【教学评一体化】Unit4 Natural disasters Reading and thinking课件-新人教必修一
文档属性
| 名称 | 【教学评一体化】Unit4 Natural disasters Reading and thinking课件-新人教必修一 |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 8.2MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-10-15 09:38:51 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
(共32张PPT)
Unit 4 Natural disasters
Reading and thinking
人教版(2019)必修第 册
人教版(2019)必修第 册
一
Learning objectives
1
Lead in
Pre-reading
3
While-reading
Post-reading
5
7
Assessment
2
4
6
8
Homework
Summary
1
Learning objectives
1. To read a text about Tangshan earthquake and gather information;
2. To reflect on the lessons that we can learn from the earthquake;
3. To analyze the language features of the text.
Look at the pictures and collect words related to natural disasters.
tornado
drought
landslide
tsunami
flood
volcano
wildfire
Lead in
2
Buildings_____________.
fell down
People were_________________________.
trapped or buried
The water pipes ______________________.
cracked and burst
The city was____________and lay_________.
destroyed
in ruins
Do you know what happened during the big earthquakes
3
Pre-Reading
When
Where
What
The passage mainly talks about a terrible ____________ (what ) that happened in __________( where ) in_______ (when ) and caused great _________ to people. (What result )
earthquake
Tangshan
1976
damage
What happened
While-Reading
4
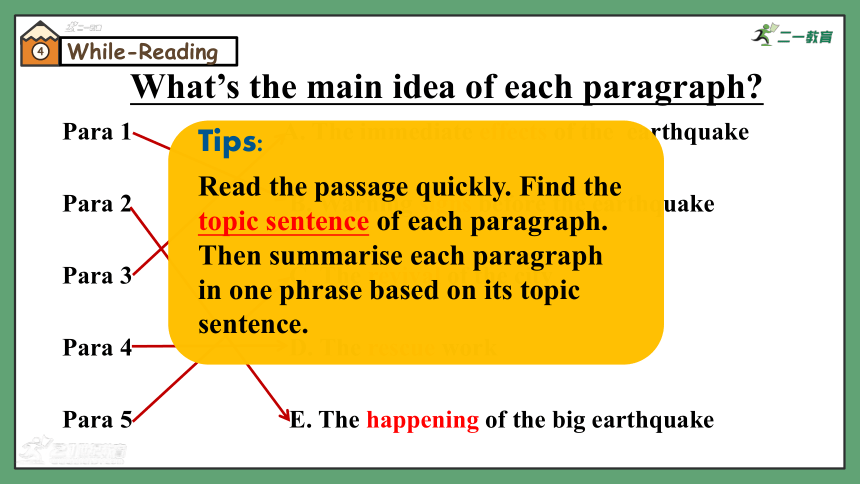
Para 1 A. The immediate effects of the earthquake
Para 2 B. Warning signs before the earthquake
Para 3 C. The revival of the city
Para 4 D. The rescue work
Para 5 E. The happening of the big earthquake
What’s the main idea of each paragraph
Read the passage quickly. Find the topic sentence of each paragraph. Then summarise each paragraph in one phrase based on its topic sentence.
Tips:
While-Reading
4
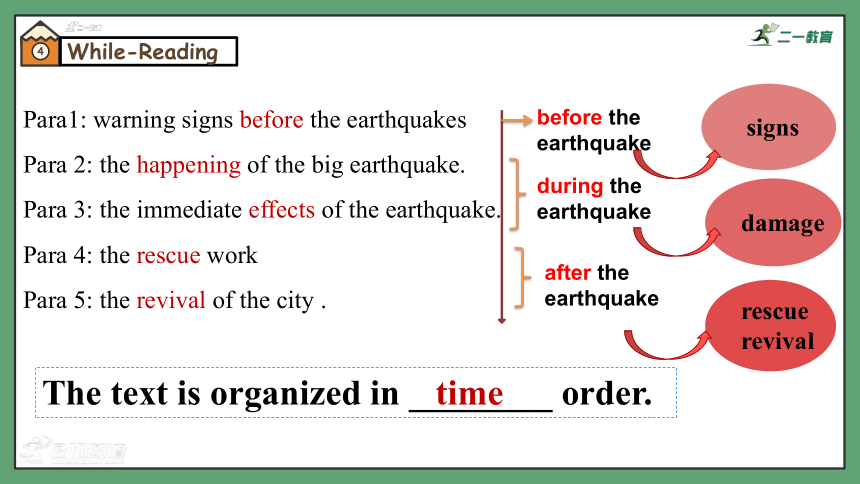
Para1: warning signs before the earthquakes
Para 2: the happening of the big earthquake.
