八年级英语上册Unit8Natural disasters Period3 Grammar上课课件(共41张PPT)牛津译林版
文档属性
| 名称 | 八年级英语上册Unit8Natural disasters Period3 Grammar上课课件(共41张PPT)牛津译林版 |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 4.1MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津译林版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-02-16 11:04:50 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共41张PPT)
Unit 8 Natural disasters
Period 3 Grammar
1
课时导入
2
课文呈现
3
考点精讲
4
单元
语法沙龙
5
课堂小结
What were you doing when it's raining yesterday
I was reading at home.
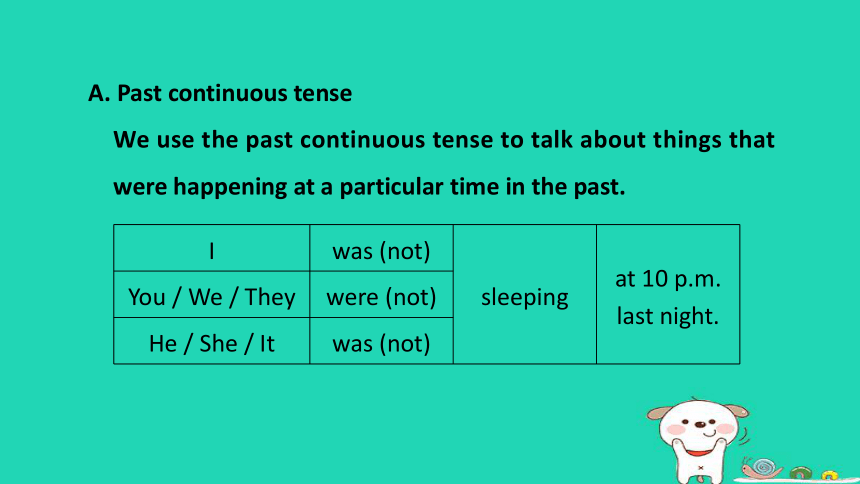
A. Past continuous tense
We use the past continuous tense to talk about things that were happening at a particular time in the past.
I was (not) sleeping at 10 p.m.
last night.
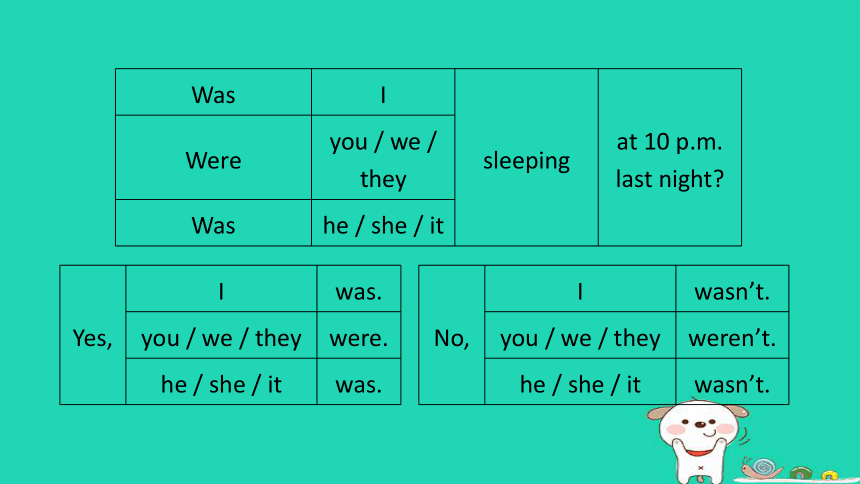
You / We / They were (not) He / She / It was (not) Was I sleeping at 10 p.m.
last night
Were you / we / they Was he / she / it Yes, I was.
you / we / they were.
he / she / it was.
No, I wasn’t.
you / we / they weren’t.
he / she / it wasn’t.
