人教版(2019)选择性必修第一册Unit 4 Body Language Reading and Thinking课件(共27张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版(2019)选择性必修第一册Unit 4 Body Language Reading and Thinking课件(共27张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 4.2MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-09-06 19:50:21 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
(共27张PPT)
Unit 4 Body Language
Reading and thinking
Act out the body language on the screen without speaking and the others guess what it is.
Lead-in
Act and guess game.
verbal
nonverbal
Ways of
communica-tion
Spoken language
Written language
Body
language
face-to-face communication
face-to-face communication
phone calls
letters
WeChat
How many ways do people use to communicate
What's the function of language
To communicate with each other.
Body
language
Eye contact
Facial expressions
Postures
Gestures
1. To read about the funciton of body language and its implicaions in different cultures;
2. To practice making inferences by looking at the clues in the passage;
3. To think critically about body language by relating it to your own culture and personal experiences.
Learning Objectives
Q1:What is the type of the passage
A. A narration
B. An argumentation
C. An exposition
D. An application
Q2: What do you think will be talked about the text
_________________
Pre-reading: prediction
Body language
While-reading
Underline the topic sentence of each para, and pay attention to the signpost words.
Task 1. Skimming
Reading skills: the topic sentence usually hide on the first or last sentence of that paragraph.
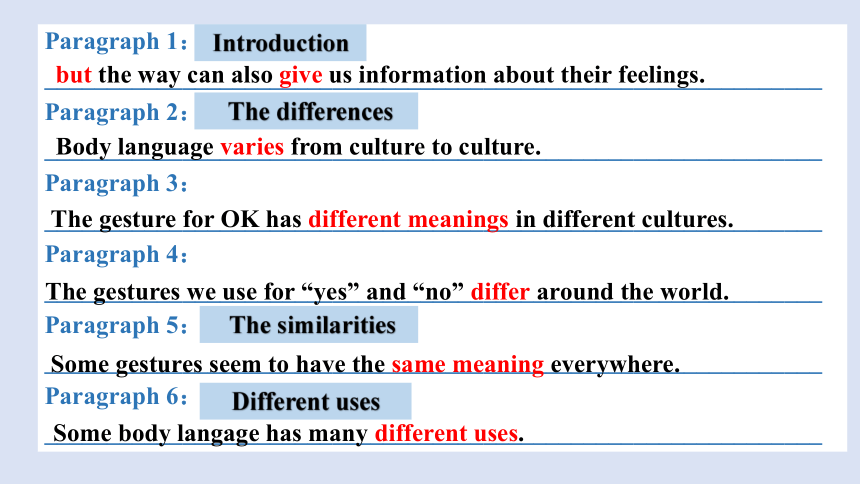
Paragraph 1:______________________________________________________________
Paragraph 2:______________________________________________________________
Paragraph 3:______________________________________________________________
Paragraph 4:______________________________________________________________
Paragraph 5:______________________________________________________________
Paragraph 6:______________________________________________________________
but the way can also give us information about their feelings.
Introduction
Body language varies from culture to culture.
The gesture for OK has different meanings in different cultures.
The gestures we use for “yes” and “no” differ around the world.
The differences
Some gestures seem to have the same meaning everywhere.
Some body langage has many different uses.
The similarities
Different uses
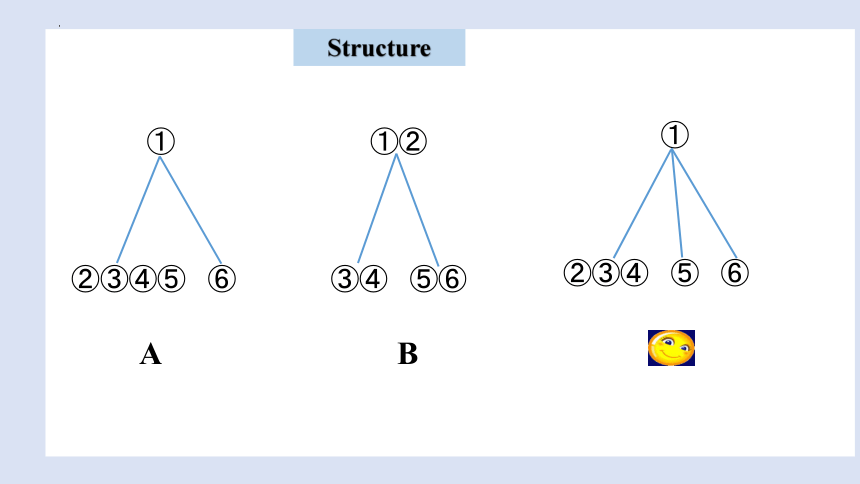
①
②③④⑤ ⑥
Structure
A B C
①②
③④ ⑤⑥
①
②③④ ⑤ ⑥
1.In which countries are men and women not permitted to make eye contact
A.China and Japan.