Para 3: the immediate effects of the earthquake.
Para 4: the rescue work
Para 5: the revival of the city .
during the earthquake
after the earthquake
before the earthquake
The text is organized in ________ order.
time
signs
damage
rescue
revival
While-Reading
4
Part 1: the signs before the earthquake
Strange things were happening in the countryside of northeastern Hebei. For several days, the water in the village wells rose and fell, rose and fell. There were deep cracks that appeared in the well walls. At least one well had some smelly gas coming out of it. Chickens and even pigs were too nervous to eat, and dogs refused to go inside buildings. Mice ran out of the fields looking for places to hide, and fish jumped out of the water. At about 3:00 a.m., on 28 July1976, bright lights were seen in the sky outside of the city of Tangshan and loud noises were heard. But the city's one million people were asleep as usual that night.
What were the strange things that were happening before the earthquake
rose and fell, rose and fell
deep cracks
Chickens and even pigs
dogs
Mice
fish
bright lights
loud noises
warning
unaware;
ignorant;
unprepared
asleep
How did people
react to these strange things
The ground
The animals
The other aspects
smelly gas
While-Reading
4
At 3:42 a.m., everything began to shake. It seemed as if the world were coming to an end! Eleven kilometres directly below the city, one of the most deadly earthquakes of the 20th century had begun, a quake that even caused damage more than 150 kilometres away in Beijing. Nearly one third of the whole nation felt it! A huge crack, eight kilometres long and 30 metres wide, cut across houses, roads and waterways. Hard hills of rock became rivers of dirt. In less than one minute, a large city lay in ruins. Two thirds of the people who lived there were dead or injured. Thousands of children were left without parents.The number of people who were killed or badly injured in the quake was more than 400,000.
Everywhere survivors looked, there was nothing but ruins. Nearly everything in the city was destroyed. About 75 percent of the city's factories and buildings, 90 percent of its homes, and all of its hospitals were gone. Bricks covered the ground like red autumn leaves, but no wind could blow them away. Most bridges had fallen or were not safe to cross. The railway trackes were now useless pieces of metal. Tens of thousands of cows, hundreds of thousands of pigs, and millions of chickens were dead. Sand now filled the wells instead of water. People were in shock-and then, later that afternoon, another bit quake shook Tangshan again. Even more buildings fell down. Water, food, and electricity were hard to get. People began to wonder how long the disaster would last.
Part 2: A huge earthquake struck Tangshan.
Why did the writer use so many numbers in the text
to show the earthquake was very ________ and it caused__________________ to people and the city.
serious
a lot of damage
What kind of damage did it cause
to make the article more ____________ and ___________ .
convincing
shocking
While-Reading
4
3:42 am
3:43 am
in less than one minute——
People
1. Two thirds of the people who lived there were or .
2. Thousands of children were parents.
Buildings
1. 75 percent of the city's factories and buildings, 90 percent of its , and all of its hospitals were .
2. Most bridges had . The were now useless.
Animals
1. Tens of thousands of cows, hundreds of thousands of pigs, and millions of chickens were .
A large city lay in ruins.
dead injured
left without
gone
fallen
dead
homes
railway tracks
While-Reading
4
Part 2: A huge earthquake struck Tangshan.
