2016中考王英语中考命题研究(遵义)专题研究突破:专题十动词的时态(练习无答案)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2016中考王英语中考命题研究(遵义)专题研究突破:专题十动词的时态(练习无答案) |
|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 36.9KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2016-04-17 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览


文档简介
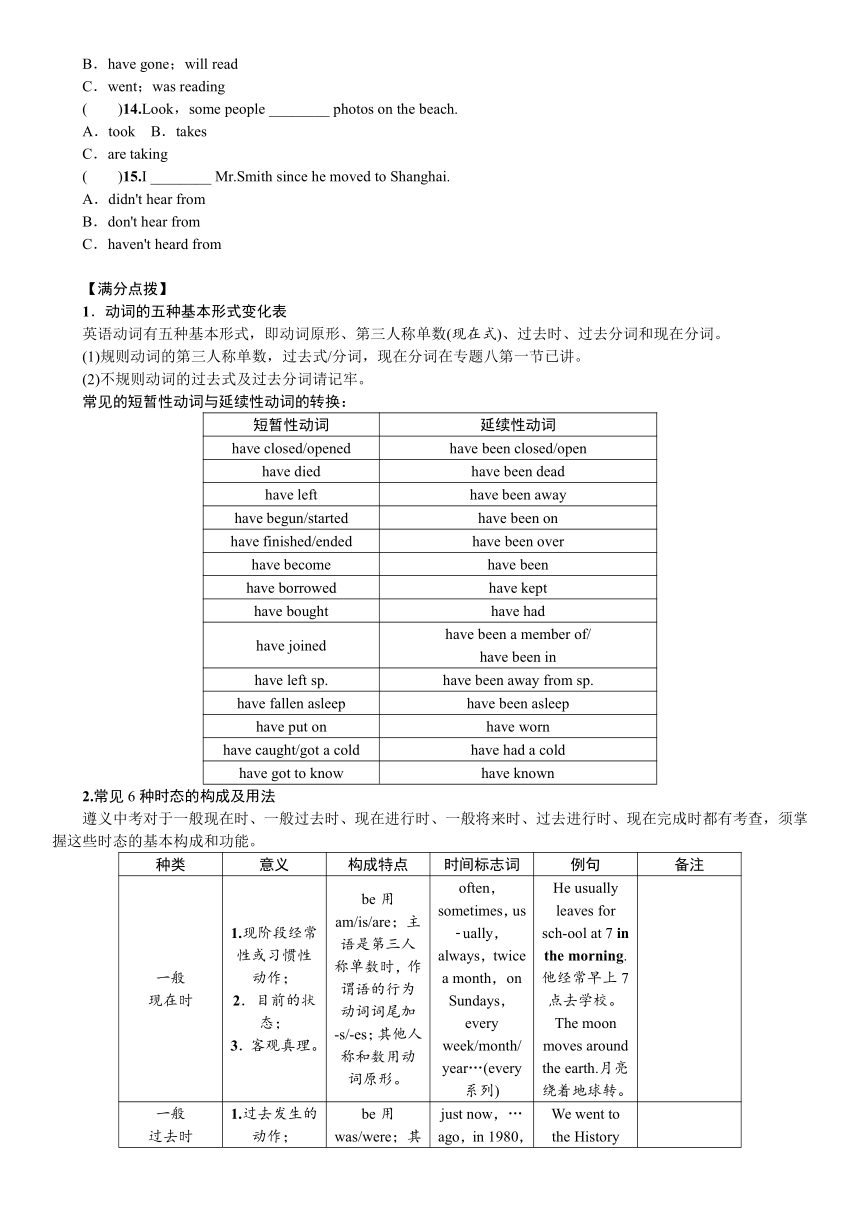
专题十 动词的时态
,中考五年命题规律及趋势
考纲要求
1.现在进行时 2.一般现在时 3.一般过去时 4.一般将来时 5.过去进行时 6.现在完成时
时态
年份
题号
选项设置
提示词
分值
一般
现在时
2015
71
do→does
He works hard and ____
1分
2014
87
will arrive→arrives
until引导的时间状语从句遵循“主将从现”原则
1分
2013
80
finish →finishes
as soon as引导状语从句同上题理由
1分
2012
88
go→goes
he和every morning
1分
2011
91
will study→studies
if引导的条件状语从句遵循“主将从现”原则
1分
一般
过去时
2014
81
cut→cut
and mixed it with milk
1分
2012
33
has been/has offered/went
无
1分
一般将来时
2013
82
be→will/is__going__to__be
next week
1分
现在
进行时
2014
35
are going to do/do you do/are__you__doing
I'm studying
1分
过去
进行时
2015
31
was__taking__a__shower/took a shower/take a shower
at that time
1分
2012
79
lie→lying
was
1.5分
现在
完成时
2014
36
cleaned/has__cleaned/had cleaned
无
1分
2013
34
has opened/has__been__open/has been opened
for 2 years
1分
2012
35
has__been__away/left/has left
for 2 weeks
1分
2011
34
has joined/has taken part in/has__been__in
for 2 years
1分
动词的时态是遵义中考题中的高频考点。语句设置多为两个单句,其语境设置灵活,有些没有明显的时间状语提示,需要分析另一语句的语境和时态来判断动作的先后顺序,淡化了古板的依赖时间状语提示来判定时态的考查方式。现在完成时为每年必考的时态,过去进行时、一般过去时、一般将来时为常考点,5年中考考了5次。一般现在时考查4次,现在完成时,现在进行时,过去进行时和一般将来时及一般过去时为轮考点。对一般现在时的考查也会和“主将从现”相结合,如2013年的80题对as soon as引导的时间状语,2014年87题对until引导状语及2011年91题对if引导的条件状语等遵循“主将从现”原则的考查。
预计2016年遵义中考题至少有2~3道时态题,其中现在完成时是必考点,一般过去时和一般将来时考查的可能性很大。
第一节 时态的基本构成
,练讲重难点
【考点抢测】
一、词语运用
1.Grandma usually ________(wake) up early in the morning.(醒来)
2.That company ________(provide) us with 3,000 dollars in 2012.