B.Middle Eastern countries.
C.Brazil and Germany.
D.Bulgaria and southern Albania.
Task 2. Scanning
Read and answer.
1.In which countries are men and women not permitted to make eye contact
A.China and Japan. B.Middle Eastern countries.
C.Brazil and Germany. D.Bulgaria and southern Albania.
2.What is the purpose of the second paragraph
A.To tell us how important body language is.
B.To show an identical gesture may have different meanings in different cultures.
C.To stop men and women making eye contact while talking.
D.To remind us to look down while talking to an older person to
show respect.
3.Which of the following is True according Para. 2-4
A. In many Middle Eastern countries, women are permitted to make eye contact with men.
B. The gesture for “OK” has the same meaning in different cultures.
C. You should avoid making the gesture OK in Brazil and Germany.
D. In Japan and Russia, people may kiss their friends on the cheek when they meet.
4.Why does the author take smiling for example in the last paragraph
A. To prove smiling is the most powerful body language.
B. To prove some body language has many different uses.
C. To prove smiling can be easily misunderstood.
D. To prove body language varies from culture to culture.
Reading for details
Para.1
We use both words and body language to express our thoughts and opinions in our interactions with other people. We can learn a lot about what people are thinking by watching their body language. Words are important, but the way people stand, hold their arms, and move their hands can also give us information about their feelings.
Q: Can you guess the meaning of the word “interaction” according to the context
“Interaction” means “communication”.
Para.2
Just like spoken language, body language varies from culture to culture. The crucial thing is using body language in a way that is appropriate to the culture you are in. For example, making eye contact—looking into someone’s eyes—in some countries is a way to display interest. In other countries, by contrast, eye contact is not always approved of. For example, in many Middle Eastern countries, men and women are not socially permitted to make eye contact. In Japan, it may demonstrate respect to look down when talking to an older person.
topic sentence
supporting idea1
(example)
supporting idea1
(example)
contrast
Body language/
Gesture
Country/Region
Meaning
Eye contact
Some countries
Interest
Middle Eastern
countries
Not polite
Look down when talking to someone
Japan
Respect
Para 2
Careful reading
Body language Meaning
Country
Eye contact
Interest
Some countries
Not polite
Middle Eastern countries
Look down when talking to someone
Respect
Japan
Para.3
The gesture for “OK” has different meanings in different cultures. In Japan, someone who witnesses another person employing the gesture might think it means money. In France, a person encountering an identical gesture may interpret it as meaning zero. However, you should avoid making this gesture in Brazil and Germany, as it is not considered polite.
topic sentence
In Japan
In France
In Brazil and Germany
contrast
Body language
Meaning
Country
Money
Japan
Zero
France
Not polite
Brazil/Germany
Yes
China
Para.4
Even the gestures we use for “yes” and “no” differ around the world. In many countries, shaking one’s head means “no”, and nodding means “yes”. By comparison, in Bulgaria and southern Albania, the gestures have the opposite meaning. There are also differences in how we touch each other, how close we stand to someone we are talking to, and how we act when we meet or part.In countries like France and Russia, people may kiss their friends on the cheek when they meet. Elsewhere, people favour shaking hands, bowing from the waist, or nodding the head when they meet someone else.
topic sentence
topic sentence
supporting idea1
(example)
paralleling
supporting idea2
(example)
contrast
supporting idea1
(example)
supporting idea2
(example)
paralleling
What can be inferred from paragraph 4
A. “Yes” and “No” gestures have the same meaning everywhere.
B. People in Bulgaria express agreement through shaking their heads.
C. People in southern Albania express agreement through nodding.
D. The Russians usually shake hands when they meet.
“In many countries, shaking one's head means “no” and nodding means “yes”. By comparison, in Bulgaria and southern Albania, the gestures have the opposite meaning.”
