2025年高考英语语法专题 课件 名词
文档属性
| 名称 | 2025年高考英语语法专题 课件 名词 |
|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 255.6KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-12-05 09:01:47 | ||
图片预览




文档简介
(共23张PPT)
板块三 名词、形容词和副词
名词
2025年高考英语专题复习
1.(2023·新课标Ⅱ卷)They also need to be ready to give __________ (interview) in English with international journalists.
2.(2023·全国乙卷)But for all its ancient buildings, Beijing is also a place that welcomes the fast-paced development of modern life, with 21st-century architectural _________ (wonder) standing side by side with historical buildings of the past.
interviews
wonders
3.(2021·全国乙卷)_________ (activity) there range from whale watching to hiking (远足) and accommodations aim to have a low impact on the natural environment.
4.(2021·全国甲卷)Supposedly you can do it in two hours, but we stopped at the different gates and ___________ (watchtower) to take pictures or just to watch the local people going about their daily routines.
Activities
watchtowers
名词按其词义可分为专有名词和普通名词。普通名词包括可数名词和不可数名词。可数名词有单数和复数之分,不可数名词没有单复数之分。
一、可数名词的数
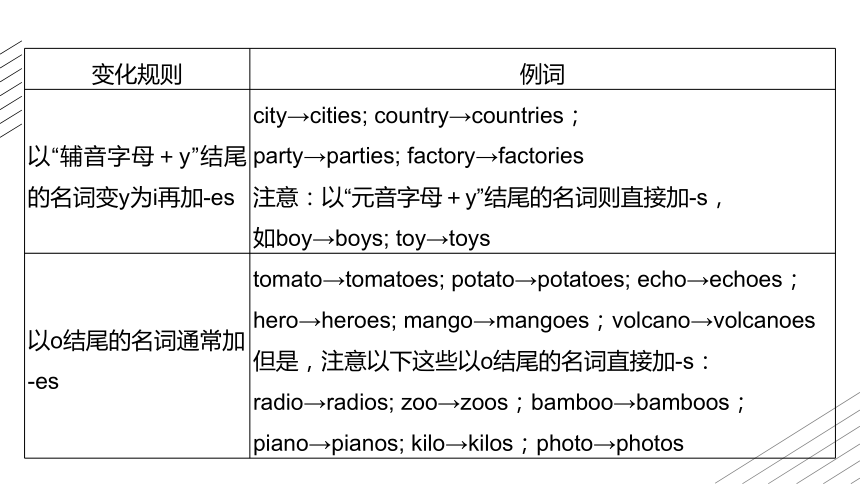
1.名词复数的规则变化
变化规则 例词
一般情况下在词尾直接加-s map→maps; girl→girls;
house→houses; mouth→mouths
以s, x, sh, ch结尾的名词加-es class→classes; box→boxes;
brush→brushes; match→matches
注意:stomach(胃)的复数是
stomachs; ox(公牛)的复数是oxen
变化规则 例词
以“辅音字母+y”结尾的名词变y为i再加-es city→cities; country→countries;
party→parties; factory→factories
注意:以“元音字母+y”结尾的名词则直接加-s,
如boy→boys; toy→toys
以o结尾的名词通常加 -es tomato→tomatoes; potato→potatoes; echo→echoes;
hero→heroes; mango→mangoes;volcano→volcanoes
但是,注意以下这些以o结尾的名词直接加-s:
