2025届高考英语一轮专项复习语法:状语从句课件(共32张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2025届高考英语一轮专项复习语法:状语从句课件(共32张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.8MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-09-28 17:31:54 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共32张PPT)
状语从句
一、状语从句的类型及关联词
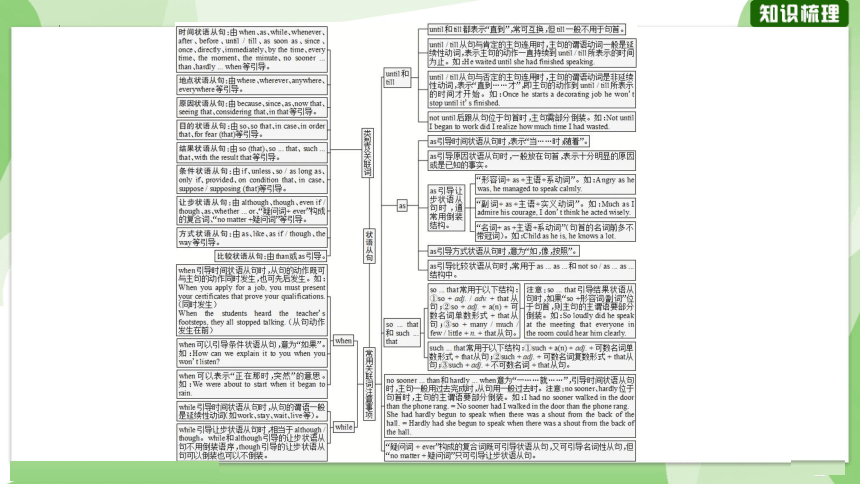
状语从句根据其用途可分为时间状语从句、地点状语从句、原因状语从句、目的状语从句、结果状语从句、条件状语从句、让步状语从句、方式状语从句、比较状语从句九种。
时间状语从句:由 when, as, while, whenever, after, before,
until / till, as soon as, since, once, directly, immediately, by the time, every time, the moment, the minute, no sooner ... than, hardly ... when等引导。
地点状语从句:由 where, wherever, anywhere, everywhere等引导。
原因状语从句:由 because, since, as, now that, seeing that, considering that, in that等引导。
目的状语从句:由 so, so that, in case, in order that, for fear (that)等引导。
结果状语从句:由 so (that), so ... that, such ... that, with the result that等引导。
条件状语从句:由 if, unless, so / as long as, only if, provided, on condition that, in case, suppose / supposing (that)等引导。
让步状语从句:由 although, though, even if / though, as, whether ... or,“疑问词+ ever”构成的复合词,“no matter +疑问词”等引导。
方式状语从句:由 as, like, as if / though, the way等引导。
比较状语从句:由than或as引导。
二、常用关联词注意事项
1. when
(1) when引导时间状语从句时,从句的动作既可与主句的动作同时发生,也可先后发生。如:
When he looked back, the woman had disappeared.
Don't get excited when you talk.
(2) when还可引导条件状语从句,意为“如果”。如:
No one can make a dress when they haven't learned how.
2. while
(1) while引导时间状语从句时,从句的谓语一般是延续性动词(如work, stay, wait, live等)。如:
While you are sorting your things upstairs, I'll pack my books.
(2) while 引导让步状语从句时,相当于 although / though。while和although引导的让步状语从句不用倒装语序,though 引导的让步状语从句可以倒装也可以不倒装。如:
While / Although / Though I admit that the problems are difficult, I don't agree that they cannot be solved.
Happy though the little girl is, she will feel homesick at the beginning.
3. until和till
(1) until和till都表示“直到”,常可互换,但till一般不用于句首。如:
He determined to stay at the office till / until his year was up.
Until I was 21, I never missed attending night school four nights a week.
(2) until / till从句与肯定的主句连用时,主句的谓语动词一般是延续性动词,表示主句的动作一直持续到until / till所表示的时间为止。如:
Julie stayed up till / until eleven o'clock last night.
(3) until / till从句与否定的主句连用时,主句的谓语动词是非延续性动词,表示“直到……才”,即主句的动作到 until / till 所表示的时间才开始。如:
I cannot comment further until / till I have all the information.