3.The thief ________ (steal) food from the supermarket and was caught by the policemen.
4.We still don't know when your friend ________ here.(come)
5.The train ________(leave) already.
6.I ________ a novel last night when I heard knocks at the door.(read)
二、改错
7.,What,A do,B you, doing,C now?,( )______
8.,Do,A you, make,B mistakes,C in class yesterday?,( )______
9.,He,A learnt,B English, for,C 3 years.,( )______
10.,I, was,A watching,B TV when you, call,C me.,( )______
三、单项选择
( )11.We make it a rule that each of us ________ the bedroom one day a week.
A.has cleaned B.have cleaned
C.cleans
( )12.Mr.Green,a famous writer,________ our school next week.
A.visited B.was visiting
C.will visit
( )13.When I ________ to the cinema last night,he ________ a book.
A.go;read
B.have gone;will read
C.went;was reading
( )14.Look,some people ________ photos on the beach.
A.took B.takes
C.are taking
( )15.I ________ Mr.Smith since he moved to Shanghai.
A.didn't hear from
B.don't hear from
C.haven't heard from
【满分点拨】
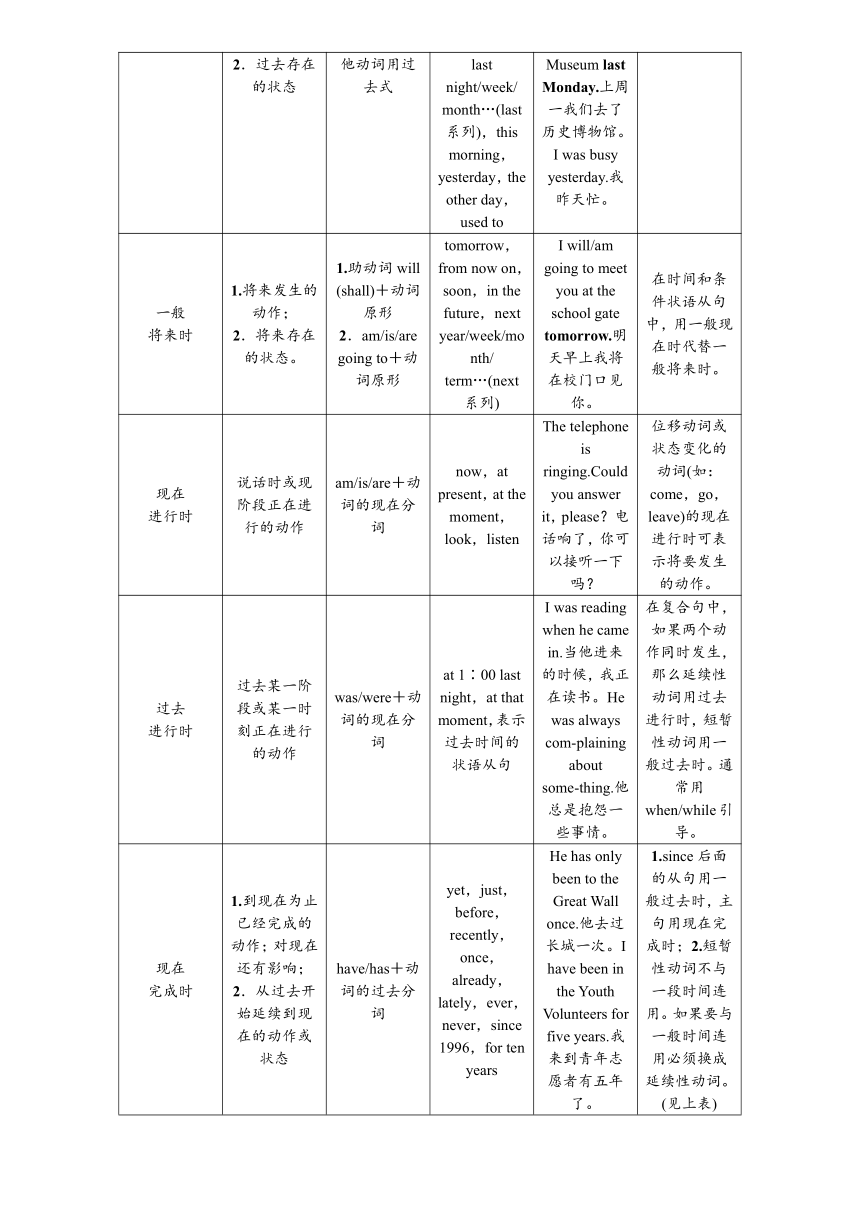
1.动词的五种基本形式变化表
英语动词有五种基本形式,即动词原形、第三人称单数(现在式)、过去时、过去分词和现在分词。
(1)规则动词的第三人称单数,过去式/分词,现在分词在专题八第一节已讲。
(2)不规则动词的过去式及过去分词请记牢。
常见的短暂性动词与延续性动词的转换:
短暂性动词
延续性动词
have closed/opened
have been closed/open
have died
have been dead
have left
have been away
have begun/started
have been on
have finished/ended
have been over
have become
have been
have borrowed
have kept
have bought
have had
have joined
have been a member of/
have been in
have left sp.
