过去完成时)
I knew who lived here.
I told me that she was talking with her mother at that time last week.
He asked whether his father would come back
the next day.
He said that he had seen it before.
3.当从句是客观真理,定义,公理,定理
时用一般现在时。
The teacher said that the earth travels
around the sun.
The teacher said that the world is made up of matter.
三、语序
宾语从句的语序用陈述语序:
连接词+主语+谓语+其他成分
1. When will he go to the library
His brother asks when he will go to the library .
His brother asks when will he go to the library .
2. What does he want to buy
I don’t know what he wants to buy .
I don’t know what does he want to buy .
3. Who are we going to meet
Can you tell me who we are going to meet
Can you tell me who are we going to meet
4. Does he know French
We want to know if/whether he knows French .
We want to know if/whether does he know French.
5. Will they go to Canada in summer
They’ re not sure if /whether they will go to Canada in summer .
They’ re not sure if /whether will they go to Canada in summer .
1.could / would是委婉语气,而不是过去式,因此宾语从句的时态根据实际情况用不同时态。
注意事项
Could you please tell me where we show our
tickets
Could you tell us which gate we have to go to
Would you like to know when he will come back
2. 如果主句的谓语动词是ask时,连词不可能是that;如果主句的谓语动词是say时,连词用that
She says (that) she will leave a message on
his desk .
He said (that) he was going to take care of
the child .
He asks if I like playing the piano .
You may ask the man over there how you
can get to the bus station .
3. 当doubt, doubtful用于肯定句时,后面的名词性从句连接词常用whether或if; 当doubt, doubtful用于否定句时,后面的名词性从句的连接词用that。
I doubt if/ whether he is at home.
We don’t doubt that they can complete the task ahead of time.
4. 当be sure引导主句是肯定句时,后面的名词性从句的连接词常用that; 当be sure引导的主句是否定句时,后面的名词性从句的连接词常用whether或if。
We are sure that he will be successful soon.
The old man didn’t seem to be sure whether / if he had met me.
5. 介词后宾语从句的注意事项:
①一般情况下介词后只能用wh-类连接词引导的宾语从句。
I am surprised at what he said.
②介词后如果接that从句,要先加上it, 再加that从句,即“介词+it+that…”结构。
You may depend on it that they will support you. (that不能省略)
③介词except, but, besides及in后可接that从句。I know nothing about him except that he lives here. (that不能省略)
7. 只能使用whether而不能使用if的几种情况:
① 介词后宾语从句用whether,不用if.
② whether 引导表语从句和同位语从句,而if则不能。
③ whether后可以加or not,但是if不可以.
④ 在不定式前只能用whether.(如:I can’t decide whether to stay.
我不能决定是否留下。)
⑤ discuss后宾语从句用whether不用if。
6. 在suggest, demand, order, insist等动词之后的宾语从句中用虚拟语气,即 “(should+)动词原形”。
He suggested that we (should) set about doing the work at once.
I insist that she (should) do her work alone.
The leader ordered that the army (should) set off at once.
主句
从句
一般将来时态
一般现在时态
祈使句
含有情态动词
Do you know if ______back next week If he ______ back , please let me know .
A. he comes , will come B. will he come , comes
C. he will come , comes D. he will come , will come
7. 连词 if 和 when 在不同从句中的区别:
I don’t know when he _________ (come) . I can’t wait here any more . When he _______ (come) , would you please ask him to call me
will come
comes
8. 连词+宾语从句 连词+to do
I don’t know what I shall do next .
I don’t know what to do next .
She didn’t decide which one she would choose .
She didn’t decide which one to choose .
Please tell me whom you’ll give the letter to .
Please tell me whom to give the letter to .
9.有些动词带宾语从句时需要在宾语从句前加it
这类动词主要有:like, hate , dislike, take , have, see to.
I hate it when they with their mouths full of food.
我讨厌他们满嘴食物时说话.
He will have it that our plan is really practical.
他会认为我们的计划确实可行.
We take it that you will agree with us.
我们认为你会同意我们的.
When you start the engine, you must see to it that car is in neutral. (确保)
开启发动机时, 一定要使汽车的离合器处于空挡位置.
10.宾语从句的否定转移
主句的谓语动词是think, believe, imagine, suppose, consider, expect, fancy, guess等,并且主句的主语是第一人称而且为一般现在时,从句的否定词一般要转移到主句上来,其反义疑问句一般与宾语从句一致.
I don’t think he will come to my party.
I don’t believe that man is killed by Jim, is he
11.宾语从句不可以省略引导词that的情况
①当一个动词带有两个或两个以上宾语从句时,此时第一个that可以省略,第二个that不可以省略。
②except(介词)后面宾语从句中that不可以省略。
③宾语从句紧接在间接宾语后时,从句中的that不可以省略。
④it作形式宾语,宾补后宾语从句中的that不省略。
I believe (that) you’ve done your best and that things will improve.
The teacher advised us that we should pay more attention to reading and writing.
We all believed it true that Mr. Smith wasn’t a thief.
1. The shocking news made me realize ____ terrible problems we would face.
A. what B. how C. that D. why
2. Our teachers always tell us to believe in _____ we do and who we are if we want to succeed.
A. why B. how C. what D. which
宾语从句专项练习题
3. We’ve offered her the job, but I don’t know _____ she’ll accept it.
A. where B. what C. whether D. which
4. Before the sales start, I make a list of _______ my kids will need for the coming season.
A. why B. what C. how D. which
宾语从句专项练习题
5. --- I wonder ____ you’ll water this kind of flower.
--- Every other day.
