UNIT 7 ART LESSON 3 课件(共71张,内嵌视频)高中英语北师大版(2019)必修第三册
文档属性
| 名称 | UNIT 7 ART LESSON 3 课件(共71张,内嵌视频)高中英语北师大版(2019)必修第三册 |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 41.4MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 北师大版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2024-12-23 19:59:36 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共72张PPT)
LESSON 3
A MUSICAL GENIUS
UNIT 7 ART
To read and talk about Ludwig van Beethoven;
To read for general understanding;
To read for specific information and deep understanding;
To understand words and expressions in context;
To learn how the musical genius Beethoven wrote and conducted his Symphony No. 9;
To learn about and practise word building.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
To answer the comprehension questions;
To get key information in the text;
To summarize the text after reading;
To learn words and expressions in context;
To identify topic sentences of each paragraph and part.
KEY POINTS AND DIFFICULT POINTS
LEADING IN
LEADING IN
Who is he
Born in Germany
Composed more than 130 musical works
Be regarded as one of the greatest composers
became deaf at the age of 26 and was completely deaf in later years
LEADING IN
Who is he
Ludwig van Beethoven
I will take fate by the throat, and it will not bend me completely to its will.
ACTIVATE AND SHARE
What do you know about Ludwig van Beethoven Complete the quiz.
1. What is Beethoven most famous for
a. His piano performances.
b. Conducting orchestras.
c. Composing music.
2. Where was Beethoven born
a. In Germany. b. In Canada. c. In France.
√
√
ACTIVATE AND SHARE
What do you know about Ludwig van Beethoven Complete the quiz.
3. What big challenge did Beethoven face
a. He became deaf.
b. He became blind.
c. He was unable to walk.
4. How many pieces of music did Beethoven write
a. More than 100. b. More than 200. c. More than 300.
√
√
READ AND EXPLORE
Everyone knows that Ludwig van Beethoven is a musical genius but few might know how he created Symphony No. 9 in D minor and how its first show went.
predict what this passage is about
READ AND EXPLORE
Read the text quickly and answer the following question.
What's the main idea of the text
A. A musical genius.
B. Achievements of Beethoven.
C. Beethoven and his Symphony No. 9 in D minor.
D. Beethoven's Symphony No.9 in D minor.
√
READ AND EXPLORE
What is the main idea of each paragraph
Para 1
The brief introduction of Ludwig van Beethoven.
Para 2
How the ninth symphony was completed.
Para 3
The before atmosphere of the performance.
Para 4
The audience’s reaction and the composer’s performance.
Para 5
After the play, the audience’s reaction and the composer’s performance.
Para 6
Caroline’s memories about Beethoven’ performance.
READ AND EXPLORE
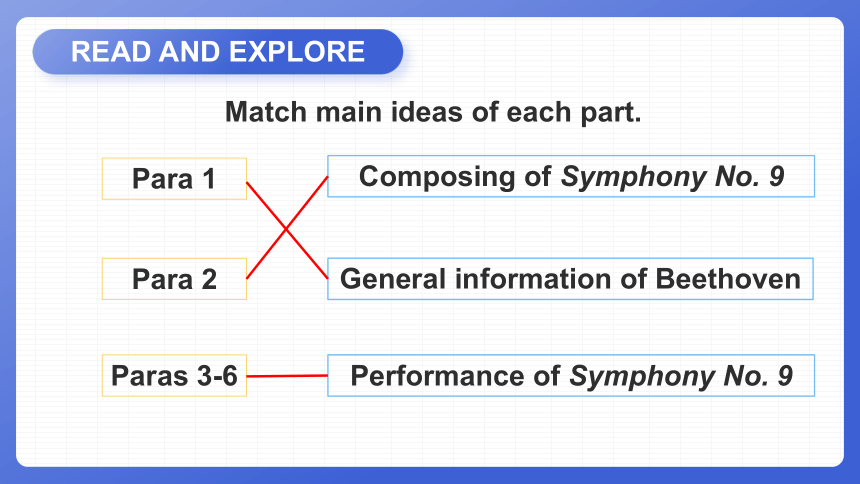
Match main ideas of each part.
Para 1
Para 2
Paras 3-6
General information of Beethoven
Composing of Symphony No. 9
Performance of Symphony No. 9
READ AND EXPLORE
Beethoven
achievement
130 musical works
nationality
German
job
great composer
problem
hearing loss
READ AND EXPLORE
Read the text carefully and answer the following question.
1. Where did Beethoven compose his Symphony No. 9 in D minor
A. In Germany. B. In Canada.
C. In France. D. In Austria.
2. (T or F) Before the performance, Beethoven believed that the performance would be a success.
√
F
READ AND EXPLORE
Read the text carefully and answer the following question.
3. Who took charge of the orchestra with Beethoven
A. Caroline Unger.
B. Michael Umlauf.
C. The audience
D. The composer of the symphony.
√
READ AND EXPLORE
Read the text carefully and answer the following question.
4. Why was the audience so shocked about Beethoven's performance
A. They didn't know Beethoven could compose such a great work.
B. Beethoven didn't know when to stop his conduct.
C. The symphony was composed by a person who had lost hearing.
√
5. When and where did Beethoven finish the symphony
In February 1824, at his little house in Vienna, Austria.
6. What was Beethoven’s feeling when he finished the symphony Can you fid some evidence
proud, happy, excited, satisfied
Beethoven sat back in his chair and smiled.
He proudly signed his name and tried to imagine how people would respond.