radio→radios; zoo→zoos;bamboo→bamboos;
piano→pianos; kilo→kilos;photo→photos
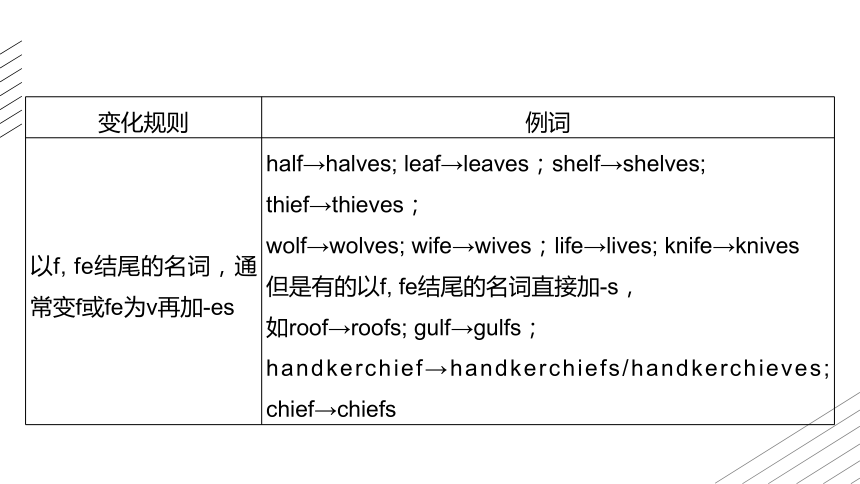
变化规则 例词
以f, fe结尾的名词,通常变f或fe为v再加-es half→halves; leaf→leaves;shelf→shelves; thief→thieves;
wolf→wolves; wife→wives;life→lives; knife→knives
但是有的以f, fe结尾的名词直接加-s,
如roof→roofs; gulf→gulfs;
handkerchief→handkerchiefs/handkerchieves; chief→chiefs
变化规则 例词
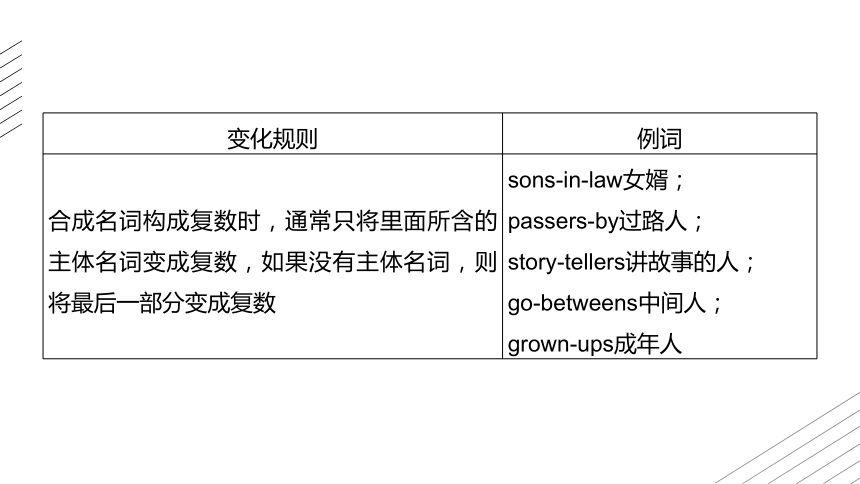
合成名词构成复数时,通常只将里面所含的主体名词变成复数,如果没有主体名词,则将最后一部分变成复数 sons-in-law女婿;
passers-by过路人;
story-tellers讲故事的人;
go-betweens中间人;
grown-ups成年人
变化情况 例词
特殊变化 child→children; foot→feet;
tooth→teeth; mouse→mice;
man→men; woman→women
注意:由man或woman构成的合成词,其复数形式也是-men和 -women,如Englishman→Englishmen;但German不是合成词,故其复数形式为Germans
单复数同形 deer, sheep, fish, Chinese,Japanese, means
2.名词复数的不规则变化
变化情况 例词
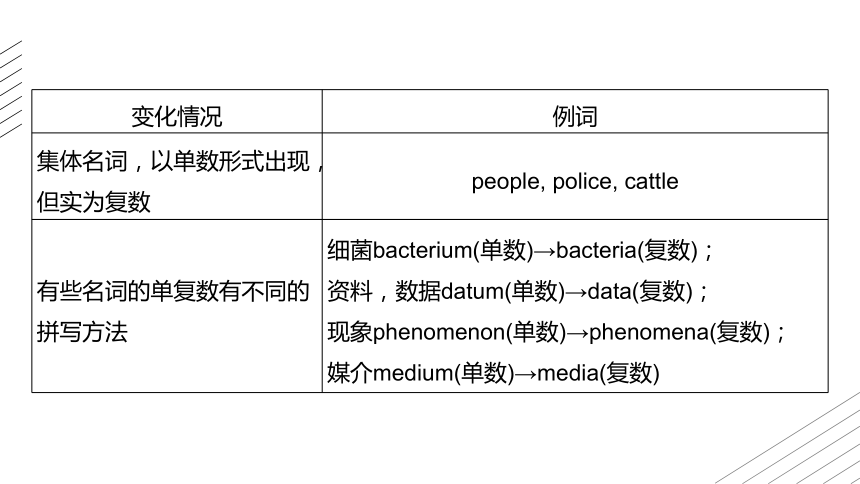
集体名词,以单数形式出现,但实为复数 people, police, cattle
有些名词的单复数有不同的拼写方法 细菌bacterium(单数)→bacteria(复数);
资料,数据datum(单数)→data(复数);
现象phenomenon(单数)→phenomena(复数);
媒介medium(单数)→media(复数)
二、不可数名词
1.常考的不可数名词
advice建议 equipment装备
experience经验(注:作“经历”讲时可数) exercise锻炼(注:作“练习;体操”讲时可数)
fun开心、快乐的事 furniture家具
news/information/word 消息,新闻 baggage/luggage行李
progress进步 practice练习
wealth财富,富裕 knowledge知识
jewellery珠宝 change零钱(注:作“变化”讲时可数)
2. 抽象名词具体化
抽象名词在表示具体的概念时,可以与不定冠词连用。
词 抽象名词意义 具体化名词意义
beauty 美;美丽 美丽的人或事物
comfort 安慰;慰藉 令人感到安慰的人或事物
success 成功 成功的人或事
failure 失败 失败的人或事
honour 荣幸 令人感到荣幸的事情
词 抽象名词意义 具体化名词意义
pride 骄傲 令人骄傲的事情
shock 震惊 令人震惊的事情
delight 高兴 令人高兴的事情
surprise 惊奇 令人惊奇的事情
pleasure 快乐 令人快乐的事情
3. 物质名词的复数现象
(1)有些物质名词用复数形式表示与原来不同的事物。
paper(纸)→papers(证件;论文)
custom(风俗习惯)→customs(海关)
arm(胳膊)→arms(武器,装备)
air(空气)→airs(摆架子,装腔作势)