have been away from sp.
have fallen asleep
have been asleep
have put on
have worn
have caught/got a cold
have had a cold
have got to know
have known
2.常见6种时态的构成及用法
遵义中考对于一般现在时、一般过去时、现在进行时、一般将来时、过去进行时、现在完成时都有考查,须掌握这些时态的基本构成和功能。
种类
意义
构成特点
时间标志词
例句
备注
一般
现在时
1.现阶段经常性或习惯性动作;
2.目前的状态;
3.客观真理。
be用am/is/are;主语是第三人称单数时,作谓语的行为动词词尾加-s/-es;其他人称和数用动词原形。
often,sometimes,us-ually,always,twice a month,on Sundays,every week/month/
year…(every系列)
He usually leaves for sch-ool at 7 in the morning.他经常早上7点去学校。The moon moves around the earth.月亮绕着地球转。
一般
过去时
1.过去发生的动作;
2.过去存在的状态
be用was/were;其他动词用过去式
just now,… ago,in 1980,
last night/week/
month…(last系列),this morning,yesterday,the other day,used to
We went to the History Museum last Monday.上周一我们去了历史博物馆。I was busy yesterday.我昨天忙。
一般
将来时
1.将来发生的动作;
2.将来存在的状态。
1.助动词will
(shall)+动词原形
2.am/is/are going to+动词原形
tomorrow,from now on,soon,in the future,next year/week/month/
term…(next系列)
I will/am going to meet you at the school gate tomorrow.明天早上我将在校门口见你。
在时间和条件状语从句中,用一般现在时代替一般将来时。
现在
进行时
说话时或现阶段正在进行的动作
am/is/are+动词的现在分词
now,at present,at the moment,look,listen
The telephone is ringing.Could you answer it,please?电话响了,你可以接听一下吗?
位移动词或状态变化的动词(如:come,go,leave)的现在进行时可表示将要发生的动作。
过去
进行时
过去某一阶段或某一时刻正在进行的动作
was/were+动词的现在分词
at 1∶00 last night,at that moment,表示过去时间的状语从句
I was reading when he came in.当他进来的时候,我正在读书。He was always com-plaining about some-thing.他总是抱怨一些事情。
在复合句中,如果两个动作同时发生,那么延续性动词用过去进行时,短暂性动词用一般过去时。通常用when/while引导。
现在
完成时
1.到现在为止已经完成的动作;对现在还有影响;
2.从过去开始延续到现在的动作或状态
have/has+动词的过去分词
yet,just,before,recently,once,already,lately,ever,never,since 1996,for ten years
He has only been to the Great Wall once.他去过长城一次。I have been in the Youth Volunteers for five years.我来到青年志愿者有五年了。
1.since后面的从句用一般过去时,主句用现在完成时;2.短暂性动词不与一段时间连用。如果要与一般时间连用必须换成延续性动词。(见上表)
第二节 时态的应用
,练讲重难点
【考点抢测】
一、用所给词的正确形式填空
1.The student ________(do) his homework.When I called him at 5:00.
2.I began watching here an hour ago,but now nothing ________(happen) yet.
3.—Have you had your lunch yet?
—Yes,Mom ________(cook) it for me.
4.I don't have time to discuss the plan.I ________(go) to an interview.
5.In recent years,the economy of China ________(increase) rapidly.
二、单项选择
( )6.His brother is a teacher.He ________ maths at a school.
A.taught B.has taught
C.teaches
( )7.I hope Tim can come to my birthday party.Then we ________ a much happier time.
A.have B.had
C.will have
( )8.I don't remember when and where I ________ this umbrella.
A.buy B.have bought
C.bought
( )9.—Why does Tony look unhappy?
—Because he ________ the chance to take part in the English contest.
A.was missing B.is missing
C.missed
( )10.Can you answer the door,Jim?I ________ the dishes.
A.do B.have done
C.am doing
( )11.—I saw Mr.Smith in the office at ten yesterday morning.
—That's impossible.He ________ an English party with us then.
A.has B.had
C.was having
( )12.Sanya is a beautiful city.I ________ there twice.
A.have gone B.have been
C.have gone to
( )13.The volunteers ________ a lot of help to the community for nearly ten years.
A.offered B.are offering
C.have offered
( )14.It will be hard for us to get up in the morning if we ________ to bed too late.
A.go B.went C.will go
( )15.—What are you going to do this weekend?
—We are going hiking if it ________.