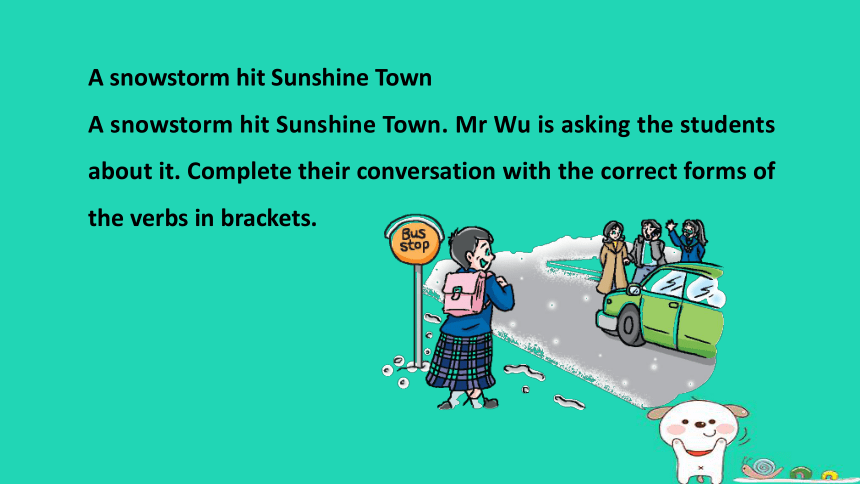
A snowstorm hit Sunshine Town
A snowstorm hit Sunshine Town. Mr Wu is asking the students about plete their conversation with the correct forms of the verbs in brackets.
Mr Wu: What a terrible snowstorm! It started at about seven this morning. I (1) ____________ (read) the newspaper then. What (2) __________ you (do), Simon
Simon: I (3) ______________(have) breakfast.
Mr Wu: What about you, Millie
Millie: I (4) ____________ (walk) to the bus stop. Sandy, I saw you and your parents standing on the side of the road. (5) _____________ you _____________(wait) for a taxi
was reading
were doing
was having
was walking
Were waiting
Sandy: Yes. My dad’s car broke down because of the cold weather. ① He (6) ____________(ring) someone to come and help when you saw us.
was ringing
B. Using when, while and as
When, while and as can be used as conjunctions of time. They all mean “during the time that”.
I was sleeping when the earthquake started.
People were running in all directions while pieces of glass and bricks were falling down.
As I was trying to find my way out, I suddenly heard some noise above me.
Note: When a shorter action happened at the same time as a longer action, we use the past
continuous tense for the longer action and the simple past tense for the shorter action. When there
are two long actions, we often use while.
If the shorter action is in the main clause, we can use when, while or as to join them.
When/While/As Millie was watching TV, Andy came into the room.
If the longer action is in the main clause, we often use when to join them.
Millie was watching TV when Andy came into the room.
TIP
We use a comma to separate the two clauses if when, while or as comes at the beginning of the sentence.
When the earthquake started, most people were sleeping.
Playing in the snow
Some Class 1, Grade 8 students went to play in the plete the sentences with the
correct forms of the verbs in brackets. Use when, while or as to connect the sentences.
1 ___________ Simon ___________ (arrive), Amy ___________ (get) some snow from the ground.
When arrived was getting
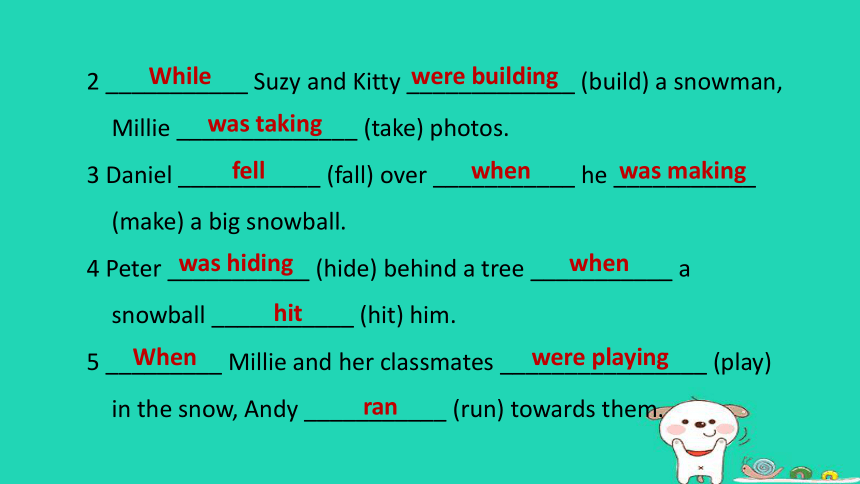
2 ___________ Suzy and Kitty _____________ (build) a snowman, Millie ______________ (take) photos.