(2)有一些物质名词用复数形式表示由大量该物质组成的事物。
sand(沙子)→sands(沙滩,沙漠)
water(水)→waters(水域,水体)
time(时间)→times(时代)
wood(木头,木材)→woods(树林)
(3)有些物质名词用复数形式表示不同的种类,如:food, wine, metal, fish, vegetable等。
The wines of France are among the best in the world.
法国的葡萄酒在世界上名列前茅。
三、与名词有关的词形转化
1.名词后缀
-(t)ion表示行为或状态;-ment表示行为或结果;-er/-or表示人物;-ist/-ian表示专家或从事……的人;-ice表示性质、状态;-dom表示集体、领域或状态。
2.名词与形容词之间的转化
(1)“名词+y”构成形容词。如rain→rainy; cloud→cloudy等。
(2)“名词+ly”构成形容词。如friend→friendly; mother→motherly等。
(3)“名词+ish”构成形容词。如fool→foolish; child→childish等。
(4)“名词+en”构成形容词。如gold→golden; wood→wooden等。
1.(2022·新高考Ⅱ卷)“He saved my _____ (son) life,” said Mrs Brown. “I don’t know how to thank him.”
2.(2021·浙江1月卷)It is calculated by dividing a ________ (person) weight in kg by their height in meters squared, and a BMI of between 19 and 25 is considered healthy.
son’s
person’s
考点二 名词的固定搭配和所有格
一、固定搭配
名词构成的固定搭配主要有两类:“介词+名词”和“动词+名词+介词”。常考的高频短语:
1.介词+名词
with patience耐心地
by chance/accident偶然
at a loss不知所措
in advance提前
in favour of支持,赞成
on purpose故意地
beyond recognition无法辨认
in great demand需求量很大
2.动词+名词+介词
have/gain access to可以获得
take advantage of利用;趁……之机
make use of利用
find fault with挑……的错
keep pace with与……同步
put an end to结束……
take notice of注意到
catch sight of看见
do damage to损害……
attach importance to重视……
take the place of取代,代替
take pride in为……感到自豪
take possession of占有
make preparations for为……做准备
make contributions to为……做出贡献
二、名词的所有格
1.有生命的名词,其所有格一般在名词后加’s。
his father’s boss 他爸爸的老板
2.表示时间、城市、地域、团体、机构等无生命的事物后也可以加’s,表示其所有格。
today’s paper 今天的报纸
England’s shore 英国的海岸
the car’s design 这辆车的设计
We accepted the invitation without a moment’s hesitation.