At 3:42 a.m., everything began to shake. It seemed as if the world were coming to an end! Eleven kilometres directly below the city, one of the most deadly earthquakes of the 20th century had begun, a quake that even caused damage more than 150 kilometres away in Beijing. Nearly one third of the whole nation felt it! A huge crack, eight kilometres long and 30 metres wide, cut across houses, roads and waterways. Hard hills of rock became rivers of dirt. In less than one minute, a large city lay in ruins. Two thirds of the people who lived there were dead or injured. Thousands of children were left without parents.The number of people who were killed or badly injured in the quake was more than 400,000.
Everywhere survivors looked, there was nothing but ruins. Nearly everything in the city was destroyed. About 75 percent of the city's factories and buildings, 90 percent of its homes, and all of its hospitals were gone. Bricks covered the ground like red autumn leaves, but no wind could blow them away. Most bridges had fallen or were not safe to cross. The railway trackes were now useless pieces of metal. Tens of thousands of cows, hundreds of thousands of pigs, and millions of chickens were dead. Sand now filled the wells instead of water. People were in shock-and then, later that afternoon, another bit quake shook Tangshan again. Even more buildings fell down. Water, food, and electricity were hard to get. People began to wonder how long the disaster would last.
How did
people feel
in shock
in panic
in despair
While-Reading
4
Part 3: The rescue and the revival after the earthquake.
But hope was not lost. Soon after the quakes, the army sent 150,000 soldiers to Tangshan to dig out those who were trapped and to bury the dead. More than 10,000 doctors and nurses came to provide medical care. Workers built shelters for survivors whose homes had been destroyed. Hundreds of thousands of people were helped. Water and food were brought into the city by train, truck, and plane. Slowly, the city began to breathe again.
Tangshan started to revive itself and get back up on its feet. With strong support from the government and the tireless efforts of the city's people, a new Tangshan was built upon the earthquake ruins. The new city has become a home to more than seven million people, with great improvements in transportation, industry, and environment. Tangshan city has proved to China and the rest of the world that in times of disaster, people must unify and show the wisdom to stay positive and rebuild for a brighter future.
hopeful
positive
come back to life or recover
Who came to the rescue
What did they do
How did people feel
But hope was not lost.
While-Reading
4
Tang shan’s new look
With strong support from the government and the tireless efforts of people, Tangshan started to revive itself and get back up on its feet.
Simile(明喻)
Exaggeration(夸张)
Repetition (重复)
Personification(拟人)
Metaphor (暗喻)
Data(数据)
Read for the language features
While-Reading
4
Question:What kind of text is it
Literary journalism usually describes real historical events and real characters. The usage of the figures of speech can stimulate readers' feelings and thus touch the readers.
literary journalism.
exposition(说明文)
argumentation(议论文)
narration(记叙文)
or
While-Reading
4
unaware
shocked
hopeless
hopeful
before the earthquake
during the earthquake
after the earthquake
when the rescue came
To describe the change of Tangshan people's feelings
While-Reading
4
During an earthquake
After an earthquake
Before an earthquake
What would you do if a big earthquake hit your city?
Post-Reading
5
make a list of what to do , where to go ,who to contact.
If you are INDOORS--STAY THERE! (Get under a desk or table and hang on to it, or move into a hallway or get against an inside wall. DON'T run downstairs or rush outside while the building is shaking
If you are OUTSIDE-- get into the OPEN .
Use a cellphone to get help.
Tap on a pipe or wall or whistle for help.
Never try to use the lift.
During an earthquake
After an earthquake
Before an earthquake
Discussion
Post-Reading
5
Faced with natural disasters, people must ____and show the ______to stay______ and ______ for a brighter future.
A man can be destroyed but not defeated.
一个人可以被毁灭,但绝不会被打败。
Disasters have no mercy, but humans do.
天灾无情,人有情。
unify
wisdom
positive
rebuild
If everyone gives a hand, the world would be full of love.