3 Daniel ___________ (fall) over ___________ he ___________ (make) a big snowball.
4 Peter ___________ (hide) behind a tree ___________ a snowball ___________ (hit) him.
5 _________ Millie and her classmates ________________ (play) in the snow, Andy ___________ (run) towards them.
While were building
was taking
fell when was making
was hiding when
hit
When were playing
ran
break down(车辆或机器) 出故障,坏掉
e.g. He was late because his bike broke down.
他迟到是因为他的自行车坏了。
My car broke down on a country road yesterday.
我的小汽车昨天在一条乡村公路上出了故障。
考点1
后不能跟宾语,不用于被动语态。
知识点
1
My dad’s car broke down because of the cold weather.
与break 相关的短语
break into 强行闯入 break off 中断
break out(战争、打斗等不愉快事件) 突然开始,爆发
break a promise 违背誓言
break one’s heart 伤某人的心
break the law 违法
break the record 打破纪录
考题1:[包头] —The computer is working again!
—It _______ yesterday, but someone has fixed it.
A. broke down B. broke out
C. broke into D. broke away
A
【点拨】考查break 相关短语的用法。根据后面的fixed 可知昨天电脑出了故障。
出故障 爆发
强行闯入 脱离
(重点) because of 因为,由于
e.g. He didn’t come to school because of the rain.
因为下雨他没来学校。
I didn’t buy it because it was too expensive.
我没有买是因为它太贵了。
He can’t come because of his illness.
= He can’t come because he is ill.
他因病不能来。
考点2
短语中of 为介词,后接名词、代词、动名词或名词性短语。
because 为连词,后接句子。
because of 可与
because 进行同义转换
返回
温馨提示:可返回原文
考题2:[绥化] She can’t sleep well _______ too much noise next door.
A. because B. because of C. since
【点拨】用语法判定法。句意为“她没能睡好觉,因为隔壁太吵了”。because 因为,后接原因状语从句;because of 因为,后接单词或短语;since 由于,既然,引导原因状语从句。空格后noise 为名词,故选B。
B
过去进行时
概念 表示在过去某个时刻或某段时间正在进行的动作。①
构成② 主语+ was(were)+ 动词的现在分词.
主语第一、三人称单数用was,其余用were。
时间状语 at eight o’clock last night, at that time, at that moment, this time yesterday, from 8:00 to 9:00 last night 以及when, while 引导的时间状语从句等。
用法③ 1. 表示在过去某一时刻正在进行的动作。
2. 表示过去一段时间内正在进行的动作。
不用进行时的动词 1. 表示心里状态、情感的动词,如love,hate,like,know。
2. 部分连系动词,如seem,appear。
3. 感官动词,如see,hear,feel,smell,sound,taste 等。
4. 短暂性动词,如decide,stop 等。
过去进行时既可以表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作,也可以表示过去某一段时间正在进行的动作。过去进行时与一般过去时一样,也常和表示过去的时间状语连用。与过去进行时连用的常见的时间状语有:
this morning, the whole afternoon,
at this time yesterday, at ten yesterday morning,
from nine to ten last night 等。
考点1
考题1:[河北] At this time yesterday, I _____ a science exam here.
A. take B. was taking
C. am taking D. will take
B
【点拨】用语法判定法。考查动词时态。句意:昨天这个时候我正在这里进行科学考试。由句中的时间状语At this time yesterday“昨天这个时候”,可知用过去进行时。
返回
过去进行时的构成:
考点2
句式 结构
肯定句 主语+was/were +doing+ 其他.
否定句 主语+was/were+not+doing+ 其他.
一般疑问句 Was/Were+ 主语+doing+ 其他
答语:Yes, 主语+was/were.
/No,主语+wasn’t/weren’t.
特殊疑问句 特殊疑问词+was/were+ 主语+doing+ 其他
e.g. I was dancing to the beautiful music then.
那时我正伴随着优美的音乐跳舞。
We were listening to the teacher carefully at eight yesterday. 昨天八点钟,我们正在认真地听老师讲课。
She was running at that time.
那时她正在跑步。
He wasn’t doing his homework just now.
刚才他没在做家庭作业。
I wasn’t singing then. 那时我没在唱歌。
They weren’t listening to music at that time.
那时他们没在听音乐。
— Were you reading a book 你在看书吗?
— Yes, I was. 是的,我在看。
— No, I wasn’t. 不,我没在看。
— Were they playing tennis 他们在打网球吗?