A. how often B. how long
C. how soon D. how much
6. Men usually go straight to ______ they want and leave quickly when shopping.
A. what B. which C. where D. that
宾语从句专项练习题
7. We haven’t discussed yet _____ we are going to place our new furniture.
A. that B. which C. what D. where
8. I want to be liked and loved for ____ I am inside.
A. who B. where C. what D. how
宾语从句专项练习题
9. Cindy shut the door heavily and burst into tears. No one in the office knew _____ she was so angry.
A. where B. whether C. that D. why
10. How much one enjoys himself travelling depends largely on _____ he goes with, whether his friends or relatives.
A. what B. who C. how D. why
宾语从句专项练习题
2025年高考英语核心语法
目录
十大词类
句子成分
简单句五种句型
句子类型
定语从句
状语从句
宾语从句
PART 01
十大词类
句子都是由单词组成的。英语单词根据词类或词性(Parts of Speech)可分为:
实词
Notionat Word
名词 Noun
代词 Pronoun
动词 Verb
形容词 Adjective
副词 Adverb
数词 Numeral
虚词
Form Word
冠词 Article
介词 Preposition
连词 Conjunction
感叹词 Interjection
PART 02
句子成分
必须有的句子成分:
主语(subject) 谓语(predicate)
选择性有的句子成分:
宾语(object) 定语(attribute)
状语(adverbial) 补语(complement)
表语(predicative) 同位语(appositive)
No. 1 主语
1. One-third of the students in this class are girls.( )
2. To swim in the river is a great pleasure.( )
3. The rich should help the poor.( )4. What benefits most to their study is reading English books.
( )
5. The arugula (芝麻菜)was to make a nice green salad, rounding out a roast chicken dinner. ( )6.Writing an essay is a difficult process for most people.
( )
7. It’s urgent for students themselves to improve their self-discipline( )
数词
不定式
名词化的形容词
主语从句
名词
动名词短语
it作形式主语,真正的主语为后面的不定式
round out 使变圆;使更完美;圆满结束
His face seemed to have rounded out.
His father insisted that he went to university to round out his education.
Chocolate cake rounded out the meal.
No. 2 谓语
简单谓语:由一个动词或动词短语构成。如:
This exhibition of some sixty masterpieces celebrating the life and work of Scotland's best loved painter, Sir Henry Raeburn, comes to London. ( )
复合谓语:(1)由情态动词或其他助动词加动词原形构成。如:By using the latest technologies, drones could also start providing higher-value services for railways, detecting faults in the rail or switches, before they can cause any safety problems.
( )(2)由系动词加表语构成。如:
Food became easier to chew at this point. ( )
实义动词
情态动词+实义动词
系动词
拓展:系动词(6大类别)
状态系动词:用来表示主语状态的只有be动词
感官系动词:主要有feel、smell、sound、taste......
表象系动词:表示外观的概念主要有seem、appear、look......
终止系动词:表示主语结束了动作,主要有prove、turn out...... 表示“证实”、“成为”的意思。
持续系动词:用来表示主语继续或维持某种情况或态度,主要有keep、remain、stay、lie、stand......
变化系动词:表示主语是怎样的,主要有become、grow、turn、fall、get、go、come、run......
1. Fitness Magazine recently ran an article titled “Five Reasons to ...”( )2. I’d appreciate it if you take my invitation into consideration.
( )3. ...,drones could also start providing higher-value services for railways, detecting faults in the rail or switches, before they can cause any safety problems. ( )4. The team showed that this change in bite was connected with the development of agriculture in the Neolithic period. ( )
5. How many dictionaries do you have I have five.( )6. They helped the old with their housework yesterday.( )7. He pretended not to see me.( )
No. 3 宾语
名词
代词it作形式宾语,if引导的条件状从为真正的宾语
动名词短语
宾语从句
数词
名词化的形容词
不定式短语
1. Helping the next generation to have a healthy and active childhood is of great importance. ( ) 2. Food became easier to chew at this point. ( )
3. I am down there in my wheelchair in the morning....( )
4. Needless to say, they were deeply moved.( )5. My dream is to become an English teacher.( )6. His hobby is playing football.( )7. The truth is that he has never been abroad.( )
No. 4 表语
介词短语
形容词
方位副词
过去分词
不定式
动名词
表语从句
No. 5 定语
1. Fruit juices, milk-based drinks and most alcoholic drinks are free of the tax.( )
2. Road accidents, which had fallen for years, are now rising sharply.( )
3. Throughout her career as a professional dancer, she toured in the UK.( )4. To perform these tasks, drones for rail don't need to be flying overhead. ( )
5. With their ability to see ahead, they could signal any problem, so that fast-moving trains would be able to react in time.
( )
名词,过去分词,形容词
定语从句
介词短语作后置定语
代词,介词
代词,不定式,代词,现在分词
动名词VS现在分词
虽然现在分词与动名词的格式完成相同,但它们在句子中的作用却是有明显的区别的。
1. 动名词相当于名词,所以在句子中可以充当的成分与名词类似,即主要充当主语、宾语、表语等成分。而现在分词的作用类似于副词和形容词,在句子主要充当状语、定语、补语、表语等。
Hearing the noise, they immediately stopped talking. 一听到有声音,他们立刻就停止谈话。(现在分词作状语)
He asked an embarrassing question. 他提了一个令人难堪的问题。(现在分词作定语)
Growing roses is her hobby. 种玫瑰是她的爱好。 (动名词作主语)
She like talking very much. 她很喜欢讲话。 (动名词作宾语)
1. Additionally from time to time I will assign group work to be completed ..( )
2. Although popular beliefs regarding emotional intelligence run far ahead of what research can reasonably support, the overall effects of the publicity have been more beneficial than harmful.( )
No. 6 状语
副词
让步状语从句
No. 7 补语
1. Cao believes this will make the hiking trip even more meaningful.( )
2. We sincerely wish you a quick recovery and an early return to China.( )
3. Beijing will make the Chinese culture better known to British students. ( )
形容词作宾补
名词短语作宾补
过去分词短语作宾补
No. 8 同位语
1.This exhibition of some sixty masterpieces celebrating the life and work of Scotland's best loved painter, Sir Henry Raeburn, comes to London. ( )
2. The news that Premier Li Keqiang passed away on Oct.27 made Chinese people deeply sad. ( )
名词
同位语从句
PART 03
简单句的五种基本句型
动作(动词)
1. 可以独立完成的动作
Michael sleeps.
主语+不及物动词
2. 有1个动作的承受者
Michael likes you.
主语+ 及物动词+宾语
3. 有2个动作的承受者
I teach you English.
主语+双及物动词+间宾+直宾
4. 有1个动作的承受者(但需补充)
单
I consider you smart.
主语+复杂及物动词+宾语+宾补
5. 非“动作”
Michael is in the room.
连系动词
Michael is tall.
主语+系动词+表语
SV
SVO
SVOO
SVOC
SVP
Michael looks tall.
Five basic patterns of sentences
Subject + Verb(SV)
Michael sleeps.
Subject + Verb + Predicative(SVP)
Michael likes you.