(4) not until后跟从句位于句首时,主句需部分倒装。如:
Not until the war was over was Einstein able to return to his homeland.
4. as
(1) as引导时间状语从句时,表示“当……时;随着”。如:
A look of surprise came into Allison's eyes as she read the message.
As I knew him better, I discovered that my impressions had been right.
(2) as引导原因状语从句时,一般放在句首,表示十分明显的原因或是已知的事实。如:
As it was getting late, I decided to book into a hotel.
(3) as引导让步状语从句时,通常用倒装结构。详情如下:
a. “形容词+ as +主语+系动词”或“副词+ as +主语+实义动词”。如:
Tired as they were, they sat up late.
Fast as you read, you can't finish the book in two days.
b. 名词+ as +主语+系动词(句首的名词前多不带冠词)。如:
Teenager as he is, he has established his own company.
(4) as引导方式状语从句时,意为“如,像,按照”。如:
I want you to tell my friend your interesting experience exactly as you have told it to me.
(5) as引导比较状语从句时,常用于as ... as ... 和not so / as ... as ... 结构中。如:
I never went through a final exam that was as difficult as that one.
There was no obvious reason why this could not be as good a film as the original.
5. no sooner ... than和hardly ... when意为“一……就……”,引导时间状语时,主句一般用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时。注意:no sooner, hardly 位于句首时,主句的主谓语要部分倒装。如:
Mrs Smith had no sooner left the room than they began to talk about her.
No sooner had Mrs Smith left the room than they began to talk about her.
The star had hardly arrived in Rome when he was surrounded by reporters.
Hardly had the star arrived in Rome when he was surrounded by reporters.
6. so ... that和such ... that
(1) so ... that 常用于以下结构:①so + adj. / adv. + that 从句;②so + adj. + a(n) +可数名词单数形式+ that从句;③so + many / much / few / little + n. + that从句。如:
He was so weak that he could hardly stand up.
There was so much smoke that they couldn't see across the hallway.
Everything happened so quickly that I hadn't time to think.
(2) such ... that 常用于以下结构:①such + a(n) + adj. +可数名词单数形式+ that 从句;②such + adj.+可数名词复数形式+ that 从句;③such + adj. +不可数名词+ that从句。如:
He was in such a hurry that he almost pushed me over on the stairs.
They are such lovely twins that everybody likes them very much.
It is such cold weather that I can see no one outside through the window.
注意:so ... that引导结果状语从句时,如果“so +形容词/副词”位于句首,则主句的主谓语要部分倒装。如:
So cold was the weather that we had to stay at home.
So quietly did she speak that I could hardly hear her.
7. “疑问词+ ever”构成的复合词既可引导状语从句,又可引导名词性从句,但“no matter +疑问词”只可引导让步状语从句。如:
Whichever (= No matter which) book you borrow, you must return it in a week.
Whatever (= No matter what) happens, you know that I'll stand by you.
Whoever uprooted that tree ought to be ashamed of themselves.(此句中的Whoever不可用No matter who替换)
1. We all need to get involved in saving energy ______ it’s at work, at home, or at school.
A. unless B. once C. whether D. because
(2021天津卷)
2. Watch out for injuries while exercising. Always stop ______ you begin to feel any pain.
A. in order that B. even if C. ever since D. as soon as
(2020天津卷)
C
I. 单项选择。
D
II. 用适当的连词填空。
1. This hit home for me_____________ I was sitting with my 2- year- old grandson on a sofa over the Spring Festival holiday. (2022新高考II )
2. David had not missed a single practice, and ___________
______________ he always finished his run long after the other children, he did always finish. (2022新高考I、II读后续写 )
as/ when/ while
although/ though/ while
3. My mother was so touched by her gesture that she decided to go back to the store and give the cashier (收银员) a five-dollar bill to keep on hand _____________ the same happened to someone else if they didn't have enough money for all of their groceries. (2021年6月浙江卷)
in case
1. The disagreement was too sharp that neither he nor I knew what to settle it. (2022全国甲卷)
2. Whether you ride a bicycle, you don’t use petrol. (2022全国甲卷)
III. 短文改错。
too— so
Whether — If / When
3. In my opinion, where in trouble, we should seek help from
those we trust mostly. (2021全国甲卷)
4. I also water the flowers in the yard and tidying up my own bedroom whatever necessary. (2021全国乙卷)
where— when/ whenever
whatever— whenever
选用括号内合适的内容完成下面短文。
A
Scientists have created a computer program which can understand simple jokes. The software can check whether each word in a sentence fits with the context. 1. ____________________ (In case, Even though) it finds a word which does not seem to fit, it quickly searches for similar-sounding words.
