Unit 5 The Value of Money Discovering Useful Structures课件(共32张PPT)人教版(2019)必修第三册 (1)
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 5 The Value of Money Discovering Useful Structures课件(共32张PPT)人教版(2019)必修第三册 (1) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-03-02 13:53:42 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共32张PPT)
UNIT 5
THE VALUE OF MONEY
Modal verbs & The past future tense
1. Oliver believes that with a million-pound bank note a man could live a month in London.
2. Young man,would you step inside a moment,please
3. May we ask what you’re doing in this country and what your plans are
4. Well,you mustn’t worry about that.
5. Well,it may seem lucky to you but not to me!
观察下列例句,观察情态动词在句中表示的含义。
Lead-in
能力
请求
许可
禁止
可能性
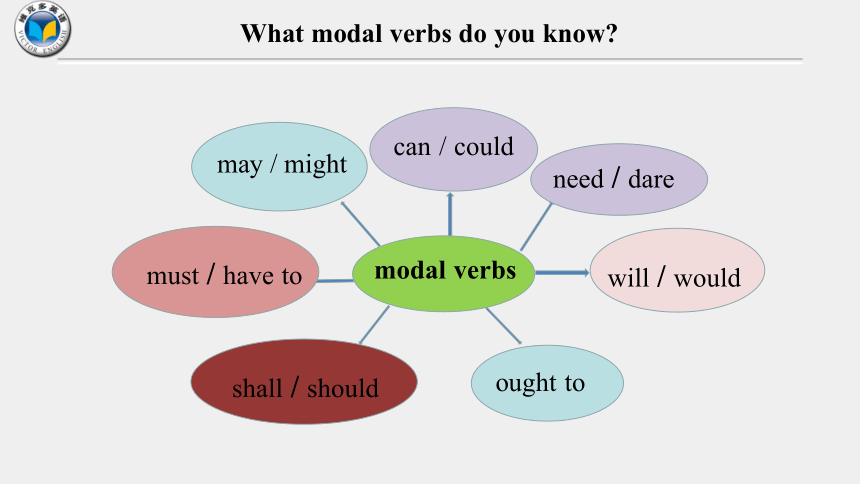
may / might
must / have to
shall / should
will / would
ought to
need / dare
can / could
What modal verbs do you know
modal verbs
情态动词有一定的意义 , 大多数情态动词有多个意义。
necessity 必要性 possibility可能性 obligation责任义务
request请求 advice建议 intention意图
2. 情态动词没有人称和数的变化 , 即不随主语的不同而变化。
3. 情态动词不能独立使用 , 须后接动词原形,一起构成谓语。
情态动词的定义
情态动词 (Modal verb)
1.只作情态动词的:
2. 可情态可实义的:
3. 可情态可助动词的:
4. 相当于情态动词的:
情态动词的分类
can/could, may/might, ought to, must
need, dare/dared
will/would,shall/should,
have to, used to,had better,used to
(一) can/could
1.表示能力,其过去式为could。
①She can speak English. 她会说英语。
②The young man can’t move the big stone. 这个年轻人搬不动那块大石头。
③He could speak Japanese when he was young, but he has forgotten most of it now. 他年轻时会说日语,不过现在已经忘得差不多了。
【温馨提示】can和 be able to在用法上的区别:
(1) can只有现在式和过去式could,而be able to有更多的时态变化。
情态动词
(2) can一般指自身具有的能力,而be able to表示经过一 段时间的努力后所具有的能力,相当于manage to do或 succeed in doing。
①This time I failed in the exam, but I'll be able to pass the exam next time.
这次考试我不及格,但下次考试我能及格。(经过努力)
②The ship was able to get to Antarctica in spite of the bad weather. (相当于managed to)
尽管天气恶劣,船还是设法到达南极洲了。
2.表示请求或许可。
当请求允许做某事时,两者均可用,但用could语气更委婉。当表示允许某人做某事时,一般要用can,而不用could。
① -Can/Could I use your bike tomorrow morning
-Yes, you can./No,I’m afraid not.
-我明天早晨能用你的自行车吗?
-是的,可以。/不,恐怕不行。
② You can go with them if you like.
如果你愿意的话,可以和他们一起去。
(二) may/might
1.表示请求或允许,用might比用may更礼貌,语气更委婉。对may的一般疑问句的肯定回答可用may或can,但作否定回答时要用mustn’t或can’t。
① You may come if you wish. 如果你想来,你就来。
②May(Might) I ask for a photo of your baby
我可以要一张你宝宝的照片吗?