READ AND EXPLORE
READ AND EXPLORE
afraid, worried
could not hear
disaster
tense
READ AND EXPLORE
Beethoven walk out onto the stage
The audience:
Michael Umlauf
Beethoven’s performance
Umlauf’s help
The function:
How
What
During the performance
not hesitate to applaud loudly
took charge of the orchestra
jumped…,
waving…,
turning…,
stood quietly,
skillfully guide…through…
1. After the performance, what were the responses of the audience
They jumped to their feet, clapping, cheering and waving their hats.
2. After the performance, what did Beethoven do
He continued conducting, his head buried in the score.
READ AND EXPLORE
It was not until Caroline Unger took his arm and turned him to face the audience that the great man realized his symphony was a success.
3. After the performance, what did the audience and Beethoven feel And why
The audience was shocked because most of them had no idea that Beethoven was deaf.
READ AND EXPLORE
Beethoven got a surprise as well because his symphony was a success.
READ AND EXPLORE
Time Evidence Beethoven’s feeling
After finishing the symphony ___________and smiled, proudly ___________ his name
Before the performance Beethoven was ___________ ... what use …
During the performance jumped about, ___________ his arms, ___________ turned the pages… ___________ in the score
The feeling of the audience ___________ to their feet, clapping, cheering and waving their ___________
proud, happy, excited, satisfied, relieved
afraid, worried
sat back
signed
afraid
concentrated, focused
waved
madly
buried
shocked, content, absorbed
jumped
hats
READ AND EXPLORE
Read the text and fill in the blanks.
Beethoven 1._____________ (regard) as one of the greatest 2._____________ (compose) in the history of music. 3.___________ (inspire) by his struggles with deafness, he composed some 4.___________ (amaze) pieces. He proceeded with the composition until his death, 5.___________ (write) more than 130 musical works.
is regarded
composers
Inspired
amazing
writing
In February 1824, Beethoven's ninth symphony was finally completed, and he 6.___________ (proud) signed his name at the bottom of the page.
Before the performance, Beethoven 7.___________ (feel) that the performance would be a disaster. The audience applauded loudly 8.___________ he walked onto the stage. Beethoven together 9.___________ Michael Umlauf took charge of the orchestra and the performance proved to be 10.___________ success.
READ AND EXPLORE
proudly
felt
as/when
with
a
READ AND EXPLORE
In 1770
Birth
Being famous for his skill on the piano.
Later
Beginning to lose his hearing.
Highlight
In 1827
Death
In his twenties
Producing some amazing pieces, including nine symphonies, five piano pieces, and an opera.
Timetable of Ludwig van Beethoven
Try to retell the life of Beethoven
Read the story. What can you find about Beethoven's composing of Symphony No. 9 and its first performance Use a graphic organiser to organise the information you find.
READ AND EXPLORE
Beethoven
General information
Composing of Symphony No. 9
Performance of Symphony No. 9
READ AND EXPLORE
Skill Builder
Graphic Organisers
Graphic Organisers are a pictorial way of organising and illustrating information in a text. These include flow charts, tables and diagrams.
Determine the type of the text (e.g. narrative, argumentation, description, or exposition).
Analyse the writing technique. Does the text include sequencing, facts and opinion, cause and effect Does it compare and contrast
Determine which type of graphic organiser will illustrate the text in the most effective way.
Read the story. What can you find about Beethoven's composing of Symphony No. 9 and its first performance Use a graphic organiser to organise the information you find.
READ AND EXPLORE
General information: last symphony written, he was afraid it would be a disaster, musical director was Michael Umlauf, audience were shocked that he was deaf
Composing of Symphony No. 9: took several years, completed in Vienna
Read the story. What can you find about Beethoven's composing of Symphony No. 9 and its first performance Use a graphic organiser to organise the information you find.
READ AND EXPLORE
Performance of Symphony No. 9: For more than an hour, Beethoven jumped about in front the orchestra, waving his arms wildly in the air, and madly turning the pages of his score, The whole time, Umlauf stood quietly by his side, skillfully guiding the orchestra through the most amazing piece of music the world had ever know.
Answer the questions based on your notes. Read the story again if needed.
1. When and how was Symphony No. 9 completed What was Beethoven thinking when he finished the symphony
READ AND EXPLORE
One day in February 1824, the famous German composer's ninth symphony was finally completed, Beethoven tried to imagine how people would respond when they heard it for the first time.
Answer the questions based on your notes. Read the story again if needed.
2. How do you think Beethoven felt while he was conducting the orchestra Find evidence from the text.
READ AND EXPLORE
He felt absorbed and passionate.
Beethoven is described as “jumped about”, “waving his arms”, and “madly turning the pages of his score”.
What qualities does Beethoven have Give your reasons.
READ AND EXPLORE
He was brave and never gave up because he can face the difficult challenge in life-nothing can destroy him.
He was passionate about music because he wrote more than 130 pieces of music even if he was deaf.
He is talented because he created many famous musical works.
Do you think Beethoven is a genius What’s your understanding of “Genius”
READ AND EXPLORE
In my opinion, Beethoven is a genius because he not only has strong will to fight against difficulties in life, but also he is crazy about music.
Doing easily what others find difficult is talent; doing what is impossible for talent is genius.
What qualities do you think made Beethoven “A Musical Genius”
READ AND EXPLORE
diligent
creative
passionate
intelligent
courageous
persistent
Genius is the ability to put into effect what is in your mind.
——F. Scott Fitzgerald
READ AND EXPLORE
Pair Work Choose one of the following topics to introduce to your partner.
· Beethoven as a musician
· The performance of Symphony No. 9
READ AND EXPLORE
Group Work Think and share.