Subject + Verb + Object (SVO)
I teach you English.
Subject + Verb + Indirect object+ Direct object(SVOO)
I consider you smart.
Subject + Verb + Object + Object complement (SVOC)
Michael is tall.
PART 04
句子类型
按句子的结构可分三种:
1. 简单句(Simple Sentence)
2. 并列句(Compound Sentence)
3. 复合句(Complex Sentence)
简单句(Simple Sentence)
一个主语+一个谓语
He often reads English in the morning.
He is a school student in No. 1 Middle School.
Confidence in yourself is the first step on the road to success.
并列句(Compound Sentence)
≥2个简单句,由并列连词或分号连接
用分号:We fished all day; we didn’t catch a thing.
用并列连词:
(but, or, yet, so, for, and, nor [记忆口诀:boy’s fan ])Fields have eyes, and woods have ears. 隔墙有耳。
复合句(Complex Sentence)
主句+从句(≥1)
主句:独立存在&完整意思
从句:依附主句&充当一个句子成分的分句,由连词、
关系代词或关系副词引导
用作主语、宾语、表语、定语、状语、同位语等
Mary told me that she visited the Great Wall last year.
只有一个主谓结构
一个主句+
一个(以上)从句
两个或两个以上的简单句
英语语法作用:
造句
长句子
短句子
(简单句)
拆分
组合
简单句:
什么 + 怎么样
(主语)
(谓语)
人/物
动作/发生了什么事
动词
Verb
谓语动词
Sentence elements
按说话人说话的目的可分四种:
1.陈述句Decalarative Sentence(肯定、否定)
He is six years old. She didn’t hear of you before.
2.疑问句Interrogative Sentence(一般、特殊、选择、反意)
Do they like skating How old is he
Is he six or seven years old Mary can swim, can’t she
3.祈使句Imperative Sentence(用来表示建议、请求、命令等语气,由动词原形开头)
Don’t talk in class. Hurry up, or you will be late.
4.感叹句Exclamatory Sentence
How clever the boy is!
PART 05
定语从句
一、几个重要概念
二、关系代词的用法
三、关系副词的用法
四、关系代词与关系副词的选择
目录
在复合句中,对名词、代词、名词性短语、句子进行修饰、限定的从句叫定语从句。
定语从句?
I like
先行词
(被修饰的成分)
关系词
(起引导作用)
that
I can dance to.
music
关系代词
(1)who指人,在定语从句中可充当主语或宾语。
Here comes the girl who wants to see you. 想见你的那个女孩过来了。
(2)whom指人,在定语从句中作宾语,在限制性定语从句中一般可以省略,也可用who代替。但如果指人的关系代词紧跟在介词之后,只能用whom, 不能用who。
The people (who/whom) you met in the campus yesterday are from England.
你昨天在校园里碰到的那些人是从英国来的。
The young man with whom I traveled could speak Spanish.
同我一起旅行的那个年轻人会说西班牙语。
单句改错
I live next door to a couple who children often make a lot of noise.
whose
Kate, whose sister I shared a room with when we were at college, has gone to work in Australia.凯特到澳大利亚去工作了,读大学的时候我和她的姐姐住一个寝室。
(3)Whose用于指人或物,在定语从句中作定语。whose= the+n.+of which/whom , 为了便于理解,可以把whose记成关系形容词。
(4) which一般指物,在定语从句中作主语、宾语或表语。作宾语时可省略,但作介词的宾语,且介词提前时,不可省略。
He cycles from home to office every day, which is pretty good for his health.他每天骑自行车从家去办公室,这对他的健康非常好。
这就是丘吉尔出生的房间。
This is the room (which) Churchill was born in. (which可省略)
This is the room in which Churchill was born. (which不可省略)
(5) that既可指人,也可指物,在定语从句中作主语宾语或表语,作宾语时可省略。作介词宾语时,介词不可提到that之前,如介词提前则需用which或whom来代替that。
The number of people that came to visit this city each year reaches one million.每年来参观这座城市的人数达一百万。
The chair (that) you broke yesterday is now being repaired. 你昨天弄坏的那把椅子正在被修。
(6) as用作关系代词,既可指人,也可指物,还可指整个句子,在句子中可作主语、宾语或表语。在限制性定语从句中,as常用在the same…as…, such/so…as… 等结构中,且不能省略。
Such teachers as know Tom think him smart. 那些认识汤姆的老师都认为他聪明。
I’ll buy the same dictionary as you have. 我要买和你一样的词典。
归纳拓展
as引导非限制性定语从句,代替整个主句的内容。从句可放在主句前、主句后或主句中间。常见的固定表达有:
as we all know 正如大家所知 as is well-known 众所周知
as often happens 这经常发生 as is often the case 情况总是如此
as (is) mentioned above 如上所述
as has been said before 如前所述
as I can remember 正如我所记得的
as may be imagined 正如可以想象出来的那样
as has been pointed out 正如已经指出的
as we expected/as is expected 正如我们预料的那样
1.宜用that不用which的情况
2. 宜用which不用that的情况
3.宜用who不用that的情况
定语从句中需注意的事项
当先行词是all, much, anything, something, everything, nothing, little, none等不定代词时
当先行词被all, no, few, any, little, the very, the only等词语修饰时
1.宜用that不用which的情况
She told me everything that she knew.
她把她知道的一切都告诉了我。
He is the only person that was presented at that time.
他是当时唯一在场的人。
1.宜用that不用which的情况
口诀:“程序问题最多”
“程”:程度
没有 no, none
不确定 any
一个 the one
只有一个 the only, the very
每一个 every, each
不到一半 a little, few
大约一半 some
一大部分 much
全部 all
everything
something
nothing
anything
There is no person ______ don’t make mistakes.
(没有人不犯错)
You can take any seat _____ is free.
(你可以去坐任何空着的位子)
This is the only thing ______ we can do now.
(这是我们现在唯一能做的事)
Much ______ I learned in this book is useful.
(我在这本书里学的很多东西都很有用)
that
that
that
that
Is there anything _____ I can do for you
(有什么我可以为你做的事情吗?)
that
Our teacher told us something ______ we should do.
(我们老师告诉了我们该做的事)
that
He knows everything ______ happened in that village.