Post-Reading
5
1. as if 似乎;好像
你好像有什么心事似的。
_______________ you have something on your mind.
她好像有些坏消息。
It seems as if she’d had some bad news.
Language points
It seemed as if the world were coming to an end!
It seems as if
Language points
In less than one minute, a large city lay in ruins.
2. ruin n. & vt. 破坏;毁坏
ruin one’s hope/ future/ health 毁掉某人的希望/将来/健康
be/ lie in ruins 成为废墟,毁灭
翻译:
吸烟毁掉你的健康,所以你最好戒烟。
Heavy smoking ruins your health,so you’d better quit smoking.
二战后,整个国家处于一片废墟中。
The country was/lay in ruins after World War Ⅱ.
Language points
People were in shock and then, later that afternoon, another bit quake
shook Tangshan again.
3. shock vt. & n. 使震惊;使吃惊
in shock 震惊地 shocked adj. 感到震惊的;
shocking adj. 令人震惊的
【语境应用】完成句子。
1) He _____________(shock) at her smoking.
2) After the __________ news spread throughout the whole city, everyone felt ________. (shock)
3) She was __________ (震惊地) for about two weeks after the accident.
was shocked
shocking
shocked
in shock
Language points
The army sent 150,000 soldiers to Tangshan to dig out those who were trapped and to bury the dead. (Par4L1)
4. trap v. 使落入陷阱,使落入圈套
be trapped in 被困在……中;陷入……中
她被困在大雨中。
She was trapped in the heavy rain.
Language points
With strong support from the government and the tireless efforts of the city’s people…(Par5L1)
5. effort n. 努力;艰难尝试
e.g. We are making progress but we need to make greater efforts.
【归纳】effort短语
make an effort/efforts/every effort to do sth.
尽一切努力做某事
spare no effort 不遗余力; 尽力
with (an) effort 努力地
without effort 毫不费力地
Language points
【语境应用】完成句子。
1) 我们必须尽一切努力以减缓病情的发展。
We must _________________ to slow down the spread of COVID-19.
2) 他毫不费力地举起那块大石头。
He lifted the big stone _____________.
3) Many excellent architects _____________________ (正做出巨大努力) to build the center stage.
make every effort
without effort
are making great efforts
Language points
Some were found alive, though they were suffering from terrible injuries.
6. suffer vt. 遭受;蒙受
suffer from 受……折磨;患……病
suffering n. 痛苦, 苦恼;劳苦, 困难
【语境应用】完成下列句子。
1) He ____________________ (受了好多苦) when he was a child.
2) Do you often ____________________ (遭受头痛的折磨吗)
suffered a lot (of pain)
suffer from a headache
signs damage rescue&revival
———|——————|——————|———→
before… during… after…
The change of
people's feeling
unaware
shocked
hopeless
hopeful
Summary
6
Assessment
Assessment
7
Items Great (5 pt.) Not bad (3 pt.) Try harder
(2 pt.)
I can know the information of Tangshan big earthquake.
I can know the rescue work and rebuilding after the big earthquake.
I can know how to do if an earthquake hit my city .
I can master reading skills of skimming and scanning.
Points(pt.) _______________in total.
提升作业
1.Finish exercise grammar filling and reading comprehension in your exercise book.
2. Retell what would happen before an earthquake.
基础作业
1. Recite new words and phrases and make sentences.
2. Listen to the tape and read the text after the tape
拓展作业
Interview your classmates about how to do if an earthquake hit your city and make a speech.
Homework
8
https://www.21cnjy.com/recruitment/home/fine
Thanks!