Body language
Meaning
Country
shake the head
nod the head
kiss on the cheek
no
yes
Many countries
Bulgaria & Southern Albania
yes
no
Many countries
Bulgaria & Southern Albania
a greeting
France & Russia
a greeting
elsewhere
shake hands, bowing,
nod the head
Para.5
Some gestures seem to have the same meaning everywhere. Placing your hands together and resting them on the side of your head while closing your eyes means “sleep”. A good way of saying “I am full” is moving your hand in circles over your stomach after a meal.
topic sentence
supporting idea1
(example)
supporting idea1
(example)
paralleling
Body language
Meaning
Country
Placing your hands together and resting them on the side of your head while closing your eyes.
Moving your hand in circles over your stomach after a meal.
sleep
I’m full.
most places
Para.6
Some body language has many different uses. Perhaps the best example is smiling. A smile can help us get through difficult situations and find friends in a world of strangers. A smile can break down barriers. We can use a smile to apologise, to greet someone, to ask for help, or to start a conversation. Experts suggest smiling at yourself in the mirror to make yourself feel happier and stronger. And if we are feeling down or lonely, there is nothing better than seeing the smiling face of a good friend.
Q: What can a smile do
A smile costs nothing, but gives so much.
一个微笑不费什么事,却可能改变他人的一生。
What have you learned from this passage
It has _________ meanings in different cultures.
It varies from ________ to __________.
When in Rome, do as Romans do.
Body language is __________ in our daily life;
Learn about body language in different cultures and use it appropriately.
Summarizing
important
culture
culture
different
Some has many different _________.
uses
How does the passage develop
A.By giving examples.
B.By giving data.
C.By showing some pictures.
D.By analysing facts.
Post-reading
1. How does the passage develop
A. By giving examples. B. By giving data.
C. By showing some pictures. D. By analysing facts.
2.What can we learn from the passage
A. In all countries, shaking one’s head means “No”.
B. A smile can get a person into difficult situations.
C.In Russia, people favour bowing from the waist when they meet someone else.
D. If a person moves his hand in circles over his stomach after a meal, that means he is full.
3. Which statement does the author possibly agree with
A. Never too old to learn.
B. Four eyes see more than two.
C. Action speaks louder than words.
D. When in Rome, do as the Romans do.
Test for goals
Body language 1._____(vary) from culture to culture. Eye contact is not always 2._______ (approve) of. In Japan, it may demonstrate respect to look down when 3.______ (talk) to an older person. In France, a person who 4._________(witness) the gesture for “OK” may interpret it 5. ___ meaning zero. You should avoid 6.______ (make) this gesture in Brazil and Germany. Even the gestures we use 7.____ “yes” and “no” differ around the world. In many countries, 8. ______(shake) hands means “no”, and nodding means yes. By 9.__________ (compare), in Bulgaria and southern Albania, the gestures have the opposite meaning. Elsewhere, people favor shaking hands, 10.________(bow) from the waists or nodding the head when they meet someone else.
varies
approved
talking
witnesses
as
making
for
shaking
comparison
bowing
Assignments
1. 《绿色通道》P65, 课文语法填空。
2. 《绿色通道》课时作业16。
Thank you !
Unit 4 Body Language
Reading and thinking
Act out the body language on the screen without speaking and the others guess what it is.
Lead-in
Act and guess game.
verbal
nonverbal
Ways of
communica-tion
Spoken language
Written language
Body
language
face-to-face communication
face-to-face communication
phone calls
letters
How many ways do people use to communicate
What's the function of language
To communicate with each other.