In case
For example, the software should understand such a joke: A man asks his friend, “How was your trip to Helsinki (the capital of Finland) ” to which his friend replies, “Terrible, all our luggage disappeared into Finn Air.” 2. ____________________ (Because, Although) “Finn” does not fit with the context of luggage and air, it does sound like “thin”. So the software can understand the joke.
However, the software doesn't find this joke funny:
Patient: Doctor, doctor, I swallowed a bone.
Doctor: Are you choking
Patient: No, I really did!
Although
Someone probably would see the doctor 3. ___________________ (when, until) he or she was choking, so the software is unable to identify the exchange as a joke.
Scientists also worked on adapting the program to personal preferences. For example, if someone has been in a car accident, the software will avoid joking about this 4. ___________________ (in order that, for fear that) the person gets upset.
when
for fear that
B
It can be tough to figure out whether it's best to eat breakfast before or after an early-morning workout. 1. __________ (Although, Since) there isn't a definitive answer for everyone, there are several factors to consider when deciding when and what to eat.
The most important thing is to pay attention to how you're feeling during your workout. 2. __________ (Since, If ) you eat before exercising and feel sick to your stomach, try skipping your pre-workout meal.
Although
If
3. __________ (Unless, If ) you don't eat and feel dizzy or struggle to make it through your fitness routine, try eating a little of something next time. It's important to experiment and determine what eating pattern works best for your body.
4. __________ (Though, If ) you choose to eat before exercising in the morning, it's best to avoid foods that are high in fat and protein, 5. __________ (as, so) they can take longer to digest.
If
If
as
A post-workout meal is crucial, 6. __________ (although, whether) you eat before exercising or not. After exercising, your body immediately begins to rebuild glycogen ( 糖原) stores and regrow muscle proteins. Fueling these processes 7. __________ (after, until) you exercise can help your body get this done faster. You'd better choose unprocessed carbohydrates (碳水化合物) and protein, which can stimulate metabolism ( 新陈代谢) and enhance recovery.
whether
after
8. __________ (Only if, Even if ) you're not trying to gain a lot of muscle, you need to eat protein. It provides essential amino acids ( 氨基酸) that your body can't provide on its own.
Opting to eat 9. __________ (before, whenever) you do a morning workout may be a personal choice, but everyone should drink water first thing. Research suggests that drinking water before breakfast helps people reduce their overall calorie intake throughout the day.
Even if
before
状语从句
一、状语从句的类型及关联词
状语从句根据其用途可分为时间状语从句、地点状语从句、原因状语从句、目的状语从句、结果状语从句、条件状语从句、让步状语从句、方式状语从句、比较状语从句九种。
时间状语从句:由 when, as, while, whenever, after, before,
until / till, as soon as, since, once, directly, immediately, by the time, every time, the moment, the minute, no sooner ... than, hardly ... when等引导。
地点状语从句:由 where, wherever, anywhere, everywhere等引导。
原因状语从句:由 because, since, as, now that, seeing that, considering that, in that等引导。
目的状语从句:由 so, so that, in case, in order that, for fear (that)等引导。
结果状语从句:由 so (that), so ... that, such ... that, with the result that等引导。
条件状语从句:由 if, unless, so / as long as, only if, provided, on condition that, in case, suppose / supposing (that)等引导。
让步状语从句:由 although, though, even if / though, as, whether ... or,“疑问词+ ever”构成的复合词,“no matter +疑问词”等引导。
方式状语从句:由 as, like, as if / though, the way等引导。
比较状语从句:由than或as引导。
二、常用关联词注意事项
1. when
(1) when引导时间状语从句时,从句的动作既可与主句的动作同时发生,也可先后发生。如:
When he looked back, the woman had disappeared.