Unit 4 Natural disasters
Reading and thinking
人教版(2019)必修第 册
人教版(2019)必修第 册
一
Learning objectives
1
Lead in
Pre-reading
3
While-reading
Post-reading
5
7
Assessment
2
4
6
8
Homework
Summary
1
Learning objectives
1. To read a text about Tangshan earthquake and gather information;
2. To reflect on the lessons that we can learn from the earthquake;
3. To analyze the language features of the text.
Look at the pictures and collect words related to natural disasters.
tornado
drought
landslide
tsunami
flood
volcano
wildfire
Lead in
2
Buildings_____________.
fell down
People were_________________________.
trapped or buried
The water pipes ______________________.
cracked and burst
The city was____________and lay_________.
destroyed
in ruins
Do you know what happened during the big earthquakes
3
Pre-Reading
When
Where
What
The passage mainly talks about a terrible ____________ (what ) that happened in __________( where ) in_______ (when ) and caused great _________ to people. (What result )
earthquake
Tangshan
1976
damage
What happened
While-Reading
4
Para 1 A. The immediate effects of the earthquake
Para 2 B. Warning signs before the earthquake
Para 3 C. The revival of the city
Para 4 D. The rescue work
Para 5 E. The happening of the big earthquake
What’s the main idea of each paragraph
Read the passage quickly. Find the topic sentence of each paragraph. Then summarise each paragraph in one phrase based on its topic sentence.
Tips:
While-Reading
4
Para1: warning signs before the earthquakes
Para 2: the happening of the big earthquake.
Para 3: the immediate effects of the earthquake.
Para 4: the rescue work
Para 5: the revival of the city .
during the earthquake
after the earthquake
before the earthquake
The text is organized in ________ order.
time
signs
damage
rescue
revival
While-Reading
4
Part 1: the signs before the earthquake
Strange things were happening in the countryside of northeastern Hebei. For several days, the water in the village wells rose and fell, rose and fell. There were deep cracks that appeared in the well walls. At least one well had some smelly gas coming out of it. Chickens and even pigs were too nervous to eat, and dogs refused to go inside buildings. Mice ran out of the fields looking for places to hide, and fish jumped out of the water. At about 3:00 a.m., on 28 July1976, bright lights were seen in the sky outside of the city of Tangshan and loud noises were heard. But the city's one million people were asleep as usual that night.
What were the strange things that were happening before the earthquake
rose and fell, rose and fell
deep cracks
Chickens and even pigs
dogs
Mice
fish
bright lights
loud noises
warning
unaware;
ignorant;
unprepared
asleep
How did people
react to these strange things
The ground
The animals
The other aspects
smelly gas
While-Reading
4
At 3:42 a.m., everything began to shake. It seemed as if the world were coming to an end! Eleven kilometres directly below the city, one of the most deadly earthquakes of the 20th century had begun, a quake that even caused damage more than 150 kilometres away in Beijing. Nearly one third of the whole nation felt it! A huge crack, eight kilometres long and 30 metres wide, cut across houses, roads and waterways. Hard hills of rock became rivers of dirt. In less than one minute, a large city lay in ruins. Two thirds of the people who lived there were dead or injured. Thousands of children were left without parents.The number of people who were killed or badly injured in the quake was more than 400,000.
Everywhere survivors looked, there was nothing but ruins. Nearly everything in the city was destroyed. About 75 percent of the city's factories and buildings, 90 percent of its homes, and all of its hospitals were gone. Bricks covered the ground like red autumn leaves, but no wind could blow them away. Most bridges had fallen or were not safe to cross. The railway trackes were now useless pieces of metal. Tens of thousands of cows, hundreds of thousands of pigs, and millions of chickens were dead. Sand now filled the wells instead of water. People were in shock-and then, later that afternoon, another bit quake shook Tangshan again. Even more buildings fell down. Water, food, and electricity were hard to get. People began to wonder how long the disaster would last.
Part 2: A huge earthquake struck Tangshan.
Why did the writer use so many numbers in the text
to show the earthquake was very ________ and it caused__________________ to people and the city.
serious
a lot of damage
What kind of damage did it cause
to make the article more ____________ and ___________ .
convincing
shocking
While-Reading
4
3:42 am
3:43 am
in less than one minute——
People
1. Two thirds of the people who lived there were or .
2. Thousands of children were parents.
Buildings
1. 75 percent of the city's factories and buildings, 90 percent of its , and all of its hospitals were .