1. The description of Beethoven’s behavior in the performance shows that he was deaf. Can you find the hints Why did most of the audience have no idea that he was deaf
"And the whole time, Umlauf stood quietly by his side, skillfully guiding the orchestra." The music ended but Beethoven continued to conduct. "It was not until Caroline Unger took his arm and turned him to face the audience that the great man had realised his symphony was a success." The audience might think Beethoven was deeply lost in his own music.
READ AND EXPLORE
Group Work Think and share.
2. How did Caroline feel when she said "The one person in the room who didn't hear the symphony—and never would—was the very man who composed it."
She felt, among other feelings, very very sorry that Beethoven couldn't hear the music he composed. It was such a pity and she might feel it unfair for him. She must have wished Beethoven was not deaf.
READ AND EXPLORE
Complete the sentences with the phrases below.
1. Before the performance, the ___________________________ was tense.
2. Michael Umlauf joined him and together the two men __________________ the orchestra.
took charge of waving their hats waving his arms wildly
jumped about turned him to face backstage atmosphere
madly turning the pages jumped to their feet with a broad smile
backstage atmosphere
took charge of
READ AND EXPLORE
3. Beethoven _______________ in front of the orchestra, _________________________ in the air, and ________________________ of his score.
4. As the final note signalled the end, the audience _____________________, clapping, cheering, and __________________.
5. Caroline Unger took Beethoven's arm and ____________________ the audience.
6. In an interview afterwards, Caroline said ___________________, "The audience was shocked as well."
jumped about
waving his arms wildly
madly turning the pages
jumped to their feet
waving their hats
turned him to face
with a broad smile
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: WORD BUILDING
Complete the Word Builder. Use a dictionary to help you.
Noun Verb Adjective
music musician ×
composition ×
performance ×
produce
× conduct ×
hesitate
joy enjoy
respond
composer
musical
compose
performer
perform
production
producer
productive
conductor
hesitation
hesitated
joyous
response
responsive
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: WORD BUILDING
Complete the sentences with the correct form of the words in the Word Builder.
1. It has always been my dream to ____________ an orchestra.
2. The musician ____________ with nervousness before he began to play.
3. Beethoven is recognised as a ____________ genius by people around the world.
4. Beethoven is the ____________ of Symphony No. 9 in D minor.
conduct
hesitated
musical
composer
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: WORD BUILDING
Complete the sentences with the correct form of the words in the Word Builder.
5. To his mother's ____________, he won first prize.
6. She told me about the wonderful ________________ that she had been to last week.
7. The audience's ____________ to the performance of the symphony was extraordinary.
8. Though Beethoven lost his hearing, he ____________ some amazing pieces of music.
joy
performance
response
produced
EXPRESS YOURSELF
Group Work Which part of the story about Beethoven impressed you most Why
When Beethoven began to lose his hearing, he didn't give up writing music. This part impressed me most, because Beethoven delivered so much energy to me when facing difficulties.
EXPRESS YOURSELF
Find some pieces of Beethoven's music online. Discuss how you feel when listening to his music.
How does the music make you feel
What does it remind you of
Do you like it or not Support your answer.
Try to figure out the answers of the following questions when listening to music.
GRAMMAR
构词法
英语中有Derivation(派生法) ,Compounding(合成法) ,Conversion(转化法),Clipping(缩略法),Blending(混合法),Acronym(首尾字母缩略法) 等构词法。主要为以下三种方法:
派生法:通过加前缀或后缀使之构成一个新词。
合成法:由两个或更多的词合成一个词。
转化法:一个单词由一种词性转化为另一种或几种词性。
GRAMMAR
构词法
一、派生法
派生法又叫词缀法,它一般借助于词缀构成新词,在词根前面加前缀或者在词根后面加后缀,从而构成一个和原单词意义相近或者相反的新词,由此构成的词称为派生词。
英语词缀分成前缀和后缀两种。加于词根前的叫前缀(prefix),加于词根后的叫后缀(suffix)。
GRAMMAR
构词法
一般说来,前缀只是改变词的意义,并不改变其词类。如形容词 unnatural (adj.不自然的;不近人情的),词义发生变化,而词类不变。
但是,一些特殊的前缀不仅能改变词的意义,还可以使单词的词类发生变化。如force →enforce (执行,实施;强调),large → enlarge (扩大),rich → enrich (使富足;使肥沃;使充实)等。
GRAMMAR
构词法
(1) 表示否定意义的前缀
dis-, il-, in-, ir-, mis-, non-, un-等,在单词前加这类前缀常构成与该词意义相反的新词。
il- → illegal 非法的
un- → unhappy 不高兴的
im- → impatient 不耐烦的
dis- → disappear 消失
in- → incorrect 不正确的
ir- → irregular 不规则的
GRAMMAR
构词法
(2) 表示其他意义的常见前缀
anti- (反对;抵抗) → antiwar 反战的
sub- (下面的) → subway 地铁
inter- (互相) → Internet 互联网
re- (再;又) → rewrite 重写
en- (使……) → enrich 使富足
pre- (前;预先) → preview 预习
GRAMMAR
构词法
post- (后的) → postwar 战后
mid- (中;半) → midnight 午夜
vice-(副) → vice-manager 副经理
micro-(微) → microscope 显微镜
for-/ fore- (先;预) → forecast 预报
co- (共;同) → cooperation 合作
mini- (小型) → miniskirt 迷你裙
bi- (双的) → bimonthly 双月的
GRAMMAR
构词法
后缀常会改变单词的词性,构成意思相近的其他词性;少数后缀还会改变词义,变为与原来词义相反的新词。
(1) 常见动词后缀
-en (多用于形容词之后);-fy (使……化);-ize (使……成为)
例:widen 加宽;beautify 美化;realize 意识到
GRAMMAR
构词法
(2) 常见名词后缀
-er/ -or (从事……的人);-ese (某地人);-ian (……的人);-ist (专业人员);-ism (主义);-ment (性质;状态);-ness (性质);-tion/ -ation (动作;过程);-dom (状态;区域)
例:teacher 教师;Chinese 中国人;musician 音乐家;artist 艺术家;movement 运动;darkness 黑暗;invention 发明;freedom 自由
GRAMMAR
构词法
(3) 常见形容词后缀
-al, -able, -an, -ble, -ern, -ful, -th, -ive, -less, -like, -ly, -y, -ous , -some
例:national 民族的;reasonable 合理的;American 美国的;careful 细心的;active 有活力的;joyous 快乐的
GRAMMAR
构词法
(4) 常见副词后缀
-ly (用于形容词后表示方式或程度);-ward(s) (表示方向);-wise (表示方向或方式);-wise (表示方向或方式);
例:quickly 迅速地;angrily 生气地;northward 朝北;upward(s) 向上;clockwise 顺时针地;crosswise 横过地
GRAMMAR
构词法
二、合成法
两个单词连在一起合成新词,前一个词修饰或限定后一个词。
1. 合成名词
例如:birthplace / grown-up / background
2. 合成形容词
例如:outstanding / takeaway
3. 合成动词
例如:overcome / undercharge / outweigh
GRAMMAR
构词法
三、转换法
单词词形不变,词性发生转换。
1. 动词转换为名词
例如:I think we'd better finish the talk now.