Don't get excited when you talk.
(2) when还可引导条件状语从句,意为“如果”。如:
No one can make a dress when they haven't learned how.
2. while
(1) while引导时间状语从句时,从句的谓语一般是延续性动词(如work, stay, wait, live等)。如:
While you are sorting your things upstairs, I'll pack my books.
(2) while 引导让步状语从句时,相当于 although / though。while和although引导的让步状语从句不用倒装语序,though 引导的让步状语从句可以倒装也可以不倒装。如:
While / Although / Though I admit that the problems are difficult, I don't agree that they cannot be solved.
Happy though the little girl is, she will feel homesick at the beginning.
3. until和till
(1) until和till都表示“直到”,常可互换,但till一般不用于句首。如:
He determined to stay at the office till / until his year was up.
Until I was 21, I never missed attending night school four nights a week.
(2) until / till从句与肯定的主句连用时,主句的谓语动词一般是延续性动词,表示主句的动作一直持续到until / till所表示的时间为止。如:
Julie stayed up till / until eleven o'clock last night.
(3) until / till从句与否定的主句连用时,主句的谓语动词是非延续性动词,表示“直到……才”,即主句的动作到 until / till 所表示的时间才开始。如:
I cannot comment further until / till I have all the information.
(4) not until后跟从句位于句首时,主句需部分倒装。如:
Not until the war was over was Einstein able to return to his homeland.
4. as
(1) as引导时间状语从句时,表示“当……时;随着”。如:
A look of surprise came into Allison's eyes as she read the message.
As I knew him better, I discovered that my impressions had been right.
(2) as引导原因状语从句时,一般放在句首,表示十分明显的原因或是已知的事实。如:
As it was getting late, I decided to book into a hotel.
(3) as引导让步状语从句时,通常用倒装结构。详情如下:
a. “形容词+ as +主语+系动词”或“副词+ as +主语+实义动词”。如:
Tired as they were, they sat up late.
Fast as you read, you can't finish the book in two days.
b. 名词+ as +主语+系动词(句首的名词前多不带冠词)。如:
Teenager as he is, he has established his own company.
(4) as引导方式状语从句时,意为“如,像,按照”。如:
I want you to tell my friend your interesting experience exactly as you have told it to me.
(5) as引导比较状语从句时,常用于as ... as ... 和not so / as ... as ... 结构中。如:
I never went through a final exam that was as difficult as that one.
There was no obvious reason why this could not be as good a film as the original.
5. no sooner ... than和hardly ... when意为“一……就……”,引导时间状语时,主句一般用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时。注意:no sooner, hardly 位于句首时,主句的主谓语要部分倒装。如:
Mrs Smith had no sooner left the room than they began to talk about her.
No sooner had Mrs Smith left the room than they began to talk about her.
The star had hardly arrived in Rome when he was surrounded by reporters.
Hardly had the star arrived in Rome when he was surrounded by reporters.
6. so ... that和such ... that
(1) so ... that 常用于以下结构:①so + adj. / adv. + that 从句;②so + adj. + a(n) +可数名词单数形式+ that从句;③so + many / much / few / little + n. + that从句。如:
He was so weak that he could hardly stand up.
There was so much smoke that they couldn't see across the hallway.
Everything happened so quickly that I hadn't time to think.
(2) such ... that 常用于以下结构:①such + a(n) + adj. +可数名词单数形式+ that 从句;②such + adj.+可数名词复数形式+ that 从句;③such + adj. +不可数名词+ that从句。如:
He was in such a hurry that he almost pushed me over on the stairs.
They are such lovely twins that everybody likes them very much.
It is such cold weather that I can see no one outside through the window.
注意:so ... that引导结果状语从句时,如果“so +形容词/副词”位于句首,则主句的主谓语要部分倒装。如:
So cold was the weather that we had to stay at home.
So quietly did she speak that I could hardly hear her.
7. “疑问词+ ever”构成的复合词既可引导状语从句,又可引导名词性从句,但“no matter +疑问词”只可引导让步状语从句。如:
Whichever (= No matter which) book you borrow, you must return it in a week.
Whatever (= No matter what) happens, you know that I'll stand by you.