我们毫不犹豫地接受了邀请。
3.在某些习惯用语中,也需要加’s表示所有格。
for friendship’s sake 为了友情
at a stone’s throw 一步之遥
at one’s finger’s tips 了如指掌
at arm’s length 保持距离
at one’s wits’ end 黔驴技穷;不知所措
4.无生命的名词,借用of表示所属关系。
the window of the room 房间的窗户
5.如果一样东西为两个人共有,则只在后一个名词后加’s;如果不是共有,则两个名词后都要加’s。
Jane and Mary’s mother 简和玛丽的妈妈(共有,暗示简和玛丽是姐妹关系)
Jane’s and Mary’s mothers 简的妈妈和玛丽的妈妈(不是共有,分别指两位妈妈)
6.双重所有格:“a/two/some...+名词+of+名词’s/名词性物主代词”构成双重所有格,“of+名词所有格”中的名词必须表示人,不能表示事物。
a friend of her mother’s 她妈妈的一个朋友
two photos of hers 她的两张照片
THANKS
板块三 名词、形容词和副词
名词
2025年高考英语专题复习
1.(2023·新课标Ⅱ卷)They also need to be ready to give __________ (interview) in English with international journalists.
2.(2023·全国乙卷)But for all its ancient buildings, Beijing is also a place that welcomes the fast-paced development of modern life, with 21st-century architectural _________ (wonder) standing side by side with historical buildings of the past.
interviews
wonders
3.(2021·全国乙卷)_________ (activity) there range from whale watching to hiking (远足) and accommodations aim to have a low impact on the natural environment.
4.(2021·全国甲卷)Supposedly you can do it in two hours, but we stopped at the different gates and ___________ (watchtower) to take pictures or just to watch the local people going about their daily routines.
Activities
watchtowers
名词按其词义可分为专有名词和普通名词。普通名词包括可数名词和不可数名词。可数名词有单数和复数之分,不可数名词没有单复数之分。
一、可数名词的数
1.名词复数的规则变化
变化规则 例词
一般情况下在词尾直接加-s map→maps; girl→girls;
house→houses; mouth→mouths
以s, x, sh, ch结尾的名词加-es class→classes; box→boxes;
brush→brushes; match→matches
注意:stomach(胃)的复数是
stomachs; ox(公牛)的复数是oxen
变化规则 例词
以“辅音字母+y”结尾的名词变y为i再加-es city→cities; country→countries;
party→parties; factory→factories
注意:以“元音字母+y”结尾的名词则直接加-s,
如boy→boys; toy→toys
以o结尾的名词通常加 -es tomato→tomatoes; potato→potatoes; echo→echoes;
hero→heroes; mango→mangoes;volcano→volcanoes
但是,注意以下这些以o结尾的名词直接加-s:
radio→radios; zoo→zoos;bamboo→bamboos;
piano→pianos; kilo→kilos;photo→photos
变化规则 例词
以f, fe结尾的名词,通常变f或fe为v再加-es half→halves; leaf→leaves;shelf→shelves; thief→thieves;
wolf→wolves; wife→wives;life→lives; knife→knives
但是有的以f, fe结尾的名词直接加-s,
如roof→roofs; gulf→gulfs;
handkerchief→handkerchiefs/handkerchieves; chief→chiefs
变化规则 例词
合成名词构成复数时,通常只将里面所含的主体名词变成复数,如果没有主体名词,则将最后一部分变成复数 sons-in-law女婿;
passers-by过路人;
story-tellers讲故事的人;
go-betweens中间人;
grown-ups成年人
变化情况 例词
特殊变化 child→children; foot→feet;
tooth→teeth; mouse→mice;
man→men; woman→women
注意:由man或woman构成的合成词,其复数形式也是-men和 -women,如Englishman→Englishmen;但German不是合成词,故其复数形式为Germans
单复数同形 deer, sheep, fish, Chinese,Japanese, means
2.名词复数的不规则变化
变化情况 例词
集体名词,以单数形式出现,但实为复数 people, police, cattle
有些名词的单复数有不同的拼写方法 细菌bacterium(单数)→bacteria(复数);
资料,数据datum(单数)→data(复数);
现象phenomenon(单数)→phenomena(复数);
媒介medium(单数)→media(复数)
二、不可数名词
1.常考的不可数名词
advice建议 equipment装备
experience经验(注:作“经历”讲时可数) exercise锻炼(注:作“练习;体操”讲时可数)
fun开心、快乐的事 furniture家具
news/information/word 消息,新闻 baggage/luggage行李
progress进步 practice练习
wealth财富,富裕 knowledge知识
jewellery珠宝 change零钱(注:作“变化”讲时可数)
2. 抽象名词具体化
抽象名词在表示具体的概念时,可以与不定冠词连用。
词 抽象名词意义 具体化名词意义
beauty 美;美丽 美丽的人或事物
comfort 安慰;慰藉 令人感到安慰的人或事物
success 成功 成功的人或事
failure 失败 失败的人或事
honour 荣幸 令人感到荣幸的事情
词 抽象名词意义 具体化名词意义
pride 骄傲 令人骄傲的事情
shock 震惊 令人震惊的事情
delight 高兴 令人高兴的事情
surprise 惊奇 令人惊奇的事情
pleasure 快乐 令人快乐的事情
3. 物质名词的复数现象
(1)有些物质名词用复数形式表示与原来不同的事物。
paper(纸)→papers(证件;论文)
custom(风俗习惯)→customs(海关)
arm(胳膊)→arms(武器,装备)
air(空气)→airs(摆架子,装腔作势)
(2)有一些物质名词用复数形式表示由大量该物质组成的事物。
sand(沙子)→sands(沙滩,沙漠)
water(水)→waters(水域,水体)
time(时间)→times(时代)
wood(木头,木材)→woods(树林)
(3)有些物质名词用复数形式表示不同的种类,如:food, wine, metal, fish, vegetable等。
The wines of France are among the best in the world.