③-May I smoke here 我可以在这里吸烟吗?
-No,you mustn’t. You’d better not. 不,不可以。你最好不要吸烟。
2.表示可能。might比may可能性更小。
① The crowds might damage the beauty of the place.
人群可能会破坏这个地方的美。
② She may not know about it. 她可能不知道这件事。
3.用于表祝愿的句子中。只能用may,且may常放在句首。
① May you succeed. 祝你成功!
② May you have a good time on you trip! 祝你旅途愉快!
(三) must/have to
1.must表示必须,没有时态变化。强调的是一种主观看法。
have to表示“必须,不得不”have to可用于多种时态中。是由于某种外界(客观)原因而“必须,不得不”做某事。
mustn’t 表示禁止做某事;have to的否定形式意为“没必要”。
① I work not because I have to, but because I want to.
我工作不是因为我不得不做,而是因为我想做。(客观上需要做这件事)
② You must keep these points in mind while setting your goals.
在设定目标时,你必须牢记这些要点。(主观上要做这件事)
【温馨提示】回答must引出的问句时,如果是否定的回答,不能用mustn’t,而要用needn’t或don’t have to。
-Must we hand in our exercise books now 我们现在就必须要交练习本吗?
-Yes, you must.(No, you needn’t./No,you don’t have to.)
是的,必须。(不,不必)。
2.must 表示猜测。意为“想必,准是,一定”,只用于肯定句。
① The book must be the one you want.
这本书一定是你要的那本。
② She’s wearing a diamond necklace. She must have a lot of money.
她戴着钻石项链,她一定很有钱。
【练习】用适当的情态动词填空。
①My sister is ill;my mother _________ look after her.
②There’s a lot of noise from next door. They ________ be having a party.
has to
must
(四) shall
1.表示征询意见,用于第一、第三人称疑问句。
① Shall I get you some more tea 再来点茶好吗?
② Shall the boy wait outside 让那男孩在外面等吗?
2.表示说话人的意愿,有“命令、允诺、警告”等意思,用于第二、第三人称陈述句。
① You shall come on time. 你必须准时到。(命令)
② He shall have the book when I finish reading it.我读完这本书就给他。(允诺)
③ No reader shall remove a book from the library without permission.
未经许可,读者不准把书带出图书馆。(警告)
3.表示强制,用于法令、条约、规章中,意为“必须;应该”。
① One of our rules is that every student shall wear school uniform while at school.
我们规定中的其中一项是:每位学生在校期间都要穿校服。
② Each part shall respect the articles of this contract.
任何一方都要尊重合同的条款。
【练习】写出下列句中shall的含义
①You shall fail if you don’t work harder.________
②You shall get an answer from me tomorrow.________
③Shall I watch TV for a while?____________
警告
允诺
征求意见
(五)should
1.表示义务、责任,意为“应该”,用于各种人称。与ought to意思相近,但语气稍弱些。
① Students should have a proper attitude towards college before thinking about which college to attend.
在考虑上哪所大学之前,学生应该对大学有一个正确的态度。
② You should be polite to your teachers.
你对老师应该有礼貌。
2.表示可能性很大的猜测,说明说话人对客观事物的真实性作出较大可能的判断,意为“想必一定,照说应该;估计”等。
The film should be very good as it is starring first-class actors.
这部电影是一流演员主演的,估计拍得很好。
3.表示说话人的惊讶、愤怒、失望等特殊情感,意为“居然,竟然”。
Amazing! You should wear slippers at work.
真令人惊讶,你竟然穿着拖鞋上班!
【练习】①Such a clever boy __________ fail the exam.
②We __________ obey the school rules and work hard.
should
should
(六) will/would
1.表示意志或意愿。过去式为would,用于否定句表示“不肯,不乐意”。
I will never do that again. 我决不会再做那种事了。
2.表示征求意见或提出请求。主要用于第二人称疑问句中,will和would均可用,would此时不表示过去,而是表示委婉语气。
Will/Would you pass me the book 请你把书递给我好吗?
3.will和would可分别表示现在和过去反复发生的动作或某种倾向,意为“总是;常常”。
① Fish will die without water. 没有水,鱼会死去。
② When my parents were away, my grandmother would take care of me.
我父母外出的时候,总是祖母照看我。
【练习】①He ________ go to the river nearby to fish on weekends when he was young.