A.will rain B.doesn't rain
C.rains
【满分点拨】
一、时态的判断
根据遵义近5年真题分析可以看出,初中阶段需掌握六种基本时态。学生应掌握动词时态的判断技巧来解题,如①根据时间状语确定时态;②利用上下文语意判断句子的时态;③根据上下文已有的时态信息确定时态;④在复合句中根据时态呼应确定时态;⑤固定句型与动词时态间的对应关系;⑥根据特定动词与时态的对应关系;⑦根据时态中的“特殊”对策(如客观真理等)。
【方法突破】
1.根据时间状语确定时态
根据时间状语判断时态在遵义中考中主要体现在词语运用和连词成句题型中。
①now,at present,at the moment,these days,look,listen等标志着现在进行时;
②just now,…ago,in 1980,this morning,yesterday,the other day,used to,last night/week/month year…(last系列)等标志着一般过去时;
③at 1∶00 last night,at that moment,this time yesterday等标志着过去进行时;
④tomorrow,from now on,soon,in the future,next week/month/year…(next系列)等标志着一般将来时;
⑤yet,just,before,recently,once,already,lately,ever,never,since 1996,for ten years等标志着现在完成时。
⑥除了上面这些时间状语提示时态外,某些副词也有这种作用,如:often,always,usually,never,seldom等表示频率的副词应用一般现在时或一般过去时。
【典例剖析】(2010年遵义37题)
( )A:I called you last night.You didn't answer it.
B:Oh,sorry,I ________ at that time.
A.was watching TV B.watched TV
C.am watch TV
【答案】A
【解题技巧】考查过去进行时,句意:—我昨天给你打电话,你没接.—对不起,我那时在浴室洗澡。时间状语at that time“在那时”,是过去进行时的标志,故选A。
2.利用上下文语意判断句子的时态(2014年36题,2012年33题)
如果一个英语句子中既没有出现时间状语,也没有可供判断时态的上下文,那么就应当把这个句子翻译成中文,利用我们的母语知识来判断这个句子该用何种时态。
【典例剖析】(2012年遵义33题)
( )—Hello,May I speak to Zhang Jun?
—Oh,sorry!He ________ to Gui Yang.
A.has been B.has offered
C.went
【答案】C
【解题技巧】考查一般过去时。句意:他去贵阳了。根据May I speak to Zhang Jun?和sorry可知动作已发生,故用一般过去时或用has gone结构,故选C。
3.根据上下文已有的时态信息确定时态
有些试题虽然看起来没有时间状语提示词,也不是出现在复合句中,但是上下句的动作存在着明显的时间顺序差距,因此可根据上下文已有的时态来判断本句所要选用的时态。
【典例剖析】(2015年遵义71题)
He works hard and ________ well in school.
【答案】does
【解题技巧】考查一般现在时,句意:他努力学习并在学校表现好。由work hard和and一词可知and之后句子与前半句是并列关系,表顺承,时态和前半句一样,故填does。
4.在复合句中根据时态呼应确定时态
主从复合句中谓语动词时态的一致主要有以下几种情况:
①“主将从现”原则。如果主句是一般将来时,从句是由when,after,before,not…until,as soon as等引导的时间状语从句以及由if,unless引导的条件状语从句中,谓语动词应用一般现在时表示将来时间。
【典例剖析】(2013年遵义80题)
Helen is going to talk with you as soon as she ________(finish) her work.
【答案】finishes
【解题技巧】考查一般现在时。as soon as引导的时间状语从句遵循“主将从现”原则,即主句用一般将来时,从句需用一般现在时,故填finishes。
②“时态一致”原则。在含有宾语从句的主从复合句中,当主句的谓语动词为过去时态时,从句的谓语动词须用相应的某种过去时态。
【典例剖析】
( )I didn't understand ________,so I raised my hand to ask.
A.what my teacher says
B.what does my teacher say
C.what my teacher said
【答案】C
【解题技巧】考查宾语从句的语序及时态。宾语从句需用陈述句语序,排除B项。再根据“时态一致”原则,即主句的谓语动词为过去时态,从句的谓语动词须用相应的某种过去时态,故选C。
③在主从复合句中,如果主句和从句的谓语动词表示的两个动作都发生在过去,而且有明显的先后顺序,那么,延续性动词用过去进行时,短暂性动词用一般过去时。通常在when和while引导的时间状语从句出现。
【典例剖析】(2013年遵义43题改编)
( )While they ________ the cakes,they remembered that they hadn't brought any money.
A.were waiting for B.are waiting for
C.waited for
【答案】A
【解题技巧】考查过去进行时,主句的动词remember是短暂性动词的一般过去时,从句wait是延续动词,应用过去进行时,故选A。
④在含有“since从句”的主从复合句中,主句常用现在完成时,从句常用一般过去时。
另外,在“It's+一段时间+since+从句”句式中,since后面的从句一般用一般过去时。
【典例剖析】(2014安徽中考改编)
( )Rick ________ a lot about Chinese culture since he came to China.
A.learns B.learned
C.has learned
【答案】C
【解题技巧】考查现在完成时。since引导的主从复合句中“主句用现在完成时,从句用一般过去时”。所以本题可根据从句中的“came”判断出主句应用现在完成时,自从他来中国后就一直学习中国文化这个学习的动作发生在过去,但是到目前为止还没有结束且可能还会持续下去,故选C。
5.固定句型与动词时态间的对应关系
在英语中,不少句型与一些动词在时态的运用方面都存在着特定的对应关系,如:
在“祈使句+and/or+陈述句”句型中,陈述句中用will表示的一般将来时。
【典例剖析】(2015年遵义一中模拟)
( )Keep practicing and you ________ your English.