2. 名词转换为动词
例如:He has booked the tickets.
3. 形容词转化为动词
例如:We'll try our best to better our living conditions.
4. 形容词转化为名词
例如: The girl in red looks pretty.
GRAMMAR
构词法
四、缩略法
将单词缩写,词义和词性保持不变。
1. 去头
例如:telephone-phone / airplane-plane
2. 去尾
例如: examination-exam / laboratory-lab
3. 去头去尾
例如:influenza-flu / prescription-script
1. conduct
conduct sb. around (=show sb. around) 带领某人参观
conduct/ do/ make/ perform/ carry out an experiment 做实验
conduct a concert 指挥音乐会
conduct a survey/ an investigation 开展调查
under the conduct of 在……的指导下/ 管理下
conductor n. 售票员,(乐队)指挥
conduction n. 传导
练习:The sport has a strict code of _____________.
conduct
VOCABULARY
VOCABULARY
2. respond
respond v. 回答,响应,作出反应
respond to... 回应/ 回答……
response n. 响应,回答
in response to 作为对……的答复/ 反应(通常作状语)
make no response (to) 没有(对……)做答/ 回答
make (a) response to 对……作出反应
练习:I ______________ to the news by bursting into tears.
respond
3. hesitate
hesitate about/ over/ at (doing)… 对(做)……感到犹豫
hesitate to do sth. 迟疑做某事,不愿做某事
hesitation n. 犹豫
without hesitation 毫不犹豫
have no hesitation in doing sth. 毫不犹豫地做某事
练习:I ______________ about taking his side until I knew the whole story.
hesitate
VOCABULARY
4. charge
in charge of 主管,负责
in the charge of... 由……负责/ 掌管
take charge of 主管,负责
free of charge 免费
charge…for… 因……收费,要价……
charge sb. with (doing) sth. 指控/ 起诉/ 指责某人(做)某事
练习:We have to make a small ___________ for refreshments.
charge
VOCABULARY
5. signal
signal (to) sb. to do sth. 示意某人做某事
signal to sb. 向某人示意
danger/ warning signal 危险/ 警告信号
traffic signals 交通信号
a stop signal 停车信号
练习:Her speech yesterday is a ___________ that her view has changed.
signal
VOCABULARY
6. compose
compose v. 作曲,创作,组成
compose mail 写邮件
be composed of 由……组成
composer n. 作曲家,设计者
composition n. 作文,作曲,成分;组合方式
练习:Ten men ______________ the committee.
compose
VOCABULARY
7. struggle
struggle with 与……斗争
struggle for 为争取……而斗争
struggle against 与……斗争;为反对……而斗争
struggle to do sth. 努力做某事
struggle to one's feet 挣扎着站起来
练习:He came to symbolize his country's ______________ for independence.
struggle
VOCABULARY
1. The theatre's musical director, Michael, joined him and together the two men took charge of the orchestra.
take charge of 主管;负责,强调动作
in charge of 主管;负责,强调状态 = in responsible for
I will take charge of the whole research.
我会负责掌管整项调研。
He was the officer in charge of operations.
他是负责指挥作战行动的军官。
LANGUAGE POINTS
2. As the final, joyous note signalled the end of the symphony, the audience jumped to their feet, clapping, cheering, and waving their hats.
signal v. 发信号;示意 n. 信号;红绿灯
signal sb. to do sth. 示意某人做某事
Signal sb. which way to go.
示意某人走哪条路。
You must signal which way you are going to turn.
你要朝哪个方向转,必须发出信号。
LANGUAGE POINTS
3. It was not until Caroline Unger, one of the singers, took his arm and turned him to face the audience that the great man realised his symphony was a success.
It is/was not until...that... 强调句,直到……才……
It is not until the professor come that they begin the test.
直到这位教授来了,他们才开始测试。
It was not until he came that I left.
直到他来我才离开。
LANGUAGE POINTS
1. The inventor was rewarded by the government for his scientific _________________ (achieve).
2. She can get angry very easily when others _____________ (agree) with her.
3. _____________ (honest) speaking, I don't like the way that you spoke to your father.
4. __________________ (fortunate), I was caught in the heavy rain and got wet through from head to foot.