Body
language
Eye contact
Facial expressions
Postures
Gestures
1. To read about the funciton of body language and its implicaions in different cultures;
2. To practice making inferences by looking at the clues in the passage;
3. To think critically about body language by relating it to your own culture and personal experiences.
Learning Objectives
Q1:What is the type of the passage
A. A narration
B. An argumentation
C. An exposition
D. An application
Q2: What do you think will be talked about the text
_________________
Pre-reading: prediction
Body language
While-reading
Underline the topic sentence of each para, and pay attention to the signpost words.
Task 1. Skimming
Reading skills: the topic sentence usually hide on the first or last sentence of that paragraph.
Paragraph 1:______________________________________________________________
Paragraph 2:______________________________________________________________
Paragraph 3:______________________________________________________________
Paragraph 4:______________________________________________________________
Paragraph 5:______________________________________________________________
Paragraph 6:______________________________________________________________
but the way can also give us information about their feelings.
Introduction
Body language varies from culture to culture.
The gesture for OK has different meanings in different cultures.
The gestures we use for “yes” and “no” differ around the world.
The differences
Some gestures seem to have the same meaning everywhere.
Some body langage has many different uses.
The similarities
Different uses
①
②③④⑤ ⑥
Structure
A B C
①②
③④ ⑤⑥
①
②③④ ⑤ ⑥
1.In which countries are men and women not permitted to make eye contact
A.China and Japan.
B.Middle Eastern countries.
C.Brazil and Germany.
D.Bulgaria and southern Albania.
Task 2. Scanning
Read and answer.
1.In which countries are men and women not permitted to make eye contact
A.China and Japan. B.Middle Eastern countries.
C.Brazil and Germany. D.Bulgaria and southern Albania.
2.What is the purpose of the second paragraph
A.To tell us how important body language is.
B.To show an identical gesture may have different meanings in different cultures.
C.To stop men and women making eye contact while talking.
D.To remind us to look down while talking to an older person to
show respect.
3.Which of the following is True according Para. 2-4
A. In many Middle Eastern countries, women are permitted to make eye contact with men.
B. The gesture for “OK” has the same meaning in different cultures.
C. You should avoid making the gesture OK in Brazil and Germany.
D. In Japan and Russia, people may kiss their friends on the cheek when they meet.
4.Why does the author take smiling for example in the last paragraph
A. To prove smiling is the most powerful body language.
B. To prove some body language has many different uses.
C. To prove smiling can be easily misunderstood.
D. To prove body language varies from culture to culture.
Reading for details
Para.1
We use both words and body language to express our thoughts and opinions in our interactions with other people. We can learn a lot about what people are thinking by watching their body language. Words are important, but the way people stand, hold their arms, and move their hands can also give us information about their feelings.
Q: Can you guess the meaning of the word “interaction” according to the context
“Interaction” means “communication”.
Para.2
Just like spoken language, body language varies from culture to culture. The crucial thing is using body language in a way that is appropriate to the culture you are in. For example, making eye contact—looking into someone’s eyes—in some countries is a way to display interest. In other countries, by contrast, eye contact is not always approved of. For example, in many Middle Eastern countries, men and women are not socially permitted to make eye contact. In Japan, it may demonstrate respect to look down when talking to an older person.
topic sentence
supporting idea1
(example)
supporting idea1
(example)
contrast
Body language/
Gesture
Country/Region
Meaning
Eye contact
Some countries
Interest
Middle Eastern
countries
Not polite
Look down when talking to someone
Japan
Respect
Para 2
Careful reading
Body language Meaning
Country
Eye contact
Interest
Some countries
Not polite
Middle Eastern countries
Look down when talking to someone
Respect
Japan
Para.3
The gesture for “OK” has different meanings in different cultures. In Japan, someone who witnesses another person employing the gesture might think it means money. In France, a person encountering an identical gesture may interpret it as meaning zero. However, you should avoid making this gesture in Brazil and Germany, as it is not considered polite.