A.improve B.will improve
C.improved
【答案】B
【解题技巧】考查一般将来时。这是“祈使句+or+陈述句”句型,陈述句的谓语要用“will+动词原形”,故选B。
6.根据特定动词与时态的对应关系
在英语里有些动词与时态有着特定的对应关系,如see(看见),hear(听见),find(找到)等词的用法与上下文的时态有对应的提示作用,如see sb. do/doing sth.,hear sb. do/doing sth.
【典例剖析】
( )I saw Jeff in the park.He ________ on the grass and reading a book.
A.sits B.sat
C.was sitting
【答案】C
【解题技巧】考查过去进行时。根据上文语境“我看到杰夫在公园里”。saw表明动作发生在过去。又根据reading a book,可知前后句表并列关系,故用过去进行时。
7.根据时态中的“特”对策(如客观真理等)
当宾语从句表述的是客观事实、科学真理、格言或现在习惯行为时,其谓语动词的时态不受主句谓语动词时态的限制,要用一般现在时。
【典例剖析】
( )The teacher told us that light ________ faster than sound.
A.traveled B.travels
C.is traveling
【答案】B
【解题技巧】考查一般现在时。由常识可知“光比声音传播得快”是客观真理,必须使用一般现在时。故选B。
二、常见易混时态辨析
1.一般现在时与现在进行时的易混辨析
一般现在时表示现在经常性、习惯性的动作,或现在的状态,强调长期性、稳定性;而现在进行时是指现在此刻或现在这一时期内正在进行的动作,强调暂时性,不稳定性。如:
He usually gets up at six in the morning.(经常性、习惯性动作)
Look!The boys are fighting.(现在此刻所发生的动作)
注意:不宜用进行时态的动词:表示心理状态、情感的动词,如:love,like,hate,care,know,understand,forget,remember,believe,want,agree,wish,mean等;表示存在的动词,如:be,lie(位于)等;表示一瞬间就发生的动作,如:get,buy,end,receive等。如:
I like English very much.我非常喜欢英语。(表示情感)
Mexico lies to the south of Texas.墨西哥位于得克萨斯州的南边。(表示存在)
2.一般过去时和现在完成时的易混辨析
两者都表示过去发生的事情。但一般过去时只强调过去发生的事情本身,不涉及与现在的关系;现在完成时则强调过去的动作对现在的影响。主要说明现在的情况。如:
I opened the door just now.我刚才打开了门。(指刚才做了“开门”的动作,但现在门是否开着,并未说明。)
I have opened the door.我已经把门打开了。(门现在还开着)
3.一般过去时和过去进行时的易混辨析
一般过去时表示过去发生过,强调动作结束了,侧重于事实。而过去进行时表示动作在过去某时间内进行,强调动作的持续性和未完成性。如:
I wrote a letter to a friend last night.(信写完了,强调事实)
I was writing a letter to a friend last night.(信不一定写完;强调动作)
4.表示“将来时态”几种形式的易混辨析
(1)will/shall表示单纯的将来(即现在之后)。如:
He will be back in a few days.他几天之后回来。(单纯将来)
注意:在含有if的条件状语从句中,主句要用will表示将来时。
(2)be going to+动词原形多用于口语,强调事先的“打算、计划”要做的事情或有某种迹象要发生的事情。如:
What are you going to do this evening?你今晚上准备做什么?(打算)
(3)be doing现在进行时。现在进行时表示即将发生的将来,多与表示位移的动词come,go,arrive,leave,fly,start等连用。如:She is leaving for Beijing.她就要启程去北京。
,中考五年命题规律及趋势
考纲要求
1.现在进行时 2.一般现在时 3.一般过去时 4.一般将来时 5.过去进行时 6.现在完成时
时态
年份
题号
选项设置
提示词
分值
一般
现在时
2015
71
do→does
He works hard and ____
1分
2014
87
will arrive→arrives
until引导的时间状语从句遵循“主将从现”原则
1分
2013
80
finish →finishes
as soon as引导状语从句同上题理由
1分
2012
88
go→goes
he和every morning
1分
2011
91
will study→studies
if引导的条件状语从句遵循“主将从现”原则
1分
一般
过去时
2014
81
cut→cut
and mixed it with milk
1分
2012
33
has been/has offered/went
无
1分
一般将来时
2013
82
be→will/is__going__to__be
next week
1分
现在
进行时
2014
35
are going to do/do you do/are__you__doing
I'm studying
1分
过去
进行时
2015
31
was__taking__a__shower/took a shower/take a shower
at that time
1分
2012
79
lie→lying
was
1.5分
现在
完成时
2014
36
cleaned/has__cleaned/had cleaned
无
1分
2013
34
has opened/has__been__open/has been opened
for 2 years
1分
2012
35
has__been__away/left/has left
for 2 weeks
1分
2011
34
has joined/has taken part in/has__been__in
for 2 years
1分
动词的时态是遵义中考题中的高频考点。语句设置多为两个单句,其语境设置灵活,有些没有明显的时间状语提示,需要分析另一语句的语境和时态来判断动作的先后顺序,淡化了古板的依赖时间状语提示来判定时态的考查方式。现在完成时为每年必考的时态,过去进行时、一般过去时、一般将来时为常考点,5年中考考了5次。一般现在时考查4次,现在完成时,现在进行时,过去进行时和一般将来时及一般过去时为轮考点。对一般现在时的考查也会和“主将从现”相结合,如2013年的80题对as soon as引导的时间状语,2014年87题对until引导状语及2011年91题对if引导的条件状语等遵循“主将从现”原则的考查。
预计2016年遵义中考题至少有2~3道时态题,其中现在完成时是必考点,一般过去时和一般将来时考查的可能性很大。
第一节 时态的基本构成
,练讲重难点
【考点抢测】
一、词语运用
1.Grandma usually ________(wake) up early in the morning.(醒来)
2.That company ________(provide) us with 3,000 dollars in 2012.