PRACTICE
achievements
disagree
Honestly
Unfortunately
5. She was such a ____________________ (warm, heart) and generous lady that all of us respected her.
6. She has ever spent three years staying in an English-speaking country, so her ___________ (speak) English is very fluent.
7. I cannot control my body well. My legs become ___________ (pain).
8. We must pay special attention to the ________________ (mystery) stranger.
PRACTICE
warm-hearted
spoken
painful
mysterious
SUMMARY
Talk about more information of Beethoven and his symphony No. 9;
Learn some good qualities from Beethoven;
Read for general understanding and specific information;
Understand and learn words and expressions in context;
Learn about and practice word building.
Thank you
LESSON 3
A MUSICAL GENIUS
UNIT 7 ART
To read and talk about Ludwig van Beethoven;
To read for general understanding;
To read for specific information and deep understanding;
To understand words and expressions in context;
To learn how the musical genius Beethoven wrote and conducted his Symphony No. 9;
To learn about and practise word building.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
To answer the comprehension questions;
To get key information in the text;
To summarize the text after reading;
To learn words and expressions in context;
To identify topic sentences of each paragraph and part.
KEY POINTS AND DIFFICULT POINTS
LEADING IN
LEADING IN
Who is he
Born in Germany
Composed more than 130 musical works
Be regarded as one of the greatest composers
became deaf at the age of 26 and was completely deaf in later years
LEADING IN
Who is he
Ludwig van Beethoven
I will take fate by the throat, and it will not bend me completely to its will.
ACTIVATE AND SHARE
What do you know about Ludwig van Beethoven Complete the quiz.
1. What is Beethoven most famous for
a. His piano performances.
b. Conducting orchestras.
c. Composing music.
2. Where was Beethoven born
a. In Germany. b. In Canada. c. In France.
√
√
ACTIVATE AND SHARE
What do you know about Ludwig van Beethoven Complete the quiz.
3. What big challenge did Beethoven face
a. He became deaf.
b. He became blind.
c. He was unable to walk.
4. How many pieces of music did Beethoven write
a. More than 100. b. More than 200. c. More than 300.
√
√
READ AND EXPLORE
Everyone knows that Ludwig van Beethoven is a musical genius but few might know how he created Symphony No. 9 in D minor and how its first show went.
predict what this passage is about
READ AND EXPLORE
Read the text quickly and answer the following question.
What's the main idea of the text
A. A musical genius.
B. Achievements of Beethoven.
C. Beethoven and his Symphony No. 9 in D minor.
D. Beethoven's Symphony No.9 in D minor.
√
READ AND EXPLORE
What is the main idea of each paragraph
Para 1
The brief introduction of Ludwig van Beethoven.
Para 2
How the ninth symphony was completed.
Para 3
The before atmosphere of the performance.
Para 4
The audience’s reaction and the composer’s performance.
Para 5
After the play, the audience’s reaction and the composer’s performance.
Para 6
Caroline’s memories about Beethoven’ performance.
READ AND EXPLORE
Match main ideas of each part.
Para 1
Para 2
Paras 3-6
General information of Beethoven
Composing of Symphony No. 9
Performance of Symphony No. 9
READ AND EXPLORE
Beethoven
achievement
130 musical works
nationality
German
job
great composer
problem
hearing loss
READ AND EXPLORE
Read the text carefully and answer the following question.
1. Where did Beethoven compose his Symphony No. 9 in D minor
A. In Germany. B. In Canada.
C. In France. D. In Austria.
2. (T or F) Before the performance, Beethoven believed that the performance would be a success.
√
F
READ AND EXPLORE
Read the text carefully and answer the following question.
3. Who took charge of the orchestra with Beethoven
A. Caroline Unger.
B. Michael Umlauf.
C. The audience
D. The composer of the symphony.
√
READ AND EXPLORE
Read the text carefully and answer the following question.
4. Why was the audience so shocked about Beethoven's performance
A. They didn't know Beethoven could compose such a great work.
B. Beethoven didn't know when to stop his conduct.
C. The symphony was composed by a person who had lost hearing.
√
5. When and where did Beethoven finish the symphony
In February 1824, at his little house in Vienna, Austria.
6. What was Beethoven’s feeling when he finished the symphony Can you fid some evidence
proud, happy, excited, satisfied
Beethoven sat back in his chair and smiled.
He proudly signed his name and tried to imagine how people would respond.
READ AND EXPLORE
READ AND EXPLORE
afraid, worried
could not hear
disaster
tense
READ AND EXPLORE
Beethoven walk out onto the stage
The audience:
Michael Umlauf
Beethoven’s performance
Umlauf’s help
The function:
How
What
During the performance
not hesitate to applaud loudly
took charge of the orchestra
jumped…,
waving…,
turning…,
stood quietly,
skillfully guide…through…
1. After the performance, what were the responses of the audience
They jumped to their feet, clapping, cheering and waving their hats.
2. After the performance, what did Beethoven do
He continued conducting, his head buried in the score.
READ AND EXPLORE
It was not until Caroline Unger took his arm and turned him to face the audience that the great man realized his symphony was a success.
3. After the performance, what did the audience and Beethoven feel And why
The audience was shocked because most of them had no idea that Beethoven was deaf.
READ AND EXPLORE
Beethoven got a surprise as well because his symphony was a success.
READ AND EXPLORE
Time Evidence Beethoven’s feeling
After finishing the symphony ___________and smiled, proudly ___________ his name
Before the performance Beethoven was ___________ ... what use …
During the performance jumped about, ___________ his arms, ___________ turned the pages… ___________ in the score
The feeling of the audience ___________ to their feet, clapping, cheering and waving their ___________
proud, happy, excited, satisfied, relieved
afraid, worried
sat back
signed
afraid
concentrated, focused
waved
madly
buried
shocked, content, absorbed
jumped
hats
READ AND EXPLORE
Read the text and fill in the blanks.