(他知道那村里发生的所有事。)
that
“序”:序数词— the first, the second, …the last
The first place _____ they visited in Guilin was Elephant Trunk Hill. (在桂林他们参观的第一个地方是象鼻山。)
that
This is the 3rd film _____ has been shown.
(这是放映的第三部影片)
that
This is the last van _____ will go to Alabama.
(这是开往阿拉巴马最后一辆货车)
that
“问题”:当主句以who/which/what开头的特殊疑问句时
Which is the bike _____ you lost
(你丢的自行车是哪一辆?)
that
Who is the boy _____ won the gold medal
(那个赢得金牌的男孩是谁?)
that
“最”:当先行词被形容词最高级修饰时
This is the best film _____ I have ever seen.
(这是我看过的最好的电影)
that
This is the most interesting guy _____ I’ve ever met.
(这是我见过最有趣的人了)
that
“多”:先行词又有人又有物的时候,用that
They are talking about the teachers and schools _____ they have just visited.
(他们在讨论他们刚刚访问过的那些学校和老师们)
that
The writer and his novel _____ you have just talked about are really well known.
(你刚刚谈起的那位作家以及他的小说确实很著名。)
that
2.宜用which不用that的情况
口诀:“都借钱,不用that”
“都”:有逗号,不用that
Until now, we have raised 50,000 pounds for the poor children, _____ is quite unexpected.
(令人意外的是,到现在我们已经为贫困孩子募捐了50,000英镑了)
which
引导非限制性定语从句时,用which
“借”:有介词,不用that
当关系词在定语从句中作介词的宾语,且介词位于关系代词前。
This is the question about _____ they have had so much discussion in the past few weeks.
(这就是过去几周来他们反复讨论的那个问题。)
which
“钱”:前面有that,不用that
当先行词是that时
在限制性定语从句中,如果前一句的关系代词是that,那么后一句的关系代词就要用which
What’s that _____ he asked for 他要的那个是什么?
which
Let me show you the novel that I borrowed from the library _____ was newly open.
(我给你看这本从新开放的图书馆借来的小说。)
which
3.宜用who不用that的情况
口诀:是人,就用who
先行词是指人的不定代词时,如:one, anyone, no one, all, nobody, anybody, none等,或先行词为those且指人时。
先行词指人且关系代词引导非限制性定语从句时。
一个句子中带有两个定语从句,且先行词都为人时,其中一个定语从句的关系代词是that,另一个一般应用who。
口诀:是人,就用who
Chances favor only those _____ are ready.
(机会总是垂青有准备的人。)
who
The famous star, _____ tries to make a comeback, draws a lot of attention. (那个试图复出的著名影星引起了很多关注。)
who
The boy that you met last night is the group leader _____ studies very hard. (昨晚你遇到的那个男孩是学习非常努力的组长。)
who
Exercises
一、填空
1. A study shows the students who are engaged in after-school activities are happier than those ______ are not.
2. Tom came back, ______ made us very happy.
who
which
二、用定语从句连接两个句子(使用关系代词)
1. They live in a room. It’s window faces south.
______________________________________________________________
2. She wants to visit the village. She grew up in it.
______________________________________________________________
They live in a room whose window faces south.
She wants to visit the village which/that she grew up in.
限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句的区别
Ⅱ. 关系副词
Winter is the time of year when the days are short while nights are long. 冬天是一年中昼短夜长的时候。
(2)When可以换成“介词+which”。
When引导定语从句的用法
She is looking forward to the day when (=on which) her daughter wins the gold medal in the Olympics. 她盼望有一天她的女儿能在奥运会上赢得金牌。
(1)当先行词是表示时间的名词(如time, day, year, month, week等),且关系词在句中作时间状语时,定语从句用when引导。
Do you still remember the days ___________ we spent together on the farm
Do you still remember the days ___________ we chatted with each other all night
when
that/which
当先行词是表示时间的名词时,既可以用when引导定语从句,也可以用that或which引导定语从句,关键要看关系词在定语从句中作何种成分。若关系词在定语从句中充当状语,则用when引导;若关系词在定语从句中充当主语或宾语,则用that或which引导。
This is the hotel where (=in which) they stayed. 这就是他们待过的旅馆。
2. Where引导定语从句的用法
(1)当先行词是表示具体地点的名词(如place, room, mountain, airport等)或表示抽象地点的名词(如case, state, stage, condition, point, situation等),且关系词在从句中作地点状语时,定语从句用where引导。
We have reached a point where a change is needed. 我们已经到了需要做出改变的地步了。
He gets into a situation where it is hard to decide where is right or wrong. 他陷入一种难以判断对错的境地。
(2)Where可以换成“介词+which”。
His father works in a factory ___________ makes radio parts.
他的父亲在一家生产收音机零件的工厂里工作。
which/that
Their child is at the stage ________ she can say individual words but not full sentence.
A. That B. where C. which D. when
B
当先行词为地点名词时,如果指代先行词的关系词在定语从句中作主语或宾语,则用that或which引导状语从句。
3. Why引导定语从句的用法
This is the reason why (=for which) he left in a hurry.这就是他匆匆离去的原因。
(1)当先行词是表示原因的名词reason,且关系词在句中作原因状语时,定语从句用why引导。
There are several reasons why…
(2)Why可以用for which来代替。
The reason ___________ he told me yesterday is a lie.
that/which
Is this the reason __________ he gave at the meeting for his careless in his work
which/that
若代替先行词reason的关系词在定语从句中不作状语,而是充当主语或宾语,则用that或which引导定语从句。
用关系副词或“介词+关系代词”将下列每对句子合并成一个句子。
1. I didn’t come this morning. The reason was that it rained heavily.
________________________________________________________
2. Yesterday Mary bought a few clothes. All of them were beautiful.
___________________________________________________________
Exercises
The reason why/for which I didn’t come this morning was that it rained heavily.
Yesterday Mary bought a few clothes, all of which were beautiful.
关系代词or关系副词?
用法 依据
根据从句的谓语动词 是及物动词,后面若无宾语,用关系代词;是不及物动词则用关系副词。
根据先行词在从句中所作的成分 把先行词放入定语从句中,若作主语或宾语用关系代词;作状语则用关系副词。
This is the house _____ he lived last year.
This is the house _____ he visited last year.