— Yes, they were. 是的,他们在打。
— No, they weren’t. 不,他们没在打。
— Was she dancing 她在跳舞吗?
— Yes, she was. 是的,她在跳。
— No, she wasn’t. 不,她没在跳。
What were you doing at eight yesterday
昨天八点你在干什么?
Where was he playing at that moment
那个时候他在哪儿玩?
考题2:[镇江] —You look tired!
—My husband ______ football matches all night. That was too noisy!
A. watches B. has watched
C. was watching D. will watch
【点拨】用语法判定法。考查动词时态。根据上句句意:你看起来很累!可知答句句意是:我丈夫整晚都在看足球比赛。那太吵了!表示“昨夜一直在干某事”,应用过去进行时,其结构是was / were + v.-ing。
C
返回
过去进行时的用法:
考点3
用法 示例
表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作。 My sister was doing her homework at eight last night.
昨天晚上八点我妹妹在做家庭作业。
表示一个动作正在进行时,另一个动作也同时进行。 I was watching TV while my father was reading the newspaper.
我爸爸在看报纸时,我在看电视。
用法 示例
表示一个动作正在进行时,另一个动作发生了。 I met one of my old friends while I was walking in the park. 我在公园散步时,遇到了我的一位老朋友。
表示过去将要发生的动作。 She told us Jack was arriving here.
她告诉我们杰克将到这儿。
考题3:[北京] I ______ about my sister when my phone rang. It was her!
A. think B. will think
C. was thinking D. am thinking
【点拨】用语法判定法。考查动词时态。句意为“我正在想我的妹妹,这时我的电话铃响了,正是她!”。这里强调过去正在发生的动作,应用过去进行时。
C
返回
when, while 与as 的用法
when 当……时 从句中的动作既可以和主句中的动作同时发生,也可以在主句的动作之前或之后发生。
while 当……的时候 强调从句中的动作与主句中的动作同时发生,但持续时间一般较长或主句的动作在从句的动作过程中发生。
as 当……时; 和……同时 从句中的动作与主句中的动作同时发生或同时进行,一般持续时间不长。
若主句表示的是一个短暂性动作,从句表示的是一个持续性动作时,三者都可用。
e.g. He fell asleep when/while/as he was reading a book.
他看书时睡着了。
考点1
若主从句表示两个同时进行的持续性动作,且强调主句表示的动作延续到从句所指的整个事件,通常要用while。
e.g. Don’t talk while you’re eating something.
当你吃东西时不要说话。
但是,若主从句表示的两个同时进行的动作含有“一边……一边……”的意思时,通常用as。
e.g. She sang as she went along. 她边走边唱。
考点2
若从句是一个短暂性动作,主句是一个持续性动作,可用as/when,但不用while。
e.g. It was raining hard when/as we arrived.
我们到达时,天正下着大雨。
考点3
若主从句表示的是两个同时发生的短暂性动作,用as/when。
e.g. I also thought of it just when/as you opened your mouth. 就在你开口的时候,我也想到了。
考点4
考题4:[扬州] _______ astronauts go on spacewalks, they wear spacesuits to keep themselves safe.
A. Though B. Till C. When D. Unless
【点拨】用语法判定法。考查连词辨析。句意为“当宇航员进行太空行走时,他们会穿上宇航服以保证自己的安全”。Though 虽然;Till 直到;When当……的时候;Unless 除非,如果不。根据句意可知答案。
C
若要表示两个正在发展变化的动作,相当于汉语的“随着”,一般用as。
e.g. Things are getting better and better as time goes on.
随着时间的推移,情况变得越来越好了。
考点5
表示“每当……的时候”(暗示一种规律性),一般要用when。
e.g. It’s cold when it snows. 下雪时天冷。
考点6
若主从句所表示的动作不是同时发生,而是有先后顺序的,一般要用when。
e.g. I will go home when he comes back.
当他回来后,我就回家。
考点7
考题5:—Learning to love is like learning to walk.
—Yes, ______ we step out bravely, we can find it easy.
A. although B. when C. unless
【点拨】用语法判定法。考查连词辨析。句意:—学习爱像学习走路。—是的,当我们勇敢地迈出去,我们会发现它很容易。although 虽然;when当……时;unless 除非。根据“we step out bravely, we can find it easy” 可知,两个动作是先后关系。
B
when 可用作连词, 表示“当…… 时”;while 也可用作连词,表示“而,然而”(表示对比); 但as 没有类似的用法。
e.g. We were about to start when it began to rain.