Beethoven 1._____________ (regard) as one of the greatest 2._____________ (compose) in the history of music. 3.___________ (inspire) by his struggles with deafness, he composed some 4.___________ (amaze) pieces. He proceeded with the composition until his death, 5.___________ (write) more than 130 musical works.
is regarded
composers
Inspired
amazing
writing
In February 1824, Beethoven's ninth symphony was finally completed, and he 6.___________ (proud) signed his name at the bottom of the page.
Before the performance, Beethoven 7.___________ (feel) that the performance would be a disaster. The audience applauded loudly 8.___________ he walked onto the stage. Beethoven together 9.___________ Michael Umlauf took charge of the orchestra and the performance proved to be 10.___________ success.
READ AND EXPLORE
proudly
felt
as/when
with
a
READ AND EXPLORE
In 1770
Birth
Being famous for his skill on the piano.
Later
Beginning to lose his hearing.
Highlight
In 1827
Death
In his twenties
Producing some amazing pieces, including nine symphonies, five piano pieces, and an opera.
Timetable of Ludwig van Beethoven
Try to retell the life of Beethoven
Read the story. What can you find about Beethoven's composing of Symphony No. 9 and its first performance Use a graphic organiser to organise the information you find.
READ AND EXPLORE
Beethoven
General information
Composing of Symphony No. 9
Performance of Symphony No. 9
READ AND EXPLORE
Skill Builder
Graphic Organisers
Graphic Organisers are a pictorial way of organising and illustrating information in a text. These include flow charts, tables and diagrams.
Determine the type of the text (e.g. narrative, argumentation, description, or exposition).
Analyse the writing technique. Does the text include sequencing, facts and opinion, cause and effect Does it compare and contrast
Determine which type of graphic organiser will illustrate the text in the most effective way.
Read the story. What can you find about Beethoven's composing of Symphony No. 9 and its first performance Use a graphic organiser to organise the information you find.
READ AND EXPLORE
General information: last symphony written, he was afraid it would be a disaster, musical director was Michael Umlauf, audience were shocked that he was deaf
Composing of Symphony No. 9: took several years, completed in Vienna
Read the story. What can you find about Beethoven's composing of Symphony No. 9 and its first performance Use a graphic organiser to organise the information you find.
READ AND EXPLORE
Performance of Symphony No. 9: For more than an hour, Beethoven jumped about in front the orchestra, waving his arms wildly in the air, and madly turning the pages of his score, The whole time, Umlauf stood quietly by his side, skillfully guiding the orchestra through the most amazing piece of music the world had ever know.
Answer the questions based on your notes. Read the story again if needed.
1. When and how was Symphony No. 9 completed What was Beethoven thinking when he finished the symphony
READ AND EXPLORE
One day in February 1824, the famous German composer's ninth symphony was finally completed, Beethoven tried to imagine how people would respond when they heard it for the first time.
Answer the questions based on your notes. Read the story again if needed.
2. How do you think Beethoven felt while he was conducting the orchestra Find evidence from the text.
READ AND EXPLORE
He felt absorbed and passionate.
Beethoven is described as “jumped about”, “waving his arms”, and “madly turning the pages of his score”.
What qualities does Beethoven have Give your reasons.
READ AND EXPLORE
He was brave and never gave up because he can face the difficult challenge in life-nothing can destroy him.
He was passionate about music because he wrote more than 130 pieces of music even if he was deaf.
He is talented because he created many famous musical works.
Do you think Beethoven is a genius What’s your understanding of “Genius”
READ AND EXPLORE
In my opinion, Beethoven is a genius because he not only has strong will to fight against difficulties in life, but also he is crazy about music.
Doing easily what others find difficult is talent; doing what is impossible for talent is genius.
What qualities do you think made Beethoven “A Musical Genius”
READ AND EXPLORE
diligent
creative
passionate
intelligent
courageous
persistent
Genius is the ability to put into effect what is in your mind.
——F. Scott Fitzgerald
READ AND EXPLORE
Pair Work Choose one of the following topics to introduce to your partner.
· Beethoven as a musician
· The performance of Symphony No. 9
READ AND EXPLORE
Group Work Think and share.
1. The description of Beethoven’s behavior in the performance shows that he was deaf. Can you find the hints Why did most of the audience have no idea that he was deaf
"And the whole time, Umlauf stood quietly by his side, skillfully guiding the orchestra." The music ended but Beethoven continued to conduct. "It was not until Caroline Unger took his arm and turned him to face the audience that the great man had realised his symphony was a success." The audience might think Beethoven was deeply lost in his own music.
READ AND EXPLORE
Group Work Think and share.
2. How did Caroline feel when she said "The one person in the room who didn't hear the symphony—and never would—was the very man who composed it."
She felt, among other feelings, very very sorry that Beethoven couldn't hear the music he composed. It was such a pity and she might feel it unfair for him. She must have wished Beethoven was not deaf.
READ AND EXPLORE
Complete the sentences with the phrases below.
1. Before the performance, the ___________________________ was tense.
2. Michael Umlauf joined him and together the two men __________________ the orchestra.
took charge of waving their hats waving his arms wildly
jumped about turned him to face backstage atmosphere
madly turning the pages jumped to their feet with a broad smile
backstage atmosphere
took charge of
READ AND EXPLORE
3. Beethoven _______________ in front of the orchestra, _________________________ in the air, and ________________________ of his score.