3.The thief ________ (steal) food from the supermarket and was caught by the policemen.
4.We still don't know when your friend ________ here.(come)
5.The train ________(leave) already.
6.I ________ a novel last night when I heard knocks at the door.(read)
二、改错
7.,What,A do,B you, doing,C now?,( )______
8.,Do,A you, make,B mistakes,C in class yesterday?,( )______
9.,He,A learnt,B English, for,C 3 years.,( )______
10.,I, was,A watching,B TV when you, call,C me.,( )______
三、单项选择
( )11.We make it a rule that each of us ________ the bedroom one day a week.
A.has cleaned B.have cleaned
C.cleans
( )12.Mr.Green,a famous writer,________ our school next week.
A.visited B.was visiting
C.will visit
( )13.When I ________ to the cinema last night,he ________ a book.
A.go;read
B.have gone;will read
C.went;was reading
( )14.Look,some people ________ photos on the beach.
A.took B.takes
C.are taking
( )15.I ________ Mr.Smith since he moved to Shanghai.
A.didn't hear from
B.don't hear from
C.haven't heard from
【满分点拨】
1.动词的五种基本形式变化表
英语动词有五种基本形式,即动词原形、第三人称单数(现在式)、过去时、过去分词和现在分词。
(1)规则动词的第三人称单数,过去式/分词,现在分词在专题八第一节已讲。
(2)不规则动词的过去式及过去分词请记牢。
常见的短暂性动词与延续性动词的转换:
短暂性动词
延续性动词
have closed/opened
have been closed/open
have died
have been dead
have left
have been away
have begun/started
have been on
have finished/ended
have been over
have become
have been
have borrowed
have kept
have bought
have had
have joined
have been a member of/
have been in
have left sp.
have been away from sp.
have fallen asleep
have been asleep
have put on
have worn
have caught/got a cold
have had a cold
have got to know
have known
2.常见6种时态的构成及用法
遵义中考对于一般现在时、一般过去时、现在进行时、一般将来时、过去进行时、现在完成时都有考查,须掌握这些时态的基本构成和功能。
种类
意义
构成特点
时间标志词
例句
备注
一般
现在时
1.现阶段经常性或习惯性动作;
2.目前的状态;
3.客观真理。
be用am/is/are;主语是第三人称单数时,作谓语的行为动词词尾加-s/-es;其他人称和数用动词原形。
often,sometimes,us-ually,always,twice a month,on Sundays,every week/month/
year…(every系列)
He usually leaves for sch-ool at 7 in the morning.他经常早上7点去学校。The moon moves around the earth.月亮绕着地球转。
一般
过去时
1.过去发生的动作;
2.过去存在的状态
be用was/were;其他动词用过去式
just now,… ago,in 1980,
last night/week/
month…(last系列),this morning,yesterday,the other day,used to
We went to the History Museum last Monday.上周一我们去了历史博物馆。I was busy yesterday.我昨天忙。
一般
将来时
1.将来发生的动作;
2.将来存在的状态。
1.助动词will
(shall)+动词原形
2.am/is/are going to+动词原形
tomorrow,from now on,soon,in the future,next year/week/month/
term…(next系列)
I will/am going to meet you at the school gate tomorrow.明天早上我将在校门口见你。
在时间和条件状语从句中,用一般现在时代替一般将来时。
现在
进行时
说话时或现阶段正在进行的动作
am/is/are+动词的现在分词
now,at present,at the moment,look,listen
The telephone is ringing.Could you answer it,please?电话响了,你可以接听一下吗?
位移动词或状态变化的动词(如:come,go,leave)的现在进行时可表示将要发生的动作。
过去
进行时
过去某一阶段或某一时刻正在进行的动作
was/were+动词的现在分词
at 1∶00 last night,at that moment,表示过去时间的状语从句
I was reading when he came in.当他进来的时候,我正在读书。He was always com-plaining about some-thing.他总是抱怨一些事情。
在复合句中,如果两个动作同时发生,那么延续性动词用过去进行时,短暂性动词用一般过去时。通常用when/while引导。
现在
完成时
1.到现在为止已经完成的动作;对现在还有影响;
2.从过去开始延续到现在的动作或状态
have/has+动词的过去分词
yet,just,before,recently,once,already,lately,ever,never,since 1996,for ten years
He has only been to the Great Wall once.他去过长城一次。I have been in the Youth Volunteers for five years.我来到青年志愿者有五年了。
1.since后面的从句用一般过去时,主句用现在完成时;2.短暂性动词不与一段时间连用。如果要与一般时间连用必须换成延续性动词。(见上表)
第二节 时态的应用
,练讲重难点
【考点抢测】
一、用所给词的正确形式填空
1.The student ________(do) his homework.When I called him at 5:00.