法国的葡萄酒在世界上名列前茅。
三、与名词有关的词形转化
1.名词后缀
-(t)ion表示行为或状态;-ment表示行为或结果;-er/-or表示人物;-ist/-ian表示专家或从事……的人;-ice表示性质、状态;-dom表示集体、领域或状态。
2.名词与形容词之间的转化
(1)“名词+y”构成形容词。如rain→rainy; cloud→cloudy等。
(2)“名词+ly”构成形容词。如friend→friendly; mother→motherly等。
(3)“名词+ish”构成形容词。如fool→foolish; child→childish等。
(4)“名词+en”构成形容词。如gold→golden; wood→wooden等。
1.(2022·新高考Ⅱ卷)“He saved my _____ (son) life,” said Mrs Brown. “I don’t know how to thank him.”
2.(2021·浙江1月卷)It is calculated by dividing a ________ (person) weight in kg by their height in meters squared, and a BMI of between 19 and 25 is considered healthy.
son’s
person’s
考点二 名词的固定搭配和所有格
一、固定搭配
名词构成的固定搭配主要有两类:“介词+名词”和“动词+名词+介词”。常考的高频短语:
1.介词+名词
with patience耐心地
by chance/accident偶然
at a loss不知所措
in advance提前
in favour of支持,赞成
on purpose故意地
beyond recognition无法辨认
in great demand需求量很大
2.动词+名词+介词
have/gain access to可以获得
take advantage of利用;趁……之机
make use of利用
find fault with挑……的错
keep pace with与……同步
put an end to结束……
take notice of注意到
catch sight of看见
do damage to损害……
attach importance to重视……
take the place of取代,代替
take pride in为……感到自豪
take possession of占有
make preparations for为……做准备
make contributions to为……做出贡献
二、名词的所有格
1.有生命的名词,其所有格一般在名词后加’s。
his father’s boss 他爸爸的老板
2.表示时间、城市、地域、团体、机构等无生命的事物后也可以加’s,表示其所有格。
today’s paper 今天的报纸
England’s shore 英国的海岸
the car’s design 这辆车的设计
We accepted the invitation without a moment’s hesitation.
我们毫不犹豫地接受了邀请。
3.在某些习惯用语中,也需要加’s表示所有格。
for friendship’s sake 为了友情
at a stone’s throw 一步之遥
at one’s finger’s tips 了如指掌
at arm’s length 保持距离
at one’s wits’ end 黔驴技穷;不知所措
4.无生命的名词,借用of表示所属关系。
the window of the room 房间的窗户
5.如果一样东西为两个人共有,则只在后一个名词后加’s;如果不是共有,则两个名词后都要加’s。
Jane and Mary’s mother 简和玛丽的妈妈(共有,暗示简和玛丽是姐妹关系)
Jane’s and Mary’s mothers 简的妈妈和玛丽的妈妈(不是共有,分别指两位妈妈)
6.双重所有格:“a/two/some...+名词+of+名词’s/名词性物主代词”构成双重所有格,“of+名词所有格”中的名词必须表示人,不能表示事物。
a friend of her mother’s 她妈妈的一个朋友
two photos of hers 她的两张照片
THANKS