③_________ you open the window, please I feel it is a little hot here.
would
Would
(七) need
1.用作情态动词,need意为“需要,有必要”,一般用于否定句或疑问句中。疑问句中把need提前,否定形式是在need后加not。
You needn’t come here this afternoon. 你今天下午不必来。
2.用作实义动词,意为“需要,有必要”,可以用于各种句式中。
① You don’t need to go now. 你不必现在就走。
② I need to have a rest. 我需要休息一下。
③ Do we need to finish all the work today 我们今天需要完成所有的工作吗?
【练习】①-Must I stay here -No, you ____________.
②You ________ not be told twice about one single thing.
needn’t
need
(八) dare
1.dare作情态动词时,常用于疑问句、否定句和条件从句中,过去形式为dared。
①How dare you say I’m unfair 你怎么敢说我不公平?
②He daren’t speak English before such a crowd, dare he
他不敢在这么多人面前说英语,是吗?
③If we dared not go there that day, we couldn’t get the beautiful flowers.
如果那天我们不敢去那里,我们就得不到美丽的花。
2.dare作实义动词用时,有人称、时态和数的变化。在肯定句中,dare后面常接带to的不定式。
① I dare to swim across this river. 我敢游过这条河。
② He doesn’t dare (to) answer. 他不敢回答。
(九) ought to
ought to后接动词原形,意思是“应该...,有义务.....”ought to和should是同义词,但ought to语气更强。在各种时态里形式无变化,其否定形式是ought not to表示“不应.....
①They oughtn’t to let their dog run on the road.
他们不该把狗放出来满街跑。
②If he started out at nine, he ought to be here by now.
要是他九点出发,现在该到这儿了。
③Look at the sky-it ought to be a fine afternoon.
看看天——下午天气应该很晴朗。
(十) had better
(1)[提出建议]某人最好还是....
① She had better see a doctor if it gets any worse.
她如果病情加重,最好还是去看医生。
② You had better compare this word with that one.
你们最好把这个词与那个词比较一下。
③You had better give him a phone yourself !你最好自已给他打个电话!
(2) [表示威胁]某人最好.....
You had better keep your mouth shut about this. 关于这件事,你最好闭上嘴。
情态动词 + have done
must have done 对过去的肯定推测,“过去肯定 ”
can’t/ could’t have done 对过去的否定推测,“过去不可能做了....”
could have done 本来能够做而没做
may / might (not) have done 可能(没有)做过某事
should (not)/ought (not) to have done 本来该做而没做/本来不该做而做了
needn’t have done 本来不必做却做了
Unit 5
THE VALUE OF MONEY
过去将来时
观察下列句子,探究划线部分的用法。
1. Our sports meeting will be put off if it rains tomorrow.
如果明天下雨的话,我们的运动会就要被推迟。
2. I am afraid they’re going to lose the game. 恐怕他们比赛会输。
3. I didn't know when she would come, but when she came I would let you know.
我不知道她什么时候来,但她来了我会告诉你。
4. We were going to go to the cinema when the phone rang.
我们正准备去电影院,这时电话响了。
第1、2句为______________(时态),第3、4句为_______________(时态)。
Lead-in
一般将来时
过去将来时
一、定义:
过去将来时表示从过去某一时间来看将要发生的动作或存在的状态,常用在宾语从句中。
二、基本结构
1. would+动词原形:表示过去的打算或在过去看来有迹象表明将要发生某事。
① She hoped that they would meet again someday.
她希望将来有一天他们能再见面。
② I rang up to tell my father that I should leave for London.我打电话告诉我父亲我要去伦敦。
过去将来时
2.was/were going to+动词原形:表示过去将要发生或很有可能发生的动作,常用于口语中,表示预言、意图或者打算等。
① He was going to start work the following week.
他打算下星期开始工作。
②-Alice, why didn’t you come yesterday
-I was going to, but I had an unexpected visitor.
-爱丽丝,你昨天为什么没来呀?
-我打算去的,但我家来了个不速之客。
3.was/were about to do:常用来表示即将发生的动作,“刚要/正要做……”。注意该结构不与具体的时间状语连用。
① I felt that something terrible was about to happen.
我感到某种可怕的事情即将发生。
② We were about to go there when it began to rain.
我们刚打算去那儿,这时天下起了雨。
4.was/were to do:表示定于过去某时将要做某事。
① She said she was to have told me about the accident.