He told her the reason _____ he is unhappy, but she doesn’t believe the reason _____ he gives her.
why
that
where
which
Examples
PART 06
状语从句
状语:修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子,常见时间、地点、原因等。
1. We work in Beijing.我们在北京工作。(“in Beijing” 作地点状语修饰谓语“work”.)
2. We are learning English now.我们正在学英语。(“now” 作时间状语修饰谓语“are learning”)
3. She reads English loudly.她大声地朗读英语。(副词“loudly”作方式状语修饰谓语“reads”)
4. Helmets are made to protect our brain. 头盔是用来保护我们的大脑的。(不定式“to prevent”作目的状语修饰谓语“are made”)
5. He works very hard. 他工作非常努力。(副词“very”作程度状语修饰“副词”“hard” )
It is a very beautiful picture.它是一幅非常美丽的图画。(“very” 修饰形容词beautiful)
6. Unluckily, he didn‘t pass the exam. 很不幸,他没通过考试。(副词“unluckily”作状语,用来修饰“整个句子”)
状语从句在复合句中一般修饰主句或主句中的谓语动词。
状语从句有时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、方式、比较、让步等种类。
位于句首时,常用逗号与主句分开,位于句末时,前面一般不用逗号。如,
I feel very happy when you come to see me.
When you are crossing the street, you must be careful.
一、时间状语从句
引导时间状语从句的连接词有: when, as, while, after, before, since, ever since, as soon as, once, till, until, whenever, no sooner…than, hardly/scarcely...when, the moment/minute/instant/second, every time, each time, any time, the first time, next time, last time, all the time, by the time, directly, immediately, instantly 等。
1、表示“一···就···”的句型
1) as soon as/once
As soon as he arrives, I'll call you. 他一到,我就给你打电话。
(as soon as 侧重时间或动作先后衔接紧,而 once 侧重条件,表示“一旦...”)
2)the moment, the instant, the minute, the second
The moment I saw him, I recognized him.
我一看见他,就认出了他。
We'll leave the minute you are ready.
你一准备好,我们就出发。
4)有些副词如:instantly, immediately, directly 可用作连词,后接从句。
I left immediately the clock struck 5.
2.、when, while, as 引导时间状语从句
1) when 的用法
①when 既指时间点,也指时间段(即:从句动词可以是短暂的也可是延续的);主从句动作可同时也可先后发生。
I was thin when I was a child. 当我是个孩子的时候,我很瘦。
It was raining when I arrived. 我到达时,天正在下雨。
②when 在下列结构中, 译成“这时”,它引导的是并列句
be about to do ... when, be doing ... when, had done ···when,
be on one's way ... when, be on the point of doing ... when
2)while 用法
while 只能指一段时间,从句中的动词必须是延续性动词。强调某一段时间内发生主句动作,相当于 during the time that....
My mother was cooking while I was doing my homework.
当我在做作业时,妈妈在做饭。
I am safe while I am here.我在这儿的时候,我很安全。
注:while 除引导时间状语从句外,还引导对比句,作“然而”讲;并可在句首引出让步状语从句作“虽然···但”讲。
I like watching TV, while he likes reading. 我喜欢看电视,而他喜欢读书。
3.、until 和 till
1)“延续性动词肯定式+until”表示“动作延续到…为止,”译为“直到…为止”,如:
I waited for him until he came back. 我一直等到他回来。
2)“终止性动词的否定式+ until”表示“直到···才”。
He didn't go to bed until he had finished his work. 直到完成工作他才睡觉。
3)用于强调句式“It is not until ...that ...”
It was not until the professor came that we began the experiment.
在教授到来之后,我们才开始实验。
4) not until 放在句首时,主句倒装。
Not until he graduated did he succeed in obtaining this compound.
直到他毕业他才成功获得这种化合物。
二、地点状语从句
1、地点状语从句主要由 where, wherever anywhere, everywhere 引导。
We must camp where we can get water.
我们必须在能找到水的地方露营。
I will follow you wherever you go.
无论你到何处我都要跟随你。
注:地点状语从句与定语从句的区别:
where 引导定语从句,从句前应有一个表示地点的名词作先行词。
Go back where you came from.(where 引导地点状语从句)
Go back to the village where you came from. (where 引导定语从句,village 为先行词)
三、原因状语从句
原因状语从句由 because, as , since, now (that)(既然), in that(因为,多于口语中),seeing
(that)(鉴于,由于),considering that(考虑到)等引导。
1、 because 用来回答 why 提出的问题,表直接的因果关系,用于告知对方不知道的原因,语气最强,可用于强调句。
He didn't attend the meeting because he was ill.
他没参加会议,因为他病了。
It was because he was ill that he didn't go with us.
因为他有病,他没有和我们一起去。
注:because 和 because of 的区别:because 是连词,引导从句,because of 是短语介词,后接名词性词语,如:
The football match was put off because it rained.
The football match was put off because of the rain.
因为下雨,足球赛延期了。
since, as, now that 也可引导原因状语从句。
2、for 也可以表示原因,属并列连词,不是说明直接原因,而是对某种情况加以推断,表示补充说明理由。而推断的理由会因人而异。语气很弱,它引出的分句必须放在另一分句后。
He must be ill, for he is absent today.
四、条件状语从句
1.由 if, unless(if...not), so/as long as, supposing(that)(假设), in case(万一…, 以防…),
so/as far as(就...而言), on condition that(条件是...), provided/providing (that)(假若)引导。
Tell me about it if you have time.
I won't go unless I'm invited.
Take an umbrella with you in case it rains.
You may use the room as/so long as you clean it up afterwards.
e.g . Should he be here tomorrow, I would give him a hand.
五、目的状语从句
由 so that(以便), in order that(为了),for fear that(= in case)(以免),lest(以防)引导,
谓语常含 may, might, can, could, will, would 等情态动词。
They set out early so that they might arrive at the station in good time.
I'll speak slowly so that/in order that you can understand.
He wrote the name down for fear that(lest)he would forget.
注:当从句与主句主语一致时,可用 to do, so as to do, in order to do 结构换。
He worked day and night in order that he could succeed.
He worked day and night in order to succeed.
六、结果状语从句
1.常用的连词有 so that,so ... that, such...that, that。(结果状语从句中一般无情态动词)
He had overslept so that he was late for work. 他起晚了,所以上班迟到了。
My pen fell under my desk that I couldn't see it. 我的笔掉到桌子底下,所以我看不到。
2. so/such ...that 所用句式
①so + adj(adv) + that 从句
The box is so heavy that I can't carry it. 这个箱子很重,以至于我拿不动它。
②so+adj +a/an+单名+ that 从句=such a/an+adj.+单名+that 从句
She is so beautiful a girl that all the boys of our class like her.