2. Most bridges had . The were now useless.
Animals
1. Tens of thousands of cows, hundreds of thousands of pigs, and millions of chickens were .
A large city lay in ruins.
dead injured
left without
gone
fallen
dead
homes
railway tracks
While-Reading
4
Part 2: A huge earthquake struck Tangshan.
At 3:42 a.m., everything began to shake. It seemed as if the world were coming to an end! Eleven kilometres directly below the city, one of the most deadly earthquakes of the 20th century had begun, a quake that even caused damage more than 150 kilometres away in Beijing. Nearly one third of the whole nation felt it! A huge crack, eight kilometres long and 30 metres wide, cut across houses, roads and waterways. Hard hills of rock became rivers of dirt. In less than one minute, a large city lay in ruins. Two thirds of the people who lived there were dead or injured. Thousands of children were left without parents.The number of people who were killed or badly injured in the quake was more than 400,000.
Everywhere survivors looked, there was nothing but ruins. Nearly everything in the city was destroyed. About 75 percent of the city's factories and buildings, 90 percent of its homes, and all of its hospitals were gone. Bricks covered the ground like red autumn leaves, but no wind could blow them away. Most bridges had fallen or were not safe to cross. The railway trackes were now useless pieces of metal. Tens of thousands of cows, hundreds of thousands of pigs, and millions of chickens were dead. Sand now filled the wells instead of water. People were in shock-and then, later that afternoon, another bit quake shook Tangshan again. Even more buildings fell down. Water, food, and electricity were hard to get. People began to wonder how long the disaster would last.
How did
people feel
in shock
in panic
in despair
While-Reading
4
Part 3: The rescue and the revival after the earthquake.
But hope was not lost. Soon after the quakes, the army sent 150,000 soldiers to Tangshan to dig out those who were trapped and to bury the dead. More than 10,000 doctors and nurses came to provide medical care. Workers built shelters for survivors whose homes had been destroyed. Hundreds of thousands of people were helped. Water and food were brought into the city by train, truck, and plane. Slowly, the city began to breathe again.
Tangshan started to revive itself and get back up on its feet. With strong support from the government and the tireless efforts of the city's people, a new Tangshan was built upon the earthquake ruins. The new city has become a home to more than seven million people, with great improvements in transportation, industry, and environment. Tangshan city has proved to China and the rest of the world that in times of disaster, people must unify and show the wisdom to stay positive and rebuild for a brighter future.
hopeful
positive
come back to life or recover
Who came to the rescue
What did they do
How did people feel
But hope was not lost.
While-Reading
4
Tang shan’s new look
With strong support from the government and the tireless efforts of people, Tangshan started to revive itself and get back up on its feet.
Simile(明喻)
Exaggeration(夸张)
Repetition (重复)
Personification(拟人)
Metaphor (暗喻)
Data(数据)
Read for the language features
While-Reading
4
Question:What kind of text is it
Literary journalism usually describes real historical events and real characters. The usage of the figures of speech can stimulate readers' feelings and thus touch the readers.
literary journalism.
exposition(说明文)
argumentation(议论文)
narration(记叙文)
or
While-Reading
4
unaware
shocked
hopeless
hopeful
before the earthquake
during the earthquake
after the earthquake
when the rescue came
To describe the change of Tangshan people's feelings
While-Reading
4
During an earthquake
After an earthquake
Before an earthquake
What would you do if a big earthquake hit your city?
Post-Reading
5
make a list of what to do , where to go ,who to contact.
If you are INDOORS--STAY THERE! (Get under a desk or table and hang on to it, or move into a hallway or get against an inside wall. DON'T run downstairs or rush outside while the building is shaking
If you are OUTSIDE-- get into the OPEN .
Use a cellphone to get help.
Tap on a pipe or wall or whistle for help.
Never try to use the lift.