我们正要开始,这时天开始下雨了。
He likes coffee, while she likes tea.
他喜欢咖啡,而她却喜欢茶。
考点8
as 和when 后均可直接跟一个名词或名词性短语,构成省略句,但while 一般不可以这样用。
e.g. As/When a little boy, he lived in America.
他小时候居住在美国。
考点9
when 和while 后可接现在分词、介词短语、形容词等构成省略句,但as 一般不可以这样用。
e.g. When/ While in trouble, ask her for help.
遇到麻烦时就去找她帮忙。
考点10
本节课主要学习了以下知识点,请同学们及时巩固练习:
过去进行时
when、while和as的用法
知识是力量,
梦想是翅膀。
Unit 8 Natural disasters
Period 3 Grammar
1
课时导入
2
课文呈现
3
考点精讲
4
单元
语法沙龙
5
课堂小结
What were you doing when it's raining yesterday
I was reading at home.
A. Past continuous tense
We use the past continuous tense to talk about things that were happening at a particular time in the past.
I was (not) sleeping at 10 p.m.
last night.
You / We / They were (not) He / She / It was (not) Was I sleeping at 10 p.m.
last night
Were you / we / they Was he / she / it Yes, I was.
you / we / they were.
he / she / it was.
No, I wasn’t.
you / we / they weren’t.
he / she / it wasn’t.
A snowstorm hit Sunshine Town
A snowstorm hit Sunshine Town. Mr Wu is asking the students about plete their conversation with the correct forms of the verbs in brackets.
Mr Wu: What a terrible snowstorm! It started at about seven this morning. I (1) ____________ (read) the newspaper then. What (2) __________ you (do), Simon
Simon: I (3) ______________(have) breakfast.
Mr Wu: What about you, Millie
Millie: I (4) ____________ (walk) to the bus stop. Sandy, I saw you and your parents standing on the side of the road. (5) _____________ you _____________(wait) for a taxi
was reading
were doing
was having
was walking
Were waiting
Sandy: Yes. My dad’s car broke down because of the cold weather. ① He (6) ____________(ring) someone to come and help when you saw us.
was ringing
B. Using when, while and as
When, while and as can be used as conjunctions of time. They all mean “during the time that”.
I was sleeping when the earthquake started.
People were running in all directions while pieces of glass and bricks were falling down.
As I was trying to find my way out, I suddenly heard some noise above me.
Note: When a shorter action happened at the same time as a longer action, we use the past
continuous tense for the longer action and the simple past tense for the shorter action. When there
are two long actions, we often use while.
If the shorter action is in the main clause, we can use when, while or as to join them.
When/While/As Millie was watching TV, Andy came into the room.
If the longer action is in the main clause, we often use when to join them.
Millie was watching TV when Andy came into the room.
TIP
We use a comma to separate the two clauses if when, while or as comes at the beginning of the sentence.
When the earthquake started, most people were sleeping.
Playing in the snow
Some Class 1, Grade 8 students went to play in the plete the sentences with the
correct forms of the verbs in brackets. Use when, while or as to connect the sentences.
1 ___________ Simon ___________ (arrive), Amy ___________ (get) some snow from the ground.
When arrived was getting
2 ___________ Suzy and Kitty _____________ (build) a snowman, Millie ______________ (take) photos.
3 Daniel ___________ (fall) over ___________ he ___________ (make) a big snowball.
4 Peter ___________ (hide) behind a tree ___________ a snowball ___________ (hit) him.
5 _________ Millie and her classmates ________________ (play) in the snow, Andy ___________ (run) towards them.
While were building
was taking
fell when was making
was hiding when
hit
When were playing
ran
break down(车辆或机器) 出故障,坏掉
e.g. He was late because his bike broke down.
他迟到是因为他的自行车坏了。
My car broke down on a country road yesterday.
我的小汽车昨天在一条乡村公路上出了故障。
考点1
后不能跟宾语,不用于被动语态。
知识点
1
My dad’s car broke down because of the cold weather.
与break 相关的短语
break into 强行闯入 break off 中断
break out(战争、打斗等不愉快事件) 突然开始,爆发
break a promise 违背誓言
break one’s heart 伤某人的心
break the law 违法
break the record 打破纪录
考题1:[包头] —The computer is working again!