她说她本来想告诉我关于事故的事。
② He said he was to meet his friend at the station at 4 p.m.
他说他下午四点去车站接他的朋友。
5. was/were+现在分词:come, go, arrive, leave, die等瞬时动词,用在过去进行时中表示过去将要发生的情况。
①He was a little surprised when I told him I was leaving.
当我告诉他我要离开时,他有点吃惊。
② He hoped his wife was coming soon. 他希望他的妻子赶快来。
【练习】用所给动词的适当形式完成句子
①She said the bus ______________(leave) at five the next morning.
②I wasn’t sure whether he _____________(lend) me his book the next morning.
③At that time he did not know that quitting the job _______________ (become) the turning point in his life.
④He said he ___________________(visit) China the next week.
⑤In his introduction, he made it clear that our credits ___________(be) hard-earned.
was leaving
would lend
was to become
was going to visit
would be
UNIT 5
THE VALUE OF MONEY
Modal verbs & The past future tense
1. Oliver believes that with a million-pound bank note a man could live a month in London.
2. Young man,would you step inside a moment,please
3. May we ask what you’re doing in this country and what your plans are
4. Well,you mustn’t worry about that.
5. Well,it may seem lucky to you but not to me!
观察下列例句,观察情态动词在句中表示的含义。
Lead-in
能力
请求
许可
禁止
可能性
may / might
must / have to
shall / should
will / would
ought to
need / dare
can / could
What modal verbs do you know
modal verbs
情态动词有一定的意义 , 大多数情态动词有多个意义。
necessity 必要性 possibility可能性 obligation责任义务
request请求 advice建议 intention意图
2. 情态动词没有人称和数的变化 , 即不随主语的不同而变化。
3. 情态动词不能独立使用 , 须后接动词原形,一起构成谓语。
情态动词的定义
情态动词 (Modal verb)
1.只作情态动词的:
2. 可情态可实义的:
3. 可情态可助动词的:
4. 相当于情态动词的:
情态动词的分类
can/could, may/might, ought to, must
need, dare/dared
will/would,shall/should,
have to, used to,had better,used to
(一) can/could
1.表示能力,其过去式为could。
①She can speak English. 她会说英语。
②The young man can’t move the big stone. 这个年轻人搬不动那块大石头。
③He could speak Japanese when he was young, but he has forgotten most of it now. 他年轻时会说日语,不过现在已经忘得差不多了。
【温馨提示】can和 be able to在用法上的区别:
(1) can只有现在式和过去式could,而be able to有更多的时态变化。
情态动词
(2) can一般指自身具有的能力,而be able to表示经过一 段时间的努力后所具有的能力,相当于manage to do或 succeed in doing。
①This time I failed in the exam, but I'll be able to pass the exam next time.
这次考试我不及格,但下次考试我能及格。(经过努力)
②The ship was able to get to Antarctica in spite of the bad weather. (相当于managed to)
尽管天气恶劣,船还是设法到达南极洲了。
2.表示请求或许可。
当请求允许做某事时,两者均可用,但用could语气更委婉。当表示允许某人做某事时,一般要用can,而不用could。
① -Can/Could I use your bike tomorrow morning
-Yes, you can./No,I’m afraid not.
-我明天早晨能用你的自行车吗?
-是的,可以。/不,恐怕不行。
② You can go with them if you like.
如果你愿意的话,可以和他们一起去。
(二) may/might
1.表示请求或允许,用might比用may更礼貌,语气更委婉。对may的一般疑问句的肯定回答可用may或can,但作否定回答时要用mustn’t或can’t。
① You may come if you wish. 如果你想来,你就来。
②May(Might) I ask for a photo of your baby
我可以要一张你宝宝的照片吗?
③-May I smoke here 我可以在这里吸烟吗?
-No,you mustn’t. You’d better not. 不,不可以。你最好不要吸烟。
2.表示可能。might比may可能性更小。
① The crowds might damage the beauty of the place.
人群可能会破坏这个地方的美。
② She may not know about it. 她可能不知道这件事。
3.用于表祝愿的句子中。只能用may,且may常放在句首。
① May you succeed. 祝你成功!
② May you have a good time on you trip! 祝你旅途愉快!
(三) must/have to
1.must表示必须,没有时态变化。强调的是一种主观看法。
have to表示“必须,不得不”have to可用于多种时态中。是由于某种外界(客观)原因而“必须,不得不”做某事。
mustn’t 表示禁止做某事;have to的否定形式意为“没必要”。
① I work not because I have to, but because I want to.