=She is such a beautiful girl that all the boys of our class like her.
③so many/few +复名+ that 从句
so much/little+不可数名词+ that 从句
There are so many apples on the desk that we each have one.
There is so little water that you can't drink.
④such +a/an + adj + 单名+ that 从句
She is such a good girl that she can help you.
⑤such + adj +复名/不可数名+ that 从句
It was such bad weather that we all stayed home.
He has such interesting books that he keeps reading all day.
知识拓展:
little 表“小,可爱”时,用 such 不用 so 修饰。
He is such a little boy that his patents often teach him something.
七、方式状语从句
由 as, as if (as though)引导。
Do as you like.
He spoke as if he had been there before.
注意 as if, as though 从句与事实相反时用虚拟语气,与事实相符,不用虚拟语气。
八、比较状语从句
①常用连词 than, as ...as..., not as/so... as
He ran as far as he could.
I'm not as/so tall as he/him.
She studies harder than I(study).
②the more ... the more...引导
The harder you try, the better you will understand.
九、让步状语从句
由 though, although, as, even if/though , no matter wh-, wh-ever 词,whether...or(不管...都),when, while 等引导。
1. though, although 这两个连词用法基本一样,只是前者口语化,后者较正式,常位于句首,都不与 but 连用,但可以和 yet,still,nevertheless 连用。though 还可作副词单独放在句尾,表示“然而”的意思。
Although the TV set is very dear, I still want to buy it.
Though /Although he was worn out, he kept on working.
2. as 引导让步状语时,从句部分用倒装语序,句型为:
①形容词/副词/名词+ as +主 +谓
②动词+ as +主 +情态动词
Child as he is, he knows a lot.
Proud as these nobles are, they are afraid to see me.
3. even if(尽管;即使), even though(尽管)
这两个复合连词意义基本相同,常用以强调让步概念,有退一步想的意思(有时用于虚拟)。
表“即使”时有假设含义,一般用 even if。
We'll make trip even if(though) the weather is bad.
Even if I were in your place, I wouldn't take the job.(虚拟)
4.“whether... or...”可引导让步状语从句
Whether you believe it or not, it is true.
5.“no matter + wh-”引导让步状语从句
引导让步状语从句时“疑问句-ever”相当于“no matter +疑问词”,此时:
no matter who = whoever
no matter what = whatever
no matter which = whichever
no matter where = wherever
no matter how = however
No matter what happened, he would not mind.
It's a nice room no matter whom (whoever) it belongs to.
6.“no matter + wh-”结构只能引导让步状语从句,而“wh-ever”形式除引导让步状语从句外,还可以引导名词性从句。
引导名词性从句时:
whoever = anyone who 任何…的人…
whatever = anything that 任何…的事(物)
whenever = anyplace where 任何…的地方
I will give the book to whoever needs it.
I like whatever you like.
7.when 引导让步状语从句时置于主句后
①虽然·却·,尽管·但·
He walks when he might take a taxi.
②本(应...,可以...)却...。
when 从句用虚拟式为:could/should ... have done
She stopped trying when she might succeed next time.
8.while 引导让步状语从句时置于主句前,与 though 同,但 though 从句可到装,while 从句不可倒装。
9.让步状语从句中用一般现在时表将来。
No matter what he is, he will be punished.
十、状语从句的省略现象
当状语从句的主语与主句的主语相同或为 it, 同时从句谓语含 be 动词,就可省去从句的主语和 be 动词。
①时间状语从句中:
Don’t speak until (you are) spoken to.
While (I was) in Beijing, I lived with my uncle.
I want to go swimming when (it is) possible.
②条件状语从句中:
Come tomorrow if (it is) possible.
If (it is) so, you would be punished.
③方式状语从句中:
She stood at the gate as if (she was) waiting for someone.
④其他状语从句中:
Though (it was) cold, he still wore a shirt.
Fill in the blanks with proper words where (it is) necessary
小测:
1.He pretended that he was ill_______ he could stay at home .
A.so that B. even if C. though D. unless
2.Some people waste a lot of food,_______others haven‘t enough to eat. 题目出错。
A. since B. when C.as D. while
3.Read it loud ______ the whole class can hear you .
A.so that B. if C. when D. although
4.Busy_________ he was,he tried his best to help you .|
A. as B. when C. since D. for
5. Leave your key with a neighbor ______you may lock yourself out one day.
A. ever since B. even if C. soon after D.in case
6.Pop music is such an important part of society_____ it has even influenced our language .
A.as B. that C. which D. where
7 ._________ you are old enough to judge things , you should start your own career .
A. Even if B. Although C. As D. Now that
8. ______much of the town is fairly new,they are older,untouched comers where locals get on quietly with their lives.
A. Since B. While C. When D. Unless
9.He hurried out of the room ______the meeting was over.
A. the moment B. a moment ago C. after a minute D. a minute later
10.We had scarcely left our school_____ the rain began短暂性动词.
A. before B. than C. while D. when
11.I agree to his suggestion _____that he drops all charges.
A. if B.as long C. on condition D.in case
12.______ we have enough evidence,we can't win the case.
A. Once B.As long as C. Unless D. Since
13.Men differ from animals_____ they can think and speak.
A. for which B. for that C.in that D.in which
14.Mark needs to learn Chinese ______his company is opening a branch in Beijing.
A. unless B. until C. although D. since
15.John thinks it won't be long _____he is ready for his new job.
A. when B. after C. before D. since
it won‘t be long before …不久就
16.You can see the product to be advertised ______you go.
A. whatever B. whoever C. wherever D. whichever
17.If you happen to get lost in the wild, you'd better stay _you are and wait for help.
A. why B. where C. who D. what
18.Jack wasn't saying anything,but the teacher smiled at him______ he had done something very
clever .
A. as if B.in case C. while D. though
19. ______happens, we shall never lose hope.
A. No matter how B. Whoever C. However D. Whatever
20. You should have put the book____ you found it.
A. which B. that C. what D. where
21.It's much easier to achieve success ______you can get help from your family.
A. unless B. when C. even though D. so that
22.I will not go to Beijing_______ the company pays for the trip.