4. As the final note signalled the end, the audience _____________________, clapping, cheering, and __________________.
5. Caroline Unger took Beethoven's arm and ____________________ the audience.
6. In an interview afterwards, Caroline said ___________________, "The audience was shocked as well."
jumped about
waving his arms wildly
madly turning the pages
jumped to their feet
waving their hats
turned him to face
with a broad smile
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: WORD BUILDING
Complete the Word Builder. Use a dictionary to help you.
Noun Verb Adjective
music musician ×
composition ×
performance ×
produce
× conduct ×
hesitate
joy enjoy
respond
composer
musical
compose
performer
perform
production
producer
productive
conductor
hesitation
hesitated
joyous
response
responsive
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: WORD BUILDING
Complete the sentences with the correct form of the words in the Word Builder.
1. It has always been my dream to ____________ an orchestra.
2. The musician ____________ with nervousness before he began to play.
3. Beethoven is recognised as a ____________ genius by people around the world.
4. Beethoven is the ____________ of Symphony No. 9 in D minor.
conduct
hesitated
musical
composer
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: WORD BUILDING
Complete the sentences with the correct form of the words in the Word Builder.
5. To his mother's ____________, he won first prize.
6. She told me about the wonderful ________________ that she had been to last week.
7. The audience's ____________ to the performance of the symphony was extraordinary.
8. Though Beethoven lost his hearing, he ____________ some amazing pieces of music.
joy
performance
response
produced
EXPRESS YOURSELF
Group Work Which part of the story about Beethoven impressed you most Why
When Beethoven began to lose his hearing, he didn't give up writing music. This part impressed me most, because Beethoven delivered so much energy to me when facing difficulties.
EXPRESS YOURSELF
Find some pieces of Beethoven's music online. Discuss how you feel when listening to his music.
How does the music make you feel
What does it remind you of
Do you like it or not Support your answer.
Try to figure out the answers of the following questions when listening to music.
GRAMMAR
构词法
英语中有Derivation(派生法) ,Compounding(合成法) ,Conversion(转化法),Clipping(缩略法),Blending(混合法),Acronym(首尾字母缩略法) 等构词法。主要为以下三种方法:
派生法:通过加前缀或后缀使之构成一个新词。
合成法:由两个或更多的词合成一个词。
转化法:一个单词由一种词性转化为另一种或几种词性。
GRAMMAR
构词法
一、派生法
派生法又叫词缀法,它一般借助于词缀构成新词,在词根前面加前缀或者在词根后面加后缀,从而构成一个和原单词意义相近或者相反的新词,由此构成的词称为派生词。
英语词缀分成前缀和后缀两种。加于词根前的叫前缀(prefix),加于词根后的叫后缀(suffix)。
GRAMMAR
构词法
一般说来,前缀只是改变词的意义,并不改变其词类。如形容词 unnatural (adj.不自然的;不近人情的),词义发生变化,而词类不变。
但是,一些特殊的前缀不仅能改变词的意义,还可以使单词的词类发生变化。如force →enforce (执行,实施;强调),large → enlarge (扩大),rich → enrich (使富足;使肥沃;使充实)等。
GRAMMAR
构词法
(1) 表示否定意义的前缀
dis-, il-, in-, ir-, mis-, non-, un-等,在单词前加这类前缀常构成与该词意义相反的新词。
il- → illegal 非法的
un- → unhappy 不高兴的
im- → impatient 不耐烦的
dis- → disappear 消失
in- → incorrect 不正确的
ir- → irregular 不规则的
GRAMMAR
构词法
(2) 表示其他意义的常见前缀
anti- (反对;抵抗) → antiwar 反战的
sub- (下面的) → subway 地铁
inter- (互相) → Internet 互联网
re- (再;又) → rewrite 重写
en- (使……) → enrich 使富足
pre- (前;预先) → preview 预习
GRAMMAR
构词法
post- (后的) → postwar 战后
mid- (中;半) → midnight 午夜
vice-(副) → vice-manager 副经理
micro-(微) → microscope 显微镜
for-/ fore- (先;预) → forecast 预报
co- (共;同) → cooperation 合作
mini- (小型) → miniskirt 迷你裙
bi- (双的) → bimonthly 双月的
GRAMMAR
构词法
后缀常会改变单词的词性,构成意思相近的其他词性;少数后缀还会改变词义,变为与原来词义相反的新词。
(1) 常见动词后缀
-en (多用于形容词之后);-fy (使……化);-ize (使……成为)
例:widen 加宽;beautify 美化;realize 意识到
GRAMMAR
构词法
(2) 常见名词后缀
-er/ -or (从事……的人);-ese (某地人);-ian (……的人);-ist (专业人员);-ism (主义);-ment (性质;状态);-ness (性质);-tion/ -ation (动作;过程);-dom (状态;区域)
例:teacher 教师;Chinese 中国人;musician 音乐家;artist 艺术家;movement 运动;darkness 黑暗;invention 发明;freedom 自由
GRAMMAR
构词法
(3) 常见形容词后缀
-al, -able, -an, -ble, -ern, -ful, -th, -ive, -less, -like, -ly, -y, -ous , -some
例:national 民族的;reasonable 合理的;American 美国的;careful 细心的;active 有活力的;joyous 快乐的
GRAMMAR
构词法
(4) 常见副词后缀
-ly (用于形容词后表示方式或程度);-ward(s) (表示方向);-wise (表示方向或方式);-wise (表示方向或方式);
例:quickly 迅速地;angrily 生气地;northward 朝北;upward(s) 向上;clockwise 顺时针地;crosswise 横过地
GRAMMAR
构词法
二、合成法
两个单词连在一起合成新词,前一个词修饰或限定后一个词。
1. 合成名词
例如:birthplace / grown-up / background
2. 合成形容词
例如:outstanding / takeaway
3. 合成动词
例如:overcome / undercharge / outweigh
GRAMMAR
构词法
三、转换法
单词词形不变,词性发生转换。
1. 动词转换为名词
例如:I think we'd better finish the talk now.