topic sentence
In Japan
In France
In Brazil and Germany
contrast
Body language
Meaning
Country
Money
Japan
Zero
France
Not polite
Brazil/Germany
Yes
China
Para.4
Even the gestures we use for “yes” and “no” differ around the world. In many countries, shaking one’s head means “no”, and nodding means “yes”. By comparison, in Bulgaria and southern Albania, the gestures have the opposite meaning. There are also differences in how we touch each other, how close we stand to someone we are talking to, and how we act when we meet or part.In countries like France and Russia, people may kiss their friends on the cheek when they meet. Elsewhere, people favour shaking hands, bowing from the waist, or nodding the head when they meet someone else.
topic sentence
topic sentence
supporting idea1
(example)
paralleling
supporting idea2
(example)
contrast
supporting idea1
(example)
supporting idea2
(example)
paralleling
What can be inferred from paragraph 4
A. “Yes” and “No” gestures have the same meaning everywhere.
B. People in Bulgaria express agreement through shaking their heads.
C. People in southern Albania express agreement through nodding.
D. The Russians usually shake hands when they meet.
“In many countries, shaking one's head means “no” and nodding means “yes”. By comparison, in Bulgaria and southern Albania, the gestures have the opposite meaning.”
Body language
Meaning
Country
shake the head
nod the head
kiss on the cheek
no
yes
Many countries
Bulgaria & Southern Albania
yes
no
Many countries
Bulgaria & Southern Albania
a greeting
France & Russia
a greeting
elsewhere
shake hands, bowing,
nod the head
Para.5
Some gestures seem to have the same meaning everywhere. Placing your hands together and resting them on the side of your head while closing your eyes means “sleep”. A good way of saying “I am full” is moving your hand in circles over your stomach after a meal.
topic sentence
supporting idea1
(example)
supporting idea1
(example)
paralleling
Body language
Meaning
Country
Placing your hands together and resting them on the side of your head while closing your eyes.
Moving your hand in circles over your stomach after a meal.
sleep
I’m full.
most places
Para.6
Some body language has many different uses. Perhaps the best example is smiling. A smile can help us get through difficult situations and find friends in a world of strangers. A smile can break down barriers. We can use a smile to apologise, to greet someone, to ask for help, or to start a conversation. Experts suggest smiling at yourself in the mirror to make yourself feel happier and stronger. And if we are feeling down or lonely, there is nothing better than seeing the smiling face of a good friend.
Q: What can a smile do
A smile costs nothing, but gives so much.
一个微笑不费什么事,却可能改变他人的一生。
What have you learned from this passage
It has _________ meanings in different cultures.
It varies from ________ to __________.
When in Rome, do as Romans do.
Body language is __________ in our daily life;
Learn about body language in different cultures and use it appropriately.
Summarizing
important
culture
culture
different
Some has many different _________.
uses
How does the passage develop
A.By giving examples.
B.By giving data.
C.By showing some pictures.
D.By analysing facts.
Post-reading
1. How does the passage develop
A. By giving examples. B. By giving data.
C. By showing some pictures. D. By analysing facts.
2.What can we learn from the passage
A. In all countries, shaking one’s head means “No”.
B. A smile can get a person into difficult situations.
C.In Russia, people favour bowing from the waist when they meet someone else.
D. If a person moves his hand in circles over his stomach after a meal, that means he is full.
3. Which statement does the author possibly agree with
A. Never too old to learn.
B. Four eyes see more than two.
C. Action speaks louder than words.
D. When in Rome, do as the Romans do.
Test for goals
Body language 1._____(vary) from culture to culture. Eye contact is not always 2._______ (approve) of. In Japan, it may demonstrate respect to look down when 3.______ (talk) to an older person. In France, a person who 4._________(witness) the gesture for “OK” may interpret it 5. ___ meaning zero. You should avoid 6.______ (make) this gesture in Brazil and Germany. Even the gestures we use 7.____ “yes” and “no” differ around the world. In many countries, 8. ______(shake) hands means “no”, and nodding means yes. By 9.__________ (compare), in Bulgaria and southern Albania, the gestures have the opposite meaning. Elsewhere, people favor shaking hands, 10.________(bow) from the waists or nodding the head when they meet someone else.
varies
approved
talking
witnesses
as
making
for
shaking
comparison
bowing
Assignments
1. 《绿色通道》P65, 课文语法填空。
2. 《绿色通道》课时作业16。
Thank you !