—It _______ yesterday, but someone has fixed it.
A. broke down B. broke out
C. broke into D. broke away
A
【点拨】考查break 相关短语的用法。根据后面的fixed 可知昨天电脑出了故障。
出故障 爆发
强行闯入 脱离
(重点) because of 因为,由于
e.g. He didn’t come to school because of the rain.
因为下雨他没来学校。
I didn’t buy it because it was too expensive.
我没有买是因为它太贵了。
He can’t come because of his illness.
= He can’t come because he is ill.
他因病不能来。
考点2
短语中of 为介词,后接名词、代词、动名词或名词性短语。
because 为连词,后接句子。
because of 可与
because 进行同义转换
返回
温馨提示:可返回原文
考题2:[绥化] She can’t sleep well _______ too much noise next door.
A. because B. because of C. since
【点拨】用语法判定法。句意为“她没能睡好觉,因为隔壁太吵了”。because 因为,后接原因状语从句;because of 因为,后接单词或短语;since 由于,既然,引导原因状语从句。空格后noise 为名词,故选B。
B
过去进行时
概念 表示在过去某个时刻或某段时间正在进行的动作。①
构成② 主语+ was(were)+ 动词的现在分词.
主语第一、三人称单数用was,其余用were。
时间状语 at eight o’clock last night, at that time, at that moment, this time yesterday, from 8:00 to 9:00 last night 以及when, while 引导的时间状语从句等。
用法③ 1. 表示在过去某一时刻正在进行的动作。
2. 表示过去一段时间内正在进行的动作。
不用进行时的动词 1. 表示心里状态、情感的动词,如love,hate,like,know。
2. 部分连系动词,如seem,appear。
3. 感官动词,如see,hear,feel,smell,sound,taste 等。
4. 短暂性动词,如decide,stop 等。
过去进行时既可以表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作,也可以表示过去某一段时间正在进行的动作。过去进行时与一般过去时一样,也常和表示过去的时间状语连用。与过去进行时连用的常见的时间状语有:
this morning, the whole afternoon,
at this time yesterday, at ten yesterday morning,
from nine to ten last night 等。
考点1
考题1:[河北] At this time yesterday, I _____ a science exam here.
A. take B. was taking
C. am taking D. will take
B
【点拨】用语法判定法。考查动词时态。句意:昨天这个时候我正在这里进行科学考试。由句中的时间状语At this time yesterday“昨天这个时候”,可知用过去进行时。
返回
过去进行时的构成:
考点2
句式 结构
肯定句 主语+was/were +doing+ 其他.
否定句 主语+was/were+not+doing+ 其他.
一般疑问句 Was/Were+ 主语+doing+ 其他
答语:Yes, 主语+was/were.
/No,主语+wasn’t/weren’t.
特殊疑问句 特殊疑问词+was/were+ 主语+doing+ 其他
e.g. I was dancing to the beautiful music then.
那时我正伴随着优美的音乐跳舞。
We were listening to the teacher carefully at eight yesterday. 昨天八点钟,我们正在认真地听老师讲课。
She was running at that time.
那时她正在跑步。
He wasn’t doing his homework just now.
刚才他没在做家庭作业。
I wasn’t singing then. 那时我没在唱歌。
They weren’t listening to music at that time.
那时他们没在听音乐。
— Were you reading a book 你在看书吗?
— Yes, I was. 是的,我在看。
— No, I wasn’t. 不,我没在看。
— Were they playing tennis 他们在打网球吗?
— Yes, they were. 是的,他们在打。
— No, they weren’t. 不,他们没在打。
— Was she dancing 她在跳舞吗?
— Yes, she was. 是的,她在跳。
— No, she wasn’t. 不,她没在跳。
What were you doing at eight yesterday
昨天八点你在干什么?
Where was he playing at that moment
那个时候他在哪儿玩?
考题2:[镇江] —You look tired!
—My husband ______ football matches all night. That was too noisy!
A. watches B. has watched
C. was watching D. will watch
【点拨】用语法判定法。考查动词时态。根据上句句意:你看起来很累!可知答句句意是:我丈夫整晚都在看足球比赛。那太吵了!表示“昨夜一直在干某事”,应用过去进行时,其结构是was / were + v.-ing。
C
返回
过去进行时的用法:
考点3
用法 示例
表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作。 My sister was doing her homework at eight last night.