2. 名词转换为动词
例如:He has booked the tickets.
3. 形容词转化为动词
例如:We'll try our best to better our living conditions.
4. 形容词转化为名词
例如: The girl in red looks pretty.
GRAMMAR
构词法
四、缩略法
将单词缩写,词义和词性保持不变。
1. 去头
例如:telephone-phone / airplane-plane
2. 去尾
例如: examination-exam / laboratory-lab
3. 去头去尾
例如:influenza-flu / prescription-script
1. conduct
conduct sb. around (=show sb. around) 带领某人参观
conduct/ do/ make/ perform/ carry out an experiment 做实验
conduct a concert 指挥音乐会
conduct a survey/ an investigation 开展调查
under the conduct of 在……的指导下/ 管理下
conductor n. 售票员,(乐队)指挥
conduction n. 传导
练习:The sport has a strict code of _____________.
conduct
VOCABULARY
VOCABULARY
2. respond
respond v. 回答,响应,作出反应
respond to... 回应/ 回答……
response n. 响应,回答
in response to 作为对……的答复/ 反应(通常作状语)
make no response (to) 没有(对……)做答/ 回答
make (a) response to 对……作出反应
练习:I ______________ to the news by bursting into tears.
respond
3. hesitate
hesitate about/ over/ at (doing)… 对(做)……感到犹豫
hesitate to do sth. 迟疑做某事,不愿做某事
hesitation n. 犹豫
without hesitation 毫不犹豫
have no hesitation in doing sth. 毫不犹豫地做某事
练习:I ______________ about taking his side until I knew the whole story.
hesitate
VOCABULARY
4. charge
in charge of 主管,负责
in the charge of... 由……负责/ 掌管
take charge of 主管,负责
free of charge 免费
charge…for… 因……收费,要价……
charge sb. with (doing) sth. 指控/ 起诉/ 指责某人(做)某事
练习:We have to make a small ___________ for refreshments.
charge
VOCABULARY
5. signal
signal (to) sb. to do sth. 示意某人做某事
signal to sb. 向某人示意
danger/ warning signal 危险/ 警告信号
traffic signals 交通信号
a stop signal 停车信号
练习:Her speech yesterday is a ___________ that her view has changed.
signal
VOCABULARY
6. compose
compose v. 作曲,创作,组成
compose mail 写邮件
be composed of 由……组成
composer n. 作曲家,设计者
composition n. 作文,作曲,成分;组合方式
练习:Ten men ______________ the committee.
compose
VOCABULARY
7. struggle
struggle with 与……斗争
struggle for 为争取……而斗争
struggle against 与……斗争;为反对……而斗争
struggle to do sth. 努力做某事
struggle to one's feet 挣扎着站起来
练习:He came to symbolize his country's ______________ for independence.
struggle
VOCABULARY
1. The theatre's musical director, Michael, joined him and together the two men took charge of the orchestra.
take charge of 主管;负责,强调动作
in charge of 主管;负责,强调状态 = in responsible for
I will take charge of the whole research.
我会负责掌管整项调研。
He was the officer in charge of operations.
他是负责指挥作战行动的军官。
LANGUAGE POINTS
2. As the final, joyous note signalled the end of the symphony, the audience jumped to their feet, clapping, cheering, and waving their hats.
signal v. 发信号;示意 n. 信号;红绿灯
signal sb. to do sth. 示意某人做某事
Signal sb. which way to go.
示意某人走哪条路。
You must signal which way you are going to turn.
你要朝哪个方向转,必须发出信号。
LANGUAGE POINTS
3. It was not until Caroline Unger, one of the singers, took his arm and turned him to face the audience that the great man realised his symphony was a success.
It is/was not until...that... 强调句,直到……才……
It is not until the professor come that they begin the test.
直到这位教授来了,他们才开始测试。
It was not until he came that I left.
直到他来我才离开。
LANGUAGE POINTS
1. The inventor was rewarded by the government for his scientific _________________ (achieve).
2. She can get angry very easily when others _____________ (agree) with her.
3. _____________ (honest) speaking, I don't like the way that you spoke to your father.
4. __________________ (fortunate), I was caught in the heavy rain and got wet through from head to foot.
PRACTICE
achievements
disagree
Honestly
Unfortunately
5. She was such a ____________________ (warm, heart) and generous lady that all of us respected her.
6. She has ever spent three years staying in an English-speaking country, so her ___________ (speak) English is very fluent.
7. I cannot control my body well. My legs become ___________ (pain).
8. We must pay special attention to the ________________ (mystery) stranger.
PRACTICE
warm-hearted
spoken
painful
mysterious
SUMMARY
Talk about more information of Beethoven and his symphony No. 9;
Learn some good qualities from Beethoven;
Read for general understanding and specific information;
Understand and learn words and expressions in context;
Learn about and practice word building.
Thank you
同课章节目录
- Unit 7 Art
- Lesson 1 Masterpieces
- Lesson 2 Beijing Opera
- Lesson 3 A Musical Genius
- Unit 8 Green living
- Lesson 1 Roots and Shoots
- Lesson 2 Greening the Desert
- Lesson 3 "White Bikes" on the Road
- Unit 9 Learning
- Lesson 1 Active Learning
- Lesson 2 Language Learning Tips
- Lesson 3 The Secrets of Your Memory