During an earthquake
After an earthquake
Before an earthquake
Discussion
Post-Reading
5
Faced with natural disasters, people must ____and show the ______to stay______ and ______ for a brighter future.
A man can be destroyed but not defeated.
一个人可以被毁灭,但绝不会被打败。
Disasters have no mercy, but humans do.
天灾无情,人有情。
unify
wisdom
positive
rebuild
If everyone gives a hand, the world would be full of love.
Post-Reading
5
1. as if 似乎;好像
你好像有什么心事似的。
_______________ you have something on your mind.
她好像有些坏消息。
It seems as if she’d had some bad news.
Language points
It seemed as if the world were coming to an end!
It seems as if
Language points
In less than one minute, a large city lay in ruins.
2. ruin n. & vt. 破坏;毁坏
ruin one’s hope/ future/ health 毁掉某人的希望/将来/健康
be/ lie in ruins 成为废墟,毁灭
翻译:
吸烟毁掉你的健康,所以你最好戒烟。
Heavy smoking ruins your health,so you’d better quit smoking.
二战后,整个国家处于一片废墟中。
The country was/lay in ruins after World War Ⅱ.
Language points
People were in shock and then, later that afternoon, another bit quake
shook Tangshan again.
3. shock vt. & n. 使震惊;使吃惊
in shock 震惊地 shocked adj. 感到震惊的;
shocking adj. 令人震惊的
【语境应用】完成句子。
1) He _____________(shock) at her smoking.
2) After the __________ news spread throughout the whole city, everyone felt ________. (shock)
3) She was __________ (震惊地) for about two weeks after the accident.
was shocked
shocking
shocked
in shock
Language points
The army sent 150,000 soldiers to Tangshan to dig out those who were trapped and to bury the dead. (Par4L1)
4. trap v. 使落入陷阱,使落入圈套
be trapped in 被困在……中;陷入……中
她被困在大雨中。
She was trapped in the heavy rain.
Language points
With strong support from the government and the tireless efforts of the city’s people…(Par5L1)
5. effort n. 努力;艰难尝试
e.g. We are making progress but we need to make greater efforts.
【归纳】effort短语
make an effort/efforts/every effort to do sth.
尽一切努力做某事
spare no effort 不遗余力; 尽力
with (an) effort 努力地
without effort 毫不费力地
Language points
【语境应用】完成句子。
1) 我们必须尽一切努力以减缓病情的发展。
We must _________________ to slow down the spread of COVID-19.
2) 他毫不费力地举起那块大石头。
He lifted the big stone _____________.
3) Many excellent architects _____________________ (正做出巨大努力) to build the center stage.
make every effort
without effort
are making great efforts
Language points
Some were found alive, though they were suffering from terrible injuries.
6. suffer vt. 遭受;蒙受
suffer from 受……折磨;患……病
suffering n. 痛苦, 苦恼;劳苦, 困难
【语境应用】完成下列句子。
1) He ____________________ (受了好多苦) when he was a child.
2) Do you often ____________________ (遭受头痛的折磨吗)
suffered a lot (of pain)
suffer from a headache
signs damage rescue&revival
———|——————|——————|———→
before… during… after…
The change of
people's feeling
unaware
shocked
hopeless
hopeful
Summary
6
Assessment
Assessment
7
Items Great (5 pt.) Not bad (3 pt.) Try harder
(2 pt.)
I can know the information of Tangshan big earthquake.
I can know the rescue work and rebuilding after the big earthquake.
I can know how to do if an earthquake hit my city .
I can master reading skills of skimming and scanning.
Points(pt.) _______________in total.
提升作业
1.Finish exercise grammar filling and reading comprehension in your exercise book.
2. Retell what would happen before an earthquake.
基础作业
1. Recite new words and phrases and make sentences.
2. Listen to the tape and read the text after the tape
拓展作业
Interview your classmates about how to do if an earthquake hit your city and make a speech.
Homework
8
https://www.21cnjy.com/recruitment/home/fine
Thanks!