我工作不是因为我不得不做,而是因为我想做。(客观上需要做这件事)
② You must keep these points in mind while setting your goals.
在设定目标时,你必须牢记这些要点。(主观上要做这件事)
【温馨提示】回答must引出的问句时,如果是否定的回答,不能用mustn’t,而要用needn’t或don’t have to。
-Must we hand in our exercise books now 我们现在就必须要交练习本吗?
-Yes, you must.(No, you needn’t./No,you don’t have to.)
是的,必须。(不,不必)。
2.must 表示猜测。意为“想必,准是,一定”,只用于肯定句。
① The book must be the one you want.
这本书一定是你要的那本。
② She’s wearing a diamond necklace. She must have a lot of money.
她戴着钻石项链,她一定很有钱。
【练习】用适当的情态动词填空。
①My sister is ill;my mother _________ look after her.
②There’s a lot of noise from next door. They ________ be having a party.
has to
must
(四) shall
1.表示征询意见,用于第一、第三人称疑问句。
① Shall I get you some more tea 再来点茶好吗?
② Shall the boy wait outside 让那男孩在外面等吗?
2.表示说话人的意愿,有“命令、允诺、警告”等意思,用于第二、第三人称陈述句。
① You shall come on time. 你必须准时到。(命令)
② He shall have the book when I finish reading it.我读完这本书就给他。(允诺)
③ No reader shall remove a book from the library without permission.
未经许可,读者不准把书带出图书馆。(警告)
3.表示强制,用于法令、条约、规章中,意为“必须;应该”。
① One of our rules is that every student shall wear school uniform while at school.
我们规定中的其中一项是:每位学生在校期间都要穿校服。
② Each part shall respect the articles of this contract.
任何一方都要尊重合同的条款。
【练习】写出下列句中shall的含义
①You shall fail if you don’t work harder.________
②You shall get an answer from me tomorrow.________
③Shall I watch TV for a while?____________
警告
允诺
征求意见
(五)should
1.表示义务、责任,意为“应该”,用于各种人称。与ought to意思相近,但语气稍弱些。
① Students should have a proper attitude towards college before thinking about which college to attend.
在考虑上哪所大学之前,学生应该对大学有一个正确的态度。
② You should be polite to your teachers.
你对老师应该有礼貌。
2.表示可能性很大的猜测,说明说话人对客观事物的真实性作出较大可能的判断,意为“想必一定,照说应该;估计”等。
The film should be very good as it is starring first-class actors.
这部电影是一流演员主演的,估计拍得很好。
3.表示说话人的惊讶、愤怒、失望等特殊情感,意为“居然,竟然”。
Amazing! You should wear slippers at work.
真令人惊讶,你竟然穿着拖鞋上班!
【练习】①Such a clever boy __________ fail the exam.
②We __________ obey the school rules and work hard.
should
should
(六) will/would
1.表示意志或意愿。过去式为would,用于否定句表示“不肯,不乐意”。
I will never do that again. 我决不会再做那种事了。
2.表示征求意见或提出请求。主要用于第二人称疑问句中,will和would均可用,would此时不表示过去,而是表示委婉语气。
Will/Would you pass me the book 请你把书递给我好吗?
3.will和would可分别表示现在和过去反复发生的动作或某种倾向,意为“总是;常常”。
① Fish will die without water. 没有水,鱼会死去。
② When my parents were away, my grandmother would take care of me.
我父母外出的时候,总是祖母照看我。
【练习】①He ________ go to the river nearby to fish on weekends when he was young.
③_________ you open the window, please I feel it is a little hot here.
would
Would
(七) need
1.用作情态动词,need意为“需要,有必要”,一般用于否定句或疑问句中。疑问句中把need提前,否定形式是在need后加not。
You needn’t come here this afternoon. 你今天下午不必来。
2.用作实义动词,意为“需要,有必要”,可以用于各种句式中。
① You don’t need to go now. 你不必现在就走。
② I need to have a rest. 我需要休息一下。
③ Do we need to finish all the work today 我们今天需要完成所有的工作吗?
【练习】①-Must I stay here -No, you ____________.
②You ________ not be told twice about one single thing.
needn’t
need
(八) dare
1.dare作情态动词时,常用于疑问句、否定句和条件从句中,过去形式为dared。
①How dare you say I’m unfair 你怎么敢说我不公平?