昨天晚上八点我妹妹在做家庭作业。
表示一个动作正在进行时,另一个动作也同时进行。 I was watching TV while my father was reading the newspaper.
我爸爸在看报纸时,我在看电视。
用法 示例
表示一个动作正在进行时,另一个动作发生了。 I met one of my old friends while I was walking in the park. 我在公园散步时,遇到了我的一位老朋友。
表示过去将要发生的动作。 She told us Jack was arriving here.
她告诉我们杰克将到这儿。
考题3:[北京] I ______ about my sister when my phone rang. It was her!
A. think B. will think
C. was thinking D. am thinking
【点拨】用语法判定法。考查动词时态。句意为“我正在想我的妹妹,这时我的电话铃响了,正是她!”。这里强调过去正在发生的动作,应用过去进行时。
C
返回
when, while 与as 的用法
when 当……时 从句中的动作既可以和主句中的动作同时发生,也可以在主句的动作之前或之后发生。
while 当……的时候 强调从句中的动作与主句中的动作同时发生,但持续时间一般较长或主句的动作在从句的动作过程中发生。
as 当……时; 和……同时 从句中的动作与主句中的动作同时发生或同时进行,一般持续时间不长。
若主句表示的是一个短暂性动作,从句表示的是一个持续性动作时,三者都可用。
e.g. He fell asleep when/while/as he was reading a book.
他看书时睡着了。
考点1
若主从句表示两个同时进行的持续性动作,且强调主句表示的动作延续到从句所指的整个事件,通常要用while。
e.g. Don’t talk while you’re eating something.
当你吃东西时不要说话。
但是,若主从句表示的两个同时进行的动作含有“一边……一边……”的意思时,通常用as。
e.g. She sang as she went along. 她边走边唱。
考点2
若从句是一个短暂性动作,主句是一个持续性动作,可用as/when,但不用while。
e.g. It was raining hard when/as we arrived.
我们到达时,天正下着大雨。
考点3
若主从句表示的是两个同时发生的短暂性动作,用as/when。
e.g. I also thought of it just when/as you opened your mouth. 就在你开口的时候,我也想到了。
考点4
考题4:[扬州] _______ astronauts go on spacewalks, they wear spacesuits to keep themselves safe.
A. Though B. Till C. When D. Unless
【点拨】用语法判定法。考查连词辨析。句意为“当宇航员进行太空行走时,他们会穿上宇航服以保证自己的安全”。Though 虽然;Till 直到;When当……的时候;Unless 除非,如果不。根据句意可知答案。
C
若要表示两个正在发展变化的动作,相当于汉语的“随着”,一般用as。
e.g. Things are getting better and better as time goes on.
随着时间的推移,情况变得越来越好了。
考点5
表示“每当……的时候”(暗示一种规律性),一般要用when。
e.g. It’s cold when it snows. 下雪时天冷。
考点6
若主从句所表示的动作不是同时发生,而是有先后顺序的,一般要用when。
e.g. I will go home when he comes back.
当他回来后,我就回家。
考点7
考题5:—Learning to love is like learning to walk.
—Yes, ______ we step out bravely, we can find it easy.
A. although B. when C. unless
【点拨】用语法判定法。考查连词辨析。句意:—学习爱像学习走路。—是的,当我们勇敢地迈出去,我们会发现它很容易。although 虽然;when当……时;unless 除非。根据“we step out bravely, we can find it easy” 可知,两个动作是先后关系。
B
when 可用作连词, 表示“当…… 时”;while 也可用作连词,表示“而,然而”(表示对比); 但as 没有类似的用法。
e.g. We were about to start when it began to rain.
我们正要开始,这时天开始下雨了。
He likes coffee, while she likes tea.
他喜欢咖啡,而她却喜欢茶。
考点8
as 和when 后均可直接跟一个名词或名词性短语,构成省略句,但while 一般不可以这样用。
e.g. As/When a little boy, he lived in America.
他小时候居住在美国。
考点9
when 和while 后可接现在分词、介词短语、形容词等构成省略句,但as 一般不可以这样用。
e.g. When/ While in trouble, ask her for help.
遇到麻烦时就去找她帮忙。
考点10
本节课主要学习了以下知识点,请同学们及时巩固练习:
过去进行时
when、while和as的用法
知识是力量,
梦想是翅膀。