A.as B. unless C. where D. while
23.Air pollution is getting more and more serious, so we must take action_____ it is too late.
A. before B. after C. until D. when
24. Provide your doctor with a detailed medical history_____ he can give you accurate treatment.
A. even if B.in case C.so that D.as though
25. The pupils were playing games in the classroom______ a gunman entered and began shooting wildly at them.
A. while B. when C. though D. before
26. _____hard you try, it is difficult to lose weight without cutting down the amount you eat.
A. However B. Whatever C. Whichever D. Whenever
27. Actually, the London Olympic Park is built_____ there used to be a poor area called East London .
What B. when C. where D. why
28.I don't mind how you do it _you finish the painting on time.
A.as well as B. as far as C.as long as D.as fast as
As soon as 一…就,as well as既……又,不仅……而且
As far as 就…而言 as long as 只要
29.One can always manage to do more things, no matter____ full one’s schedule is in life.
A. how B. what C. when D. where
30.Greal changes have taken place in our school _____you left.
A. since B. until C. before D. when
PART 07
宾语从句
语法—名词性从句
之宾语从句
英语句子的种类
简单句 (simple sentence)
并列句 (compound sentence)
复合句 (complex sentence)
英语句子概论
简单句的五种基本句型
The weather is very cold.
主语+谓语(连系动词)+表语
He laughed.
主语+谓语(vi.)
I like Chinese food.
主语+谓语(vt.)+宾语
She taught them physics.
主语+谓语(vt.)+间接宾语+直接宾语
We must keep the room warm.
主语+谓语(vt.) +宾语+宾语补足语
并列句
把两个或几个简单句用并列连词连接起来。
I turned on the TV. My sister and I watched it.
I turned on the TV and my sister and I watched it.
I bought my sister a present. She didn’t like it.
I bought my sister a present,but she didn’t like it.
并列句
并列句
常用并列连词:
平行并列连词:
转折并列连词:
因果并列连词:
选择并列连词:
and, both…and, not only… but also, neither…nor
but, however, while, yet,
or,either…or
for, so
复合句:主句+从句
名词性从句
定语从句
状语从句
1.The boy who is standing over there is Tom
2.Because it is raining ,we have to stay at home
定语从句
状语从句
3.I know (that)he is from America
(宾语从句)
名词性从句---
Noun Clauses
(名词性从句)
Subject Clause
(主语从句)
Appositive Clause
(同位语从句)
Object Clause
(宾语从句)
Predicative Clause
(表语从句)
名词性从句在功能上相当于名词, 在复合句
中能担任主语、宾语、表语、同位语等。
主语
{
His job is important.
What he does is important.
表语
This is his job.
This is what he does every day.
{
宾语
I don’t like his job.
I don’t like what he does every day.
同位语
I don’t know about the man, Mr. White.
I don’t know about the fact that he is a teacher.
Who will win the match is still unknown.
I want to know what he has told you.
The fact is that we have lost the game.
The news that we won the game is exciting.
主语从句
宾语从句
表语从句
名词性从句的作用相当于名词,因此主语从句、表语从句 、宾语从句和同位语从句分别作主句的主语、表语、宾语和同位语。
同位语从句
宾语从句的定义
置于动词、介词等词性后面起宾语作用的从句叫宾语从句。
宾语从句的语序必须是陈述语序。谓语动词、介词、动词不定式,v.-ing形式后面都能带宾语从句。
有些形容词(afraid,sure,glad等)之后也可以带宾语从句。
宾语从句中引导词的用法
在复合句中作主句的宾语,引导词有:
从属连词:that (that 常可省略),whether, if
连接代词:who, whose, what ,which,whom,whatever,whoever等
连接副词:when ,where, how, why 等。
I know him .
2. I know who he is .
主语
谓语
宾语
(简单句)
主语
谓语
宾 语 从 句
连词
从句主语
从句谓语
主 句
(复合句)
宾语从句的概念:
宾语从句在复合句中作主句的宾语。
句子结构:
主句 +连词(引导词)+ 宾语从句
1)主句的谓语动词可以是及物动词:
2)如果主句的谓语动词是一个带有介词的词组,那么后接的从句做介词宾语从句。
3)有些形容词后也可以带有宾语从句。
I’m afraid (that) he won’t pass the exam .
He wondered if he could pass the exam .
They are talking about whether they can pass the exam .
注意:动词+副词形成的谓语动词词组后也可以带宾语从句。
一、从属连词
1. 当宾语从句是陈述句时(包括肯定句和否定
句),连词由that引导,因为that在从句中不作
任何成分,也没有任何具体意思,因此在口语
或非正式文体中常省略
Lin Tao knows (that) his own team is even better. (肯)
She says (that) she won’t take part in the sports meeting
next Sunday.(否)
Jim thought (that) the train was like a big moving party.
He said (that) he would like to see the headmaster.
引导词种类
2. 当宾语从句是一般疑问句时,由连词whether或if引导(口语中常用if),因为if/whether翻译成:“是否”,具有一定的意义,所以不能省略
Lily wanted to know if /whether her grandma liked the handbag .
Let’s see if /whether we can find out some information about that city .
It all depends on whether she likes the boss or not.
引导词种类
二、连接代词
which, what, whose, who, whom, whatever, whoever, whomever, whichever;连接代词在从句中作主语、宾语、表语、定语。
I wonder who will teach us.
Mr. Wang asked whose book that was.
You can take whatever you like.
引导词种类
三、连接副词
where, when, why, how等连接副词在句中作状语。
He didn’t tell me when we should meet again.
Could you please tell me how you use the new panel
None of us knows where these new parts can be bought.
引导词种类
带how的词组也都可以引导宾语从句
Could you tell us how often you go abroad for a holiday
Could you tell us how long the meeting will last
I don’t know how far it is to the cinema .
Please tell us how many students there are in your school
Can you tell us how old his brother is
Please tell us how soon you will be ready .
Could you tell us how much it costs to fly to Hainan
二、时态
1. 如果主句是现在的时态 (包括一般现在时 ,
现在进行时,现在完成时),从句的时态可根
据实际情况而定,(包括一般现在时,一般过
去时,一般将来时,现在完成时等)
I know he lives here .
I know he lived here ten years ago .
I have heard that he will come tomorrow .