②He daren’t speak English before such a crowd, dare he
他不敢在这么多人面前说英语,是吗?
③If we dared not go there that day, we couldn’t get the beautiful flowers.
如果那天我们不敢去那里,我们就得不到美丽的花。
2.dare作实义动词用时,有人称、时态和数的变化。在肯定句中,dare后面常接带to的不定式。
① I dare to swim across this river. 我敢游过这条河。
② He doesn’t dare (to) answer. 他不敢回答。
(九) ought to
ought to后接动词原形,意思是“应该...,有义务.....”ought to和should是同义词,但ought to语气更强。在各种时态里形式无变化,其否定形式是ought not to表示“不应.....
①They oughtn’t to let their dog run on the road.
他们不该把狗放出来满街跑。
②If he started out at nine, he ought to be here by now.
要是他九点出发,现在该到这儿了。
③Look at the sky-it ought to be a fine afternoon.
看看天——下午天气应该很晴朗。
(十) had better
(1)[提出建议]某人最好还是....
① She had better see a doctor if it gets any worse.
她如果病情加重,最好还是去看医生。
② You had better compare this word with that one.
你们最好把这个词与那个词比较一下。
③You had better give him a phone yourself !你最好自已给他打个电话!
(2) [表示威胁]某人最好.....
You had better keep your mouth shut about this. 关于这件事,你最好闭上嘴。
情态动词 + have done
must have done 对过去的肯定推测,“过去肯定 ”
can’t/ could’t have done 对过去的否定推测,“过去不可能做了....”
could have done 本来能够做而没做
may / might (not) have done 可能(没有)做过某事
should (not)/ought (not) to have done 本来该做而没做/本来不该做而做了
needn’t have done 本来不必做却做了
Unit 5
THE VALUE OF MONEY
过去将来时
观察下列句子,探究划线部分的用法。
1. Our sports meeting will be put off if it rains tomorrow.
如果明天下雨的话,我们的运动会就要被推迟。
2. I am afraid they’re going to lose the game. 恐怕他们比赛会输。
3. I didn't know when she would come, but when she came I would let you know.
我不知道她什么时候来,但她来了我会告诉你。
4. We were going to go to the cinema when the phone rang.
我们正准备去电影院,这时电话响了。
第1、2句为______________(时态),第3、4句为_______________(时态)。
Lead-in
一般将来时
过去将来时
一、定义:
过去将来时表示从过去某一时间来看将要发生的动作或存在的状态,常用在宾语从句中。
二、基本结构
1. would+动词原形:表示过去的打算或在过去看来有迹象表明将要发生某事。
① She hoped that they would meet again someday.
她希望将来有一天他们能再见面。
② I rang up to tell my father that I should leave for London.我打电话告诉我父亲我要去伦敦。
过去将来时
2.was/were going to+动词原形:表示过去将要发生或很有可能发生的动作,常用于口语中,表示预言、意图或者打算等。
① He was going to start work the following week.
他打算下星期开始工作。
②-Alice, why didn’t you come yesterday
-I was going to, but I had an unexpected visitor.
-爱丽丝,你昨天为什么没来呀?
-我打算去的,但我家来了个不速之客。
3.was/were about to do:常用来表示即将发生的动作,“刚要/正要做……”。注意该结构不与具体的时间状语连用。
① I felt that something terrible was about to happen.
我感到某种可怕的事情即将发生。
② We were about to go there when it began to rain.
我们刚打算去那儿,这时天下起了雨。
4.was/were to do:表示定于过去某时将要做某事。
① She said she was to have told me about the accident.
她说她本来想告诉我关于事故的事。
② He said he was to meet his friend at the station at 4 p.m.
他说他下午四点去车站接他的朋友。
5. was/were+现在分词:come, go, arrive, leave, die等瞬时动词,用在过去进行时中表示过去将要发生的情况。
①He was a little surprised when I told him I was leaving.
当我告诉他我要离开时,他有点吃惊。
② He hoped his wife was coming soon. 他希望他的妻子赶快来。
【练习】用所给动词的适当形式完成句子
①She said the bus ______________(leave) at five the next morning.
②I wasn’t sure whether he _____________(lend) me his book the next morning.
③At that time he did not know that quitting the job _______________ (become) the turning point in his life.
④He said he ___________________(visit) China the next week.
⑤In his introduction, he made it clear that our credits ___________(be) hard-earned.
was leaving
would lend
was to become
was going to visit
would be