Whoever uprooted that tree ought to be ashamed of themselves.(此句中的Whoever不可用No matter who替换)
1. We all need to get involved in saving energy ______ it’s at work, at home, or at school.
A. unless B. once C. whether D. because
(2021天津卷)
2. Watch out for injuries while exercising. Always stop ______ you begin to feel any pain.
A. in order that B. even if C. ever since D. as soon as
(2020天津卷)
C
I. 单项选择。
D
II. 用适当的连词填空。
1. This hit home for me_____________ I was sitting with my 2- year- old grandson on a sofa over the Spring Festival holiday. (2022新高考II )
2. David had not missed a single practice, and ___________
______________ he always finished his run long after the other children, he did always finish. (2022新高考I、II读后续写 )
as/ when/ while
although/ though/ while
3. My mother was so touched by her gesture that she decided to go back to the store and give the cashier (收银员) a five-dollar bill to keep on hand _____________ the same happened to someone else if they didn't have enough money for all of their groceries. (2021年6月浙江卷)
in case
1. The disagreement was too sharp that neither he nor I knew what to settle it. (2022全国甲卷)
2. Whether you ride a bicycle, you don’t use petrol. (2022全国甲卷)
III. 短文改错。
too— so
Whether — If / When
3. In my opinion, where in trouble, we should seek help from
those we trust mostly. (2021全国甲卷)
4. I also water the flowers in the yard and tidying up my own bedroom whatever necessary. (2021全国乙卷)
where— when/ whenever
whatever— whenever
选用括号内合适的内容完成下面短文。
A
Scientists have created a computer program which can understand simple jokes. The software can check whether each word in a sentence fits with the context. 1. ____________________ (In case, Even though) it finds a word which does not seem to fit, it quickly searches for similar-sounding words.
In case
For example, the software should understand such a joke: A man asks his friend, “How was your trip to Helsinki (the capital of Finland) ” to which his friend replies, “Terrible, all our luggage disappeared into Finn Air.” 2. ____________________ (Because, Although) “Finn” does not fit with the context of luggage and air, it does sound like “thin”. So the software can understand the joke.
However, the software doesn't find this joke funny:
Patient: Doctor, doctor, I swallowed a bone.
Doctor: Are you choking
Patient: No, I really did!
Although
Someone probably would see the doctor 3. ___________________ (when, until) he or she was choking, so the software is unable to identify the exchange as a joke.
Scientists also worked on adapting the program to personal preferences. For example, if someone has been in a car accident, the software will avoid joking about this 4. ___________________ (in order that, for fear that) the person gets upset.
when
for fear that
B
It can be tough to figure out whether it's best to eat breakfast before or after an early-morning workout. 1. __________ (Although, Since) there isn't a definitive answer for everyone, there are several factors to consider when deciding when and what to eat.
The most important thing is to pay attention to how you're feeling during your workout. 2. __________ (Since, If ) you eat before exercising and feel sick to your stomach, try skipping your pre-workout meal.
Although
If
3. __________ (Unless, If ) you don't eat and feel dizzy or struggle to make it through your fitness routine, try eating a little of something next time. It's important to experiment and determine what eating pattern works best for your body.
4. __________ (Though, If ) you choose to eat before exercising in the morning, it's best to avoid foods that are high in fat and protein, 5. __________ (as, so) they can take longer to digest.
If
If
as
A post-workout meal is crucial, 6. __________ (although, whether) you eat before exercising or not. After exercising, your body immediately begins to rebuild glycogen ( 糖原) stores and regrow muscle proteins. Fueling these processes 7. __________ (after, until) you exercise can help your body get this done faster. You'd better choose unprocessed carbohydrates (碳水化合物) and protein, which can stimulate metabolism ( 新陈代谢) and enhance recovery.
whether
after
8. __________ (Only if, Even if ) you're not trying to gain a lot of muscle, you need to eat protein. It provides essential amino acids ( 氨基酸) that your body can't provide on its own.
Opting to eat 9. __________ (before, whenever) you do a morning workout may be a personal choice, but everyone should drink water first thing. Research suggests that drinking water before breakfast helps people reduce their overall calorie intake throughout the day.
Even if
before