2.I began watching here an hour ago,but now nothing ________(happen) yet.
3.—Have you had your lunch yet?
—Yes,Mom ________(cook) it for me.
4.I don't have time to discuss the plan.I ________(go) to an interview.
5.In recent years,the economy of China ________(increase) rapidly.
二、单项选择
( )6.His brother is a teacher.He ________ maths at a school.
A.taught B.has taught
C.teaches
( )7.I hope Tim can come to my birthday party.Then we ________ a much happier time.
A.have B.had
C.will have
( )8.I don't remember when and where I ________ this umbrella.
A.buy B.have bought
C.bought
( )9.—Why does Tony look unhappy?
—Because he ________ the chance to take part in the English contest.
A.was missing B.is missing
C.missed
( )10.Can you answer the door,Jim?I ________ the dishes.
A.do B.have done
C.am doing
( )11.—I saw Mr.Smith in the office at ten yesterday morning.
—That's impossible.He ________ an English party with us then.
A.has B.had
C.was having
( )12.Sanya is a beautiful city.I ________ there twice.
A.have gone B.have been
C.have gone to
( )13.The volunteers ________ a lot of help to the community for nearly ten years.
A.offered B.are offering
C.have offered
( )14.It will be hard for us to get up in the morning if we ________ to bed too late.
A.go B.went C.will go
( )15.—What are you going to do this weekend?
—We are going hiking if it ________.
A.will rain B.doesn't rain
C.rains
【满分点拨】
一、时态的判断
根据遵义近5年真题分析可以看出,初中阶段需掌握六种基本时态。学生应掌握动词时态的判断技巧来解题,如①根据时间状语确定时态;②利用上下文语意判断句子的时态;③根据上下文已有的时态信息确定时态;④在复合句中根据时态呼应确定时态;⑤固定句型与动词时态间的对应关系;⑥根据特定动词与时态的对应关系;⑦根据时态中的“特殊”对策(如客观真理等)。
【方法突破】
1.根据时间状语确定时态
根据时间状语判断时态在遵义中考中主要体现在词语运用和连词成句题型中。
①now,at present,at the moment,these days,look,listen等标志着现在进行时;
②just now,…ago,in 1980,this morning,yesterday,the other day,used to,last night/week/month year…(last系列)等标志着一般过去时;
③at 1∶00 last night,at that moment,this time yesterday等标志着过去进行时;
④tomorrow,from now on,soon,in the future,next week/month/year…(next系列)等标志着一般将来时;
⑤yet,just,before,recently,once,already,lately,ever,never,since 1996,for ten years等标志着现在完成时。
⑥除了上面这些时间状语提示时态外,某些副词也有这种作用,如:often,always,usually,never,seldom等表示频率的副词应用一般现在时或一般过去时。
【典例剖析】(2010年遵义37题)
( )A:I called you last night.You didn't answer it.
B:Oh,sorry,I ________ at that time.
A.was watching TV B.watched TV
C.am watch TV
【答案】A
【解题技巧】考查过去进行时,句意:—我昨天给你打电话,你没接.—对不起,我那时在浴室洗澡。时间状语at that time“在那时”,是过去进行时的标志,故选A。
2.利用上下文语意判断句子的时态(2014年36题,2012年33题)
如果一个英语句子中既没有出现时间状语,也没有可供判断时态的上下文,那么就应当把这个句子翻译成中文,利用我们的母语知识来判断这个句子该用何种时态。
【典例剖析】(2012年遵义33题)
( )—Hello,May I speak to Zhang Jun?
—Oh,sorry!He ________ to Gui Yang.
A.has been B.has offered
C.went
【答案】C
【解题技巧】考查一般过去时。句意:他去贵阳了。根据May I speak to Zhang Jun?和sorry可知动作已发生,故用一般过去时或用has gone结构,故选C。
3.根据上下文已有的时态信息确定时态
有些试题虽然看起来没有时间状语提示词,也不是出现在复合句中,但是上下句的动作存在着明显的时间顺序差距,因此可根据上下文已有的时态来判断本句所要选用的时态。
【典例剖析】(2015年遵义71题)
He works hard and ________ well in school.
【答案】does
【解题技巧】考查一般现在时,句意:他努力学习并在学校表现好。由work hard和and一词可知and之后句子与前半句是并列关系,表顺承,时态和前半句一样,故填does。
4.在复合句中根据时态呼应确定时态
主从复合句中谓语动词时态的一致主要有以下几种情况:
①“主将从现”原则。如果主句是一般将来时,从句是由when,after,before,not…until,as soon as等引导的时间状语从句以及由if,unless引导的条件状语从句中,谓语动词应用一般现在时表示将来时间。
【典例剖析】(2013年遵义80题)
Helen is going to talk with you as soon as she ________(finish) her work.
【答案】finishes
【解题技巧】考查一般现在时。as soon as引导的时间状语从句遵循“主将从现”原则,即主句用一般将来时,从句需用一般现在时,故填finishes。
②“时态一致”原则。在含有宾语从句的主从复合句中,当主句的谓语动词为过去时态时,从句的谓语动词须用相应的某种过去时态。
【典例剖析】
( )I didn't understand ________,so I raised my hand to ask.