2.如果主句是过去的时态(包括一般过去时,过去进行时),那么从句的时态一定要用相对应的过去的某种时态(包括一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时, 过去完成时)
I knew who lived here.
I told me that she was talking with her mother at that time last week.
He asked whether his father would come back
the next day.
He said that he had seen it before.
3.当从句是客观真理,定义,公理,定理
时用一般现在时。
The teacher said that the earth travels
around the sun.
The teacher said that the world is made up of matter.
三、语序
宾语从句的语序用陈述语序:
连接词+主语+谓语+其他成分
1. When will he go to the library
His brother asks when he will go to the library .
His brother asks when will he go to the library .
2. What does he want to buy
I don’t know what he wants to buy .
I don’t know what does he want to buy .
3. Who are we going to meet
Can you tell me who we are going to meet
Can you tell me who are we going to meet
4. Does he know French
We want to know if/whether he knows French .
We want to know if/whether does he know French.
5. Will they go to Canada in summer
They’ re not sure if /whether they will go to Canada in summer .
They’ re not sure if /whether will they go to Canada in summer .
1.could / would是委婉语气,而不是过去式,因此宾语从句的时态根据实际情况用不同时态。
注意事项
Could you please tell me where we show our
tickets
Could you tell us which gate we have to go to
Would you like to know when he will come back
2. 如果主句的谓语动词是ask时,连词不可能是that;如果主句的谓语动词是say时,连词用that
She says (that) she will leave a message on
his desk .
He said (that) he was going to take care of
the child .
He asks if I like playing the piano .
You may ask the man over there how you
can get to the bus station .
3. 当doubt, doubtful用于肯定句时,后面的名词性从句连接词常用whether或if; 当doubt, doubtful用于否定句时,后面的名词性从句的连接词用that。
I doubt if/ whether he is at home.
We don’t doubt that they can complete the task ahead of time.
4. 当be sure引导主句是肯定句时,后面的名词性从句的连接词常用that; 当be sure引导的主句是否定句时,后面的名词性从句的连接词常用whether或if。
We are sure that he will be successful soon.
The old man didn’t seem to be sure whether / if he had met me.
5. 介词后宾语从句的注意事项:
①一般情况下介词后只能用wh-类连接词引导的宾语从句。
I am surprised at what he said.
②介词后如果接that从句,要先加上it, 再加that从句,即“介词+it+that…”结构。
You may depend on it that they will support you. (that不能省略)
③介词except, but, besides及in后可接that从句。I know nothing about him except that he lives here. (that不能省略)
7. 只能使用whether而不能使用if的几种情况:
① 介词后宾语从句用whether,不用if.
② whether 引导表语从句和同位语从句,而if则不能。
③ whether后可以加or not,但是if不可以.
④ 在不定式前只能用whether.(如:I can’t decide whether to stay.
我不能决定是否留下。)
⑤ discuss后宾语从句用whether不用if。
6. 在suggest, demand, order, insist等动词之后的宾语从句中用虚拟语气,即 “(should+)动词原形”。
He suggested that we (should) set about doing the work at once.
I insist that she (should) do her work alone.
The leader ordered that the army (should) set off at once.
主句
从句
一般将来时态
一般现在时态
祈使句
含有情态动词
Do you know if ______back next week If he ______ back , please let me know .
A. he comes , will come B. will he come , comes
C. he will come , comes D. he will come , will come
7. 连词 if 和 when 在不同从句中的区别:
I don’t know when he _________ (come) . I can’t wait here any more . When he _______ (come) , would you please ask him to call me
will come
comes
8. 连词+宾语从句 连词+to do
I don’t know what I shall do next .
I don’t know what to do next .
She didn’t decide which one she would choose .
She didn’t decide which one to choose .
Please tell me whom you’ll give the letter to .
Please tell me whom to give the letter to .
9.有些动词带宾语从句时需要在宾语从句前加it
这类动词主要有:like, hate , dislike, take , have, see to.
I hate it when they with their mouths full of food.
我讨厌他们满嘴食物时说话.
He will have it that our plan is really practical.
他会认为我们的计划确实可行.
We take it that you will agree with us.
我们认为你会同意我们的.
When you start the engine, you must see to it that car is in neutral. (确保)
开启发动机时, 一定要使汽车的离合器处于空挡位置.
10.宾语从句的否定转移
主句的谓语动词是think, believe, imagine, suppose, consider, expect, fancy, guess等,并且主句的主语是第一人称而且为一般现在时,从句的否定词一般要转移到主句上来,其反义疑问句一般与宾语从句一致.
I don’t think he will come to my party.
I don’t believe that man is killed by Jim, is he
11.宾语从句不可以省略引导词that的情况
①当一个动词带有两个或两个以上宾语从句时,此时第一个that可以省略,第二个that不可以省略。
②except(介词)后面宾语从句中that不可以省略。
③宾语从句紧接在间接宾语后时,从句中的that不可以省略。
④it作形式宾语,宾补后宾语从句中的that不省略。
I believe (that) you’ve done your best and that things will improve.
The teacher advised us that we should pay more attention to reading and writing.
We all believed it true that Mr. Smith wasn’t a thief.
1. The shocking news made me realize ____ terrible problems we would face.
A. what B. how C. that D. why
2. Our teachers always tell us to believe in _____ we do and who we are if we want to succeed.
A. why B. how C. what D. which
宾语从句专项练习题
3. We’ve offered her the job, but I don’t know _____ she’ll accept it.
A. where B. what C. whether D. which
4. Before the sales start, I make a list of _______ my kids will need for the coming season.
A. why B. what C. how D. which
宾语从句专项练习题
5. --- I wonder ____ you’ll water this kind of flower.
--- Every other day.
A. how often B. how long
C. how soon D. how much
6. Men usually go straight to ______ they want and leave quickly when shopping.
A. what B. which C. where D. that
宾语从句专项练习题
7. We haven’t discussed yet _____ we are going to place our new furniture.
A. that B. which C. what D. where
8. I want to be liked and loved for ____ I am inside.
A. who B. where C. what D. how
宾语从句专项练习题
9. Cindy shut the door heavily and burst into tears. No one in the office knew _____ she was so angry.
A. where B. whether C. that D. why
10. How much one enjoys himself travelling depends largely on _____ he goes with, whether his friends or relatives.
A. what B. who C. how D. why
宾语从句专项练习题