A.what my teacher says
B.what does my teacher say
C.what my teacher said
【答案】C
【解题技巧】考查宾语从句的语序及时态。宾语从句需用陈述句语序,排除B项。再根据“时态一致”原则,即主句的谓语动词为过去时态,从句的谓语动词须用相应的某种过去时态,故选C。
③在主从复合句中,如果主句和从句的谓语动词表示的两个动作都发生在过去,而且有明显的先后顺序,那么,延续性动词用过去进行时,短暂性动词用一般过去时。通常在when和while引导的时间状语从句出现。
【典例剖析】(2013年遵义43题改编)
( )While they ________ the cakes,they remembered that they hadn't brought any money.
A.were waiting for B.are waiting for
C.waited for
【答案】A
【解题技巧】考查过去进行时,主句的动词remember是短暂性动词的一般过去时,从句wait是延续动词,应用过去进行时,故选A。
④在含有“since从句”的主从复合句中,主句常用现在完成时,从句常用一般过去时。
另外,在“It's+一段时间+since+从句”句式中,since后面的从句一般用一般过去时。
【典例剖析】(2014安徽中考改编)
( )Rick ________ a lot about Chinese culture since he came to China.
A.learns B.learned
C.has learned
【答案】C
【解题技巧】考查现在完成时。since引导的主从复合句中“主句用现在完成时,从句用一般过去时”。所以本题可根据从句中的“came”判断出主句应用现在完成时,自从他来中国后就一直学习中国文化这个学习的动作发生在过去,但是到目前为止还没有结束且可能还会持续下去,故选C。
5.固定句型与动词时态间的对应关系
在英语中,不少句型与一些动词在时态的运用方面都存在着特定的对应关系,如:
在“祈使句+and/or+陈述句”句型中,陈述句中用will表示的一般将来时。
【典例剖析】(2015年遵义一中模拟)
( )Keep practicing and you ________ your English.
A.improve B.will improve
C.improved
【答案】B
【解题技巧】考查一般将来时。这是“祈使句+or+陈述句”句型,陈述句的谓语要用“will+动词原形”,故选B。
6.根据特定动词与时态的对应关系
在英语里有些动词与时态有着特定的对应关系,如see(看见),hear(听见),find(找到)等词的用法与上下文的时态有对应的提示作用,如see sb. do/doing sth.,hear sb. do/doing sth.
【典例剖析】
( )I saw Jeff in the park.He ________ on the grass and reading a book.
A.sits B.sat
C.was sitting
【答案】C
【解题技巧】考查过去进行时。根据上文语境“我看到杰夫在公园里”。saw表明动作发生在过去。又根据reading a book,可知前后句表并列关系,故用过去进行时。
7.根据时态中的“特”对策(如客观真理等)
当宾语从句表述的是客观事实、科学真理、格言或现在习惯行为时,其谓语动词的时态不受主句谓语动词时态的限制,要用一般现在时。
【典例剖析】
( )The teacher told us that light ________ faster than sound.
A.traveled B.travels
C.is traveling
【答案】B
【解题技巧】考查一般现在时。由常识可知“光比声音传播得快”是客观真理,必须使用一般现在时。故选B。
二、常见易混时态辨析
1.一般现在时与现在进行时的易混辨析
一般现在时表示现在经常性、习惯性的动作,或现在的状态,强调长期性、稳定性;而现在进行时是指现在此刻或现在这一时期内正在进行的动作,强调暂时性,不稳定性。如:
He usually gets up at six in the morning.(经常性、习惯性动作)
Look!The boys are fighting.(现在此刻所发生的动作)
注意:不宜用进行时态的动词:表示心理状态、情感的动词,如:love,like,hate,care,know,understand,forget,remember,believe,want,agree,wish,mean等;表示存在的动词,如:be,lie(位于)等;表示一瞬间就发生的动作,如:get,buy,end,receive等。如:
I like English very much.我非常喜欢英语。(表示情感)
Mexico lies to the south of Texas.墨西哥位于得克萨斯州的南边。(表示存在)
2.一般过去时和现在完成时的易混辨析
两者都表示过去发生的事情。但一般过去时只强调过去发生的事情本身,不涉及与现在的关系;现在完成时则强调过去的动作对现在的影响。主要说明现在的情况。如:
I opened the door just now.我刚才打开了门。(指刚才做了“开门”的动作,但现在门是否开着,并未说明。)
I have opened the door.我已经把门打开了。(门现在还开着)
3.一般过去时和过去进行时的易混辨析
一般过去时表示过去发生过,强调动作结束了,侧重于事实。而过去进行时表示动作在过去某时间内进行,强调动作的持续性和未完成性。如:
I wrote a letter to a friend last night.(信写完了,强调事实)
I was writing a letter to a friend last night.(信不一定写完;强调动作)
4.表示“将来时态”几种形式的易混辨析
(1)will/shall表示单纯的将来(即现在之后)。如:
He will be back in a few days.他几天之后回来。(单纯将来)
注意:在含有if的条件状语从句中,主句要用will表示将来时。
(2)be going to+动词原形多用于口语,强调事先的“打算、计划”要做的事情或有某种迹象要发生的事情。如:
What are you going to do this evening?你今晚上准备做什么?(打算)
(3)be doing现在进行时。现在进行时表示即将发生的将来,多与表示位移的动词come,go,arrive,leave,fly,start等连用。如:She is leaving for Beijing.她就要启程去北京。
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
